Ultra-Pure Hydrogen via Co-Valorization of Olive Mill Wastewater and Bioethanol in Pd-Membrane Reactors
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Experimental Details
2.1. Olive Mill Wastewater Conditioning
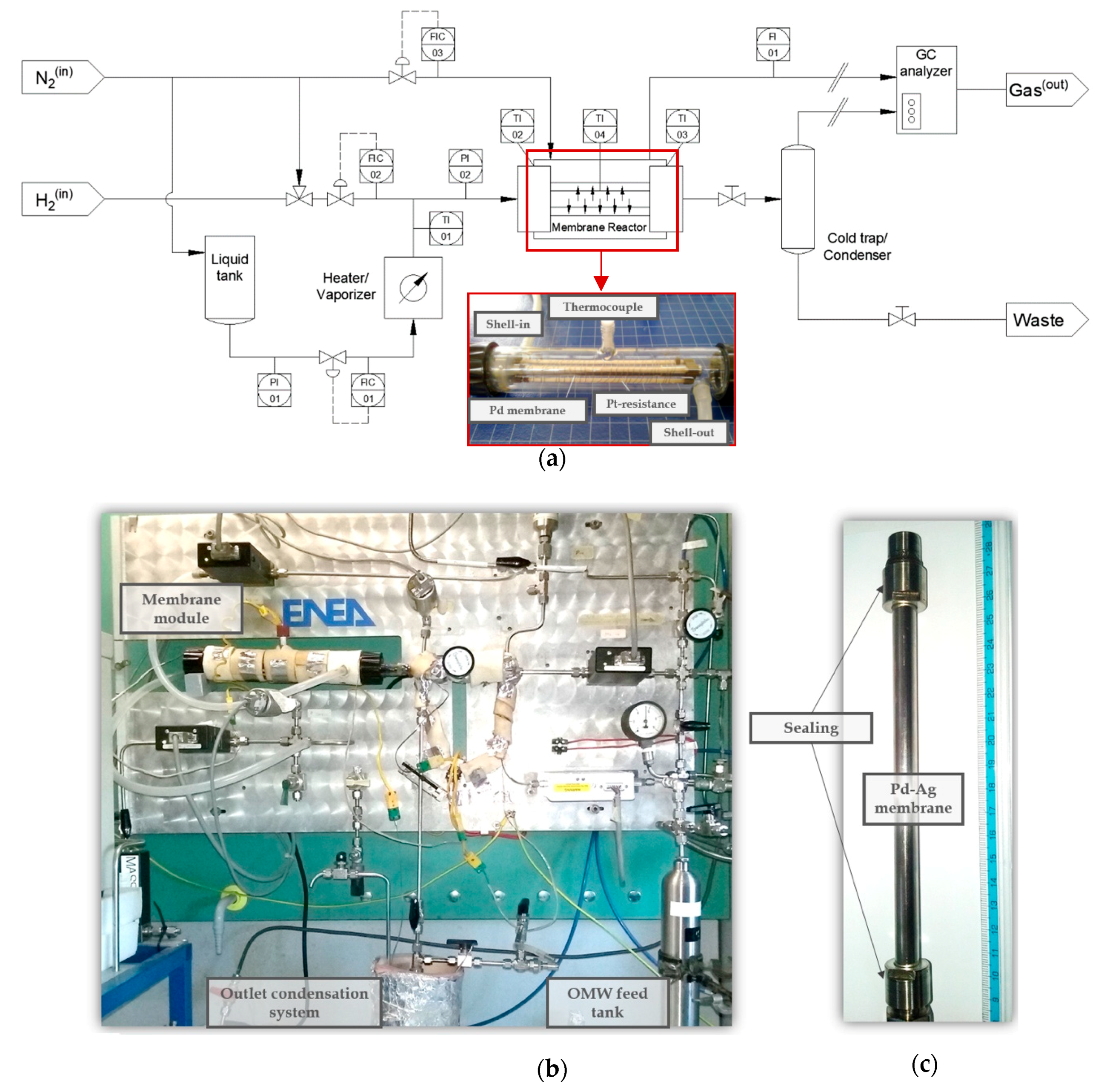
2.2. Membrane and Permeation Setup
2.3. Catalyst and Membrane Reformer Setup
3. Results and Discussion
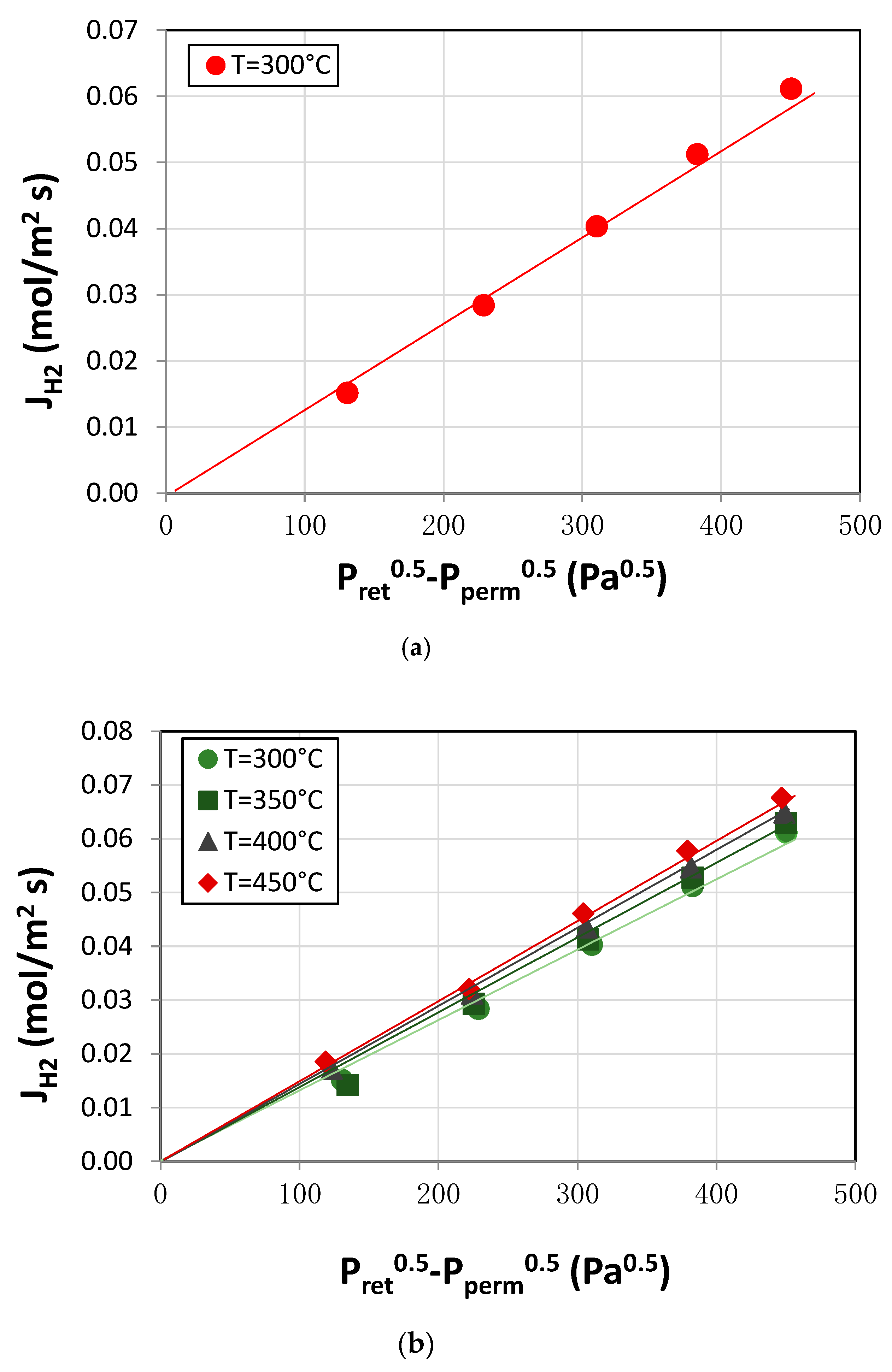
3.1. Membrane Characterization: Permeation Analysis
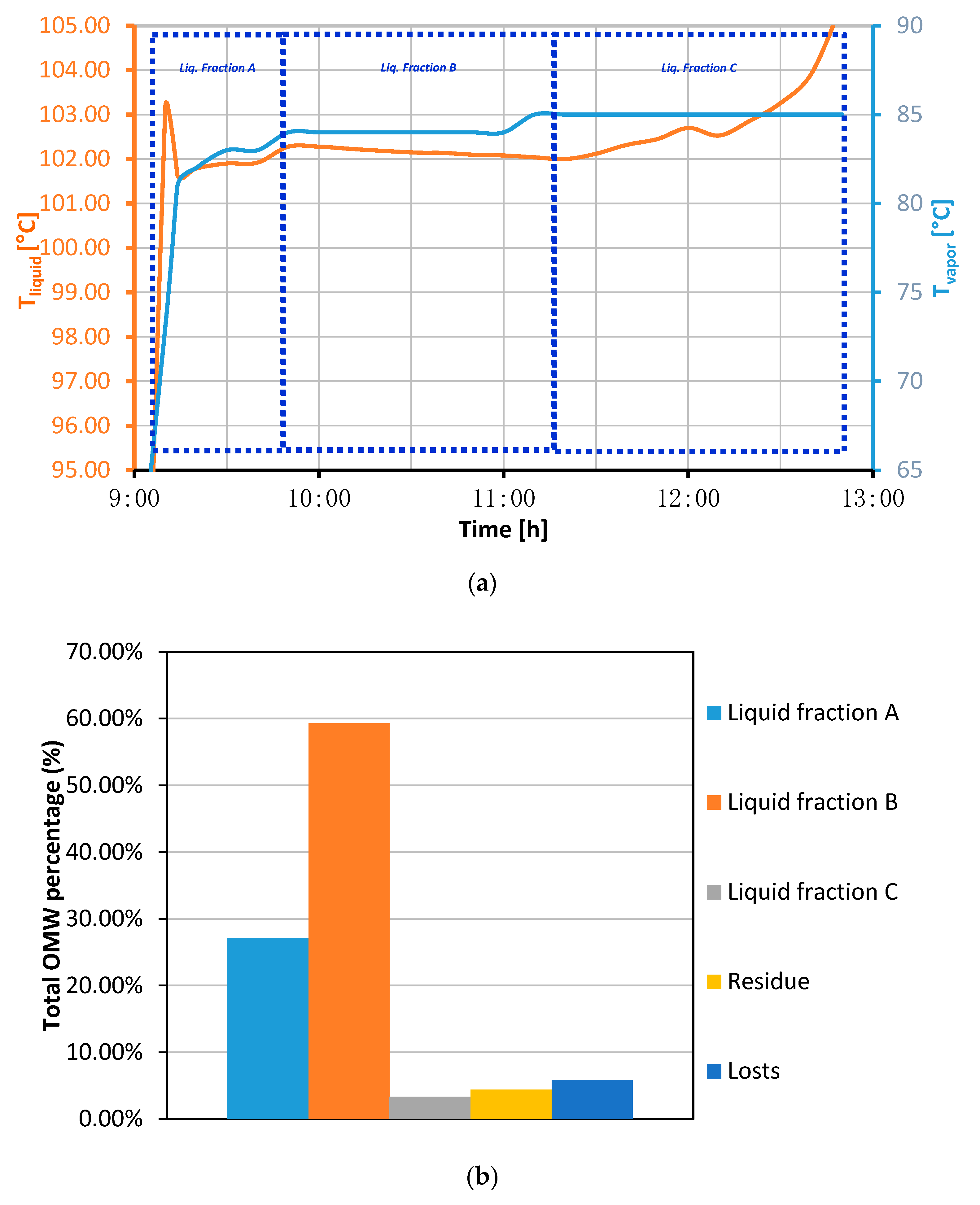
3.2. Olive Mill Wastewater Conditioning
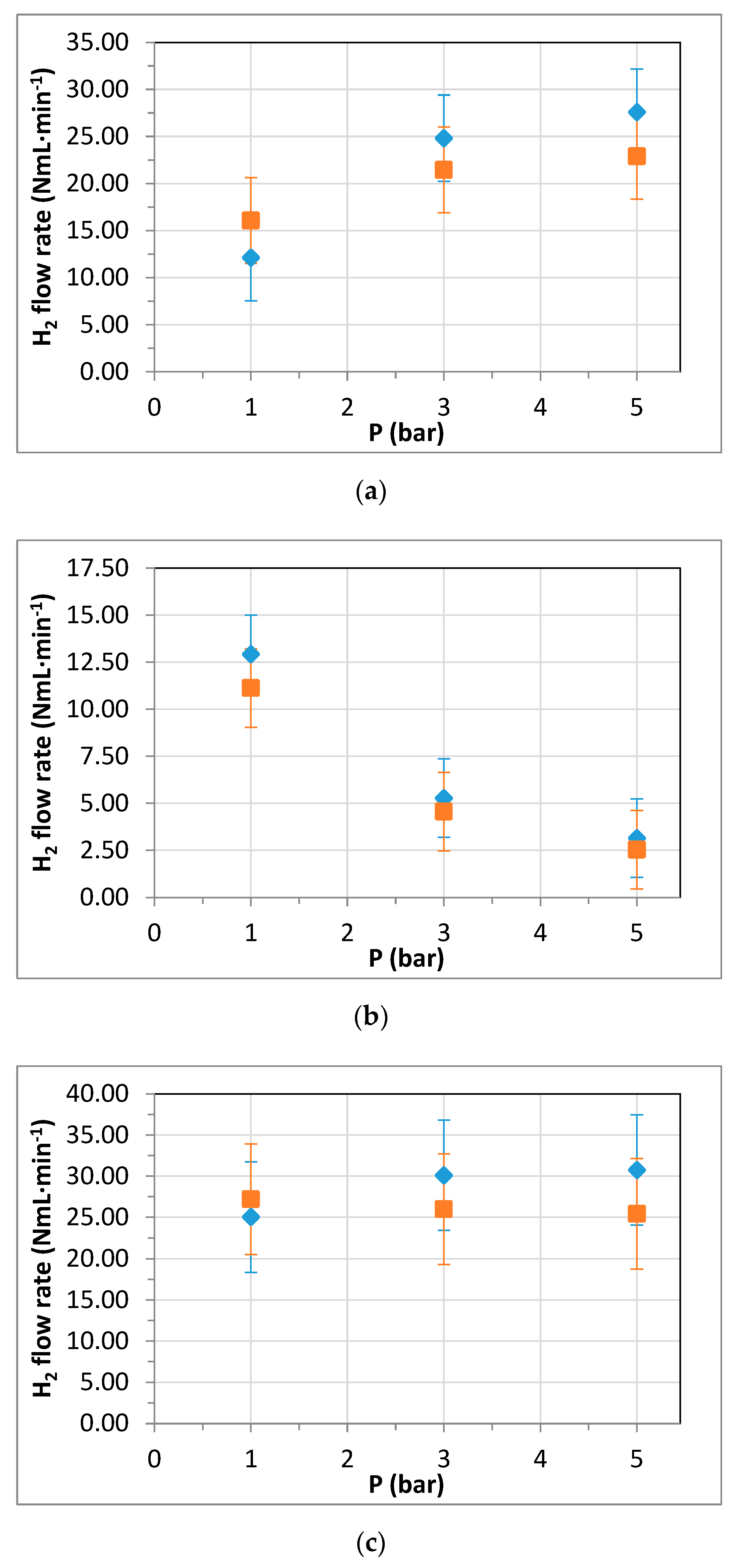
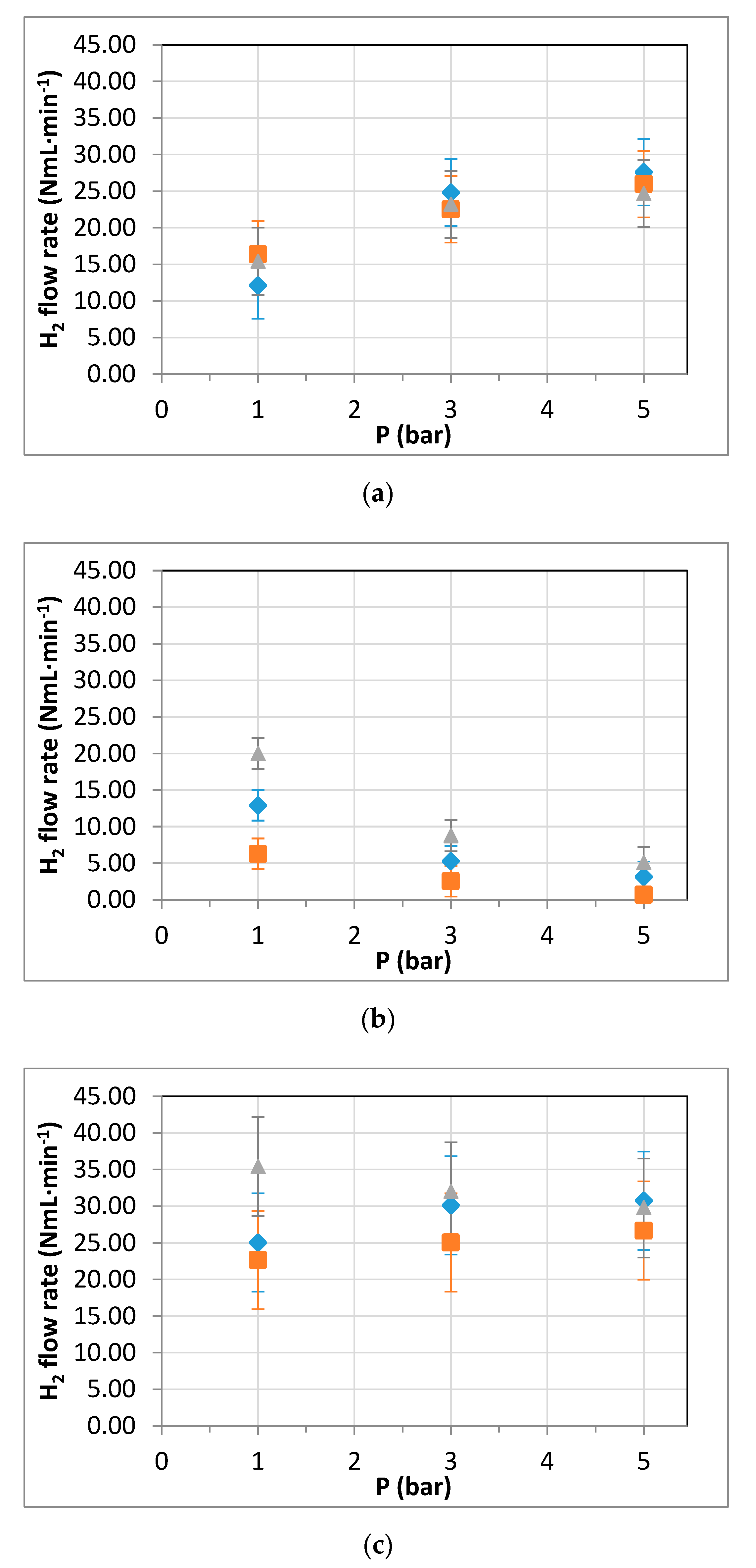
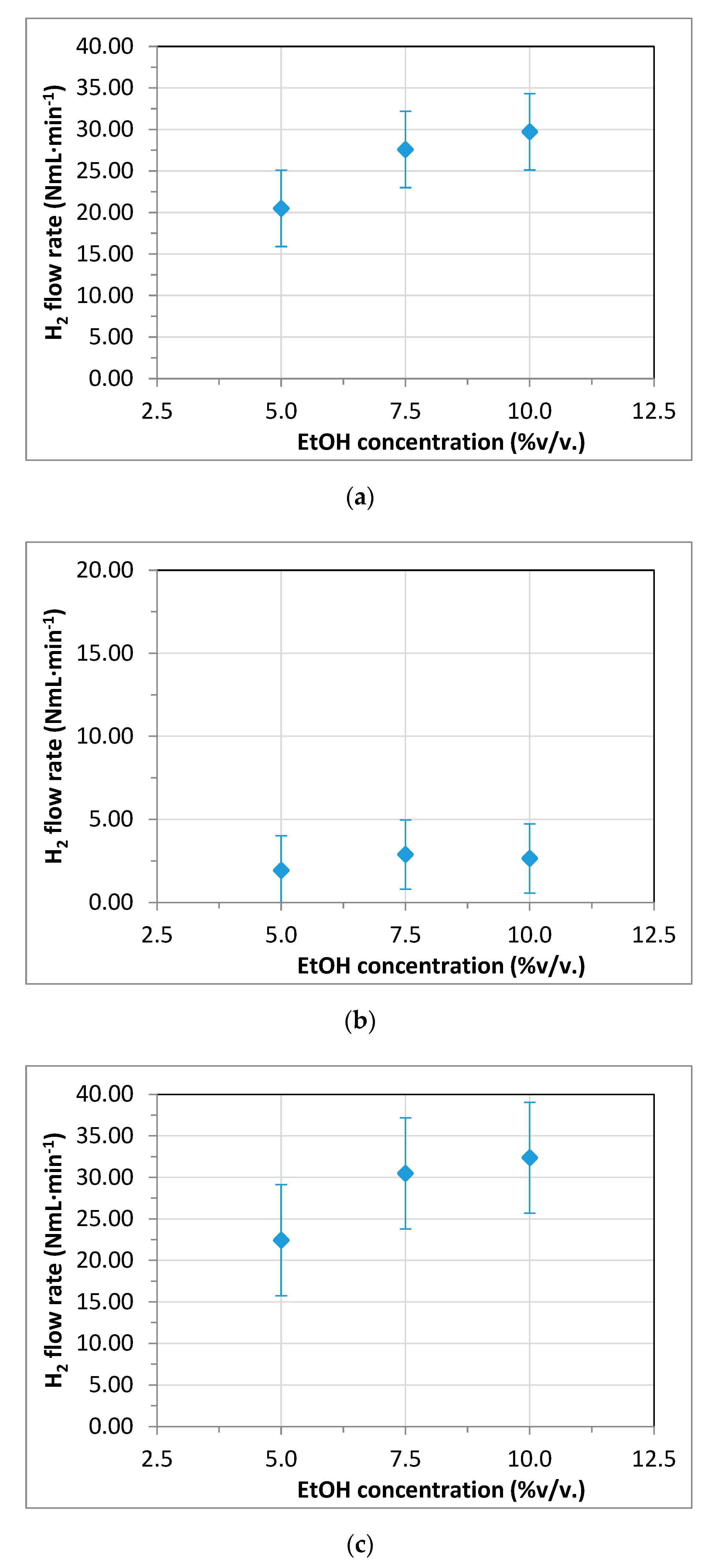
3.3. Membrane Reformer for Hydrogen Production
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Souilem, S.; El-Abbassi, A.; Kiai, H.; Hafidi, A.; Sayadi, S. Olive oil production sector: Environmental effects and sustainability challenges. Olive Mill Waste 2017, 2017, 1–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aggoun, M.; Arhab, R.; Cornu, A.; Portelli, J.; Barkat, M.; Graulet, B. Olive mill wastewater microconstituents composition according to olive variety and extraction process. Food Chem. 2016, 209, 72–80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, Z.S.; Chin, S.Y.; Lim, J.W.; Witoon, T.; Cheng, C.K. Treatment technologies of palm oil mill effluent (POME)and olive mill wastewater (OMW): A brief review. Environ. Technol. Innov. 2019, 15, 100377. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Víctor-Ortega, M.D.; Ochando-Pulido, J.M.; Hodaifa, G.; Martínez-Ferez, A. Ion exchange as an efficient pretreatment system for reduction of membrane fouling in the purification of model OMW. Desalination 2014, 343, 198–207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cassano, A.; Conidi, C.; Giorno, L.; Drioli, E. Fractionation of olive mill wastewaters by membrane separation techniques. J. Hazard. Mater. 