Syngas Production from Combined Steam Gasification of Biochar and a Sorption-Enhanced Water–Gas Shift Reaction with the Utilization of CO2
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Material Synthesis
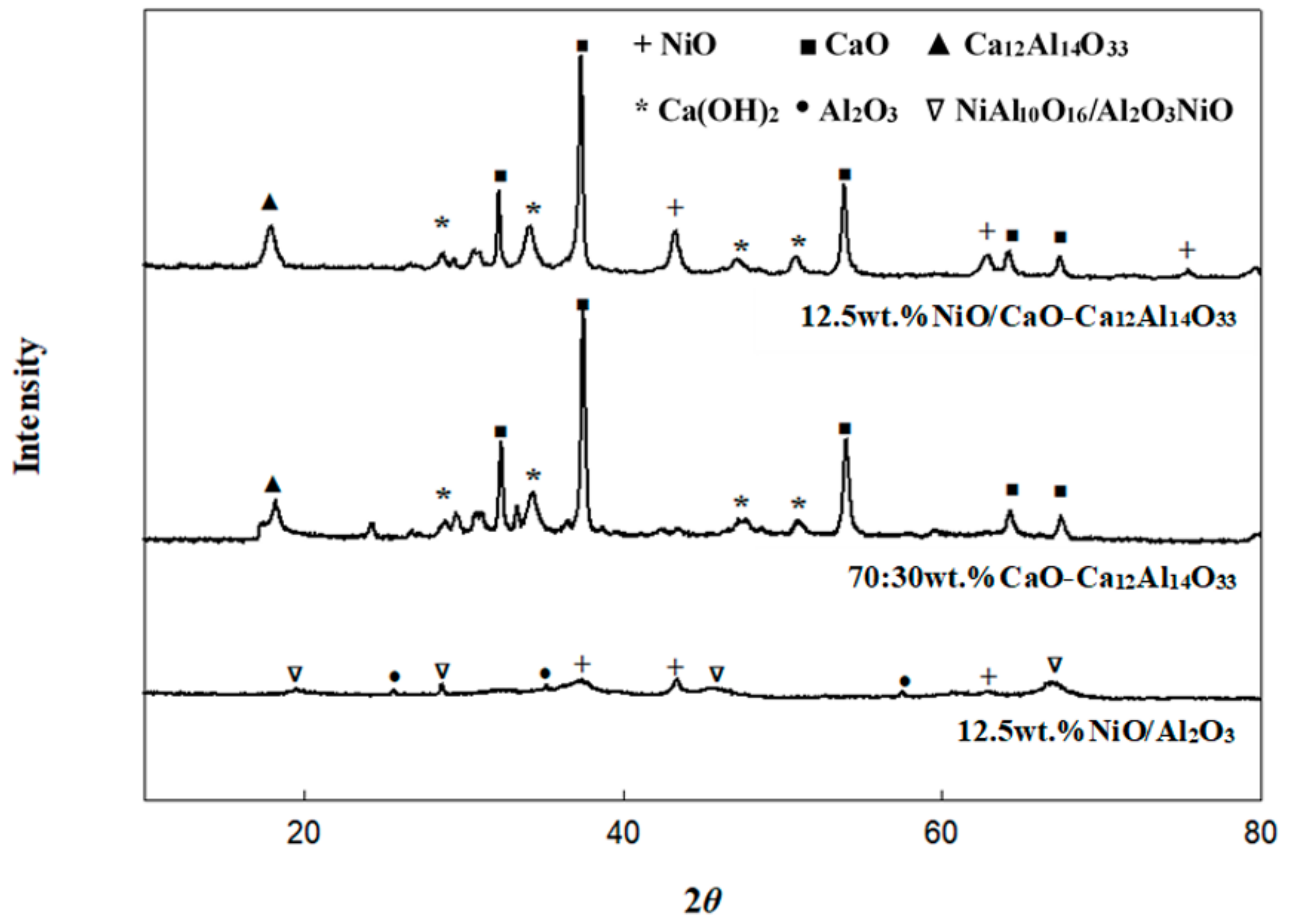
2.2. Material Characterization
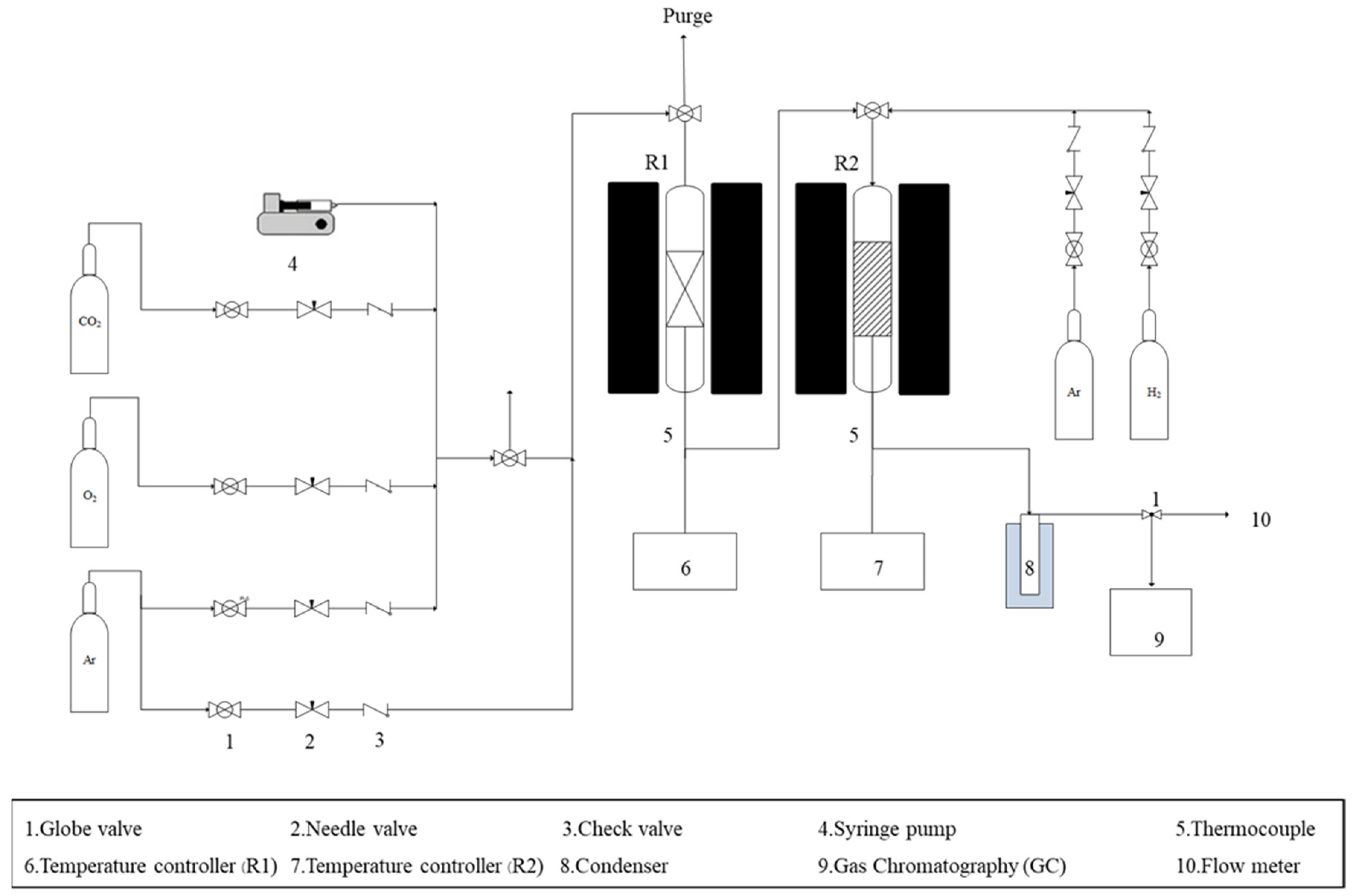
2.3. Syngas Production Test
3. Results and Discussions
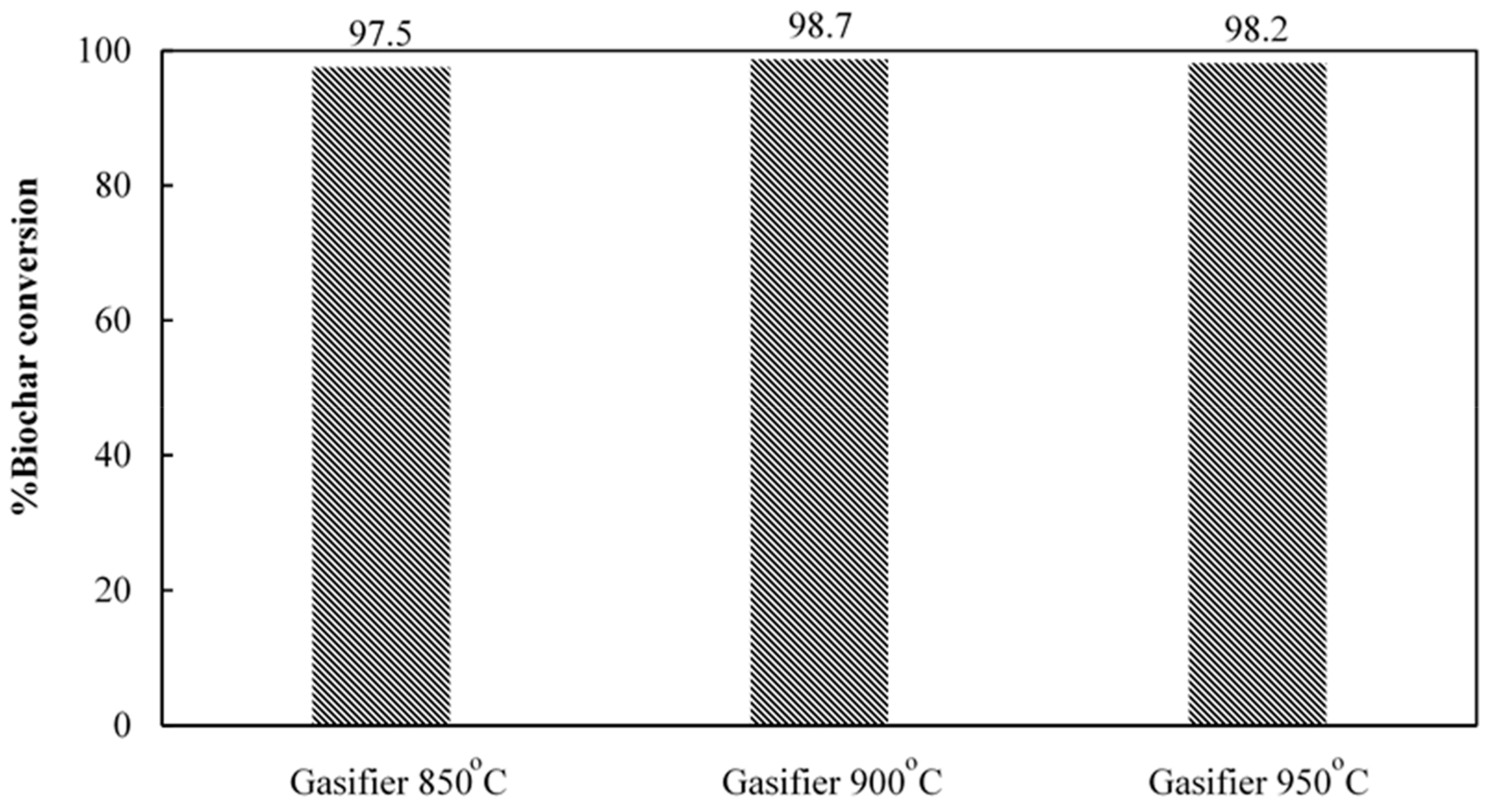
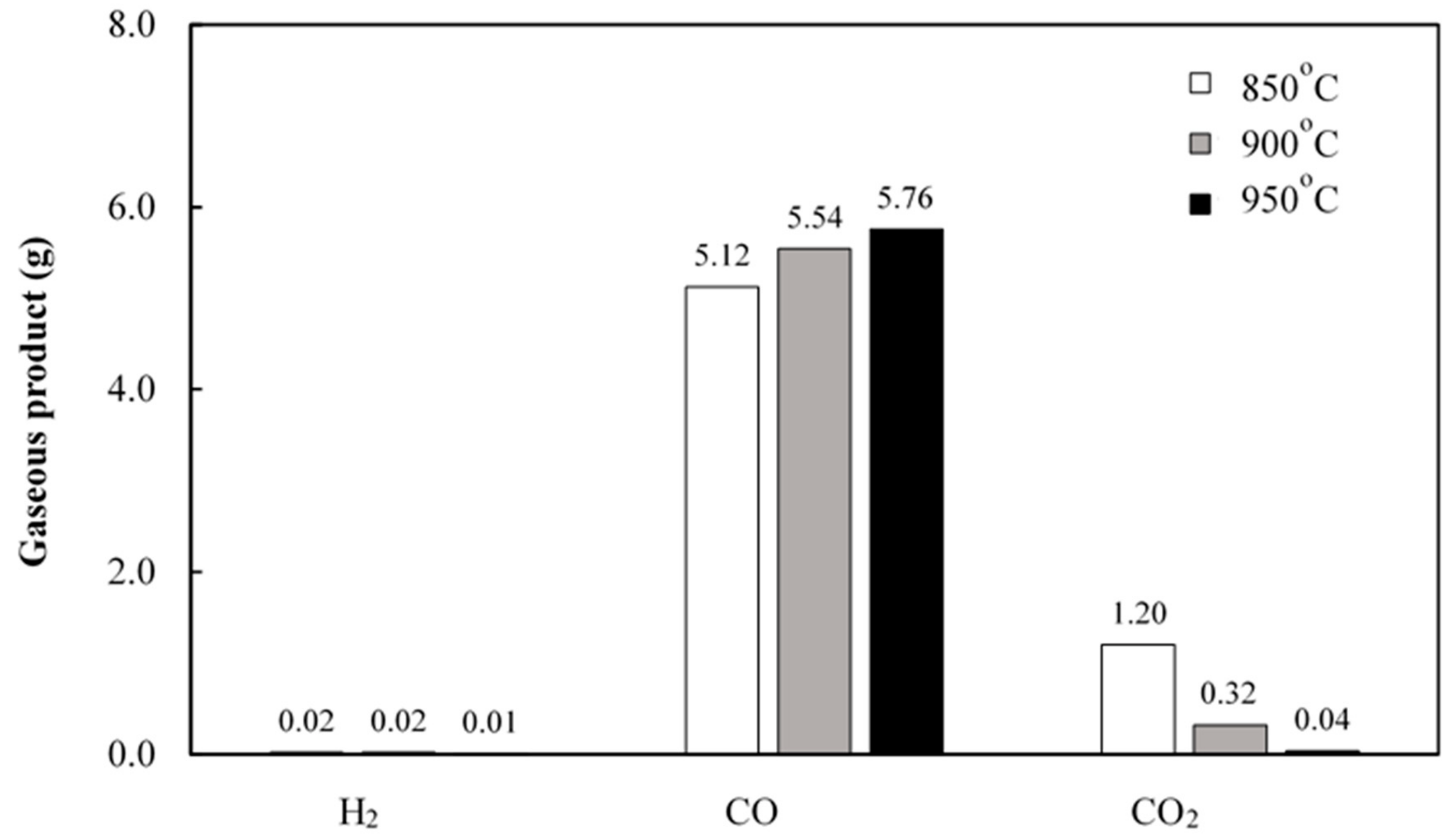
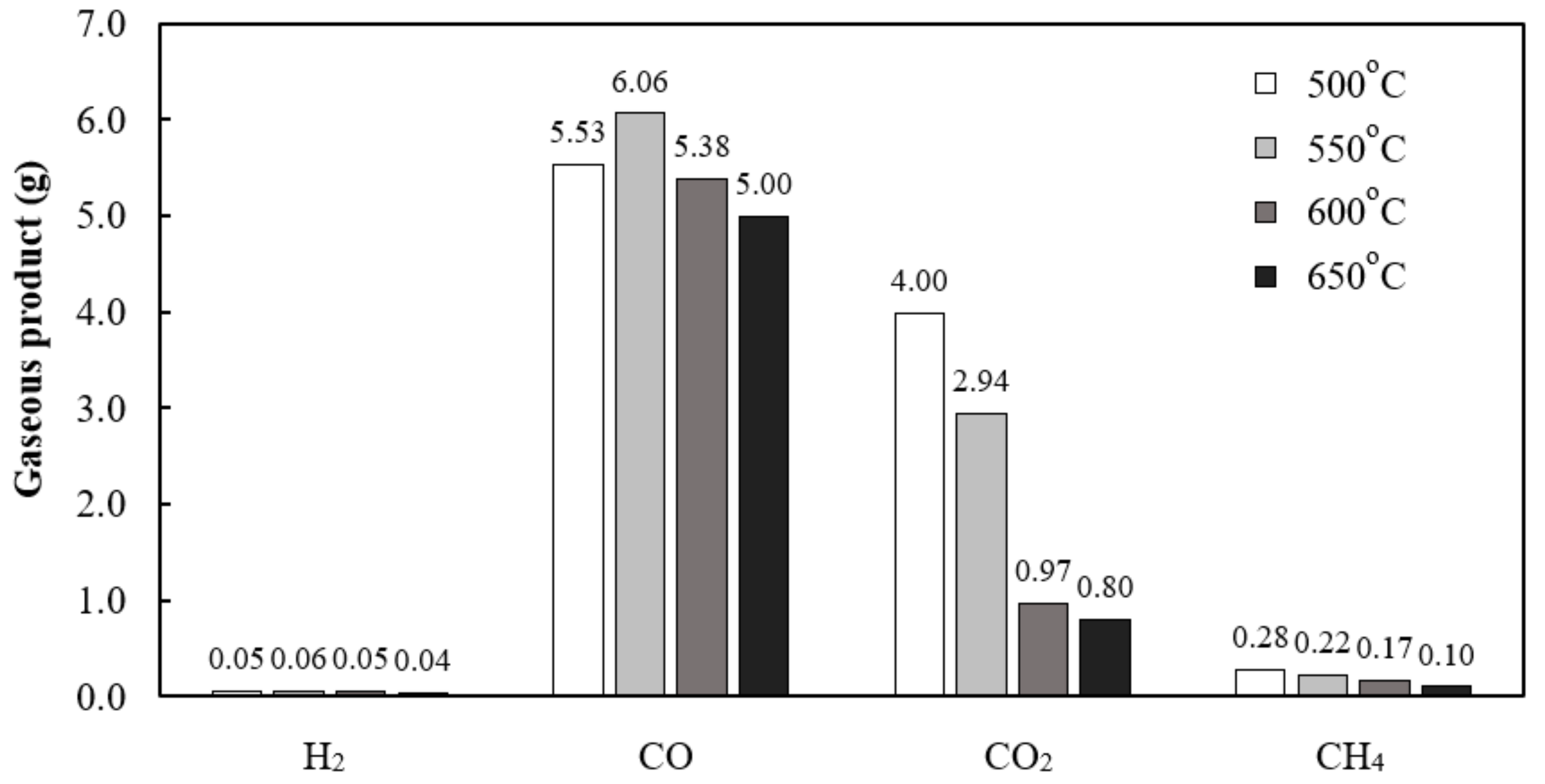
3.1. Effect of Gasification Temperature
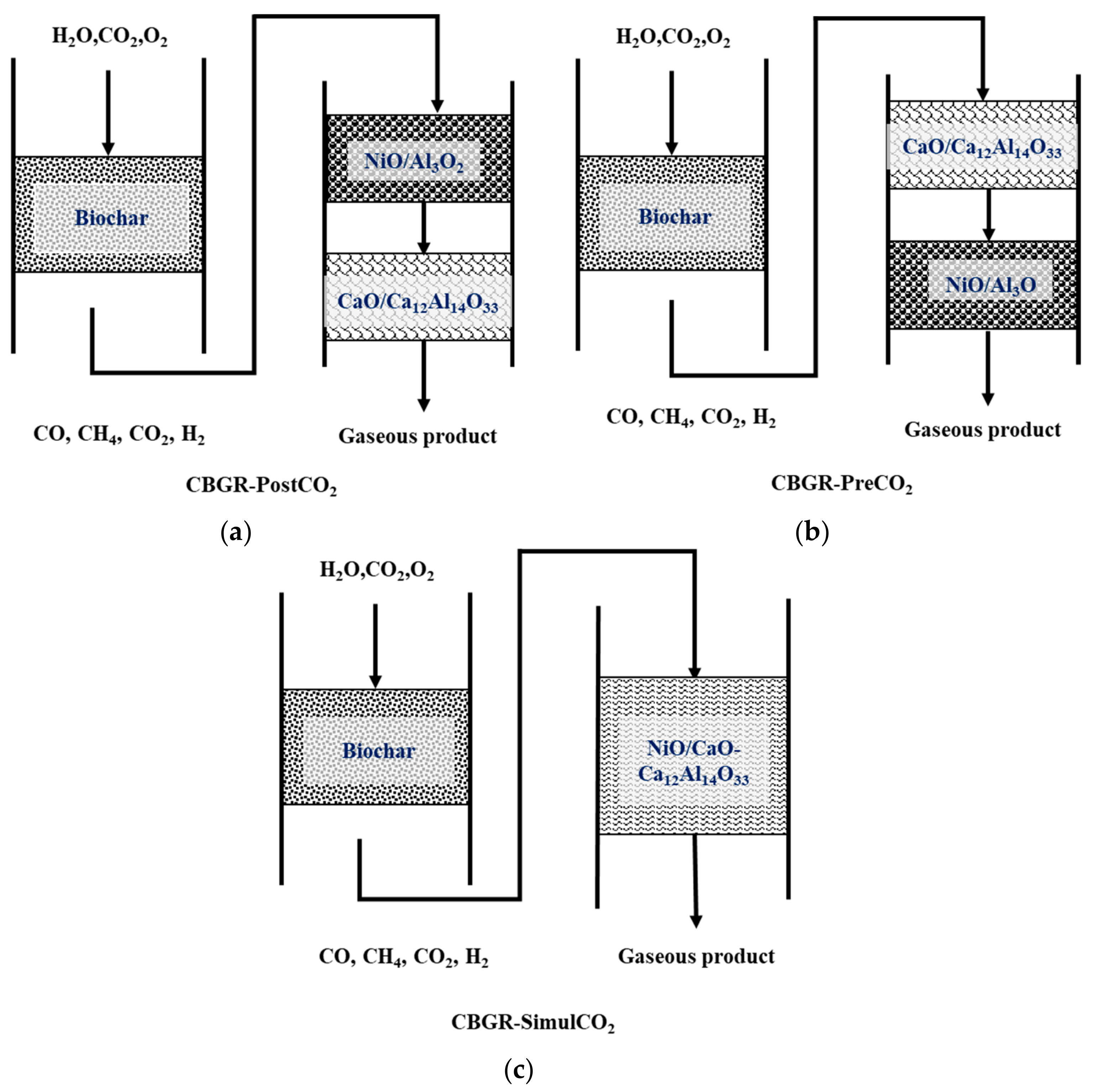
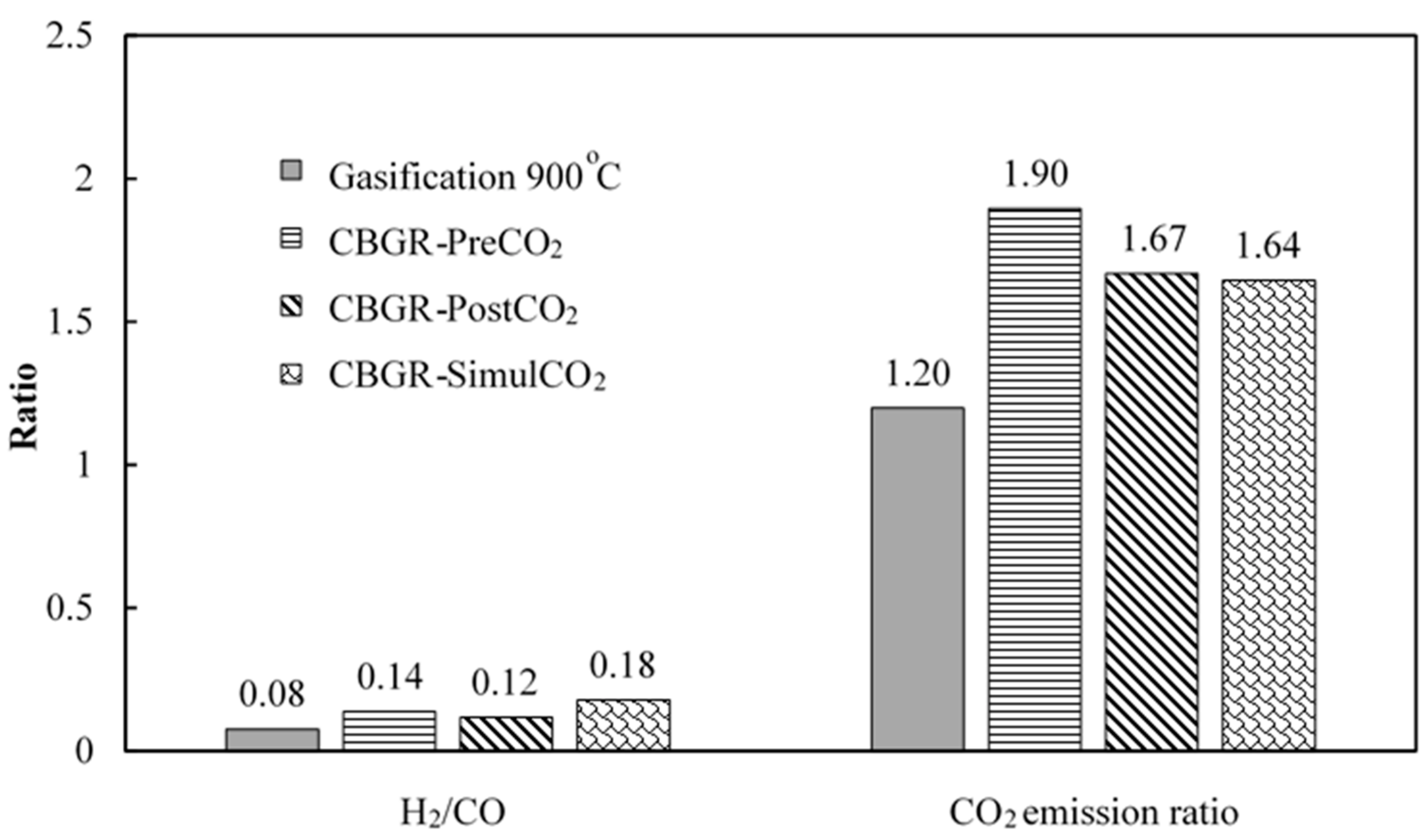
3.2. Effect of Combined Gasification and Reforming Reaction
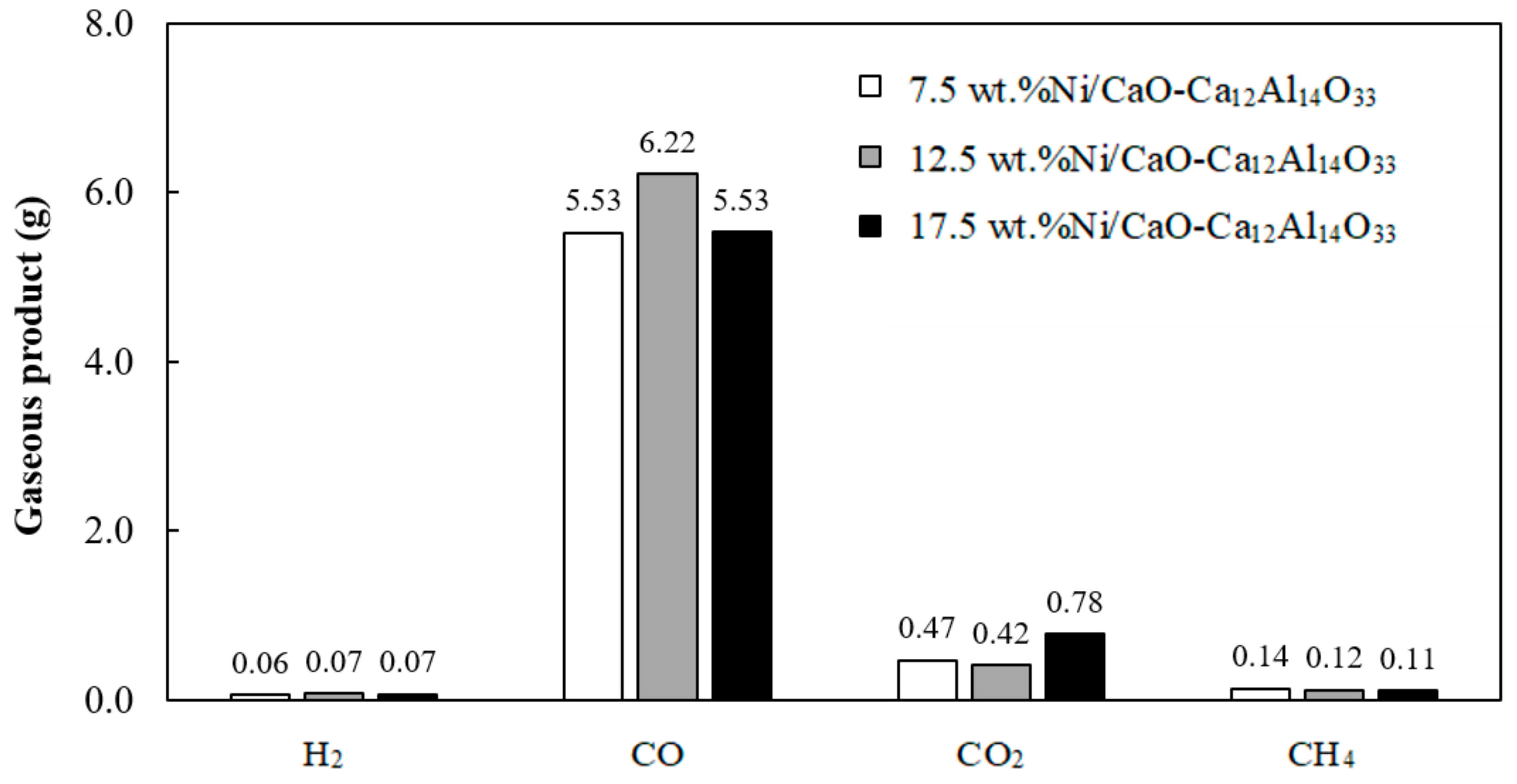
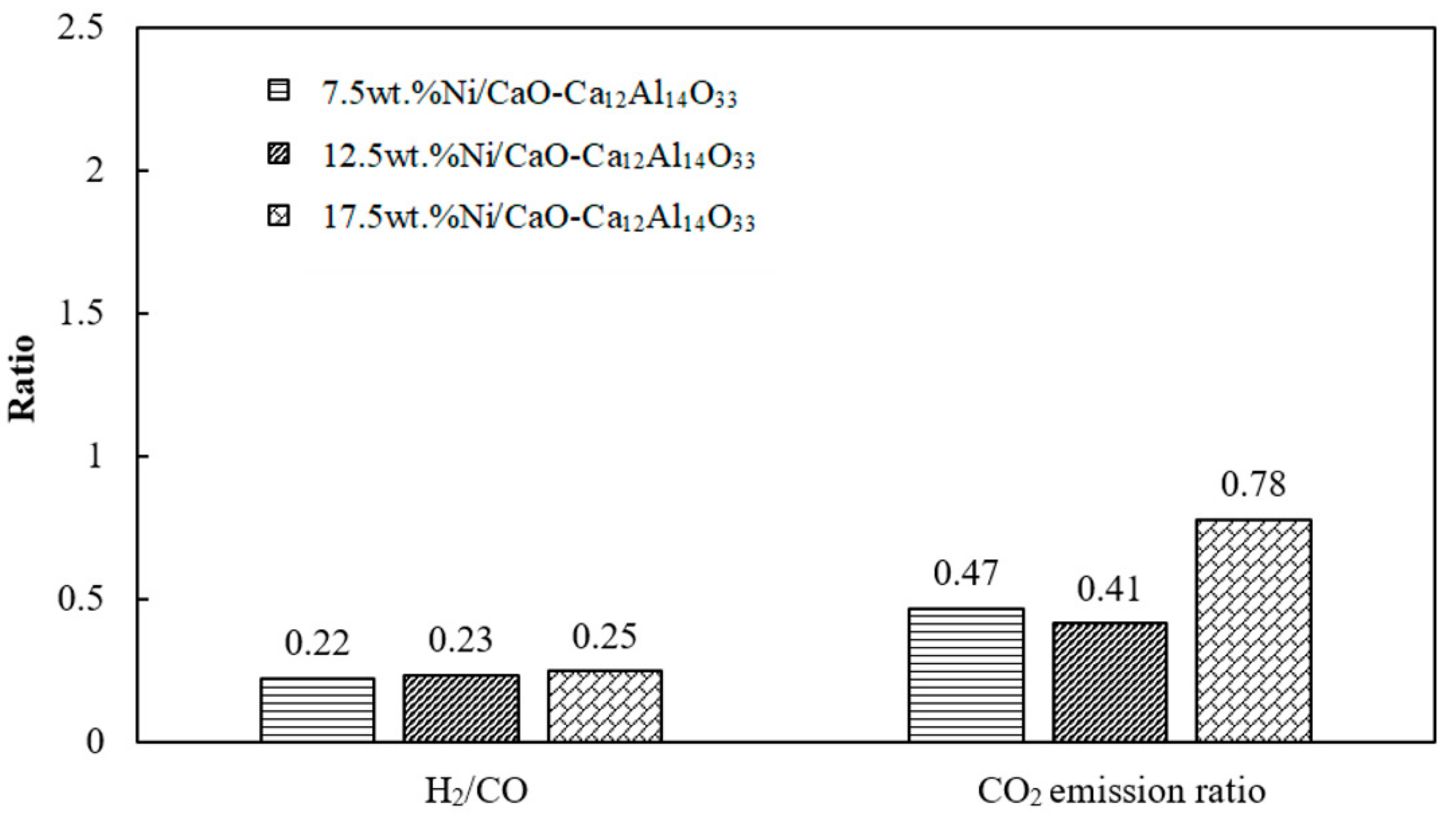
3.3. Effect of Catalyst Amount
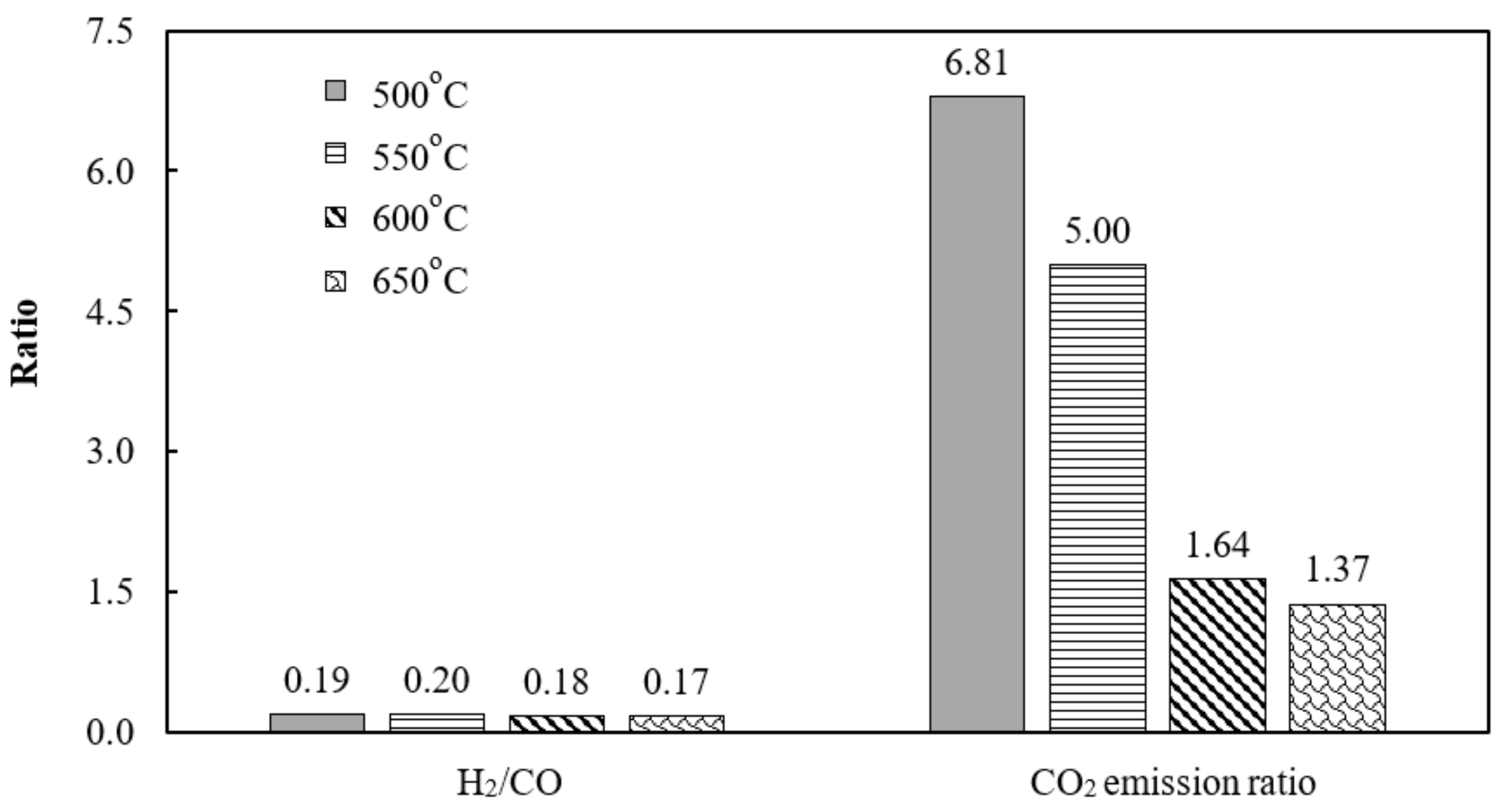
3.4. Effect of Sorption-Enhanced Water–Gas Shift (SEWGS) Temperature
3.5. Effect of Gasifying Agent
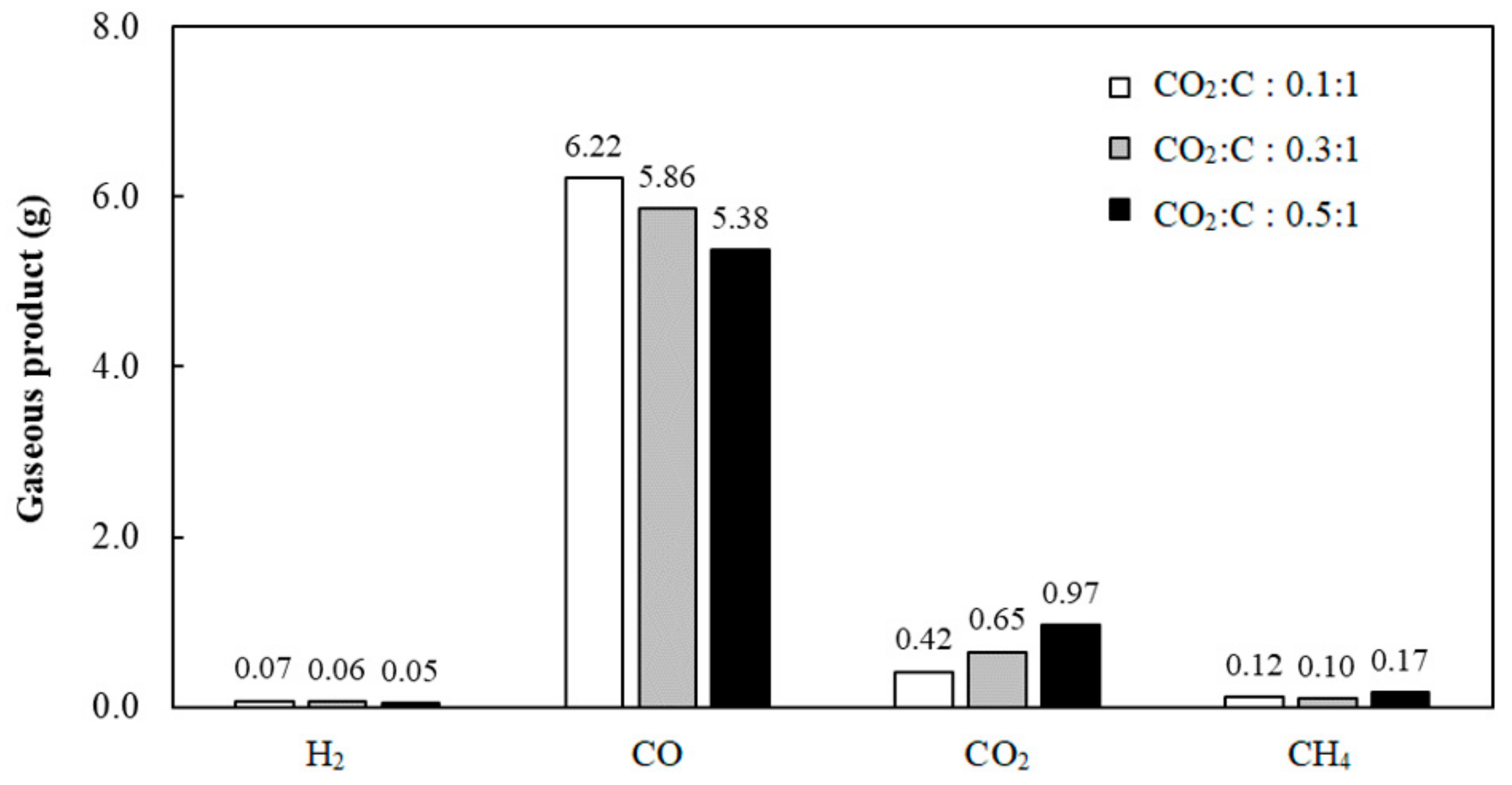
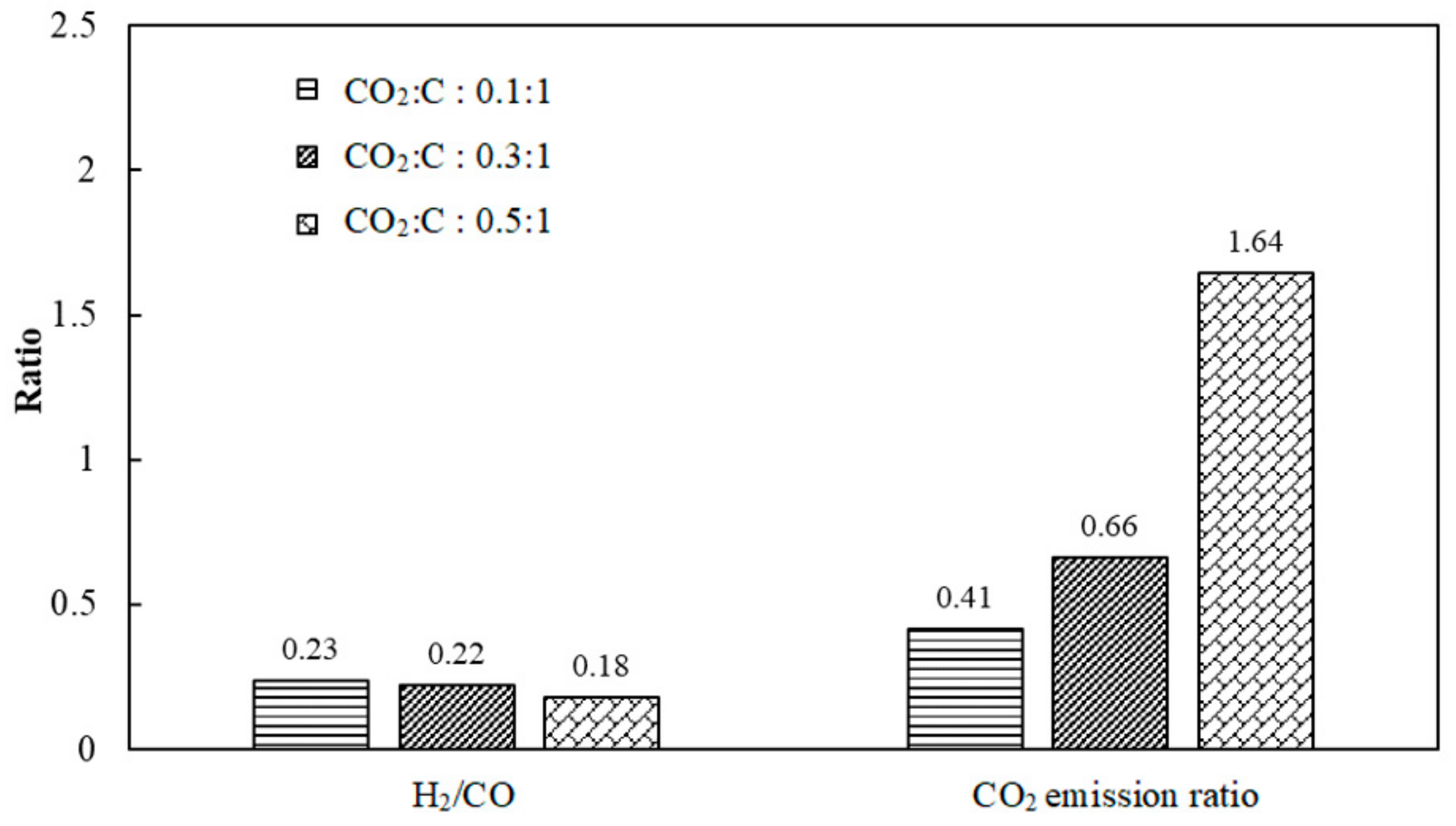
3.5.1. Effect of CO2 Feed
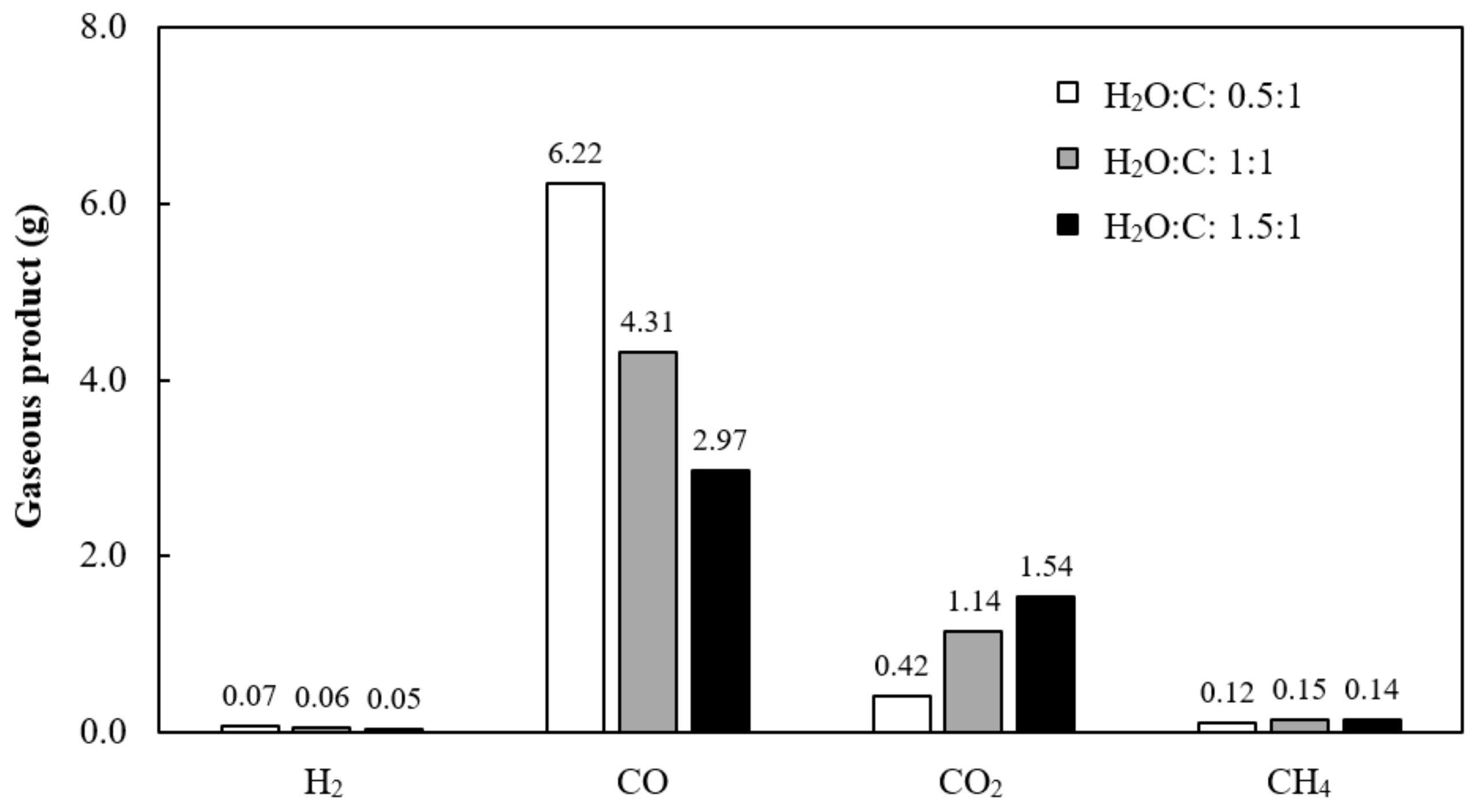
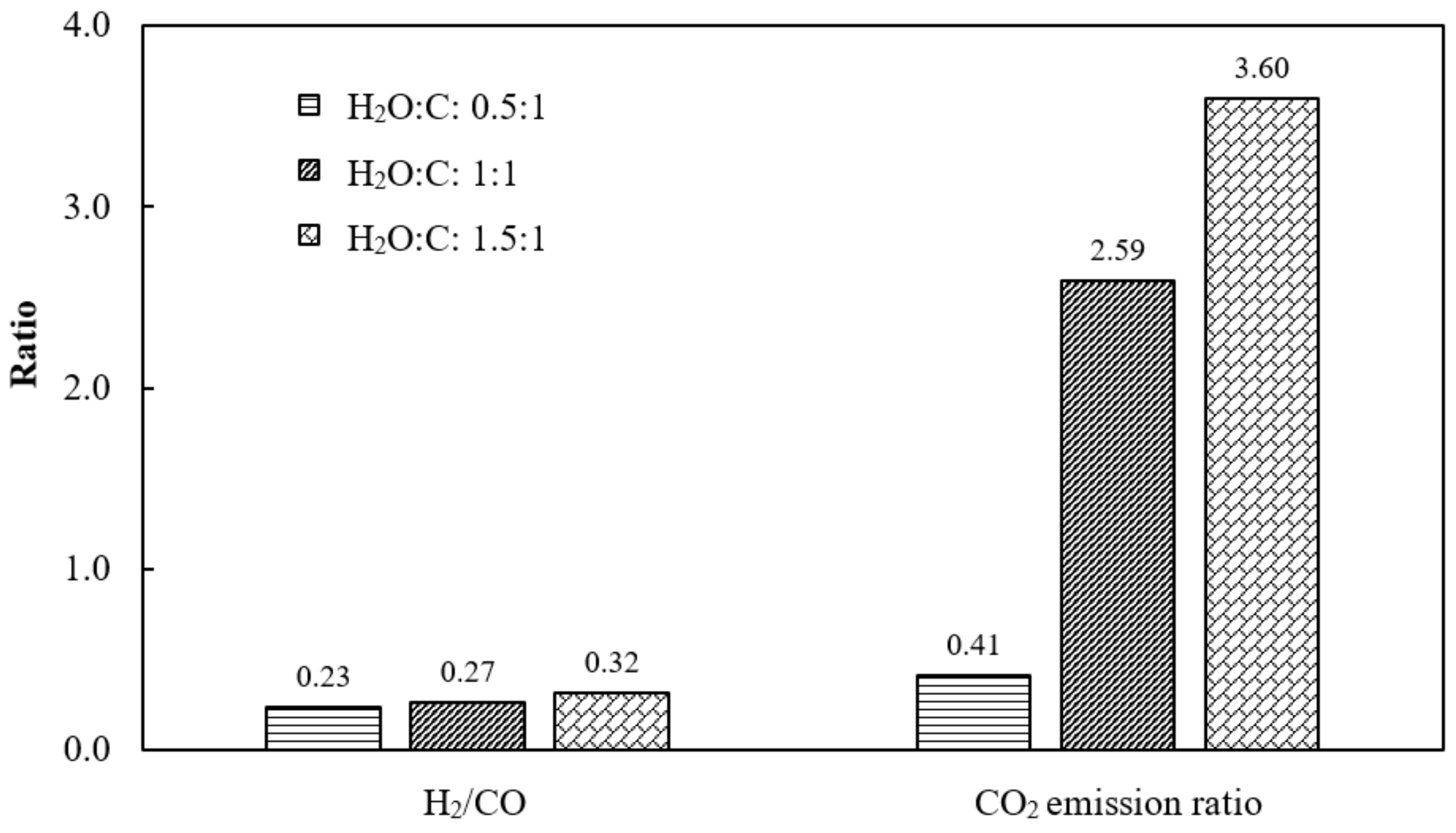
3.5.2. Effect of H2O Feed
