Abstract
The current study introduces a new technique for the analysis of uncertain systems and uncertain processes in geothermics/earth sciences. The method is the second synthetic grey relational analysis (SSGRA) model, which incorporated the advantages of both Deng’s GRA model and the bidirectional absolute GRA model. The SSGRA model has been earlier successfully applied in project management and healthcare systems. The current study is a pioneer in demonstrating the feasibility of the SSGRA model in a geothermal environment. In the current study, the model was used to determine the associations between thermal conductivity and petrophysical parameters in an Algerian reservoir. The results revealed that thermal conductivity is most strongly associated with porosity followed by density and permeability. Their relationships are also discussed. The study concludes with valuable insights about the model and its application in engineering and natural sciences especially when the system contains uncertainty, which may arise either due to insufficient data or uncertain relationships among the parameters associated with the system or its processes.
1. Introduction
Uncertainty is an everyday word in the industry as it surrounds all processes within industrial systems. Irrespective of the nature of a system, whether biological, chemical, geothermal, engineering or even socio-economical, the processes make the system contain uncertainty due to different reasons. Uncertainty in the process parameters and designs prompts the uncertainty in the system. However, managing the systems containing uncertainty is never a simple task for the system/processes analysts. Traditional approaches to handling such issues involve statistical techniques where processes are dealt with as stochastic processes, and larger sample data are encouraged. For example, process design and simulation seriously count on property data, which is subject to varying uncertainties [1]. Further, uncertainty may prevent process designs, supposed to be optimal, from successful attainment of specific process design objectives and making them unfeasible in the presence of unexpected and sudden changes in the system [2]. Unlike traditional approaches, “grey system theory looks at each stochastic variable as a grey quantity that varies within a fixed region and within a certain time frame, and each stochastic process as a grey process” [3] (p. 45). Further, its feasibility on small samples is well recognized in the literature [4,5]. In grey system theory, the concept of ‘grey’ has been borrowed from the engineering concept of grey-box, a partially structured box within black-box and white-box [6]. In this paradigm, greyness implies incompleteness, thus a grey quantity or grey parameter is a parameter that is between two extreme parameters and the grey process is a process associated with these grey parameters.
Like fuzzy theory, grey system theory (GST) is a feasible mathematical approach for systems analysis described by imperfect information [7] (p. 103). In engineering and technical literature, Deng’s grey relational analysis (GRA) model is a popular technique for multi-objective optimization and evaluation of process parameters. Hussain et al. [8] used the GRA model coupled with the Taguchi method for the optimization of powder metallurgy processing parameters of the Al2O3/Cu composite. Maniyar and Ingole [9] used Taguchi-based GRA method for the multi-response optimization of electrical discharge machining process parameters for aluminum hybrid composites. Chauhan et al. [10] used the GRA model coupled with the Taguchi method for the optimization of the micromachining process parameters. Gandhi and Rahul [11] used the GRA model coupled with the Taguchi method for the optimization of process parameters. Umamaheswarrao et al. [12] used GRA coupled with principle component analysis (PCA) multi-objective optimization of process parameters for the hard turning of AISI 52100 steel. Aslantas et al. [13] used a Taguchi-based GRA method for the optimization of process parameters for micro-milling of Ti-6Al-4V alloy. Luo et al. [14] used AHP integrated GRA model to analyze the integrated cascade utilization system of waste geothermal water. Liu et al. [15] used the GRA model to study the relationships between some parameters and to study the degree of the relative importance of the influencing factors about fractal dimensions of superfine pulverized coal particles. These are just a few cases from a pool of studies involving GRA model or its variants. One of the characteristics that distinguish GRA from conventional statistical techniques is that this method enables evaluation of quantitative and qualitative relationships between parameters characterized by a comparatively insufficient amount of data [16].
The first GRA model was proposed by Deng Julong, the founder of grey system theory (GST), in the 1980s and it was followed by the development of other GRA models by different scholars. Dong et al. [17] and Delcea et al. [18] highlighted several succeeding models. However, Deng’s GRA model is still the most influential one among all GRA models [3] (p. 68). Initially, it was popular in engineering fields, having seen its application in other fields during nearly 40 years of its development as well [19]. Another popular GRA model was the one proposed by Sifeng Liu, and its simplified version can be found in References [20,21]. It is known as the absolute GRA model, also called the absolute degree grey incidence analysis (ADGIA) model. If Deng’s GRA model reveals partial closeness/proximity, then absolute GRA reveals integral closeness/proximity between two data sequences [17,22]. On the other hand, the second synthetic GRA aims to reveal a more comprehensive closeness (inclusive proximity), while incorporating the advantages of both Deng’s GRA and absolute GRA models [6,22]. The fundamental concept of GRA is to gauge the relational degree of data sequences in line with the similarity between their geometric shapes of the curves of the data sequences [23]. In other words, the basic idea of GRA models is to determine the proximity/closeness between two data sequences representing two curves through different perspectives. These perspectives distinguish one GRA model from the other.
In light of above the discussion, the current study attempted to investigate the relations between thermal conductivity and three parameters; density, porosity and permeability associated with the Hamra Quartzites reservoir of Algeria. The first study, which was a preliminary study on the case, was done by Zerrouki et al. [24]. Preliminary studies are usually incomplete and provide a lot of grey areas for future researchers that need to be reinvestigated. The current study uses a novel method, which has never been used in earth sciences or geothermic studies before, to better investigate the relationship between the thermal conductivity of Hamra quartzites and three petrophysical parameters.
The rest of the study is organized in the following way. After the introduction, a literature review of the important concepts is presented. These concepts are related to the four factors under the study and the grey relational analysis models that the current study intends to use. Afterward, the research methodology of the study is discussed. This is followed by the data analysis and results while discussing and comparing the results obtained through novel approaches with the results earlier obtained by Zerrouki et al. [24]. In the last part of the paper, conclusions and recommendations are presented.
2. Literature Review
2.1. Grey Relational Analysis
Grey relational analysis (GRA), grey incidence analysis (GIA) and grey correlation analysis are three names for the same phenomenon; first reported by Javed in 2018 [6,22,25,26]. Scholars from engineering fields are more familiar with the term “GRA” [6] and this convention has been followed throughout the current study. GRA methods constitute one of the core areas of grey system theory (GST), which was proposed by Chinese scientist, Deng Julong, in 1982 to manage the uncertain systems containing poor information. GST belongs to the family of uncertainty theories, where other family members are fuzzy theory, interval theory, rough set theory, so on [27,28]. However, grey system theory, guided by its own distinct approaches, deals with uncertainty unlike other uncertainty theories [29,30]. GST categorizes all systems of the world into three classes; black, white and grey [31]. A black system implies a system for which no information is available and the white system is the system for which the entire information is available. Thus, a grey system becomes a system with partially known and partially unknown information [32]. The key strength of GST and its models is their predictions and decision making using small sample size, poor data and incomplete information [33,34,35,36]. The GRA models strive to understand the uncertain relations among the parameters associated with the grey systems. GRA is not only an important part of GST, but also the cornerstone of the grey system analysis, modeling, prediction, and decision making [37]. GRA models have been used for many years to analyze the relationships between system factors [33]. The underlying notion of GRA is that the closeness of a relationship between the system parameters is predicted based on the level of similarity of the geometrical pattern of the data sequences representing those parameters [38]. This closeness is also known as proximity in the literature [6,39]. Here, a misconception in the literature needs to be addressed. Even though Zhang et al. [37] argued that GRA models (e.g., Deng’s GRA and absolute GRA) “can only be applied to times series”, the influential work by Liu et al. [3] (p. 69) maintained that a series of observations may or may not be over time. It can be observations, experiments, years, indexes, etc. The work of Javed [6] supports this notion, so does the current study.
