Operational Stress and Degradation of Inverters in Renewable and Industrial Power Systems
Abstract
1. Introduction
1.1. Overall Inverter Performance
1.2. Degradation Mechanisms in Inverters
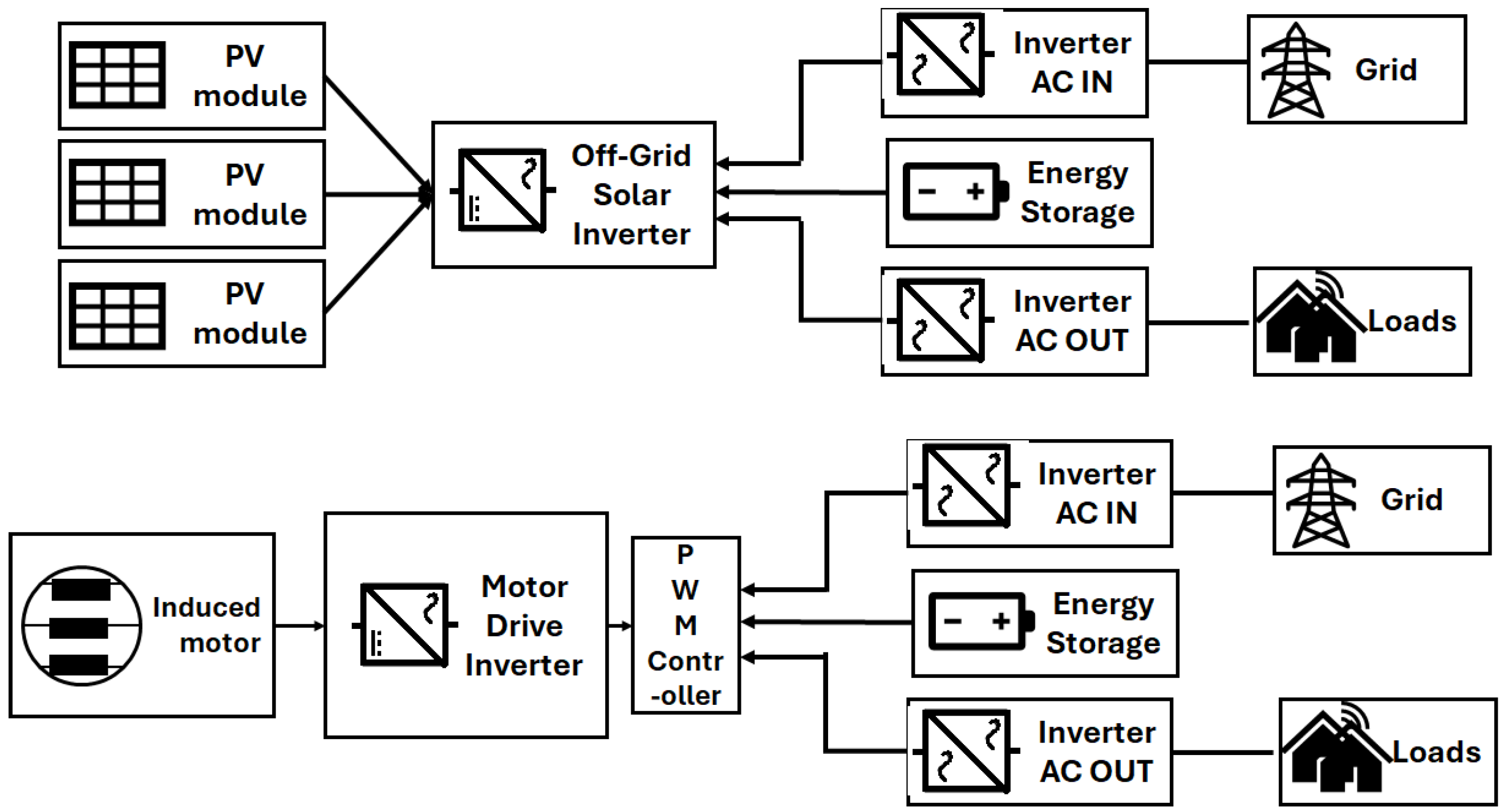
1.2.1. Role of Inverters in Induction Motors
1.2.2. Operational Factors Affecting Performance
1.3. Related Works
Central Research Question
2. Methods and Materials
2.1. Data Source and Preprocessing
Scope and Limitations
2.2. Statistical Modelling Approach
- Linear regression
- Normal distribution
- Log-normal distribution
- Gamma distribution
- Poisson distribution
2.3. Information Criteria
2.4. Modelling Tools and Implementation
2.5. Modelling Assumptions
- The operational conditions were stable over each recording window.