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Rodrigues, M.; Faaij, A.P.C.; Walter, A. Technol-economic analysis of co-fired biomass integrated gasification/combined cycle systems with inclusion of economies of scale. Energy 2003, 28, 1229–1258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hamelinck, C.N.; Faaij, A.P.C.; den Uil, H.; Boerrigter, H. Production of FT transportation fuels from biomass; technical options, process analysis and optimization, and development potential. Energy 2004, 29, 1743–1771. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adams, T.A.; Hoseinzade, L.; Madabhushi, P.B.; Okeke, I.J. Comparison of CO2 capture approaches for fossil-based power generation: Review and Meta-study. Processes 2017, 5, 44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Acharya, B.; Dutta, A.; Basu, P. Chemical-looping gasification of biomass for hydrogen-enriched gas production with in-process carbon dioxide capture. Energy Fuels 2009, 23, 5077–5083. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pang, Y.; Hammer, T.; Müller, D.; Karl, J. Investigation of nonthermal plasma assisted charcoal gasification for production of hydrogen-rich syngas. Processes 2019, 7, 114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chaiwatanodom, P.; Vivanpatarakij, S.; Assabumrungrat, S. Thermodynamic analysis of biomass gasification with CO2 recycle for synthesis gas production. Appl. Energy 2014, 14, 10–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kraisornkachit, P.; Vivanpatarakit, S.; Amornraksa, S.; Simasatitkul, L.; Assabumrungrat, S. Performance evaluation of different combined systems of biochar gasifier, reformer and CO2 capture unit for synthesis gas production. Int. J. Hydrog. Energy 2016, 41, 13408–13418. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, Z.; Zhang, S.; Xie, D.; Yan, Y. A novel integrated process for hydrogen production from biomass. Int. J. Hydrog. Energy 2014, 39, 1274–1279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Waheed, Q.M.K.; Williams, P.T. Hydrogen production from high temperature pyrolysis/steam reforming of waste biomass: Rice husk, sugar cane bagasse, and wheat straw. Energy Fuels 2013, 27, 6695–6704. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, N.; Lia, A.; Quan, C.; Gao, F. Hydrogen-rich gas production from biomass steam gasification in an updraft fixed-bed gasifier combined with a porous ceramic reformer. Int. J. Hydrog. Energy 2008, 33, 5430–5438. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, S.; Zhu, J.; Chen, M.; Xin, W.; Yang, Z.; Kong, L. Hydrogen production via catalytic pyrolysis of biomass in a two-stage fixed bed reactor system. Int. J. Hydrog. Energy 2014, 39, 13128–13135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Waheed, Q.M.K.; Wu, C.; Williams, P.T. Hydrogen production from high temperature steam catalytic gasification of bio-char. J. Energy Inst. 2016, 89, 222–230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, C.; Liu, Q.; Ji, N.; Deng, S.; Zhao, J.; Li, Y.; Song, Y. Alternative pathways for efficient CO2 capture by hybrid processes—A review. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 2018, 82, 215–231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- La Villetta, M.; Costa, M.; Massarotti, N. Modelling approaches to biomass gasification: A review with emphasis on the stoichiometric method. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 2017, 74, 71–88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Indrawan, N.; Thapa, S.; Bhoi, P.R.; Huhnke, R.L.; Kumar, A. Engine power generation and emission performance of syngas generated from low-density biomass. Energy Convers. Manag. 2017, 148, 593–603. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ruiz, J.A.; Juárez, M.C.; Morales, M.P.; Muñoz, P.; Mendívil, M.A. Biomass gasification for electricity generation: Review of current technology barriers. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 2013, 18, 174–183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guohui, L.; Linjie, H.; Josephine, M.H. Comparison of reducibility and stability of alumina-supported Ni catalysts prepared by impregnation and co-precipitation. Appl. Catal. A 2006, 301, 16–24. [Google Scholar]
- Cong, L.; Ying, Z.; Ning, D.; Chuguang, Z. Enhanced cyclic stability of CO2 adsorption capacity of CaO-based sorbents using La2O3 or Ca12Al14O33 as additives. Korean J. Chem. Eng. 2011, 28, 1042–1046. [Google Scholar]
- Changjun, Z.; Zhiming, Z.; Cheng, Z.; Fang, X. Sol-gel-derived, CaZrO3-stabilized Ni/CaO-CaZrO3 bifunctional catalyst for sorption-enhanced steam methane reforming. Appl. Catal. B 2016, 196, 16–26. [Google Scholar]