2013, 248–249, 185–193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Casanovas, A.; Galvis, A.; Llorca, J. Catalytic steam reforming of olive mill wastewater for hydrogen production. Int. J. Hydrog. Energy 2015, 40, 7539–7545. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eroǧlu, E.; Eroǧlu, I.; Gündüz, U.; Yücel, M. Treatment of olive mill wastewater by different physicochemical methods and utilization of their liquid effluents for biological hydrogen production. Biomass Bioenergy 2009, 33, 701–705. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ochando-Pulido, J.M.; Pimentel-Moral, S.; Verardo, V.; Martinez-Ferez, A. A focus on advanced physico-chemical processes for olive mill wastewater treatment. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2017, 179, 161–174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gonçalves, M.R.; Costa, J.C.; Pereira, M.A.; Abreu, A.A.; Alves, M.M. On the independence of hydrogen production from methanogenic suppressor in olive mill wastewater. Int. J. Hydrog. Energy 2014, 39, 6402–6406. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Battista, F.; Fino, D.; Mancini, G.; Ruggeri, B. Mixing in digesters used to treat high viscosity substrates: The case of olive oil production wastes. J. Environ. Chem. Eng. 2016, 4, 915–923. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eroǧlu, E.; Eroǧlu, I.; Gündüz, U.; Türker, L.; Yücel, M. Biological hydrogen production from olive mill wastewater with two-stage processes. Int. J. Hydrog. Energy 2006, 31, 1527–1535. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pintucci, C.; Padovani, G.; Giovannelli, A.; Traversi, M.L.; Ena, A.; Pushparaj, B.; Carlozzi, P. Hydrogen photo-evolution by Rhodopseudomonas palustris 6A using pre-treated olive mill wastewater and a synthetic medium containing sugars. Energy Convers. Manag. 