Abstract
Low-cost activated carbons were prepared from waste polyurethane foam by physical activation with CO2 for the first time and chemical activation with Ca(OH)2, NaOH, or KOH. The activation conditions were optimized to produce microporous carbons with high CO2 adsorption capacity and CO2/N2 selectivity. The sample prepared by physical activation showed CO2/N2 selectivity of up to 24, much higher than that of chemical activation. This is mainly due to the narrower microporosity and the rich N content produced during the physical activation process. However, physical activation samples showed inferior textural properties compared to chemical activation samples and led to a lower CO2 uptake of 3.37 mmol·g−1 at 273 K. Porous carbons obtained by chemical activation showed a high CO2 uptake of 5.85 mmol·g−1 at 273 K, comparable to the optimum activated carbon materials prepared from other wastes. This is mainly attributed to large volumes of ultra-micropores (<1 nm) up to 0.212 cm3·g−1 and a high surface area of 1360 m2·g−1. Furthermore, in consideration of the presence of fewer contaminants, lower weight losses of physical activation samples, and the excellent recyclability of both physical- and chemical-activated samples, the waste polyurethane foam-based carbon materials exhibited potential application prospects in CO2 capture.
1. Introduction
CO2 emission from the combustion of coal and natural gas is mainly responsible for global warming [1,2]. The “least-cost” solution is to limit greenhouse gas emissions to meet the Paris Agreement pledges, wherein 60% of CO2 emissions are hoped to be reduced in 2030 relative to 2005 [3]. To reduce the emission of CO2, the selective and energy-efficient capture and storage of CO2 is considered to be a satisfactory approach. Until now, three main CO2 capturing strategies, namely pre-combustion, post-combustion, and oxy-combustion, have been discussed. For pre-combustion, the coal must be gasified first; the typical technology used is called an integrated gasification combined cycle. Post-combustion involves capturing CO2 from the flue gases produced after fossil fuels are burned. Both of these methods have been widely accepted and used in gas-stream purification in industry. Oxy-combustion can produce a relatively pure CO2 stream in emissions, but it is still in development due to the high cost of the technology involved [4]. In addition to these, several technologies have also been investigated to separate and store CO2, such as membrane separation, solution absorption, cryogenic refrigeration, and adsorption approaches [5,6,7]. Although these CCUS (Carbon Capture, Utilization and Storage) technologies are intended to reduce CO2 emission, reaching the Paris Agreement targets is still a serious challenge. Nevertheless, in these techniques, adsorption is considered to be the approach with the most potential, since it involves simple operation and has low-cost and energy-saving benefits [8].
Many adsorbents have been intensively studied for CO2 capture, including zeolites [9], metal-organic frameworks [10], metallic oxide [11], graphene-based adsorbents [12], and porous carbon materials [13]. For future commercialization application, the selection of adsorbents is strongly dependent not only on CO2 capture capacity but also the cost, including the availability of the raw materials, the preparation of the adsorbent, and the operating costs. Porous carbons (PCs) are considered to be the most competitive candidates due to their controlled pore structure, low cost, stable physicochemical properties, ease of chemical modification, and regeneration [14]. Micropore sizes smaller than 1 nm are beneficial to high-density CO2 filling at ambient conditions [15,16]. In addition, a high surface area (>1000 m2·g−1) and a rich nitrogen environment can improve the CO2 adsorption capacity.
The route of preparation, especially activation, will significantly affect the performance of CO2 absorption. The porous carbons can be activated either by physical or chemical methods. Physical activation is usually achieved by carbonization in an inert atmosphere followed by oxidizing in CO2 [17], steam [18], or air. In this way, activated carbons with a narrower pore size distribution can be obtained [19]. Generally, chemical activation takes advantage of oxidizing or dehydrating agents, such as KOH [1,15,20], NaOH, H3PO4, or CaCl2, and being subjected to calcination under N2 between 773 and 1223 K. Chemical activation contributes to the formation of pores and lead to carbons with higher textural development. However, it is an energy-consuming process and is also associated with the corrosion of equipment and environmental problems [21].
To achieve green and sustainable development, the production of low-cost porous carbons from original waste materials is a good, established technique [22]. Polyurethane foams (PUFs), as one of the most important thermoset polymers, are widely used in the chemical industry, electronics, textiles, and medical and other fields due to their high strength, excellent wear resistance, and wide hardness range. The total annual production of polyurethane products in the Asia Pacific region was about 11.5 million tons in 2014, and it is predicted to be over 15.5 million tons by 2019 [23]. As a result, large amounts of useless waste and spent product were generated. Since the processes used for recycling polyurethane foams, like mechanical recycling [24] or chemical depolymerization [25,26], are highly time- and energy-consuming [27], most of the wastes are discarded in landfills or directly burnt, leading to serious environmental issues [28]. However, the ease of availability of the raw materials helps to make waste PUFs a potential activated carbon adsorbent. This would not only alleviate pollution and protect the environment, but it could also convert PUF into a high-value-added product.
Herein, low-cost activated carbons were prepared from waste PUF materials using physical activation with CO2 for the first time, and chemical activation with metal hydroxide. The synthetic procedure is simple and clear, and production costs are low. The activation conditions, like physical activation temperature and chemical activating agent, were discussed and optimized to produce porous carbons with high CO2 adsorption capacity and CO2/N2 selectivity. The richness of N content and narrower microporosity produced by physical activation may be responsible for the higher CO2/N2 selectivity of up to 24. Furthermore, physical activation leads to less contaminant and lower weight losses but also lower CO2 uptake. Porous carbons obtained by chemical activation with KOH possess large volumes of micropores (<1 nm) and high surface areas of up to 0.212 cm3·g−1 and 1360 m2·g−1, respectively. This material exhibits a high CO2 adsorption capacity of 5.85 mmol·g−1 at 273 K and excellent recyclability. The easy regeneration of the PUF-based carbon adsorbent requires minimum energy input, thus reducing operational costs. Therefore, the waste PUFs have the potential to be utilized for the production of activated carbon adsorbents on an industrial scale.
