Thermal Hysteresis Control in Fe49Rh51 Alloy through Annealing Process
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
3. Results and Discussion
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Fullerton, J. The 2017 Magnetism Roadmap. J. Phys. D Appl. Phys. 2017, 50, 363001. [Google Scholar]
- Franco, V.; Blázquez, J.S.; Ipus, J.J.; Law, J.Y.; Moreno-Ramírez, L.M. Magnetocaloric effect: From materials research to refrigeration devices. Conde Prog. Mater. Sci. 2018, 93, 112–232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, J.; Gottschall, T.; Skokov, K.P.; Moore, J.D.; Gutfleisch, O. Giant magnetocaloric effect driven by structural transitions. Nat. Mater. 2012, 11, 620–626. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Annaorazov, M.P.; Asatryan, K.A.; Myalikgulyev, G.; Nikitin, S.A.; Tishin, A.M.; Tyurin, A.L. Alloys of the FeRh system as a new class of working material for magnetic refrigerators. Cryogenics 1992, 32, 867–872. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aliev, A.M.; Batdalov, A.B.; Khanov, L.N.; Kamantsev, A.P.; Koledov, V.V.; Mashirov, A.V.; Shavrov, V.G.; Grechishkin, R.M.; Kaul, A.R.; Sampath, V. Reversible magnetocaloric effect in materials with first order phase transitions in cyclic magnetic fields: Fe48Rh52 and Sm0.6Sr0.4MnO3. Appl. Phys. Lett. 2016, 109, 202407. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nikitin, S.A.; Myalikgulyev, G.; Tishin, A.M.; Annaorazov, M.P.; Asatryan, K.A.; Tyurin, A.L. The magnetocaloric effect in Fe49Rh51 compound. Phys. Lett. A 1990, 148, 363–366. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Popescu, A.; Rodriguez-Lopez, P.; Haney, P.M.; Wood, L.M. Thermally driven anomalous Hall effect transitions in FeRh. Phys. Rev. B 2018, 97, 140407. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Arreguín-Hernández, M.L.; Sánchez-Valdés, C.F.; Sánchez Llamazaresa, J.L.; Ríos-Jara, D.; Pecharsky, V.K.; Blinov, M.I.; Prudnikov, V.N.; Kovalev, B.B.; Zverev, V.I.; Tishin, A.M. Magnetoelastic transition and magnetocaloric effect in induction melted Fe100−xRhx bulk alloys with x = 50, 51. J. Alloy Compd. 2021, 871, 159586. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Batdalov, A.B.; Aliev, A.M.; Khanov, L.N.; Kamantsev, A.P.; Mashirov, A.V.; Koledov, V.V.; Shavrov, V.G. Specific heat, electrical resistivity, and magnetocaloric study of phase transition in Fe48Rh52 alloy. J. Appl. Phys. 2020, 128, 013902. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baranov, N.V.; Barabanova, E.A. Electrical resistivity and magnetic phase transitions in modified FeRh compounds. J. Alloys Compd. 1995, 219, 139–148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Churyukanova, M.; Kaloshkina, S.; Shuvaeva, E.; Mitra, A.; Pand, A.K.; Roy, R.K.; Murugaiyan, P.; Corte-Leon, P.; Zhukova, V.; Zhukov, A. The effect of heat treatment on magnetic and thermal properties of Finemet-type ribbons and microwires. J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 2019, 492, 165598. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kamantsev, A.P.; Amirov, A.A.; Koshkid’ko, Y.S.; Mejía, C.S.; Mashirov, A.V.; Aliev, A.M.; Koledov, V.V. Shavrov Magnetocaloric effect in alloy Fe49Rh51 in pulsed magnetic fields up to 50 T. Phys. Solid State 2020, 62, 161–163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tohki, A.; Aikoh, K.; Iwase, A.; Yoneda, K.; Kosugi, S.; Kume, K.; Batchuluun, T.; Ishigami, R.; Matsui, T.J. Effect of high temperature annealing on ion-irradiation induced magnetization in FeRh thin films. Appl. Phys. 2012, 111, 07A742. