Multi-Time-Scale Rolling Optimal Dispatch for Grid-Connected AC/DC Hybrid Microgrids
Abstract
1. Introduction
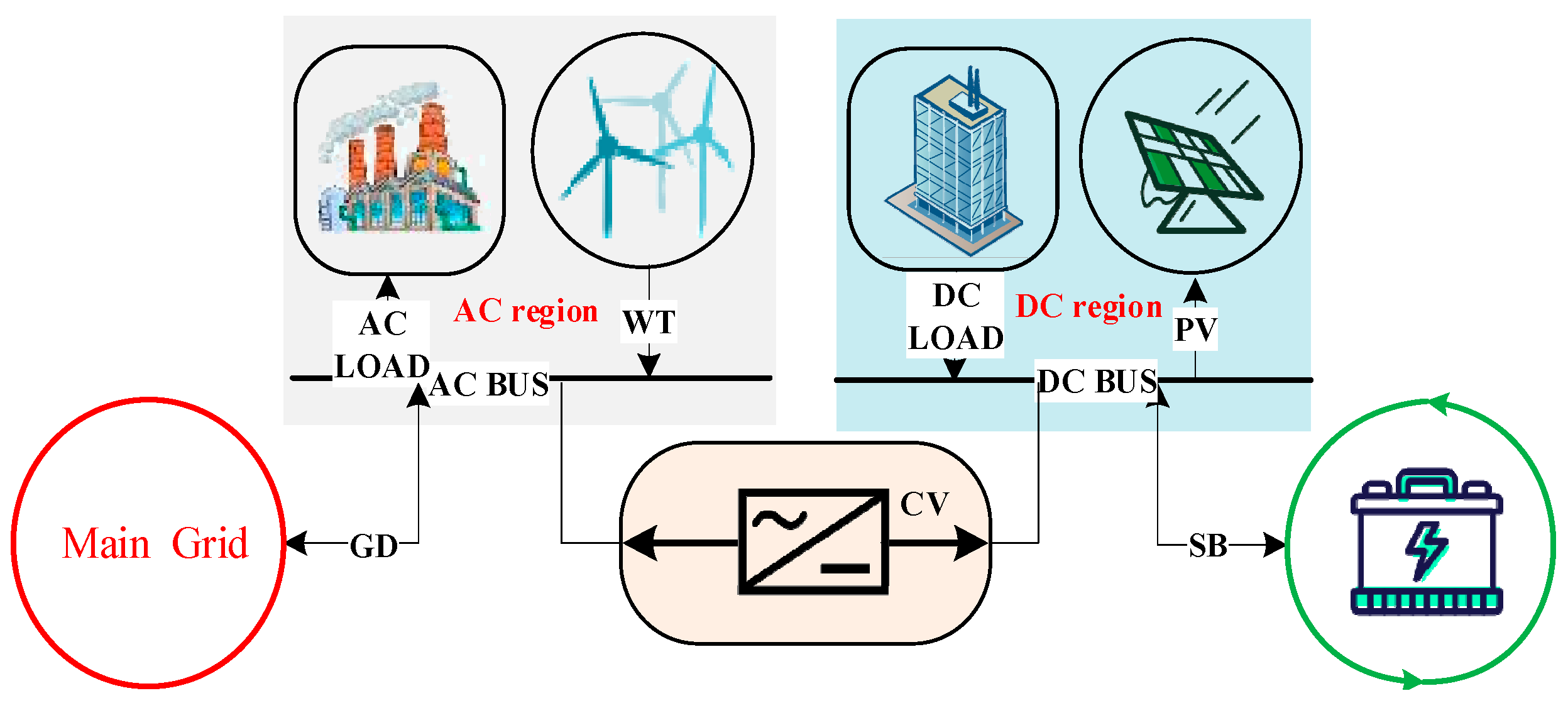
2. Microgrid Structure and Operation Characteristics
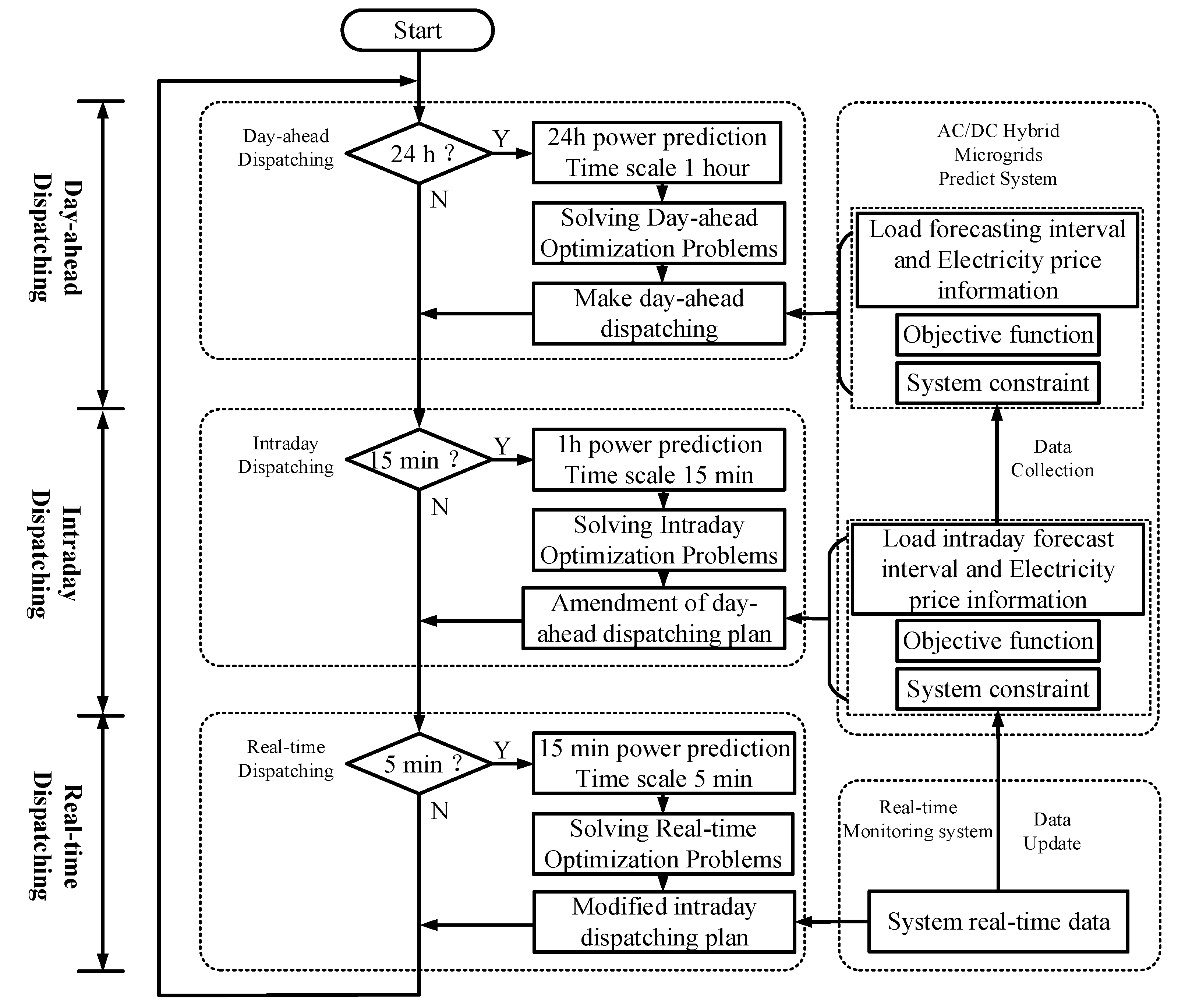
3. Multi-time Scale Rolling Optimization Architecture
4. Optimal Scheduling Model
4.1. Day-Ahead Dispatching
- (1)
- System Power Balance Constraints
- (a)
- Total power balance constraintswhere , is the AC side load in t period, , is the DC side load in t period, and ηCV is the commutation efficiency of the converter.
- (b)
- DC power balance constraintswhere Δ is the net power of the DC side. When the is positive, the converting power flows from the DC side to the AC side. Conversely, the converting power flows from the AC side to the DC side.
- (c)
- AC side power balance constraintswhere Δ is AC side net power.
- (2)
- Power constraints of wind and solar power generationwhere is the maximum output power of the fan in t period, and is the maximum output power of photovoltaic in t period.
- (3)
- Energy storage system constraints
- (a)
- Energy storage constraintswhere and are the lower and upper limits of the state of charge for energy storage, and are the remaining power of the energy storage system in t and t − 1 period, EC is the rated capacity of energy storage, and ηC and ηD are the charging and discharging efficiencies of the energy storage system, respectively.
- (b)
- Maximum charge and discharge power constraintswhere , and are the allowable maximum charging and discharging power values of energy storage t period, and Pch-max and Pdisch-max are the maximum charging and discharging continuous power set by the energy storage system itself.