2. Materials and Methods
Prior to carrying out chemical or physical activation, a batch of waste PUFs were carbonized in a porcelain boat inside a horizontal tube furnace at 673 K for 1 h under nitrogen flow (60 mL·min−1). The obtained material was designated as PUF/C. Chemical activation was conducted by treating the carbonized PUFs in alkaline solutions. First, 0.8 g PUF/C was dipped into 10 mL of separate aqueous solutions containing 1.6 g of Ca(OH)2, NaOH, and KOH; was stirred uniformly for 1 h at room temperature; and was subsequently dried at 383 K for 12 h to remove water. Then, the mixture was heated up to 973 K under N2 flow (60 mL·min−1) for 2 h. The samples were thoroughly washed in diluted HCl and distilled water until pH = 7. The products were dried at 373 K for 6 h and denoted as PUF/C-Ca(OH)2-973, PUF/C-NaOH-973, and PUF/C-KOH-973, respectively.
Physical activation of PUFs was accomplished by one-step carbonization and CO2 activation. Certain amounts of PUFs were carbonized in the same procedure followed above, and then N2 was switched to CO2; the obtained PUF/C char was heated up to 1073–1273 K for 2 h under CO2 flow (15 mL·min−1). After physical activation, the sample was cooled to ambient temperature under nitrogen protection and was labeled as PUF/C-CO2-x, where x represents the CO2 activation temperature.
Nitrogen sorption isotherms and the textural properties of the porous carbons were measured at 77 K on an ASAP 2020 apparatus. Before N2 adsorption measurements, all samples were degassed at 493 K for 4 h. The specific surface area was obtained using the BET method (p/p0 = 0–0.5). The total pore volume was estimated with the amount of N2 adsorbed at p/p0 = 0.99. The morphology and structure of the obtained samples were investigated by scanning electron microscopy (SEM, JEOL JSM-700) and transmission electron microscopy (TEM, JEOL JEM-2001F). The amount of N in this paper was determined by elemental analysis using an Elemntar Vario EL Cube microanalyzer. X-ray photoelectron spectra (XPS) were collected on a Krato AXIS Ultra DLD spectrometer. CO2 temperature-programmed-desorption (CO2-TPD) was measured on a Micromeritics Autochem II 2920 chemisorption analyzer.
The CO2 adsorption capacity and adsorption–desorption cycles were investigated at 273 K and ordinary pressure on a BEL-SORP-max instrument. The activated carbon materials were degassed at 453 K for at least 2 h before the measurement.
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Pyrolysis of Wasted PUF and Morphologies of Activated Carbons
Figure 1 shows the pyrolysis of the waste polyurethane foam at a heating rate of 5 K·min−1 in a nitrogen atmosphere. Water adsorbed on the surface is released at about 373 K. The weight loss of the raw materials mainly occurs between 523–773 K, which include three differentiated weight loss peaks. The first peak nears 593 K, resulting from the formation of amines, methylene methyl, and methane species. The second peak around 653 K is due to the decomposition of isocyanate, and the third one near 733 K results from the production of quaternary N, aromatics, CH4, and other species [15]. It is clear that the carbonized precursor mainly results from the former two peaks. Therefore, the carbonization temperature was subsequently set to 673 K.
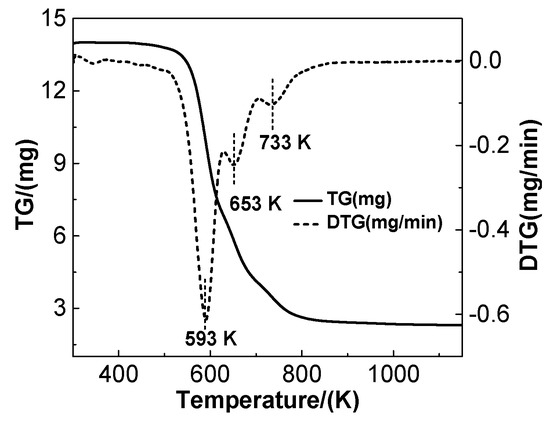
Figure 1.
Pyrolysis of polyurethane foam measured at the heating rate of 5 K·min−1 in N2 atmosphere.
Figure 2 shows the SEM and TEM images of carbonized and chemical and physical activation samples. A slightly rough surface appeared when the carbonized precursor was activated by Ca(OH)2, but the activation degree was so limited that only few macropores existed on the surface (Figure 2b). In comparison, as it was activated by NaOH and KOH, the smooth surface changes to a multi-hole morphology to a large extent (Figure 2a,c,d). In addition, NaOH activation resulted in more macropores on the surface, while KOH activation led to the plentiful generation of micropores. These observations indicate that the carbonized precursor was etched increasingly severely by the chemical activation of Ca(OH)2, NaOH, and KOH (Figure 2a–d). Furthermore, in the physical activation process, the activation temperature determines the development of porosity. It can be observed that the surface of the carbonized precursor became rugged after physical activation by CO2 at 1173 K and formed many micropores during the gasification reaction between CO2 and carbon and the following diffusion processes of the generated products (Figure 2e,g). Micropore generation would possibly benefit the fast, dynamic CO2 adsorption-desorption. Nevertheless, much higher physical activation temperatures should be avoided as they can broaden the average micropore width, producing few mesopores (Figure 2f,h), which is not good for CO2 capture.
