Insulin Release from NPH Insulin-Loaded Pluronic® F127 Hydrogel in the Presence of Simulated Tissue Enzyme Activity
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials
2.2. Methods
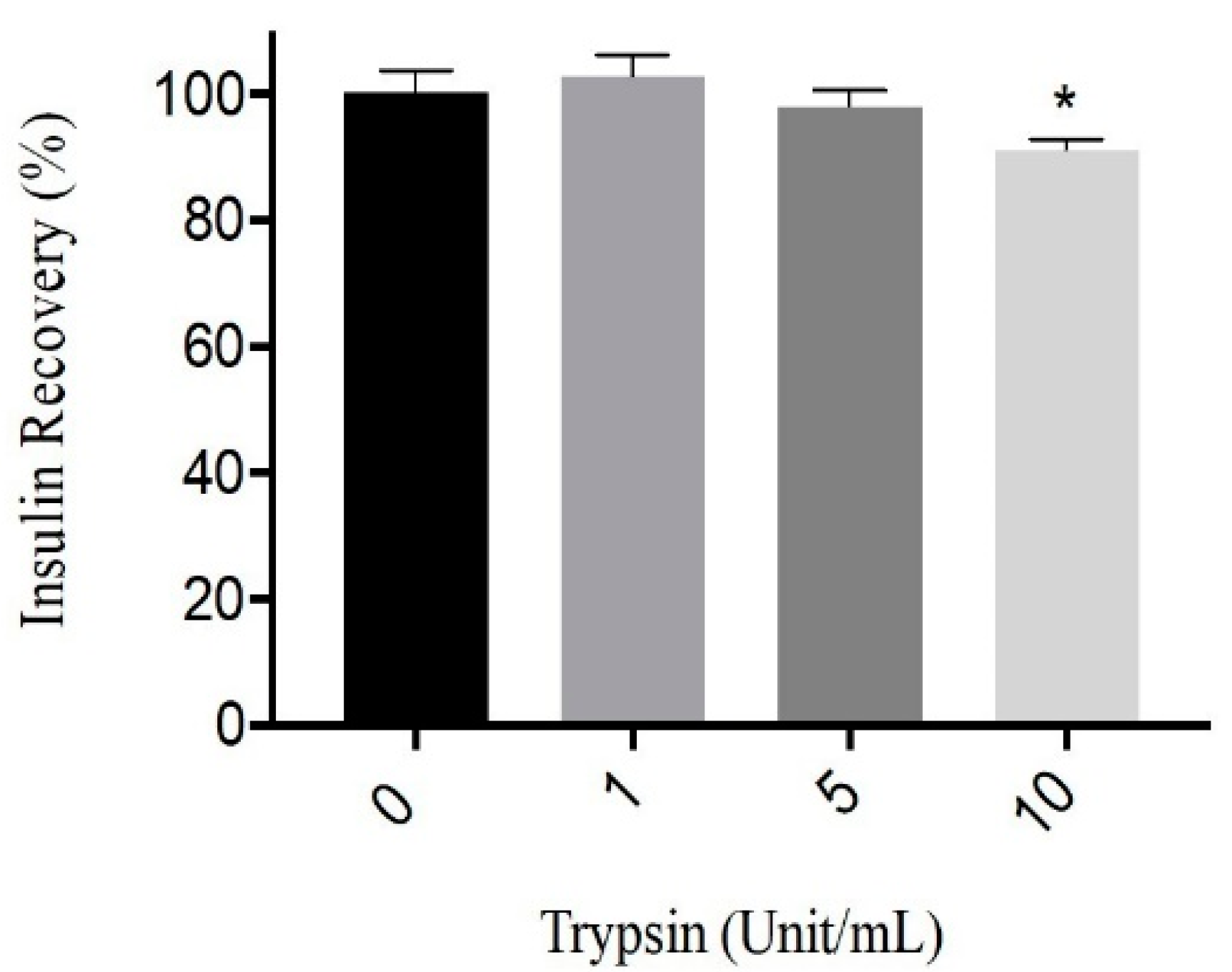
2.2.1. Trypsin Activity on Human Insulin
2.2.2. Preparation of PF 127 Microcrystals Formulations
2.2.3. Gelation Temperature of NPH-PF 127
2.2.4. FTIR Spectroscopy
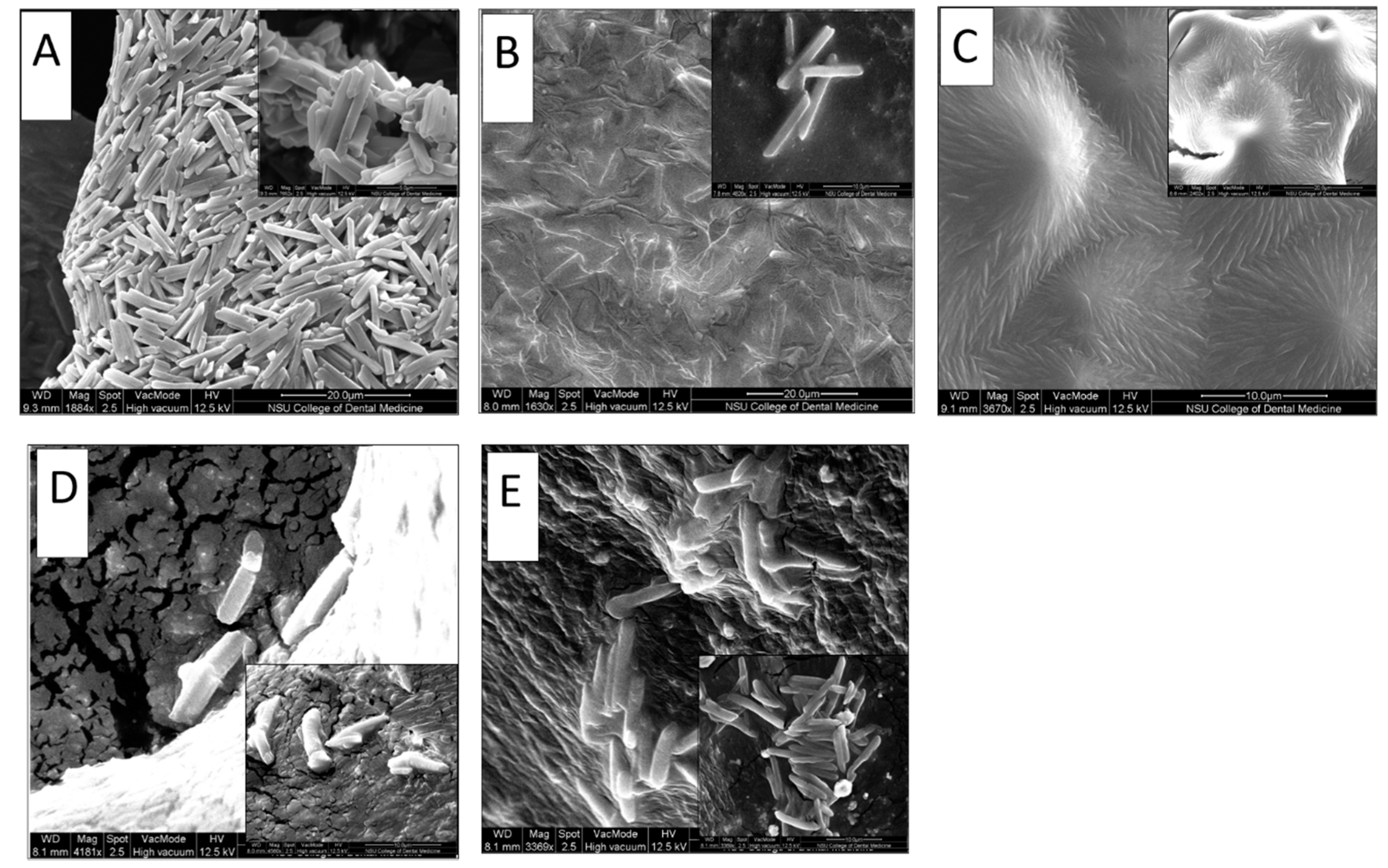
2.2.5. Scanning Electron Microscopy (SEM) of NPH-Microcrystals Loaded in PF127 Hydrogel
Gel Erosion and Insulin Release In Vitro
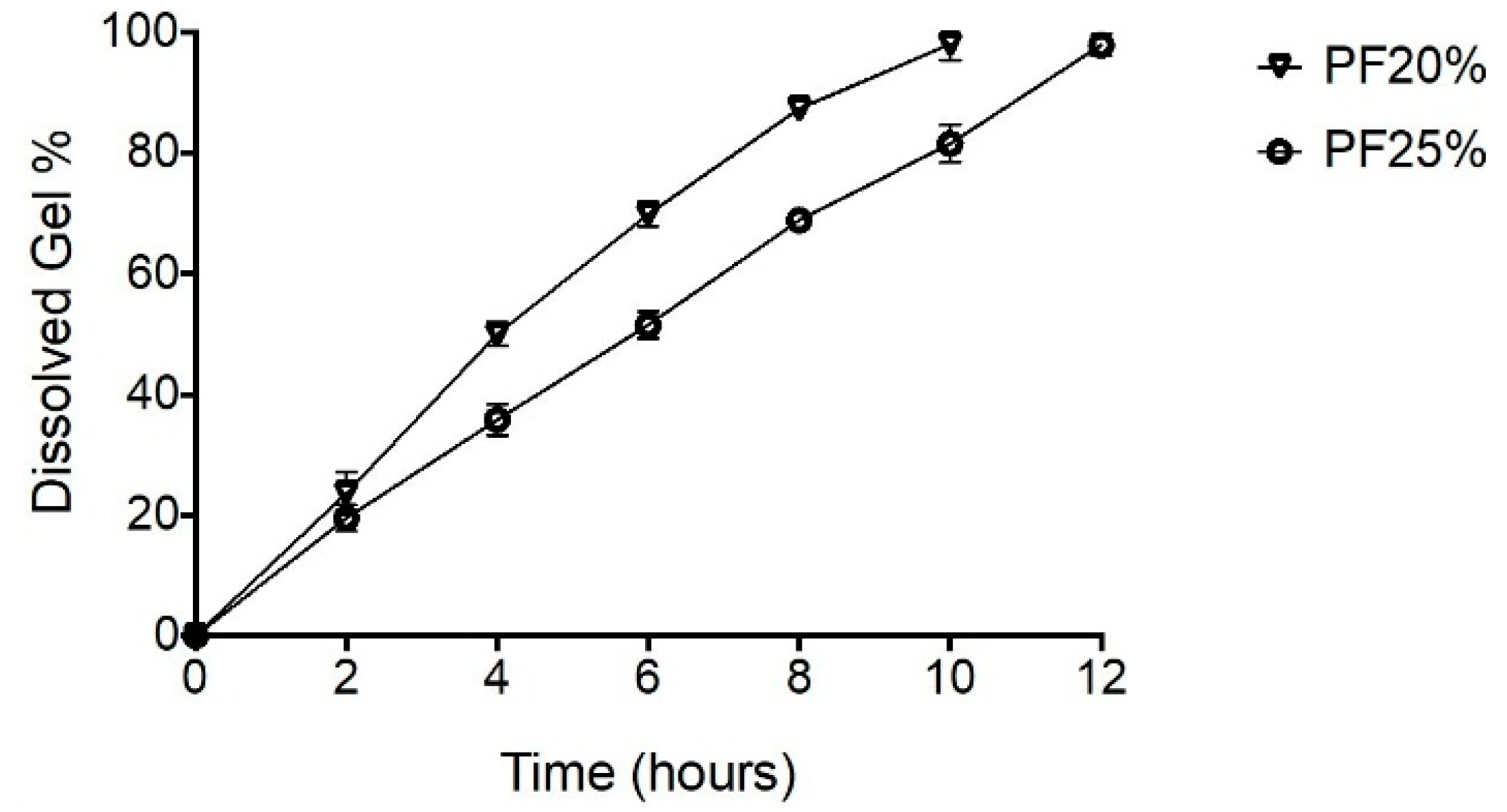
2.2.6. Erosion Profiles for NPH-PF127 Microcrystals Hydrogel
2.2.7. In Vitro Release of Insulin
2.2.8. Effect of PF 127 Concentration on the Insulin Release from NPH-PF127
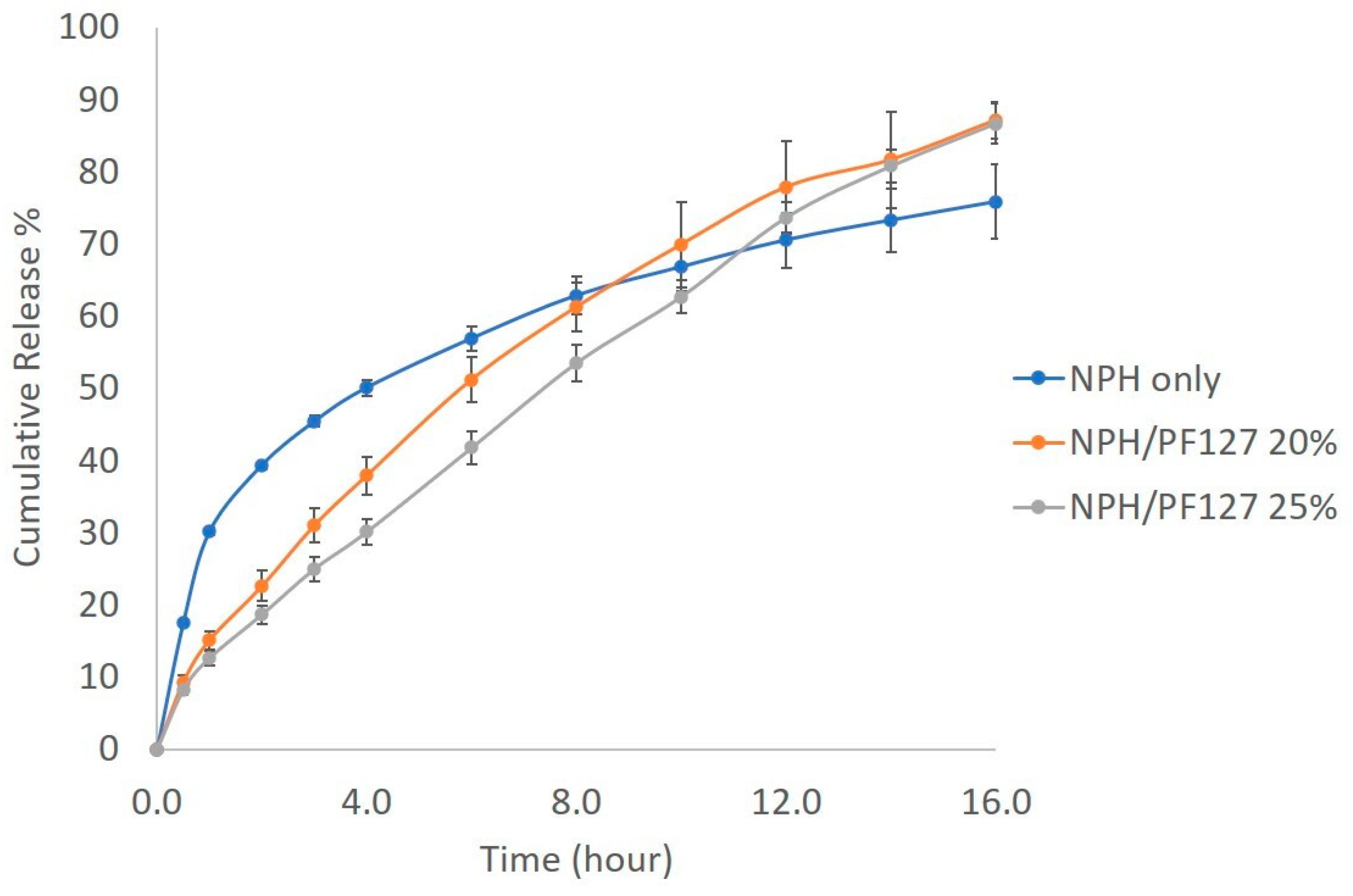
2.2.9. Effect of Enzyme Concentration on Insulin Release from Both NPH and NPH-PF127
2.2.10. Effect of Short-Term Storage on Insulin Release from NPH-PF127
Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Trypsin Activity on Human Insulin
3.2. Gelation Temperatures of NPH-PF 127
3.3. FTIR Spectroscopy
3.4. Microcrystals Morphological Characterization
3.5. Gel Erosion and Drug Release In Vitro
3.5.1. Erosion Profiles for NPH-PF127 Microcrystal Hydrogel
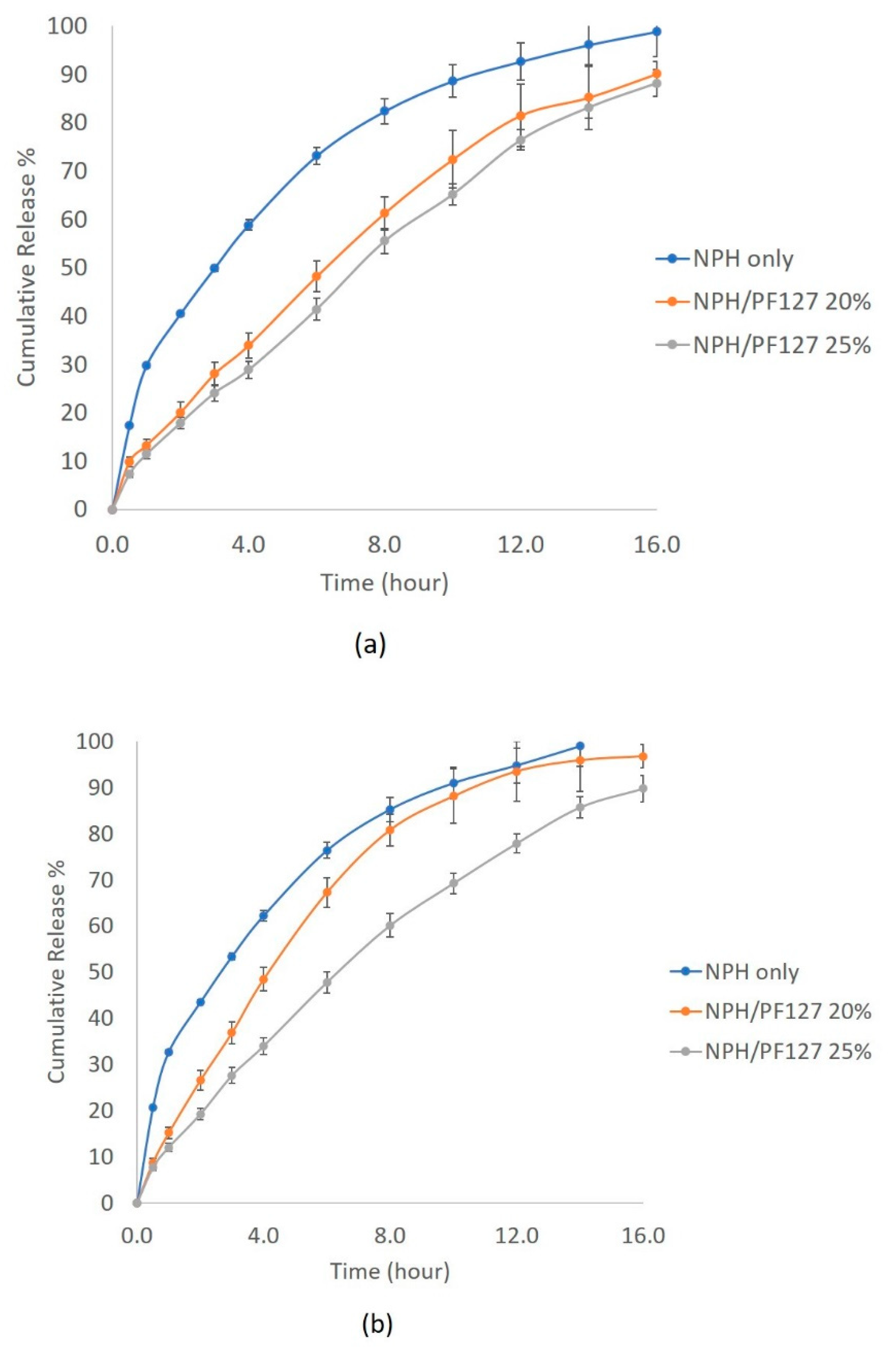
3.5.2. In Vitro Release of NPH Insulin from PF127
3.6. Effect of Storage on Insulin Release from NPH-PF127
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Niswender, K.D. Basal insulin: Physiology, pharmacology, and clinical implications. Postgrad Med. 2011, 123, 17–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Petznick, A. Insulin management of type 2 diabetes mellitus. Am. Fam. Physician 2011, 4, 183–190. [Google Scholar]
