Glycemic Response to White Kidney Beans as Part of a Rice Meal: A Thermal Processing Method
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials
2.2. Single-Factor Experiment
2.3. Orthogonal Test
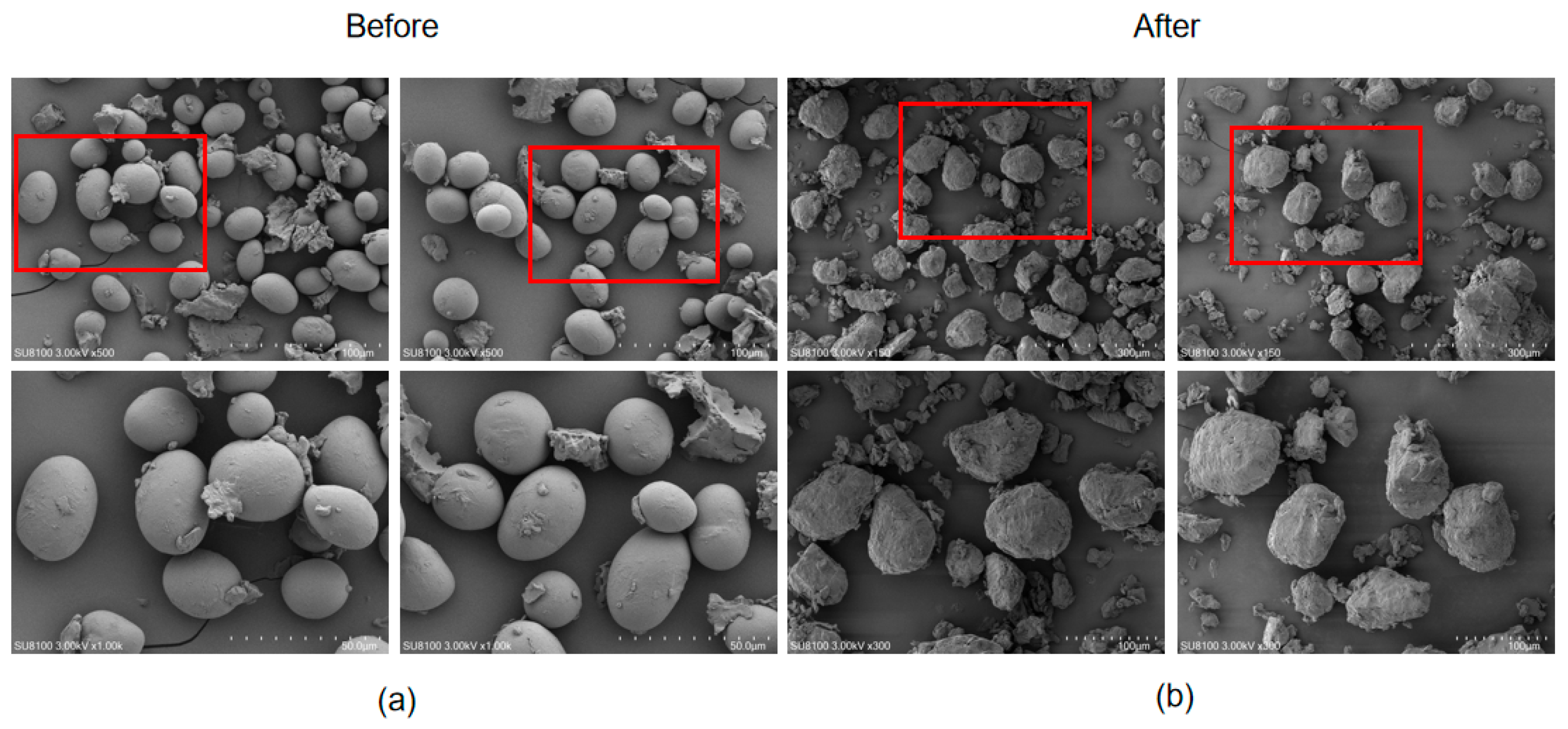
2.4. SEM Analysis
2.5. Detection of Nutritional Indexes of Boiled White Kidney Beans
2.6. Preparation of Low-GI White Kidney Beans and Refined White Rice
2.7. Sensory Evaluation
2.8. Analysis of in Vitro Digestion Characteristics
2.9. Texture Analysis
2.10. Chromaticity Analysis
2.11. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
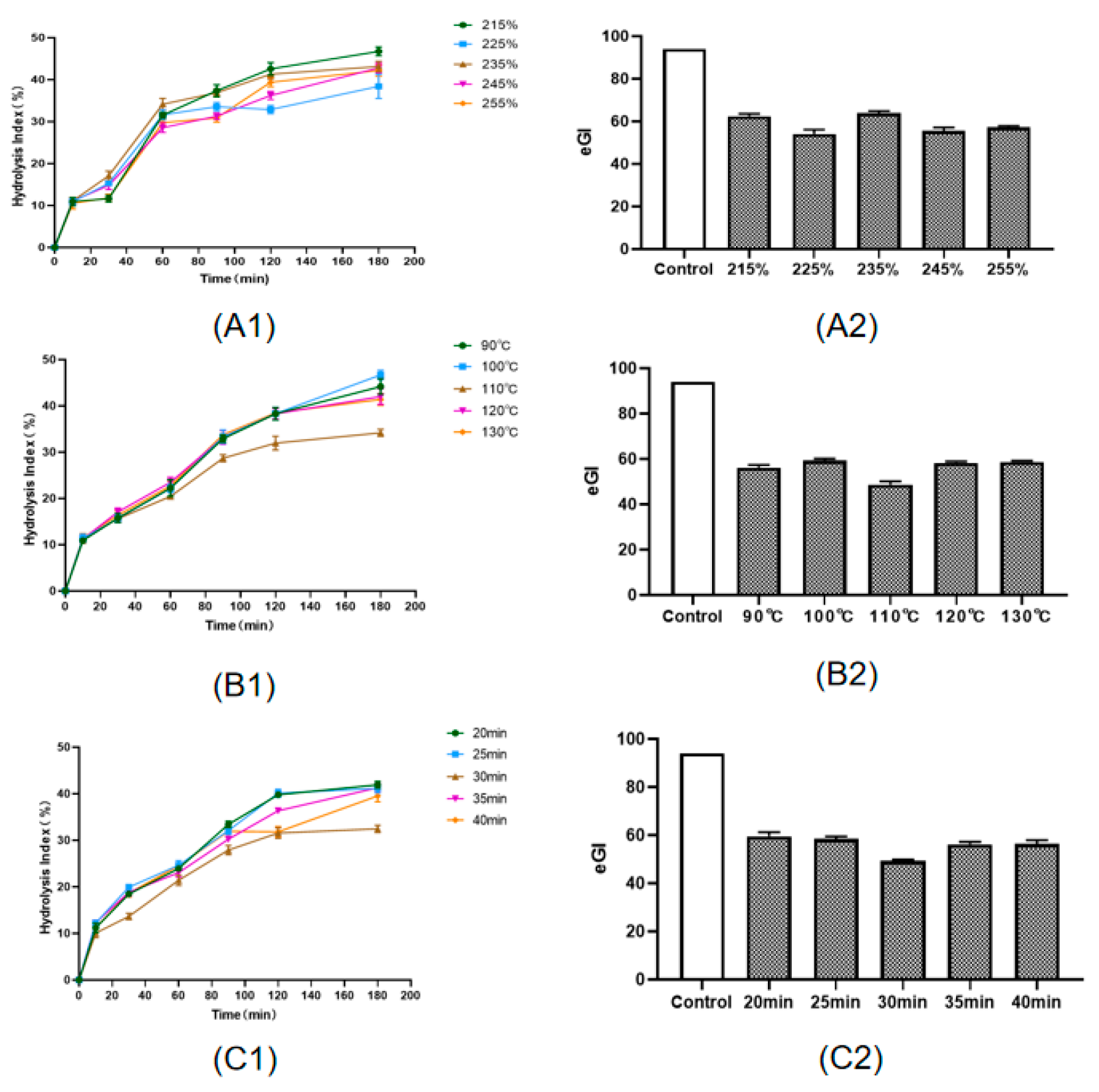
3.1. Single-Factor and Orthogonal Test Analysis
3.2. Cell Micromorphology
3.3. Determination of Nutritional Components
3.4. Determination of the Physical and Chemical Properties of Refined Rice with Low-GI White Kidney Beans
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Kan, L.; Nie, S.; Hu, J.; Wang, S.; Cui, S.W.; Li, Y.; Xu, S.; Wu, Y.; Wang, J.; Bai, Z.; et al. Nutrients, phytochemicals and antioxidant activities of 26 kidney bean cultivars. Food Chem. Toxicol. 2016, 108 Pt B, 467–477. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gomez, F.E.; Kelly, J.D.; Wright, E.M.; Awale, H.E.; Bales, S. Registration of ‘Denali’ white kidney bean. J. Plant Regist. 2024, 18, 479–484. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, T.; Gu, Y.; Waleed, A.-A.; Wang, L.; Li, Y.; Qian, H. Challenges and opportunities in developing low glycemic index foods with white kidney bean α-amylase inhibitor. Trends Food Sci. Technol. 2024, 147, 104397. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Okelo, E.O.; Wainaina, I.; Duijsens, D.; Onyango, A.; Sila, D.; Grauwet, T.; Hendrickx, M.E.G. Targeted hydrothermally induced cell biopolymer changes explain the in vitro digestion of starch and proteins in common bean (Phaseolus vulgaris) cotyledons. Food Funct. 2024, 15, 8848–8864. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aziz, A.; Millat, S.; Akter, T.; Hossain, S.; Islam, M.; Mohsin, S.; Ansari, F.; Kabir, A.; Amin, M.N.; Islam, M.S. A comprehensive review on clinically proven medicinal plants in the treatment of overweight and obesity, with mechanistic insights. Heliyon 2023, 9, e13493. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tormo, M.A.; Gil-Exojo, I.; de Tejada, A.R.; Campillo, J.E. Hypoglycaemic and anorexigenic activities of an α-amylase inhibitor from white kidney beans (Phaseolus vulgaris) in Wistar rats. Br. J. Nutr. 2004, 92, 785–790. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hasani-Ranjbar, S.; Nayebi, N.; Larijani, B.; Abdollahi, M. A systematic review of the efficacy and safety of herbal medicines used in the treatment of obesity. World J. Gastroenterol. 2009, 15, 3073–3085. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ma, Y.; Rang, Y.; Yang, R.; Zhao, W. Effect of white kidney bean extracts on estimated glycemic index of different kinds of porridge. LWT 2018, 96, 576–582. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Houghton, D.; Shannon, O.M.; Chater, P.I.; Wilcox, M.D.; Pearson, J.P.; Stanforth, K.; Jordan, C.; Avery, L.; Blain, A.P.; Joel, A.; et al. White kidney bean extract as a nutraceutical: Effects on gut microbiota, alpha-amylase inhibition, and user experiences. Gut Microbiome 2023, 4, e8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jäger, R.; Sawan, S.A.; Purpura, M.; Grube, B.; Röske, Y.; De Costa, P.; Chong, P.-W. Proprietary alpha-amylase inhibitor formulation from white kidney bean (Phaseolus vulgaris L.) promotes weight and fat loss: A 12-week, double-blind, placebo-controlled, randomized trial. Sci. Rep. 2024, 14, 12685. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yao, A.; Gbakayoro, J.-B.; Tan, C.; N’guessan, A.; Danho, J.; Kouassi, F.; Hué, A.; Koffi-Dago, P.; Traoré, M.; Maman, S.; et al. Glycemic Responses of Food Formulations Based on White Rice and White Bean. Food Nutr. Sci. 2023, 14, 225–232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, H.; Saeedi, P.; Karuranga, S.; Pinkepank, M.; Ogurtsova, K.; Duncan, B.B.; Stein, C.; Basit, A.; Chan, J.C.; Mbanya, J.C.; et al. Erratum to “IDF Diabetes Atlas: Global, regional and country-level diabetes prevalence estimates for 2021 and projections for 2045” [Diabetes Res. Clin. Pract. 183 (2022) 109119]. Diabetes Res. Clin. Pract. 2023, 204, 110945. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, J.; Ren, Z.-H.; Qiang, H.; Wu, J.; Shen, M.; Zhang, L.; Lyu, J. Trends in the incidence of diabetes mellitus: Results from the Global Burden of Disease Study 2017 and implications for diabetes mellitus prevention. BMC Public Health 2020, 20, 1415. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saeedi, P.; Petersohn, I.; Salpea, P.; Malanda, B.; Karuranga, S.; Unwin, N.; Colagiuri, S.; Guariguata, L.; Motala, A.A.; Ogurtsova, K.; et al. Global and regional diabetes prevalence estimates for 2019 and projections for 2030 and 2045: Results from the International Diabetes Federation Diabetes Atlas, 9th edition. Diabetes Res. Clin. Pract. 2019, 157, 107843. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mushtaq, F.; Amjad, A.; Qureshi, M.J.; Butt, A.; Ahmad, M.; Haider, H.M.A.; Raza, A. Effect of Thyroid Disorders on Cardiovascular Risk in Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus Patients. Indus J. Biosci. Res. 2024, 3, 75–80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- American Diabetes Association. 5. Lifestyle Management: Standards of Medical Care in Diabetes—2019. Diabetes Care 2019, 42 (Suppl. S1), S46–S60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peres, M.; Costa, H.S.; Silva, M.A.; Albuquerque, T.G. The Health Effects of Low Glycemic Index and Low Glycemic Load Interventions on Prediabetes and Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus: A Literature Review of RCTs. Nutrients 2023, 15, 5060. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- E Järvi, A.; E Karlström, B.; E Granfeldt, Y.; E Björck, I.; Asp, N.G.; O Vessby, B. Improved glycemic control and lipid profile and normalized fibrinolytic activity on a low-glycemic index diet in type 2 diabetic patients. Diabetes Care 1999, 22, 10–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, D.; Zhang, P.; Guo, H.; Ling, W. Taking a low glycemic index multi-nutrient supplement as breakfast improves glycemic control in patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus: A randomized controlled trial. Nutrients 2014, 6, 5740–5755. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, S.; Hu, Y.; Zhao, C.; Li, Y.; Zhang, Z.; Wang, W.; Bai, Y.; Zhou, J.; Xue, Y.; Zou, L.; et al. Effects of enzymatic hydrolysis technology on the physicochemical properties and biological activities of American ginseng beverages. Food Sci. Nutr. 2024, 12, 3674–3687. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, C.; Dhital, S.; Gilbert, R.G.; Gidley, M.J. High-amylose wheat starch: Structural basis for water absorption and pasting properties. Carbohydr. Polym. 