The concept of GRA was pioneered by Deng in the 1980s. The foundation of Deng’s GRA model rests on the estimation of a degree of proximity, grey relational grade (GRG). According to Javed [6], GRG is “a degree of partial proximity (or, partial closeness) between two curves and is estimated by taking the average of the grey relational coefficients” at each point in a data sequence. Deng’s GRA model measures the trend similarity of system factors according to the distance between corresponding points of the sequences [39]. Later, in 1991, Liu Sifeng proposed another degree, absolute GRG, and laid the foundation of the absolute degree grey incidence analysis model, also called the absolute GRA model [39]. A detailed discussion on the absolute GRA model can be found in Liu et al. [3,20,21]. According to Javed [6], absolute GRG is “a degree of integral proximity between two curves represented by two data sequences and is estimated by considering the integral perspective on the proximity (closeness) between the two curves”.
Deng’s GRG and absolute GRG are mutually exclusive thus they can produce different orders/ranks for the parameters under study. However, this dilemma failed to seek the attention of scholars [6]. For instance, according to Arce et al. [16], grey relational grade (GRG) indicates the “degree of correlation” between the reference data sequence and the data sequences to be compared, which can also be considered the “degree of influence” of the comparison sequence on the reference sequence. In a statistical paradigm, correlation and influence have totally different meanings. Correlation simply means two factors are correlated with no information about whether they are influencing each other or not. Further, in the works of Tung and Lee [40] and Yu et al. [41], absolute GRG serves as a correlational measure. Javed [6] discussed a number of studies that lead him to argue that the real purpose of [Deng’s] GRG and absolute GRG is not clear in the literature. Meanwhile, Javed et al. [4] tried resolving this dilemma by stating “in a nutshell, Deng’s GRA model gives the measure of influence that one variable represented by a data sequence exerts on the other and absolute GRA model gives the measure of association between them.” Here, the measure of association can be loosely translated as a measure of correlation [6]. Considering the fact that the change in the order of sequences can affect the value of GRG but not of absolute GRG, this proposal can be supported as it is hard to imagine, correlation can vary if two variables switch their positions. Acknowledging this dilemma in the literature where two different versions of GRG were being used for comparison purposes, Javed [6] proposed the “second synthetic GRG” and demonstrated its feasibility through an application in a project management environment. To date, the associated model, the second synthetic GRA (SSGRA) model, has been successfully tested and applied in healthcare systems by Javed and colleagues [22,25], in construction project management environment by Sheikh et al. [42] and in supply chain environment by Diba and Xie [43].
Building upon the work of Liu et al. [3], Javed and Liu [22] argued that Deng’s GRA methodology is driven by the grey relational coefficient (GRC) of particular points while the absolute GRA model is governed by an integral (rather comprehensive) perspective. Thus, the closeness or proximity, as reported by Deng’s GRG, can be referred to as “partial proximity” (or partial closeness) and the closeness or proximity as reported by absolute GRG can be referred to as “integral proximity” (or integral closeness) [6]. The work of Dong et al. [17] presents a theorem that proves “the absolute degree of grey incidence satisfies the integral closeness of Deng’s grey incidence axiom, but does not satisfy the partial closeness.” This theorem justified the understanding on which the second synthetic GRG was proposed as a measure of “inclusive proximity” that synthesizes both partial proximity and integral proximity of grey relation (grey incidence). The theorem and its proof have been reproduced below.
Theorem 1.
The absolute GRG satisfies the integral proximity/closeness of Deng’s grey relational axiom but does not satisfy the partial proximity/closeness [17].
Proof
[17]. The partial proximity of Deng’s grey relational axiom pertains to the grey relational grade (GRG) as estimated in line with the distance between the corresponding points of the data sequences i.e., the smaller the distance between the reference sequence X0 and the comparison sequence Xi at point k, the higher the grey relational coefficient (GRC) at point k. From the definition of Absolute GRG, when
then = 1, where and are the zero-starting images of the sequences X0 and Xi, respectively. Due to the positive and negative offsets of the integral operation, as long as oscillates around and the area of the parts of located above equals to that of the parts of located beneath , = 1 can be satisfied. In fact, the proximity of Deng’s grey relational axiom pertains to GRC between the points of the data sequences, whereas the absolute GRG is based on the integral (rather comprehensive) perspective. Thus, the absolute GRG, which predicts similarity based on proximity, is valid in the situations where zero-starting point sequences do not cross each other or do not affect the degree of grey relation after the intersection. For further discussion on this theorem, the readers are directed to Dong et al. [17]. □
2.2. Thermal Conductivity and Petrophysical Parameters
Thermal conductivity is an important physical property of rocks that describes how well, but not how fast, heat is conducted through a material [44]. Thermal conductivity (TC) is a property that can be determined by different measuring methods. It can be defined as the capability of a material to transfer heat with respect to a temperature gradient. It is not only an essential criterion to evaluate the heat transfer in rocks but also has applications in the geoscientific and geotechnical field [45]. Thermal conductivity results in the heat accumulation and determines where and how much heat flows resulting from the temperature differences in rocks [46]. Conduction and convection are the two fundamental phenomena that determine the heat transfer in the rock formation. According to Fourier’s law, rocks with low-porous and high density possess higher conduction than convention. However, in rocks such as porous sediments are dominated by convection heat transfer. Different rocks have a different heterogeneous mineral composition, so it shows significant differences in the thermal conductivity. Different groups of rocks show the variability of thermal conductivity in the range of 2 to 4 Wm−1K−1 [47]. Two very important parameters associated with a material’s thermal conductivity are porosity and density. The porosity describes the fraction of void space in the rock, where the voids may contain some fluid (e.g., air, water etc.) [48]. The rock density is defined as the quotient of the mass and the volume of the material [24] i.e., mass per unit volume. Permeability of a material is another property that may not directly be associated to thermal conductivity but is closely related to porosity as both permeability and porosity intrinsically depend on the microstructure of pores in porous materials [49]. These properties frequently find their mention in the geothermic and earth sciences literature.