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zakharov, A.I.; Kadomtsewa, A.M.; Levitin, R.Z.; Ponyatovskii, E.G. Magnetic and magnetoelastic properties of a metamagnetic iron-rhodium alloy. Soviet Phys. JETP 1964, 19, 1348. [Google Scholar]
- Walter, P.H.L. Exchange Inversion in Ternary Modifications of Iron Rhodium. J. Appl. Phys. 1964, 35, 938–939. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Polovov, V.M.; Ponomarev, B.K.; Antonov, V.E. Some peculiarities of thermodynamics of transition antiferro-ferromagnetism in iron-rhodium alloys. Fiz. Met. I Metalloved. 1975, 39, 977–986. [Google Scholar]
- Amirov, A.A.; Cugini, F.; Kamantsev, A.P.; Gottschall, T.; Solzi, M.; Aliev, A.M.; Spichkin, Y.I.; Koledov, V.V.; Shavrov, V.G. Direct measurements of the magnetocaloric effect of Fe49Rh51 using the mirage effect. J. Appl. Phys. 2020, 127, 233905. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stern-Taulats, E.; Castan, T.; Planes, A.; Lewis, L.H.; Barua, R.; Pramanick, S.; Majumdar, S.; Manosa, L. Giant multicaloric response of bulk Fe49Rh51. Phys. Rev. B 2017, 95, 104424. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Flippen, R.B.; Darnell, F.J. Entropy Changes of Ferromagnetic-Antiferromagnetic Transitions from Magnetic Measurements. J. Appl. Phys. 1963, 34, 1094–1095. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zakharov, A. Crystal lattice parameter and structural distortions in Fe-Rh alloy during phase transformations. Fiz. Met. I Metalloved. 1967, 24, 84–90. [Google Scholar]
