Abstract
Olive mill wastewater (OMW) presents high environmental impact due to the fact of its elevated organic load and toxicity, especially in Mediterranean countries. Its valorization for simultaneous pollutants degradation and green energy production is receiving great attention, mainly via steam reforming for hydrogen generation. Following previous works, the present research goes into detail about OMW valorization, particularly investigating for the first time the potential benefits of OMW–bioethanol mixtures co-reforming for ultra-pure hydrogen production in Pd-membrane reactors. In this manner, the typical large dilution of OMW and, hence, excess water can be used as a reactant for obtaining additional hydrogen from ethanol. Fresh OMW was previously conditioned by filtration and distillation processes, analyzing later the effect of pressure (1–5 bar), oxidizing conditions (N2 or air as carrier gas), gas hourly space velocity (150–1500 h−1), and alcohol concentration on the co-reforming process (5–10% v/v). In all cases, the exploitation of OMW as a source of environmentally friendly hydrogen was demonstrated, obtaining up to 30 NmL·min−1 of pure H2 at the most favorable experimental conditions. In the membrane reactor, higher pressures up to 5 bar promoted both total H2 production and pure H2 recovery due to the increase in the permeate flux despite the negative effect on reforming thermodynamics. The increase of ethanol concentration also provoked a positive effect, although not in a proportional relation. Thus, a greater effect was obtained for the increase from 5% to 7.5% v/v in comparison to the additional improvement up to 10% v/v. On the contrary, the use of oxidative conditions slightly decreased the hydrogen production rate, while the effect of gas hourly space velocity needs to be carefully analyzed due to the contrary effect on potential total H2 generation and pure H2 recovery.
1. Introduction
Olive oil is highly appreciated for its flavor and proven health benefits, and it represents a fundamental economic component of European Mediterranean countries, especially Spain, Italy, and Greece, where most of the olive farms are concentrated [1]. The olive oil production process consists of consecutive olive pulp pressings and decantation (the traditional process) or direct centrifugal extraction of diluted olive pulp in water (the modern process). Usually, the oily phase represents only approximately 20% of the resulting product, while the rest is formed by a solid waste (approximately 30%) and a liquid waste effluent (up to 50%) that is called vegetation water or, most commonly, olive mill wastewater (OMW) [2,3]. The solid waste is typically used as fertilizer, but the aqueous effluent creates a substance with a potentially high environmental impact because of its elevated organic load and toxicity. Olive mill wastewater has a dark brown color, is slightly acid pH (~5–6), and has very high carbon and biological oxygen demands (COD = 40–220 g/L and BOD 35–110 g/L) including diverse sugars, tannins, organic acids, polyphenols, and minerals. However, the real composition can differ significantly depending on the olive variety, production process, and climatology as demonstrated by the diverse characterizations published by Víctor-Ortega et al. [4], Cassano et al. [5], Casanovas et al. [6], and Souilem et al. [1].
Trying to mitigate the negative effects of OMW on the environment, two different strategies can be considered: (i) conventional water treatments for domestic and industrial wastewaters including physical–chemical [7,8], biological [9,10,11,12,13], and advanced processes such as photocatalytic or electro-hydrolysis reactions [14,15,16,17,18]; or (ii) valorization for green energy production [1,19,20,21]. The latter alternative represents a very promising approach to cover future worldwide energy needs in a sustainable way, obtaining renewable and distributed energy while potentially harmful wastes are removed [22]. In this context, the production of a syngas rich in hydrogen appears as a particularly interesting alternative fuel and clean energy carrier for the future with limited CO2 emissions [23]. This hydrogen, derived from OMW treatment, can be mainly obtained through biological processes [9,11,12,13] or steam reforming [6,24,25,26], the last alternative being very attractive due to the large production capacity, broad previous experience with renewable feedstock, and the maturity grade of the technology [27,28,29,30,31]. Casanovas et al. [6] presented the results for catalytic steam reforming of distillate three-phase OMW at atmospheric pressures with space velocities of 4500–16,000 h−1 and temperatures in the range 600–750 °C on a honeycomb catalyst functionalized with La-CeO2 doped with diverse metals. In the most favorable conditions (1% w/w Pt over La–Ce2 honeycomb, 600 °C and GHSV = 16,000 h−1), they achieved a reduction near to 90%–96% of total organic carbon present in the OMW with a generation of 40 mL of hydrogen per mL of feedstock. Most final applications of hydrogen generated in these thermal processes require a very high level of purity that needs to be achieved by a subsequent purification step [32]. In this context, an interesting proposal is based on the combination of both reaction and separation steps in a unique device, denoted as membrane reactor, in which ultra-pure H2 produced by the reaction can be directly separated through the membrane [33]. Besides the logical advantage of reducing the amount of equipment in the plant layout design for saving capital expenses, the use of a membrane reactor could also save operating costs due to the possibility of obtaining a similar performance at milder working conditions. It is produced because of the continuous extraction of hydrogen and the consequent shift of chemical conversion beyond the equilibrium, according to the Le Châtelier principle [34,35]. Considering these potential benefits as well as the large amount of previous experience on designing dense metal membranes modules for hydrogen purification [36,37,38], the research group headed by Tosti also investigated the exploitation of OMW for hydrogen production in palladium membrane reactors [24,25,39]. Palladium-based dense membranes are a widespread alternative for hydrogen separation in independent equipment or coupled with a catalytic chemical reaction in a membrane reactor at moderate–high temperatures with an extremely elevated perm-selectivity, up to infinite for completely free-defect systems [33,40,41,42]. The hydrogen permeation through these membranes can be divided in different steps, including transport in the gas phase, adsorption on the membrane surface, hydrogen dissociation, diffusion through the bulk metal membrane, hydrogen recombination, and desorption on the contrary membrane side. Among all of them, the limiting step is usually the diffusion through the bulk palladium which can be described by the Sieverts’ law. This equation (Equation (1)) suggests that the hydrogen permeate flux is proportional to the difference of the square root of hydrogen partial pressures at retentate and permeate sides (driving force) but inversely proportional to the membrane thickness [43,44].
where JH2 represents the hydrogen permeate flux through the membrane film, k’H2 the hydrogen permeability, kH2 the hydrogen permeance, t the membrane thickness, and PH2 the hydrogen partial pressure in the retentate (subscript “ret”) or the permeate side (subscript “perm”).
