Characterization of Pyrolysis Products and Kinetic Analysis of Waste Jute Stick Biomass
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials
2.2. Thermogravimetric Analysis
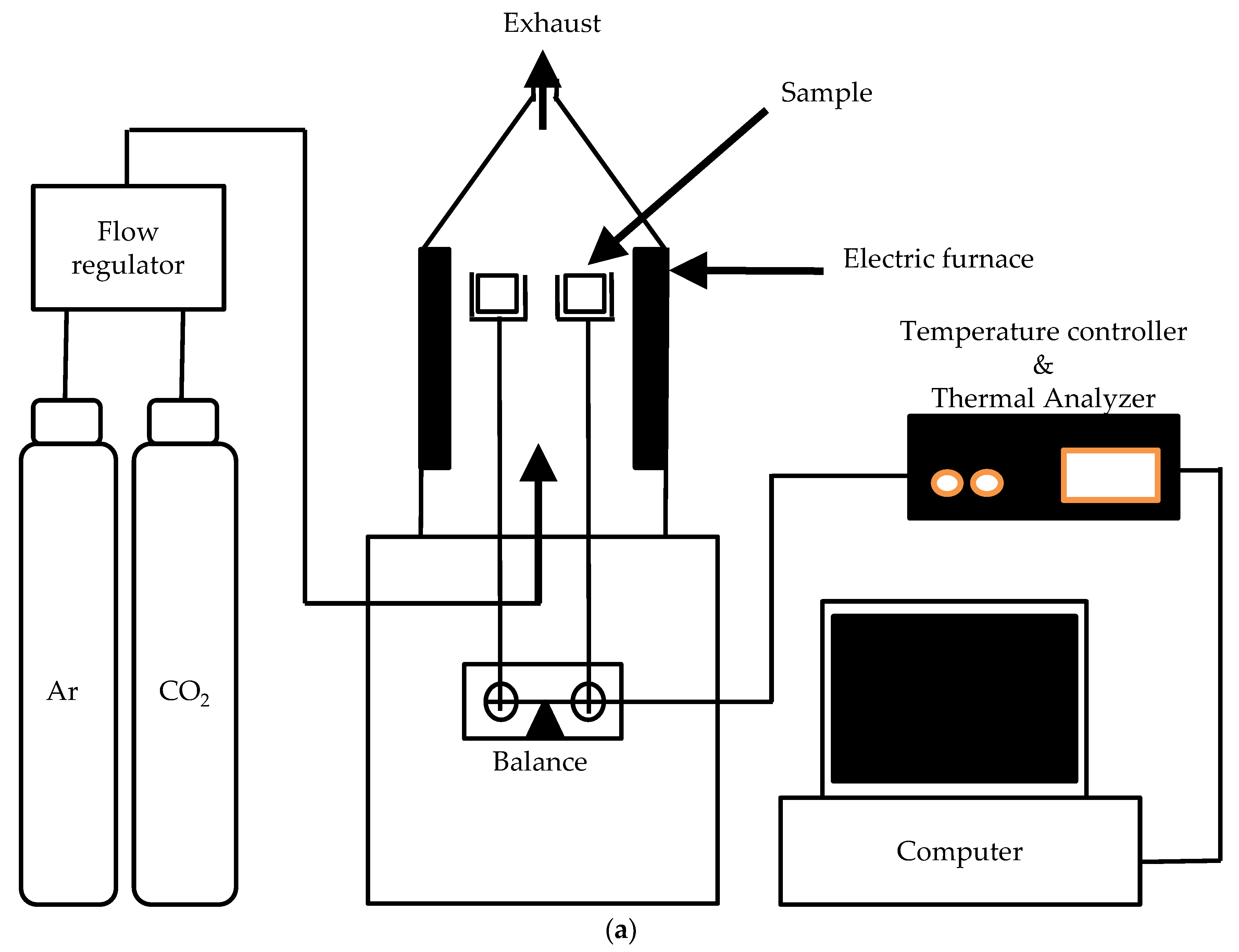
2.3. Experimental Apparatus for Jute Stick Fixed-Bed Pyrolysis
2.4. Pyrolysis Procedure
2.5. Kinetic Study
2.6. Model-Free Methods
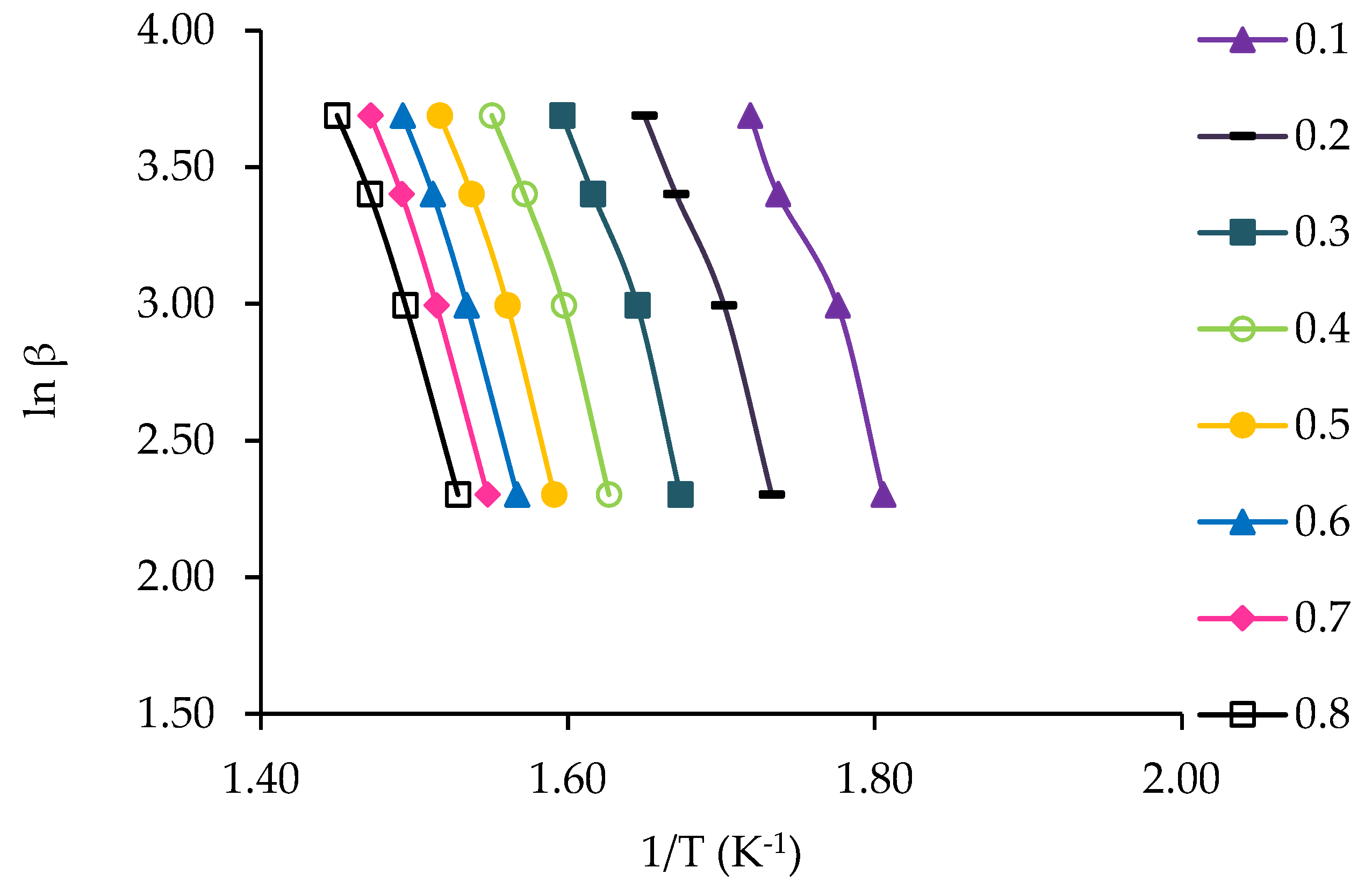
2.6.1. Flynn–Wall–Ozawa (FWO) Method
2.6.2. Kissinger–Akahira–Sunose (KAS) Method
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Proximate and Ultimate Analysis of Jute Stick
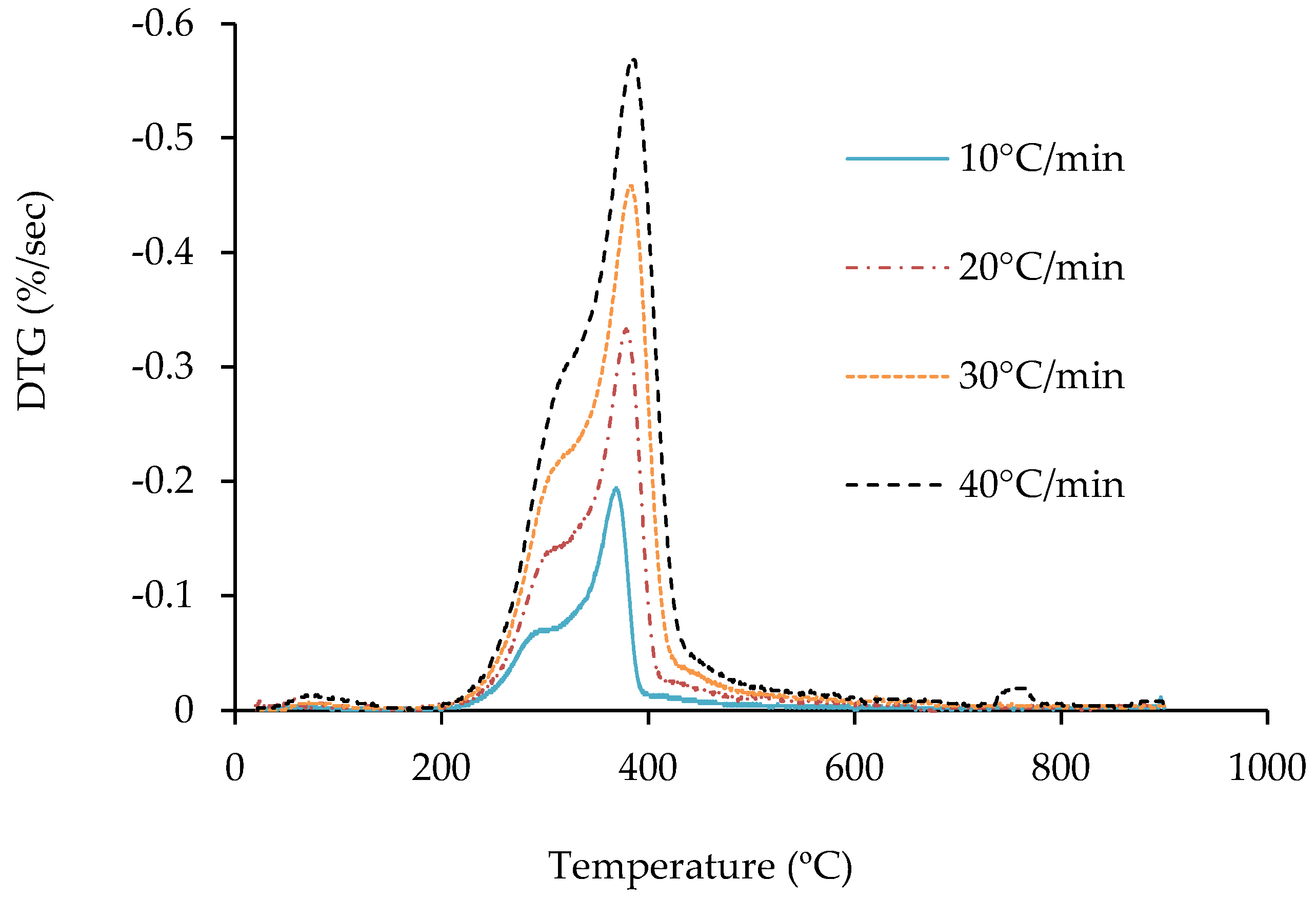
3.2. Thermogravimetric Analysis of Jute Stick
3.3. The Yield of Pyrolysis Products
3.3.1. Influence of Heating Rate on Bio-Oil Properties
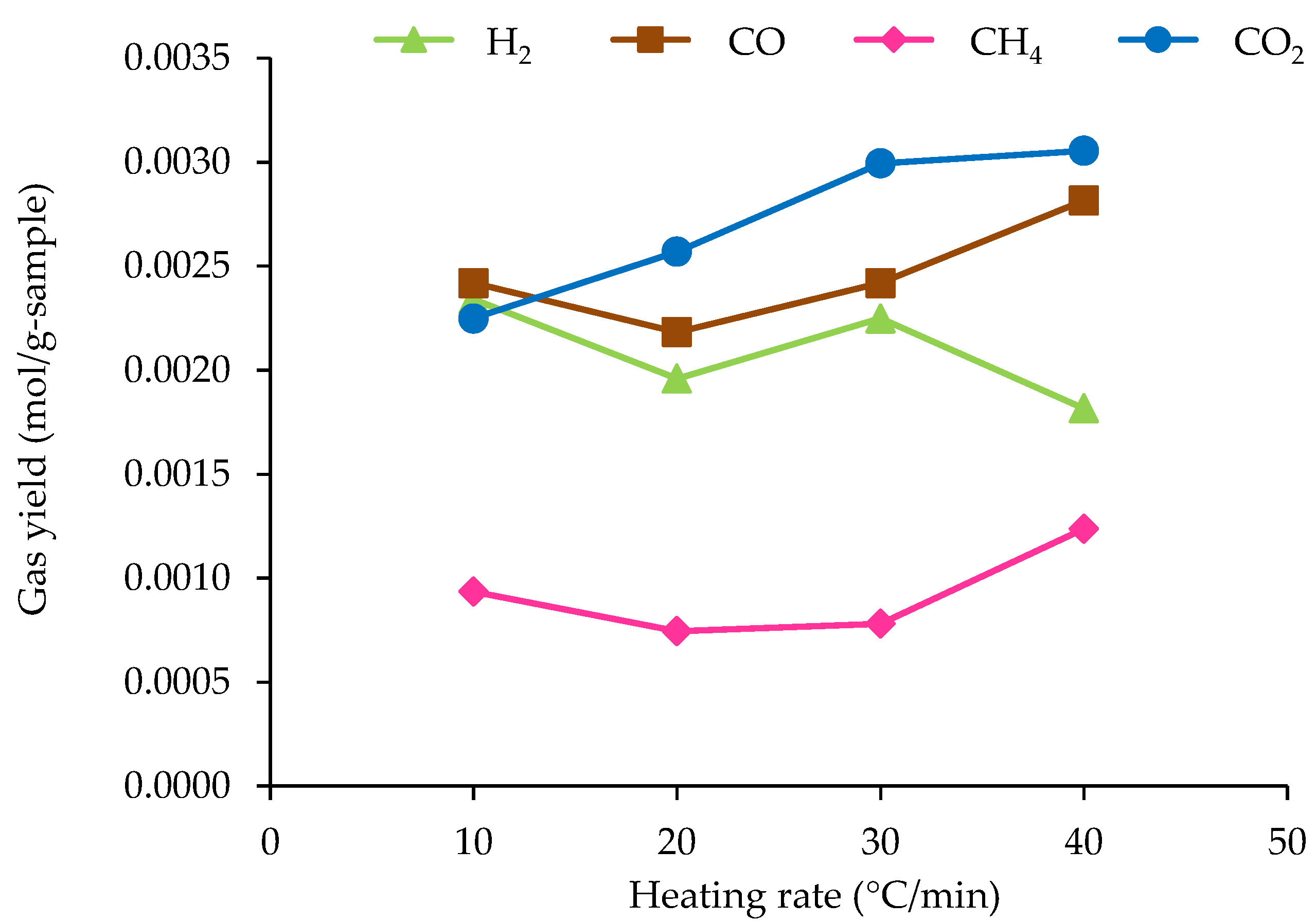
3.3.2. Effect of Heating Rate on Non-Condensable Gas
3.3.3. Influence of Heating Rate on Bio-Char
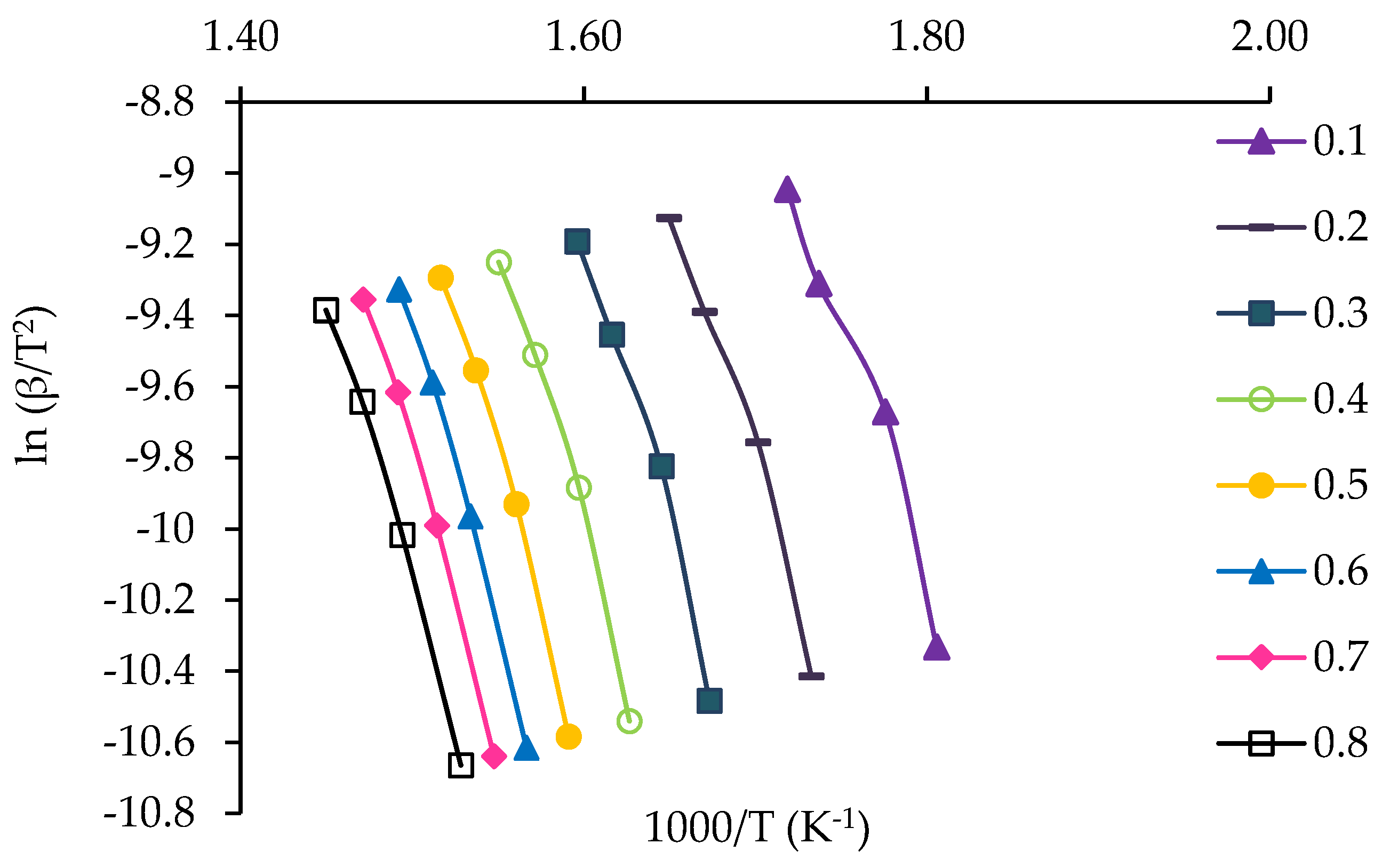
3.4. Kinetic Study of Jute Stick
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Uddin, M.N.; Techato, K.; Taweekun, J.; Rahman, M.M.; Rasul, M.G.; Mahlia, T.M.I.; Ashrafur, S.M. An overview of recent developments in biomass pyrolysis technologies. Energies 2018, 11, 3115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kraan, S. Mass-cultivation of carbohydrate rich macroalgae, a possible solution for sustainable biofuel production. Mitig. Adapt. Strateg. Glob. Chang. 2013, 18, 27–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ceylan, S.; Topcu, Y.; Ceylan, Z. Thermal behaviour and kinetics of alga Polysiphonia elongata biomass during pyrolysis. Bioresour. Technol. 2014, 171, 193–198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Uzun, B.B.; Yaman, E. Pyrolysis kinetics of walnut shell and waste polyolefins using thermogravimetric analysis. J. Energy Inst. 2017, 90, 825–837. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cardoso, C.R.; Miranda, M.R.; Santos, K.G.; Ataíde, C.H. Determination of kinetic parameters and analytical pyrolysis of tobacco waste and sorghum bagasse. J. Anal. Appl. Pyrolysis 2011, 92, 392–400. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Asadullah, M.; Rahman, M.A.; Ali, M.M.; Motin, M.A.; Sultan, M.B.; Alam, M.R.; Rahman, M.S. Jute stick pyrolysis for bio-oil production in fluidized bed reactor. Bioresour. Technol. 2008, 99, 44–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, X.; Zhu, J.L.; Zheng, A.L.; Wei, X.Y.; Zhao, Y.P.; Cao, J.P.; You, C.Y. Rapid characterization of heteroatomic molecules in a bio-oil from pyrolysis of rice husk using atmospheric solids analysis probe mass spectrometry. J. Anal. Appl. Pyrolysis 2015, 115, 16–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rulkens, W. Sewage sludge as a biomass resource for the production of energy: Overview and assessment of the various options. Energy Fuels 2008, 22, 9–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Slopiecka, K.; Bartocci, P.; Fantozzi, F. Thermogravimetric analysis and kinetic study of poplar wood pyrolysis. Appl. Energy 2012, 97, 491–497. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bridgwater, A.V. Review of fast pyrolysis of biomass and product upgrading. Biomass Bioenergy 2012, 38, 68–94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Auta, M.; Ern, L.M.; Hameed, B.H. Fixed-bed catalytic and non-catalytic empty fruit bunch biomass pyrolysis. J. Anal. Appl. Pyrolysis 2014, 107, 67–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Colantoni, S.; Della Gatta, S.; De Prosperis, R.; Russo, A.; Fantozzi, F.; Desideri, U. Gas turbines fired with biomass pyrolysis syngas: Analysis of the overheating of hot gas path components. J. Eng. Gas Turbines Power 2010, 132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mishra, G.; Kumar, J.; Bhaskar, T. Kinetic studies on the pyrolysis of pinewood. Bioresour. Technol. 