- Kouvel, J.S. Unusual Nature of the Abrupt Magnetic Transition in FeRh and Its Pseudobinary Variants. J. Appl. Phys. 1966, 37, 1257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wayne, R. Pressure Dependence of the Magnetic Transitions in Fe-Rh Alloys. Phys. Rev. 1968, 170, 523–527. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stern-Taulats, E.; Planes, A.; Lloveras, P.; Barrio, M.; Tamarit, J.-L.; Pramanick, S.; Majumdar, S.; Frontera, C.; Manosa, L. Barocaloric and magnetocaloric effects in Fe49Rh51. Phys. Rev. B 2014, 89, 214105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cherifi, R.O.; Ivanovskaya, V.; Phillips, L.C.; Zobelli, A.; Infante, I.C.; Jacquet, E.; Garcia, V.; Fusil, S.; Briddon, P.R.; Guiblin, N.; et al. Electric-field control of magnetic order above room temperature. Nat. Mater. 2014, 13, 345. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Amirov, A.A.; Baraban, I.A.; Grachev, A.A.; Kamantsev, A.P.; Rodionov, V.V.; Yusupov, D.M.; Rodionova, V.V.; Sadovnikov, A.V. Voltage-induced strain to control the magnetization of bi FeRh/PZT and tri PZT/FeRh/PZT layered magnetoelectric composites. AIP Adv. 2020, 10, 025124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amirov, A.A.; Rodionov, V.V.; Starkov, I.A.; Starkov, A.S.; Aliev, A.M. Magneto-electric coupling in FeRh -PZT multiferroic composite. J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 2019, 470, 77–80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lommel, J.M. Effects of Mechanical and Thermal Treatment on the Structure and Magnetic Transitions in FeRh. J. Appl. Phys. 1967, 38, 1263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chirkova, A.; Bittner, F.; Nenkov, K.; Schultz, N.V.B.L.; Nielsch, K.; Woodcock, T.G. The effect of the microstructure on the antiferromagnetic to ferromagnetic transition in FeRh alloys. Acta Mater. 