Palladium-based membranes are usually configured as self-supported, trying to maximize the hydrogen selectivity and facilitate the conformation process, or as a composite (Pd-layers over supports) in case of prevailing thickness limitations and noble metal expenses [45]. Tosti et al. [24] employed 150 μm thick PdAg dense tubes to generate approximately 2 kg of pure hydrogen per ton of real OMW (original total organic carbon (TOC), approximately 10,600 mg/L) for the first time, obtaining, in addition, a syngas in the retentate stream. The reforming tests were conducted at 450 °C by varying the space velocity from 2.78 × 10−3 to 8.33 × 10−3 mol·h−1·gcat−1, noting a positive effect of the pressure on hydrogen recovery due to the increase in the permeation flux as predicted Sieverts’ law. However, side reactions, such as cracking or hydrogenolysis, provoked carbon formation and catalyst deactivation. Later, similar experiments were performed replacing the original catalyst by a new one consisting of Al2O3 pellets coated with CeO2–ZrO2 doped up to a 3 wt% with Pt, Rh, and Pd noble metals [25]. In this manner, original TOC and phenol concentration of real OMW were reduced by about 90%, increasing the hydrogen production up to 3.25 kg of hydrogen per ton of wastewater. The new catalyst exhibited a better performance with higher selectivity towards the main reaction (steam reforming) and, consequently, minimizing the generation of methane and coke by side reactions. Recently, the simultaneous treatment of OMW and methane in a palladium-based membrane reformer has been also presented, trying to take advantage of the large water excess in OMW for reforming the methane [39]. A similar hydrogen yield to that of the separated OMW reforming were obtained, not affecting the ability to reduce pollution from this wastewater. However, at certain experimental conditions a synergetic effect was observed, increasing the amount of ultra-pure hydrogen produced in 2.1 kg respect to the reforming of methane alone. Thermodynamics studies about these processes have been lately published by Rocha et al. [26], analyzing in detail the effect of simultaneous hydrogen and/or carbon dioxide removal for OMW steam reforming at diverse operational conditions. With the perspective of valorizing the OMW from waste to energy, the use of a sorption-enhance membrane reactor with simultaneous H2 and CO2 removal provided a hydrogen yield very close to the stoichiometric value at P = 1 bar, T = 500 °C, and water content in the range 60–92 wt%, enhancing this parameter up to 141% comparative to a traditional fixed-bed reactor.
Finally, it is also necessary to mention the growing interest in bio-alcohols produced from fermentative processes of diverse biomass resources and, consequently, the use of this feedstock for green hydrogen synthesis [46,47]. In this manner, another possibility for OMW treatment (or, in general, any agricultural waste) could be the fermentation to obtain alcohols followed by a reforming process to transform them into hydrogen. In these cases, the use of a membrane reactor configuration to move the equilibrium of the reforming reaction, usually fed by bioethanol, to the products side where hydrogen is generated, can also enhance the hydrogen yield [48,49,50]. Even the combination of this bioethanol with methane, that can also come from biological processes, in a membrane reformer has been proposed in order to improve the overall economy of these processes [51].
Based on the previous experience acquired in ENEA-Frascati laboratories (Italy) over the past years [24,25,39], the present work goes into detail about reforming the OMW for the production of ultra-pure hydrogen in a membrane reactor. The reproducibility of the previous results was analyzed by replacing the original membrane and taking new OMW samples in different seasons. The permeation membrane behavior, the effect of both pressure and GHSV during the steam reforming were analyzed again, obtaining new data on the required previous conditioning for raw OMW samples. In a previous study [39], the energy efficiency of the system was improved by co-reforming OMW–CH4 mixtures in order to obtain higher hydrogen yields and the effective reduction of the TOC of the biomass, taking advantage of the original large amount of water. Accordingly, a similar strategy was considered in this work but replacing, for the first time, the methane with ethanol in the OMW membrane reformer.
2. Experimental Details
All experiments were performed using home-made equipment with a hydrogen perm-selective finger-type membrane operating as simple gas separator or, in case of combining with some catalyst pellets, membrane reactor for reforming tests (Figure 1). Complete details about the experimental apparatus are reported in previous works [24,25,39], although basic descriptions about each particular configuration are provided in the next subsections. For the reforming experiments, new, real olive-mill wastewater samples were obtained from a traditional olive mill located near Frascati (Italy), while a synthetic bioethanol was prepared by dilution of pure ethanol in water.
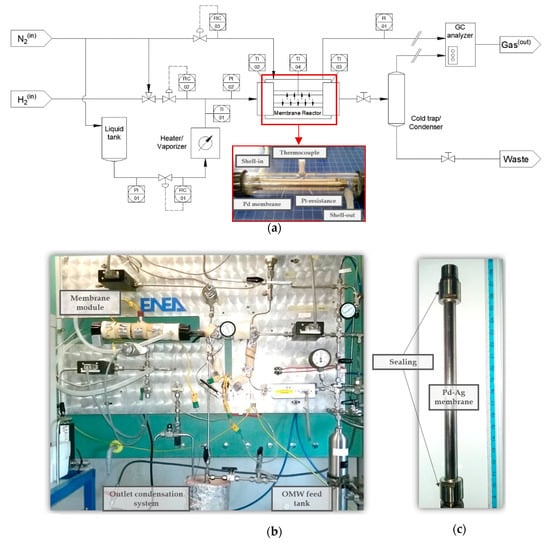
Figure 1.