2020, 245, 116557. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Arise, A.K.; Oriade, K.F.; Asogwa, T.N.; Nwachukwu, I. Amino acid profile, physicochemical and sensory properties of noodles produced from wheat-Bambara protein isolate. Meas. Food 2022, 5, 100020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Molchanova, E.N.; Shchegoleva, I.D.; Arnautova, Y.D. Justification for the use of beans in dessert mousse technology. Proc. Voronezh State Univ. Eng. Technol. 2021, 83, 88–94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, T. Research of Precook Process and Physicochemical Properties of Kidney Beans. Master’s Thesis, Jilin Agricultural University, Changchun, China, 2017; pp. 31–33. [Google Scholar]
- Cheng, B.; Zhang, L.; An, Y.X.; Li, M.Q. Study on the structural characteristics and in vitro digestion characteristics of potato resistant starch. J. Food Saf. Qual. Insp. 2021, 12, 6975–6981. [Google Scholar]
- Hong, T.; Zhao, Q.; Xu, D.; Yuan, Y.; Ma, Y.; Wu, F.; Xu, X. Effect of heat-treated flour on the quality and storage stability of fresh noodles. LWT 2021, 146, 111463. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, Y.; Xu, X.; Sheng, L. Effects of different plant proteins on the quality and characteristics of heat induced egg white protein gel under freezing conditions. Food Hydrocoll. 2024, 146, 109281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jo, Y.; Bang, W.-S.; Kim, M.K. Changes of Physiochemical and Enzymatic Activities of doenjang Prepared with Different Amount of Rice koji during 30 Days of Fermentation. Foods 2021, 10, 372. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ai, Z.; Zhang, Y.; Li, X.; Sun, W.; Liu, Y. Widely Targeted Metabolomics Analysis to Reveal Transformation Mechanism of Cistanche Deserticola Active Compounds During Steaming and Drying Processes. J. Front. Nutr. 2021, 8, 742511. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, J.; Pang, L.; Bao, L.; Ye, X.; Lu, G. Effect of White Kidney Bean Flour on the Rheological Properties and Starch Digestion Characteristics of Noodle Dough. Foods 2022, 11, 3680. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Atkinson, F.S.; Brand-Miller, J.C.; Foster-Powell, K.; Buyken, A.E.; Goletzke, J. International tables of glycemic index and glycemic load values 2021: A systematic review. Am. J. Clin. Nutr. 2021, 114, 1625–1632. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dhital, S.; Bhattarai, R.R.; Gorham, J.; Gidley, M.J. Intactness of cell wall structure controls the in vitro digestion of starch in legumes. Food Funct. 2016, 7, 1367–1379. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]