2015, 182, 282–288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhou, L.; Zhang, G.; Zhang, L.; Klinger, D.; Meyer, B. Effects of Contact Conditions between Particles and Volatiles during Co-Pyrolysis of Brown Coal and Wheat Straw in a Thermogravimetric Analyzer and Fixed-Bed Reactor. Processes 2019, 7, 179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, X.; Cao, J.P.; Zhao, X.Y.; Wang, J.X.; Fan, X.; Zhao, Y.P.; Wei, X.Y. Pyrolysis kinetics of soybean straw using thermogravimetric analysis. Fuel 2016, 169, 93–98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Szufa, S.; Wielgosiński, G.; Piersa, P.; Czerwińska, J.; Dzikuć, M.; Adrian, Ł.; Lewandowska, W.; Marczak, M. Torrefaction of straw from oats and maize for use as a fuel and additive to organic fertilizers—TGA analysis, kinetics as products for agricultural purposes. Energies 2020, 13, 2064. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ceylan, S.; Topçu, Y. Pyrolysis kinetics of hazelnut husk using thermogravimetric analysis. Bioresour. Technol. 2014, 156, 182–188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lopez-Velazquez, M.A.; Santes, V.; Balmaseda, J.; Torres-Garcia, E. Pyrolysis of orange waste: A thermo-kinetic study. J. Anal. Appl. Pyrolysis 2013, 99, 170–177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sarkar, J.K.; Wang, Q. Different Pyrolysis Process Conditions of South Asian Waste Coconut Shell and Characterization of Gas, Bio-Char, and Bio-Oil. Energies 2020, 13, 1970. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dhyani, V.; Kumar, J.; Bhaskar, T. Thermal decomposition kinetics of sorghum straw via thermogravimetric analysis. Bioresour. Technol. 2017, 245, 1122–1129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Islam, M.N.; Joardder, M.U.H.; Hoque, S.M.; Uddin, M. A comparative study on pyrolysis for liquid oil from different biomass solid wastes. Procedia Eng. 2013, 56, 643–649. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gai, C.; Dong, Y.; Zhang, T. The kinetic analysis of the pyrolysis of agricultural residue under non-isothermal conditions. Bioresour. Technol. 2013, 127, 298–305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kumar, A.; Wang, L.; Dzenis, Y.A.; Jones, D.D.; Hanna, M.A. Thermogravimetric characterization of corn stover as gasification and pyrolysis feedstock. Biomass Bioenergy 2008, 32, 460–467. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amutio, M.; Lopez, G.; Aguado, R.; Artetxe, M.; Bilbao, J.; Olazar, M. Kinetic study of lignocellulosic biomass oxidative pyrolysis. Fuel 2012, 95, 305–311. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Damartzis, T.; Vamvuka, D.; Sfakiotakis, S.; Zabaniotou, A. Thermal degradation studies and kinetic modeling of cardoon (Cynara cardunculus) pyrolysis using thermogravimetric analysis (TGA). Bioresour. Technol. 2011, 102, 6230–6238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mythili, R.; Venkatachalam, P.; Subramanian, P.; Uma, D. Characterization of bioresidues for biooil production through pyrolysis. Bioresour. Technol. 2013, 138, 71–78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sait, H.H.; Hussain, A.; Salema, A.A.; Ani, F.N. Pyrolysis and combustion kinetics of date palm biomass using thermogravimetric analysis. Bioresour. Technol. 2012, 118, 382–389. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vyazovkin, S.; Burnham, A.K.; Criado, J.M.; Pérez-Maqueda, L.A.; Popescu, C.; Sbirrazzuoli, N. ICTAC Kinetics Committee recommendations for performing kinetic computations on thermal analysis data. Thermochim. Acta 2011, 520, 1–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Flynn, J.H.; Wall, L.A. A quick, direct method for the determination of activation energy from thermogravimetric data. J. Polym. Sci. Part B Polym. Lett. 1966, 4, 323–328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ozawa, T. A new method of analyzing thermogravimetric data. Bull. Chem. Soc. Jpn. 1965, 38, 1881–1886. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kissinger, H.E. Reaction kinetics in differential thermal analysis. Anal. Chem. 1957, 29, 1702–1706. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Akahira, T.; Sunose, T. Method of determining activation deterioration constant of electrical insulating materials. Res. Rep. Chiba Inst. Technol. (Sci. Technol.) 1971, 16, 22–31. [Google Scholar]
- Kan, T.; Strezov, V.; Evans, T.J. Lignocellulosic biomass pyrolysis: A review of product properties and effects of pyrolysis parameters. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 2016, 57, 1126–1140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ceranic, M.; Kosanic, T.; Djuranovic, D.; Kaludjerovic, Z.; Djuric, S.; Gojkovic, P.; Bozickovic, R. Experimental investigation of corn cob pyrolysis. J. Renew. Sustain. Energy 2016, 8, 063102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Q.; Endo, T.; Wang, Q. Characterization of bamboo after ionic liquid-H2O pretreatment for the pyrolysis process. BioResources 2015, 10, 2797–2808. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Suriapparao, D.V.; Pradeep, N.; Vinu, R. Bio-oil production from Prosopis juliflora via microwave pyrolysis. Energy Fuels 2015, 29, 2571–2581. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Q.; Sarkar, J. Pyrolysis behaviors of waste coconut shell and husk biomasses. Int. J. Energy Prod. Manag. 2018, 3, 34–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lv, G.; Wu, S. Analytical pyrolysis studies of corn stalk and its three main components by TG-MS and Py-GC/MS. J. Anal. Appl. Pyrolysis 2012, 97, 11–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gašparovič, L.; Koreňová, Z.; Jelemenský, Ľ. Kinetic study of wood chips decomposition by TGA. Chem. Pap. 2010, 64, 174–181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mishra, R.K.; Mohanty, K. Pyrolysis kinetics and thermal behavior of waste sawdust biomass using thermogravimetric analysis. Bioresour. Technol. 