Innovative Magnetite Based Polymeric Nanocomposite for Simultaneous Removal of Methyl Orange and Hexavalent Chromium from Water
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Chemicals
2.2. Polypyrrole Magnetic Chitosan Synthesis
2.3. Nanocomposite Characterization
2.4. Adsorption Batch Experiments
3. Results and Discussions
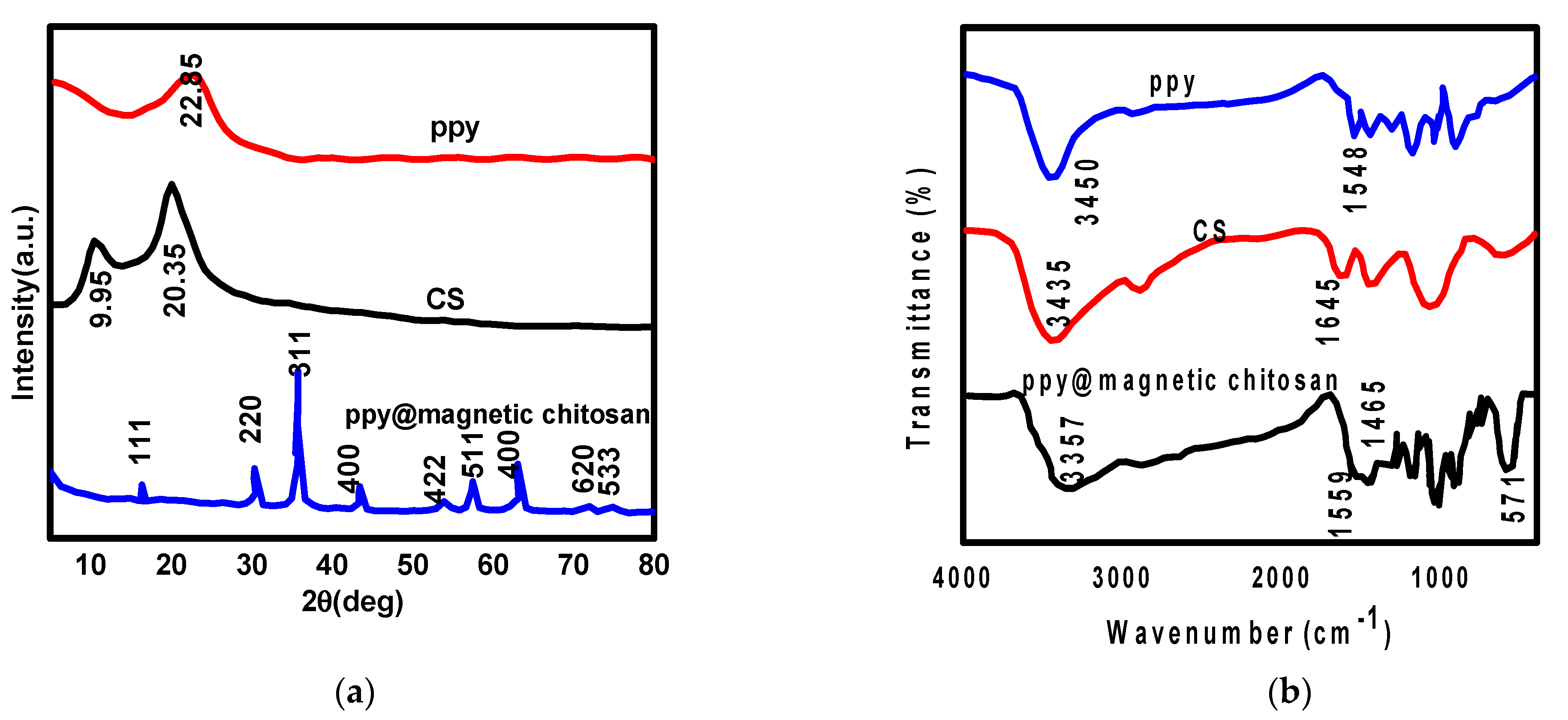
3.1. Nanocomposite Characterization
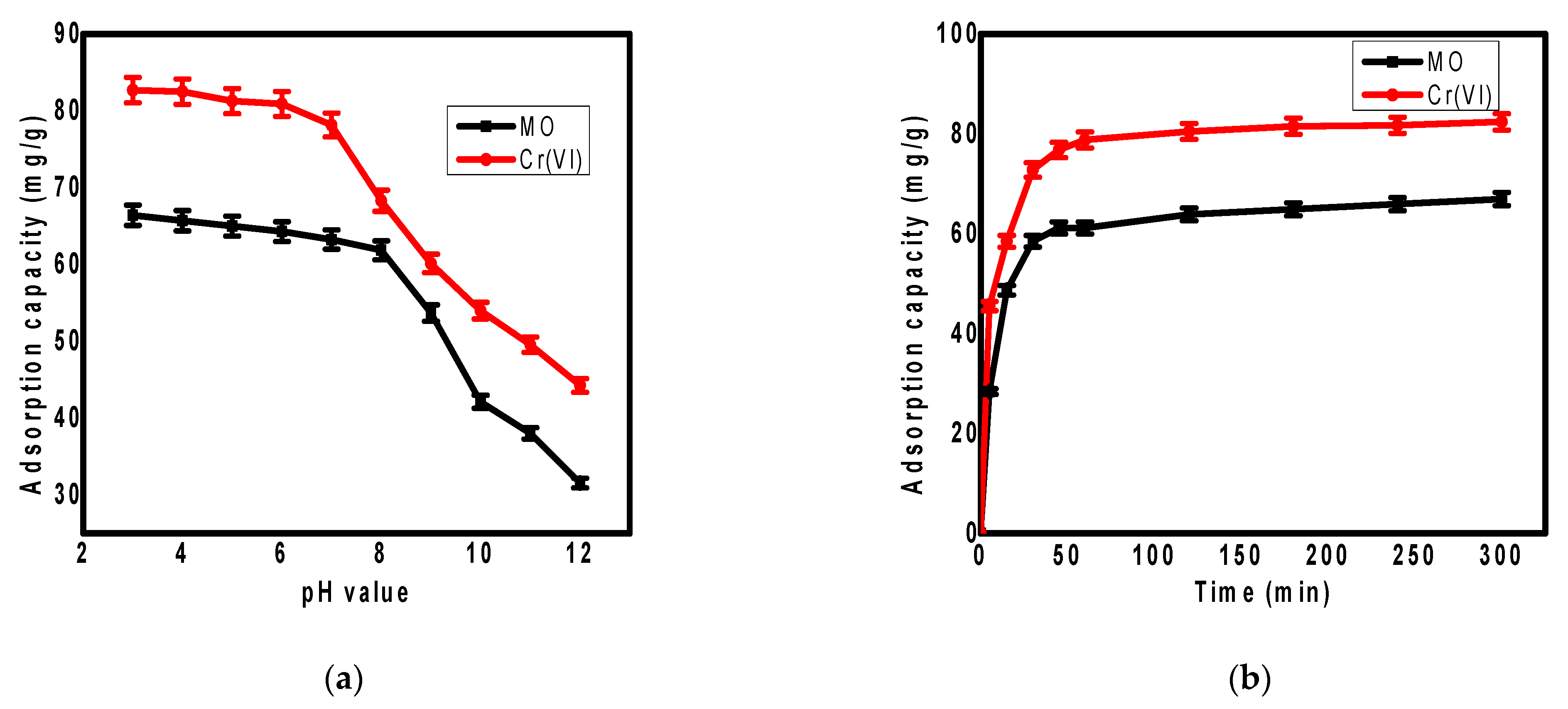
3.2. pH Effect on the Adsorption
3.3. Contact Time Effect on the Adsorption
3.4. Competitive Ions Effect
3.5. Reusability of the Adsorbent
3.6. Adsorption Isotherm
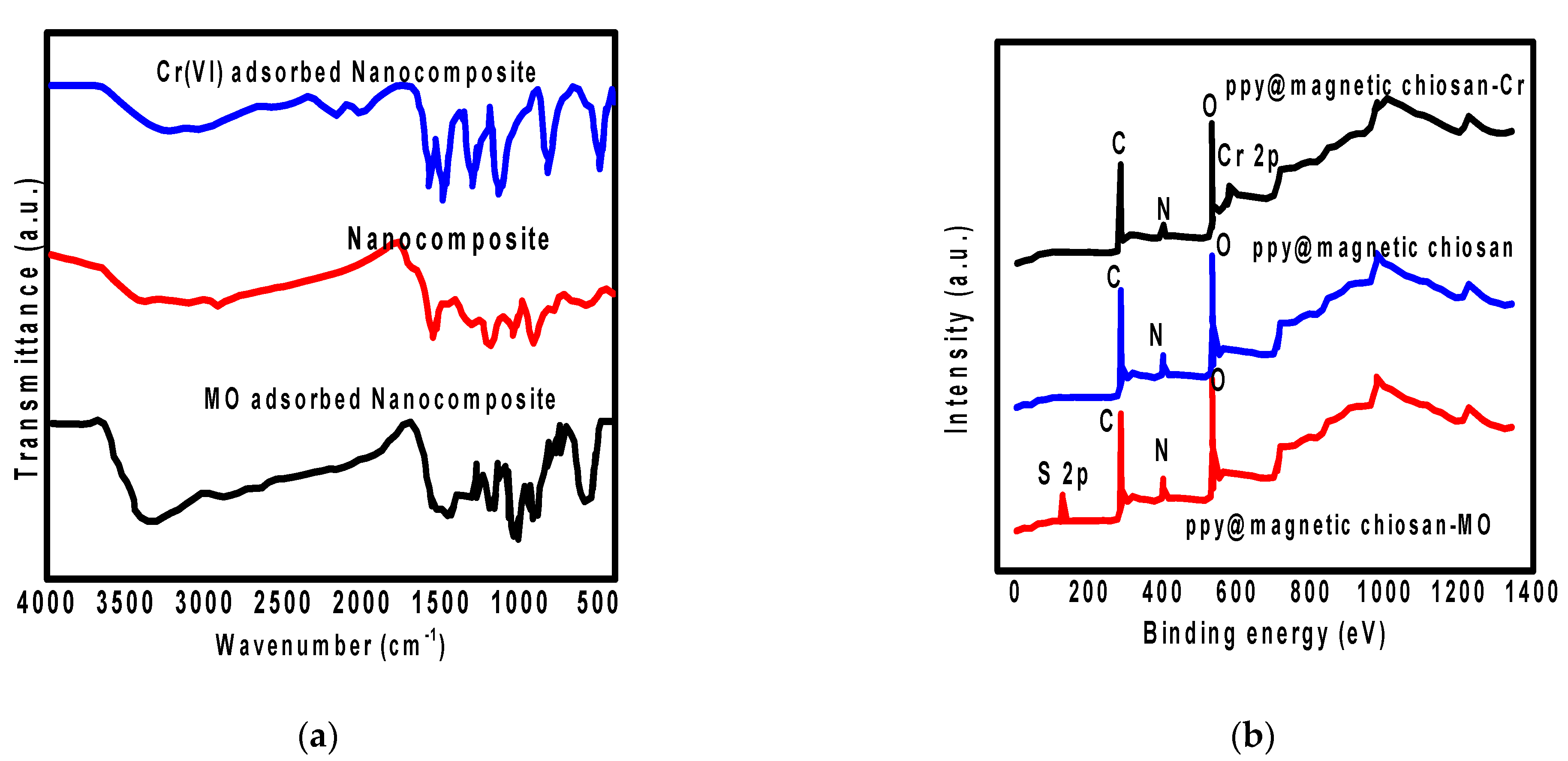
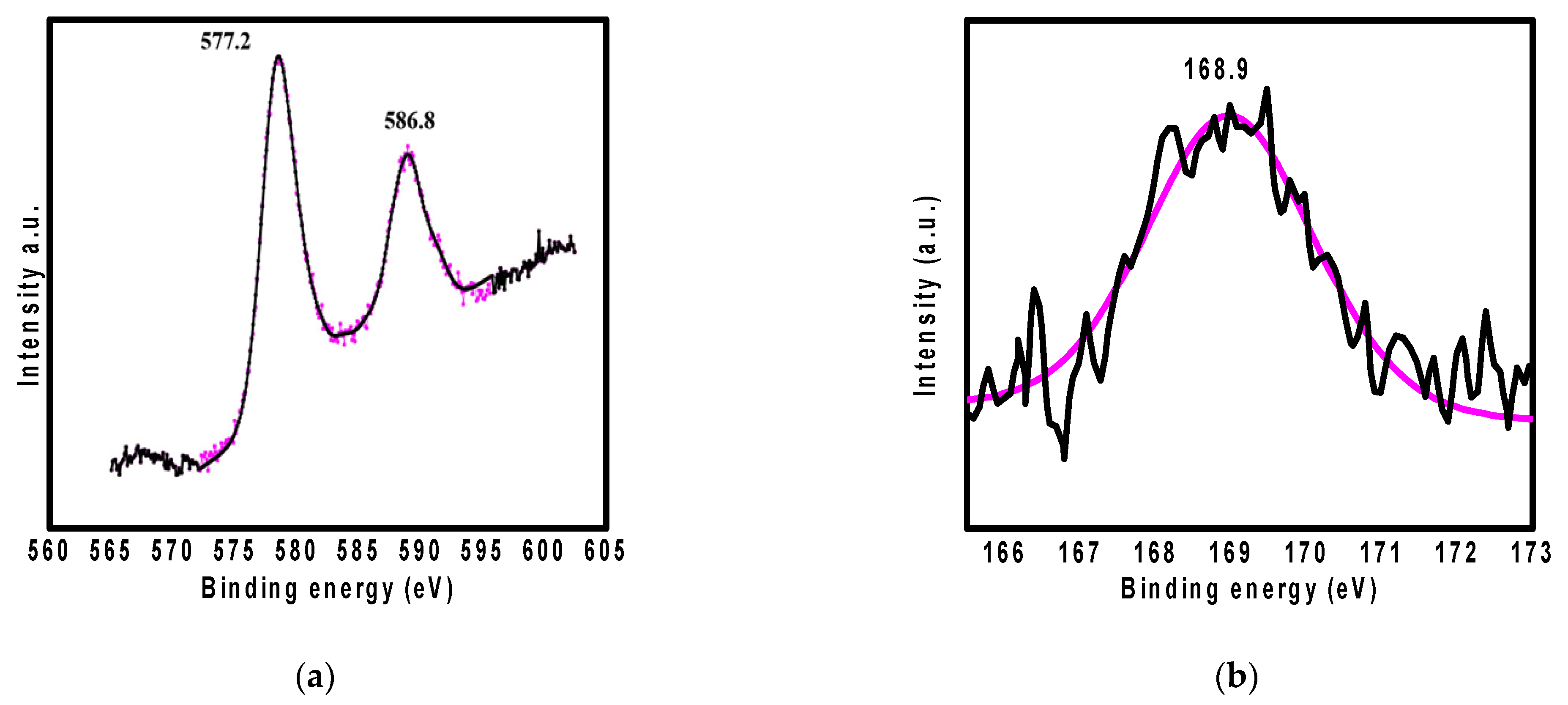
3.7. Adsorption Mechanism
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Tahoon, M.A.; Siddeeg, S.M.; Salem Alsaiari, N.; Mnif, W.; Ben Rebah, F. Effective heavy metals removal from water using nanomaterials: A review. Processes 2020, 8, 645. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Siddeeg, S.M.; Tahoon, M.A.; Ben Rebah, F. Agro-industrial waste materials and wastewater as growth media for microbial bioflocculants production: A review. Mater. Res. Express 2019, 7, 012001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Siddeeg, S.M.; Tahoon, M.A.; Alsaiari, N.S.; Shabbir, M.; Ben Rebah, F. Application of Functionalized Nanomaterials as Effective Adsorbents for the Removal of Heavy Metals from Wastewater: A Review. Curr. Anal. Chem. 2021, 17, 4–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, K.; Miwornunyuie, N.; Chen, L.; Jingyu, H.; Amaniampong, P.S.; Ato Koomson, D.; Ewusi-Mensah, D.; Xue, W.; Li, G.; Lu, H. Sustainable Application of ZIF-8 for Heavy-Metal Removal in Aqueous Solutions. Sustainability 2021, 13, 984. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohd Makhtar, N.S.; Idris, J.; Musa, M.; Andou, Y.; Ku Hamid, K.H.; Puasa, S.W. Plant-Based Tacca leontopetaloides Biopolymer Flocculant (TBPF) Produced High Removal of Heavy Metal Ions at Low Dosage. Processes 2021, 9, 37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khalil, U.; Shakoor, M.B.; Ali, S.; Ahmad, S.R.; Rizwan, M.; Alsahli, A.A.; Alyemeni, M.N. Selective