Abrasive Water Jet Cutting of Hardox Steels—Quality Investigation
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Experimental Section
2.1. Characteristics of the Samples
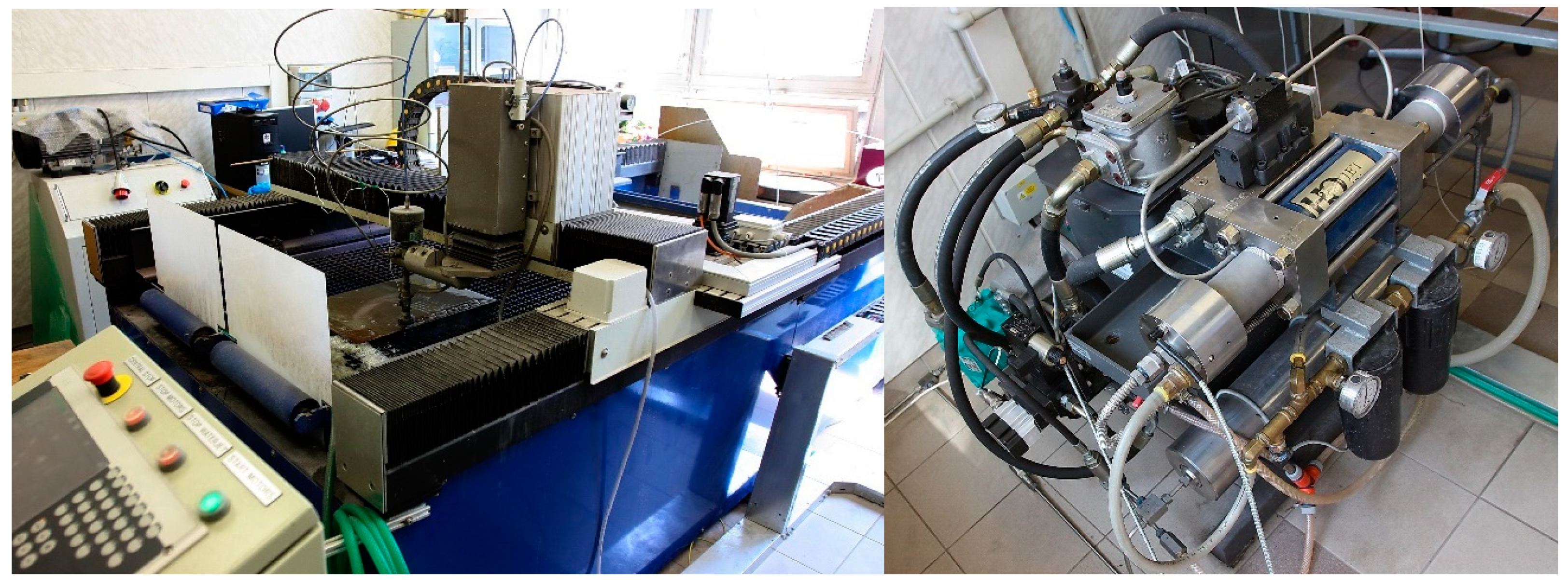
2.2. Characteristics of the AWJ System and Procedure
| Water orifice diameter do | 0.25 mm |
| Stand-off distance L | 2 mm |
| Focusing tube diameter da | 1.02 mm |
| Focusing tube length la | 76 mm |
| Abrasive material average grain size ao | 0.275 mm (MESH 80) |
| Abrasive material type | Australian garnet |
| Angle of impact θ | 0 rad |
| Water jet pressure p | 300, 340, 380 MPa |
| Abrasive mass flow rates ma | 170, 220, 270 g/min |
| Experimental traverse speeds v | 40, 60 80 mm/min for each thickness 6, 10 15 mm |
| 10, 15, 20 mm/min for thickness 40 mm | |
| 60, 90, 120 mm/min for thickness 6 mm |
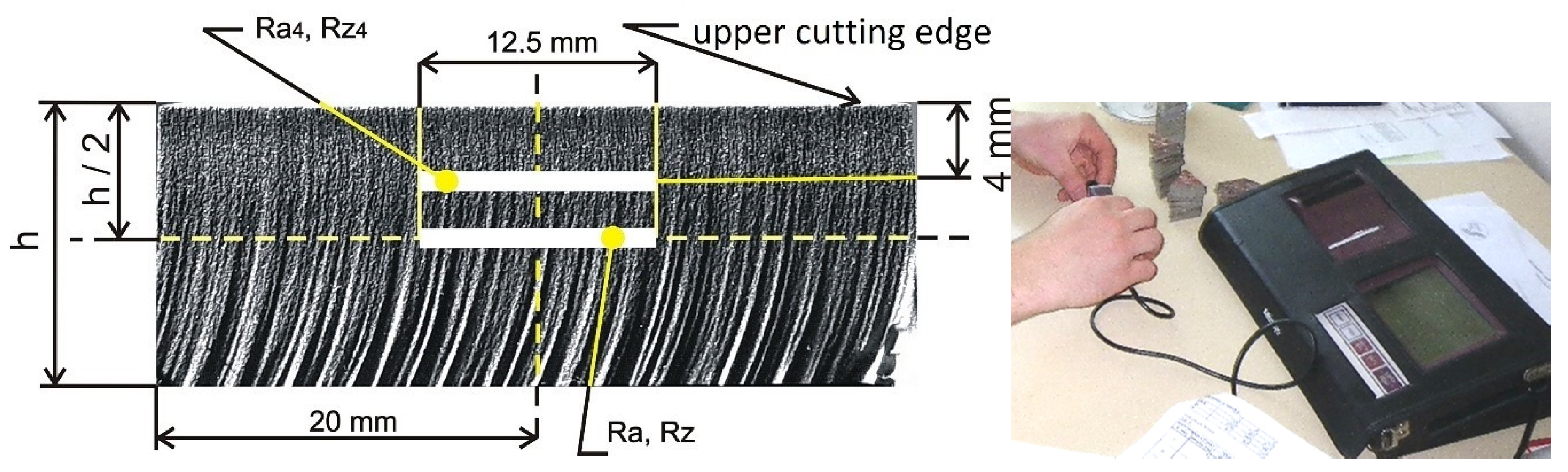
2.3. Roughness Measurement of Cut Surfaces
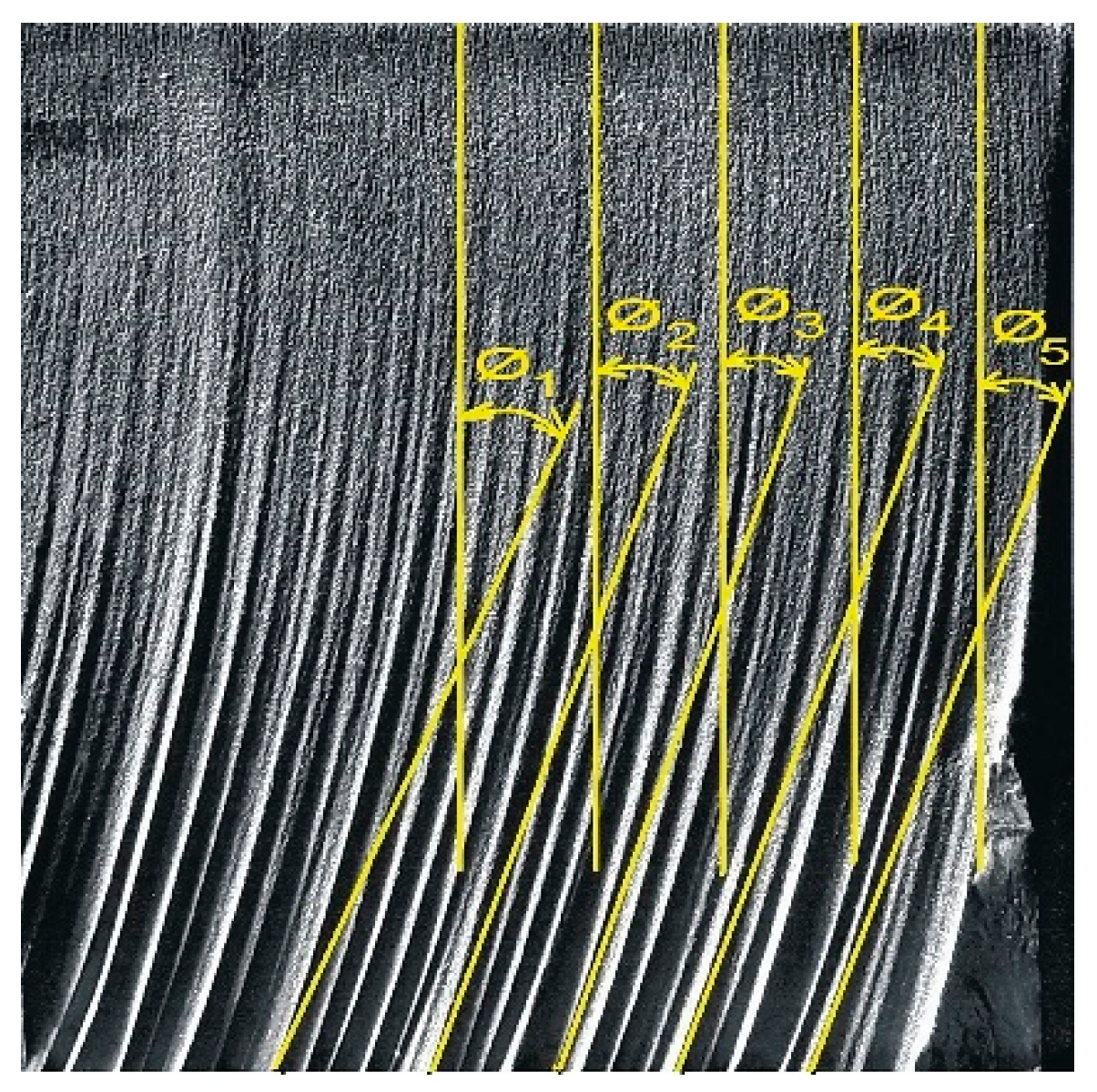
2.4. Measurements of the Angle of Declination of the Jet
3. Discussion
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Nomenclature
| angle between impinging jet axis and tangent to the striation curve in the selected depth h…[°] | |
| average mean size of abrasive particles formed in the mixing process…[m] | |
| average mean size of abrasive particles entering the mixing process…[m] | |
| water nozzle diameter…[mm] | |
| focusing tube diameter…[mm] | |
| material thickness…[mm] | |
| focusing tube length…[mm] | |
| stand-off distance…[mm] | |
| water jet pressure…[MPa] | |
| abrasive mass flow rate…[g/min] | |
| traverse speed…[mm/min] | |
| Ra | arithmetic average roughness…[µm] |
| Rz | maximum peak to valley height of the profile…[µm] |
References
- Hashish, M. Modeling study of metal cutting with abrasive waterjets. J. Eng. Mater. Technol. Trans. ASME 1984, 106, 88–100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hashish, M. A Model for Abrasive—Waterjet (AWJ) Machining. J. Eng. Mater. Technol. Trans. ASME 1989, 111, 154–162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zeng, J.; Kim, T.J. Development of an abrasive waterjet kerf cutting model for brittle materials. In Jet Cutting Technology; Lichtarowicz, A., Ed.; Kluwer Academic Publishers: Dordrecht, The Netherlands, 1992; pp. 483–501. [Google Scholar]
- Zeng, J.; Kim, T.J. An erosion model of polycrystalline ceramics in abrasive waterjet cutting. Wear 1996, 193, 207–217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kovacevic, R.; Yong, Z. Modelling of 3D abrasive waterjet machining, part 1—Theoretical basis. In Jetting Technology; Gee, C., Ed.; Mechanical Engineering Publications Ltd.: Bury St Edmunds, UK; London, UK, 1996; pp. 73–82. [Google Scholar]