The relationships between thermal conductivity (TC) and the influencing parameters/properties have been studied by numerous scholars in the past. Somerton [50] is considered as one of the pioneers to study the correlation of TC with petrophysical parameters. He found that variation in temperature significantly affects the thermal diffusivity of rocks. In later years, several scholars [51,52,53,54,55,56,57] studied the effect of density, rock texture, permeability, fluid saturation, mineral composition and porosity of rocks on thermal conductivity. For instance, Barry-Macaulay et al. [54] reported the variation in TC of soils and rocks with the variation in density. Duchkov et al. [55] revealed a stable linear relationship between the thermal conductivity of the dry samples of Mesozoic sedimentary rocks and, porosity and permeability. Haffen et al. [58] studied the correlation of TC and porosity maps for granite and sandstone. Their study developed the porosity maps for air and water saturated conditions. Asadi et al. [57] and Ouali [59] stressed the significant role of porosity in the thermal conductivity of materials. Duchkov et al. [60] reported that TC of sedimentary rocks is determined by the composition of the mineral skeleton, porosity and permeability of the rock, as well as the type of fluid that fills the pores. Literature suggests that TC of rocks is influenced, directly or indirectly and with varying degree of extents, by various kinds of petrophysical parameters, which are highlighted in Figure 1.
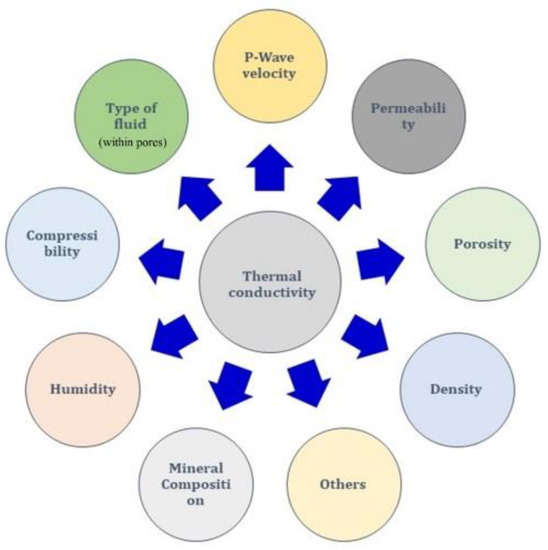
Figure 1.
Parameters associated with the thermal conductivity of rocks.
Finding an association between two continuous variables is usually performed by a correlation method. Finding a correlation is essential to reduce the range of uncertainty. It helps us to understand the causal effects, economic benefits and helps us to screen the parameter. There is a dire need to find an accurate correlation between TC and other parameters, especially relatively less explored quartzite. The literature suggests thermal conductivity is inversely and significantly related to porosity [59,60,61,62]. Duchov et al. [60] reported this relationship to be linear while Ouali [59] reported a harmonic average relationship. Since porosity and permeability are known to have a positive correlation [48,63,64,65] it is very plausible to assume that thermal conductivity and permeability are likely to have inverse relationship as well. This can be confirmed from Duchkov et al. [59] who reported inverse linear relation between thermal conductivity and permeability. However, Mielke et al. [66] failed to identify a consistent correlation between thermal conductivity and permeability. Also, since porosity and density are known to be inversely related [46,48,60] it is very plausible to assume that thermal conductivity and density are likely to be positively (directly) related. This can be confirmed from the studies [60,61,67] that reported a positive correlation between thermal conductivity and density. To our surprise, among all the literature reviewed by us, only Zerrouki et al. [24], through one of their figures, reported an inverse relation between thermal conductivity and density. To confirm (or disconfirm) their results through a different approach the current study provided a promising avenue where GRA models were used to reevaluate the relationships. Based to the authentic literature, it can be emphasized that thermal conductivity is a function of density, porosity and permeability while its relation to density is positive and to porosity, and thus to permeability, is inverse. This can be represented as
or,
where, λ, D, and K represent thermal conductivity, density, porosity and permeability, respectively.
3. Definitions
3.1. Definition I: Grey Data Sequence
Grey data sequence [6,31] is an array of data values (xi) available for grey data analysis. It is generally represented as
where “i” implies the number of sequences (i.e., i = 1, 2, …, k), “n” implies the total number of grey numbers in the ith sequence, “xi” represent data values in the sequence Xi and “k” implies an index of the last sequence.
Xi = (xi(1), xi(2), …, xi(n))
3.2. Definition II: Mirror of Grey Data Sequence
If Xi = (xi(1), xi(2), …, xi(n)) represents a grey data sequence then its mirror is given by [6,31]
where represents the mirror sequence of Xi.
3.3. Definition-III: Grey Relation
Grey relations refer to the uncertain relations among things, among elements of a system, or among behaviors [7] (p. 104). In other words, it defines the relationships among the parameters of a grey system. It can also be referred to as a proximity or closeness between the grey data sequences representing different variables/factors/parameters associated with a system [6,31].
3.4. Definition-IV: Grey Relational Grade
Grey relational grade (GRG: γ0i) [6], or Deng’s degree of grey incidence, is a degree of partial proximity between two curves and is estimated by taking the average of the grey relational coefficients (γ0i(k)) at each point k. GRG is the measure of closeness of geometrical distance between two curves [17]. It has also been reported as a measure of influence that the comparison sequence exerts on the reference sequence [4].
3.5. Definition-V: Absolute Grey Relational Grade
Absolute GRG [6], or absolute degree of grey incidence, is a degree of integral proximity between two curves represented by two data sequences and is estimated by considering the integral perspective on the proximity (closeness) between the two curves. Unlike Deng’s GRG, absolute GRG is independent of the order of the sequences thus it is more likely to yield a measure of association (or correlation) [4,6]. If the absolute GRG can reveal both the degree of integral proximity and the direction of integral proximity, then it would be referred as bidirectional absolute GRG and would be estimated following the steps mentioned by Javed and Liu [31].
3.6. Definition-VI: Second Synthetic Grey Relational Grade
Second synthetic GRG [6], or the second synthetic degree of grey incidence, is a degree of inclusive proximity between two curves represented by two data sequences and is estimated by considering both partial and integral perspectives of the proximity (closeness) between the two curves.
3.7. Definition-VII: Zero-Starting Point Image
Let Xi = (xi(1), xi(2), …, xi(n)) be the data sequence of a system’s behavior and D1 the sequence operator which satisfies XiD1 = (xi(1)d1, xi(2)d1, …, xi(n)d1) and xi(k)d1 = xi(k)d1 − xi(1); k = 1, 2, …, n. Then D1 is referred to as a zero-starting point operator and XiD1 is the zero-starting point image of Xi. XiD1 is often written as XiD1 = Xi0 = (xi0(1), xi0(2), …, xi0(n)) [3] (p. 77), [22].
3.8. Definition-VIII: |si|, |sj|, and |si sj|
Following Liu et al. [3], as reported in [22], assume that Xi and Xj are 1-time-interval sequences of the same length, and the following are zero-starting point images of Xi and Xj:
Then,
Xi0 = (xi0(1), xi0(2), …, xi0(n))
Xj0 = (xj0(1), xj0(2), …, xj0(n)).
3.9. Definition-IX: Initialing Operator
Let Xi = (xi(1), xi(2), …, xi(n)) be the data sequence representing the behavior of a parameter Xi, and D2 as sequence operator such that XiD2 = (xi(1)d2, xi(2)d2, …, xi(n)d2), where:
Here, D2 is referred to as the Initialing Operator and XiD2 is its image, called the initial image of Xi [3] (p.70).