Removal of Hexavalent Chromium from Wastewater by Rice Husk: Kinetic, Isotherm and Spectroscopic Investigation. Water 2021, 13, 263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Campisi, S.; Evangelisti, C.; Postole, G.; Gervasini, A. Combination of interfacial reduction of hexavalent chromium and trivalent chromium immobilization on tin-functionalized hydroxyapatite materials. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2021, 539, 148227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Athira, T.; Roshith, M.; Babu, T.S.; Kumar, D.V.R. Fibrous red phosphorus as a non-metallic photocatalyst for the effective reduction of Cr (VI) under direct sunlight. Mater. Lett. 2021, 283, 128750. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- WHO. Guidelines for Drinking Water Quality, 4th ed.; WHO: Geneva, Switzerland, 2011. [Google Scholar]
- Mystrioti, C.; Koursari, S.; Xenidis, A.; Papassiopi, N. Hexavalent Chromium Reduction by Gallic Acid. Chemosphere 2021, 273, 129737. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ihlenburg, R.B.; Lehnen, A.-C.; Koetz, J.; Taubert, A. Sulfobetaine Cryogels for Preferential Adsorption of Methyl Orange from Mixed Dye Solutions. Polymers 2021, 13, 208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Deng, M.; Wang, X.; Wang, Y.; Li, J.; Xia, S.; Zhao, J. In-situ remediation of oxytetracycline and Cr (VI) co-contaminated soil and groundwater by using blast furnace slag-supported nanosized Fe0/FeSx. Chem. Eng. J. 2021, 412, 128706. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stern, C.M.; Jegede, T.O.; Hulse, V.A.; Elgrishi, N. Electrochemical reduction of Cr (VI) in water: Lessons learned from fundamental studies and applications. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2021, 50, 1642–1667. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sabri, M.A.; Sara, Z.; Al-Sayah, M.H.; Ibrahim, T.H.; Khamis, M.I.; El-Kadri, O.M. Simultaneous Adsorption and Reduction of Cr (VI) to Cr (III) in Aqueous Solution Using Nitrogen-Rich Aminal Linked Porous Organic Polymers. Sustainability 2021, 13, 923. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gallo-Cordova, A.; Lemus, J.; Palomares, F.J.; Morales, M.; Mazarío, E. Superparamagnetic nanosorbent for water purification: Assessment of the adsorptive removal of lead and methyl orange from aqueous solutions. Sci. Total Environ. 2020, 711, 134644. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Niazi, L.; Lashanizadegan, A.; Sharififard, H. Chestnut oak shells activated carbon: Preparation, characterization and application for Cr (VI) removal from dilute aqueous solutions. J. Clean. Prod. 2018, 185, 554–561. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, J.; Zhou, Q.; Chen, J.; Zhang, L.; Chang, N. Phosphate adsorption on hydroxyl–iron–lanthanum doped activated carbon fiber. Chem. Eng. J. 2013, 215, 859–867. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, N.; Reddy, L.; Parashar, V.; Ngila, J.C. Controlled synthesis of microsheets of ZnAl layered double hydroxides hexagonal nanoplates for efficient removal of Cr (VI) ions and anionic dye from water. J. Environ. Chem. Eng. 2017, 5, 1718–1731. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karthikeyan, P.; Banu, H.A.T.; Meenakshi, S. Removal of phosphate and nitrate ions from aqueous solution using La3+ incorporated chitosan biopolymeric matrix membrane. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2019, 124, 492–504. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anbinder, P.S.; Macchi, C.; Amalvy, J.; Somoza, A. A study of the structural changes in a chitosan matrix produced by the adsorption of copper and chromium ions. Carbohydr. Polym. 2019, 222, 114987. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaur, M.; Kaur, N.; Jeet, K.; Kaur, P. MgFe2O4 nanoparticles loaded on activated charcoal for effective removal of Cr (VI)—A novel approach. Ceram. Int. 2015, 41, 13739–13750. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Y.; Yang, J.; Du, Y.; Li, C.; Wei, K.; Lu, J.; Chen, W.; Yang, L. Preparation and Characterization of Cationic Water-Soluble Pillar [5] arene-Modified Zeolite for Adsorption of Methyl Orange. ACS Omega 2019, 4, 17741–17751. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Fu, R.; Yang, Y.; Xu, Z.; Zhang, X.; Guo, X.; Bi, D. The removal of chromium (VI) and lead (II) from groundwater using sepiolite-supported nanoscale zero-valent iron (S-NZVI). Chemosphere 2015, 138, 726–734. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, P.; Xie, F.; Tang, F.; McNally, T. Influence of plasticiser type and nanoclay on the properties of chitosan-based materials. Eur. Polym. J. 2021, 144, 110225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, S.; Liu, Z.; Wu, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Hu, H.; Huang, Z.; Qin, Y.; Liang, J. 3D porous tubular network-structured chitosan-based beads with multifunctional groups: Highly efficient and selective removal of Cu2+. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2021, 171, 17–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Saravanan, A.; Kumar, P.S.; Govarthanan, M.; George, C.S.; Vaishnavi, S.; Moulishwaran, B.; Kumar, S.P.; Jeevanantham, S.; Yaashikaa, P. Adsorption characteristics of magnetic nanoparticles coated mixed fungal biomass for toxic Cr (VI) ions in aquatic environment. Chemosphere 2021, 267, 129226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zeng, H.; Zhai, L.; Zhang, J.; Li, D. As (V) adsorption by a novel core-shell magnetic nanoparticles prepared with Iron-containing water treatment residuals. Sci. Total Environ. 2021, 753, 142002. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qiu, X.; Wang, S.; Miao, S.; Suo, H.; Xu, H.; Hu, Y. Co-immobilization of laccase and ABTS onto amino-functionalized ionic liquid-modified magnetic chitosan nanoparticles for pollutants removal. J. Hazard. Mater. 2021, 401, 123353. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ren, Y.; Abbood, H.A.; He, F.; Peng, H.; Huang, K. Magnetic EDTA-modified chitosan/SiO2/Fe3O4 adsorbent: Preparation, characterization, and application in heavy metal adsorption. Chem. Eng. J. 2013, 226, 300–311. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Pan, K.; He, Q.; Cao, B. Polyacrylonitrile/polypyrrole core/shell nanofiber mat for the removal of hexavalent chromium from aqueous solution. J. Hazard. Mater. 2013, 244, 121–129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Siddeeg, S.M.; Tahoon, M.A.; Mnif, W.; Ben Rebah, F. Iron oxide/chitosan magnetic nanocomposite immobilized manganese peroxidase for decolorization of textile wastewater. Processes 2020, 8, 5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Yuvaraj, H.; Woo, M.H.; Park, E.J.; Jeong, Y.T.; Lim, K.T. Polypyrrole/γ-Fe2O3 magnetic nanocomposites synthesized in supercritical fluid. Eur. Polym. J. 2008, 44, 637–644. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Govindan, S.; Nivethaa, E.; Saravanan, R.; Narayanan, V.; Stephen, A. Synthesis and characterization of chitosan–silver nanocomposite. Appl. Nanosci. 2012, 2, 299–303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- M Siddeeg, S.; A Tahoon, M.; Ben Rebah, F. Simultaneous Removal of Calconcarboxylic Acid, NH4+ and PO43− from Pharmaceutical Effluent Using Iron Oxide-Biochar Nanocomposite Loaded with Pseudomonas putida. Processes 2019, 7, 800. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Siddeeg, S.M.; Amari, A.; Tahoon, M.A.; Alsaiari, N.S.; Ben Rebah, F. Removal of meloxicam, piroxicam and Cd+ 2 by Fe3O4/SiO2/glycidyl methacrylate-S-SH nanocomposite loaded with laccase. Alex. Eng. J. 2020, 59, 905–914. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhaumik, M.; Maity, A.; Srinivasu, V.; Onyango, M.S. Enhanced removal of Cr (VI) from aqueous solution using polypyrrole/Fe3O4 magnetic nanocomposite. J. Hazard. Mater. 2011, 190, 381–390. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Robati, D.; Mirza, B.; Rajabi, M.; Moradi, O.; Tyagi, I.; Agarwal, S.; Gupta, V. Removal of hazardous dyes-BR 12 and methyl orange using graphene oxide as an adsorbent from aqueous phase. Chem. Eng. J. 2016, 284, 687–697. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, K.; Li, P.; Cai, J.; Xiao, S.; Yang, H.; Li, A. Efficient adsorption of both methyl orange and chromium from their aqueous mixtures using a quaternary ammonium salt modified chitosan magnetic composite adsorbent. Chemosphere 2016, 154, 310–318. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, S.; Huang, Y.; Han, X.; Wu, Z.; Lai, C.; Wang, J.; Deng, Q.; Zeng, Z.; Deng, S. Simultaneous and efficient removal of Cr (VI) and methyl orange on LDHs decorated porous carbons. Chem. Eng. J. 2018, 352, 306–315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karthikeyan, P.; Elanchezhiyan, S.S.; Preethi, J.; Meenakshi, S.; Park, C.M. Mechanistic performance of polyaniline-substituted hexagonal boron nitride composite as a highly efficient adsorbent for the removal of phosphate, nitrate, and hexavalent chromium ions from an aqueous environment. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2020, 511, 145543. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, Y.; Cao, X.; Ouyang, X.; Sohi, S.P.; Chen, J. Adsorption kinetics of magnetic biochar derived from peanut hull on removal of Cr (VI) from aqueous solution: Effects of production conditions and particle size. Chemosphere 2016, 145, 336–341. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, P.; Zhang, R.; Wang, J. Adsorption of methyl orange from aqueous solution using chitosan/diatomite composite. Water Sci. Technol. 2017, 75, 1633–1642. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Annadurai, G.; Juang, R.-S.; Lee, D.-J. Use of cellulose-based wastes for adsorption of dyes from aqueous solutions. J. Hazard. Mater. 2002, 92, 263–274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, B.; Luo, H. Adsorption of hexavalent chromium onto montmorillonite modified with hydroxyaluminum and cetyltrimethylammonium bromide. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2010, 257, 769–775. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lazaridis, N.; Pandi, T.; Matis, K. Chromium (VI) removal from aqueous solutions by Mg–Al–CO3 hydrotalcite: Sorption–desorption kinetic and equilibrium studies. Ind. Eng. Chem. Res. 2004, 43, 2209–2215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chang, N.; Zhang, H.; Shi, M.-S.; Li, J.; Shao, W.; Wang, H.