- Yong, Z.; Kovacevic, R. Modelling of 3D abrasive waterjet machining. Part 2—Simulation of machining. In Jetting Technology; Gee, C., Ed.; Mechanical Engineering Publications Ltd.: Bury St Edmunds, UK; London, UK, 1996; pp. 83–89. [Google Scholar]
- Hlaváč, L.M. JETCUT—Software for prediction of high-energy waterjet efficiency. In Jetting Technology; Louis, H., Ed.; Prof. Eng. Pub. Ltd.: Bury St Edmunds, UK; London, UK, 1998; pp. 25–37. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, F.L.; Wang, J.; Lemma, E.; Siores, E. Striation formation mechanism on the jet cutting surface. J. Mater. Process. Technol. 2003, 141, 213–218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Henning, A.; Westkämper, E. Analysis of the cutting front in abrasive waterjet cutting. In Water Jetting; Longman, P., Ed.; BHR Group: Cranfield, UK; Bedford, UK, 2006; pp. 425–434. [Google Scholar]
- Monno, M.; Pellegrini, G.; Ravasio, C. An experimental investigation of the kerf realised by AWJ: The influence of the pressure fluctuations. In Water Jetting; Longman, P., Ed.; BHR Group: Cranfield, UK; Bedford, UK, 2006; pp. 309–321. [Google Scholar]
- Sutowska, M.; Kapłonek, W.; Pimenov, D.Y.; Gupta, M.K.; Mia, M.; Sharma, S. Influence of variable radius of cutting head trajectory on quality of cutting kerf in the abrasive water jet process for soda–lime glass. Materials 2020, 13, 4277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Filip, A.C.; Mihail, L.A.; Vasiloni, M.A. An experimental study on the dimensional accuracy of holes made by abrasive waterjet machining of Hardox steels. MATEC Web Conf. 2017, 137, 02003. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Filip, A.C.; Vasiloni, M.A.; Mihail, L.A. Experimental research on the machinability of Hardox steel by abrasive waterjet cutting. MATEC Web Conf. 2017, 94, 03003. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Krenický, T. Non-contact study of surfaces created using the AWJ technology. Manuf. Technol. 2015, 15, 61–64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maščenik, J.; Gašpár, Š. Experimental assessment of roughness changes in the cutting surface and microhardness changes of the material S 355 J2 G3 after being cut by non-conventional technologies. Adv. Mater. Res. 2011, 314–316, 1944–1947. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pahuja, R.; Ramulu, M.; Hashish, M. Surface quality and kerf width prediction in abrasive water jet machining of metal-composite stacks. Compos. Part B Eng. 2019, 175, 107134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hlaváč, L.M. Investigation of the abrasive water jet trajectory curvature inside the kerf. J. Mater. Process. Technol. 2009, 209, 4154–4161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deam, R.T.; Lemma, E.; Ahmed, D.H. Modelling of the abrasive water jet cutting process. Wear 2004, 257, 877–891. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Orbanic, H.; Junkar, M. Analysis of striation formation mechanism in abrasive water jet cutting. Wear 2008, 265, 821–830. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rahman, M.A.; Mustafizur, R.; Kumar, A.S. Chip perforation and ‘Burnishing–like’ finishing of Al alloy in precision machining. Precis. Eng. 2017, 50, 393–409. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hlaváč, L.M.; Hlaváčová, I.M.; Arleo, F.; Viganò, F.; Annoni, M.; Geryk, V. Shape distortion reduction method for abrasive water jet (AWJ) cutting. Precis. Eng. 2018, 53, 194–202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hlaváč, L.M.; Štefek, A.; Tyč, M.; Krajcarz, D. Influence of material structure on forces measured during Abrasive Waterjet (AWJ) machining. Materials 2020, 13, 3878. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hlaváč, L.M.; Hlaváčová, I.M.; Plančár, Š.; Krenický, T.; Geryk, V. Deformation of products cut on AWJ x-y tables and its suppression. IOP Conf. Ser. Mater. Sci. Eng. 2018, 307, 012015. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mascenik, J. Experimental determination of cutting speed influence on cutting surface character in material laser cutting. MM Sci. J. 2016, 3, 960–963. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Servátka, M. Modelling, simulation and optimization of the technological parameters in binding on the demanded quality of products in manufacturing technologies with water jet. Ph.D. Thesis, FMT TUKE, Prešov, Slovak, 2009. [Google Scholar]
- Olejárová, Š.; Ružbarský, J.; Krenický, T. Introduction into the issue of water jet machining. In Vibrations in the Production System. SpringerBriefs in Applied Sciences and Technology; Springer: Cham, Swizerland, 2019; pp. 1–10. ISBN 978-3-030-01736-1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hardox 500 Data Sheet, Version 2005-07-04. Available online: www.ssab.com (accessed on 11 July 2012).