- No component replacements or reconfigurations occurred during the measurements.
- Measurement noise was Gaussian and independently distributed.
- Power and current signals were treated as continuous, while voltage spikes were considered for potential Poisson modeling (though ultimately found unsuitable).
3. Results
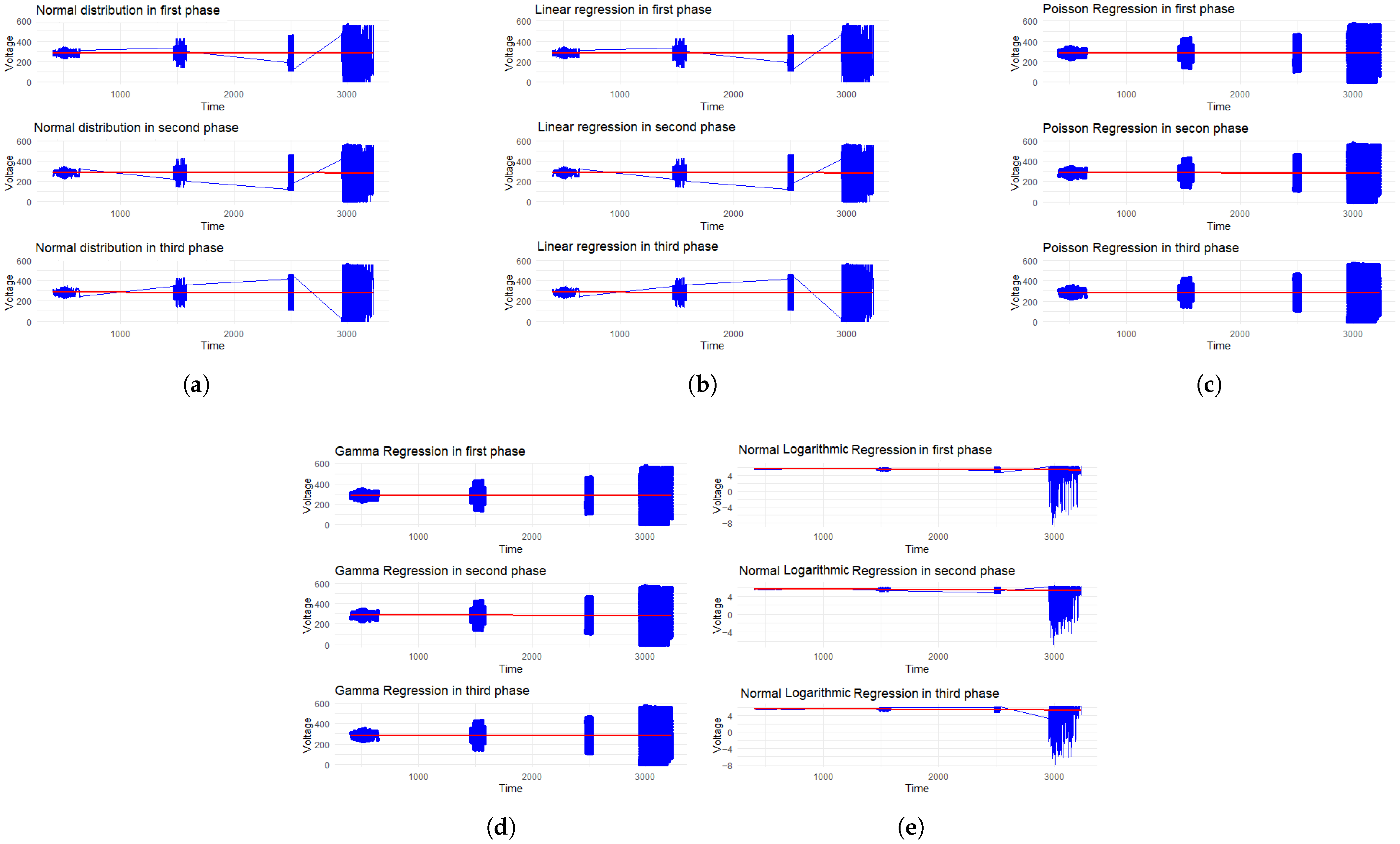
3.1. Viability of Statistical Models
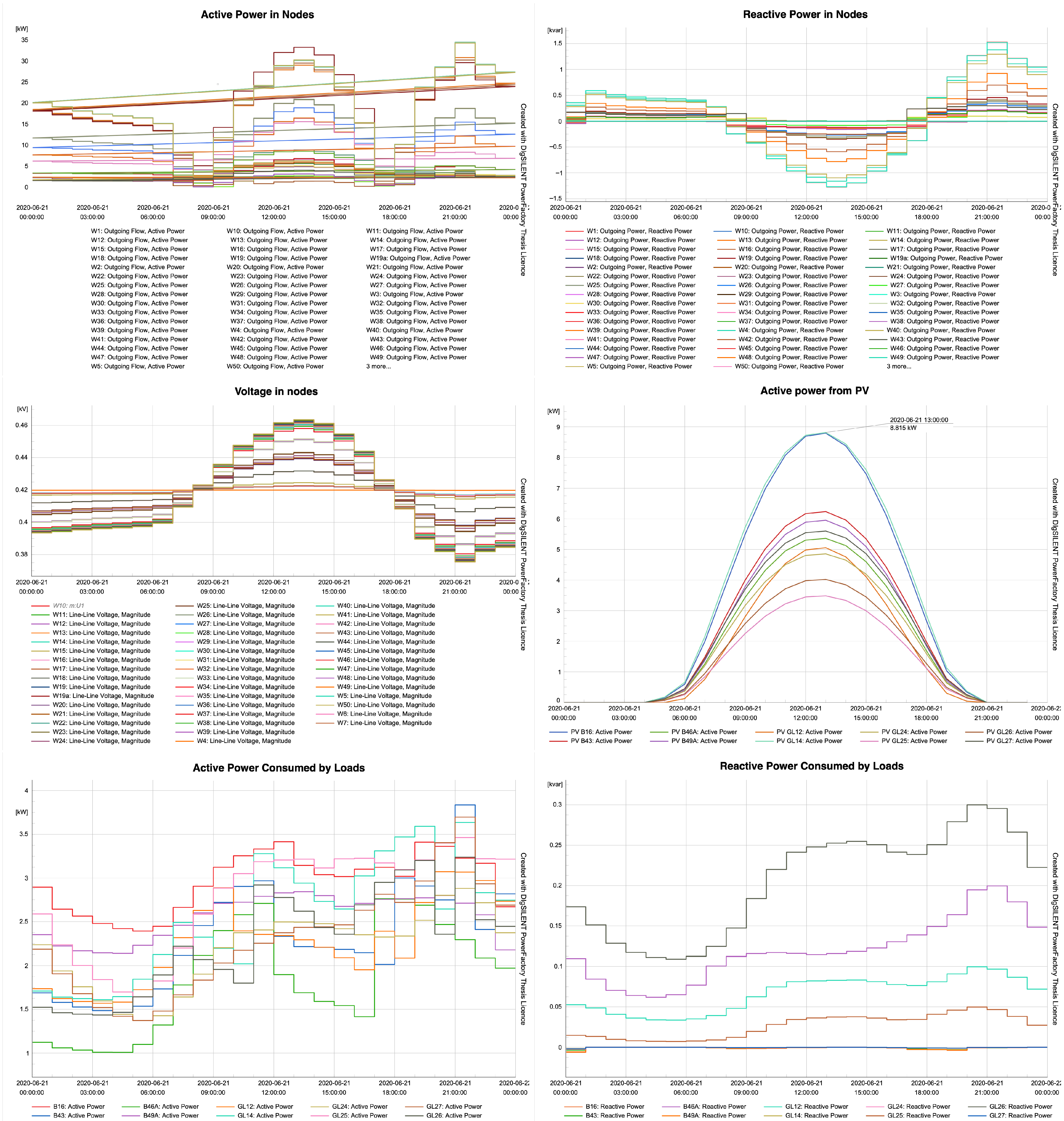
3.2. Voltage Regulation Issues in Microgrids
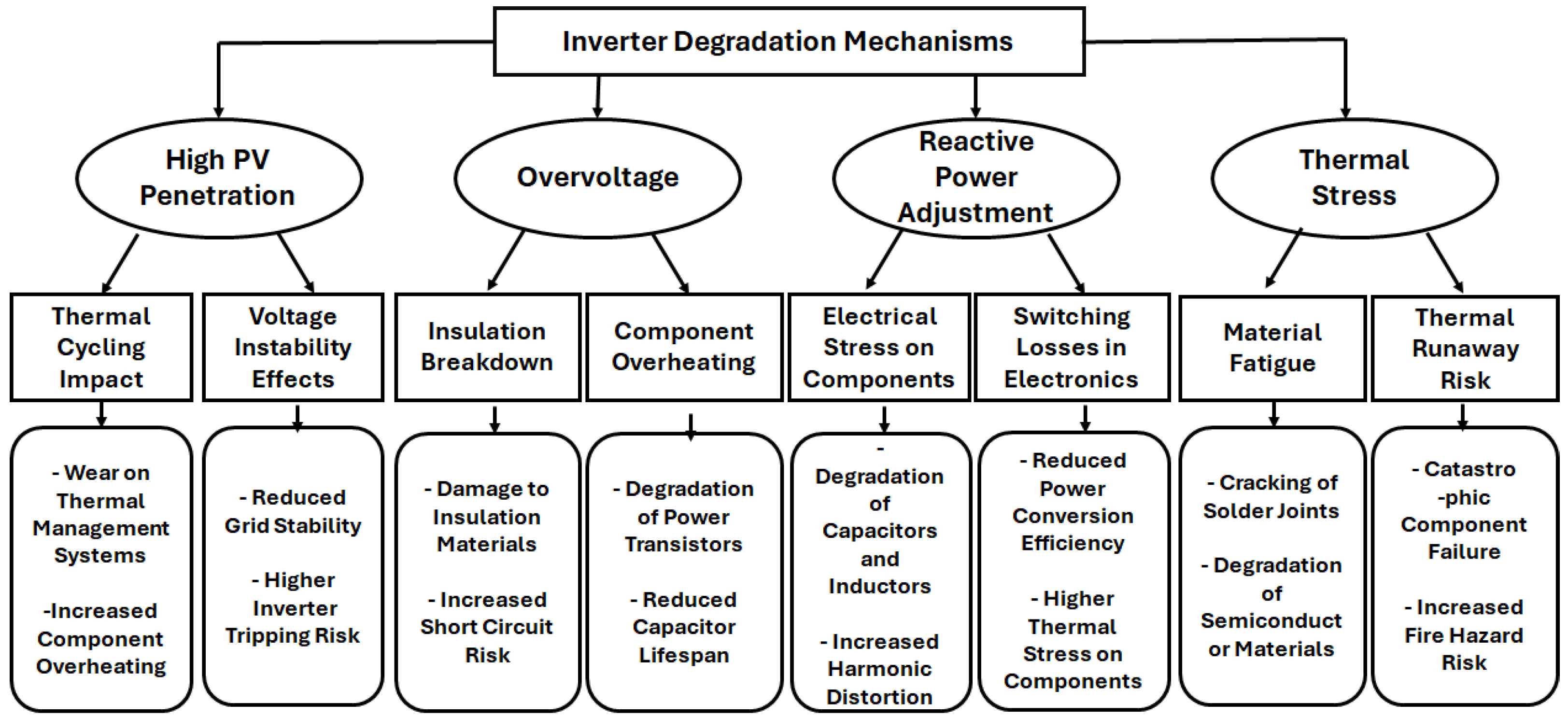
3.3. Degradation Mechanisms in PV Inverters
4. Discussion
4.1. International Statistics on Cost and Efficiency
4.2. Economic Considerations
4.3. Example Application and Annual Savings
4.4. Operational Demands and Stress on Components
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| PV | Photovoltaic |
| DC | Direct Current |
| AC | Alternating Current |
| PWM | Pulse-Width Modulation |
| HVAC | Heating, Ventilation, and Air Conditioning |
| AIC | Akaike Information Criterion |
| BIC | Bayesian Information Criterion |
| PID | Potential Induced Degradation |
| IGBT | Insulated Gate Bipolar Transistor |
References
- Fidone, G.; Migliazza, G.; Carfagna, E.; Buticchi, G.; Lorenzani, E. Common Architectures and Devices for Current Source Inverter in Motor-Drive Applications: A Comprehensive Review. Energies 2023, 16, 5645. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blaabjerg, F.; Teodorescu, R.; Liserre, M.; Timbus, A.V. Overview of Control and Grid Synchronization for Distributed Power Generation Systems. IEEE Trans. Ind. Electron. 2006, 53, 1398–1409. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dhanamjayulu, C.; Padmanaban, S.; Holm-Nielsen, J.; Blaabjerg, F. Design and Implementation of a Single-Phase 15-Level Inverter with Reduced Components for Solar PV Applications. IEEE Access 2021, 9, 581–594. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ji, Z.; Cheng, S.; Li, X.; Lv, Y.; Wang, D. An Optimal Periodic Carrier Frequency PWM Scheme for Suppressing High-Frequency Vibrations of Permanent Magnet Synchronous Motors. IEEE Trans. Power Electron. 2023, 38, 13008–13018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Asadi, Y.; Eskandari, M.; Mansouri, M.; Savkin, A.; Pathan, E. Frequency and Voltage Control Techniques through Inverter-Interfaced Distributed Energy Resources in Microgrids: A Review. Energies 2022, 15, 8580. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rokrok, E.; Shafie-khah, M.; Catalão, J. Review of primary voltage and frequency control methods for inverter-based islanded microgrids with distributed generation. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 2018, 82, 3225–3235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gonzalez-Cordoba, J.; Osornio-Rios, R.; Granados-Lieberman, D.; Romero-Troncoso, R.; Valtierra-Rodriguez, M. Correlation Model between Voltage Unbalance and Mechanical Overload Based on Thermal Effect at the Induction Motor Stator. IEEE Trans. Energy Convers. 2017, 32, 1602–1610. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koteleva, N.; Korolev, N.; Zhukovskiy, Y.; Baranov, G. A soft sensor for measuring the wear of an induction motor bearing by the Park’s vector components of current and voltage. Sensors 2021, 21, 7900. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, H.; Zhang, M.; Wang, X. Fracture failure analysis of insulation with initial crack defect for stator end-winding in induction motor by using magnetic-structural coupling model. Eng. Fail. Anal. 2023, 149, 107239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chisedzi, L.; Muteba, M. Detection of Broken Rotor Bars in Cage Induction Motors Using Machine Learning Methods. Sensors 2023, 23, 9079. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Herz, M.; Friesen, G.; Jahn, U.; Lindig, S.; Moser, D. Identify, analyse and mitigate—Quantification of technical risks in PV power systems. Prog. Photovol. Res. Appl. 2023, 31, 1285–1298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Damo, U.; Ozoegwu, C.; Ogbonnaya, C.; Maduabuchi, C. Effects of light, heat and relative humidity on the accelerated testing of photovoltaic degradation using Arrhenius model. Sol. Energy 2023, 250, 335–346. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Syamsuddin, A.; Adhi, A.; Kusumawardhani, A.; Prahasto, T.; Widodo, A. Predictive maintenance based on anomaly detection in photovoltaic system using SCADA data and machine learning. Results Eng. 2024, 24, 103589. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marangis, D.; Livera, A.; Tziolis, G.; Kyprianou, A.; Georghiou, G. Trend-Based Predictive Maintenance and Fault Detection Analytics for Photovoltaic Power Plants. Sol. Rrl 2024, 8, 2400473. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ballal, M.; Verma, S.; Suryawanshi, H.; Wakode, S.; Mishra, M. An Improved Voltage Regulation and Effective Power Management by Coordinated Control Scheme in Multibus DC Microgrid. IEEE Access 2022, 10, 72301–72311. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, S.H.; Byun, H.J.; Jeong, W.S.; Yi, J.; Won, C.Y. Hierarchical Control With Voltage Balancing and Energy Management for Bipolar DC Microgrid. IEEE Trans. Ind. Electron. 2023, 70, 9147–9157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chakraborty, A.; Datta, G.; Mandal, A. Robust Hierarchical Bayes Small Area Estimation for the Nested Error Linear Regression Model. Int. Stat. Rev. 2019, 87, S158–S176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heba, A.; Assaf, G. Bayes Linear Regression Performance Model Depending on Experts’ Knowledge and Current Road Condition. Adv. Civ. Eng. Mater. 2018, 7, 428–445. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aggarwal, P.; Mehta, S. Robustness of Bayes Estimation of Coefficient of Variation for Normal Distribution for a Class of Moderately Non-Gamma Prior Distributions. Stat. Appl. 2022, 20, 135–146. [Google Scholar]