3.10. Definition-X: Averaging Operator
Let Xi = (xi(1), xi(2), …, xi(n)) be the data sequence representing the behavior of a parameter Xi, and D3 as sequence operator such that XiD3= (xi(1)d3, xi(2)d3, …, xi(n)d3), where:
here, D3 is referred to as the averaging operator and XiD3 is its image, called the average image of Xi [3] (p.70).
3.11. Definition-XI: Minimizing Operator
For a grey data sequence Xi = (xi(1), xi(2), …, xi(n)), D4 is said to be the minimizing operator if
where,
for all values of k = 1, 2, …, n [68].
XiD4 = (xi(1)d4, xi(2)d4, …, xi(n)d4)
3.12. Definition-XII: Grey Incidence Direction
The direction of grey incidence [31] implies the nature of the relationship (positive/negative) between the data sequences. Grey incidence direction is represented by +/− sign in the bidirectional absolute grey relational grade (ε ±). The positive sign implies directly proportional relation and the negative sign implies inversely proportional relation.
3.13. Definition-XIII: Javed’s Grey Incidence Scale
The Javed’s Grey Incidence (JGI) [31] scale is a distribution of the range of the bidirectional absolute grey relational grades (ε ±) into five levels depending on the strength of association between the sequences. The scale tells the extent of the strength of the grey incidence relationship between the sequences. The JGI scale is shown in Table 1.

Table 1.
The Javed’s grey incidence (JGI) scale [31].
3.14. Definition-XIV: Javed’s Confidence Level Scale
The Javed’s confidence level (JCL) [31] scale is the scale that guides a researcher in manifesting the extent of trust in the results produced from the BAGRA model. If Δ is the difference, named as the ε-Difference, between and then the JCL scale will be defined as shown in Table 2. When the confidence level (JCL) is low, then the model should be applied to new data sequences.

Table 2.
The Javed’s confidence level (JCL) scale [31].
where,
0 < Δn ≤ εmin; n = 1, 2, 3, … i
εmin < ε ≤ εmax; εmin = ½; εmax = 1.
The JCL scale tells the extent of confidence (or certainty) in the reliability of the grey direction among the data sequences representing the grey system parameters. According to the JCL scale, “confidence in the results increases with the increase in |Δ|”. Further, in a nutshell, ε gives the strength of proximity, ε ± gives strength of proximity (along with positive or negative direction), Δ gives direction (positive, negative or uncertain), and |Δ| yields the level of uncertainty in the direction of proximity.
4. Methods
4.1. Data Collection
Four factors were involved in the study; thermal conductivity (TC) and three petrophysical parameters (rock density, inferred porosity (so-called Helium-porosity) and permeability). Experimental data concerning these factors were collected from a recent study by Zerrouki et al. [24]. Their data was associated with the Hamra Quartzites reservoir in Hassi Messaoud oil field of Algeria. The study of Zerrouki et al. [24] contains 28 samples or rock grains; 15 cemented and 13 uncemented grain sets. For this classification, they deployed plane polarized light microscopy analysis.
4.2. Data Analysis Methods
To determine the partial proximity among the factors, Deng’s GRA model (as introduced by Liu, Yang and Forrest, 2016) was executed. To determine the integral proximity among the factors, the bidirectional absolute GRA model was applied following the steps mentioned in Javed and Liu [54]. To get an overall picture, i.e., to determine the inclusive proximity, the second synthetic GRA model was applied following the steps mentioned in Javed and Liu [22] and Javed et al. [25]. In the present study, Deng’s GRG and Absolute GRG values were calculated using grey systems modeling software (by NUAA) where the data, after being normalized through the minimizing operator (definition-XI), were used. Further, bidirectional absolute GRG and second synthetic GRG values were calculated through Microsoft Excel. In the succeeding sections, the algorithms associated with the methods are discussed.
4.2.1. Deng’s GRA Method
The computing procedures to calculate Deng’s grey relational grade (GRG) for two data sequences X0 and X1 are shown in Javed et al. [4,22] and have been reproduced below:
- (a)
- Calculating the initial image (or average image) of X0 and Xi, i = 1, 2, …, m,whereXi’ = Xi/xi(1) = (xi’(1), xi’(2), …, xi’(n)); i = 0, 1, 2, …, m.
- (b)
- Computing the difference sequences of X0’ and Xi’, i = 1, 2, …, m, asΔi(k) = |x0’(k) − xi’(k)|, Δ = (Δi(1), Δi(2), …, Δi(n)), i = 1, 2, …, m.
- (c)
- Finding the maximum and minimum differencesM = maxi maxk Δi(k)m = mini mink Δi(k).
- (d)
- Calculating grey relational coefficients bywhere ξ is the distinguishing coefficient and in the literature its value is usually assumed to be 0.5.
- (e)
- Computing the grey relational grade (Deng’s degree of grey incidence) by
In the abovementioned formula, 1/n can be replaced by the weights wk, as shown in the formula below, if the effect of each factor on the system is not same, where Σwk = 1.
In short, 1/n implies the weights of criteria are equally distributed and wk implies weights are unequally distributed, which is a usual case in real life problems. Both forms of GRA models are comparable and an important discussion on them can be found in Javed et al. [26]. In the case discussed in the current study, the first form of Deng’s GRA model can be conveniently applied as all independent variables are equally weighted.
4.2.2. Bidirectional Absolute GRA Method
Let us say Xi and Xj are two data sequences representing an uncertain system. Then the algorithm to calculate the bidirectional absolute GRG is listed below.
- (a)
- Prepare the data sequences and their mirror sequences (see definitions I and II)
- (b)
- Normalize the data sequences, using the minimizing operator (see definition-XI), to bring the range of data values in each sequence within 0 and 1.
- (c)
- Calculate the zero-starting point images of the data sequences (see definition-VII).
- (d)
- Calculate |si|, |sj| and |sj – si| (see definition-VIII).
- (e)
- Calculate Absolute GRG (ε) by [3]
- (f)
- Calculate the bidirectional absolute GRG (ε ±), given by [6,54]
Here “” represents an inverse direction of grey relation (i.e., an inverse relationship) and “+” represents the direct relationship, and the measure with which either of these signs is attached represents the strengths of the grey relation (i.e., degree of integral proximity). To interpret the results, the JGI scale (definition-XIII) and JCL scale (definition-XIV) may be needed. Details of these scales and the bidirectional absolute GRG can be found in References [6,31].
4.2.3. Second Synthetic GRA Method
The second synthetic GRA model is a way to determine SSGRG and the steps involved are listed below.
- (a)
- Calculate Deng’s GRG.
- (b)
- Calculate the bidirectional absolute GRG (or absolute GRG).