Experimental device for permeation/reaction tests: (a) general scheme and membrane cell details; (b) real assembly photography; and (c) finger-type Pd membrane.
2.1. Olive Mill Wastewater Conditioning
Similar to previous investigations, the real OMW was conditioned prior to the reforming test. Typically, this wastewater presents very diluted organic compounds with solid particles eventually resulting from the olive fruits. The initial conditioning consisted of successive steps for the removal of solids and water content reduction as published in previous works [24,25,39]. Thus, the first OMW filtration with gradually decreasing mesh sieves was carried out to ensure the complete removal of most solid particles coming from the olive fruits. After that, a concentration step was also performed with the aim of partially reducing the water content of the OMW and, hence, to improve the energy requirements of the next reforming process. This concentration treatment was based on the distillation of the raw OMW into different fractions, then removing those containing a negligible amount of organic compounds. In this manner, the water content decreased, and the original OMW was concentrated. Particular details about the criteria considered for differentiation of the abovementioned OMW fractions and their composition are presented for the first time in this study (see Section 3.2).
2.2. Membrane and Permeation Setup
As previously mentioned, the use of a unique finger-type membrane tube in the experimental apparatus without the presence of a catalyst was used to analyze the membrane permeation behavior. A tubular self-supported PdAg membrane a 152 mm in length, an outside diameter of 10 mm, 150 μm thick, and prepared by a metal alloy containing a 23–25 wt.% of silver balanced with palladium (meaning a Pd content in the range 77–75 wt.%) was placed into a permeation cell under controlled temperature and pressure conditions. Different tests with pure gases (i.e., nitrogen and hydrogen) were performed in order to determine the permeation capacity and the ideal hydrogen separation factor of the membrane for diverse operating conditions. In all cases, the inlet stream was fed into the lumen side of the membrane, while permeate was collected in the shell side with nitrogen as the carrier gas. All stream rates were measured by MKS 1179B (MKS Instruments Deutschland GmbH) calibrated digital mass flow indicators/controllers with a maximum detection limit of 1000 NmL/min (instruments in Figure 1a, labeled as FIC-xx or FI-xx, being xx the equipment number). The accuracy of all these measurements was calculated according to the following expression:
2.3. Catalyst and Membrane Reformer Setup
For the reaction tests, the lumen side of the finger-type PdAg membrane was filled with a mixture of catalyst particles and glass spheres with a diameter of approximately 2 mm and a volumetric ratio of 1/1. The catalyst consisted of spherical Al2O3 particles coated with a CeO2–ZrO2 layer as a support, maintaining a weight ratio between the ceramic external layer and the alumina core of approximately 0.08. This support was homogeneously doped with Pt, Rh, and Pd noble metals as active species (total loading up to a 3 wt.%; the loading for each individual metal being approximately 1 wt.%). This catalyst, non-commercial and provided by the University of Salerno (Italy), was selected on the basis of its good performance in previous studies [25,39]. For each experimental condition, concentrated OMW or mixtures of the biomass with the synthetic bioethanol were evaporated and fed to the lumen side of the membrane, where the catalyst was placed, using nitrogen or air as the carrier gas. Then, the reforming was carried out, and part of the produced hydrogen by the steam reforming was separated through the PdAg membrane. In order to analyze the performance of the membrane reactor for diverse operating conditions, besides the previously described mass-flow meters in permeate and retentate streams for the membrane permeation setup, a gas chromatograph Chrompack Micro-GC CP-2002 was also employed to determine the precise composition of each stream. The GC was equipped with a thermal conductivity detector (TCD) and two analytical columns, Molsieve-5Å and PoraPlot-Q, using argon as carrier gas. The analysis of the gas phase is mainly used for discussion in the present study. However, a cold trap was also placed just after the retentate outlet in order to collect the condensable fraction. These liquid samples as well as the pre-treated OMW used as feed stream were analyzed for total phenols, COD, and TOC as described in detail in previous works [24,25,39]. All results obtained from the characterization of the liquid phase are provided in a separate file in Supplementary Materials (Tables S1 and S2). Between each set of experiments, a regeneration treatment with air for 30 min was carried out to recover both the initial permeation capacity of the membrane and catalyst activity.
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Membrane Characterization: Permeation Analysis
The quality of both the PdAg film and membrane cell fittings were confirmed through leak tests with nitrogen at operating temperature (450 °C) up to 5.0 bar before and after each experiment. The lumen of the membrane tube was pressurized with the gas, maintaining the initial fixed value for at least 12 h. Therefore, a complete retention of nitrogen at these conditions was ensured. After this preliminary verification, permeation tests with pure hydrogen were performed at diverse pressures and temperatures in the range 0.5–5.0 bar and 300–450 °C, respectively. A continuous nitrogen sweep gas flow rate of 200 NmL/min was applied in the shell side to maximize the permeation driving force of experiments, maintaining the total permeate pressure at room conditions. In this manner, the absence of defects and a total ideal hydrogen separation factor could be assumed and permeate hydrogen fluxes obtained for each particular condition were depicted in Figure 2.
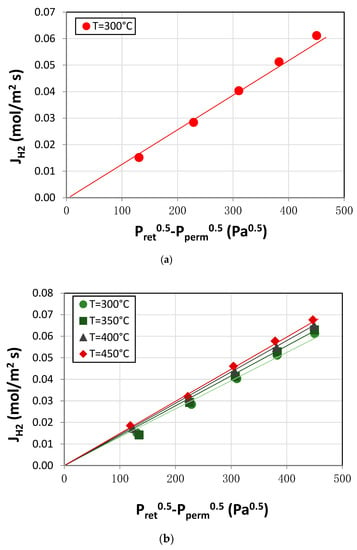
Figure 2.
Effect of pressure (a) and temperature (b) in H2 permeation tests for the finger-type PdAg membrane.