- Durante, D. Conjugate Bayes for Probit Regression via Unified Skew-Normal Distributions. Biometrika 2019, 106, 765–779. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Uzan, H.; Sardi, S.; Goldental, A.; Vardi, R.; Kanter, I. Stationary log-normal distribution of weights stems from spontaneous ordering in adaptive node networks. Sci. Rep. 2018, 8, 13091. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singhasomboon, L.; Panichkitkosolkul, W.; Volodin, A. Point Estimation for the Ratio of Medians of Two Independent Log-Normal Distributions. Lobachevskii J. Math. 2021, 42, 415–425. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuan, M.; Zhang, Q.; Wei, L.S. One-sided empirical Bayes test for location parameter in Gamma distribution. Appl. Math. 2018, 33, 287–297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, J.; Zhang, Y.Y.; Sun, Y. The empirical Bayes estimators of the rate parameter of the inverse gamma distribution with a conjugate inverse gamma prior under Stein’s loss function. J. Stat. Comput. Simul. 2021, 91, 1504–1523. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hamura, Y.; Kubokawa, T. Proper Bayes minimax estimation of parameters of Poisson distributions in the presence of unbalanced sample sizes. Braz. J. Probab. Stat. 2020, 34, 728–751. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.Y.; Wang, Z.Y.; Duan, Z.M.; Mi, W. The empirical Bayes estimators of the parameter of the Poisson distribution with a conjugate gamma prior under Stein’s loss function. J. Stat. Comput. Simul. 2019, 89, 3061–3074. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Selig, K.; Shaw, P.; Ankerst, D. Bayesian information criterion approximations to Bayes factors for univariate and multivariate logistic regression models. Int. J. Biostat. 2021, 17, 241–266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zanini, A.; Woodbury, A. Contaminant source reconstruction by empirical Bayes and Akaike’s Bayesian Information Criterion. J. Contam. Hydrol. 