1. Introduction
The reaction of Suzuki-Miyaura (S-M) cross-coupling between aryl halides and arylboronic acids is one of the most common and effective methods for the synthesis of biaryls, which are important intermediates in the synthesis of pharmaceuticals, ligands, and polymers [
1,
2]. It is known that this reaction is a palladium-catalyzed condensation reaction, which proceeds via a Pd(0)/Pd(II) cycle involving the oxidative addition of the starting components and the reductive elimination of the resulting reaction products. The loss of the catalyst activity is an important issue of all the cross-coupling reactions. Various processes (e.g., aggregation, dissociation, leaching, etc.) can contribute to changes of the catalyst nature and, as a result, its activity and selectivity [
3,
4,
5]. Aryl halides cause very low palladium dissolution, while arylboronic acids, on the contrary, causes significant palladium leaching accompanied by its reduction and formation of palladium black. However, in the presence of both substrates, Pd(0) formed in the solution with participation of arylboronic acid is converted by aryl halide without precipitation of nanoparticles (NPs) [
6].
This work addresses the catalytic behavior of palladium NPs stabilized within hyper-cross-linked polystyrene (HPS) support during the repeated reaction runs. HPS of two types was used, non-functionalized (MN270) and bearing tertiary amino groups (MN100), both relate to so-called “Davankov-type” resins [
7,
8]. In our previous works we have shown that Pd/HPS catalysts are highly active and selective in S-M reaction between phenylboronic acid (PBA) and 4-bromoanisole (BrAn) as model compounds [
9,
10,
11]. However, due to the complex homo-heterogeneous mechanism [
12] of this reaction, especially in the case of so-called “cocktail” type catalysts (containing metal NPs as reservoirs for catalytically active species [
4,
13]), the question about deactivation during the reaction course and the reasons for such behavior remains open. The term “cocktail” catalyst was proposed by Ananikov and coworkers [
3,
4] for cross-coupling processes and describes catalytic systems containing more than one form of palladium including Pd(0) NPs, were the latter serve as pre-catalysts generating active species during the reaction. For such catalysts it was established that virtually any form of Pd (small clusters, NPs, inorganic salts, complexes containing palladium ions or atoms) might start catalytic cycle. General scheme of catalytic cycle of S-M cross-coupling is presented in
Figure 1.
In many works [
4,
6,
14,
15,
16], the leaching of Pd and the formation of inert Pd(0)NPs are considered as the main reasons hampering catalyst reuse. There are two main ways to study catalyst deactivation and the nature (homogeneous vs. heterogeneous) of the active species: (i) hot filtration test and (ii) mercury test [
16]. Each of them has certain disadvantages when working with a complex “cocktail” type catalyst with high porosity support. The pores of polymeric support can play a role of nanoreactors, in which Pd NPs can undergo dissolution, migration, reprecipitation and aggregation during the reaction course; hence actually the reaction location may shift to the polymer volume rather than being catalyzed by soluble Pd species in the reaction mixture. In this study, we chose the hot filtration test. We carried it out with the samples of Pd/HPS preliminarily reduced in hydrogen to form Pd(0) NPs, in order to see if any loss of Pd species takes place. However, the nature of deactivation was completely different and didn’t rely on Pd leaching but was due to a strong adsorption of the target product 4-methoxybiphenyl (MBP) on hydrophobic HPS support. Therefore, catalyst reuse is possible and is just a matter of suitable regeneration between the cycles.
2. Results and Discussion
The catalyst Pd/MN270, synthesized by the impregnation of non-functionalized HPS with Pd(OAc)
2 and containing small Pd NPs formed during the reduction in hydrogen flow, allows nearly complete conversion of aryl halide in the reaction between BrAn and PBA for 60 min at mild conditions (70°C, NaOH as a base, EtOH-water mixture as a solvent). By the end of the reaction the share of the target cross-coupling product, MBP, among possible products (MBP and biphenyl (BP)—the result of PBA homocoupling) was relatively high–96.3%. At the same time, during the repeated reaction runs we observed a considerable catalyst deactivation from cycle to cycle with the decrease of not only the initial transformation rate,
R0 (from 411 μmol(BrAn)/min to 291 μmol(BrAn)/min after the first run and to 75 μmol(BrAn)/min after the second run), but also the achieved BrAn conversion: from 99.7% to 54.8% and 14.1% for the first, second and third cycle, respectively (see
Figure 2a). The decrease of catalytic activity was supposed to be due to the loss of catalytically active species. However, it was found (
Figure 2b) that after filtration of the reaction mixture (separation of the solid catalyst) the S-M reaction stopped, which indicated the absence of any active Pd species in filtrate.