- Ma, C.; Deam, R.T. A correlation for predicting the kerf profile from abrasive water jet cutting. Exp. Therm. Fluid Sci. 2006, 30, 337–343. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Štefek, A.; Hlaváč, L.M.; Tyč, M.; Barták, P.; Kozelský, J. Remarks to Abrasive Waterjet (AWJ) Forces Measurements; Advances in Water Jetting. Water Jet 2019. In Lecture Notes in Mechanical Engineering; Klichová, D., Sitek, L., Hloch, S., Valentinčič, J., Eds.; Springer: Cham, Switzerland, 2021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hlaváč, L.M.; Hlaváčová, I.M.; Gembalová, L.; Jonšta, P. Experimental investigation of depth dependent kerf width in abrasive water jet cutting. In Water Jetting; Trieb, F.H., Ed.; BHR Group: Cranfield, UK; Bedford, UK, 2010; pp. 459–467. [Google Scholar]

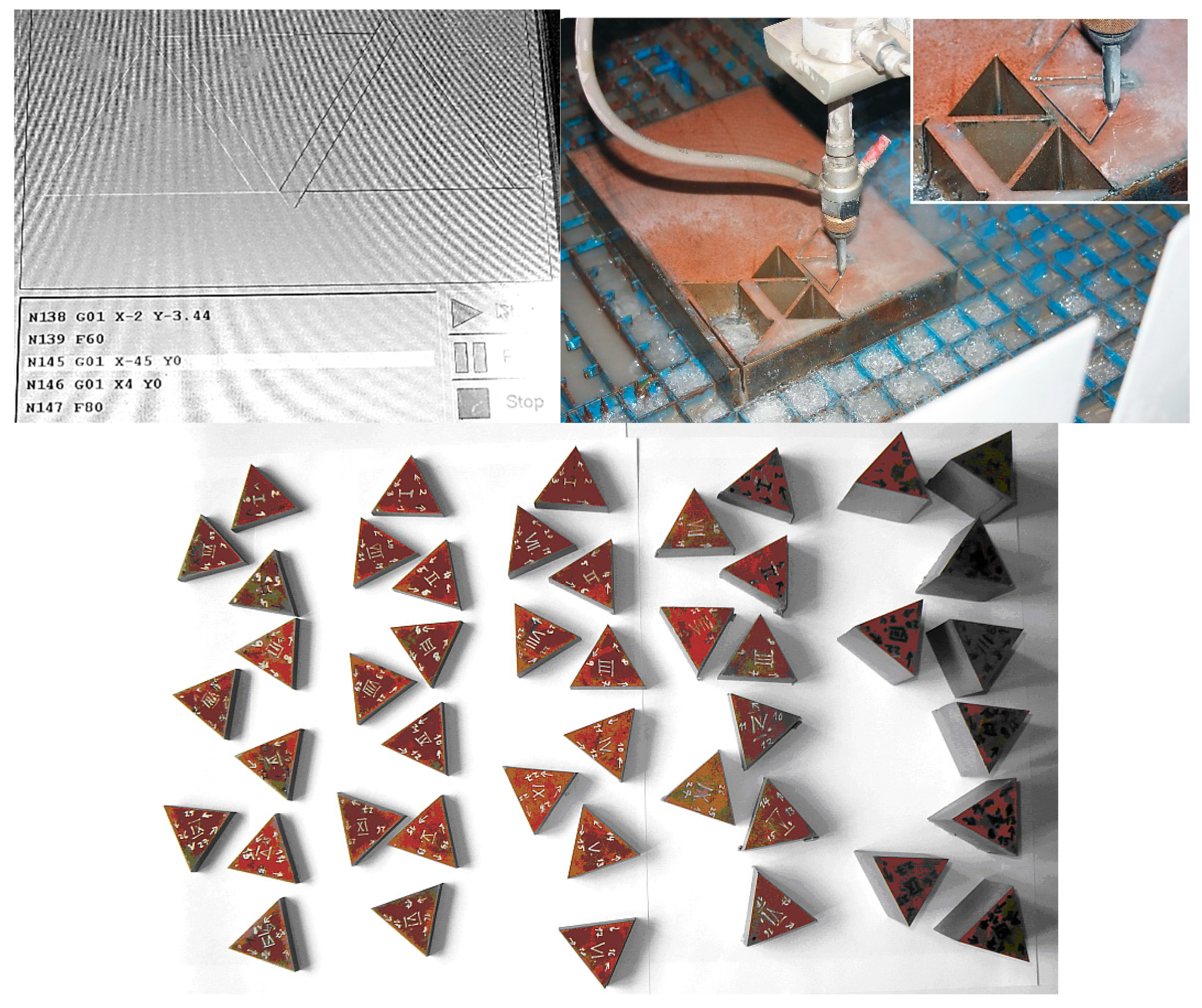

| Plate Thickness mm | C Max % | Si Max % | Mn Max % | P Max % | S Max % | Cr Max % | Ni Max % | Mo Max % | B Max % |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 4-13 | 0.27 | 0.70 | 1.60 | 0.025 | 0.010 | 1.00 | 0.25 | 0.25 | 0.004 |
| (13)-32 | 0.29 | 0.70 | 1.60 | 0.025 | 0.010 | 1.00 | 0.50 | 0.30 | 0.004 |
| (32)-40 | 0.29 | 0.70 | 1.60 | 0.025 | 0.010 | 1.00 | 1.00 | 0.60 | 0.004 |
| Combination of Technological Values Parameters (Cutting No.) | Technological Parameter | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| ma | p | v | v+ | v− | |
| 1 | 170 | 300 | 40 | 60 | 10 |
| 2 | 170 | 300 | 60 | 90 | 15 |
| 3 | 170 | 300 | 80 | 120 | 20 |
| 4 | 170 | 340 | 40 | 60 | 10 |
| 5 | 170 | 340 | 60 | 90 | 15 |
| 6 | 170 | 340 | 80 | 120 | 20 |
| 7 | 170 | 380 | 40 | 60 | 10 |
