The Effects of Lung-Moistening Herbal Medicines on Bleomycin-Induced Pulmonary Fibrosis Mouse Model
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Sample Preparation
2.2. PF Mouse Model Induction and Sample Administration
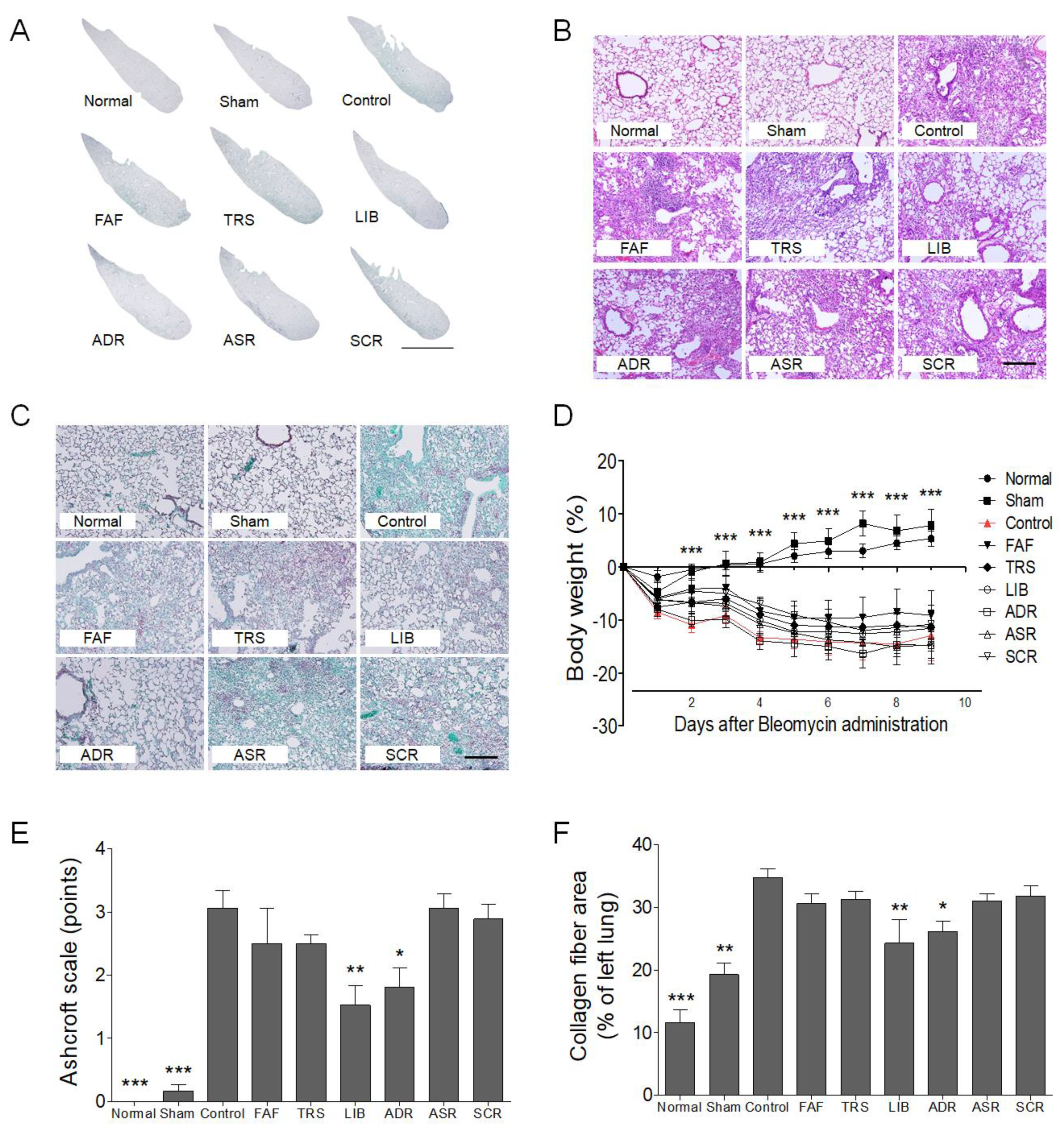
2.3. Histological Analysis
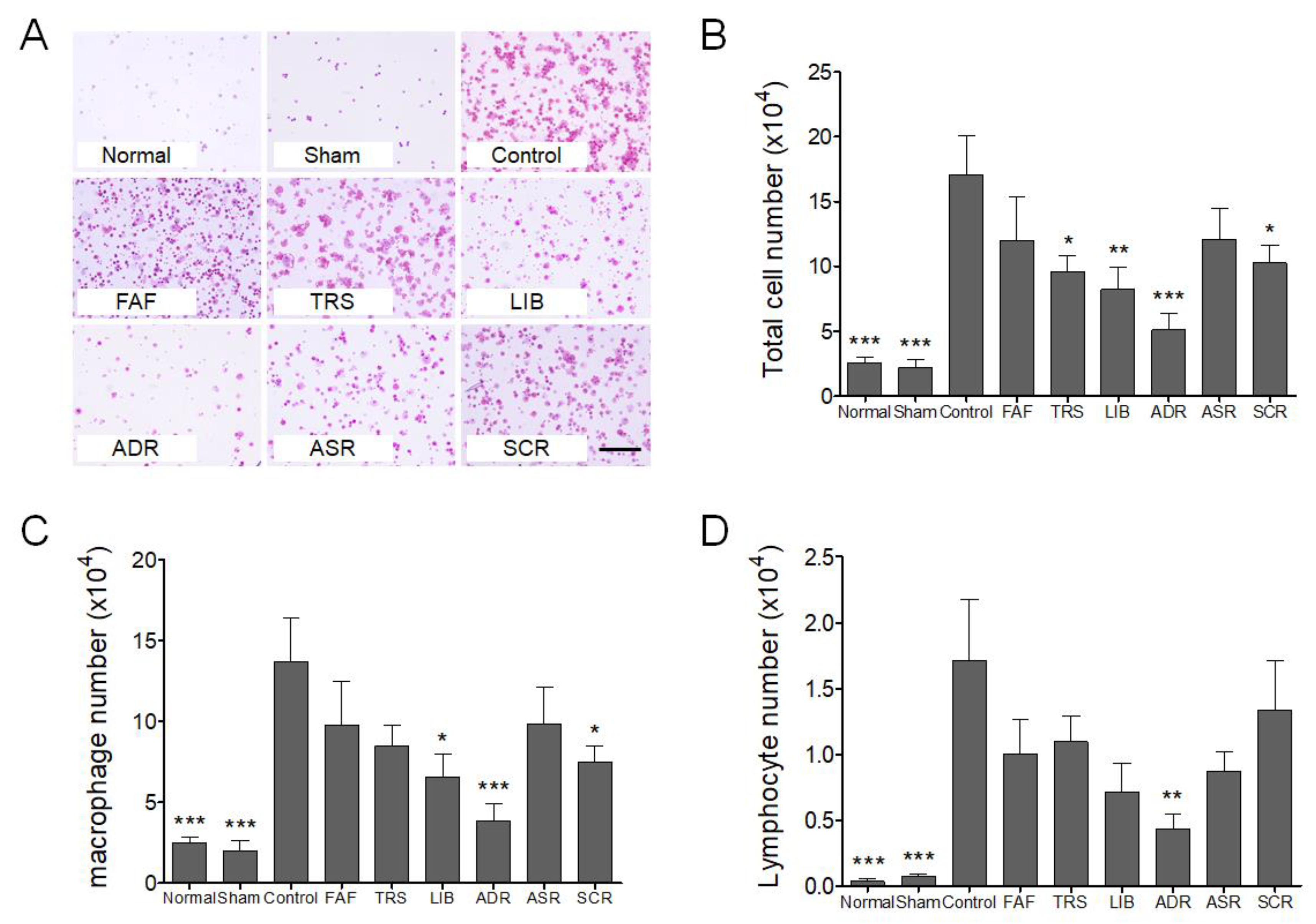
2.4. Broncho Alveolar Lavage Fluid (BALF) Isolation and Immune Cell Count
2.5. Statistical Analysis
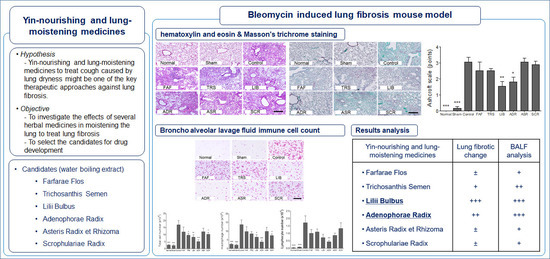
3. Results and Discussion
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Richeldi, L.; Collard, H.R.; Jones, M.G. Idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis. Lancet 2017, 389, 1941–1952. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raghu, G.; Remy-Jardin, M.; Myers, J.L.; Richeldi, L.; Ryerson, C.J.; Lederer, D.J.; Behr, J.; Cottin, V.; Danoff, S.K.; Morell, F.; et al. Diagnosis of Idiopathic Pulmonary Fibrosis. An Official ATS/ERS/JRS/ALAT Clinical Practice Guideline. Am. J. Respir. Crit. Care Med. 2018, 198, e44–e68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kato, E.; Takayanagi, N.; Takaku, Y.; Kagiyama, N.; Kanauchi, T.; Ishiguro, T.; Sugita, Y. Incidence and predictive factors of lung cancer in patients with idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis. ERJ Open Res. 2018, 4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vancheri, C.; Failla, M.; Crimi, N.; Raghu, G. Idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis: A disease with similarities and links to cancer biology. Eur. Respir. J. 2010, 35, 496–504. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Abid, S.H.; Malhotra, V.; Perry, M.C. Radiation-induced and chemotherapy-induced pulmonary injury. Curr. Opin. Oncol. 2001, 13, 242–248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ballester, B.; Milara, J.; Cortijo, J. Idiopathic Pulmonary Fibrosis and Lung Cancer: Mechanisms and Molecular Targets. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2019, 20, 593. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Raghu, G.; Collard, H.R.; Egan, J.J.; Martinez, F.J.; Behr, J.; Brown, K.K.; Colby, T.V.; Cordier, J.F.; Flaherty, K.R.; Lasky, J.A.; et al. An official ATS/ERS/JRS/ALAT statement: Idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis: Evidence-based guidelines for diagnosis and management. Am. J. Respir. Crit. Care Med. 2011, 183, 788–824. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Raghu, G.; Rochwerg, B.; Zhang, Y.; Garcia, C.A.; Azuma, A.; Behr, J.; Brozek, J.L.; Collard, H.R.; Cunningham, W.; Homma, S.; et al. An Official ATS/ERS/JRS/ALAT Clinical Practice Guideline: Treatment of Idiopathic Pulmonary Fibrosis. An Update of the 2011 Clinical Practice Guideline. Am. J. Respir. Crit. Care Med. 2015, 192, e3–e19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jung, S.K.; Jung, H.J.; Lee, B.J.; Choi, J.Y.; Park, Y.C.; Kim, K.T.; Kim, J.D.; Choi, H.Y.; Suh, W.G.; Park, D.I.; et al. Internal Medicine Pulmonary System; Nado: Seoul, Korea, 2011; pp. 510–511. [Google Scholar]
- Shunan, Z.; Lanquan, L.; Hongchun, Z. Clinical Study on Treating Idiopathic Pulmonary Fibrosis with TCM Method of Invigorating Qi, Moisturizing the Lung and Removing Blood Stasis and Toxic Substance. J. Beijing Univ. Tradit. Chin. Med. 1999, 3, 58–61. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, S.; Wu, H.; Liu, J.; Gu, H.; Li, X.; Zhang, T. Medication regularity of pulmonary fibrosis treatment by contemporary traditional Chinese medicine experts based on data mining. J. Thorac. Dis. 2018, 10, 1775–1787. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, M.J.; Yang, G.L.; Ding, Y.X.; Tong, Z.Q. Efficacy of TCM therapy of tonifying lung-kidney’s Qi-deficiency in a case of idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis: A case report. Medicine (Baltimore) 2019, 98, e15140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shi, X.; Qu, N.; Pang, L.; Liu, C. Discussion on the pathogenesis of “Yin deficiency of lung-kidney and Phlegm in meridian” in idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis. Jilin J. Tradit. Chin. Med. 2014, 34, 220–222. [Google Scholar]
- Moore, B.B.; Hogaboam, C.M. Murine models of pulmonary fibrosis. Am. J. Physiol. Lung Cell Mol. Physiol. 2008, 294, L152–L160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhonghua Bencao Edit Committee. Pharmacopoeia of the People’s Republic of China; Zhonghua Bencao Edit Committee: Shanghai, China, 2015. [Google Scholar]
- Ashcroft, T.; Simpson, J.M.; Timbrell, V. Simple method of estimating severity of pulmonary fibrosis on a numerical scale. J. Clin. Pathol. 1988, 41, 467–470. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhou, X.M.; Wen, G.Y.; Zhao, Y.; Liu, Y.M.; Li, J.X. Inhibitory effects of alkaline extract of Citrus reticulata on pulmonary fibrosis. J. Ethnopharmacol. 2013, 146, 372–378. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Majeed, H.; Okoro, C.; Kajdacsy-Balla, A.; Toussaint, K.C., Jr.; Popescu, G. Quantifying collagen fiber orientation in breast cancer using quantitative phase imaging. J. Biomed. Opt. 2017, 22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Williamson, J.D.; Sadofsky, L.R.; Hart, S.P. The pathogenesis of bleomycin-induced lung injury in animals and its applicability to human idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis. Exp. Lung Res. 2015, 41, 57–73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mouratis, M.A.; Aidinis, V. Modeling pulmonary fibrosis with bleomycin. Curr. Opin. Pulm. Med. 2011, 17, 355–361. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