- (c)
- Constraints of equal starting and ending statesIn order to ensure the cyclic charging and discharging operation of energy storage, the starting and ending states of energy storage need to be balanced.
- (4)
- Interactive power constraint of tie-linewhere PGDmax is the maximum reverse power of the microgrids, only considering the selling time.
4.2. Intraday Dispatching
4.3. Real-Time Dispatching
5. Case Study
5.1. Case Parameters
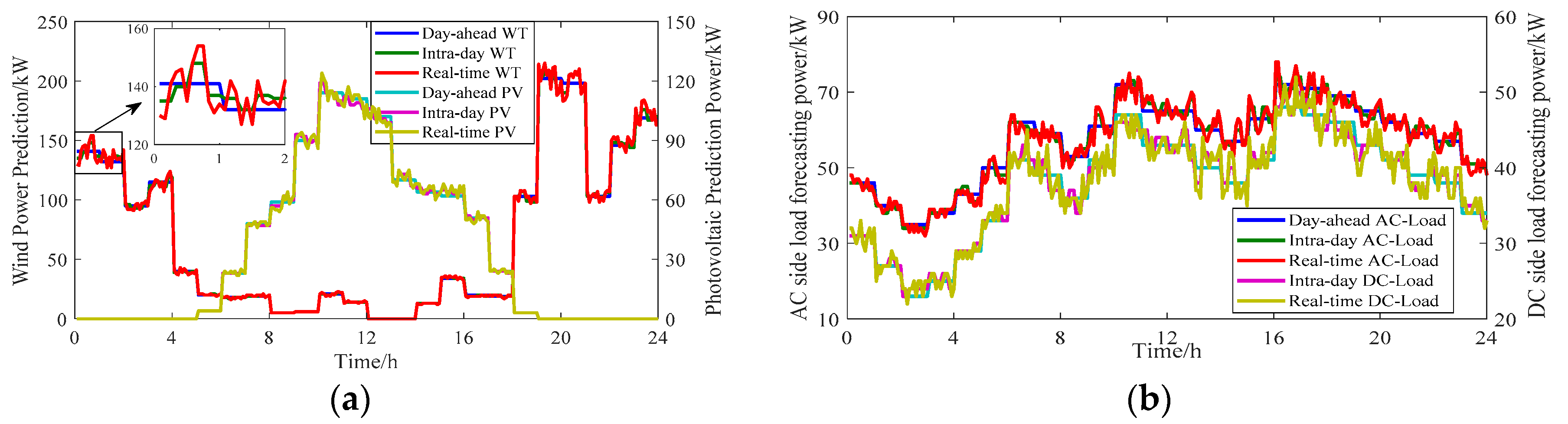
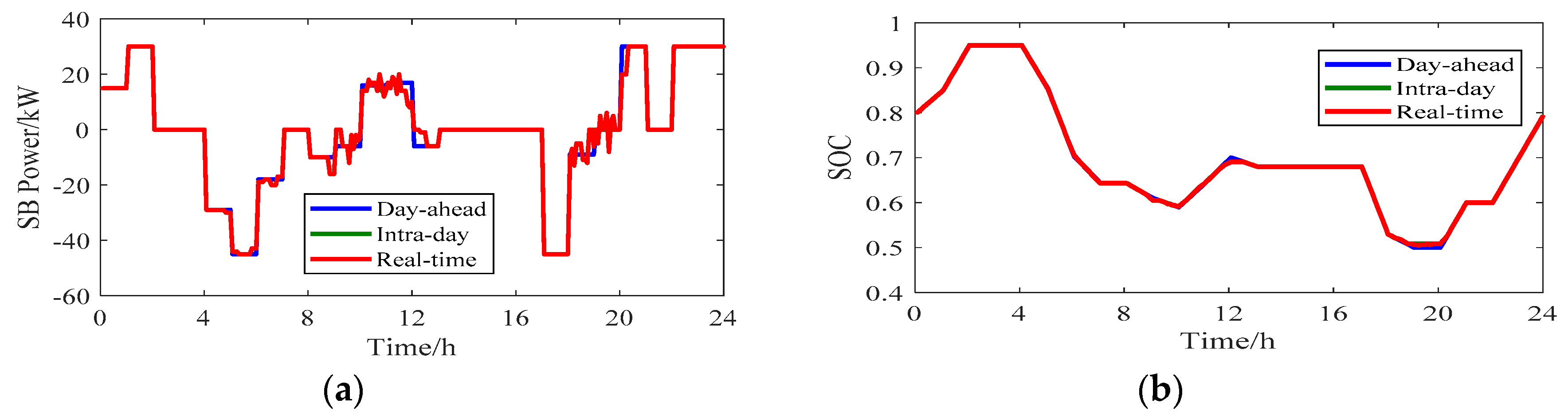
5.2. Analysis of Optimization Results
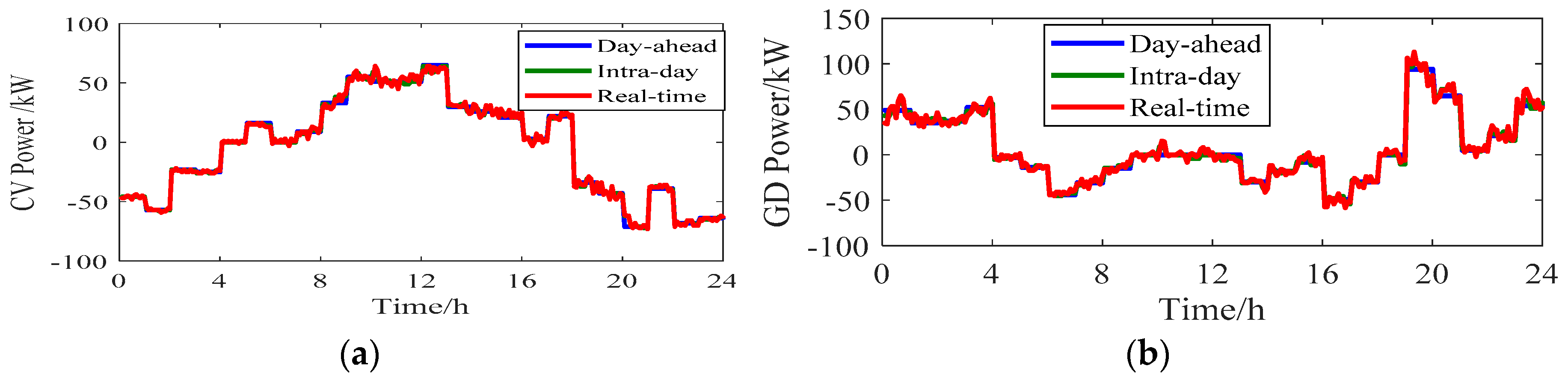
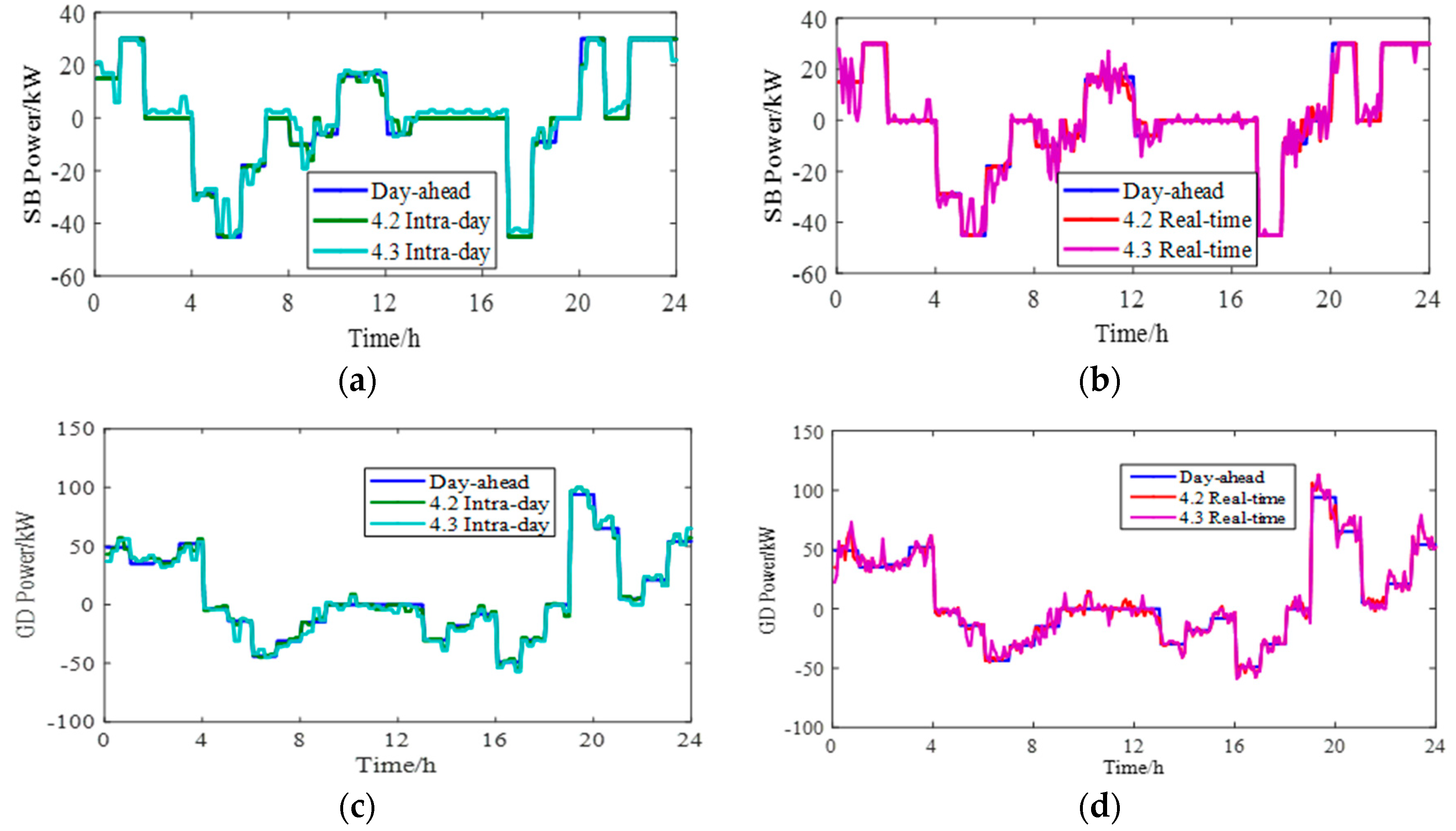
5.3. Analysis of Operating Power Correction Constraints
5.4. Constraints on the Initial and Final State of Energy Storage
6. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Liu, F.; Yang, X.; Shi, S. Economic operation of micro-grid based on sequence operation. Trans. China Electrotech. Soc. 2015, 30, 227–237. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, N.; Li, Y.; Zhang, J. Hour-ahead optimization and real-time control method for micro-grid interconnection. Trans. China Electrotech. Soc. 2016, 31, 1–11. [Google Scholar]
- Hosseinzadeh, M.; Salmasi, F.R. Power management of an isolated hybrid AC/DC micro-grid with fuzzy control of battery banks. IET Renew. Power Gener. 2015, 9, 484–493. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shaaban, M.F.; Eajal, A.A.; El-Saadany, E.F. Coordinated charging of plug-in hybrid electric vehicles in smart hybrid AC/DC distribution systems. Renew. Energy 2015, 82, 92–99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Zhao, B.; Wu, H.; Zhang, X. Optimal sizing analysis of grid-connected hybrid AC-DC microgrids. Autom. Electr. Power Syst. 2016, 40, 55–62. [Google Scholar]