- (c)
- Calculate the second synthetic GRG given by [6,22,25]:where ρ represents the second synthetic GRG, ε represents the absolute GRG and γ represents the GRG between the grey data sequences Xi and Xj [25]. Considering θ = 0.5 is suggested when the decision maker wants a comprehensive ranking that equally incorporates the advantages of both γ and ε without favoring one over the other. If favoring is necessary, then the value of θ can be varied. If one intends to favor γ then θ can be reduced and if one desires to favor ε then θ can be increased [22]. In the current study θ = 0.5 was considered. Further, the absolute GRG was replaced by the bidirectional absolute GRG (without signs) in the SSGRA’s formula. Javed [6] also suggested that when the relationships within a system are uncertain, then the absolute GRG can be replaced by the bidirectional absolute GRG.
5. Results
5.1. Determining the Overall Relationships Through Second Synthetic Grey Relational Analysis
In this section, the second synthetic grey relational analysis was executed to evaluate the relations between thermal conductivity and the three parameters for both samples; cemented and uncemented. The results were also compared with the correlational measures reported by Zerrouki et al. [24]. Table 3 summarizes the analyses.

Table 3.
Relationships between TC and three parameters.
Since it is unclear how did Zerrouki et al. [24] calculated R whom they referred to as the “correlation coefficient”, the Pearson’s correlation coefficient was calculated to compare the results with that of SSGRA model. Zerrouki’s [24] results and Pearson’s r showed a weak to moderate correlation between thermal conductivity (TC) and density (R = 0.18 to 0.51; r = 0.26 to 0.50) for cemented and uncemented samples, respectively. Both correlational measures showed a weak correlation between TC and permeability (R 0.1; r 0.3) for both cemented and uncemented samples. However, both correlational measures showed a weak to strong correlation between TC and porosity (R = 0.44 to 0.73; r = 0.43 to 0.73) for cemented and uncemented samples, respectively.
The sequence for their analysis, in terms of the correlation of the three parameters to thermal conductivity, can be expressed as
| For cemented samples: | Porosity > Density > Permeability |
| For uncemented samples: | Porosity > Density > Permeability. |
According to the second synthetic grey relational analysis, a significant association was found between thermal conductivity and density (0.8277 to 0.8346) for uncemented and cemented samples. The significant association was found between thermal conductivity and permeability (0.7567 to 0.8232) for cemented and uncemented samples. Significant association, but relatively stronger, was also found between thermal conductivity and porosity (0.8793 to 0.9511) for cemented and uncemented samples. The sequence obtained through the grey relational analysis, in terms of the association (inclusive proximity) of the three parameters to thermal conductivity, can be expressed as
| For cemented samples: | Porosity > Density > Permeability |
| For uncemented samples: | Porosity > Density > Permeability. |
One can see that the sequences/trends obtained through two different approaches are very comparable. However, the key point of distinction was the relative strengths. When Zerrouki et al. [24] reported a very weak to a strong relationship, the grey relational analysis revealed a strong to very strong relationship. On the other hand, some studies (e.g., [69]) indicated that the thermal conductivity of rock is “closely associated” with porosity and density. Further, as mentioned in the literature review, the negative relationship between TC and, porosity and density is also not unknown in literature. Thus the results obtained by SSGRA are feasible in light of the literature as well. Here it should be noted that since both computations resulted from two very different data analyses measures thus the two scales for describing the strength of correlations between the parameters are not one-to-one comparable e.g., for positive relations, the range of Pearson’s correlation coefficient’s scale is [0,1] where values less than 0.5 indicate weak correlation nevertheless for the similar relationship, the scale of Absolute GRA is (0.5, 1] and that of Deng’s GRA model is [0,1]. This makes the scale of SSGRA model ranges from (0, 1]. Thus, the scales of GRA models and that of statistical correlational coefficients are not comparable however their interpretations can be compared as both scales can guide the decision maker in determining whether the relationship is weak, strong or very strong.
Zerrouki et al. [24] argued that “TC is generally influenced by the porosity and density. The permeability has not any effect on the thermal conductivity.” The results obtained in the current study support their first argument however it is difficult to say that permeability has no effect on TC as permeability’s effect on TC is likely to be minimum, relative to others, but not zero. Since Zerrouki et al. [24] themselves considered their investigation a “preliminary study” therefore expecting more insightful and advanced discussions on the associations between TC and the petrophysical parameters is not beyond question.
5.2. Determining the Direction of Relationships through Bidirectional Absolute Grey Relational Analysis (BAGRA)
Identifying the extent of the relationships between variables is not the last step in the relationships evaluations. More profound insights can be drawn from the nature of relationships between different factors. For instance, how one variable behaves with the increase or decrease in the other variable is an interesting topic in natural and social sciences alike. This question also sought the attention of Zerrouki et al. [24]. In the current study, one of the latest developments in grey systems research has been utilized to determine the relationship between thermal conductivity and the three parameters. The bidirectional absolute grey relational analysis (BAGRA) model, also called the Javed’s bidirectional absolute degree grey incidence analysis (JBADGIA) model, was developed by Javed [6]. In the current study the BAGRA model as available in Javed and Liu [54] was used for the analysis of the grey direction among the parameters. One of the key advantages of this model is that it can work well for both linear and nonlinear data sequences. The results of the analysis are presented in Table 4. In Table 4, the symbol represents the ε-Difference (see definition-XIV) and the confidence level was obtained through the JCL scale (see definition-XIV). None of the bidirectional absolute grey relational grades (BAGRGs) reported weak relation. All values were between appropriately strong to extremely strong (see definition-XIII).

Table 4.
Nature of relationships between the factors through the Bidirectional Absolute Grey Relational Analysis (BAGRA) model.
The bidirectional absolute GRA (BAGRA) model based results show that porosity (with high confidence) and density (with low to medium confidence) of Hamra Quartzites (Algeria) are likely to increase with a decrease in thermal conductivity (and vice versa) as they have an inverse relationship. Pearson’s r also revealed similar relationships. However, as Zerrouki et al. [24] noted, the quartzite’s porosity, which increases with decreasing thermal conductivity, is one of the main factors to control the thermal conductivity of Hamra quartzites. What about the density’s control of thermal conductivity? What about permeability-TC relationships if uncertainties (associated with data or the system) are not beyond question? In short, Zerrouki et al.’s study successfully provided areas for further investigations for inquisitive minds. Especially, the relation of thermal conductivity to density and permeability was strange, if one keeps the literature in mind. The revaluation of the system through an entirely different approach, SSGRA, again revealed the same nature of relationships as were reported by Zeroukki et al. [24]. Considering the fact that SSGRA allows more comprehensive analysis of the system while incorporating the uncertainties it can be argued that as far as the experimental data, collected by Reference [24], is concerned the relation of TC with that of other three variables is correctly predicted by both approaches however in light of literature some relations may look odd. Here two points need discussion: (a) Firstly, here comprehensive implies the estimation of inclusive proximity (or, inclusive closeness), which determines the association between two parameters from both partial and integral perspectives. Thus, the closeness between two parameters determined through SSGRA model is technically more comprehensive than the closeness determine by the Pearson’s correlational coefficient and if one accounts the concerns like sample size and probability distributions, which are serious issues in the probability theory-based statistical analyses but not in the grey system heory-based data analyses, one may argue that the information obtained through SSGRA model are more insightful, as it accounts both direct and indirect relationships. For example, in the current case, when Zerrouki and colleagues did not consider any relationship as strong, for the reasons better known to them, and even though the apparently strong relations were taken as moderate in their study, the second synthetic grey relational analysis in the current study clearly demonstrated that none of the relationships are weak and some relations are in fact strong or very strong. Since the grey system theory is well known for its ability to handle uncertain systems containing insufficient data thus the current study argue that the difference between the two analyses is likely because of the difference of ability of each methodology to handle uncertainty; (b) secondly, why certain results don’t go smooth with that of the literature? To sum up the discussion from the geothermic perspective and in light of our understanding developed through the review of the literature, it is stated that the dependence of thermal conductivity upon porosity has been reported countless times for clastic sedimentary rocks and quartz. In addition, equally known is the dependence of thermal conductivity on bulk density, which is coupled on the porosity (reduced bulk density resulting from an increasing amount of pore fluid). In general, permeability, however, has no direct influence on the bulk thermal conductivity. It is only indirectly related to thermal conductivity as permeability and porosity are related to each other, hence increasing porosity should yield a decreased thermal conductivity and increased permeability. Here it is worth mentioning that the relationships reported in the current study are merely reporting physical dependencies of the sample under study (i.e., Hamra Quartzites reservoir, Hassi Messaoud field of Algeria). The measured conductivity and density are a result of the sample’s porosity. Not the other way around. In the given sample, with increasing porosity, a fraction of small density was increased with lowering conductivity (water in the pore space). However, further studies of the same quartz, as were studied by Zeroukki et al. [24], are needed to enrich our understanding of the Hamra Quartzites reservoir.