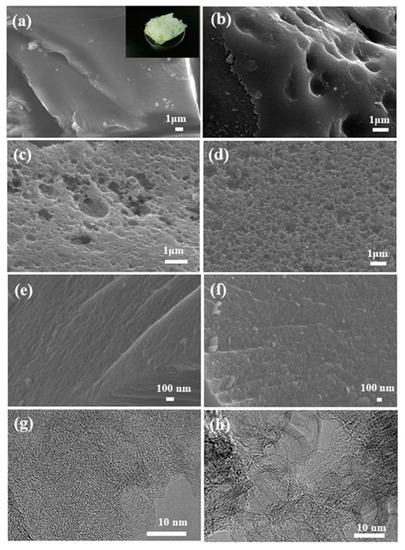
Figure 2.
SEM images of the PUF/C (a), PUF/C-Ca(OH)2-973 (b), PUF/C-NaOH-973 (c), PUF/C-KOH-973 (d), PUF/C-CO2-1173 (e), PUF/C-CO2-1273 (f), and TEM images of PUF/C-CO2-1173 (g) and PUF/C-CO2-1273 (h). The inset in (a) is a photo showing the morphology of waste polyurethane foams.
3.2. Surface Oxygen and Nitrogen Species Analyses
Figure 3 exhibits the FT-IR spectra of PUF-based activated carbons. The broad band around 3440 cm−1 could be ascribed to the N–H/O–H symmetric stretching vibration [29]. The intense bands at 1090 cm−1 and 1584 cm−1 are related to C–O stretching [29] and N–H in-plane deformation. The relatively weak band around 1383 cm−1 is attributed to the C–N stretching vibration. Bands at 2927 and 2851 cm−1 could be ascribed to the C–H stretching vibrations of –CH2 and –CH3 [15]. The presence of oxygen and nitrogen species were further confirmed by XPS. The O 1s spectra show the presence of three main peaks at 531, 532.1, and 533.5 eV, which are attributed to –C=O, C–O–C/C–OH, and O–C=O, respectively (Figure 4) [30]. The results confirm that plentiful amounts of oxygen-rich functional groups are incorporated onto the surface of the PUF-based activated carbons, which play an important role in enhancing the overall CO2 adsorption.
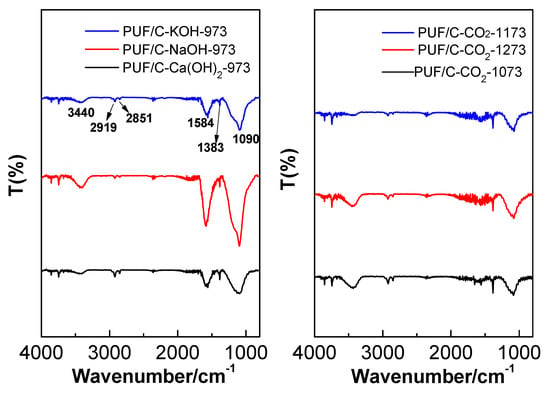
Figure 3.
FT-IR spectra of the obtained samples prepared by physical and chemical activation.
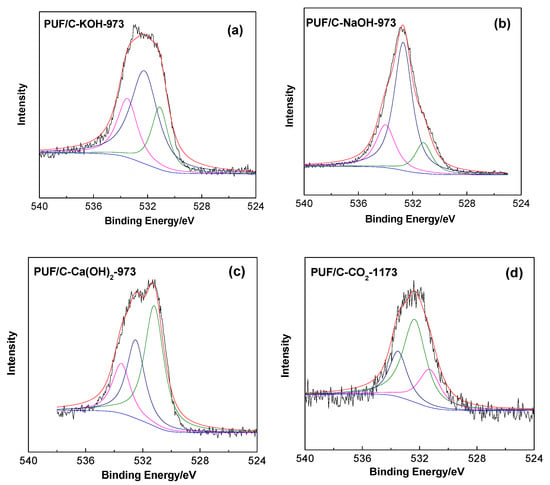
Figure 4.
XPS spectra O 1s of PUF/C-KOH-973 (a), PUF/C-NaOH-973 (b), PUF/C-Ca(OH)2-973 (c), and PUF/C-CO2-1173 (d).
It is well-known that the type and content of N-containing species of carbon adsorbents can greatly affect CO2 adsorption capacity. As shown in Figure 5, pyridinic (N-6), pyrrolic (N-5), quaternary N (N-Q), and pyridine N-oxide (N-X) species with binding energies of 398.5, 399.7, 400.9, and 403.0 eV, respectively, can be identified by deconvolving the N 1s signal of the activated carbons [31]. The specific components depend on the physical activation temperature or the degree of chemical activation with R(OH)x (R = Ca, Na, K; x = 1/2). The relative amount of pyridine N-oxide species increased with increasing CO2 activation temperature. This can also apply to the quaternary N species (Figure 5a–c). Conversely, upon increasing the CO2 activation temperature from 1073 to 1273 K, the contents of pyridinic and pyrrole N species dropped from 35% and 24% to 18% and 21%, respectively (Table 1), indicating that elevating the CO2 activation temperature can decrease the total amount of N species and also convert the pyridinic nitrogen and pyrrole nitrogen to quaternary N and pyridine N-oxide species (Figure 5a–c). This trend was also observed upon increasing the degree of chemical activation using Ca(OH)2, NaOH, and KOH as activated reagents (Figure 5d–f). The pyridinic and pyrrole-type N declined from 28% and 72% to 21% and 41%, respectively. Quaternary-N and pyridine N-oxide species are considered less effective in CO2 capture than pyridinic and pyrrolic nitrogen [32], since basic N species are superior at capturing CO2. Therefore, CO2 uptake on the activated carbons would increase with decreasing the physical activation temperature or the degree of chemical activation under the conditions of similar porous structures. Actually, CO2 uptake and physical activation temperature or the degree of chemical activation show a volcano relationship or a positive relationship, respectively, implying that the porous structure of the activated carbons may greatly affect their CO2 capture.