- Howaniec, N.; Smolinski, A.; Stanczyk, K.; Pichlak, M. Steam co-gasification of coal and biomass derived chars with synergy effect as an innovative way of hydrogen-rich gas production. Int. J. Hydrog. Energy 2011, 36, 14455–14463. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pan, X.; Miaomiao, X.; Zhenmin, C.; Zhiming, Z. CO2 capture performance of CaO-based sorbents prepared by a pol−gel method. Ind. Eng. Chem. Res. 2013, 52, 12161–12169. [Google Scholar]
- Lu, H.; Reddy, E.P.; Smirniotis, P.G. Calcium oxide based sorbents for capture of carbon dioxide at high temperatures. Ind. Eng. Chem. Res. 2006, 45, 3944–3949. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, C.H.; Huang, C.H.; Tan, C.S. A review of CO2 capture by absorption and adsorption. Aerosol Air Qual. Res. 2012, 12, 745–769. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Butterman, H.C.; Castaldi, M.J. CO2 as a carbon neutral fuel source via enhanced biomass gasification. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2009, 43, 9030–9037. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kale, G.R.; Kulkarni, B.D.; Chavan, R.N. Combined gasification of lignite coal: Thermodynamic and application study. J. Taiwan Inst. Chem. Eng. 2013, 45, 163–173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Proximate (wt.%) | Ultimate (wt.%) | ||
|---|---|---|---|
| Moisture | 5.30 | C | 80.20 |
| Volatile matters | 36.26 | H | 2.83 |
| Fixed carbon | 56.40 | O (balance) | 16.39 |
| Ash | 2.05 | N | 0.58 |
| Sample | Surface Area (m2/g) | Pore Volume (cm3/g) | Pore Size (nm) |
|---|---|---|---|
| 12.5 wt.% NiO/Al2O3 | 59.1 | 0.150 | 0.09 |
| CaO-Ca12Al14O33 | 5.91 | 0.009 | 0.13 |
| 12.5 wt.% NiO/CaO-Ca12Al14O33 | 13.5 | 0.016 | 0.16 |
| Sample | Surface Area (m2/g) | Pore Volume (cm3/g) | Pore Size (nm) |
|---|---|---|---|
| 7.5 wt.% NiO/CaO-Ca12Al14O33 | 11.70 | 0.026 | 0.11 |
| 12.5 wt.% NiO/CaO-Ca12Al14O33 | 13.50 | 0.016 | 0.16 |
| 17.5 wt.% NiO/CaO-Ca12Al14O33 | 12.45 | 0.023 | 0.11 |
© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Chimpae, S.; Wongsakulphasatch, S.; Vivanpatarakij, S.; Glinrun, T.; Wiwatwongwana, F.; Maneeprakorn, W.; Assabumrungrat, S. Syngas Production from Combined Steam Gasification of Biochar and a Sorption-Enhanced Water–Gas Shift Reaction with the Utilization of CO2. Processes 2019, 7, 349. https://doi.org/10.3390/pr7060349