2017, 131, 31–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Takahashi, M.; Oshima, R. Annealing Effect on Phase Transition of Equiatomic FeRh Alloy. Mater. Trans. JIM 1995, 36, 735–742. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Manekar, M.; Roy, S.B. Very large refrigerant capacity at room temperature with reproducible magnetocaloric effect in Fe0.975Ni0.025Rh. J. Phys. D Appl. Phys. 2011, 44, 242001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barua, R.; Jimenez-Villacorta, F.; Lewis, L.H. Towards tailoring the magnetocaloric response in FeRh-based ternary compounds. J. Appl. Phys. 2014, 115, 17A903. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kosugi, S.; Fujita, N.; Matsui, T.; Hori, F.; Saitoh, Y.; Ishikawa, N.; Okamoto, Y.; Iwase, A. Modification of magnetic properties of FeRh intermetallic compounds by energetic ion beam bombardment. Nucl. Instrum. Methods B 2009, 267, 1612–1615. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kushwaha, P.; Lakhani, A.; Rawat, R.; Chaddah, P. Influence of thermal annealing and magnetic field on first order magnetic transition in Pd substituted FeRh. J. Phys. Conf. Ser. 2010, 200, 032038. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chirkova, A.; Skokov, K.; Schultz, L.; Baranov, N.; Gutfleisch, O.; Woodcock, T. Magnetic response of FeRh to static and dynamic disorder. Acta Mater. 