2018, 251, 63–74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Strezov, V.; Moghtaderi, B.; Lucas, J. Thermal study of decomposition of selected biomass samples. J. Therm. Anal. Calorim. 2003, 72, 1041–1048. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mastral, A.M.; Murillo, R.; Callen, M.S.; Garcia, T.; Snape, C.E. Influence of process variables on oils from tire pyrolysis and hydropyrolysis in a swept fixed bed reactor. Energy Fuels 2000, 14, 739–744. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, B.; O’Connor, D.; Zhang, J.; Peng, T.; Shen, Z.; Tsang, D.C.; Hou, D. Effect of pyrolysis temperature, heating rate, and residence time on rapeseed stem derived biochar. J. Clean. Prod. 2018, 174, 977–987. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Angın, D. Effect of pyrolysis temperature and heating rate on biochar obtained from pyrolysis of safflower seed press cake. Bioresour. Technol. 2013, 128, 593–597. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fu, P.; Hu, S.; Xiang, J.; Sun, L.; Su, S.; Wang, J. Evaluation of the porous structure development of chars from pyrolysis of rice straw: Effects of pyrolysis temperature and heating rate. J. Anal. Appl. Pyrolysis 2012, 98, 177–183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oyedun, A.O.; Gebreegziabher, T.; Hui, C.W. Mechanism and modelling of bamboo pyrolysis. Fuel Process. Technol. 2013, 106, 595–604. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gerçel, H.F. Bio-oil production from Onopordum acanthium L. by slow pyrolysis. J. Anal. Appl. Pyrolysis 2011, 92, 233–238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salehi, E.; Abedi, J.; Harding, T. Bio-oil from sawdust: Effect of operating parameters on the yield and quality of pyrolysis products. Energy Fuels. 