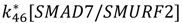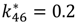Integrated Computational Model of Intracellular Signaling and microRNA Regulation Predicts the Network Balances and Timing Constraints Critical to the Hepatic Stellate Cell Activation Process
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Methods
3. Results and Discussion
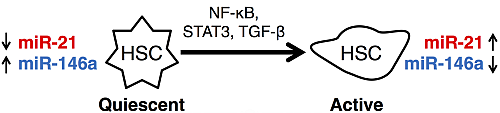
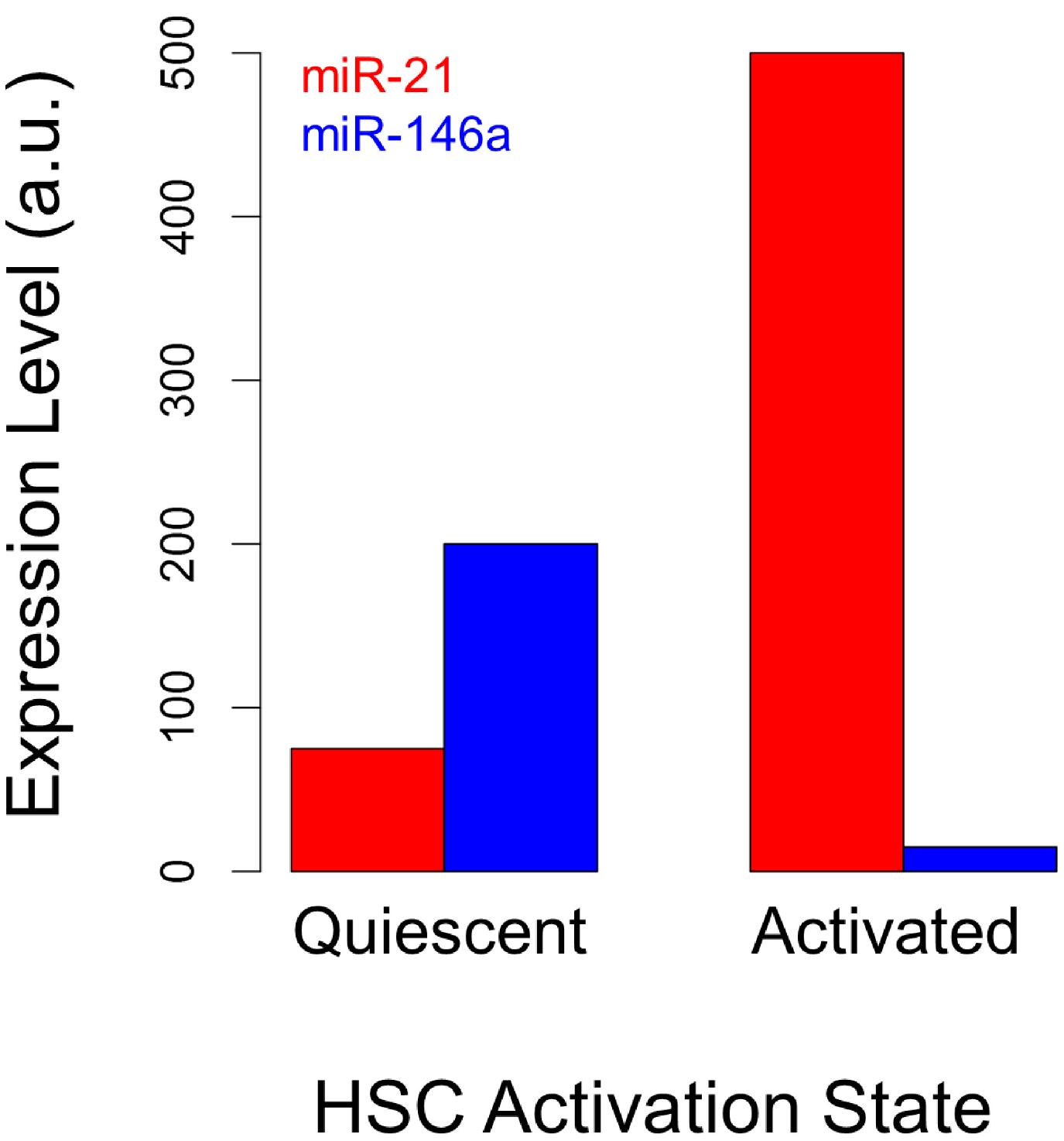
3.1. microRNAs as Markers of Hepatic Stellate Cell Molecular Phenotypes
3.2. Integrated Model of Signaling and microRNA Regulation
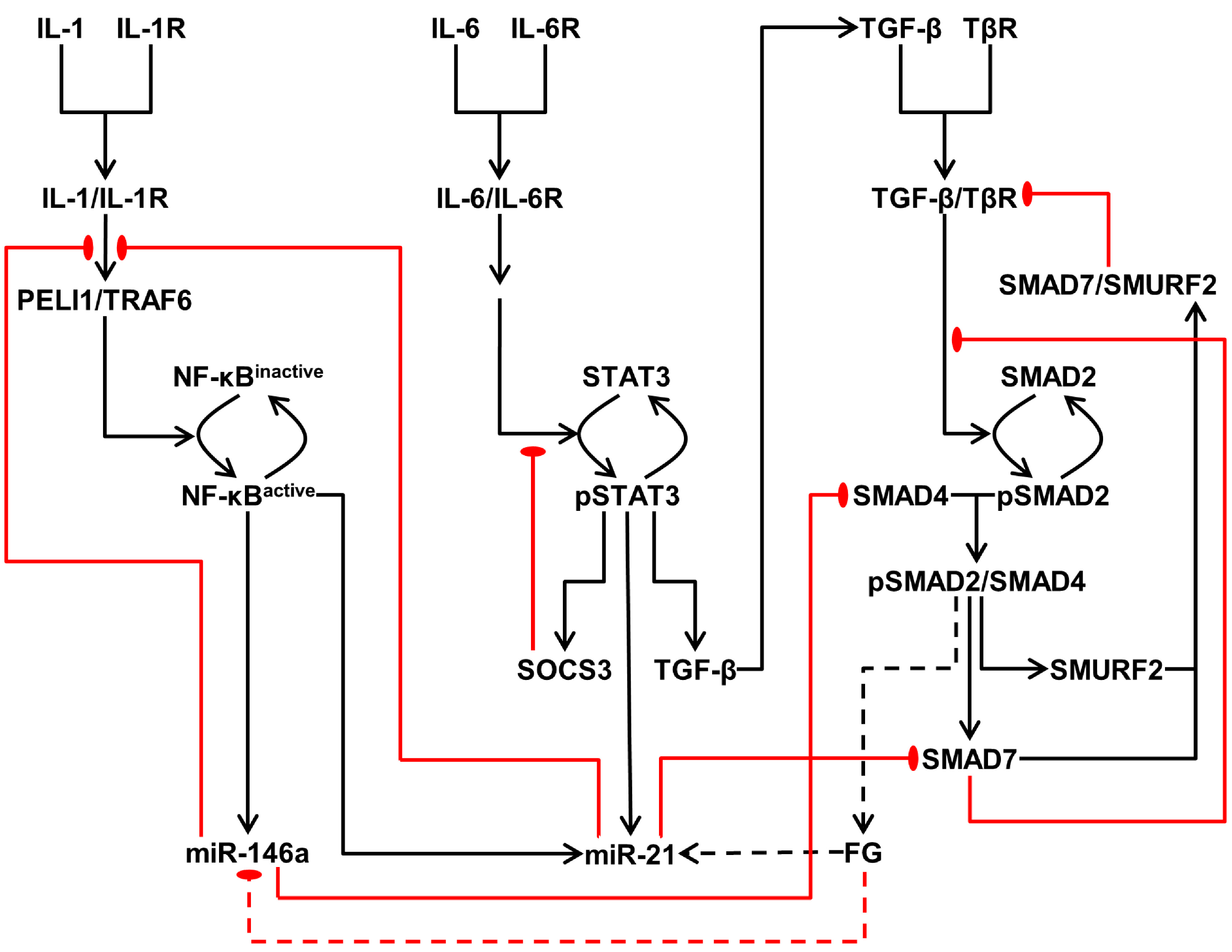
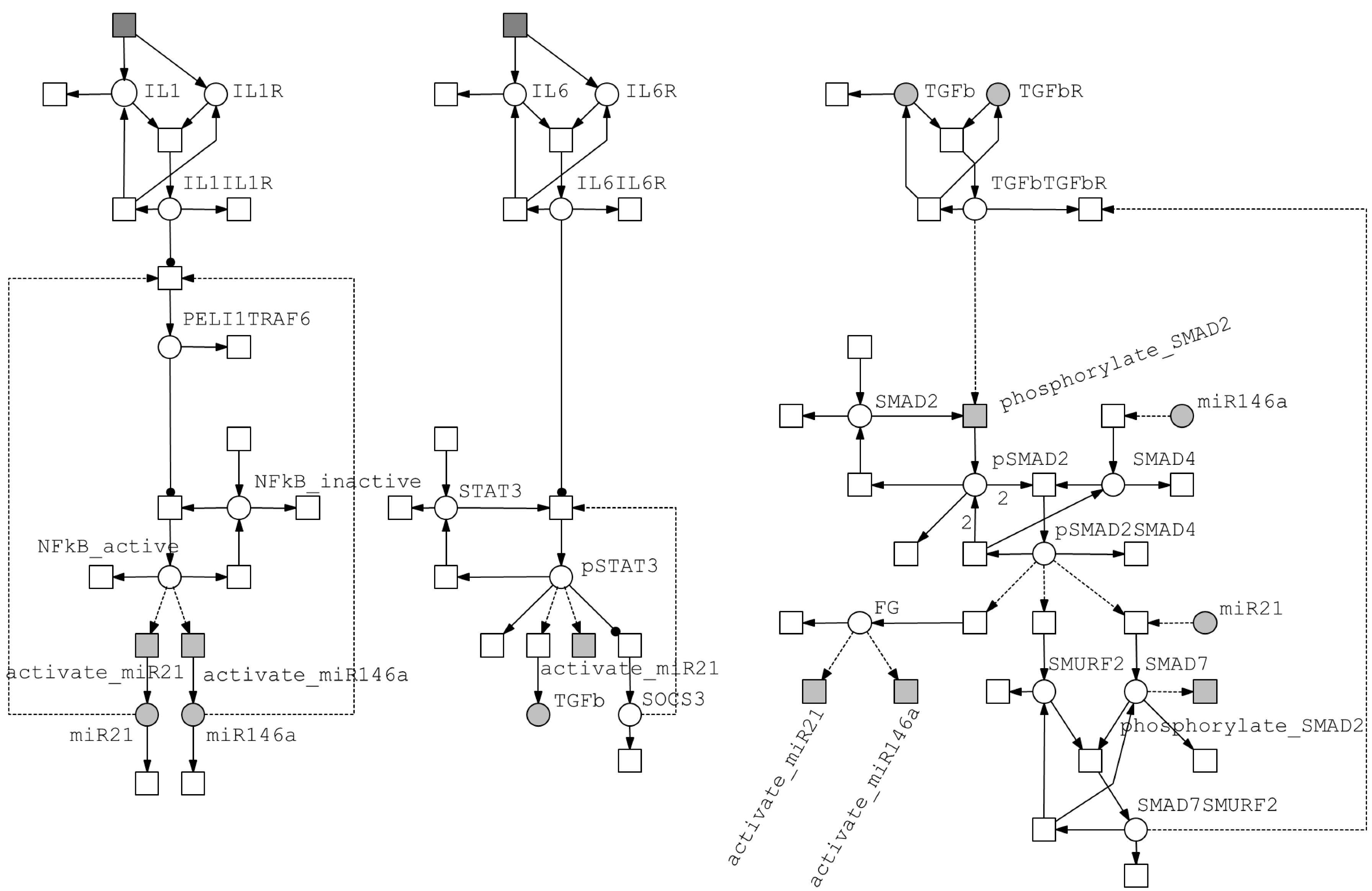
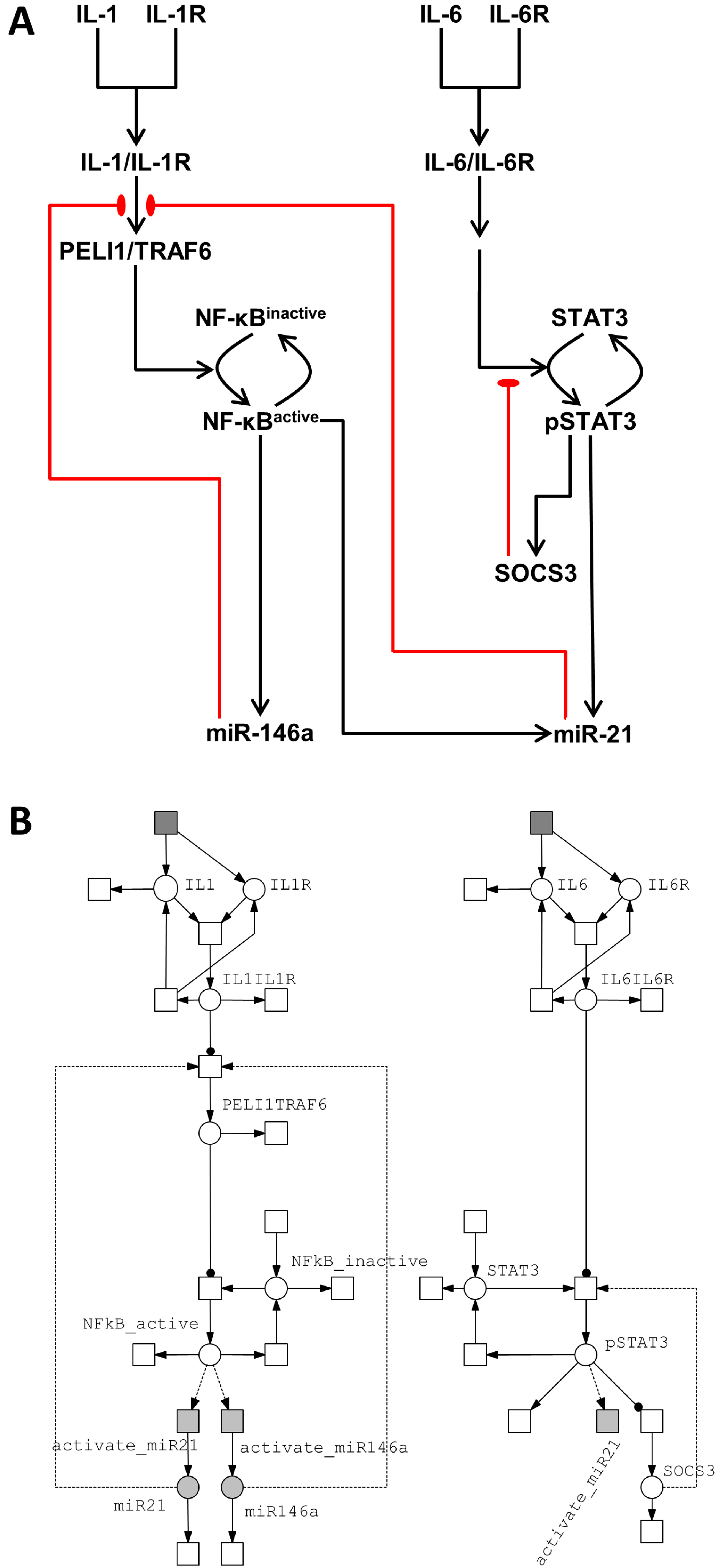
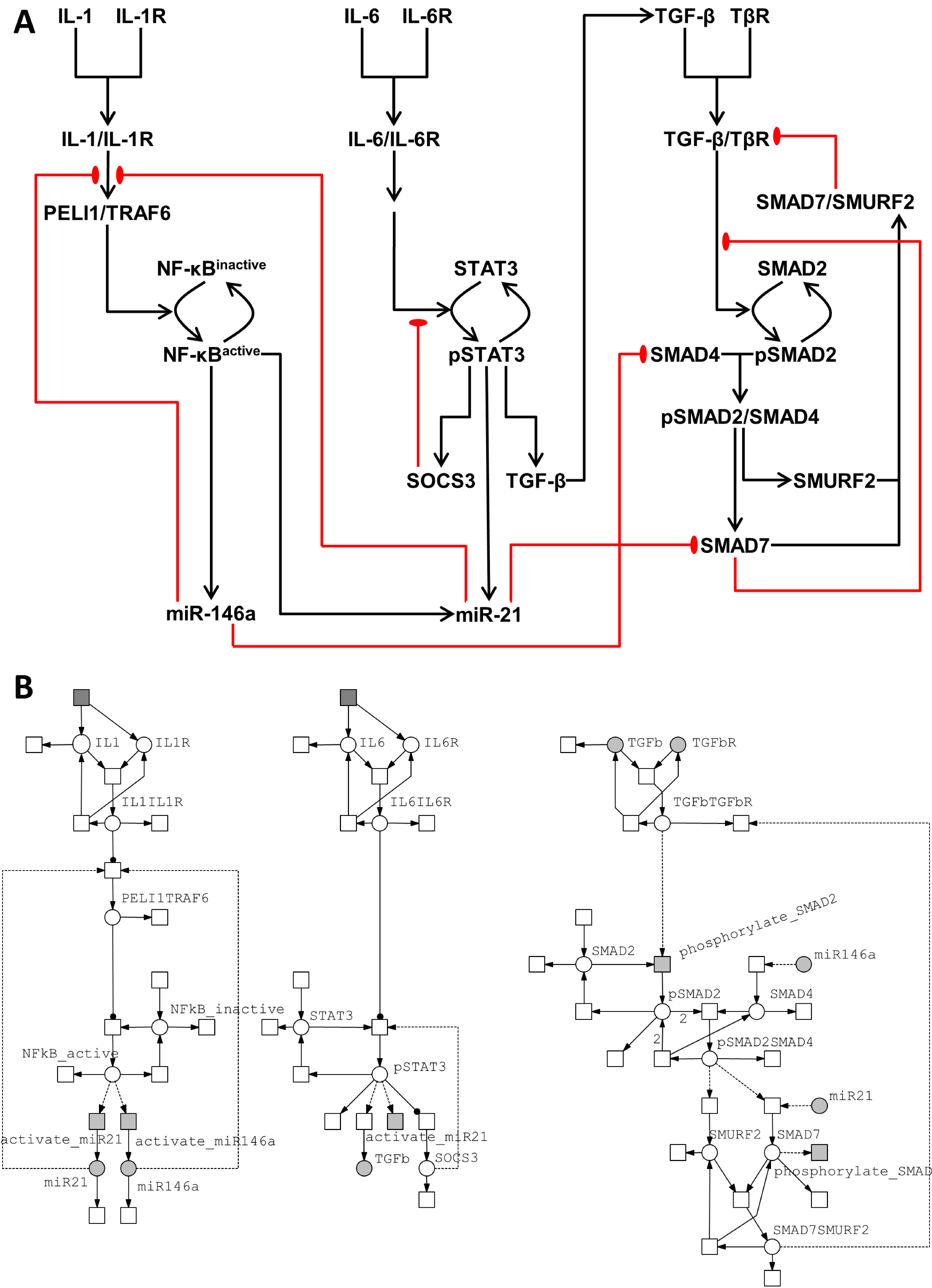
3.2.1. Model of the IL-1/NF-κB Pathway
3.2.2. Model of the IL-6/STAT3 Pathway
3.2.3. Model of the TGF-β/SMAD Pathway
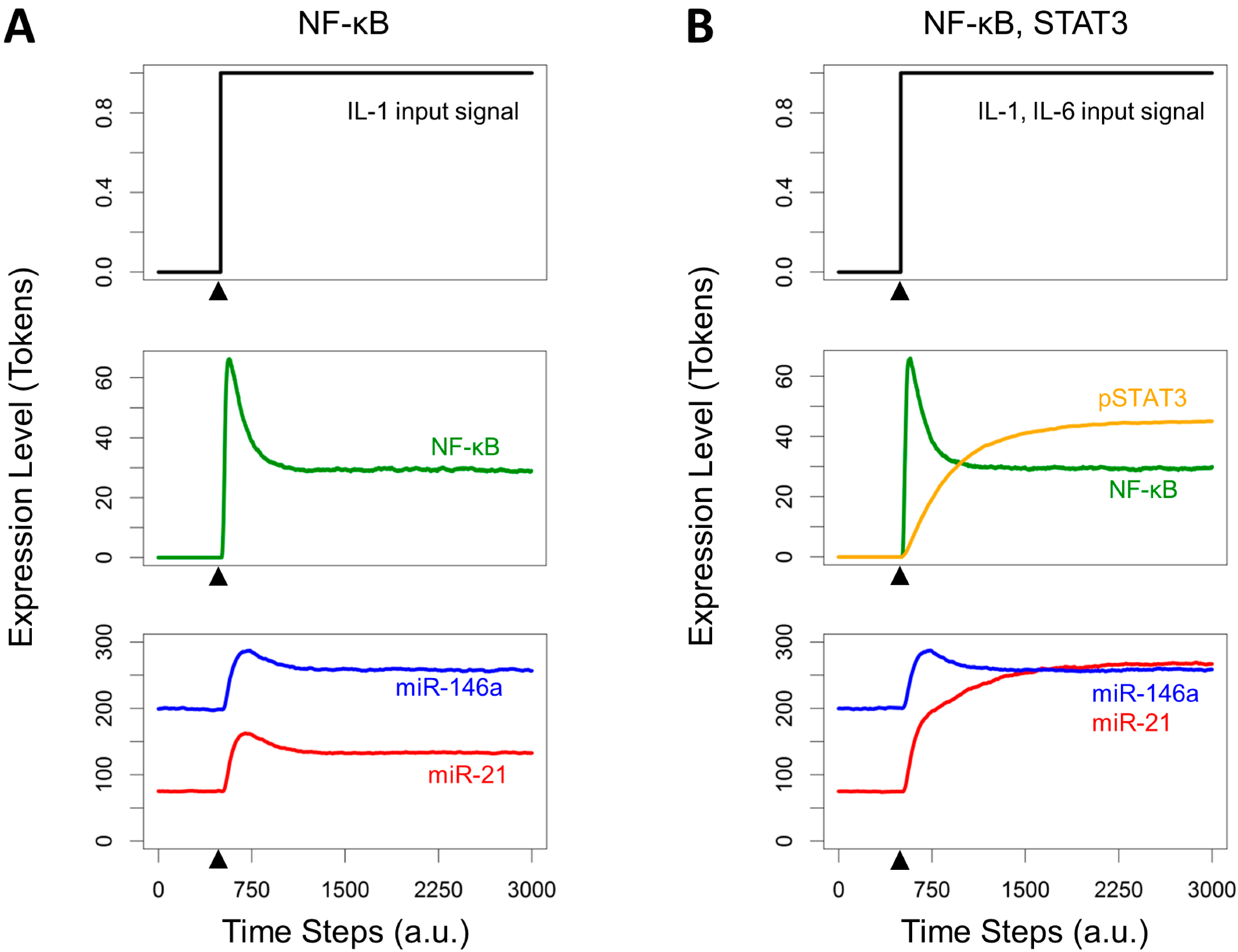
3.3. Crosstalk between Signaling Pathways and Effect on microRNA Levels
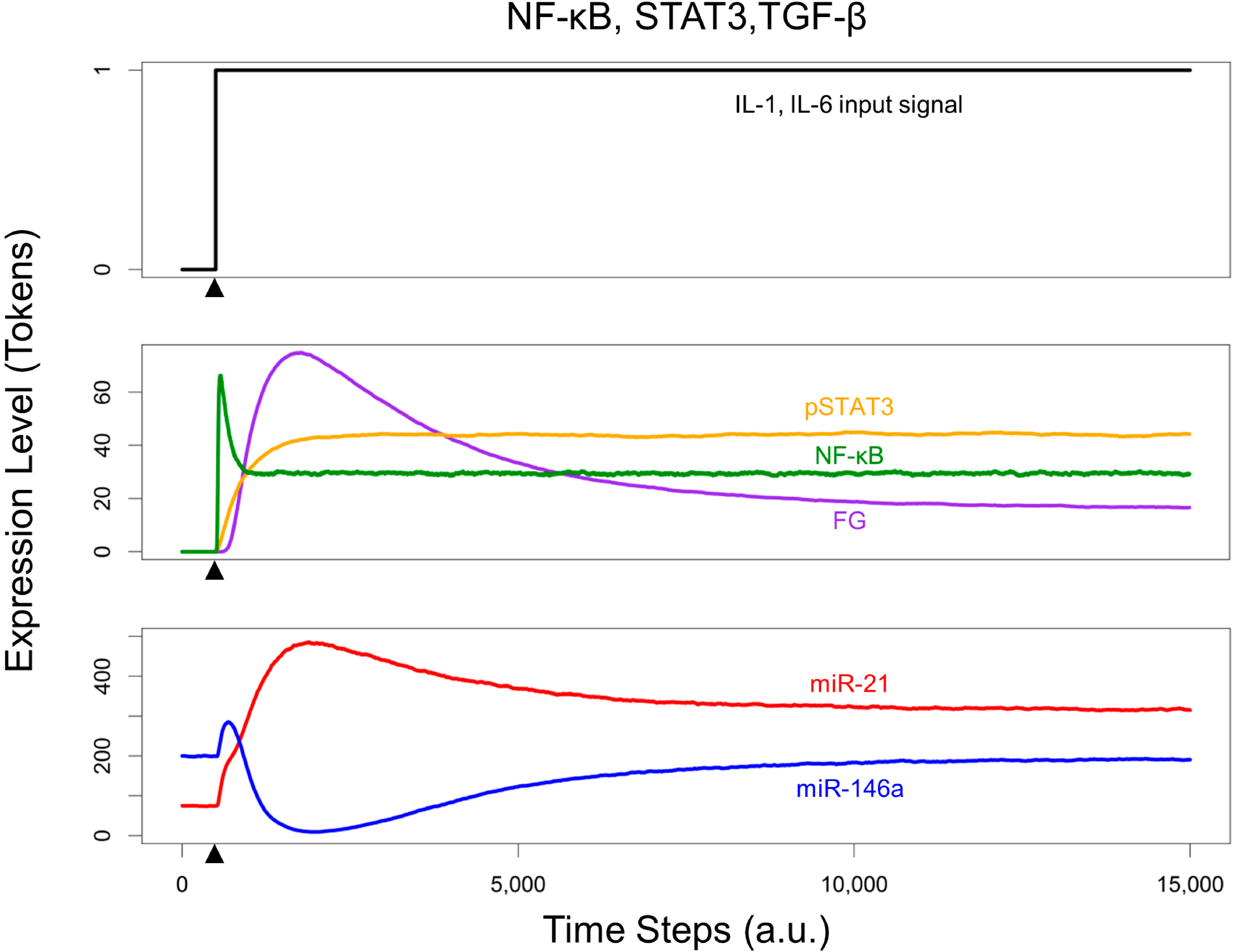
3.4. Effects of Timing Differences in NF-κB and STAT3 Activation
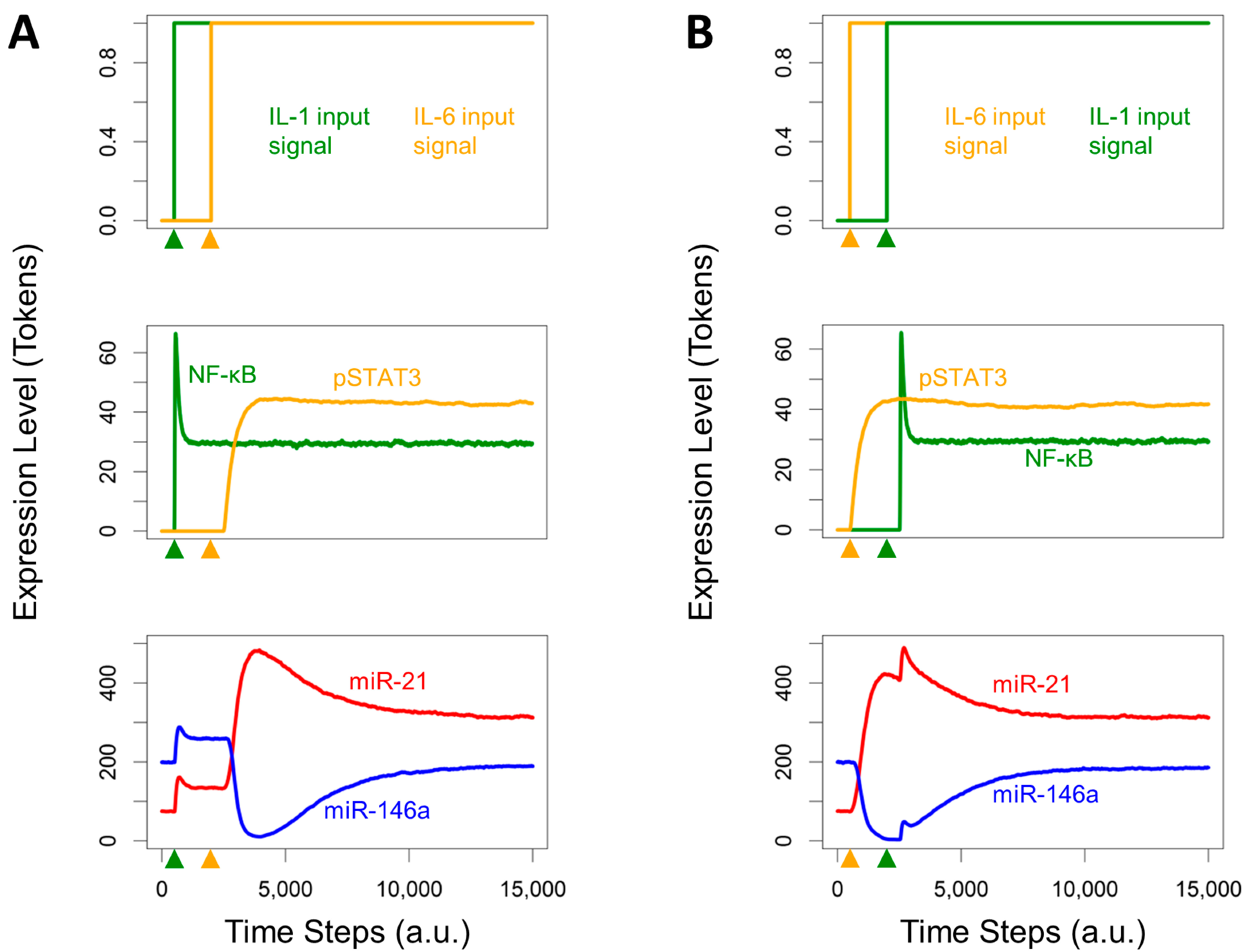
3.5. Re-Quiescence from the Activated HSC State
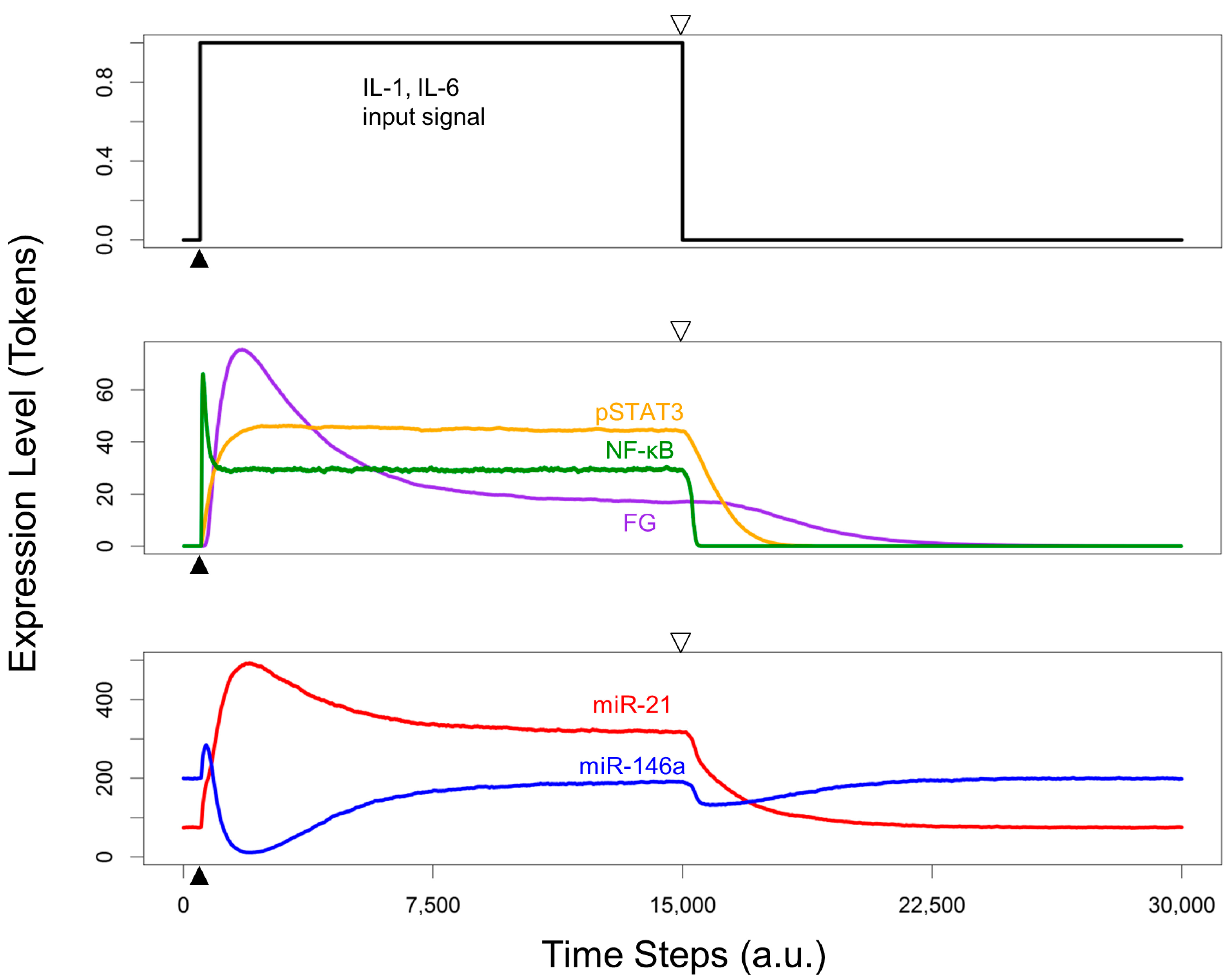
4. Conclusions
Acknowledgments
Author Contributions
Appendix
| Reaction | Equation | Parameters |
|---|---|---|
| IL-1/IL-1R association | k1[IL1][IL1R] | k1 = 0.001 |
| IL-1/IL-1R dissociation | 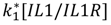 | 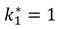 |
| IL-1 degradation | k2[IL1] | k2 = 0.001 |
| IL-1/IL-1R degradation | k3[IL1/IL1R] | k3 = 0.01 |
| PELI1/TRAF6 activation | k4[IL1/IL1R] − k5[miR21] − k6[miR146a] | k4 = 0.5 |
| PELI1/TRAF6 degradation | k7[PELI1/TRAF6] | k7 = 0.1 |
| NF-κBinactive production | k8 | k8 = 0.3 |
| NF-κB activation |  | v1 = 0.5 |
| NF-κBinactive degradation | k10[NFκBinactive] | k10 = 0.003 |
| NF-κBactive inactivation | k11[NFκBactive] | k11 = 0.1 |
| NF-κBactive degradation | k12[NFκBactive] | k12 = 0.01 |
| IL-6/IL-6R association | k13[IL6][IL6R] | k13 = 0.001 |
| IL-6/IL-6R dissociation | 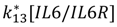 | 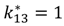 |
| IL-6 degradation | k14[IL6] | k14 = 0.001 |
| IL-6/IL-6R degradation | k15[IL6/IL6R] | k15 = 0.01 |