-T. Metal-organic framework templated synthesis of TiO2@ MIL-101 core-shell architectures for high-efficiency adsorption and photocatalysis. Mater. Lett. 2017, 200, 55–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gandhi, M.R.; Meenakshi, S. Preparation and characterization of La (III) encapsulated silica gel/chitosan composite and its metal uptake studies. J. Hazard. Mater. 2012, 203, 29–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pérez, E.; Ayele, L.; Getachew, G.; Fetter, G.; Bosch, P.; Mayoral, A.; Díaz, I. Removal of chromium (VI) using nano-hydrotalcite/SiO2 composite. J. Environ. Chem. Eng. 2015, 3, 1555–1561. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zeng, L.; Xie, M.; Zhang, Q.; Kang, Y.; Guo, X.; Xiao, H.; Peng, Y.; Luo, J. Chitosan/organic rectorite composite for the magnetic uptake of methylene blue and methyl orange. Carbohydr. Polym. 2015, 123, 89–98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deng, L.; Shi, Z.; Peng, X.; Zhou, S. Magnetic calcinated cobalt ferrite/magnesium aluminum hydrotalcite composite for enhanced adsorption of methyl orange. J. Alloys Compd. 2016, 688, 101–112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]




| Pollutant | Freundlich | Langmuir | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| qe (mg/g) | qm (mg/g) | KF (L·mg/g) | n | R2 | qe (mg/g) | qm (mg/g) | KL (L·mg/g) | R2 | |
| MO | 88.8 | 97.9 | 46.9 | 4.789 | 0.880 | 94.9 | 97.9 | 0.323 | 0.998 |
| Cr (VI) | 101.5 | 106.4 | 32.7 | 4.679 | 0.847 | 104.8 | 106.4 | 0.268 | 0.997 |
| Adsorbent | Operating Conditions | Removal Efficiency (mg/g) | Ref. | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| MO | Cr (VI) | |||
| ppy@magnetic chitosan | dosage: 100 mg/L, contact time: 40 min, 25 °C; 200 rpm, pH 4.5 | 95 | 105 | This study |
| Magnetic biochar | dosage: 200 mg/L; contact time: 5 days, 25 °C, 160 rpm, pH 5 | - | 77.54 | [41] |
| Chitosan/diatomite composite | dosage: 0.2 g/L, contact time: 40 min, 25 °C, pH 5 | 35 | - | [42] |
| CuO NPs Graphene oxide | dosage: 25 mg/L, contact time: 100 min, 25–40 °C, pH 3 | - | 16.83 | [37] |