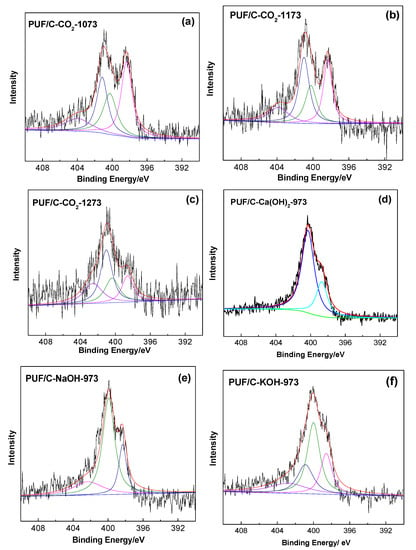
Figure 5.
XPS N 1s spectra of PUF/C-CO2-1073 (a), PUF/C-CO2-1173 (b), and PUF/C-CO2-1273 (c), PUF/C-Ca(OH)2-973 (d), PUF/C-NaOH-973 (e), and PUF/C-KOH-973 (f).

Table 1.
Surface nitrogen contents of polyurethane foam-based activated carbons prepared by physical and chemical activation.
Figure 6 shows the CO2-TPD profiles of the porous carbons prepared by physical and chemical activation from wasted polyurethane foam. In general, physical and chemical adsorption are the two main routes for CO2 capture. An intense peak was present between 343 and 358 K, indicating that most of the CO2 molecules physically adsorbed on the activated carbons due to their developed pore structures. In contrast, a very weak peak was also observed around 448 K, implying that there exists a weak chemical interaction between CO2 and N species. Thus, physical adsorption occupies the dominant position during the CO2 capture process in this studied case.
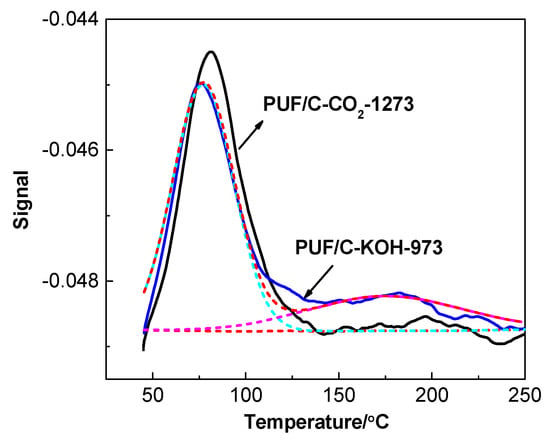
Figure 6.
CO2- temperature-programmed-desorption (TPD) profile of PUF/C-KOH-973 and PUF/C-CO2-1273.
3.3. Effect of Physical and Chemical Activation on the Textural Properties of PUF-Based Porous Carbon Materials
Figure 7 shows the N2 adsorption isotherms and pore size distributions (PSDs) of carbon materials after physical and chemical activation. Clearly, the prepared samples exhibit a typical micropore structure that is mainly responsible for CO2 capture at ambient conditions [33]. Meanwhile, the hysteresis loops of the adsorption isotherm of PUF/C-KOH-973 or PUF/C-NaOH-973 are of type-IV, representing slit-shaped pores and implying the generation of mesopores (Figure 7a). It is well-known that carbon materials with narrow micropores can be obtained by physical activation [18]. It can be observed from Table 2 that, upon increasing CO2 activation temperature from 1073 to 1273 K, the surface area and pore volume of the samples significantly rose from 15 m2·g−1 and 0.04 cm3·g−1 to 865 m2·g−1 and 0.42 cm3·g−1, respectively, and the PSDs (<1 nm) of samples widened from 0.58 to 0.87 nm (Figure 7b). In particular, the ultra-micropore (<1 nm) volume increased from 0.085 to 0.122 cm3·g−1 and then decreased to 0.119 cm3·g−1 upon elevating the activation temperature (Table 2 and Figure 8). A much higher physical activation temperature will make the reaction rate between carbon and CO2 faster than the diffusion rate, which is not helpful for the formation of micropores. From the above, we can conclude that the pore structure of activated carbons could be controlled by adjusting the CO2 activation temperature. In this work, the developed ultra-micropore can be obtained at 1173 K with a CO2 flowrate of 15 mL·min−1.
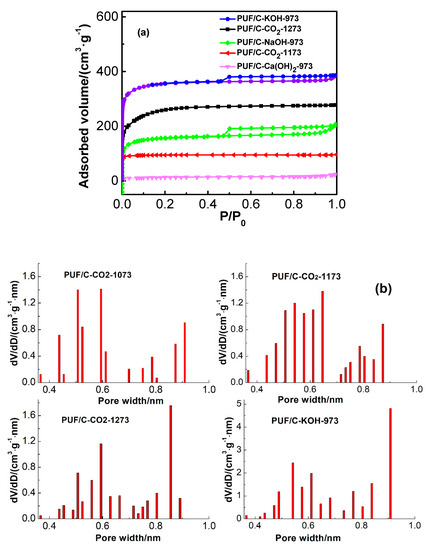
Figure 7.
Adsorption isotherms of N2 at 77 K (a) and pore size distributions determined by the Dubinin–Radushkevich equation applied to Table 2 adsorption data at 273 K (b) of the obtained samples prepared by physical and chemical activation.

Table 2.
Textural parameters of prepared samples from adsorption isotherms of N2 and CO2.