| STAT3 phosphorylation | 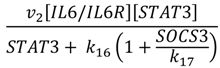 | v2 = 0.008 |
| STAT3 production | k18 | k18 = 0.08 |
| STAT3 degradation | k19[STAT3] | k19 = 0.0008 |
| pSTAT3 degradation |  | v3 = 0.025 |
| SOCS3 production |  | v4 = 0.1 |
| SOCS3 degradation | k22[SOCS3] | k22 = 0.001 |
| TGF-β production | k23[pSTAT3] | k23 = 0.04 |
| TGF-β degradation | k24[TGFβ] | k24 = 0.001 |
| TGF-β/TβR1 association | k25[TGFβ][TβRI] | k25 = 0.001 |
| TGF-β/TβR1 dissociation | 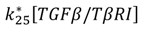 | 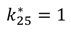 |
| TGF-β/TβR1 degradation | k26[TGFβ/TβRI] + k27[SMAD7/SMURF2] | k26 = 0.01 |
| SMAD2 production | k28 | k28 = 0.01 |
| SMAD2 phosphorylation | 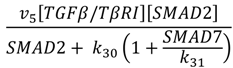 | v5 = 10 |
| SMAD2 dephosphorylation |  | v6 = 0.001 |
| pSMAD2 degradation | k33[pSMAD2] | k33 = 0.0005 |
| SMAD4 production | k34 − k35[miR146a] | k34 = 0.024 |
| SMAD4 degradation | k36[SMAD4] | k36 = 0.0001 |
| SMAD7 production | k39 + k40[pSMAD2/SMAD4] − k41[miR21] | k39 = 0.057 |
| SMAD7 degradation | k42[SMAD7] | k42 = 0.001 |
| SMURF2 production | k43 + k44[pSMAD2/SMAD4] | k43 = 0.05 |
| SMURF2 degradation | k45[SMURF2] | k45 = 0.001 |
| miR-21 activation | k50 + k51[NFκBactive ] + k52[pSTAT3] + k53[FG] | k50 = 0.75 |
| miR-146a activation | k54 + k55[NFκBactive ] − k56[FG] | k54 = 2 |
| miR-21 degradation | k57[miR21] | k57 = 0.01 |

Conflicts of Interest
References
- Bataller, R.; Brenner, D. Liver fibrosis. J. Clin. Investig. 2005, 115, 209–218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Friedman, S. Hepatic stellate cells: Protean, multifunctional, and enigmatic cells of the liver. Physiol. Rev. 2008, 88, 125–172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hendriks, H.; Verhoofstad, W. Perisinusoidal fat-storing cells are the main vitamin A storage sites in rat liver. Exp. Cell Res. 1985, 160, 138–149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paik, Y.-H.; Lee, K.S.; Lee, H.J.; Yang, K.M.; Lee, S.J.; Lee, D.K.; Han, K.-H.; Chon, C.Y.; Lee, S.I.; Moon, Y.M.; Brenner, D.A. Hepatic stellate cells primed with cytokines upregulate inflammation in response to peptidoglycan or lipoteichoic acid. Lab. Invest. 2006, 86, 676–686. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paik, Y.