| 8 | 170 | 380 | 60 | 90 | 15 |
| 9 | 170 | 380 | 80 | 120 | 20 |
| 10 | 220 | 300 | 40 | 60 | 10 |
| 11 | 220 | 300 | 60 | 90 | 15 |
| 12 | 220 | 300 | 80 | 120 | 20 |
| 13 | 220 | 340 | 40 | 60 | 10 |
| 14 | 220 | 340 | 60 | 90 | 15 |
| 15 | 220 | 340 | 80 | 120 | 20 |
| 16 | 220 | 380 | 40 | 60 | 10 |
| 17 | 220 | 380 | 60 | 90 | 15 |
| 18 | 220 | 380 | 80 | 120 | 20 |
| 19 | 270 | 300 | 40 | 60 | 10 |
| 20 | 270 | 300 | 60 | 90 | 15 |
| 21 | 270 | 300 | 80 | 120 | 20 |
| 22 | 270 | 340 | 40 | 60 | 10 |
| 23 | 270 | 340 | 60 | 90 | 15 |
| 24 | 270 | 340 | 80 | 120 | 20 |
| 25 | 270 | 380 | 40 | 60 | 10 |
| 26 | 270 | 380 | 60 | 90 | 15 |
| 27 | 270 | 380 | 80 | 120 | 20 |
| Sample Number | Cut Surface Number | ma g/min | P MPa | v mm/min | 6 mm Ra µm | 6 mm Rz µm | 10 mm Ra µm | 10 mm Rz µm | 15 mm Ra µm | 15 mm Rz µm |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| I | 1 | 170 | 300 | 40 | 3.17 | 21.88 | 4.44 | 23.82 | 4.92 | 26.76 |
| 2 | 170 | 300 | 60 | 3.52 | 22.02 | 4.36 | 24.58 | 6.12 | 32.26 | |
| 3 | 170 | 300 | 80 | 3.69 | 22.11 | 4.98 | 29.25 | 7.93 | 35.97 | |
| II | 4 | 170 | 340 | 40 | 3.06 | 21.73 | 3.87 | 23.41 | 4.62 | 26.32 |
| 5 | 170 | 340 | 60 | 3.42 | 21.90 | 4.44 | 23.66 | 5.96 | 29.49 | |
| 6 | 170 | 340 | 80 | 3.63 | 22.02 | 4.72 | 24.77 | 7.11 | 35.25 | |
| III | 7 | 170 | 380 | 40 | 3.04 | 21.59 | 3.76 | 22.80 | 4.23 | 24.45 |
| 8 | 170 | 380 | 60 | 3.18 | 21.61 | 3.67 | 22.87 | 5.74 | 28.42 | |
| 9 | 170 | 380 | 80 | 3.56 | 21.91 | 4.26 | 23.78 | 6.86 | 34.65 | |
| IV | 10 | 220 | 300 | 40 | 2.98 | 21.45 | 3.68 | 22.50 | 4.18 | 23.14 |