2015, 90, 499–505. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pintucci, C.; Giovannelli, A.; Traversi, M.L.; Ena, A.; Padovani, G.; Carlozzi, P. Fresh olive mill waste deprived of polyphenols as feedstock for hydrogen photo-production by means of Rhodopseudomonas palustris 42OL. Renew. Energy 2013, 51, 358–363. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lafi, W.K.; Shannak, B.; Al-Shannag, M.; Al-Anber, Z.; Al-Hasan, M. Treatment of olive mill wastewater by combined advanced oxidation and biodegradation. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2009, 70, 141–146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Badawy, M.I.; Ghaly, M.Y.; Ali, M.E.M. Photocatalytic hydrogen production over nanostructured mesoporous titania from olive mill wastewater. Desalination 2011, 267, 250–255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Speltini, A.; Sturini, M.; Maraschi, F.; Dondi, D.; Fisogni, G.; Annovazzi, E.; Profumo, A.; Buttafava, A. Evaluation of UV-A and solar light photocatalytic hydrogen gas evolution from olive mill wastewater. Int. J. Hydrog. Energy 2015, 40, 4303–4310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- García, C.A.; Hodaifa, G. Real olive oil mill wastewater treatment by photo-Fenton system using artificial ultraviolet light lamps. J. Clean. Prod. 2017, 162, 743–753. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kargi, F.; Catalkaya, E.C. Hydrogen gas production from olive mill wastewater by electrohydrolysis with simultaneous COD removal. Int. J. Hydrog. Energy 2011, 36, 3457–3464. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ntaikou, I.; Kourmentza, C.; Koutrouli, E.C.; Stamatelatou, K.; Zampraka, A.; Kornaros, M.; Lyberatos, G. Exploitation of olive oil mill wastewater for combined biohydrogen and biopolymers production. Bioresour. Technol. 2009, 100, 3724–3730. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oz, N.A.; Uzun, A.C. Ultrasound pretreatment for enhanced biogas production from olive mill wastewater. Ultrason. Sonochem 2015, 22, 565–572. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Siciliano, A.; Stillitano, M.A.; de Rosa, S. Biogas production from wet olive mill wastes pretreated with hydrogen peroxide in alkaline conditions. Renew. Energy 2016, 85, 903–916. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kapdan, I.K.; Kargi, F. Bio-hydrogen production from waste materials. Enzym. Microb. Technol. 2006, 38, 569–582. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dincer, I.; Acar, C. Innovation in hydrogen production. Int. J. Hydrog. Energy 2017, 42, 14843–14864. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tosti, S.; Accetta, C.; Fabbricino, M.; Sansovini, M.; Pontoni, L. Reforming of olive mill wastewater through a Pd-membrane reactor. Int. J. Hydrog. Energy 2013, 38, 10252–10259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tosti, S.; Cavezza, C.; Fabbricino, M.; Pontoni, L.; Palma, V.; Ruocco, C. Production of hydrogen in a Pd-membrane reactor via catalytic reforming of olive mill wastewater. Chem. Eng. J. 2015, 275, 366–373. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rocha, C.; Soria, M.A.; Madeira, L.M. Steam reforming of olive oil mill wastewater with in situ hydrogen and carbon dioxide separation—Thermodynamic analysis. Fuel 2017, 207, 449–460. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choi, D.H.; Chun, S.M.; Ma, S.H.; Hong, Y.C. Production of hydrogen-rich syngas from methane reforming by steam microwave plasma. J. Ind. Eng. Chem. 2016, 34, 286–291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, F.; Shi, Y.; Yang, L.; Du, X. Kinetics for hydrogen production by methanol steam reforming in fluidized bed reactor. Sci. Bull. 2016, 61, 401–405. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, C.C.; Tseng, H.H.; Lin, Y.L.; Chen, W.H. Hydrogen production and carbon dioxide enrichment from ethanol steam reforming followed by water gas shift reaction. J. Clean. Prod. 2017, 162, 1430–1441. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nabgan, W.; Abdullah, T.A.T.; Mat, R.; Nabgan, B.; Gambo, Y.; Ibrahim, M.; Ahmad, A.; Jalil, A.A.; Triwahyono, S.; Saeh, I. Renewable hydrogen production from bio-oil derivative via catalytic steam reforming: An overview. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 2017, 79, 347–357. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sabio, E.; Álvarez-Murillo, A.; González, J.F.; Ledesma, B.; Román, S. Modelling the composition of the gas obtained by steam reforming of glycerine. Energy Convers. Manag. 2017, 146, 147–157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zornoza, B.; Casado, C.; Navajas, A. Chapter 11-Advances in Hydrogen Separation and Purification with Membrane Technology. In Renew. Hydrog. Technol.; Gandía, L.M., Arzamendi, G., Diéguez, P.M., Eds.; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2013; pp. 245–268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rahimpour, M.R.; Samimi, F.; Babapoor, A.; Tohidian, T.; Mohebi, S. Palladium membranes applications in reaction systems for hydrogen separation and purification: A review. Chem. Eng. Process. Process. Intensif. 2017, 121, 24–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- D Alique, D.; Martinez-Diaz, R.; Sanz, J.A. Calles, Review of Supported Pd-Based Membranes Preparation by Electroless Plating for Ultra-Pure Hydrogen Production. Membranes 2018, 8, 5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tosto, E.; Alique, D.; Martinez-Diaz, D.; Sanz, R.; Calles, J.A.; Caravella, A.; Medrano, J.A.; Gallucci, F. Stability of pore-plated membranes