By the XFA method it was shown that Pd content in the catalyst remains the same (2.5 wt%) after the catalytic reaction. Thus, the loss of catalytic activity can’t be associated with a detectable loss of palladium. Other reasons could be either aggregation of Pd NPs or clogging of HPS pores making active Pd-species inaccessible for reactants.
S/TEM studies showed (
Figure 3) that for Pd/MN270 taken after the first use in the S-M reaction, Pd NPs decreased in size (D
m = 6.8 ± 2.9 nm) and formed grape-type clusters (
Figure 3c,d).The original fresh sample (see
Figure 2a,b) contained Pd NPs with an average diameter of 8.2 ± 2.4 nm. Thus, we came to the conclusion that NPs aggregation, which is mentioned as an important factor in catalyst deactivation [
17], cannot lead to the observed loss of Pd/MN270 activity upon repeated use.
Low-temperature physisorption of nitrogen showed that all catalyst samples have a predominant microporosity (
Figure 4a). It is noteworthy that after the formation of NPs in the hydrogen flow, the SSA of the sample Pd(OAc)
2 decreased (
Table 1,
Figure 4b) from 1084 m
2/g to 842 m
2/g, mainly due to a decrease in microporosity (SSA of micropores decreased from 945 m
2/g to 623 m
2/g). However, after the first use in S-M reaction SSA of Pd/MN270 increased up to 977 m
2/g (BET model) due to the increase of the share of both micro- and meso-pores, which in turn can be due to the NPs reprecipitation inside the HPS pores and is in good agreement with the results of S/TEM, obviously showing that no pore blockage took place during the use of Pd/MN270 in S-M cross-coupling.
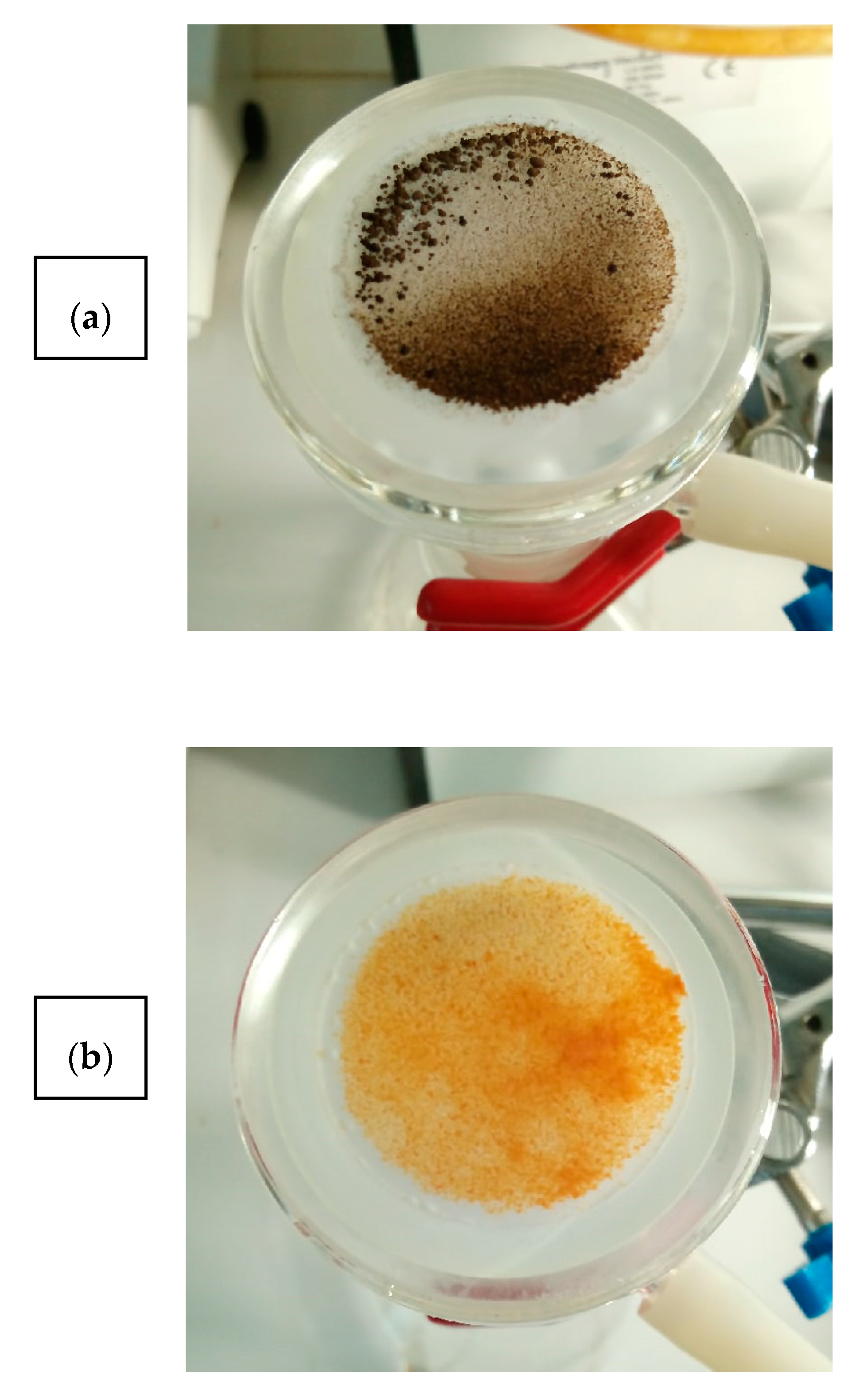
At the same time, after the second use of Pd/MN270 in S-M reaction between BrAn and BPA we observed unusual behavior of the catalyst on the membrane filter: there was a tendency to form aggregates during washing of the catalyst suspension with polar solvents. It is noteworthy that initial suspension in the reactor was without any aggregates. This tendency was typical not only for the catalyst (