2016, 185–186, 74–86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lorah, J.; Womack, A. Value of sample size for computation of the Bayesian information criterion (BIC) in multilevel modeling. Behav. Res. Methods 2019, 51, 440–450. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, H.; Fai Cheung, S.; On Leung, S. Simple use of BIC to Assess Model Selection Uncertainty: An Illustration using Mediation and Moderation Models. Multivar. Behav. Res. 2020, 55, 1–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jarosz, A. Achieving grid resilience through energy storage and model reference adaptive control for effective active power voltage regulation. Energy Convers. Manag. X 2024, 22, 100533. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deloitte. Predictive Maintenance and the Smart Factory; Technical Report; Deloitte: Jeddah, Saudi Arabia, 2017; Available online: https://www.deloitte.com/us/en/services/consulting/services/predictive-maintenance-and-the-smart-factory.html (accessed on 10 July 2025).
- McKinsey Company. Digital Manufacturing: The Revolution Will Be Virtualized; McKinsey Insights: New York, NY, USA, 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, Y.; Tolbert, L.; Kritprajun, P.; Schneider, K.; Prabakar, K. Fast Quasi-Static Time-Series Simulation for Accurate PV Inverter Semiconductor Fatigue Analysis with a Long-Term Solar Profile. Energies 2022, 15, 9104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guerra, G.; Ruiz, P.M.; Anamiati, G.; Landberg, L. Uncertainty-aware estimation of inverter field efficiency using Bayesian neural networks. EPJ Photovolt. 2024, 15, 33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roy, S.; Tufail, S.; Tariq, M.; Sarwat, A. Photovoltaic Inverter Failure Mechanism Estimation Using Operational Data; Technical Report; US Department of Energy, Office of Scientific and Technical Information (OSTI): Oak Ridge, TN, USA, 2024.