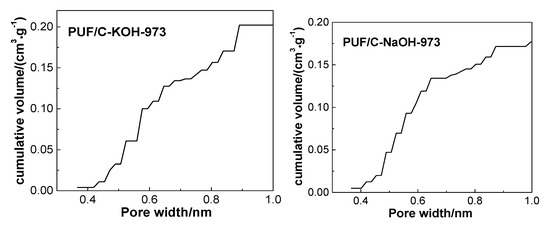
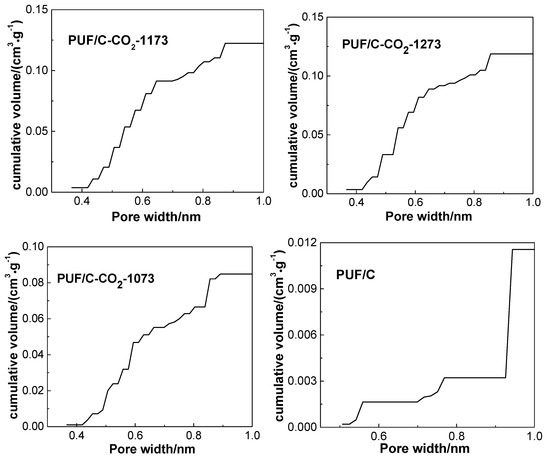
Figure 8.
Cumulative volumes of ultramicropores (≤1 nm) calculated by the nonlocal density functional theory (NLDFT) method of PUF-based activated carbons. Adapted with permission from [15]. Copyright 2016 American Chemical Society.
In addition, the textural parameters of chemical activation samples are also shown in Table 2. The carbonized precursor was activated by chemical reagents Ca(OH)2, NaOH, and KOH at 973 K. In addition to the sharp increase of surface area and pore volume from 39 m2·g−1 and 0.04 cm3·g−1 to 1360 m2·g−1 and 0.59 cm3·g−1, respectively, and the volumes of ultra-micropores (<1 nm) increased from barely detectable to 0.212 cm3·g−1 (Table 2 and Figure 8). It can be inferred that the pore structure of the carbon adsorbents could also be controlled by adjusting the chemical activation degree, and that increasing the degree of chemical activation is helpful for the formation of pores, especially the ultra-micropores, although a small number of mesopores were generated simultaneously.
Comparing physical activation with chemical activation, it can be concluded that physical activation mainly develops micropores and results in porous carbon materials with lower textural properties, which may affect the adsorption performance and lead to lower CO2 uptake. However, it involves less contaminant, which avoids the emission of metal ions and the corrosion of equipment.
By increasing the activation temperature from 1073 to 1273 K (Table 2), the yield of porous carbons with physical activation decreased from 16% to 9.3%, as a result of CO2 gas reacting with the walls of the pores (Equation (1)) [34]. In addition, the higher the burn-off temperature, the wider the pore size distribution becomes, as mentioned above. Regardless, higher carbon yield can be produced by physical activation due to lower burn-off degrees compared with effective chemical activation.
CO2 + C → 2CO
Similarly, the yield of carbon materials, as expected, decreased from 25.5% to 12.3% when enhancing the chemical activation degree using Ca(OH)2, NaOH, or KOH as activated reagents (Table 2), which can be explained by graphitic C being oxidized by KOH beginning at 673 K, while for NaOH the temperature needs to be higher than 843 K, not even mentioning Ca(OH)2 [35].
The porosity formed upon KOH, NaOH, and Ca(OH)2 activation is considered to be the intercalation of metallic K, Na, and Ca in the carbon matrix, causing the deformation and expansion of the carbon lattice [36]. CO2, H2O, and H2 generated in the redox reaction (take KOH and C for example) can also contribute to the development of pores. As shown in Equations (2)–(4) [35].
4KOH + C → 4K + CO2 + 2H2O
4KOH + 2CO2 → 2K2CO3 + 2H2O
6KOH + 2C → 2K + 3H2 + 2K2CO3
3.4. CO2 Adsorption Performances
CO2 adsorption performances of samples with physical and chemical activation at 273 K are shown in Figure 9. For physically-activated samples, CO2 adsorption capacities increased from 2.4 to 3.4 mmol·g−1 upon increasing activation temperature from 1073 to 1173 K. This cannot be simply attributed to surface area and pore volume (Table 2), since PUF/C-CO2-1273 possesses larger surface area and pore volume but a lower CO2 adsorption capacity than that of PUF/C-CO2-1173. It was reported recently that small micropores are dominant in CO2 capture for activated carbon materials [9]. This is attributed to the fact that the interaction between CO2 and carbon adsorbents can be enhanced in small pores, especially at elevated temperatures and low pressures. The correlation of CO2 uptake of PUF-based activated carbons at 273 K and 1 bar with the volumes of micropores (<1 nm) is presented in Figure 10a. Clearly, the CO2 adsorption capacity shows a perfect linear correlation with the volumes of micropores less than 1 nm. Severe activation at higher temperature results in widening the pore size distribution, reducing the amount of ultra-micropores, which is responsible for the lower CO2 uptake of PUF/C-CO2-1273 compared to PUF/C-CO2-1173.
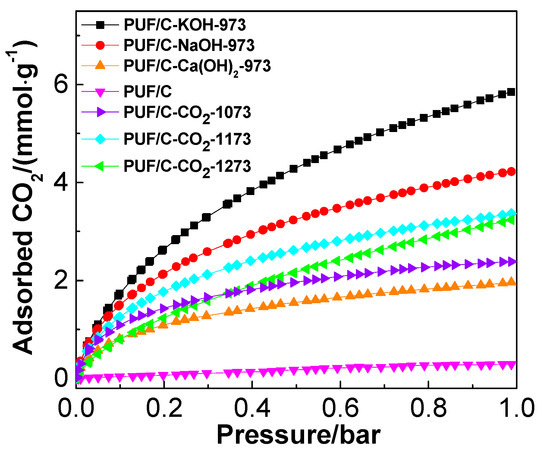
Figure 9.
Adsorption isotherms of CO2 at 273 K for the studied samples.