Now a question arises, how the application of GRA provides any substantial advantages compared to correlation or regression analysis? The statistical techniques like correlational and regression analyses are driven by the law of large numbers and concerns like probability distribution. “Probability theory and statistics deal with the data nexus or relation of the systems encompassing large samples embodied in statistic history laws, regression models or probability relations, and subject to laws, such as the law of large samples” (Ng and Deng as quoted in [4]). Thus the independence of the grey system theory and its models from the large sample size and concern of probability distribution [3,6] and the theory’s known superiority for handling uncertain systems containing uncertain information are primary reasons, which puts GST and its models like GRA in a very promising position in terms of intelligent evaluation of a system and its parameters when the decision makers are not certain about the sufficiency and completeness of data at hand. Further, GRA models like the second synthetic GRA model that consider multiple perspectives while evaluating a system and its parameters have a definite advantage over conventional statistical approaches, usually represent one particular perspective. Here it should be emphasized that by no mean the current study nullifies the significance of statistical methods however just as within statistical paradigm there are different perspectives (e.g., parametric statistics, nonparametric statistics) so does the intelligent approaches like grey system theory, fuzzy theory, rough set theory etc. have their own perspectives on data, data uncertainty and data handling. Through the current study, an alternative perspective on the evaluation of parameters, which are geothermic in the current study but can be different in future studies, is presented.
6. Conclusions and Recommendations
Grey relational analysis (GRA) is an important segment of the grey system theory (GST) that not only facilitates the decision makers in multi-objective optimizations but also helps in comparative evaluation of relationships between different factors. Deng’s GRA model is the flagship model of GST and is in use for more than three decades. Initially, its application was though limited to engineering disciplines; however, since the recent past, it has been increasingly applied in social sciences as well [6,19]. However, like any other model or theory, it is also not free from flaws. In 1991 when Liu Sifeng proposed generalized GRA model, it was a kind of breakthrough in GST research. The absolute GRA model was one of the generalized GRA models [39]. However, Deng’s GRA model estimated the closeness/proximity between data curves based on corresponding points and the absolute GRA model estimated closeness/proximity using integral perspective, a more comprehensive perspective. However, both models had their own strengths and their integration was likely to yield a more robust measure of proximity. This was done by Javed [6] when the second synthetic GRA model was introduced. The model yielded a grey relational grade based on overall perspective. It produced a degree of inclusive proximity/closeness, which incorporated the advantages of both partial proximity (Deng’s grey relational grade) and integral proximity (absolute grey relational grade). Later, the model saw its successful applications in different studies [22,25,42,43].
The current study is a pioneer in finding its application in geothermics and earth sciences. The current study demonstrated the trend/order obtained through the second synthetic GRA model could be compared with that obtained through statistical correlational measures. However, this comparability is coincidental or generalizable is difficult to establish at this level. Future studies are expected to settle this issue. Further, even though permeability turned out to be the least significant factor in both analyses however the overall strengthen (relative to other parameters) was stronger in SSGRA when compared the analysis through Pearson’s r. These are some areas of further research so better explanations can be sought.
At the conclusion, the current study intends to make few comments on SSGRA model, as first made by Javed [6], to facilitate the readers. 1) Each GRA model has its own strengths and limitations, but if they are built of the principles of grey system theory each one of them is likely to work for small samples and inadequate information. 2) Deng’s GRA model and absolute GRA models are mutually exclusive and independent so do the rankings of variables obtained through them, however, the second synthetic GRA model is indeed dependent on both of these models. These dependencies are controlled by θ, the coefficient of relative weights. Therefore, the reliability of the results obtained from the SSGRA models depends on the reliability of the results from the two constituent models.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, S.A.J., A.R. and S.L.; methodology, S.A.J. and S.L.; software, S.A.J. and A.M.K.; validation, W.D. and A.M.K.; data curation, A.M.K. and S.A.J.; writing—original draft preparation, S.A.J., A.M.K. and W.D.; writing—review and editing, S.L., W.D. and A.R.; supervision, S.L.; funding acquisition, S.A.J.
Funding
The work was supported by Funding for Outstanding Doctoral Dissertation in NUAA (No. BCXJ18-10).