- Li, J.H.; Wang, S.; Ye, L.; Fang, J.K. A coordinated dispatch method with pumped-storage and battery-storage for compensating the variation of wind power. Prot. Control Mod. Power Syst. 2018, 3, 21–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, D.; Ge, S.; Jia, H.; Wang, C.; Zhou, Y.; Lu, N.; Kong, X. A Demand Response and Battery Storage Coordination Algorithm for Providing Microgrids Tie-Line Smoothing Services. IEEE Trans. Sustain. Energy 2014, 5, 476–486. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kinhekar, N.; Padhy, N.P.; Li, F.; Gupta, H.O. Utility Oriented Demand Side Management Using Smart AC and Micro DC Grid Cooperative. IEEE Trans. Power Syst. 2015, 31, 1151–1160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hosseinzadeh, M.; Salmasi, F.R. Robust Optimal Power Management System for a Hybrid AC/DC Micro-Grid. IEEE Trans. Sustain. Energy 2015, 6, 675–687. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eajal, A.A.; Shaaban, M.F.; Ponnambalam, K.; El-Saadany, E.F. Stochastic Centralized Dispatch Scheme for AC/DC Hybrid Smart Distribution Systems. IEEE Trans. Sustain. Energy 2016, 7, 1046–1059. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bao, Y.; Wang, B.; Li, Y.; Yang, S. Rolling Dispatch Model Considering Wind Penetration and Multi-scale Demand Response Resources. Proc. Csee 2016, 36, 4589–4599. [Google Scholar]