Figure 5a), but also for initial MN270, which was sustained in the MBP solution (
Figure 5b). Taking into account the aromatic nature of HPS, we considered the adsorption of MBP, which may increase hydrophobicity of the surface leading to the aggregation.
Although different reactants can potentially adsorb on the catalyst surface during the S-M reaction, we supposed that MBP is responsible for the observed deactivation due to the following reasons:
– bromine and boron were not detected on the surface of Pd/MN270 neither after the first run nor after the second run, which exclude strong adsorption of BrAn and PBA;
– sodium was found on the Pd/MN270 surface in trace amounts (less than 0.2 at.%), so, sodium-containing compounds can not be considered as the main adsorbed species;
– high selectivity of the catalyst with respect to MBP (share of MBP among the reaction products is higher than 96%) excludes the strong influence of BP;
– sharp increase of oxygen content was found after the repeated reaction runs, and this oxygen does not belong to the oxygen of polymeric matrix itself (see below).
The adsorption of MBP was confirmed by the XPS (
Figure 6). On the surface of Pd/MN270 taken after the first use in S-M reaction all the Pd was belonging to partially oxidized metallic Pd NPs (
Figure 6a). While oxygen included two components (
Figure 6b): (i) oxygen belonging to HPS matrix and (ii) oxygen of the ether bond (-O-CH
3). Oxygen of PdO was not considered in O 1s deconvolution because of relatively low signal of Pd.
DRIFT study confirmed the above assumption. Normalized FTIR spectra of Pd/MN270 (
Figure S1) clearly show that after the second use in S-M reaction, the intensity of adsorption bands belonging to C-H of alkanes (ν
C-H = 2857 cm
−1, δ
C-H = 1452 and 1418 cm
−1) and benzene rings (ν
C-H = 3019 cm
−1, in-plane vibrations δ
C-H in the range of 1250–950 cm
−1, out-of-plane vibrations δ
C-H in the range of 900–650 cm
−1) increased. Moreover, noticeable increase of the intensity of the adsorption band belonging to C-O bond (ν
C-O = 1294 cm
−1) occurred.