| Banana peel | dosage: 100 mg/L, contact time: 24 h, 30 °C, 180 rpm, pH 6–7 | 21 | - | [43] |
| Cetylpyridinium bromide modified Montmorillonite | Dosage: 50 mg/L, contact time: 60 min, 25 °C,150 rpm, pH 4 | 6.54 | - | [44] |
| Modified wheat straw Hydrotalcite | Dosage: 5–10 mg/L; contact time: 24 h, 30 °C, 250 rpm, pH 6 | - | 17 | [45] |
| Hydrotalcite sepiolite-supported nanoscale zero-valent iron (S-NZVI) | Dosage: 0.05–3.2 g/L contact time: 11 min, 28 °C, 200 rpm, pH 6 | 43.86 | [23] | |
| TiO2@MIL-101 core–shell | Dosage: 150 mg/L contact time: 4 h | 19.23 | - | [46] |
| Chitosan/alumina composite | Dosage: 10 mg/L contact time: 60 min, 303 °C, 200 rpm, pH 4 | - | 6.127 | [47] |
| Nano-hydrotalcite SiO2 composite | Dosage: 1 g/L contact time: 24 h | 35 | - | [48] |
| Chitosan/organic rectorite-Fe3O4 | Dosage: 40 mg/L contact time: 80 min, 25 °C, 200 rpm, pH 3 | 5.56 | [49] | |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Alsaiari, N.S.; Amari, A.; Katubi, K.M.; Alzahrani, F.M.; Rebah, F.B.; Tahoon, M.A. Innovative Magnetite Based Polymeric Nanocomposite for Simultaneous Removal of Methyl Orange and Hexavalent Chromium from Water. Processes 2021, 9, 576. https://doi.org/10.3390/pr9040576
Alsaiari NS, Amari A, Katubi KM, Alzahrani FM, Rebah FB, Tahoon MA. Innovative Magnetite Based Polymeric Nanocomposite for Simultaneous Removal of Methyl Orange and Hexavalent Chromium from Water. Processes. 2021; 9(4):576. https://doi.org/10.3390/pr9040576
Chicago/Turabian StyleAlsaiari, Norah Salem, Abdelfattah Amari, Khadijah Mohammedsaleh Katubi, Fatimah Mohammed Alzahrani, Faouzi Ben Rebah, and Mohamed A. Tahoon. 2021. "Innovative Magnetite Based Polymeric Nanocomposite for Simultaneous Removal of Methyl Orange and Hexavalent Chromium from Water" Processes 9, no. 4: 576. https://doi.org/10.3390/pr9040576
APA StyleAlsaiari, N. S., Amari, A., Katubi, K. M., Alzahrani, F. M., Rebah, F. B., & Tahoon, M. A. (2021). Innovative Magnetite Based Polymeric Nanocomposite for Simultaneous Removal of Methyl Orange and Hexavalent Chromium from Water. Processes, 9(4), 576. https://doi.org/10.3390/pr9040576