Chimpae S, Wongsakulphasatch S, Vivanpatarakij S, Glinrun T, Wiwatwongwana F, Maneeprakorn W, Assabumrungrat S. Syngas Production from Combined Steam Gasification of Biochar and a Sorption-Enhanced Water–Gas Shift Reaction with the Utilization of CO2. Processes. 2019; 7(6):349. https://doi.org/10.3390/pr7060349
Chicago/Turabian StyleChimpae, Supanida, Suwimol Wongsakulphasatch, Supawat Vivanpatarakij, Thongchai Glinrun, Fasai Wiwatwongwana, Weerakanya Maneeprakorn, and Suttichai Assabumrungrat. 2019. "Syngas Production from Combined Steam Gasification of Biochar and a Sorption-Enhanced Water–Gas Shift Reaction with the Utilization of CO2" Processes 7, no. 6: 349. https://doi.org/10.3390/pr7060349
APA StyleChimpae, S., Wongsakulphasatch, S., Vivanpatarakij, S., Glinrun, T., Wiwatwongwana, F., Maneeprakorn, W., & Assabumrungrat, S. (2019). Syngas Production from Combined Steam Gasification of Biochar and a Sorption-Enhanced Water–Gas Shift Reaction with the Utilization of CO2. Processes, 7(6), 349. https://doi.org/10.3390/pr7060349