In order to prove the loss of catalytic activity due to the MBP adsorption, the sample Pd/MN270 taken after the first use in S-M reaction was washed additionally with chloroform for 5 h at room temperature and intensive stirring. After that, washed sample was tested again (see
Figure 7), and the catalytic activity was almost fully recovered.
As the further step of investigation, we compared stability of two catalysts, Pd/MN270 and Pd/MN100 under equal reaction conditions, in order to find if there is any deactivation during the repeated use in the case of MN100 containing tertiary amino groups, which make this polymer relatively more hydrophilic than MN270 (non-functionalized). As it can be seen in
Figure 8a, Pd/MN100 can be recycled without noticeable loss of catalytic activity. At the same time the oxygen belonging to the ether bond (-O-CH
3) increases after the second use only slightly (
Figure 8b) in comparison with the sample Pd/MN270 (see
Figure 6b). It is noteworthy that Pd/MN100 did not undergo additional washing procedure between the catalytic cycles.
It should be also mentioned that the observed “plateau” on the kinetic curves (
Figure 8a) is due to the lack of PBA and corresponding NaOH, as monometallic catalysts of S-M cross-coupling based on MN100 typically possesses lower selectivity (the share of MBP is about 94% at complete conversion of BrAn) and requires higher excess of PBA with respect to BrAn in the reaction mixture. In this particular case, if PBA will be taken in 2.5-fold excess with respect to BrAn (at 3.0 mmol of NaOH), more than 95% of BrAn conversion will be achieved by 20 min of the reaction. The necessity to use high excess of PBA can be likely due to the side reactions, e.g., PBA deboronation, which might take place in the presence of water [
18] in case of more hydrophilic polymer.
3. Materials and Methods
3.1. Materials
HPS (Purolite Int., Llantrisant, UK) used as catalyst support was of two types: hyper-cross-linked non-functionalized polystyrene, Macronet MN270, and HPS containing tertiary amino groups, MN100. Both supports were washed with distilled water and acetone and then dried under vacuum as described elsewhere [
19]. 4-Bromoanisole (BrAn, ≥98%) was purchased from Merck KGaA. 4-Methoxybiphenyl (MBP, >99%) was purchased from Tokyo Chemical Industry Co. Ltd. Phenylboronic acid (PBA, 95%), diphenylamine (99%), biphenyl (BP, 99.5%), tetrahydrofuran (THF, ≥99.9%), ethanol (EtOH, ≥99.8%), isopropanol (
i-PrOH, ≥99.5%), chloroform (CHCl
3, ≥99%, anhydrous, containing 0.5% EtOH as a stabilizer), sodium hydroxide (NaOH, ≥98%) were obtained from Sigma-Aldrich. Palladium acetate (Pd(CH
3COO)
2, Pd content 47.68%) was purchased from JSC “Aurat” (Moscow, Russia). All chemicals were used as received. Distilled water was purified with an Elsi-Aqua water purification system.
3.2. Catalyst Synthesis
HPS MN270-based catalyst containing Pd was synthesized via wet-impregnation method. In a typical experiment, 1 g of pretreated, dried and crushed (<63 μm) granules of MN270 were impregnated with 2.8 mL of the THF solution of precursor (Pd(CH3COO)2) of a certain concentration. The sample was dried at 70°C until the constant weight. Thus the catalyst Pd(OAc)2/MN270 was synthesized containing 2.5 wt% of Pd (confirmed by the XFA). This catalyst was also reduced in a hydrogen flow (100 mL/min) at 300°C for 3 h (the catalysts was designated as Pd/MN270).
By the same method, the catalyst based on HPS MN100 was synthesized (Pd(OAc)2/MN100,with 1.0 wt% of Pd as confirmed by the XFA) and after reduction in a hydrogen flow was designated as Pd/MN100.