| 11 | 220 | 300 | 60 | 3.05 | 21.50 | 3.58 | 23.12 | 5.36 | 28.21 | |
| 12 | 220 | 300 | 80 | 3.52 | 21.77 | 4.40 | 24.15 | 6.24 | 34.49 | |
| V | 13 | 220 | 340 | 40 | 2.87 | 21.05 | 3.32 | 21.18 | 3.84 | 22.24 |
| 14 | 220 | 340 | 60 | 3.02 | 21.41 | 3.47 | 21.51 | 5.08 | 26.73 | |
| 15 | 220 | 340 | 80 | 3.28 | 21.52 | 3.33 | 22.00 | 6.02 | 33.20 | |
| VI | 16 | 220 | 380 | 40 | 2.73 | 19.39 | 3.07 | 20.00 | 3.22 | 20.48 |
| 17 | 220 | 380 | 60 | 2.99 | 21.12 | 3.33 | 20.70 | 3.78 | 21.30 | |
| 18 | 220 | 380 | 80 | 3.26 | 21.08 | 3.30 | 21.58 | 5.62 | 31.66 | |
| VII | 19 | 270 | 300 | 40 | 2.71 | 18.39 | 3.05 | 19.37 | 3.11 | 19.48 |
| 20 | 270 | 300 | 60 | 2.92 | 21.02 | 3.40 | 20.30 | 3.56 | 20.25 | |
| 21 | 270 | 300 | 80 | 3.20 | 20.90 | 3.28 | 20.82 | 5.49 | 30.80 | |
| VIII | 22 | 270 | 340 | 40 | 2.42 | 17.45 | 2.79 | 18.54 | 2.95 | 19.02 |
| 23 | 270 | 340 | 60 | 2.78 | 19.87 | 3.14 | 19.75 | 3.27 | 19.68 | |
| 24 | 270 | 340 | 80 | 3.08 | 20.22 | 3.25 | 20.01 | 5.40 | 28.00 | |
| IX | 25 | 270 | 380 | 40 | 2.27 | 17.20 | 2.75 | 17.81 | 3.10 | 18.27 |
| 26 | 270 | 380 | 60 | 2.44 | 19.11 | 2.89 | 19.05 | 3.08 | 19.33 | |
| 27 | 270 | 380 | 80 | 2.80 | 19.35 | 3.22 | 19.62 | 3.76 | 24.01 |
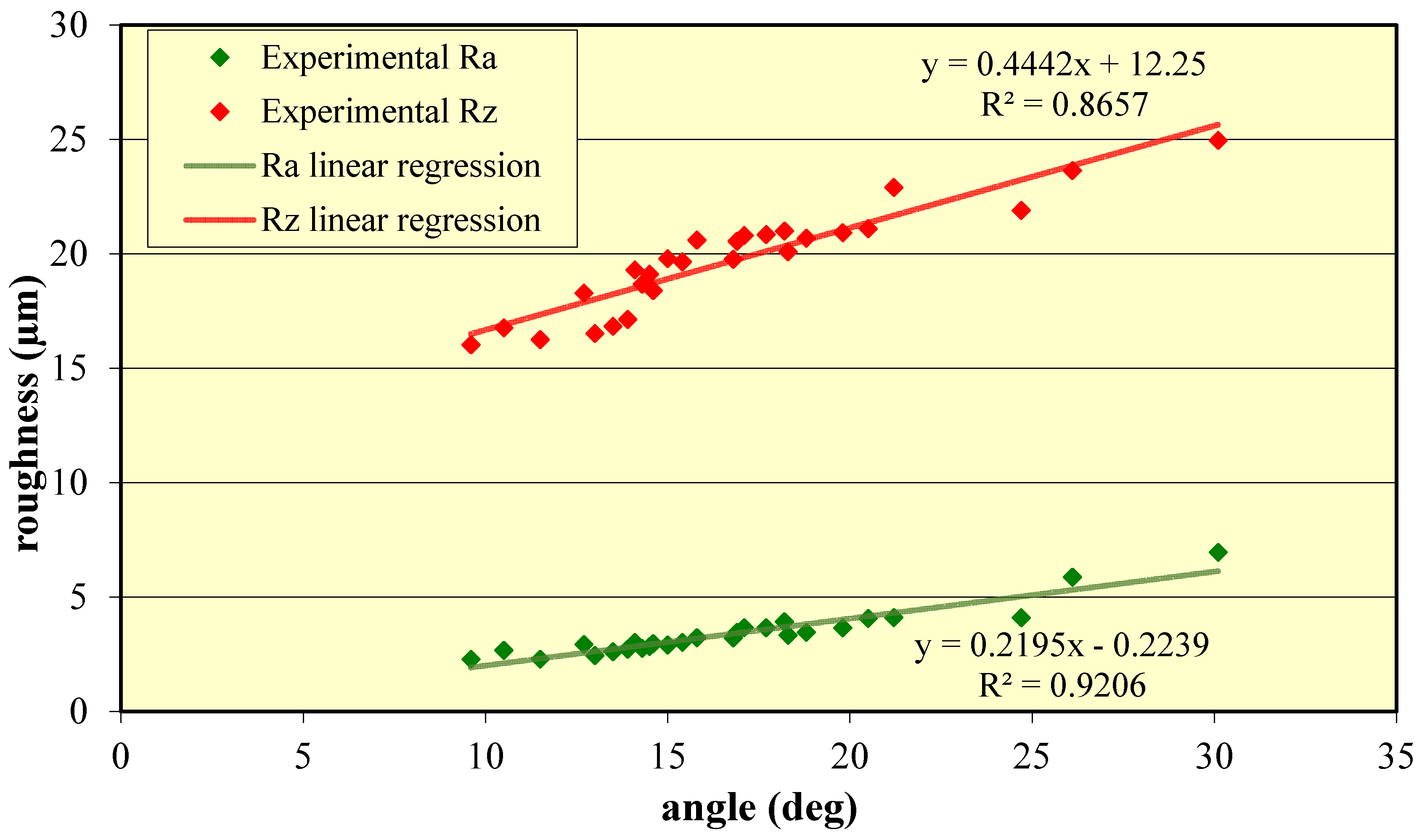
| Sample Number | Surface Number | ma g/min | p MPa | v mm/min | θ deg | Ra µm | Rz µm |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| I | 1 | 170 | 300 | 10 | 17.7 | 3.65 | 20.84 |
| 2 | 170 | 300 | 15 | 24.7 | 4.09 | 21.90 | |
| 3 | 170 | 300 | 20 | 30.1 | 6.95 | 24.96 | |
| II | 4 | 170 | 340 | 10 | 15.0 | 2.90 | 19.79 |
| 5 | 170 | 340 | 15 | 18.2 | 3.92 | 21.00 | |