2016, 106, 15–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chichay, K.; Rodionova, V.; Zhukova, V.; Kaloshkin, S.; Churyuknova, M.; Zhukov, A.J. Investigation of the magnetostriction coefficient of amorphous ferromagnetic glass coated microwires. Appl. Phys. 2014, 116, 173904. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Swartzendruber, L.J. The Fe–Rh (Iron-Rhodium) system. Bull. Alloy Phase Diagr. 1984, 5, 456–462. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Okamoto, H.J. Phase Equilibria Diffus. J. Phase Equilibria Diffus. 2011, 32, 472. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pal, L.; Tarnoczi, T.; Szabo, P.; Kren, E.; Toth, J. Investigation of antiferromagnetic-ferromagnetic transformation in iron-rhodium alloys. Proc. Int. Conf. Magn. (Nottingham) 1964, 158–161. [Google Scholar]
- Zverev, V.I.; Saletsky, A.M.; Gimaev, R.R.; Tishin, A.M.; Miyanaga, T.; Staunton, J.B. Influence of structural defects on the magnetocaloric effect in the vicinity of the first order magnetic transition in Fe50.4Rh49.6. Appl. Phys. Lett. 2016, 108, 192405. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sánchez-Valdés, C.F.; Gimaev, R.R.; López-Cruz, M.; Llamazares, J.L.S.; Zverev, V.I.; Tishin, A.M.; Carvalho, A.M.G.; Aguiar, D.J.M.; Mudryk, Y.; Pecharsky, V.K. The effect of cooling rate on magnetothermal properties of Fe49Rh51. J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 2020, 498, 166130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
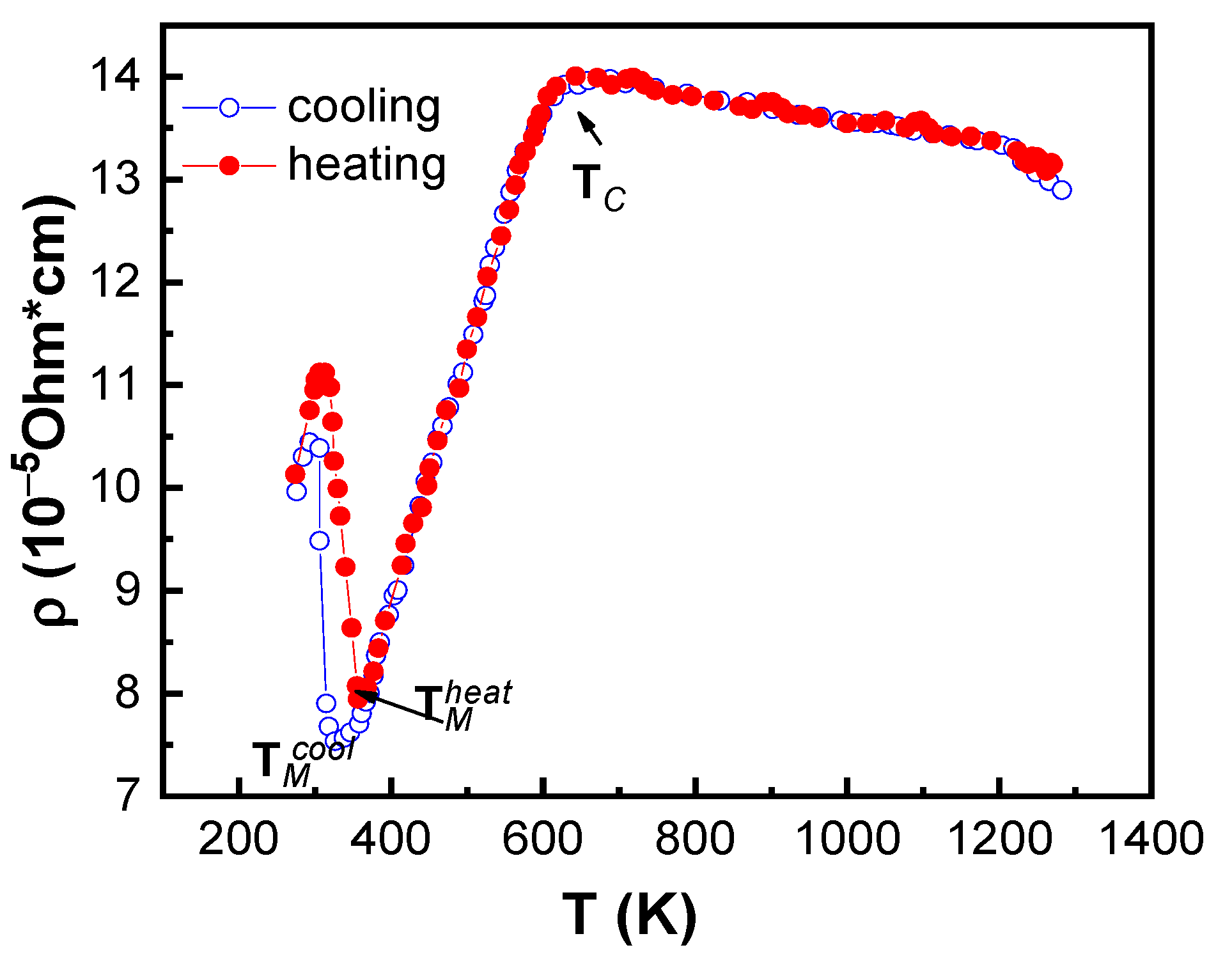
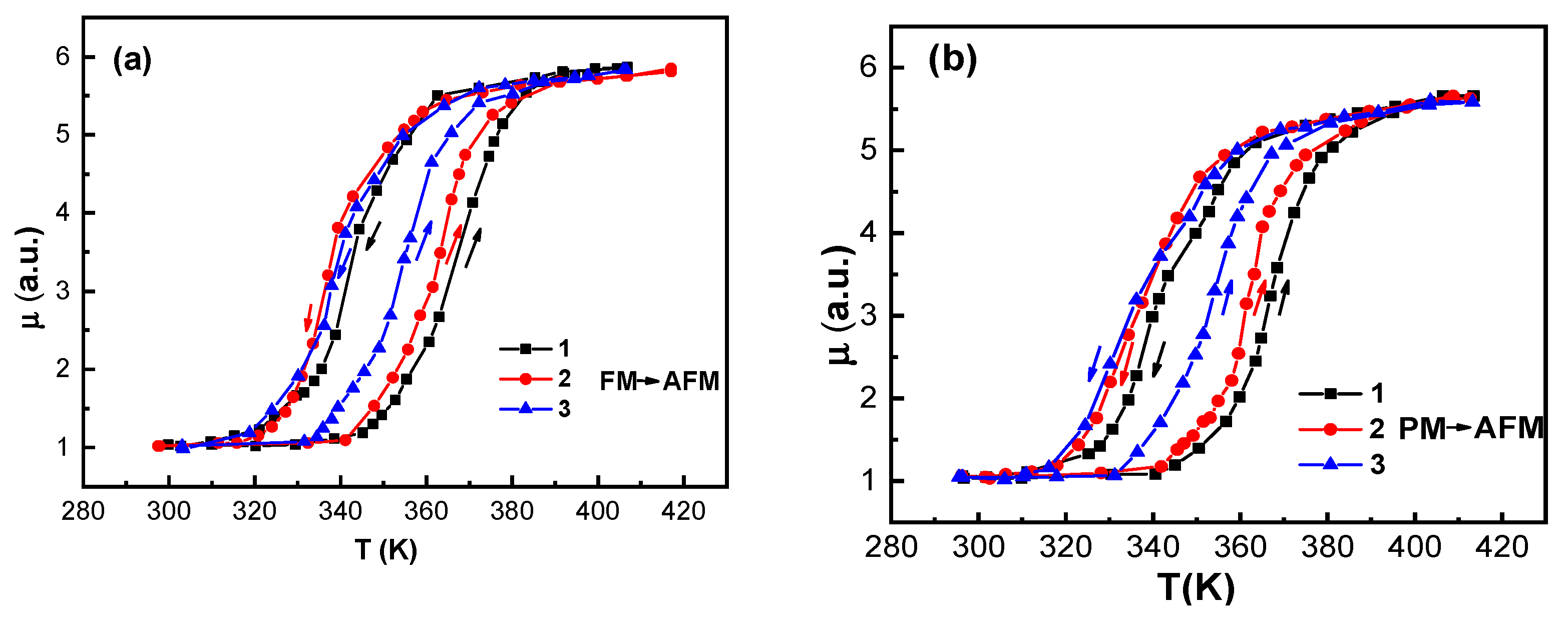

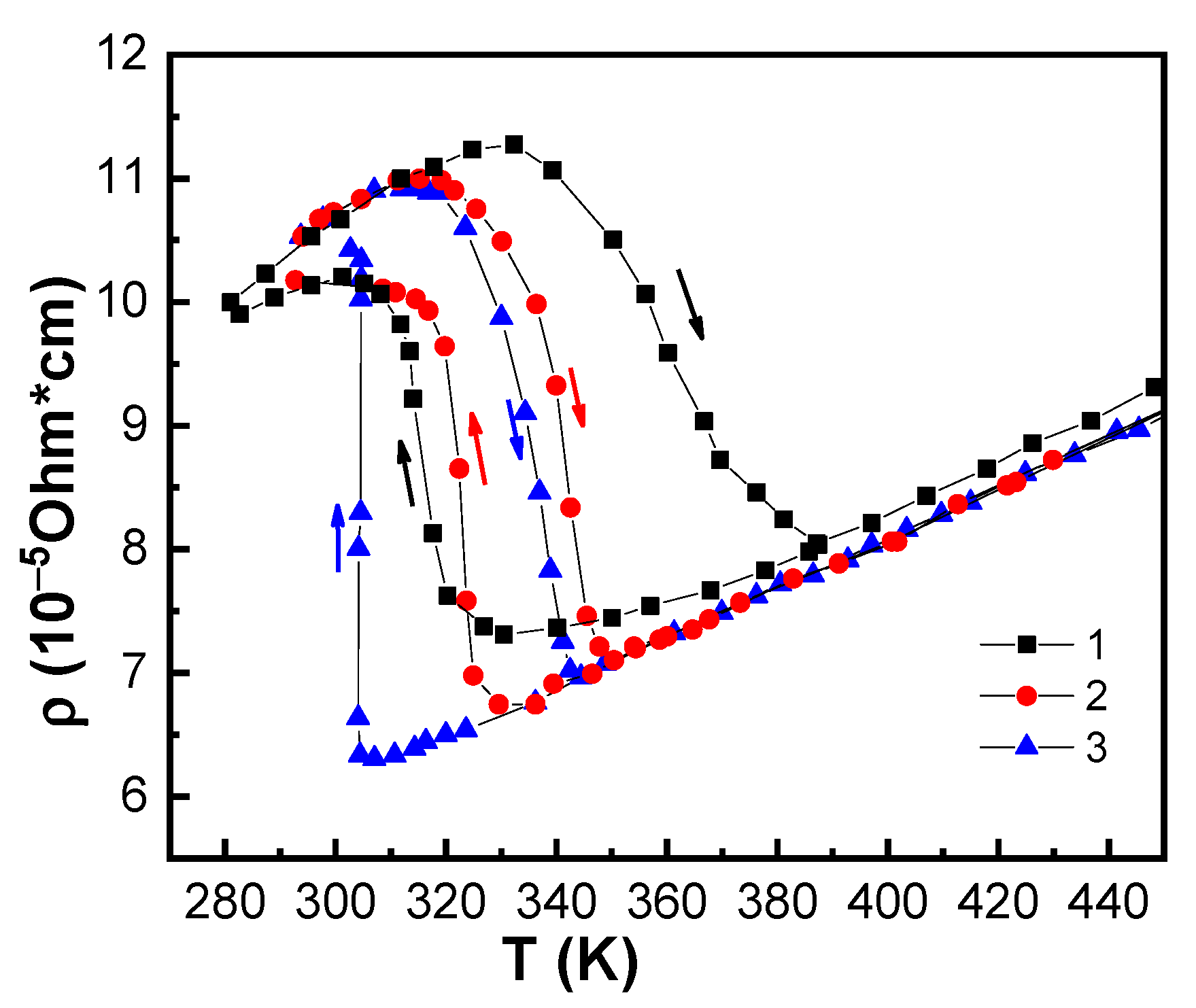
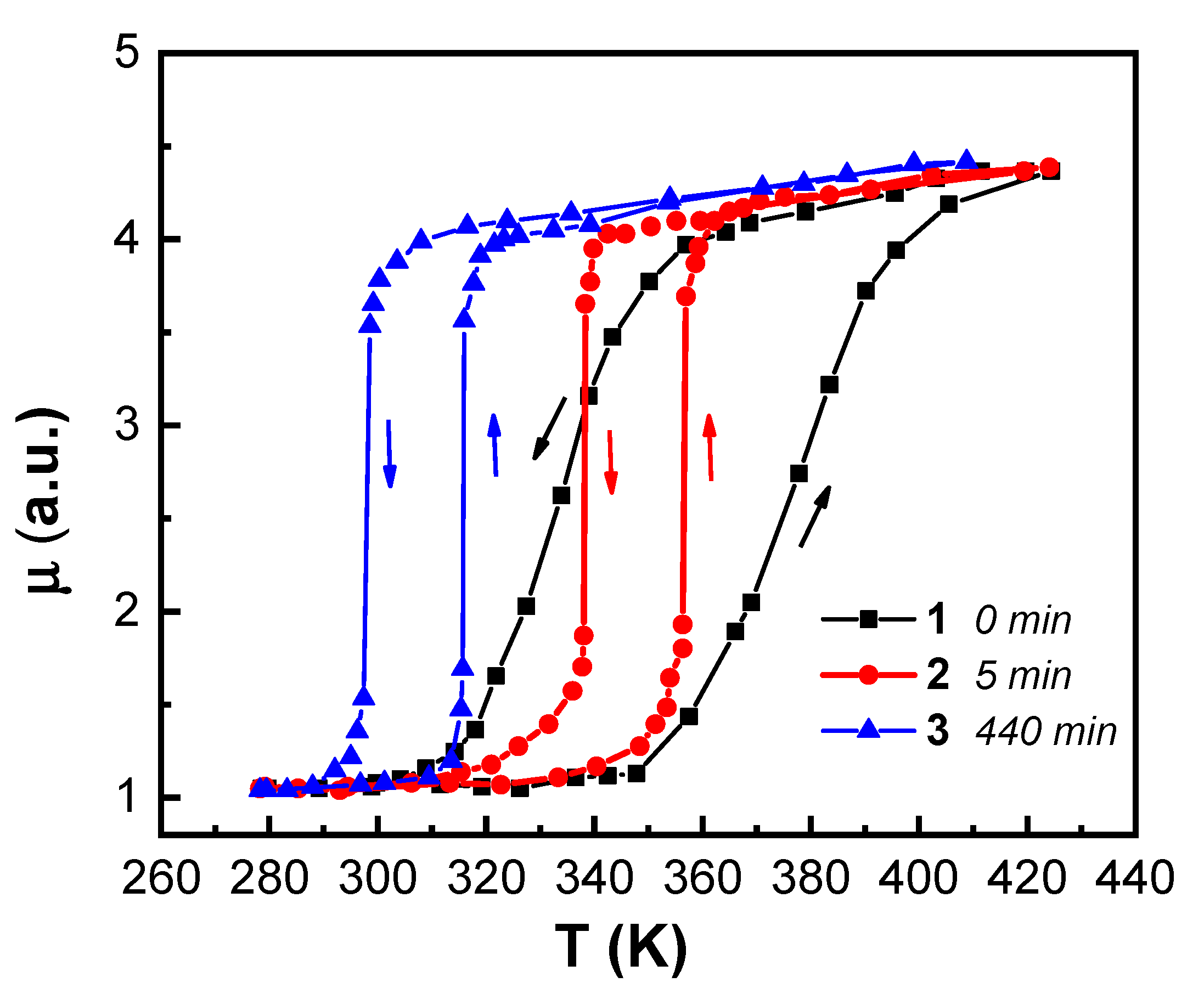
| № | T1, K | t, min | T2, K | T3, K | Treatment Protocol | TAFM–FM, K | T/AFM–FM, K | TFM–AFM, K | T/FM–AFM, K | τ, K | τ/, K |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Before | After | Before | After | Before | After | ||||||