Acknowledgments
The paper is one of the spinoffs of the PhD work of the corresponding author. The authors want to thank the editor and the anonymous reviewers as their comments helped us improve the quality of the paper. The authors also want to thank the Grey Systems Society of Pakistan, GreySys Foundation, Pakistan, for its technical support.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
- Frutiger, J.; Jones, M.; Ince, N.G.; Sin, G. From property uncertainties to process simulation uncertainties–Monte Carlo methods in SimSci PRO/II process simulator. In Computer Aided Chemical Engineering; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2018; Volume 44, pp. 1489–1494. [Google Scholar]
- Cerrillo-Briones, I.M.; Ricardez-Sandoval, L.A. Robust optimization of a post-combustion CO2 capture absorber column under process uncertainty. Chim. Eng. Res. Des. 2019, 144, 386–396. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, S.F.; Yang, Y.; Forrest, J. Grey Data Analysis—Methods, Models and Applications; Springer: Singapore, 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Javed, S.A.; Syed, A.M.; Javed, S. Perceived Organizational Performance and Trust in project manager and top management in Project-based organizations: Comparative Analysis using Statistical and Grey Systems methods. Grey Syst. Theory Appl. 2018, 8, 230–245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, B.C.; Tasi, S.L.; Wang, C.C. Machine vision-based gray relational theory applied to IC marking inspection. IEEE Trans. Semicond. Manuf. 2002, 15, 531–539. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Javed, S.A. A novel research on Grey Incidence Analysis models and its application in Project Management. Ph.D. Thesis, Nanjing University of Aeronautics and Astronautics, Nanjing, China, 2019. [Google Scholar]
- Tzeng, G.H.; Huang, J.J. Multiple Attribute Decision Making: Methods and Applications; Chapman and Hall/CRC: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 2011. [Google Scholar]
- Hussain, M.Z.; Khan, S.; Sarmah, P. Optimization of Powder Metallurgy Processing Parameters of Al2O3/Cu Composite through Taguchi Method with Grey Relational Analysis. J. King Saud Univ. -Eng. Sci. 2019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maniyar, K.G.; Ingole, D.S. Multi response Optimization of EDM Process Parameters for Aluminium Hybrid Composites by GRA. Mater. Today Proc. 2018, 5, 19836–19843. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chauhan, N.K.; Das, A.K.; Rajesha, S. Optimization of process parameters using grey relational analysis and Taguchi method during micro-EDMing. Mater. Today Proc. 2018, 5, 27178–27184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gandhi, S.V.; Rahul, M.C. Experimental Investigation of Wet Chemical Machining and Optimization of Process Parameters Using Grey Relational Analysis for SS 316L. Mater. Today Proc. 2018, 5, 23908–23916. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Umamaheswarrao, P.; Raju, D.R.; Suman, K.N.S.; Sankar, B.R. Multi objective optimization of process parameters for hard turning of AISI 52100 steel using Hybrid GRA-PCA. Procedia Comput. Sci. 2018, 133, 703–710. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aslantas, K.; Ekici, E.; Çiçek, A. Optimization of process parameters for micro milling of Ti-6Al-4V alloy using Taguchi-based gray relational analysis. Measurement 2018, 128, 419–427. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, X.; Wang, Y.; Zhao, J.; Chen, Y.; Mo, S.; Gong, Y. Grey relational analysis of an integrated cascade utilization system of geothermal water. Int. J. Green Energy 2016, 13, 14–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, J.; Jiang, X.; Huang, X.; Wu, S. Morphological characterization of superfine pulverized coal particles. 1. Fractal characteristics and economic fineness. Energy Fuels 2010, 24, 844–855. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arce, M.E.; Saavedra, Á.; Míguez, J.L.; Granada, E. The use of grey-based methods in multi-criteria decision analysis for the evaluation of sustainable energy systems: A review. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 2015, 47, 924–932. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, W.; Liu, S.; Fang, Z. On modeling mechanisms and applicable ranges of grey incidence analysis models. Grey Syst. Theory Appl. 2018, 8, 448–461. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Delcea, C.; Popa, C.D.S.; Boloş, M. Consumers’ Decisions in Grey Online Social Networks. J. Grey Syst. 2015, 27, 12–27. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, C.; Duan, L.; Liu, H.; Zhang, Y.; Yin, L.; Sun, Q.; Lu, Q. Analysis of patients’ attitudes towards medical service prices in different regions based on grey relational theory. Grey Syst. Theory Appl. 2019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, S.F.; Fang, Z.G.; Lin, Y. Study on a new definition of degree of grey incidence. J. Grey Syst. 2006, 9, 115–122. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, S.F.; Fang, Z.G.; Lin, Y. A new definition for the degree of grey incidence. Sci. Inq. 2006, 7, 111–124. [Google Scholar]
- Javed, S.A.; Liu, S.F. Evaluation of Outpatient Satisfaction and Service Quality of Pakistani Healthcare Projects: Application of a novel Synthetic Grey Incidence Analysis model. Grey Syst. Theory Appl. 2018, 8, 462–480. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.; Liu, S.; Ren, H. Sensitivity analysis of grey relational ordering. In Proceedings of the 2007 IEEE International Conference on Systems, Man and Cybernetics, Montréal, Canada, 7–10 October 2007; IEEE: Piscataway, NJ, USA, 2007; pp. 2210–2221. [Google Scholar]
- Zerrouki, A.A.; Geraud, Y.; Diraison, M.; Baddari, K. A Preliminary study of relationships between thermal conductivity and petrophysical parameters in Hamra Quartzites reservoir, Hassi Messaoud field (Algeria). J. Afr. Earth Sci. 2019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Javed, S.A.; Liu, S.F.; Mahmoudi, A.; Nawaz, M. Patients’ Satisfaction and Public and Private Sectors’ Healthcare Service Quality in Pakistan: Application of Grey Decision Analysis approaches. Int. J. Health Plan. Manag. 2019, 34, e168–e182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Javed, S.A.; Mahmoudi, A.; Khan, A.M.; Javed, S.; Liu, S.F. A Critical Review: Shape Optimization of Welded Plate Heat Exchangers Based on Grey Correlation Theory. Appl. Therm. Eng. 2018, 144, 593–599. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, W.; Liang, J. Information fusion in rough set theory: An overview. Inf. Fusion 2019, 48, 107–118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mahmoudi, A.; Feylizadeh, M.R.; Darvishi, D.; Liu, S. Grey-fuzzy solution for multi-objective linear programming with interval coefficients. Grey Syst. Theory Appl. 2018, 8, 312–327. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, Q.; Lu, Z. Real formal concept analysis based on grey-rough set theory. Knowl. -Based Syst. 2009, 22, 38–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mahmoudi, A.; Bagherpour, M.; Javed, S.A. Grey Earned Value Management: Theory and Applications. IEEE Trans. Eng. Manag. 2019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Javed, S.A.; Liu, S.F. Bidirectional Absolute GRA/GIA model for Uncertain Systems: Application in Project Management. IEEE Access. 2019, 7, 60885–60896. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mahmoudi, A.; Liu, S.F.; Javed, S.A.; Abbasi, M. A Novel Method of Solving Linear Programming with Grey parameters. J. Intell. Fuzzy Syst. 2019, 36, 161–172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Javed, S.A.; Liu, S.F. Predicting the Research Output/Growth of Selected Countries: Application of Even GM (1, 1) and NDGM Models. Scientometrics 2018, 115, 395–413. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhicheng, Y.; Lijun, W.; Zhaokuo, Y.; Haowen, L. Shape optimization of welded plate heat exchangers based on grey correlation theory. Appl. Therm. Eng. 2017, 123, 761–769. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chambers, N.; Hamzacebi, C.; Bayramoglu, M.F. Grey System Theory Supported Markowitz Portfolio Optimization during High Volatility Periods. J. Grey Syst. 2016, 28, 79–95. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, S.F.; Forrest, J. The mysteries for continual growth of grey system theory. In Proceedings of the 2007 IEEE International Conference on Systems, Man and Cybernetics, Montréal, Canada, 7–10 October 2007; IEEE: Piscataway, NJ, USA, 2007; pp. 2155–2159. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, K.; Wang, Y.; Xin, J.; Xu, Y. Multivariate Absolute Degree of Grey Incidence Based On Distribution Characteristics Of Points. Trans. Nanjing Univ. Aeronaut. Astronaut 2012, 29, 145–151. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, S.F.; Lin, Y. Grey Systems—Theory and Applications; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2010. [Google Scholar]