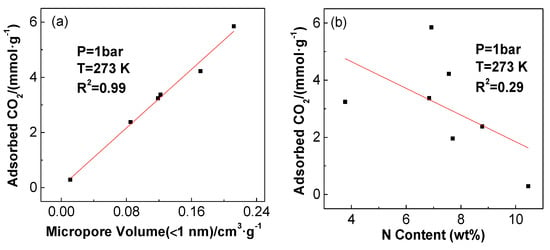
Figure 10.
Correlation of CO2 adsorption capacity with ultra-micropore volume (a) and with sample N content (b) at 273 K.
This trend can also be applied to the CO2 adsorption performances of samples after chemical activation. Figure 8 shows that the adsorption capacity of CO2 at 273 K and 1 bar increases as follows: PUF/C-Ca(OH)2-973 < PUF/C-NaOH-973 < PUF/C-KOH-973. The PUF/C-KOH-973 sample exhibits the highest CO2 uptake at 5.85 mmol·g−1. This is mainly due to it having the largest ultra-micropore volume (<1 nm) of 0.212 cm3·g−1 coupled with the largest surface area, pore volume, and abundance of basic N species. Chemical activation can be described by two steps: The formation of micropores, which is beginning with the redox reaction between activated agents and carbonized precursors; and the broadening of pores inside the opened porous channel [37]. Hence, the stage of creating micropores is primary when enhancing the activation degree from Ca(OH)2 to KOH activation at 973 K.
N content in the prepared carbon materials may also contribute to the CO2 adsorption capacity, wherein the correlation coefficient of CO2 uptake with the N content (3.5–10.5 wt.%) of PUF-based activated carbons was only 0.29 (Figure 10b). This indicates that N content in the samples should not be the primary effect in this experiment. Thus, the superior CO2 adsorption capabilities of the studied activated carbons predominantly result from the ultra-micropores (<1 nm).
Table 3 shows a comparation of CO2 uptakes of carbon adsorbents prepared from PUF and other different waste materials at 273 K. It is worth mentioning that samples prepared with the waste polyurethane foams under CO2 activation at 1173 K and KOH activation at 973 K exhibit comparable or better CO2 adsorption capacities than those adsorbents obtained from many types of waste materials, such as ocean pollutant, sawdust, and coal fly ash (see Table 3). Whereas, some new derived activated carbons from biomass porous materials, like Arundo donax [29] or lotus seed [38], show a relatively higher adsorption capacity. The results mentioned above suggest that activated carbon prepared from waste PUF is a potential candidate for use in capturing CO2.

Table 3.
CO2 adsorption capacities at 273 K and 1 bar of activated carbons prepared from different waste materials.
3.5. CO2 Adsorption Recyclability and Selectivity
CO2 and N2 adsorption behaviors of PUF/C-CO2-1173 and PUF/C-KOH-973 at 273 K were compared, as shown in Figure 11. The N2 adsorption capacity is 0.59 mmol g−1, which is almost one-tenth of the CO2 uptake of chemically-activated sample PUF/C-KOH-973. While, the selectivity of CO2/N2 of PUF/C-CO2-1173 outperforms PUF/C-KOH-973 with a lower N2 adsorption of only 0.14 mmol g−1 at 273 K, which is much higher than CO2 adsorbents from other waste materials, such as mangosteen peel waste (24 vs. 12) [45]. This can be ascribed to the rich and narrower microporosity [39], as well as the nitrogen content of 6.84 wt% and the presence of other functional groups [46].
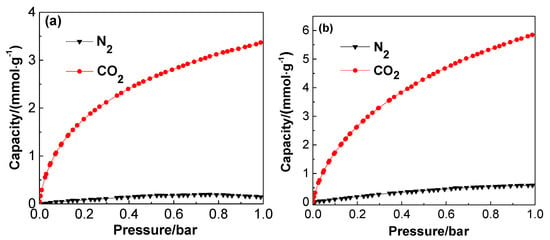
Figure 11.
CO2 and N2 adsorption isotherms at 273 K on the PUF/C-CO2-1173 (a) and PUF/C-KOH-973 (b).
The CO2 adsorption performances of PUF/C-CO2-1173 at 273 K and PUF/C-KOH-973 at 298 K are completely the same in the four repeated runs, as shown in Figure 12a,b, indicating that the physically-activated sample has as high of a recyclability as the chemically-activated sample. Hence, in comparison with the environmental pollution and cumbersome process associated with chemical activation, CO2 sorbent from waste polyurethane foam by physical activation is encouraged, due to the higher CO2/N2 selectivity and the relatively higher carbon yield.
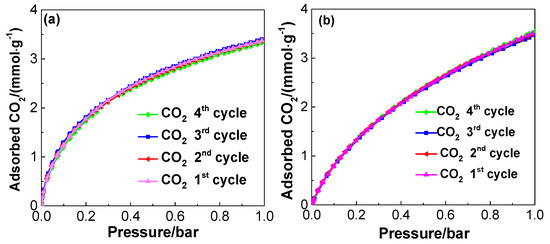
Figure 12.
CO2 adsorption performances on the PUF/C-CO2-1173 at 273 K (a) and PUF/C-KOH-973 at 298 K (b) within four repeated cycles with regeneration.
4. Conclusions
In this work, waste polyurethane foam was physically activated by CO2 for the first time and chemically activated with Ca(OH)2, NaOH, or KOH, and was compared for the preparation of the low-cost activated carbons with a highly-developed porosity. To achieve high CO2 adsorption capacity and CO2/N2 selectivity, activation conditions of the waste polyurethane foam were optimized. The low CO2 flowrate (15 mL·min−1) and temperature of 1173 K for CO2 activation are beneficial to the formation of a narrower microporosity. This, combined with relatively high nitrogen content, resulted in the high CO2/N2 selectivity of up to 24, much higher than samples that underwent chemical activation. However, physical activation samples showed inferior textural properties compared to chemical activation samples and led to lower CO2 uptake. The sample activated with KOH possessed a high volume of ultramicropores (<1 nm) and surface area up to 0.212 cm3·g−1 and 1360 m2·g−1, respectively. A high CO2 adsorption capacity of 5.85 mmol·g−1 was obtained at 273 K and 1 bar, which was better than the physical activation sample with 3.37 mmol·g−1, and is comparable to the best reported carbon materials prepared from other waste materials. Moreover, in consideration of the decreased presence of the contaminant, the lower weight losses of physical activation samples, and the excellent recyclability of both physical and chemical activated samples, the waste polyurethane foam-based carbon materials exhibited potential application prospects in CO2 capture.