for hydrogen production in fluidized-bed membrane reactors. Int. J. Hydrog. Energy 2019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tosti, S.; Basile, A.; Bettinali, L.; Borgognoni, F.; Gallucci, F.; Rizzello, C. Design and process study of Pd membrane reactors. Int. J. Hydrog. Energy 2008, 33, 5098–5105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tosti, S. Overview of Pd-based membranes for producing pure hydrogen and state of art at ENEA laboratories. Int. J. Hydrog. Energy 2010, 35, 12650–12659. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bruni, G.; Cordiner, S.; Tosti, S. A novel procedure for the preliminary design of dense metal membrane modules for hydrogen separation. Int. J. Hydrog. Energy 2016, 41, 20198–20209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tosti, S.; Fabbricino, M.; Pontoni, L.; Palma, V.; Ruocco, C. Catalytic reforming of olive mill wastewater and methane in a Pd-membrane reactor. Int. J. Hydrog. Energy 2016, 41, 5465–5474. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sanz, R.; Calles, J.A.; Alique, D.; Furones, L.; Ordóñez, S.; Marín, P. Hydrogen production in a Pore-Plated Pd-membrane reactor: Experimental analysis and model validation for the Water Gas Shift reaction. Int. J. Hydrog. Energy 2015, 40, 3472–3484. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alique, D.; Imperatore, M.; Sanz, R.; Calles, J.A.; Baschetti, M.G. Hydrogen permeation in composite Pd-membranes prepared by conventional electroless plating and electroless pore-plating alternatives over ceramic and metallic supports. Int. J. Hydrog. Energy 2016, 41, 19430–19438. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peters, T.A.; Rørvik, P.M.; Sunde, T.O.; Stange, M.; Roness, F.; Reinertsen, T.R.; Ræder, J.H.; Larring, Y.; Bredesen, R. Palladium (Pd) Membranes as Key Enabling Technology for Pre-combustion CO2 Capture and Hydrogen Production. Energy Procedia 2017, 114, 37–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vadrucci, M.; Borgognoni, F.; Moriani, A.; Santucci, A.; Tosti, S. Hydrogen permeation through Pd–Ag membranes: Surface effects and Sieverts’ law. Int. J. Hydrog. Energy 2013, 38, 4144–4152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Santucci, A.; Borgognoni, F.; Vadrucci, M.; Tosti, S. Testing of dense Pd–Ag tubes: Effect of pressure and membrane thickness on the hydrogen permeability. J. Memb. Sci. 2013, 444, 378–383. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tosti, S. Supported and laminated Pd-based metallic membranes. Int. J. Hydrog. Energy 2003, 28, 1445–1454. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gallucci, F.; Basile, A.; Tosti, S.; Iulianelli, A.; Drioli, E. Methanol and ethanol steam reforming in membrane reactors: An experimental study. Int. J. Hydrog. Energy 2007, 32, 1201–1210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Manzolini, G.; Tosti, S. Hydrogen production from ethanol steam reforming: Energy efficiency analysis of traditional and membrane processes. Int. J. Hydrog. Energy 2008, 33, 5571–5582. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gallucci, F.; de Falco, M.; Tosti, S.; Marrelli, L.; Basile, A. Ethanol steam reforming in a dense Pd-Ag membrane reactor: A modelling work. Comparison with the traditional system. Int. J. Hydrog. Energy 2008, 33, 644–651. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iulianelli, A.; Liguori, S.; Vita, A.; Italiano, C.; Fabiano, C.; Huang, Y.; Basile, A. The oncoming energy vector: Hydrogen produced in Pd-composite membrane reactor via bioethanol reforming over Ni/CeO 2 catalyst. Catal. Today 2016, 259, 368–375. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, R.; Castro-Dominguez, B.; Mardilovich, I.P.; Dixon, A.G.; Ma, Y.H. Experimental and simulation studies of the production of renewable hydrogen through ethanol steam reforming in a large-scale catalytic membrane reactor. Chem. Eng. J. 2016, 303, 302–313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Borgognoni, F.; Tosti, S.; Vadrucci, M.; Santucci, A. Combined methane and ethanol reforming for pure hydrogen production through Pd-based membranes. Int. J. Hydrog. Energy 2013, 38, 1430–1438. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| T (°C) | P (bar) | Thickness (μM) | k (mol·m−2·s−1·Pa−0.5) | Ea (kJ·mol−1) | Reference |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 300–450 | 0.5–5.0 | 150 | 1.325 × 10−4–1.512 × 10−4 | 3.035 | This work |
| 400–450 | 1.0–1.5 | 150 | 1.206 × 10−5 | 6.198 | [24] |
| 250–450 | 1.0–6.0 | 143 | 4.942 × 10−6 | 2.107 | [25] |
| 250–450 | 1.1–5.0 | 150 | 7.015 × 10−6 | 4.519 | [39] |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Alique, D.; Bruni, G.; Sanz, R.; Calles, J.A.; Tosti, S. Ultra-Pure Hydrogen via Co-Valorization of Olive Mill Wastewater and Bioethanol in Pd-Membrane Reactors. Processes 2020, 8, 219. https://doi.org/10.3390/pr8020219
Alique D, Bruni G, Sanz R, Calles JA, Tosti S. Ultra-Pure Hydrogen via Co-Valorization of Olive Mill Wastewater and Bioethanol in Pd-Membrane Reactors. Processes. 2020; 8(2):219. https://doi.org/10.3390/pr8020219
Chicago/Turabian StyleAlique, David, Giacomo Bruni, Raúl Sanz, José Antonio Calles, and Silvano Tosti. 2020. "Ultra-Pure Hydrogen via Co-Valorization of Olive Mill Wastewater and Bioethanol in Pd-Membrane Reactors" Processes 8, no. 2: 219. https://doi.org/10.3390/pr8020219
APA StyleAlique, D., Bruni, G., Sanz, R., Calles, J. A., & Tosti, S. (2020). Ultra-Pure Hydrogen via Co-Valorization of Olive Mill Wastewater and Bioethanol in Pd-Membrane Reactors. Processes, 8(2), 219. https://doi.org/10.3390/pr8020219