To confirm the state of Pd, the synthesized samples were analyzed by the X-Ray Photoelectron Spectroscopy (XPS). The XPS data revealed (see
Figure 9) that both Pd/MN270 (
Figure 9a) and Pd/MN100 (
Figure 9b) contain palladium in the form of partly oxidized NPs (
Eb is 335.0 eV for metallic Pd and 336.3 for PdO/Pd [
20]) and PdO (
Eb = 337.2 eV [
20]) on their surfaces. For simplification of discussion we suppose that predominant form of palladium is metallic form, Pd(0), in the case of the reduced catalysts (Pd/HPS).
3.3. Reaction Procedure and Analysis of Reaction Mixture
The Suzuki-Miyaura (S-M) cross-coupling was carried in a temperature controlled shaker-type glass batch reactor at following reaction parameters: Pd concentration 0.157 mmol/L (which is equal to 0.47 mol% with respect to BrAn), PBA amount 1.5 mmol, NaOH amount 2.0 mmol, BrAn amount 1.0 mmol, stirring intensity 800 two-sided shaking per minute, reaction temperature 70°C, EtOH-to-H2O volumetric ratio 5:1 (total volume of liquid phase 30 mL), and nitrogen as gas phase. Preliminary experiments showed that the reaction of BrAn and PBA at chosen conditions when using Pd/MN270 as a catalyst proceeds almost quantitatively (97–99 mol%); the formation of BP does not exceed 2% molar, and the formation of σ,σ’-dianisoles is not detected.
The excess of PBA with respect to BrAn was used due to the possible non-selective catalyst behavior as a result of PBA homocoupling with the formation of BP. It is noteworthy that before the catalyst addition in the reactor, in each experiment the blank test (duration of 60 min) was carried out in order to ensure that the is no reaction without catalyst.
The choice of EtOH/water mixture as a solvent was, from one hand, due to the environmentally benign nature of these solvents, and from the other hand, by the no need of phase-transfer agents, since the system remained all time homogeneous in the range of selected concentrations of reactants (BrAn, PBA and NaOH) and the products formed (MBP and BP). Moreover, it is known that addition of water to an organic solvent avoids the formation of inactive trimers of boronic acid [
21].
Regarding the inert gas atmosphere, it should be noted that Pd/HPS catalysts can be used in air, but the rate of BrAn transformation is lower (
Figure 10) and the share of target MBP in the reaction products also decreased from 98.4% to 95.9% at 94% of BrAn conversion due to the increase of BP accumulation. Adrio et al., also reported accelerated PBA homocoupling in the presence of air [
22]. The role of oxygen is presumably in partial oxidation of palladium as it was shown by McGlacken et al. [
23], while Pd(II) is able to react with PBA prior to BrAn. In our opinion, the interaction of oxygen in the aqueous medium with Pd(0) leads to formation of tightly bound ligands in Pd(OH)
2, blocking “hot” atoms of the Pd and reducing its activity.
In each catalytic experiment, samples of reaction mixture were periodically taken and analyzed via GC-MS (Shimadzu GCMS-QP2010S) equipped with a capillary column HP-1MS (100 m × 0.25 mm i.d., 0.25 μm film thickness). Helium was used as a carrier gas at pressure of 74.8 kPa and linear velocity of 36.3 cm/s. Oven temperature was programmed: 120 °C (0 min) → 10 °C/min (160 °C) → 25 °C/min (300 °C) → 300 °C (2.4 min). Temperature of injector, interface and ion source was at 260 °C, range from 10 up to 500 m/z. The concentrations of the reaction mixture components were calculated using the internal standard calibration method (diphenylamine was used as an internal standard). It is noteworthy that during the GS-MS analysis, PBA underwent dehydration and trimerization, which negatively affected the signal intensity. Due to the low level of confidence in the quantitative analysis of PBA content, its consumption was not studied.
Catalytic activity was characterized by the initial transformation rate, (R0) and defined as a tangent of slope of the initial linear part on kinetic curves of BrAn consumption: R0 = (NBrAn,0 − NBrAn,i) × τi−1, where NBrAn is number of moles of BrAn (μmol); and τ is the reaction time (min).
Conversion (X,%) of BrAn was defined as X = (NBrAn,0 − NBrAn,i) × NBrAn,0−1× 100.