Author Contributions
Writing—original draft, C.G.; data curation, D.L.; investigation, S.C.; formal analysis, J.G.; supervision, J.L.
Funding
This research was funded by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (No. 21802101), Scientific and Technological Innovation Programs of Higher Education Institutions in Shanxi, and Shanxi Province Science Foundation for Youths (No. 201801D221129).
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
References
- Wang, J.; Heerwig, A.; Lohe, M.R.; Oschatz, M.; Borchardt, L.; Kaskel, S. Fungi-based porous carbons for CO2 adsorption and separation. J. Mater. Chem. 2012, 22, 13911–13913. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schrag, D.P. Preparing to capture carbon. Science 2007, 315, 812–813. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Morris, J.; Paltsev, S.; Ku, A.Y. Impacts of China’s emissions trading schemes on deployment of power generation with carbon capture and storage. Energy Econ. 2019, 81, 848–858. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wilberforce, T.; Baroutaji, A.; Soudan, B.; Al-Alami, A.H.; Olabi, A.G. Outlook of carbon capture technology and challenges. Sci. Total Environ. 2019, 657, 56–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, S.; Li, W.C.; Zhang, L.; Jin, Z.Y.; Lu, A.H. Polybenzoxazine-based monodisperse carbon spheres with low-thermal shrinkage and their CO2 adsorption properties. J. Mater. Chem. A 2014, 2, 4406–4412. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, P.; Wang, Z.; Li, W.; Liu, Y.; Wang, J.; Wang, S. High-performance multilayer composite membranes with mussel-inspired polydopamine as a versatile molecular bridge for CO2 separation. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2015, 7, 15481–15493. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Du, N.; Park, H.B.; Robertson, G.P.; Dal-Cin, M.M.; Visser, T.; Scoles, L.; Guiver, M.D. Polymer nanosieve membranes for CO2-capture applications. Nat. Mater. 2011, 10, 372–375. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bae, Y.S.; Snurr, R.Q. Development and Evaluation of Porous Materials for Carbon Dioxide Separation and Capture. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2011, 50, 11586–11596. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Su, F.; Lu, C. CO2 capture from gas stream by zeolite 13X using a dual-column temperature/vacuum swing adsorption. Energy Environ. Sci. 2012, 5, 9021–9027. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khan, I.U.; Othman, M.H.D.; Ismail, A.; Ismail, N.; Jaafar, J.; Hashim, H.; Rahman, M.A.; Jilani, A. Structural transition from two-dimensional ZIF-L to three-dimensional ZIF-8 nanoparticles in aqueous room temperature synthesis with improved CO2 adsorption. Mater. Charact. 2018, 136, 407–416. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, H.; Wang, X.; Shu, Z.; Fujii, M.; Song, C. Al2O3 and CeO2-promoted MgO sorbents for CO2 capture at moderate temperatures. Front. Chem. Sci. Eng. 2018, 12, 83–93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chandra, V.; Yu, S.U.; Kim, S.H.; Yoon, Y.; Kim, D.Y.; Kwon, A.H.; Meyyappan, M.; Kim, K.S. Highly selective CO2 capture on N-doped carbon produced by chemical activation of polypyrrole functionalized graphene sheets. Chem. Commun. 2012, 48, 735–737. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gu, J.M.; Kim, W.S.; Hwang, Y.K.; Huh, S. Template-free synthesis of N-doped porous carbons and their gas sorption properties. Carbon 2013, 56, 208–217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, J.; Shen, W.; Wang, J.; Fan, W. Superior carbon-based CO2 adsorbents prepared from poplar anthers. Carbon 2014, 69, 255–263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ge, C.; Song, J.; Qin, Z.; Wang, J.; Fan, W. Polyurethane Foam-Based Ultramicroporous Carbons for CO2 Capture. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2016, 8, 18849–18859. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, Z.; Zhou, J.; Xing, W.; Xue, Q.; Yan, Z.; Zhuo, S.; Qiao, S.Z. Critical role of small micropores in high CO2 uptake. Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys. 2013, 15, 2523–2529. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ello, A.S.; De Souza, L.K.; Trokourey, A.; Jaroniec, M. Coconut shell-based microporous carbons for CO2 capture. Microporous Mesoporous Mater. 2013, 180, 280–283. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heo, Y.J.; Park, S.J. H2O2/steam activation as an eco-friendly and efficient top-down approach to enhancing porosity on carbonaceous materials: The effect of inevitable oxygen functionalities on CO2 capture. Green Chem. 2018, 20, 5224–5234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prauchner, M.J.; Rodríguez-Reinoso, F. Chemical versus physical activation of coconut shell: A comparative study. Microporous Mesoporous Mater. 2012, 152, 163–171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sevilla, M.; Fuertes, A.B.; Solis, M.S.; Valle-Vigón, P. N-Doped Polypyrrole-Based Porous Carbons for CO2 Capture. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2011, 21, 2781–2787. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nandi, M.; Okada, K.; Dutta, A.; Bhaumik, A.; Maruyama, J.; Derks, D.; Uyama, H. Unprecedented CO2 uptake over highly porous N-doped activated carbon monoliths prepared by physical activation. Chem. Commun. 2012, 48, 10283–10285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Meng, F.Z.; Gong, Z.Q.; Wang, Z.B.; Fang, P.W.; Li, X.Y. Study on a nitrogen-doped porous carbon from oil sludge for CO2 adsorption. Fuel 2019, 251, 562–571. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Agrawal, A.; Kaur, R.; Walia, R. PU foam derived from renewable sources: Perspective on properties enhancement: An overview. Eur. Polym. J. 2017, 95, 255–274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shinko, A. Introduction to Mechanical Recycling and Chemical Depolymerization. Recycl. Polyurethane Foam. 2018, 4, 45–55. [Google Scholar]