| Botanical Name | Scientific Name | Part of Use | Main Traditional Use [15] | Sample Specimen * | Yield (%) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Farfarae Flos | Tussilago farfara L. | flower | Moisten the lung to suppress cough | HLL-001 | 30.3 |
| Trichosanthis Semen | Trichosanthes kirilowii Maxim. | seed | Moisten the lung and resolve phlegm | HLL-002 | 4.2 |
| Lilii Bulbus | Lilium lancifolium Thunb. | bulb | Nourish Yin and Moistening the lung | HLL-003 | 9.5 |
| Adenophorae Radix | Adenophora triphylla (Thunb.) A.DC. | root | Nourish Yin and Moistening the lung | HLL-004 | 20.9 |
| Asteris Radix et Rhizoma | Aster tataricus L.f. | root | Moisten the lung to suppress cough | HLL-005 | 25.9 |
| Scrophulariae Radix | Scrophularia buergeriana Miq. | root | Nourish Yin and clear lung fire | HLL-006 | 13.1 |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Ahn, J.; Joo, H.; Park, J.; Park, J.-W.; Kim, K.-I.; Jung, H.-J.; Bu, Y.; Lee, B.-J. The Effects of Lung-Moistening Herbal Medicines on Bleomycin-Induced Pulmonary Fibrosis Mouse Model. Processes 2020, 8, 102. https://doi.org/10.3390/pr8010102
Ahn J, Joo H, Park J, Park J-W, Kim K-I, Jung H-J, Bu Y, Lee B-J. The Effects of Lung-Moistening Herbal Medicines on Bleomycin-Induced Pulmonary Fibrosis Mouse Model. Processes. 2020; 8(1):102. https://doi.org/10.3390/pr8010102
Chicago/Turabian StyleAhn, Junmo, Hyejin Joo, Jihye Park, Jae-Woo Park, Kwan-Il Kim, Hee-Jae Jung, Youngmin Bu, and Beom-Joon Lee. 2020. "The Effects of Lung-Moistening Herbal Medicines on Bleomycin-Induced Pulmonary Fibrosis Mouse Model" Processes 8, no. 1: 102. https://doi.org/10.3390/pr8010102
APA StyleAhn, J., Joo, H., Park, J., Park, J.-W., Kim, K.-I., Jung, H.-J., Bu, Y., & Lee, B.-J. (2020). The Effects of Lung-Moistening Herbal Medicines on Bleomycin-Induced Pulmonary Fibrosis Mouse Model. Processes, 8(1), 102. https://doi.org/10.3390/pr8010102