- Yuan, C.; Yang, Y.; Chen, D.; Liu, S.F. Proximity and Similitude of Sequences Based on Grey Relational Analysis. J. Grey Syst. 2014, 26, 57–74. [Google Scholar]
- Tung, C.T.; Lee, Y.J. The innovative performance evaluation model of grey factor analysis: A case study of listed biotechnology corporations in Taiwan. Expert Syst. Appl. 2010, 37, 7844–7851. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, J.; Zhang, X.; Xiong, C. A methodology for evaluating micro-surfacing treatment on asphalt pavement based on grey system models and grey rational degree theory. Constr. Build. Mater. 2017, 150, 214–226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sheikh, A.H.A.; Ikram, M.; Ahmad, M.; Qadeer, H.; Nawaz, M. Evaluation of key Factors influencing Process Quality during Construction Projects in Pakistan. Grey Syst. Theory and Appl. 2019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Diba, S.; Xie, N. Sustainable Supplier Selection for Satrec Vitalait Milk Company in Senegal using novel Grey Relational Analysis method. Grey Syst. Theory Appl. 2019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gu, Y.; Rühaak, W.; Bär, K.; Sass, I. Using seismic data to estimate the spatial distribution of rock thermal conductivity at reservoir scale. Geothermics 2017, 66, 61–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mielke, P.; Bär, K.; Sass, I. Determining the relationship of thermal conductivity and compressional wave velocity of common rock types as a basis for reservoir characterization. J. Appl. Geophys. 2017, 140, 135–144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arafin, S. Thermophysical properties of reservoir rocks. J. Phys. Chem. Solids 2019, 129, 99–110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cermak, V.; Rybach, L. Thermal Properties. In Zahlenwerte und Funktionen aus Naturwissenschaft und Technik: Neue Serie.—Numerical Data and Functional Relationships in Science and Technology: New Series c; Angenheister, G., Cermák, V., Hellwege, K.-H., Landolt, H., Eds.; Springer: Berlin, Germany, 1982; pp. 310–314. [Google Scholar]
- Šperl, J.; Trčková, J. Permeability and porosity of rocks and their relationship based on laboratory testing. Acta Geodyn Geomater 2008, 5, 41–47. [Google Scholar]
- Shen, X.; Li, L.; Cui, W.; Feng, Y. Improvement of fractal model for porosity and permeability in porous materials. Int. J. Heat Mass Transf. 2018, 121, 1307–1315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Somerton, W.H. Some Thermal Characteristics of Porous Rocks; Society of Petroleum Engineers: Kuala Lumpur, Malaysia, 1958. [Google Scholar]
- Brigaud, F.; Vasseur, G. Mineralogy, porosity and fluid control on thermal conductivity of sedimentary rocks. Geophys. J. Int. 1989, 98, 525–542. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Clauser, C.; Huenges, E. Thermal conductivity of rock and minerals. In Rock Physics and Phase Relation-a Handbook of Physical Constants; Ahrens, T.J., Ed.; AGU Reference Shelf: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 1995; Volume 3, pp. 105–126. [Google Scholar]
- Midttomme, K.; Roaldset, E. The effect of grain size on thermal conductivity of quartz sands and silts. Pet. Geosci. 1998, 4, 165–172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barry-Macaulay, D.; Bouazza, A.; Singh, R.M.; Wang, B.; Ranjith, P.G. Thermal conductivity of soils and rocks from the Melbourne (Australia) region. Eng. Geol. 2013, 164, 131–138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duchkov, A.D.; Sokolova, L.S.; Rodyakin, S.V.; Chernysh, P.S. Thermal conductivity of the sedimentary-cover rocks of the West Siberian Plate in relation to their humidity and porosity. Russ. Geol. Geophys. 2014, 55, 784–792. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schön, J. (Ed.) Physical Properties of Rocks: Fundamentals and Principles of Petrophysics; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2015. [Google Scholar]
- Asadi, I.; Shafigh, P.; Hassan, Z.F.B.A.; Mahyuddin, N.B. Thermal conductivity of concrete—A review. J. Build. Eng. 2018, 20, 81–93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haffen, S.; Géraud, Y.; Rosener, M.; Diraison, M. Thermal conductivity and porosity maps for different materials: A combined case study of granite and sandstone. Geothermics 2017, 66, 143–150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ouali, S. Thermal conductivity in relation to porosity and geological stratigraphy. Geotherm. Train. Rep. Cent. Dev. Renew. Energ. Alger. 2009, 4, 23–29. [Google Scholar]
- Duchkov, A.D.; Ayunov, D.E.; Rodyakin, S.V.; Yan, P.A. The study of the relationship between thermal conductivity and porosity, permeability, humidity of sedimentary rocks of the West Siberian Plate. Геoресурсы 2018, 20. [Google Scholar]
- Nagy, B.; Nehme, S.G.; Szagri, D. Thermal properties and modeling of fiber reinforced concretes. Energy Procedia 2015, 78, 2742–2747. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Łydżba, D.; Rajczakowska, M.; Różański, A.; Stefaniuk, D. Influence of the moisture content and temperature on the thermal properties of soils: Laboratory investigation and theoretical analysis. Procedia Eng. 2014, 91, 298–303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Weibel, R.; Olivarius, M.; Jakobsen, F.C.; Whitehouse, M.; Larsen, M.; Midtgaard, H.; Nielsen, K. Thermogenetic degradation of early zeolite cement: An important process for generating anomalously high porosity and permeability in deeply buried sandstone reservoirs? Mar. Pet. Geol. 2019, 103, 620–645. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Costa, A. Permeability-porosity relationship: A reexamination of the Kozeny-Carman equation based on a fractal pore-space geometry assumption. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2006, 33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Q.; Wang, T.; Liu, W.; Zhang, J.; Feng, Q.; Lu, H.; Peng, P.A. Relationships among composition, porosity and permeability of Longmaxi Shale reservoir in the Weiyuan Block, Sichuan Basin, China. Mar. Pet. Geol. 2019, 102, 33–47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mielke, P.; Bignall, G.; Sass, I. Permeability and thermal conductivity measurements of near surface units at the Wairakei Geothermal Field, New Zealand. In Proceedings of the World Geothermal Congress 2010, Bali, Indonesia, 25–29 April 2010. [Google Scholar]
- Jiang, L.; Roskilly, A.P. Thermal conductivity, permeability and reaction characteristic enhancement of ammonia solid sorbents: A review. Int. J. Heat Mass Transf. 2019, 130, 1206–1225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, B.; Hu, L.; He, C.; Mi, C. The Reverse Order of Grey Incidence Analysis and Two Judgment Principles. In Proceedings of the 2010 IEEE International Conference on Systems Man and Cybernetics (ICSMC), Istanbul, Turkey, 10–13 October 2010. [Google Scholar]
- Zhao, X.G.; Xu, H.R.; Zhao, Z.; Guo, Z.; Cai, M.; Wang, J. Thermal conductivity of thermally damaged Beishan granite under uniaxial compression. Geothermics 2019, 66, 61–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).