- Silvente, J.; Kopanos, G.M.; Pistikopoulos, E.N.; Espuña, A. A rolling horizon optimization framework for the simultaneous energy supply and demand planning in microgrids. Appl. Energy 2015, 155, 485–501. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Palma-Behnke, R.; Benavides, C.; Lanas, F.; Severino, B.; Reyes, L.; Llanos, J.; Sáez, D. A Microgrisd Energy Management System Based on the Rolling Horizon Strategy. IEEE Trans. Smart Grid 2013, 4, 996–1006. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, S.; Yuan, Y.; Zhang, X. Energy Management Strategy of Isolated Microgrids Based on Multi-time Scale Coordinated Control. Trans. China Electrotech. Soc. 2014, 29, 122–129. [Google Scholar]
- Dou, X.; Xu, M.; Dong, J.; Quan, X.J.; Wu, Z.J.; Sun, J. Multi-time Scale Based Improved Energy Management Model for Microgrids. Autom. Electr. Power Syst. 2016, 40, 48–55. [Google Scholar]
- Hao, X.; Wei, P.; Li, K. Multi-time Scale Coordinated Optimal Dispatch of Microgrid Based on Model Predictive Control. Autom. Electr. Power Syst. 2016, 40, 7–14. [Google Scholar]

| Equipment | Configuration Paramete | Cost Coefficient/(yuan/kW·h) |
|---|---|---|
| WT | 250 kW | 0.01 |
| PV | 150 kW | 0.01 |
| SB | 300 kW·h | 0.01 |
| CV | 100 kW | 0.04 |
| Target Value | Day-Ahead | Intraday | Real-Time |
|---|---|---|---|
| f/(yuan) | 41.04 | 40.15 | 37.26 |
| /(kW) | — | 234 | 56 |
| /(kW) | — | 3894 | 3934 |
| PSB Correction rate/(%) | — | 6.0 | 1.4 |
| /(kW) | — | 765 | 376 |
| /(kW) | — | 8031 | 8129 |
| PGD Correction rate/(%) | — | 9.5 | 4.6 |