-H.; Schwabe, R.F.; Bataller, R.; Russo, M.P.; Jobin, C.; Brenner, D.A. Toll-like receptor 4 mediates inflammatory signaling by bacterial lipopolysaccharide in human hepatic stellate cells. Hepatology 2003, 37, 1043–1055. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maher, J.J. Cell-specific expression of hepatocyte growth factor in liver. J. Clin. Invest. 1993, 91, 2244–2252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Malik, R.; Selden, C.; Hodgson, H. The role of non-parenchymal cells in liver growth. Semin. Cell Dev. Biol. 2002, 13, 425–431. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mullhaupt, B.; Feren, A.; Fodor, E.; Jones, A. Liver expression of epidermal growth factor RNA. Rapid increases in immediate-early phase of liver regeneration. J. Biol. Chem. 1994, 2883, 19667–19670. [Google Scholar]
- Yin, C.; Evason, K.J.; Asahina, K.; Stainier, D.Y.R. Hepatic stellate cells in liver development, regeneration, and cancer. J. Clin. Invest. 2013, 123, 1902–1910. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, M.-Y.; Hu, J.-J.; Shen, J.; Wang, M.-L.; Zhang, Q.-Q.; Qu, Y.; Lu, L.-G. Stat3 signaling activation crosslinking of TGF-β1 in hepatic stellate cell exacerbates liver injury and fibrosis. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 2014, 1842, 2237–2245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hellerbrand, C.; Jobin, C.; Licato, L.L.; Sartor, R.B.; Brenner, D.A. Cytokines induce NF-κB in activated but not in quiescent rat hepatic stellate cells. Am. J. Physiol. 1998, 275, G269–G278. [Google Scholar]
- Gieling, R.G.; Wallace, K.; Han, Y.-P. Interleukin-1 participates in the progression from liver injury to fibrosis. Am. J. Physiol. Gastrointest. Liver Physiol. 2009, 296, G1324–G1331. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yoshida, K.; Matsuzaki, K. Differential regulation ofTGF-β/Smad signaling in hepatic stellate cells between acute and chronic liver injuries. Front. Physiol. 2012, 3, 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tahashi, Y.; Matsuzaki, K.; Date, M.; Yoshida, K.; Furukawa, F.; Sugano, Y.; Matsushita, M.; Himeno, Y.; Inagaki, Y.; Inoue, K. Differential regulation of TGF-beta signal in hepatic stellate cells between acute and chronic rat liver injury. Hepatology 2002, 35, 49–61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shigekawa, M.; Takehara, T.; Kodama, T.; Hikita, H.; Shimizu, S.; Li, W.; Miyagi, T.; Hosui, A.; Tatsumi, T.; Ishida, H.; et al. Involvement of STAT3-regulated hepatic soluble factors in attenuation of stellate cell activity and liver fibrogenesis in mice. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2011, 406, 614–620. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsukamoto, H. Cytokine regulation of hepatic stellate cells in liver fibrosis. Alcohol. Clin. Exp. Res. 1999, 23, 911–916. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kerr, T.A.; Korenblat, K.M.; Davidson, N.O. MicroRNAs and liver disease. Transl. Res. 2011, 157, 241–252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ji, J.; Zhang, J.; Huang, G.; Qian, J.; Wang, X.; Mei, S. Over-expressed microRNA-27a and 27b influence fat accumulation and cell proliferation during rat hepatic stellate cell activation. FEBS Lett. 2009, 583, 759–766. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, C.-J.; Pan, Q.; Li, D.-G.; Sun, H.; Liu, B.-W. miR-15b and miR-16 are implicated in activation of the rat hepatic stellate cell: An essential role for apoptosis. J. Hepatol. 2009, 50, 766–778. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sekiya, Y.; Ogawa, T.; Yoshizato, K.; Ikeda, K.; Kawada, N. Suppression of hepatic stellate cell activation by microRNA-29b. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2011, 412, 74–79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, C.J.; Pan, Q.; Cheng, T.; Jiang, B.; Chen, G.Y.; Li, D.G. Changes in microRNAs associated with hepatic stellate cell activation status identify signaling pathways. FEBS J. 2009, 276, 5163–5176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maubach, G.; Chin, M.; Lim, C.; Chen, J.; Yang, H.; Zhuo, L. miRNA studies in in vitro and in vivo activated hepatic stellate cells. World J. Gastroenterol. 2011, 17, 2748–2773. [Google Scholar]