2011, 25, 4145–4154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Acikgoz, C.; Kockar, O.M. Characterization of slow pyrolysis oil obtained from linseed (Linum usitatissimum L.). J. Anal. Appl. Pyrolysis 2009, 85, 151–154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, H.; Huan, B.; Chen, Y.; Gao, Y.; Li, J.; Chen, H. Biomass-based pyrolytic polygeneration system for bamboo industry waste: Evolution of the char structure and the pyrolysis mechanism. Energy Fuels 2016, 30, 6430–6439. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, H.; Yan, R.; Chen, H.; Lee, D.H.; Zheng, C. Characteristics of hemicellulose, cellulose and lignin pyrolysis. Fuel 2007, 86, 1781–1788. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaur, R.; Gera, P.; Jha, M.K.; Bhaskar, T. Pyrolysis kinetics and thermodynamic parameters of castor (Ricinus communis) residue using thermogravimetric analysis. Bioresour. Technol. 2018, 250, 422–428. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]



| Ultimate Analysis (wt%) | Proximate Analysis (wt%) | ||
|---|---|---|---|
| Carbon | 43.41 | moisture content | 8.59 |
| Hydrogen | 5.78 | Volatile matter | 86.64 |
| Nitrogen | 7.81 | fixed carbon | 3.59 |
| Oxygen | 43.00 | ash | 1.18 |
| Sulfur | ND | ||
| HHV (MJ/kg) | 15.26 | ||
| Heating Rate (°C/min) | Ultimate Analysis (%) | Water Content (%) | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| H | C | O | N | ||
| 10 | 5.65 | 56.32 | 37.73 | 0.30 | 33.59 |
| 20 | 5.70 | 54.39 | 39.61 | 0.31 | 32.95 |
| 30 | 5.66 | 54.16 | 39.86 | 0.31 | 31.12 |
| 40 | 5.72 | 52.97 | 41.01 | 0.30 | 30.71 |
| Heating Rate | Ultimate Analysis (%) | Proximate Analysis (%) | HHV (MJ/kg) | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| C | H | O | N | Fixed Carbon | Volatiles | Ash | ||