| Target Value | Day-Ahead | Intraday | Real-Time |
|---|---|---|---|
| f/(yuan) | 41.47 | 40.56 | 37.52 |
| /(kW) | — | 729 | 163 |
| /(kW) | — | 4077 | 4093 |
| PSB Correction rate/(%) | — | 17.9 | 4.0 |
| /(kW) | — | 1050 | 458 |
| /(kW) | — | 8214 | 8088 |
| PGD Correction rate/(%) | — | 12.8 | 5.7 |
| Target Value | Day-Ahead | Intraday | Real-Time |
|---|---|---|---|
| f/(yuan) | 41.31 | 40.42 | 37.46 |
| /(kW) | — | 54 | 39 |
| /(kW) | — | 4032 | 4077 |
| PSB Correction rate/(%) | — | 1.3 | 1.0 |
| /(kW) | — | 831 | 389 |
| /(kW) | — | 8097 | 8166 |
| PGD Correction rate/(%) | — | 10.3 | 4.8 |
© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Luo, Z.; Zhu, Z.; Zhang, Z.; Qin, J.; Wang, H.; Gao, Z.; Yang, Z. Multi-Time-Scale Rolling Optimal Dispatch for Grid-Connected AC/DC Hybrid Microgrids. Processes 2019, 7, 961. https://doi.org/10.3390/pr7120961
Luo Z, Zhu Z, Zhang Z, Qin J, Wang H, Gao Z, Yang Z. Multi-Time-Scale Rolling Optimal Dispatch for Grid-Connected AC/DC Hybrid Microgrids. Processes. 2019; 7(12):961. https://doi.org/10.3390/pr7120961
Chicago/Turabian StyleLuo, Zhao, Zhendong Zhu, Zhiyuan Zhang, Jinghui Qin, Hao Wang, Zeyong Gao, and Zhichao Yang. 2019. "Multi-Time-Scale Rolling Optimal Dispatch for Grid-Connected AC/DC Hybrid Microgrids" Processes 7, no. 12: 961. https://doi.org/10.3390/pr7120961
APA StyleLuo, Z., Zhu, Z., Zhang, Z., Qin, J., Wang, H., Gao, Z., & Yang, Z. (2019). Multi-Time-Scale Rolling Optimal Dispatch for Grid-Connected AC/DC Hybrid Microgrids. Processes, 7(12), 961. https://doi.org/10.3390/pr7120961