- Huang, J.; Yu, X.; Fries, J.W.U.; Zhang, L.; Odenthal, M. MicroRNA function in the profibrogenic interplay upon chronic liver disease. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2014, 15, 9360–9371. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Z.; Zha, Y.; Hu, W.; Huang, Z.; Gao, Z.; Zang, Y.; Chen, J.; Dong, L.; Zhang, J. The autoregulatory feedback loop of MicroRNA-21/programmed cell death protein 4/Activation protein-1 (MiR-21/PDCD4/AP-1) as a driving force for hepatic fibrosis development. J. Biol. Chem. 2013, 288, 37082–37093. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, X.; Tsitsiou, E.; Herrick, S.E.; Lindsay, M.A. MicroRNAs and the regulation of fibrosis. FEBS J. 2010, 277, 2015–2021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, G.; Li, G.; Wang, Y.; Lei, W.; Xiao, Z. Aberrant miRNA expression response to UV irradiation in human liver cancer cells. Mol. Med. Rep. 2014, 9, 904–910. [Google Scholar]
- Karakatsanis, A.; Papaconstantinou, I.; Gazouli, M.; Lyberopoulou, A.; Polymeneas, G.; Voros, D. Expression of microRNAs, miR-21, miR-31, miR-122, miR-145, miR-146a, miR-200c, miR-221, miR-222, and miR-223 in patients with hepatocellular carcinoma or intrahepatic cholangiocarcinoma and its prognostic significance. Mol. Carcinog. 2013, 52, 297–303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rosato, P.; Anastasiadou, E.; Garg, N.; Lenze, D.; Boccellato, F.; Vincenti, S.; Severa, M.; Coccia, E.M.; Bigi, R.; Cirone, M.; et al. Differential regulation of miR-21 and miR-146a by Epstein-Barr virus-encoded EBNA2. Leukemia 2012, 26, 2343–2352. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marquez, R.T.; Wendlandt, E.; Galle, C.S.; Keck, K.; Mccaffrey, A.P. MicroRNA-21 is upregulated during the proliferative phase of liver regeneration, targets Pellino-1, and inhibits NF-κB signaling. Am. J. Physiol. Gastrointest. Liver Physiol. 2010, 298, 535–541. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Taganov, K.; Boldin, M. NF-κB-dependent induction of microRNA miR-146, an inhibitor targeted to signaling proteins of innate immune responses. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2006, 103, 12481–12486. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Petri, C. Kommunikation mit Automaten; Technische Universität Darmstadt: Darmstadt, Germany, 1962; p. 128. [Google Scholar]