- Horvath, K.; Jeitler, K.; Berghold, A.; Ebrahim, S.H.; Gratzer, T.W.; Plank, J.; Siebenhofer, A. Long-acting insulin analogues versus NPH insulin (human isophane insulin) for type 2 diabetes mellitus. Cochrane Database Syst. Rev. 2007, CD005613. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Laubner, K.; Molz, K.; Kerner, W.; Karges, W.; Lang, W.; Dapp, A.; Holl, R.W. Daily insulin doses and injection frequencies of neutral protamine hagedorn (NPH) insulin, insulin detemir and insulin glargine in type 1 and type 2 diabetes: A multicenter analysis of 51 964 patients from the German/Austrian DPV-wiss database. Diabetes Metab. Res. Rev. 2014, 30, 395–404. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Simkin, R.D.; Cole, S.A.; Ozawa, H.; Magdoff-Fairchild, B.; Eggena, P.; Rudko, A.; Low, B.W. Precipitation and crystallization of insulin in the presence of lysozyme and salmine. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 1970, 200, 385–394. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lepore, M.; Pampanelli, S.; Fanelli, C.; Porcellati, F.; Bartocci, L.; Di Vincenzo, A.; Bolli, G.B. Pharmacokinetics and pharmacodynamics of subcutaneous injection of long-acting human insulin analog glargine, NPH insulin, and ultralente human insulin and continuous subcutaneous infusion of insulin lispro. Diabetes 2000, 49, 2142–2148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hilgenfeld, R.; Seipke, G.; Berchtold, H.; Owens, D.R. The evolution of insulin glargine and its continuing contribution to diabetes care. Drugs 2014, 74, 911–927. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, J.W.; Azoulay, L.; Majdan, A.; Boivin, J.F.; Pollak, M.; Suissa, S. Long-Term Use of Long-Acting Insulin Analogs and Breast Cancer Incidence in Women with Type 2 Diabetes. J. Clin. Oncol. 2017, 35, 3647–3653. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prentice, J.C.; Conlin, P.R.; Gellad, W.F.; Edelman, D.; Lee, T.A.; Pizer, S.D. Long-term outcomes of analogue insulin compared with NPH for patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus. Am. J. Manag. Care 2015, 21, e235–e243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Redwan, E.M.; Linjawi, M.H.; Uversky, V.N. Looking