Analyzing in detail the results for a constant temperature (T = 300 °C) but diverse pressure differences between permeate and retentate sides with an exponent coefficient of n = 0.5 (Figure 2a), it is clear that permeate flux increased linearly with the applied driving force. Thus, fitting to the Sieverts’ law with good accuracy (R2 = 0.99975) can be carried out, meaning that diffusion through the bulk PdAg layer is the limiting step of the permeation process and a reference permeance value of k = 1.325 × 10−4 mol·m−2·s−1·Pa−0.5 at these conditions was obtained. This general behavior was maintained for temperatures ranging from 300 to 450 °C (Figure 2b), with the permeate flux increasing as the temperature rose. Thus, permeances between 1.325 × 10−4 and 1.512 × 10−4 mol·m−2·s−1·Pa−0.5 were observed at these conditions, respectively. This fact is in good agreement with the typical Arrhenius-type dependence between permeance and temperature, obtaining an activation energy of 3.035 kJ·mol−1, within the range of other calculated values for similar membranes in previous works [25,39]. For an easier comparison, Table 1 summarizes the main results of permeation tests for this membrane together with other similar self-supported membranes produced by ENEA.

Table 1.
Main parameters obtained from permeation tests for PdAg self-supported membranes.
3.2. Olive Mill Wastewater Conditioning
As previously indicated in the experimental section, prior to valorization of the OMW to obtain pure hydrogen via steam reforming, a first conditioning step was carried out in order to remove the solid particles and concentrate the organic load of the wastewater. Here, it is important to note that the new seasonal OMW sample used in this study contained an almost identical composition to the detailed ones in our previous studies, despite being taken some years later [24,25,39]. The most important treatment for conditioning the raw biomass is the OMW distillation in terms of concentration level requirements for maximizing the hydrogen production. It could represent an important effect on the economy depending on the energy source considered for the process. As presented in previous works [24,25,39], three different liquid fractions can be separated from distillation: one rich in water and the other two more concentrated in organic matter, besides a residual semi-solid fraction. For the first time, the distillation curve of the process is presented in Figure 3a, indicating the temperature evolution in liquid and vapor fractions during the distillation, together with the fraction distilled distribution in Figure 3b. As it can be seen, the boiling point of the OMW sample was maintained very close to 100 °C during the entire process and only slight changes appeared, indicating a very high water content. Nevertheless, these small variations in both liquid and vapor temperatures were used to separate the different liquid fractions. The analysis of filtered OMW provides a TOC value around 10,440 mg·L−1 which is considered as a reference value to follow in the distillation process. The first distilled fraction, denoted with the capital letter A, comprises the lightest distillates up to approximately 102 °C with around a 27% of filtered OMW, presenting a noticeably higher TOC of 24,982 mg·L−1. The intermediate fraction, denoted as fraction B, is the greatest one with around a 57% filtered OMW. The analysis of this fraction reveals a very low TOC value (<150 mg·L−1), evidencing that it mainly consists of water. Finally, the heaviest liquid fraction (fraction C) boils up between 102 and 104 °C with only a 3% of filtered OMW, remaining a semi-solid residue of around 4%. The fraction C presents a TOC of 24,795 mg·L−1, very similar to the value reached by fraction A. The difference between the total amount of filtered OMW and the diverse collected fractions in the distillation equipment is around 4% due to the presence of non-condensable gases. Distilled fractions A and C were mixed again to constitute the concentrate OMW introduced into the membrane reactor. In this manner, it was possible to increase the initial value of TOC from 10,440 mg·L−1 to approximately 25,000 mg·L−1 in the OMW used as a hydrogen source. Complete details about the characterization of OMW and distillate fractions are included in the Supplementary Materials (see Table S1). Additionally, the solid waste obtained from the distillation operation could be used to generate bio-alcohols, i.e., by fermentation processes. The transformation of this residue into bio-alcohols was not carried out in the present work, although the combination of a synthetic bio-ethanol with liquid A+C OMW distilled fractions has been considered in the present study due to its probable availability in most olive farms.
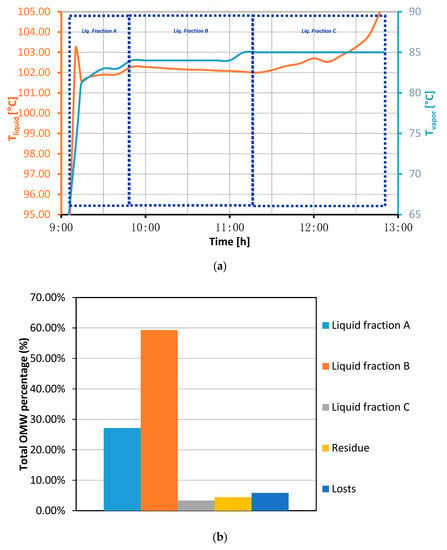
Figure 3.
(a) Distillation curve of real olive mill wastewater (OMW) and (b) distilled mass fraction distribution.
3.3. Membrane Reformer for Hydrogen Production
After the OMW concentration by distillation, diverse reforming experiments for hydrogen production were carried out in the above-described membrane reactor. In accordance to previous results, all tests were performed at 450 °C to obtain a relevant amount of hydrogen (it demonstrated a negligible production level operating with lower temperatures). First, identical operating conditions to previously published ones [39] were repeated to analyze the reproducibility of the study, replacing both the PdAg membrane tube and the OMW sample with new ones. From these experiments, feeding a mixture of distilled OMW and methane (15 g·h−1 and 15 mL·min−1, respectively), similar hydrogen was produced with a permeate flow rate around 28.1 mL·min−1 at T = 450 °C, P = 5.0 bar. In this manner, the validity of the previous studies was confirmed as well as the performance of the membrane reactor with the new membrane and seasonal feedstock. After these preliminary experiments, as a main novelty of the present work, the methane was replaced with synthetic bioethanol, and the new mixture with the pre-concentrated OMW (liquid distillate fractions A + C) was fed into the system for steam co-reforming. Diverse concentrations of ethanol were considered, taking also into consideration the effect of pressure, simultaneous partial oxidation, and space velocity as the most relevant operating conditions. As it has been previously suggested, this bioethanol could be obtained from the solid waste generated during the OMW distillation by fermentation but also from other raw materials available in a typical olive farm. The particular results obtained for each case are discussed in the next paragraphs.