| 6 | 170 | 340 | 20 | 26.1 | 5.87 | 23.64 | |
| III | 7 | 170 | 380 | 10 | 14.5 | 2.83 | 19.11 |
| 8 | 170 | 380 | 15 | 17.1 | 3.66 | 20.81 | |
| 9 | 170 | 380 | 20 | 21.2 | 4.10 | 22.90 | |
| IV | 10 | 220 | 300 | 10 | 14.3 | 2.75 | 18.67 |
| 11 | 220 | 300 | 15 | 16.9 | 3.46 | 20.56 | |
| 12 | 220 | 300 | 20 | 20.5 | 4.07 | 21.10 | |
| V | 13 | 220 | 340 | 10 | 13.9 | 2.71 | 17.14 |
| 14 | 220 | 340 | 15 | 15.8 | 3.22 | 20.60 | |
| 15 | 220 | 340 | 20 | 19.8 | 3.65 | 20.93 | |
| VI | 16 | 220 | 380 | 10 | 13.5 | 2.60 | 16.83 |
| 17 | 220 | 380 | 15 | 15.4 | 3.02 | 19.66 | |
| 18 | 220 | 380 | 20 | 18.8 | 3.46 | 20.69 | |
| VII | 19 | 270 | 300 | 10 | 13.0 | 2.44 | 16.52 |
| 20 | 270 | 300 | 15 | 14.1 | 3.01 | 19.30 | |
| 21 | 270 | 300 | 20 | 18.3 | 3.33 | 20.10 | |
| VIII | 22 | 270 | 340 | 10 | 11.5 | 2.28 | 16.25 |
| 23 | 270 | 340 | 15 | 12.7 | 2.93 | 18.29 | |
| 24 | 270 | 340 | 20 | 16.8 | 3.21 | 19.77 | |
| IX | 25 | 270 | 380 | 10 | 9.6 | 2.27 | 16.02 |
| 26 | 270 | 380 | 15 | 10.5 | 2.67 | 16.77 | |
| 27 | 270 | 380 | 20 | 14.6 | 2.96 | 18.40 |
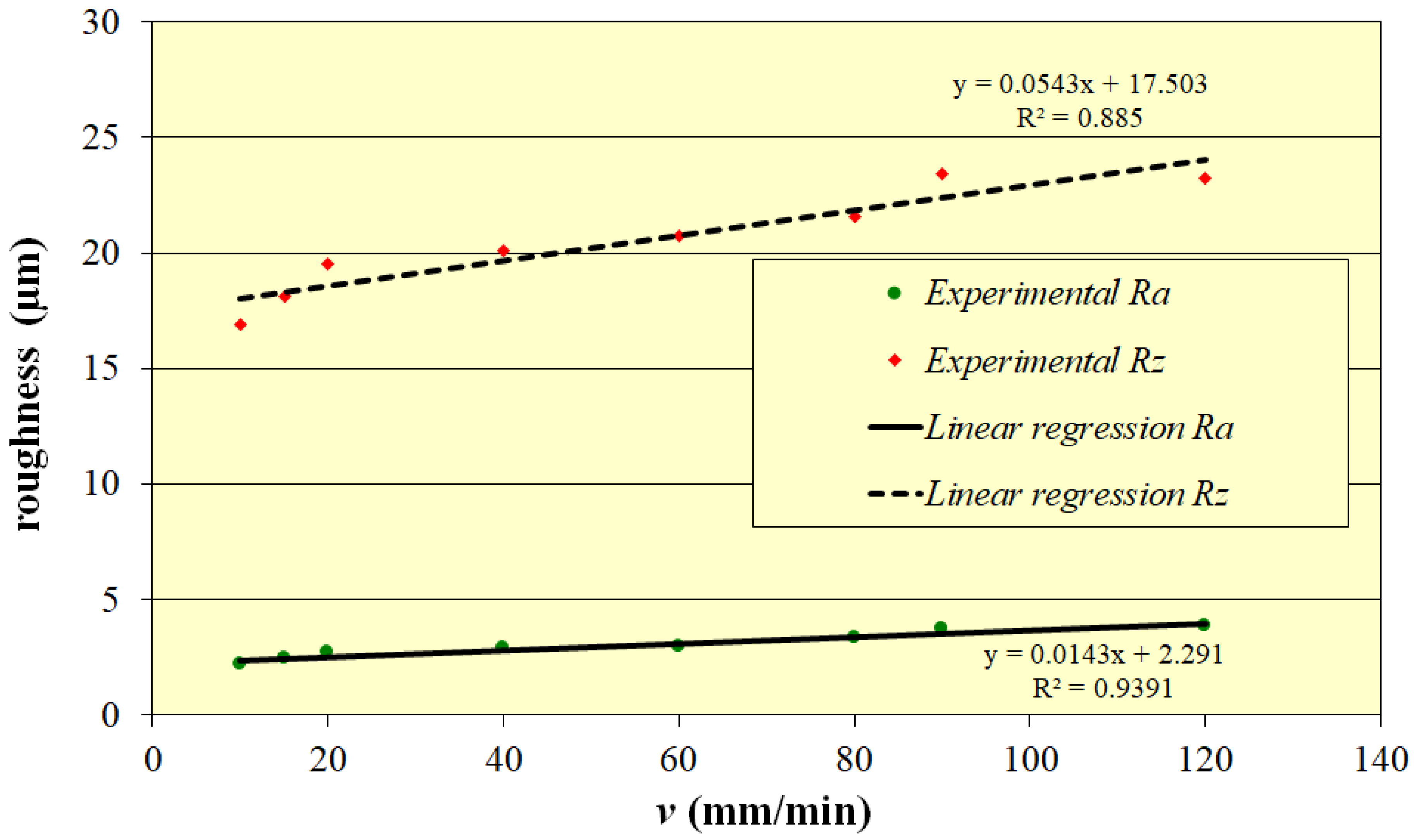
| v mm/min | ma g/min | p MPa | Ra4 µm | Rz4 µm |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 10 | 220 | 380 | 2.16 | 16.90 |
| 15 | 220 | 380 | 2.44 | 18.09 |
| 20 | 220 | 380 | 2.71 | 19.53 |
| 40 | 220 | 380 | 2.89 | 20.11 |
| 60 | 220 | 380 | 2.98 | 20.75 |
| 80 | 220 | 380 | 3.32 | 21.58 |
| 90 | 220 | 380 | 3.70 | 23.45 |
| 120 | 220 | 380 | 3.85 | 23.22 |
| Technological Parameters | Quality Parameters | Deviation of Calculated Value Regarding the Experimental Value | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Abrasive Mass Flow Rate | Pump Pressure | Traverse Speed | Values Calculated from Model | Measured Experimental Values | ||||