- Sheel, A.; Pant, D. Chemical Depolymerization of Polyurethane Foams via Glycolysis and Hydrolysis. Recycl. Polyurethane Foam. 2018, 6, 67–75. [Google Scholar]
- Padhan, R.K. Chemical Depolymerization of Polyurethane Foams via Combined Chemolysis Methods. Recycl. Polyurethane Foam. 2018, 8, 89–96. [Google Scholar]
- Quadrini, F.; Bellisario, D.; Santo, L. Recycling of thermoset polyurethane foams. Polym. Eng. Sci. 2013, 53, 1357–1363. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferdan, T.; Pavlas, M.; Nevrlý, V.; Šomplák, R.; Stehlík, P. Greenhouse gas emissions from thermal treatment of non-recyclable municipal waste. Front. Chem. Sci. Eng. 2018, 12, 815–831. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, G.; Kim, I.Y.; Lakhi, K.S.; Srivastava, P.; Naidu, R.; Vinu, A. Single step synthesis of activated bio-carbons with a high surface area and their excellent CO2 adsorption capacity. Carbon 2017, 116, 448–455. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pevida, C.; Drage, T.; Snape, C.; Drage, T.; Snape, C. Silica-templated melamine–formaldehyde resin derived adsorbents for CO2 capture. Carbon 2008, 46, 1464–1474. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Su, F.; Poh, C.K.; Chen, J.S.; Xu, G.; Wang, D.; Li, Q.; Lin, J.; Lou, X.W. Nitrogen-containing microporous carbon nanospheres with improved capacitive properties. Energy Environ. Sci. 2011, 4, 717–724. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hao, G.P.; Li, W.C.; Qian, D.; Lu, A.H. Rapid Synthesis of Nitrogen-Doped Porous Carbon Monolith for CO2Capture. Adv. Mater. 2010, 22, 853–857. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Martín, C.; Plaza, M.; Pis, J.; Rubiera, F.; Pevida, C.; Centeno, T.A. On the limits of CO2 capture capacity of carbons. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2010, 74, 225–229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chaudhary, A.; Kumari, S.; Kumar, R.; Teotia, S.; Singh, B.P.; Singh, A.P.; Dhawan, S.K.; Dhakate, S.R. Lightweight and easily foldable MCMB-MWCNTs composite paper with exceptional electromagnetic interference shielding. ACS Appl. Mater. Interface 2016, 8, 10600–10608. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lillo-Ródenas, M.A.; Cazorla-Amorós, D.; Linares-Solano, A. Understanding chemical reactions between carbons and NaOH and KOH: An insight into the chemical activation mechanism. Carbon 2003, 41, 267–275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dıaz-Terán, J.; Nevskaia, D.; Fierro, J.; Lopez-Peinado, A.J.; Jerez, A. Study of chemical activation process of a lignocellulosic material with KOH by XPS and XRD. Microporous Mesoporous Mater. 2003, 60, 173–181. [Google Scholar]
- Rodriguez-Reinoso, F.; Molina-Sabio, M. Activated carbons from lignocellulosic materials by chemical and/or physical activation: An overview. Carbon 1992, 30, 1111–1118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, G.; Lakhi, K.S.; Ramadass, K.; Sathish, C.I.; Vinu, A. High-performance biomass-derived activated porous biocarbons for combined pre- and post-combustion CO2 capture. ACS Sustain. Chem. Eng. 2019, 7, 7412–7420. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Plaza, M.; Gonzalez, A.; Pevida, C.; Pis, J.; Rubiera, F. Valorisation of spent coffee grounds as CO2 adsorbents for postcombustion capture applications. Appl. Energy 2012, 99, 272–279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sevilla, M.; Fuertes, A.B. Sustainable porous carbons with a superior performance for CO2 capture. Energy Environ. Sci. 2011, 4, 1765–1771. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rodríguez, E.; García, R. Low-cost hierarchical micro/macroporous carbon foams as efficient sorbents for CO2 capture. Fuel Process. Technol. 2017, 156, 235–245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Z.; Wang, K.; Atkinson, J.D.; Yan, X.; Li, X.; Rood, M.J.; Yan, Z. Sustainable and hierarchical porous Enteromorpha prolifera based carbon for CO2 capture. J. Hazard. Mater. 2012, 229, 183–191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, L.; Singh, R.; Xiao, P.; Webley, P.A.; Zhai, Y. Zeolite synthesis from waste fly ash and its application in CO2 capture from flue gas streams. Adsorption 2011, 17, 795–800. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ren, M.; Zhang, T.; Wang, Y.; Jia, Z.; Cai, J. A highly pyridinic N-doped carbon from macroalgae with multifunctional use toward CO2 capture and electrochemical applications. J. Mater. Sci. 2018, 54, 1606–1615. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Wang, X.; Cao, M. Three-dimensional porous carbon frameworks derived from mangosteen peel waste as promising materials for CO2 capture and supercapacitors. J. CO2 Util. 2018, 27, 204–216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhai, Q.G.; Bai, N.; Li, S.; Bu, X.; Feng, P. Design of Pore Size and Functionality in Pillar-Layered Zn-Triazolate-Dicarboxylate Frameworks and Their High CO2/CH4 and C2 Hydrocarbons/CH4 Selectivity. Inorg. Chem. 2015, 54, 9862–9868. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).