- Rohr, C.; Marwan, W.; Heiner, M. Snoopy—A unifying Petri net framework to investigate biomolecular networks. Bioinformatics 2010, 26, 974–975. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chung, S.-W.; Miles, F.L.; Sikes, R.A.; Cooper, C.R.; Farach-Carson, M.C.; Ogunnaike, B.A. Quantitative modeling and analysis of the transforming growth factor beta signaling pathway. Biophys. J. 2009, 96, 1733–1750. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Furchtgott, L.A.; Chow, C.C.; Periwal, V. A model of liver regeneration. Biophys. J. 2009, 96, 3926–3935. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wegner, K.; Bachmann, A.; Schad, J.-U.; Lucarelli, P.; Sahle, S.; Nickel, P.; Meyer, C.; Klingmüller, U.; Dooley, S.; Kummer, U. Dynamics and feedback loops in the transforming growth factor β signaling pathway. Biophys. Chem. 2012, 162, 22–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dippold, R.P.; Vadigepalli, R.; Gonye, G.E.; Hoek, J.B. Chronic ethanol feeding enhances miR-21 induction during liver regeneration while inhibiting proliferation in rats. Am. J. Physiol. Gastrointest. Liver Physiol. 2012, 303, G733–G743. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elsharkawy, A.M.; Mann, D.A. Nuclear factor-κB and the hepatic inflammation-fibrosis-cancer axis. Hepatology 2007, 46, 590–597. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, K.S.; Buck, M.; Houglum, K.; Chojkier, M. Activation of Hepatic Stellate Cells by TGFa and Collagen Type I Is Mediated by Oxidative Stress Through c-myb Expression. J. Clin. Invest. 1995, 96, 2461–2468. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, Z.; Johnson, H.J.; Nie, H.; Qin, J.; Bird, T.A.; Li, X. Pellino 1 is required for interleukin-1 (IL-1)-mediated signaling through its interaction with the IL-1 receptor-associated kinase 4 (IRAK4)-IRAK-tumor necrosis factor receptor-associated factor 6 (TRAF6) complex. J. Biol. Chem. 2003, 278, 10952–10956. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, G.; Karin, M. NF-κB and STAT3—Key players in liver inflammation and cancer. Cell Res. 2011, 21, 159–168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iliopoulos, D.; Jaeger, S.A.; Hirsch, H.A.; Bulyk, M.L.; Struhl, K. STAT3 activation of miR-21 and miR-181b-1 via PTEN and CYLD are part of the epigenetic switch linking inflammation to cancer. Mol. Cell 2010, 39, 493–506. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, H.; Lafdil, F.; Kong, X.; Gao, B. Signal transducer and activator of transcription 3 in liver diseases: A novel therapeutic target. Int. J. Biol. Sci. 2011, 7, 536–550. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Francis, H.; McDaniel, K.; Han, Y.; Liu, X.; Kennedy, L.; Yang, F.; McCarra, J.; Zhou, T.; Glaser, S.; Venter, J.; et al. Regulation of the extrinsic apoptotic pathway by microRNA-21 in alcoholic liver injury. J. Biol. Chem. 2014. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marquez, R.T.; Bandyopadhyay, S.; Wendlandt, E.B.; Keck, K.; Hoffer, B.A.; Icardi, M.S.; Christensen, R.N.; Schmidt, W.N.; McCaffrey, A.P. Correlation between microRNA expression levels and clinical parameters associated with chronic hepatitis C viral infection in humans. Lab. Invest. 2010, 90, 1727–1736. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, Y.; Huang, C.; Sun, X.; Long, X.; Lv, X.; Li, J. MicroRNA-146a modulates TGF-beta1-induced hepatic stellate cell proliferation by targeting SMAD4. Cell. Signal. 2012, 24, 1923–1930. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yoshida, K.; Murata, M.; Yamaguchi, T.; Matsuzaki, K. TGF-β/Smad signaling during hepatic fibro-carcinogenesis (Review). Int. J. Oncol. 2014, 45, 1363–1371. [Google Scholar]
- Hayashi, H.; Abdollah, S.; Qiu, Y.; Cai, J.; Xu, Y.Y.; Grinnell, B.W.; Richardson, M.A.; Topper, J.N.; Gimbrone, M.A.; Wrana, J.L.; et al. The MAD-related protein Smad7 associates with the TGFbeta receptor and functions as an antagonist of TGFbeta signaling. Cell 1997, 89, 1165–1173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, X.; Liu, Z.; Chen, Y. Regulation of TGF- b signaling by Smad7 Overview of TGF-b Signaling Pathways. Acta Biochim. Biophys. Sin. (Shanghai) 2009, 41, 263–272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Davis, B.N.; Hilyard, A.C.; Lagna, G.; Hata, A. SMAD proteins control DROSHA-mediated microRNA maturation. Nature 2008, 454, 56–61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salazar-Montes, A.; Ruiz-Corro, L.; Sandoval-Rodriguez, A.; Lopez-Reyes, A.; Armendariz-Borunda, J. Increased DNA binding activity of NF-kappaB, STAT-3, SMAD3 and AP-1 in acutely damaged liver. World J. Gastroenterol. 2006, 12, 5995–6001. [Google Scholar]