Figure 4 shows the amount of hydrogen produced after the reforming experiments at diverse conditions of inlet pressure. In all cases, the permeate side was purged with nitrogen in the counter-current mode at 1 bar, while the retentate pressure varied from 1 to 5 bar. Hydrogen in the permeate (Figure 4a) and retentate sides (Figure 4b), besides the total amount of hydrogen produced in the reformer (Figure 4c), are presented in the figure. For each experiment, 15 g/h of a mixture of OMW and synthetic bioethanol was fed into the equipment with the help of a carrier gas, nitrogen (blue diamond symbols) or air (orange square symbols). When using the former, nitrogen—an inert gas— the positive effect of increasing pressure on the lumen side was clear, obtaining an increase in the permeate flow rate (Figure 4a) and a consequent decrease in hydrogen in the retentate (Figure 4b). This fact implies an increase in the hydrogen recovery for the process. It is well known that an increase in pressure provokes a negative effect in the steam reforming thermodynamics of high molecular weight molecules present in both OMW and ethanol. This behavior was predicted by Rocha et al. [26] in a previous modelling study and experimentally determined by Borgognoni et al. [51]. However, in the case of using a hydrogen-selective membrane, an increase in pressure improves the permeation rate, as previously shown in Figure 2, but produces a contrary effect on thermodynamics. In this particular study, for some operating conditions, the positive effect of pressure on the membrane’s performance seemed to prevail against the thermodynamics deterioration. According to the predictions of Sieverts’ law and the permeation tests described in the previous section, a pressure increase provokes a clear promotion of the permeation process. Thus, the equilibrium of dehydrogenation reactions is also shifted to the product’s side (shift effect of the membrane), obtaining an overall increase in the total hydrogen produced in the membrane reactor as the pressure rises (Figure 4c). In general, it can be considered that the main reactions involved in the process are:
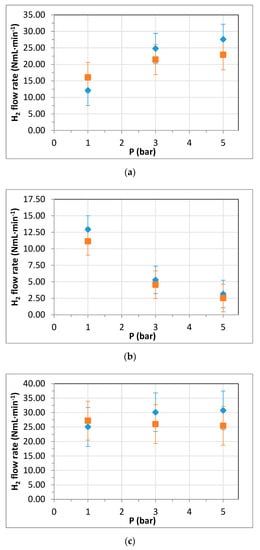
Figure 4.
Effect of pressure in OMW–EtOH co-reforming experiments (T = 450 °C, EtOH concentration 7.5% v/v, feed: 15 g/h OMW–EtOH mixture and 15 mL/min carrier gas): (a) permeate, (b) retentate, and (c) total produced hydrogen. Diamonds (◆) represent experiments with nitrogen, while squares (■) are obtained with air as the carrier gas.
However, there are also other possible secondary reactions occurring during the reforming process such as cracking, carbon formation, methanation or methane steam reforming. In all experiments conducted in the present study, no carbon deposits were detected, and a minimum amount of methane was observed, evidencing the low impact of these secondary reactions, probably due to the temperature conditions at which the process was performed (T = 450 °C). Additionally, no evidence of non-reversible contamination or degradation of the catalyst and membrane were obtained during the reforming process, always recovering both initial catalytic activity and hydrogen permeability after the regeneration processes.
Replacing nitrogen with air as the carrier gas during the co-reforming experiments, thus forcing partial oxidative conditions in the lumen side of the membrane reactor (orange square symbols in Figure 4), negligible improvements in terms of hydrogen production were obtained, decreasing the total amount of hydrogen produced as the pressure increased. Only in the case of the lower pressure (Pret = 1 bar) can some positive effects be observed, with a slight increase in the total amount of hydrogen and, consequently, the permeate flow rate. On the contrary, greater pressures provoke a decrease of the shift effect of the membrane, achieving a nearly constant hydrogen production level. In this manner, it can be concluded that, in general, the increase in hydrogen production with pressure for co-reforming with air as the carrier gas is slightly lower than when using nitrogen. This behavior could be due to the lower membrane shift effect when using oxidative reforming conditions and, hence, a lower hydrogen yield. Note that details about the characterization of the liquid phase generated during the process is included in the Supplementary Materials (see Table S2).
Below, the effect of space velocity was also analyzed. Figure 5 collects the hydrogen production rate during these experiments following a similar structure that was used in the last figure. Total produced hydrogen as well as hydrogen collected in both permeate and retentate streams are depicted separately. Different feed flow rates of biomass (OMW–EtOH mixture) and nitrogen carrier, always maintaining a constant biomass/N2 ratio in the lumen side, were used to obtain a variation in the space velocity inside the membrane reformer.
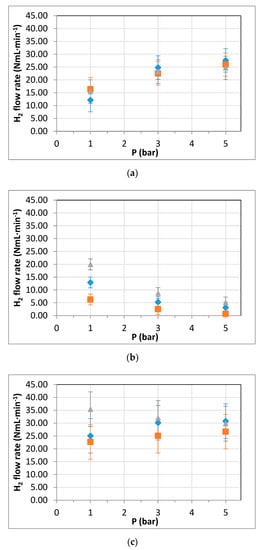
Figure 5.
Effect of space velocity in OMW–EtOH co-reforming experiments (T = 450 °C, EtOH concentration 7.5% v/v, feed: variable): (a) permeate, (b) retentate, and (c) total produced hydrogen. Squares (■): 10 g/h OMW–EtOH and 10 mL/min N2; diamonds (◆): 15 g/h OMW–EtOH and 15 mL/min N2; and triangles (▲): 20 g/h OMW–EtOH and 20 mL/min N2.