at the carcinogenicity of human insulin analogues via the intrinsic disorder prism. Sci. Rep. 2016, 6, 23320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brader, M.L.; Sukumar, M.; Pekar, A.H.; McClellan, D.S.; Chance, R.E.; Flora, D.B.; Myers, S.R. Hybrid insulin cocrystals for controlled release delivery. Nat. Biotechnol. 2002, 20, 800–804. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Norrman, M.; Hubalek, F.; Schluckebier, G. Structural characterization of insulin NPH formulations. Eur. J. Pharm. Sci. 2007, 30, 414–423. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- DeFelippis, M.R.; Bakaysa, D.L.; Bell, M.A.; Heady, M.A.; Li, S.; Pye, S.; Frank, B.H. Preparation and characterization of a cocrystalline suspension of [LysB28,ProB29]-human insulin analogue. J. Pharm. Sci. 1998, 87, 170–176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Uy, J.; Fogelfeld, L.; Guerra, Y. Cumulative clinical experience with use of insulin lispro: Critical appraisal, role in therapy, and patient considerations. Diabetes Metab. Syndr. Obes. 2012, 5, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chou, H.S.; Larsson, M.; Hsiao, M.H.; Chen, Y.C.; Roding, M.; Nyden, M.; Liu, D.M. Injectable insulin-lysozyme-loaded nanogels with enzymatically-controlled degradation and release for basal insulin treatment: In vitro characterization and in vivo observation. J. Control Release 2016, 224, 33–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fonte, P.; Araujo, F.; Reis, S.; Sarmento, B. Oral insulin delivery: How far are we? J. Diabetes Sci. Technol. 2013, 7, 520–531. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, X.; Wang, W. Challenges and recent advances in the subcutaneous delivery of insulin. Expert Opin. Drug Deliv. 