- Kurinna, S.; Barton, M.C. Cascades of transcription regulation during liver regeneration. Int. J. Biochem. Cell Biol. 2011, 43, 189–197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miller, G.M.; Ogunnaike, B.A.; Schwaber, J.S.; Vadigepalli, R. Robust dynamic balance of AP-1 transcription factors in a neuronal gene regulatory network. BMC Syst. Biol. 2010, 4, 171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kong, X.; Feng, D.; Wang, H.; Hong, F.; Bertola, A.; Wang, F.-S.; Gao, B. Interleukin-22 induces hepatic stellate cell senescence and restricts liver fibrosis in mice. Hepatology 2012, 56, 1150–1159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Olsen, A.L.; Bloomer, S.A.; Chan, E.P.; Gaça, M.D.A.; Georges, P.C.; Sackey, B.; Uemura, M.; Janmey, P.A.; Wells, R.G. Hepatic stellate cells require a stiff environment for myofibroblastic differentiation. Am. J. Physiol. Gastrointest. Liver Physiol. 2011, 301, G110–G118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
© 2014 by the authors; licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Kuttippurathu, L.; Parrish, A.; Vadigepalli, R. Integrated Computational Model of Intracellular Signaling and microRNA Regulation Predicts the Network Balances and Timing Constraints Critical to the Hepatic Stellate Cell Activation Process. Processes 2014, 2, 773-794. https://doi.org/10.3390/pr2040773
Kuttippurathu L, Parrish A, Vadigepalli R. Integrated Computational Model of Intracellular Signaling and microRNA Regulation Predicts the Network Balances and Timing Constraints Critical to the Hepatic Stellate Cell Activation Process. Processes. 2014; 2(4):773-794. https://doi.org/10.3390/pr2040773
Chicago/Turabian StyleKuttippurathu, Lakshmi, Austin Parrish, and Rajanikanth Vadigepalli. 2014. "Integrated Computational Model of Intracellular Signaling and microRNA Regulation Predicts the Network Balances and Timing Constraints Critical to the Hepatic Stellate Cell Activation Process" Processes 2, no. 4: 773-794. https://doi.org/10.3390/pr2040773
APA StyleKuttippurathu, L., Parrish, A., & Vadigepalli, R. (2014). Integrated Computational Model of Intracellular Signaling and microRNA Regulation Predicts the Network Balances and Timing Constraints Critical to the Hepatic Stellate Cell Activation Process. Processes, 2(4), 773-794. https://doi.org/10.3390/pr2040773