Results evidence the different effects of this parameter on the reforming chemical reaction and the membrane’s performance. In fact, by increasing the number of reactants and, consequently, the space velocity in the membrane reformer, very similar permeation values were obtained with a previously described trend as the pressure increases (Sieverts’ law prediction). However, greater disposal of organic compounds generated a positive effect on the hydrogen production rate, increasing both hydrogen on the retentate side and total hydrogen but decreasing the hydrogen recovery as a pure gas through the membrane. This effect was clear for lower pressure values, in which the shift effect of the membrane was not very important. On the contrary, as the pressure increased, the mentioned effect was diluted due to the minor contribution of the membrane shift effect to the global reforming. As previously mentioned, the effect of secondary reactions were not very significant due to the operating temperature, avoiding the formation of carbon deposits. As it was indicated in the previous analysis, the characterization of the liquid phase generated during the reforming process is included in the Supplementary Materials (see Table S2). In general, a decrease of the organic content can be noticed thus evidencing the benefits of this procedure for OMW remediation.
Finally, the effect of the synthetic bioethanol concentration in reforming experiments was also analyzed. The total hydrogen produced for each concentration as well as the fraction separated in permeate or retentate sides are shown in Figure 6. Low ethanol concentrations and, consequently, relatively high dilution levels of the OMW–EtOH mixtures were adopted after considering the typical concentration levels of a real bioethanol. In general, the increase of synthetic bioethanol concentration in the mixture provokes a positive effect in the hydrogen production rate due to the additional reforming of increasing alcohol molecules with the excess of water present in the OMW. As it can be clearly seen in Figure 6, hydrogen in both permeate and retentate sides rises as the ethanol concentration does and, consequently, also the total produced hydrogen, although not with a linear trend. In fact, this positive effect of synthetic bioethanol concentration on the hydrogen production rate seems to be moderated for concentrations higher than 7.5% v/v. This indicates the benefits of using a mixture of OMW and diluted EtOH for reforming experiments with an excess of water present in the feed stream. However, this positive effect was not maintained so clearly when the liquid phase was analyzed (see Table S2). Despite a relevant decrease of the initial organic load of the OMW being observable for all cases, the increase in the ethanol concentration and the abovementioned increase in the total amount of hydrogen produced cannot be correlated with TOC values obtained in the liquid phase.
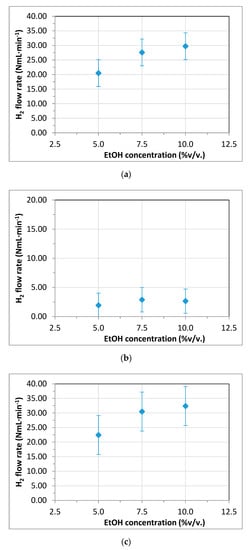
Figure 6.
Effect of ethanol concentration in co-reforming experiments (T = 450 °C, P = 5.0 bar, feed: 15 g/h mixture OMW–EtOH and 15 mL/min N2): (a) permeate, (b) retentate, and (c) total produced hydrogen.
4. Conclusions
The ultra-pure H2 production via co-valorization of OMW and bioethanol in a membrane reformer was presented for the first time together with the required pretreatment for the wastewater feeding. The initial OMW conditioning, based on filtration and distillation steps, doubles the initial TOC of the raw organic matter to facilitate the reforming process, while a self-supported Pd77Ag23 membrane (thickness 150 μm) with permeance values of 1.325–1.512 × 10−4 mol·m−2·s−1·Pa−0.5 and complete selectivity extracts the generated H2 with ultra-high purity. In the membrane reactor, higher pressures increased the H2 permeate, prevailing the shift effect of the chemical reaction against the negative effect on thermodynamics of the reforming reactions. Thus, an overall increase in H2 production was reached as the pressure increased. An increase in the ethanol concentration also provoked a positive effect, although H2 tended to stabilize for higher ethanol concentration values. On the contrary, oxidative reforming conditions did not show any potential benefit, slightly decreasing the obtained H2. Finally, lower residence times helped to increase both the membrane shift effect and H2 recovery on the permeate side, although more reactants potentially generate more hydrogen. The entire study is still ongoing, and we are completing the experimental results with numerical simulations to determine the most favorable operating conditions and to optimize the energy efficiency of the process.
Supplementary Materials
The following are available online at https://www.mdpi.com/2227-9717/8/2/219/s1, Table S1: Characterization of initial OMW samples, and Table S2: Characterization of residue samples obtained in reforming experiments.
Author Contributions
S.T and D.A. conceived and designed the experiments; the experimental work was mainly performed by D.A. with help of G.B. for the OMW pre-treatment; D.A. analyzed the results, doing the required calculations with help of R.S. and J.A.C.; D.A. wrote the paper; S.T. supervised all tasks involved in the present study. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research was funded by ENEA International Fellowship Programme 2015 grant number [260/2015/COMM].
