Evaluation of the Engineering Properties of Powdered Activated Carbon Amendments in Porous Asphalt Pavement
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Material and Methods
2.1. Materials
2.2. Methodology
2.2.1. Design and Preparation of PAP and PRP-PAC
2.2.2. Aqueous BTEX Adsorption Capacity Experiments
2.3. Analysis
3. Results and Discussion
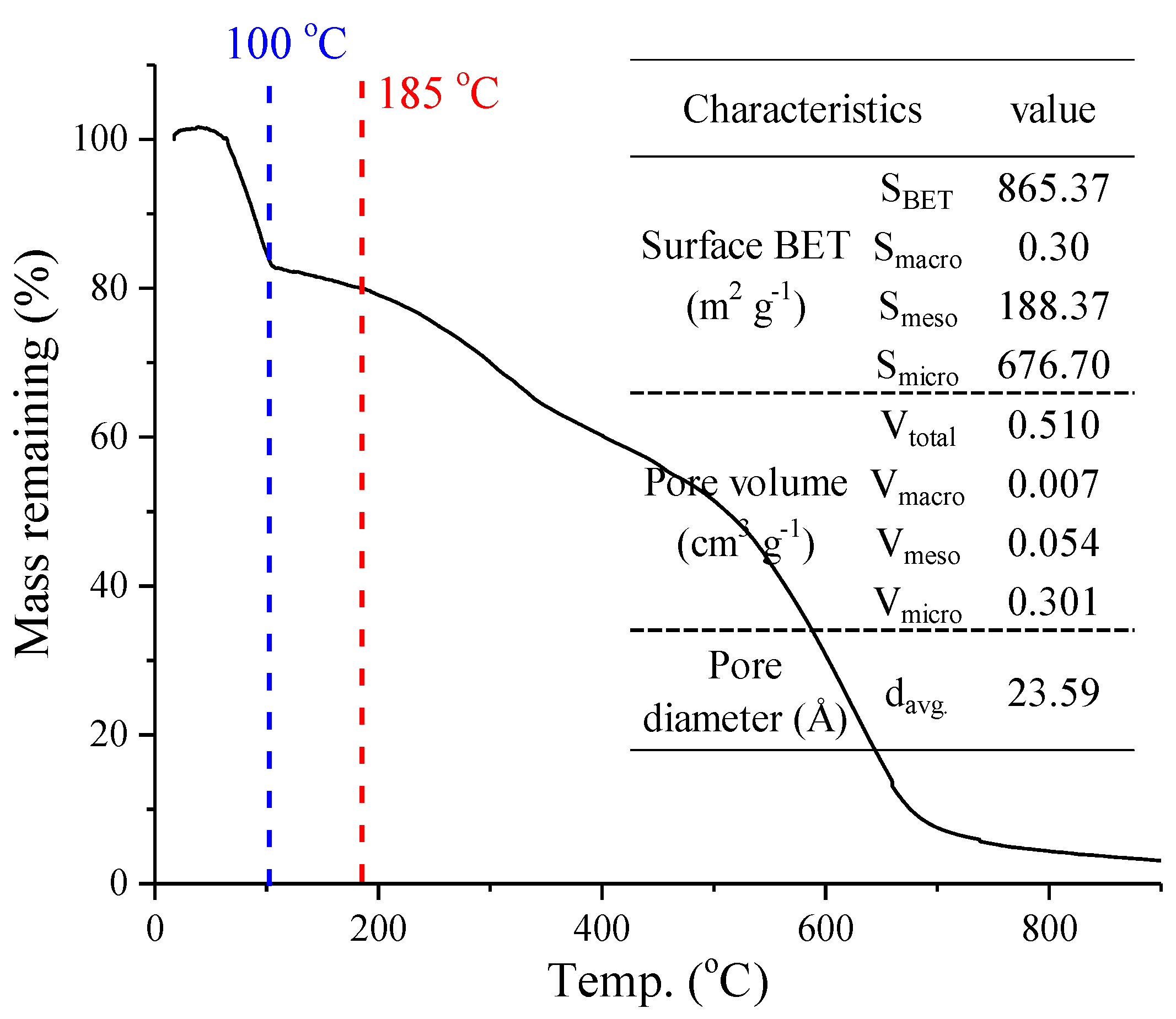
3.1. Characterization of PACs
3.2. Permeable Reactive Pavement
3.2.1. PAP and PRP-PAC Preparation
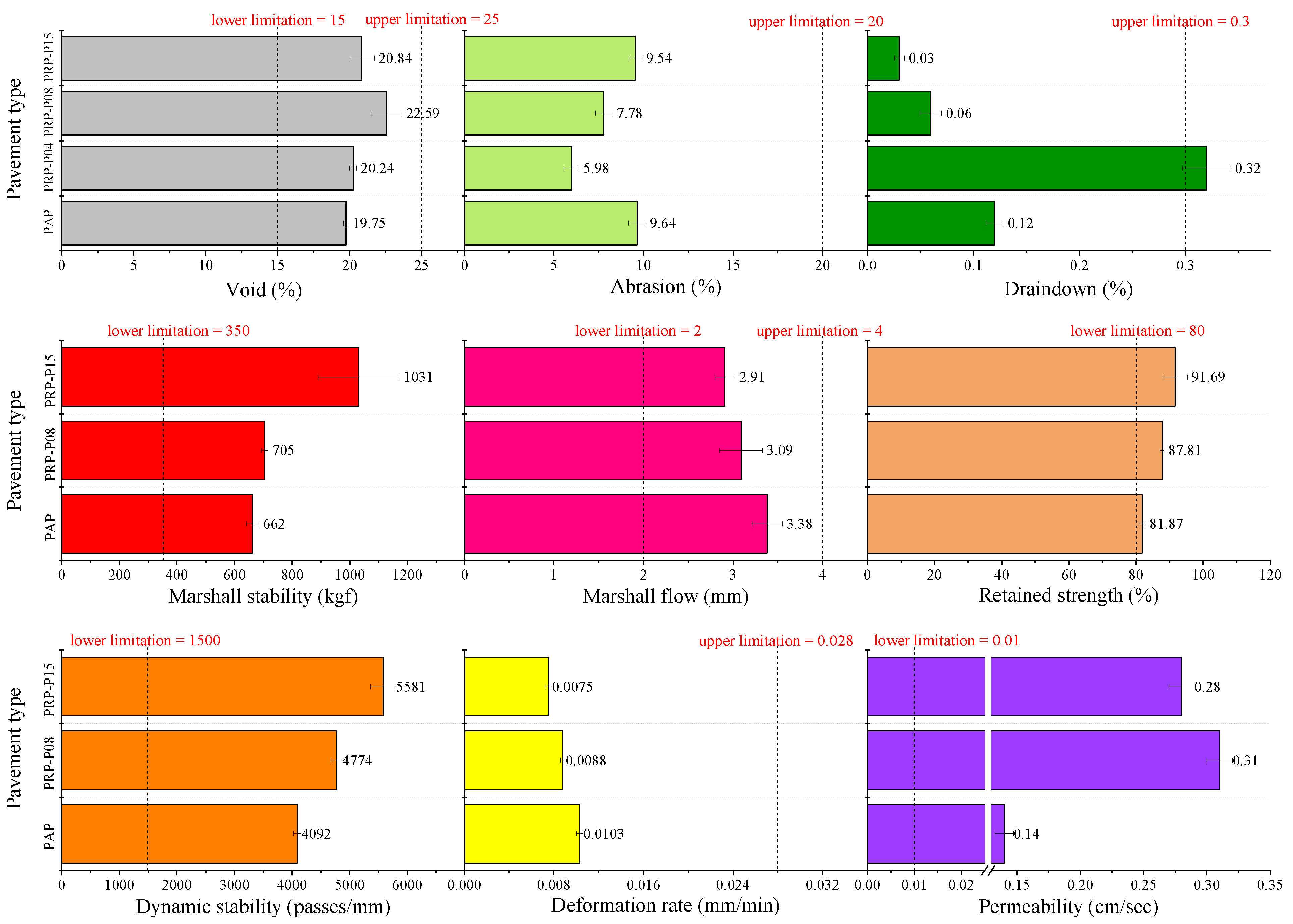
3.2.2. PAP and PRP-PAC Performance
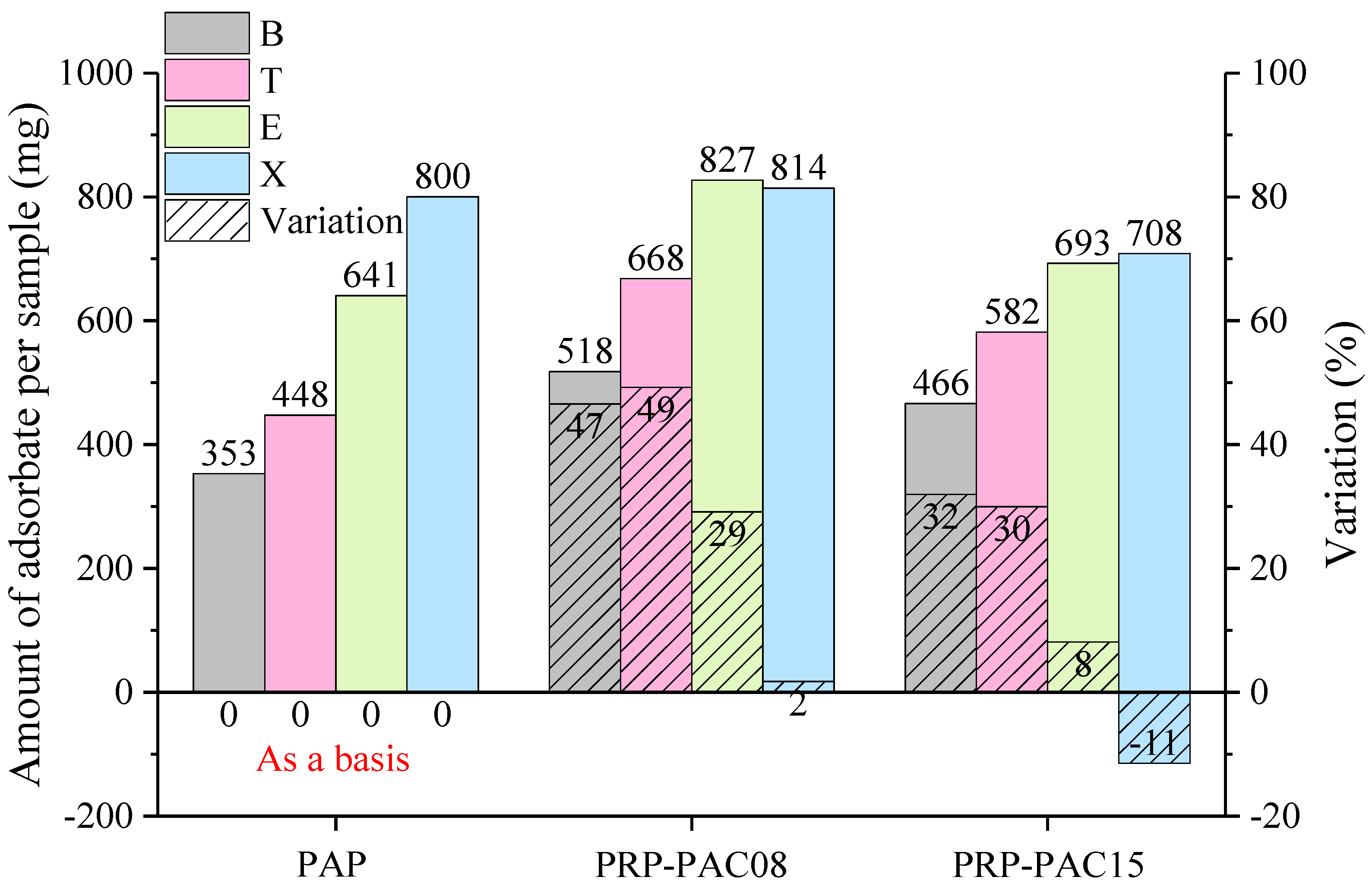
3.2.3. Comparison of Adsorption Capacity of PRP-PAC vs. PAP
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Iordache, A.; Iordache, M.; Sandru, C.; Voica, C.; Stegarus, D.; Zgavarogea, R.; Ionete, R.E.; Ticu, S.C.; Miricioiu, M.G. A Fugacity Based Model for the Assessment of Pollutant Dynamic Evolution of VOCS and BTEX in the Olt River Basin (Romania). Rev. Chim. 2019, 70, 3456–3463. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moradpour, M.; Afshin, H.; Farhanieh, B. A numerical investigation of reactive air pollutant dispersion in urban street canyons with tree planting. Atmos. Pollut. Res. 2016, 8, 253–266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mbanaso, F.U.; Coupe, S.J.; Charlesworth, S.M.; Nnadi, E.O. Laboratory-based experiments to investigate the impact of glyphosate-containing herbicide on pollution attenuation and biodegradation in a model pervious paving system. Chemosphere 2013, 90, 737–746. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- MOTC. 2015 Statistical Yearbook; Directorate General of Highways of Ministry of Transportation and Communications (MOTC): Taipei, Taiwan, 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, H.; Li, H.; Zhang, Y.; Wang, D.; Harvey, J.; Wang, H. Performance enhancement of porous asphalt pavement using red mud as alternative filler. Constr. Build. Mater. 2018, 160, 707–713. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, M.; Huang, X.; Xue, G. Effects of double layer porous asphalt pavement of urban streets on noise reduction. Int. J. Sustain. Built. Environ. 2016, 5, 183–196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smit, A.D.F.; Prozzi, J.A. Quantification of the Reduction of Wet Weather Accidents Using Porous Friction Courses (PFC). Procedia Soc. Behav. Sci. 2013, 96, 2745–2755. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qiu, J.; Huurman, M.; De Bruin, B.; Demmink, E.; Frunt, M. Towards 90% warm re-use of porous asphalt using foaming technology. J. Clean. Prod. 2018, 190, 251–260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, J.; Yin, X.; Wang, H.; Ding, Y. Evaluation of durability and functional performance of porous polyurethane mixture in porous pavement. J. Clean. Prod. 2018, 188, 12–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, S.; Liang, C. A conceptual study on the formulation of a permeable reactive pavement with activated carbon additives for controlling the fate of non-point source environmental organic contaminants. Chemosphere 2018, 193, 438–446. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, S.; Liang, C.; Chen, Y.-J. Persulfate chemical functionalization of carbon nano-tubes and associated adsorption behavior in aqueous phase. Ind. Eng. Chem. Res. 2016, 55, 6060–6068. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- MOTC. Highway Construction Norms; Ministry of Transportation and Communications (MOTC): Taipei, Taiwan, 2015. [Google Scholar]
- Hammes, G.; Thives, L.P.; Ghisi, E. Application of stormwater collected from porous asphalt pavements for non-potable uses in buildings. J. Environ. Manag. 2018, 222, 338–347. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhu, C.; Xu, G.; Zhang, H.; Xiao, F.; Amirkhanian, S.; Wu, C. Influence of different an-ti-stripping agents on the rheological properties of asphalt binder at high temperature. Constr. Build. Mater. 2018, 164, 317–325. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sangiorgi, C.; Eskandarsefat, S.; Tataranni, P.; Simone, A.; Vignali, V.; Lantieri, C.; Dondi, G. A complete laboratory assessment of crumb rubber porous asphalt. Constr. Build. Mater. 2017, 132, 500–507. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

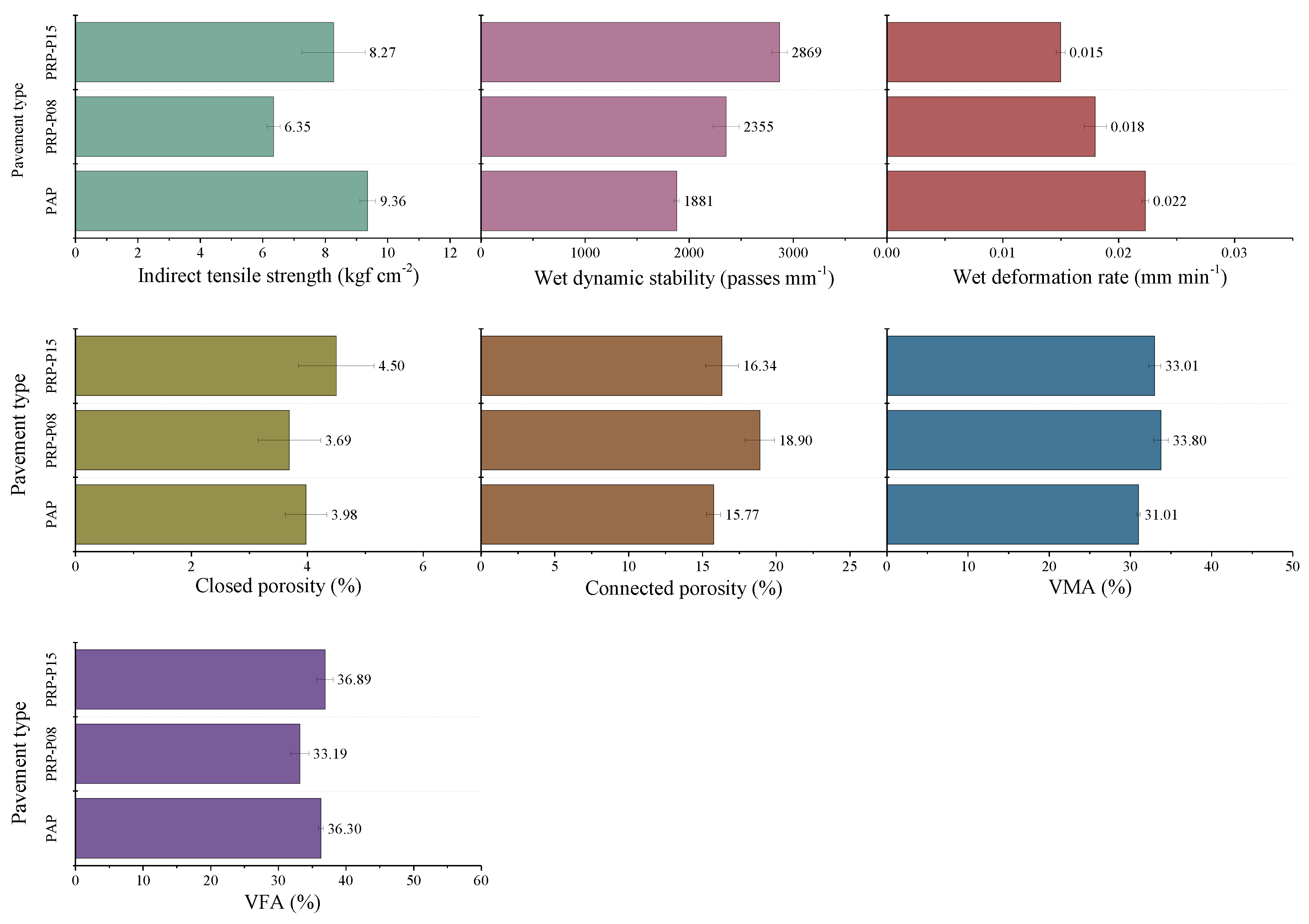
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Huang, S.; Liang, C. Evaluation of the Engineering Properties of Powdered Activated Carbon Amendments in Porous Asphalt Pavement. Processes 2021, 9, 582. https://doi.org/10.3390/pr9040582
Huang S, Liang C. Evaluation of the Engineering Properties of Powdered Activated Carbon Amendments in Porous Asphalt Pavement. Processes. 2021; 9(4):582. https://doi.org/10.3390/pr9040582
Chicago/Turabian StyleHuang, Shengyi, and Chenju Liang. 2021. "Evaluation of the Engineering Properties of Powdered Activated Carbon Amendments in Porous Asphalt Pavement" Processes 9, no. 4: 582. https://doi.org/10.3390/pr9040582
APA StyleHuang, S., & Liang, C. (2021). Evaluation of the Engineering Properties of Powdered Activated Carbon Amendments in Porous Asphalt Pavement. Processes, 9(4), 582. https://doi.org/10.3390/pr9040582