| 10 | 85.46 | 0.81 | 13.29 | 0.44 | 84.32 | 11.63 | 4.06 | 27.66 |
| 20 | 84.94 | 1.09 | 13.48 | 0.49 | 85.03 | 10.33 | 4.64 | 27.86 |
| 30 | 84.26 | 1.11 | 14.16 | 0.47 | 84.87 | 9.61 | 5.52 | 27.54 |
| 40 | 84.08 | 1.45 | 13.89 | 0.58 | 85.32 | 8.84 | 5.84 | 28.01 |
| α | FWO Method | KAS Method | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Fitted Equation | R2 | Eα | Fitted Equation | R2 | Eα | |
| 0.1 | y = −15.17x + 29.78 | 0.97 | 119.90 | y = −14.04x + 15.10 | 0.97 | 116.70 |
| 0.2 | y = −16.41x + 30.80 | 0.98 | 129.67 | y = −15.22x + 16.03 | 0.98 | 126.57 |
| 0.3 | y = −17.68x + 31.96 | 0.98 | 139.73 | y = −16.46x + 17.13 | 0.98 | 136.82 |
| 0.4 | y = −18.15x + 31.88 | 0.98 | 143.42 | y = −16.90x + 16.99 | 0.98 | 140.41 |
| 0.5 | y = −18.63x + 32.00 | 0.99 | 147.25 | y = −17.35x + 17.07 | 0.99 | 144.21 |
| 0.6 | y = −18.74x + 31.70 | 0.99 | 148.12 | y = −17.44x + 16.73 | 0.99 | 144.95 |
| 0.7 | y = −18.33x + 30.71 | 0.99 | 144.88 | y = −17.01x + 15.72 | 0.99 | 141.40 |
| 0.8 | y = −17.80x + 29.55 | 0.99 | 140.71 | y = −16.46x + 14.53 | 0.99 | 136.86 |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Sarkar, J.K.; Wang, Q. Characterization of Pyrolysis Products and Kinetic Analysis of Waste Jute Stick Biomass. Processes 2020, 8, 837. https://doi.org/10.3390/pr8070837
Sarkar JK, Wang Q. Characterization of Pyrolysis Products and Kinetic Analysis of Waste Jute Stick Biomass. Processes. 2020; 8(7):837. https://doi.org/10.3390/pr8070837
Chicago/Turabian StyleSarkar, Jayanto Kumar, and Qingyue Wang. 2020. "Characterization of Pyrolysis Products and Kinetic Analysis of Waste Jute Stick Biomass" Processes 8, no. 7: 837. https://doi.org/10.3390/pr8070837
APA StyleSarkar, J. K., & Wang, Q. (2020). Characterization of Pyrolysis Products and Kinetic Analysis of Waste Jute Stick Biomass. Processes, 8(7), 837. https://doi.org/10.3390/pr8070837