Acknowledgments
The authors acknowledge the financial support received through the ENEA International Fellowship Programme 2015 for a research stay of approximately 6 months in their laboratories. Particularly, D.A. thanks ENEA-Frascati, which hosted this research.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
- Souilem, S.; El-Abbassi, A.; Kiai, H.; Hafidi, A.; Sayadi, S. Olive oil production sector: Environmental effects and sustainability challenges. Olive Mill Waste 2017, 2017, 1–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aggoun, M.; Arhab, R.; Cornu, A.; Portelli, J.; Barkat, M.; Graulet, B. Olive mill wastewater microconstituents composition according to olive variety and extraction process. Food Chem. 2016, 209, 72–80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, Z.S.; Chin, S.Y.; Lim, J.W.; Witoon, T.; Cheng, C.K. Treatment technologies of palm oil mill effluent (POME)and olive mill wastewater (OMW): A brief review. Environ. Technol. Innov. 2019, 15, 100377. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Víctor-Ortega, M.D.; Ochando-Pulido, J.M.; Hodaifa, G.; Martínez-Ferez, A. Ion exchange as an efficient pretreatment system for reduction of membrane fouling in the purification of model OMW. Desalination 2014, 343, 198–207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cassano, A.; Conidi, C.; Giorno, L.; Drioli, E. Fractionation of olive mill wastewaters by membrane separation techniques. J. Hazard. Mater. 2013, 248–249, 185–193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Casanovas, A.; Galvis, A.; Llorca, J. Catalytic steam reforming of olive mill wastewater for hydrogen production. Int. J. Hydrog. Energy 2015, 40, 7539–7545. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eroǧlu, E.; Eroǧlu, I.; Gündüz, U.; Yücel, M. Treatment of olive mill wastewater by different physicochemical methods and utilization of their liquid effluents for biological hydrogen production. Biomass Bioenergy 2009, 33, 701–705. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ochando-Pulido, J.M.; Pimentel-Moral, S.; Verardo, V.; Martinez-Ferez, A. A focus on advanced physico-chemical processes for olive mill wastewater treatment. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2017, 179, 161–174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gonçalves, M.R.; Costa, J.C.; Pereira, M.A.; Abreu, A.A.; Alves, M.M. On the independence of hydrogen production from methanogenic suppressor in olive mill wastewater. Int. J. Hydrog. Energy 2014, 39, 6402–6406. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Battista, F.; Fino, D.; Mancini, G.; Ruggeri, B. Mixing in digesters used to treat high viscosity substrates: The case of olive oil production wastes. J. Environ. Chem. Eng. 2016, 4, 915–923. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eroǧlu, E.; Eroǧlu, I.; Gündüz, U.; Türker, L.; Yücel, M. Biological hydrogen production from olive mill wastewater with two-stage processes. Int. J. Hydrog. Energy 2006, 31, 1527–1535. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pintucci, C.; Padovani, G.; Giovannelli, A.; Traversi, M.L.; Ena, A.; Pushparaj, B.; Carlozzi, P. Hydrogen photo-evolution by Rhodopseudomonas palustris 6A using pre-treated olive mill wastewater and a synthetic medium containing sugars. Energy Convers. Manag. 2015, 90, 499–505. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pintucci, C.; Giovannelli, A.; Traversi, M.L.; Ena, A.; Padovani, G.; Carlozzi, P. Fresh olive mill waste deprived of polyphenols as feedstock for hydrogen photo-production by means of Rhodopseudomonas palustris 42OL. Renew. Energy 2013, 51, 358–363. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lafi, W.K.; Shannak, B.; Al-Shannag, M.; Al-Anber, Z.; Al-Hasan, M. Treatment of olive mill wastewater by combined advanced oxidation and biodegradation. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2009, 70, 141–146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Badawy, M.I.; Ghaly, M.Y.; Ali, M.E.M. Photocatalytic hydrogen production over nanostructured mesoporous titania from olive mill wastewater. Desalination 2011, 267, 250–255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Speltini, A.; Sturini, M.; Maraschi, F.; Dondi, D.; Fisogni, G.; Annovazzi, E.; Profumo, A.; Buttafava, A. Evaluation of UV-A and solar light photocatalytic hydrogen gas evolution from olive mill wastewater. Int. J. Hydrog. Energy 2015, 40, 4303–4310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- García, C.A.; Hodaifa, G. Real olive oil mill wastewater treatment by photo-Fenton system using artificial ultraviolet light lamps. J. Clean. Prod. 2017, 162, 743–753. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kargi, F.; Catalkaya, E.C. Hydrogen gas production from olive mill wastewater by electrohydrolysis with simultaneous COD removal. Int. J. Hydrog. Energy 2011, 36, 3457–3464. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ntaikou, I.; Kourmentza, C.; Koutrouli, E.C.; Stamatelatou, K.; Zampraka, A.; Kornaros, M.; Lyberatos, G. Exploitation of olive oil mill wastewater for combined biohydrogen and biopolymers production. Bioresour. Technol. 2009, 100, 3724–3730. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oz, N.A.; Uzun, A.C. Ultrasound pretreatment for enhanced biogas production from olive mill wastewater. Ultrason. Sonochem 2015, 22, 565–572. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Siciliano, A.; Stillitano, M.A.; de Rosa, S. Biogas production from wet olive mill wastes pretreated with hydrogen peroxide in alkaline conditions. Renew. Energy 2016, 85, 903–916. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kapdan, I.K.; Kargi, F. Bio-hydrogen production from waste materials. Enzym. Microb. Technol. 2006, 38, 569–582. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dincer, I.; Acar, C. Innovation in hydrogen production. Int. J. Hydrog. Energy 2017, 42, 14843–14864. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tosti, S.; Accetta, C.; Fabbricino, M.; Sansovini, M.; Pontoni, L. Reforming of olive mill wastewater through a Pd-membrane reactor. Int. J. Hydrog. Energy 2013, 38, 10252–10259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tosti, S.; Cavezza, C.; Fabbricino, M.; Pontoni, L.; Palma, V.; Ruocco, C. Production of hydrogen in a Pd-membrane reactor via catalytic reforming of olive mill wastewater. Chem. Eng. J. 2015, 275, 366–373. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rocha, C.; Soria, M.A.; Madeira, L.M. Steam reforming of olive oil mill wastewater with in situ hydrogen and carbon dioxide separation—Thermodynamic analysis. Fuel 2017, 207, 449–460. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choi, D.H.; Chun, S.M.; Ma, S.H.; Hong, Y.C. Production of hydrogen-rich syngas from methane reforming by steam microwave plasma. J. Ind. Eng. Chem. 2016, 34, 286–291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, F.; Shi, Y.; Yang, L.; Du, X. Kinetics for hydrogen production by methanol steam reforming in fluidized bed reactor. Sci. Bull. 2016, 61, 401–405. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, C.C.; Tseng, H.H.; Lin, Y.L.; Chen, W.H. Hydrogen production and carbon dioxide enrichment from ethanol steam reforming followed by water gas shift reaction. J. Clean. Prod. 2017, 162, 1430–1441. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nabgan, W.; Abdullah, T.A.T.; Mat, R.; Nabgan, B.; Gambo, Y.; Ibrahim, M.; Ahmad, A.; Jalil, A.A.; Triwahyono, S.; Saeh, I. Renewable hydrogen production from bio-oil derivative via catalytic steam reforming: An overview. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 2017, 79, 347–357. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sabio, E.; Álvarez-Murillo, A.; González, J.F.; Ledesma, B.; Román, S. Modelling the composition of the gas obtained by steam reforming of glycerine. Energy Convers. Manag. 2017, 146, 147–157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zornoza, B.; Casado, C.; Navajas, A. Chapter 11-Advances in Hydrogen Separation and Purification with Membrane Technology. In Renew. Hydrog. Technol.; Gandía, L.M., Arzamendi, G., Diéguez, P.M., Eds.; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2013; pp. 245–268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rahimpour, M.R.; Samimi, F.; Babapoor, A.; Tohidian, T.; Mohebi, S. Palladium membranes applications in reaction systems for hydrogen separation and purification: A review. Chem. Eng. Process. Process. Intensif. 2017, 121, 24–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- D Alique, D.; Martinez-Diaz, R.; Sanz, J.A. Calles, Review of Supported Pd-Based Membranes Preparation by Electroless Plating for Ultra-Pure Hydrogen Production. Membranes 2018, 8, 5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tosto, E.; Alique, D.; Martinez-Diaz, D.; Sanz, R.; Calles, J.A.; Caravella, A.; Medrano, J.A.; Gallucci, F. Stability of pore-plated membranes for hydrogen production in fluidized-bed membrane reactors. Int. J. Hydrog. Energy 2019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tosti, S.; Basile, A.; Bettinali, L.; Borgognoni, F.; Gallucci, F.; Rizzello, C. Design and process study of Pd membrane reactors. Int. J. Hydrog. Energy 2008, 33, 5098–5105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tosti, S. Overview of Pd-based membranes for producing pure hydrogen and state of art at ENEA laboratories. Int. J. Hydrog. Energy 2010, 35, 12650–12659. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bruni, G.; Cordiner, S.; Tosti, S. A novel procedure for the preliminary design of dense metal membrane modules for hydrogen separation. Int. J. Hydrog. Energy 2016, 41, 20198–20209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tosti, S.; Fabbricino, M.; Pontoni, L.; Palma, V.; Ruocco, C. Catalytic reforming of olive mill wastewater and methane in a Pd-membrane reactor. Int. J. Hydrog. Energy 2016, 41, 5465–5474. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sanz, R.; Calles, J.A.; Alique, D.; Furones, L.; Ordóñez, S.; Marín, P. Hydrogen production in a Pore-Plated Pd-membrane reactor: Experimental analysis and model validation for the Water Gas Shift reaction. Int. J. Hydrog. Energy 2015, 40, 3472–3484. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alique, D.; Imperatore, M.; Sanz, R.; Calles, J.A.; Baschetti, M.G. Hydrogen permeation in composite Pd-membranes prepared by conventional electroless plating and electroless pore-plating alternatives over ceramic and metallic supports. Int. J. Hydrog. Energy 2016, 41, 19430–19438. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peters, T.A.; Rørvik, P.M.; Sunde, T.O.; Stange, M.; Roness, F.; Reinertsen, T.R.; Ræder, J.H.; Larring, Y.; Bredesen, R. Palladium (Pd) Membranes as Key Enabling Technology for Pre-combustion CO2 Capture and Hydrogen Production. Energy Procedia 2017, 114, 37–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vadrucci, M.; Borgognoni, F.; Moriani, A.; Santucci, A.; Tosti, S. Hydrogen permeation through Pd–Ag membranes: Surface effects and Sieverts’ law. Int. J. Hydrog. Energy 2013, 38, 4144–4152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Santucci, A.; Borgognoni, F.; Vadrucci, M.; Tosti, S. Testing of dense Pd–Ag tubes: Effect of pressure and membrane thickness on the hydrogen permeability. J. Memb. Sci. 2013, 444, 378–383. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tosti, S. Supported and laminated Pd-based metallic membranes. Int. J. Hydrog. Energy 2003, 28, 1445–1454. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gallucci, F.; Basile, A.; Tosti, S.; Iulianelli, A.; Drioli, E. Methanol and ethanol steam reforming in membrane reactors: An experimental study. Int. J. Hydrog. Energy 2007, 32, 1201–1210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Manzolini, G.; Tosti, S. Hydrogen production from ethanol steam reforming: Energy efficiency analysis of traditional and membrane processes. Int. J. Hydrog. Energy 2008, 33, 5571–5582. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gallucci, F.; de Falco, M.; Tosti, S.; Marrelli, L.; Basile, A. Ethanol steam reforming in a dense Pd-Ag membrane reactor: A modelling work. Comparison with the traditional system. Int. J. Hydrog. Energy 2008, 33, 644–651. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iulianelli, A.; Liguori, S.; Vita, A.; Italiano, C.; Fabiano, C.; Huang, Y.; Basile, A. The oncoming energy vector: Hydrogen produced in Pd-composite membrane reactor via bioethanol reforming over Ni/CeO 2 catalyst. Catal. Today 2016, 259, 368–375. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, R.; Castro-Dominguez, B.; Mardilovich, I.P.; Dixon, A.G.; Ma, Y.H. Experimental and simulation studies of the production of renewable hydrogen through ethanol steam reforming in a large-scale catalytic membrane reactor. Chem. Eng. J. 2016, 303, 302–313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Borgognoni, F.; Tosti, S.; Vadrucci, M.; Santucci, A. Combined methane and ethanol reforming for pure hydrogen production through Pd-based membranes. Int. J. Hydrog. Energy 2013, 38, 1430–1438. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).