- Wang, L.; Thiagarajan, J.; Jin, C.; Zhang, W. Accelerating Simulation for High-Fidelity PV Inverter System Reliability Assessment with HPC; Technical Report; National Renewable Energy Laboratory (NREL): Golden, CO, USA, 2022. [CrossRef]


| Degradation Mechanism | Causes | Negative Effects |
|---|---|---|
| Thermal Overload [7] | Excessive current due to voltage imbalance or overloading | Insulation degradation and reduced motor lifespan |
| Bearing Wear [8] | Mechanical stress from misalignment or vibration | Increased friction, overheating, and eventual motor failure |
| Electrical Insulation Breakdown [9] | High voltage spikes or harmonics | Short circuits and reduced motor efficiency |
| Rotor Bar [10] | Cyclic mechanical stress and thermal cycling | Reduced torque and motor performance |
| Model | Phase | Min | Max | Average | AIC | BIC |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Linear | 1 | −2.288 | 573.339 | 283.412 | 2,854,100 | 2,854,132 |
| 2 | −2.088 | 573.202 | 283.468 | 2,847,739 | 2,847,770 | |
| 3 | −2.312 | 573.172 | 283.746 | 2,853,894 | 2,853,925 | |
| Normal | 1 | −2.288 | 573.339 | 283.412 | 2,889,722 | 2,889,753 |
| 2 | −2.088 | 573.202 | 283.468 | 2,888,268 | 2,888,299 | |
| 3 | −2.312 | 573.172 | 283.746 | 2,889,556 | 2,889,588 | |
| Log-Normal | 1 | −2.288 | 573.339 | 283.412 | 447,315.4 | 447,346.4 |
| 2 | −2.088 | 573.202 | 283.468 | 541,018.1 | 541,049.2 | |
| 3 | −2.312 | 573.172 | 283.746 | 521,441.3 | 521,472.4 | |
| Gamma | 1 | 10−6 | 573.339 | 283.429 | 3,102,113 | 3,102,144 |
| 2 | 10−6 | 573.202 | 283.479 | 3,085,535 | 3,085,566 | |
| 3 | 10−6 | 573.172 | 283.760 | 3,096,033 | 3,096,064 | |
| Poisson | 1 | 0 | 573.339 | 283.429 | Inf | Inf |
| 2 | 0 | 573.202 | 283.479 | Inf | Inf | |
| 3 | 0 | 573.172 | 283.760 | Inf | Inf |
| Model | Phase | Min | Max | Average | AIC | BIC |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Linear | A | −7.300 | 7.470 | 0.0005 | 1,035,254 | 1,035,285 |
| B | −6.320 | 6.668 | −0.0077 | 1,025,782 | 1,025,813 | |
| C | −7.113 | 7.437 | −0.0090 | 1,038,845 | 1,038,876 | |
| Normal | A | −7.300 | 7.470 | 0.0005 | 1,035,254 | 1,035,285 |
| B | −6.320 | 6.668 | −0.0077 | 1,025,782 | 1,025,813 | |
| C | −7.113 | 7.437 | −0.0090 | 1,038,845 | 1,038,876 | |
| Log-Normal | A | −7.300 | 7.470 | 0.0005 | 352,285.4 | 352,314.4 |
| B | −6.320 | 6.668 | −0.0077 | 346,475.3 | 346,504.4 | |
| C | −7.113 | 7.437 | −0.0090 | 351,299.3 | 351,328.3 | |
| Gamma | A | 10−6 | 7.470 | 0.9014 | Inf | Inf |
| B | 10−6 | 6.668 | 0.8872 | Inf | Inf | |
| C | 10−6 | 7.437 | 0.9052 | Inf | Inf | |
| Poisson | A | 10−6 | 7.470 | 0.9014 | Inf | Inf |
| B | 10−6 | 6.668 | 0.8872 | Inf | Inf | |
| C | 10−6 | 7.437 | 0.9052 | Inf | Inf |
| Model | Phase | Min | Max | Average | AIC | BIC |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Linear | A | −2976.961 | 3626.644 | 94.839 | 2,854,100 | 2,854,132 |
| B | −2583.185 | 3688.165 | 95.983 | 2,847,739 | 2,847,770 | |
| C | −2626.442 | 3962.193 | 92.886 | 2,853,894 | 2,853,925 | |
| Normal | A | −2976.961 | 3626.644 | 94.839 | 2,854,100 | 2,854,132 |