| ma (x1) g/min | p (x2) MPa | v (x3) mm/min | Ra (y) µm | Rz (y) µm | Ra µm | Rz µm | for Ra % | for Rz % |
| 160 | 270 | 35 | 4.48 | 25.58 | 4.70 | 26.91 | −4.7 | −4.9 |
| 180 | 285 | 38 | 4.17 | 24.34 | 4.41 | 25.22 | −5.4 | −3.5 |
| 190 | 310 | 45 | 3.95 | 23.49 | 3.84 | 24.04 | 2.9 | −2.3 |
| 190 | 310 | 45 | 3.82 | 22.99 | 3.95 | 22.90 | −3.3 | 0.3 |
| 200 | 320 | 50 | 3.70 | 22.53 | 3.90 | 22.85 | −5.1 | −1.4 |
| 210 | 330 | 57 | 3.41 | 21.37 | 3.48 | 22.27 | −2.0 | −4.0 |
| 230 | 350 | 65 | 3.13 | 20.26 | 3.11 | 20.95 | 0.6 | −3.3 |
| 250 | 360 | 68 | 3.04 | 19.92 | 2.88 | 20.08 | 5.6 | −0.8 |
| 260 | 370 | 77 | 2.75 | 18.76 | 2.81 | 19.55 | −2.1 | −4.0 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Krenicky, T.; Servatka, M.; Gaspar, S.; Mascenik, J. Abrasive Water Jet Cutting of Hardox Steels—Quality Investigation. Processes 2020, 8, 1652. https://doi.org/10.3390/pr8121652
Krenicky T, Servatka M, Gaspar S, Mascenik J. Abrasive Water Jet Cutting of Hardox Steels—Quality Investigation. Processes. 2020; 8(12):1652. https://doi.org/10.3390/pr8121652
Chicago/Turabian StyleKrenicky, Tibor, Milos Servatka, Stefan Gaspar, and Jozef Mascenik. 2020. "Abrasive Water Jet Cutting of Hardox Steels—Quality Investigation" Processes 8, no. 12: 1652. https://doi.org/10.3390/pr8121652
APA StyleKrenicky, T., Servatka, M., Gaspar, S., & Mascenik, J. (2020). Abrasive Water Jet Cutting of Hardox Steels—Quality Investigation. Processes, 8(12), 1652. https://doi.org/10.3390/pr8121652