3.4. Isolation of the Catalysts from the Reaction Mixture for Reuse
After the completion of the S-M reaction, the catalysts were filtered under vacuum using membrane filter (cellulose acetate, 0.45 μm pore size, 50 mm diameter) and sequentially washed with EtOH (30 mL), i-PrOH (30 mL), water (500 mL), i-PrOH (30 mL) and chloroform (50 mL). Then they were dried till constant weight at 70 °C. It is noteworthy that for the repeated use, several (at least 4) catalyst samples were collected from previous runs and averaged catalyst sample was taken for further run. In this way all the reaction conditions remained unchanged including the catalyst weight.
3.5. Procedure of Hot-Filtration of the Reaction Mixture
The S-M reaction was started as usual according to the procedure described in
Section 3.3. After 1 min, 10 mL of the reaction mixture was separated (start of hot-filtration) using syringe equipped with membrane (0.22 μm pore size) and promptly transferred to the second glass batch reactor (end of hot-filtration process), which was preliminarily thermostated and sealed. After that the filtrate was kept under the reaction conditions for 60 min with periodic sampling and analysis.
3.6. Catalyst Characterization
Pd/HPS catalysts were characterized by liquid nitrogen physisorption, X-ray Fluorescence Analysis (XFA), X-ray Photoelectron Spectroscopy (XPS), Diffuse Reflectance Infrared Fourier Transform Spectroscopy (DRIFTS) and Scanning Transmission Electron Microscopy (STEM).
Liquid nitrogen physisorption was carried out using Beckman Coulter SA 3100 (Coulter Corporation, USA). Prior to the analysis, each sample was placed in a quartz cell installed in the Becman Coulter SA-PREP. The samples were pretreated over 60 min under nitrogen at 120 °C. Once the pretreatment was complete, the cell was cooled and weighed, and then transferred to the analytical port. Analysis was performed at −196 °C and a relative pressure of 0.9814 (for pores less than 100 nm in diameter) to obtain a PSD (ADS) profile.
XFA was carried out to determine the Pd content. It was performed with a Zeiss Jena VRA-30 spectrometer (Mo anode, LiF crystal analyzer and SZ detector). Analyses were based on the Co Kα line and a series of standards prepared by mixing 1 g of polystyrene with 10–20 mg of standard compounds. The time of data acquisition was constant at 10 s.
XPS data were obtained using Mg Kα (hν= 1253.6 eV) radiation with ES-2403 spectrometer (Institute for Analytic Instrumentation of RAS, St. Petersburg, Russia) equipped with energy analyzer PHOIBOS 100-MCD5 (SPECS, Berlin, Germany) and X-ray source XR-50 (SPECS, Berlin, Germany). All the data were acquired at X-ray power of 250 W. Survey spectra were recorded at an energy step of 0.5 eV with an analyzer pass energy 40 eV, and high resolution spectra were recorded at an energy step of 0.05 eV with an analyzer pass energy 7 eV. Samples were outgassed for 180 min before analysis and were stable during the examination. The data analysis was performed via CasaXPS.
DRIFTS was carried out using an IRPrestige-21 FTIR spectrometer (Shimadzu, Kyoto, Japan) equipped with a DRS-8000 diffuse reflectance accessory (Shimadzu, Kyoto, Japan). The background sample was a mirror of the material of the optical system of the DRS-8000 accessory. All spectra were recorded in the range of 4000–500 cm−1 wave numbers with the resolution of 4 cm−1.
STEM characterization was carried out using FEI Tecnai Osiris instrument (Thermo Fisher Scientific, Waltham, MA, USA) operating at an accelerating voltage of 200 kV, equipped with high-angle annular dark field (HAADF) detector (Fischione, Export, PA, USA) and energy-dispersive X-ray (EDX) microanalysis spectrometer (EDAX, Mahwah, NJ, USA). Samples were prepared by embedding the catalyst in epoxy resin with following microtomming (ca. 50 nm thick) at ambient temperature. For the image processing Digital Micrograph (Gatan, Pleasanton, CA, USA) software and TIA (Thermo Fisher Scientific, Waltham, MA, USA) were used. Holey carbon/Cu grid was used as a sample support.