| 1 | - | - | - | - | Annealing 1273 K, 72 h, cooling to RT with rate ~100 K/h | 371.8 | 358.5 | 344.8 | 345.4 | 27.0 | 13.1 |
| 1273 | 35 | 1273 | 473 | Quenching in oil | 334.2 | 332.3 | 321.2 | 321.7 | 13.0 | 10.6 | |
| 2 | - | - | - | - | Annealing 1273 K, 72 h, cooling to RT with rate ~100 K/h | 369.4 | 359.8 | 344.4 | 345.2 | 25.0 | 11.6 |
| 1273 | 35 | 1273 | 274 | Quenching in water | 325.2 | 324.2 | 313.2 | 313.2 | 12.0 | 11.0 | |
| 3 | - | - | - | - | Annealing 1273 K, 72 h, cooling to RT with rate ~100 K/h | 368.6 | - | 343.2 | - | 25.4 | - |
| 1273 | 35 | 513 | 275 | Quenching in water | 362.2 | 354.2 | 337.2 | 338.4 | 25.0 | 15.8 | |
| 4 | - | - | - | - | Annealing 1273 K, 72 h, cooling to RT with rate ~100 K/h | 367.8 | - | 344.2 | - | 23.6 | - |
| 1273 | 35 | 723 | 278 | Quenching in water | 362.8 | 355.6 | 341.0 | 339.1 | 21.8 | 16.5 | |
| 5 | - | - | - | - | Annealing 1273 K, 72 h, cooling to RT with rate ~100 K/h | 368.2 | - | 341.9 | - | 26.3 | - |
| 1273 | 60 | 1258 | 753 | Quenching in liquid Ga | 337.5 | 331.6 | 325.4 | 329.3 | 12.1 | 6.3 | |
| 6 | 1300 | 5 | 1300 | 275 | Quenching in water | 339.5 | 333.7 | 325.8 | 326.8 | 13.7 | 6.9 |
| 7 | 1300 | 440 | 1300 | 275 | Quenching in water | 324.7 | 318.0 | 311.0 | 311.0 | 13.7 | 7.0 |
| 8 | - | - | - | - | Annealing 1273 K, 72 h, cooling to RT with rate ~100 K/h | 353.2 | - | 319.1 | - | 34.1 | - |
| 9 | 1371 | - | 1208 | 789 | Quenching in air | 333.0 | - | 317.0 | - | 16.0 | - |
| 1371 | - | 1364 | 987 | Quenching in air | 323.2 | 320.7 | 303.2 | 303.4 | 20.0 | 17.3 |