| B | −2583.185 | 3688.165 | 95.983 | 2,847,739 | 2,847,770 | |
| C | −2626.442 | 3962.193 | 92.886 | 2,853,894 | 2,853,925 | |
| Log-Normal | A | −2976.961 | 3626.644 | 94.839 | 430,388.0 | 430,419.0 |
| B | −2583.185 | 3688.165 | 95.983 | 523,117.1 | 523,148.2 | |
| C | −2626.442 | 3962.193 | 92.886 | 506,667.8 | 506,698.8 | |
| Gamma | A | 10−6 | 573.339 | 283.429 | 3,093,952 | 3,093,983 |
| B | 10−6 | 573.202 | 283.479 | 3,074,709 | 3,074,740 | |
| C | 10−6 | 573.172 | 283.760 | 3,087,287 | 3,087,318 | |
| Poisson | A | 0 | 573.339 | 283.429 | Inf | Inf |
| B | 0 | 573.202 | 283.479 | Inf | Inf | |
| C | 0 | 573.172 | 283.760 | Inf | Inf |
| Model | Phase | Min | Max | Average | AIC | BIC |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Linear | A | −2976.961 | 3626.644 | 94.839 | 3,724,558 | 3,724,589 |
| B | −2583.185 | 3688.165 | 95.983 | 3,712,701 | 3,712,732 | |
| C | −2626.442 | 3962.193 | 92.886 | 3,726,838 | 3,726,869 | |
| Normal | A | −2976.961 | 3626.644 | 94.839 | 3,724,558 | 3,724,589 |
| B | −2583.185 | 3688.165 | 95.983 | 3,712,701 | 3,712,732 | |
| C | −2626.442 | 3962.193 | 92.886 | 3,726,838 | 3,726,869 | |
| Log-Normal | A | −13.816 | 8.196 | −3.970 | 1,739,614 | 1,739,645 |
| B | −13.816 | 8.213 | −4.095 | 1,740,573 | 1,740,604 | |
| C | −13.816 | 8.285 | −4.049 | 1,740,519 | 1,740,550 | |
| Gamma | A | 0 | 3626.644 | 302.853 | Inf | Inf |
| B | 0 | 3688.165 | 300.030 | Inf | Inf | |
| C | 0 | 3962.193 | 304.167 | Inf | Inf | |
| Poisson | A | 0 | 3626.644 | 302.853 | Inf | Inf |
| B | 0 | 3688.165 | 300.030 | Inf | Inf | |
| C | 0 | 3962.193 | 304.167 | Inf | Inf |
| Degradation Mechanism | Causes | Negative Effects |
|---|---|---|
| Increased Operating Temperatures | Overvoltage conditions and reactive power adjustments | Reduced lifespan of heat-sensitive components like capacitors and semiconductors |
| Wear on Components | Frequent reactive power adjustments causing mechanical stress on switching devices (e.g., IGBTs) | Premature failure of critical components |
| Insulation Breakdown | Voltage stress over time | Increased risk of short circuits and component failures |
| Potential Induced Degradation (PID) | Stray currents and high system voltages | Power loss of up to ~30% in PV modules |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Jarosz-Kozyro, A.; Baranowski, J. Operational Stress and Degradation of Inverters in Renewable and Industrial Power Systems. Processes 2025, 13, 2987. https://doi.org/10.3390/pr13092987
Jarosz-Kozyro A, Baranowski J. Operational Stress and Degradation of Inverters in Renewable and Industrial Power Systems. Processes. 2025; 13(9):2987. https://doi.org/10.3390/pr13092987
Chicago/Turabian StyleJarosz-Kozyro, Anna, and Jerzy Baranowski. 2025. "Operational Stress and Degradation of Inverters in Renewable and Industrial Power Systems" Processes 13, no. 9: 2987. https://doi.org/10.3390/pr13092987
APA StyleJarosz-Kozyro, A., & Baranowski, J. (2025). Operational Stress and Degradation of Inverters in Renewable and Industrial Power Systems. Processes, 13(9), 2987. https://doi.org/10.3390/pr13092987