2016, 14, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Henkin, R.I. Inhaled insulin-intrapulmonary, intranasal, and other routes of administration: Mechanisms of action. Nutrition 2010, 26, 33–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mitragotri, S.; Burke, P.A.; Langer, R. Overcoming the challenges in administering biopharmaceuticals: Formulation and delivery strategies. Nat. Rev. Drug Discov. 2014, 13, 655–672. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Richter, W.F.; Bhansali, S.G.; Morris, M.E. Mechanistic determinants of biotherapeutics absorption following SC administration. AAPS J. 2012, 14, 559–570. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Richter, W.F.; Jacobsen, B. Subcutaneous absorption of biotherapeutics: Knowns and unknowns. Drug Metab. Dispos. 2014, 42, 1881–1889. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Komada, F.; Okumura, K.; Hori, R. Fate of porcine and human insulin at the subcutaneous injection site. II. In vitro degradation of insulins in the subcutaneous tissue of the rat. J. Pharmacobiodyn. 1985, 8, 33–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed][Green Version]
- Okumura, K.; Komada, F.; Hori, R. Fate of porcine and human insulin at the subcutaneous injection site. I. Degradation and absorption of insulins in the rat. J. Pharmacobiodyn. 1985, 8, 25–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Takeyama, M.; Ishida, T.; Kokubu, N.; Komada, F.; Iwakawa, S.; Okumura, K.; Hori, R. Enhanced bioavailability of subcutaneously injected insulin by pretreatment with ointment containing protease inhibitors. Pharm. Res. 1991, 8, 60–64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Soeborg, T.; Rasmussen, C.H.; Mosekilde, E.; Colding-Jorgensen, M. Absorption kinetics of insulin after subcutaneous administration. Eur. J. Pharm. Sci. 2009, 36, 78–90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, Y.; Ding, J.; Qin, W. Potentiometric determination of trypsin using a polymeric membrane polycation-sensitive electrode based on current-controlled reagent delivery. Bioelectrochemistry 2012, 88, 144–147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mort, J.S.; Buttle, D.J. Cathepsin B. Int. J. Biochem. Cell Biol. 1997, 29, 715–720. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vernigora, A.N.; Gengin, M.T. Basic (cleaving arginine and lysine residues) metallocarboxypeptidase of mammalian tissue: Structure, properties, and function. Ukr. Biokhim. Zhurnal 1998, 70, 16–24. [Google Scholar]
- Weiss, M.; Blass, J.; Detruit, H.; Aime, L.; Baudet, B.; Fiancette, J.Y.; Verriest, C. Determination of “in vitro” degradation of protamine in plasma by three different methods. Thromb. Res. 1986, 41, 593–604. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schilling, R.J.; Mitra, A.K. Degradation of insulin by trypsin and alpha-chymotrypsin. Pharm. Res. 1991, 8, 721–727. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Manno, M.; Craparo, E.F.; Podesta, A.; Bulone, D.; Carrotta, R.; Martorana, V.; San Biagio, P.L. Kinetics of different processes in human insulin amyloid formation. J. Mol. Biol. 2007, 366, 258–274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, Y.; Lu, W.L.; Wang, J.C.; Zhang, X.; Zhang, H.; Wang, X.Q.; Zhou, T.Y.; Zhang, Q. Controlled delivery of recombinant hirudin based on thermo-sensitive Pluronic F127 hydrogel for subcutaneous administration: In vitro and in vivo characterization. J. Control. Release 2007, 117, 387–395. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shi, K.; Wang, Y.L.; Qu, Y.; Liao, J.F.; Chu, B.Y.; Zhang, H.P.; Qian, Z.Y. Synthesis, characterization, and application of reversible PDLLA-PEG-PDLLA copolymer thermogels in vitro and in vivo. Sci. Rep. 2016, 6, 19077. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Krebs, M.R.; Macphee, C.E.; Miller, A.F.; Dunlop, I.E.; Dobson, C.M.; Donald, A.M. The formation of spherulites by amyloid fibrils of bovine insulin. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2004, 101, 14420–14424. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Butler, J.A.; Dodds, E.C.; Phillips, D.M.; Stephen, J.M. The action of chymotrypsin and trypsin on insulin. Biochem. J. 1948, 42, 116–122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Akash, M.S.; Rehman, K.; Li, N.; Gpao, J.Q.; Sun, H.; Chen, S. Sustained delivery of IL-1Ra from pluronic F127-based thermosensitive gel prolongs its therapeutic potentials. Pharm. Res. 2012, 29, 3475–3485. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nie, S.; Hsiao, W.L.; Pan, W.; Yang, Z. Thermoreversible Pluronic F127-based hydrogel containing liposomes for the controlled delivery of paclitaxel: In vitro drug release, cell cytotoxicity, and uptake studies. Int. J. Nanomed. 2011, 6, 151–166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alexandridis, P.; Hatton, T.A. Poly (ethylene oxide)-poly (propylene oxide)-poly (ethylene oxide) block copolymer surfactants in aqueous solutions and at interfaces: Thermodynamics, structure, dynamics, and modeling. Colloids Surf. A Physicochem. Eng. Asp. 1995, 96, 1–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Balschmidt, P.; Hansen, F.B.; Dodson, E.J.; Dodson, G.G.; Korber, F. Structure of porcine insulin cocrystallized with clupeine Z. Acta Cryst. B 1991, 47, 975–986. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brange, J. Galenics of Insulin; Springer: Berlin, Germany, 1987; pp. 18–100. [Google Scholar]
- Pisal, D.S.; Kosloski, M.P.; Balu-Iyer, S.V. Delivery of therapeutic proteins. J. Pharm. Sci. 2010, 99, 2557–2575. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jeong, B.; Bae, Y.H.; Lee, D.S.; Kim, S.W. Biodegradable block copolymers as injectable drug-delivery systems. Nature 1997, 388, 860–862. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, Y.J.; Choi, S.; Koh, J.J.; Lee, M.; Ko, K.S.; Kim, S.W. Controlled release of insulin from injectable biodegradable triblock copolymer. Pharm. Res. 2001, 18, 548–550. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kwon, Y.M.; Kim, S.W. Biodegradable triblock copolymer microspheres based on thermosensitive sol-gel transition. Pharm. Res. 2004, 21, 339–343. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gong, C.; Qi, T.; Wei, X.; Qu, Y.; Wu, Q.; Luo, F.; Qian, Z. Thermosensitive polymeric hydrogels as drug delivery systems. Curr. Med. Chem. 2013, 20, 79–94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barichello, J.M.; Morishita, M.; Takayama, K.; Nagai, T. Absorption of insulin from pluronic F-127 gels following subcutaneous administration in rats. Int. J. Pharm. 1999, 184, 189–198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, X.; Wong, B.C.K.; Chen, H.; Zhang, S.; Bian, Z.; Zhang, G.; Lin, C.; Riaz, M.K.; Tyagi, D.; Lu, A.; et al. Long-lasting Insulin Treatment Via a Single Subcutaneous Administration of Liposomes in Thermoreversible Pluronic® F127 Based Hydrogel. Curr. Pharm. Des. 2018, 23, 6079–6085. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Das, N.; Madan, P.; Lin, S. Development and in vitro evaluation of insulin-loaded buccal Pluronic F-127 gels. Pharm. Dev. Technol. 2010, 15, 192–208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Das, N.; Madan, P.; Lin, S. Statistical optimization of insulin-loaded Pluronic F-127 gels for buccal delivery of basal insulin. Pharm. Dev. Technol. 2012, 17, 363–374. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nasir, F.; Iqbal, Z.; Khan, A.; Khan, J.A.; Khan, A.; Khuda, F.; Zakir, S.; Yousaf, N.; Khan, I.; Shah, Y.; et al. Development and evaluation of pluronic- and methylcellulose-based thermoreversible drug delivery system for insulin. Drug Dev. Ind. Pharm. 2014, 40, 1503–1508. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morishita, M.; Barichello, J.M.; Takayama, K.; Chiba, Y.; Tokiwa, S.; Nagai, T. Pluronic F-127 gels incorporating highly purified unsaturated fatty acids for buccal delivery of insulin. Int. J. Pharm. 2001, 212, 289–293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Chu, M.K.; Lu, B.; Mirzaie, S.; Chen, K.; Gordijo, C.R. Enhancing thermal stability of a highly concentrated insulin formulation with Pluronic F-127 for long-term use in microfabricated implantable devices. Drug Deliv. Transl. Res. 2017, 7, 529–543. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Karolewicz, B.; Górniak, A.; Owczarek, A.; Żurawska-Płaksej, E.; Piwowar, A.; Pluta, J. Thermal, spectroscopic, and dissolution studies of ketoconazole–Pluronic F127 system. J. Therm. Anal. Calorim. 2014, 115, 2487–2493. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chandler, C.; Gryniewicz, C.M.; Pringle, T.; Cunningham, F. Insulin temperature and stability under simulated transit conditions. Am. J. Health Syst. Pharm. 2008, 65, 953–963. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Röder, P.V.; Wu, B.; Liu, Y.; Han, W. Pancreatic regulation of glucose homeostasis. Exp. Mol. Med. 2016, 48, e219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]




| Component | Composition | ||
|---|---|---|---|
| A | B | C | |
| NPH suspension (% w/w) | 85 | 80 | 75 |
| PF127 (% w/w) | 15 | 20 | 25 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Sultan, M.H.; Mahdi, W.A.; Kwon, Y.M. Insulin Release from NPH Insulin-Loaded Pluronic® F127 Hydrogel in the Presence of Simulated Tissue Enzyme Activity. Processes 2020, 8, 1320. https://doi.org/10.3390/pr8101320
Sultan MH, Mahdi WA, Kwon YM. Insulin Release from NPH Insulin-Loaded Pluronic® F127 Hydrogel in the Presence of Simulated Tissue Enzyme Activity. Processes. 2020; 8(10):1320. https://doi.org/10.3390/pr8101320
Chicago/Turabian StyleSultan, Muhammad H., Wael A. Mahdi, and Young M. Kwon. 2020. "Insulin Release from NPH Insulin-Loaded Pluronic® F127 Hydrogel in the Presence of Simulated Tissue Enzyme Activity" Processes 8, no. 10: 1320. https://doi.org/10.3390/pr8101320
APA StyleSultan, M. H., Mahdi, W. A., & Kwon, Y. M. (2020). Insulin Release from NPH Insulin-Loaded Pluronic® F127 Hydrogel in the Presence of Simulated Tissue Enzyme Activity. Processes, 8(10), 1320. https://doi.org/10.3390/pr8101320