| Sample | Treatment Protocol | TAFM–FM, K | TFM–AFM, K | τ, K | Type of Measurement | Ref. |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Fe49Rh51 | Annealing 1273 K, 72 h in vacuum, quenching in air | 320.5 | 314 | 6.5 | M(T) at 0.1 T | [17] |
| 314 | 308 | 6 | M(T) at 1 T | |||
| Fe48Rh52 | Annealing 1273 K, 336 h in vacuum, quenching in water | 321 | 318 | 3 | M(T) at 1 T | [28] |
| Fe49.5Rh50.5 | Annealing 1370 K, 48 h in vacuum, quenching in water | 309 | 300 | 9 | ρ(T) | [29] |
| Fe49Rh51 | Annealing 1273 K, 168 h in vacuum, quenching in air | 316 | 308.5 | 7.5 | M(T) at 1 T | [34] |
| Fe49Rh51 | Annealing 1273 K, 48 h in vacuum, quenching in ice water | 329 | 318 | 11 | M(T) at 5 mT | [40] |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Rodionov, V.; Amirov, A.; Annaorazov, M.; Lähderanta, E.; Granovsky, A.; Aliev, A.; Rodionova, V. Thermal Hysteresis Control in Fe49Rh51 Alloy through Annealing Process. Processes 2021, 9, 772. https://doi.org/10.3390/pr9050772
Rodionov V, Amirov A, Annaorazov M, Lähderanta E, Granovsky A, Aliev A, Rodionova V. Thermal Hysteresis Control in Fe49Rh51 Alloy through Annealing Process. Processes. 2021; 9(5):772. https://doi.org/10.3390/pr9050772
Chicago/Turabian StyleRodionov, Vladimir, Abdulkarim Amirov, Murad Annaorazov, Erkki Lähderanta, Alexander Granovsky, Akhmed Aliev, and Valeria Rodionova. 2021. "Thermal Hysteresis Control in Fe49Rh51 Alloy through Annealing Process" Processes 9, no. 5: 772. https://doi.org/10.3390/pr9050772
APA StyleRodionov, V., Amirov, A., Annaorazov, M., Lähderanta, E., Granovsky, A., Aliev, A., & Rodionova, V. (2021). Thermal Hysteresis Control in Fe49Rh51 Alloy through Annealing Process. Processes, 9(5), 772. https://doi.org/10.3390/pr9050772