| Level | Factor | ||
|---|---|---|---|
| Water Addition A (%) | Temperature B (°C) | Time C (min) | |
| 1 | 215 | 100 | 25 |
| 2 | 225 | 110 | 30 |
| 3 | 235 | 120 | 35 |
| A (%) | B (°C) | C (min) | HI (%) | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 215 | 100 | 25 | 53.46 |
| 2 | 215 | 110 | 30 | 62.73 |
| 3 | 215 | 120 | 35 | 60.01 |
| 4 | 225 | 100 | 30 | 58.36 |
| 5 | 225 | 110 | 35 | 55.98 |
| 6 | 225 | 120 | 25 | 53.58 |
| 7 | 235 | 100 | 35 | 61.73 |
| 8 | 235 | 110 | 25 | 58.67 |
| 9 | 235 | 120 | 30 | 54.62 |
| Average 1 | 57.4 | 54.183 | 57.237 | |
| Average 2 | 58.64 | 58.46 | 59.57 | |
| Average 3 | 55.007 | 58.403 | 54.24 | |
| Range | 3.633 | 4.277 | 5.33 |
| SS | df | MS | F | P | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Water addition (A) | 51.3924 | 2 | 25.6962 | 8.57 | 0.001 |
| Temperature (B) | 42.9000 | 2 | 21.4500 | 7.15 | 0.003 |
| Time (C) | 56.2674 | 2 | 28.1337 | 9.40 | 0.001 |
| Error (E) | 13.7638 | 2 | 6.8819 | - | - |
| Total | 164.3236 | 8 | - | - | - |
| Protein (%) | Fat (%) | Moisture (%) | Ash (%) | Starch (%) | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Before | 22.0 | 1.0 | 3.07 | 3.6 | 62.0 |
| After | 24.3 | 1.8 | 4.15 | 4.2 | 49.0 |
| Sample (%) | Texture | Chromaticity | Sensory Score | In Vitro Digestion Rate | |||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Hardness | Resilience | Viscosity | Chewiness | L * | a * | b * | Color | Stickiness | Softness | Overall Liking | HI (%) | eGI | |
| 0% | 837.4 ± 37.01 f | 2.17 ±0.01 a | 1080.96 ± 6.67 a | 69.9 ± 0.51 f | 70.52 ± 0.24 a | 4.05 ± 0.12 f | 14.91 ± 0.25 f | 6.19 ± 0.03 a | 6.99 ± 0.18 a | 7.09 ± 1.33 a | 6.73 ± 0.69 a | 99.40 | 93.88 |
| 10% | 4728.02 ± 25.32 e | 2.15 ± 0.03 ab | 1001.28 ± 14.36 b | 73.65 ±0.87 e | 68.04 ± 0.11 b | 4.26 ± 0.38 e | 15.16 ± 0.66 de | 6.22 ± 0.02 a | 6.87 ± 0.09 a | 6.98 ± 0.96 a | 6.58 ± 0.44 a | 91.06 | 86.69 |
| 20% | 5899.26 ± 17.64 d | 1.97 ± 0.02 c | 895.72 ± 23.07 c | 99.78 ±0.53 d | 67.18 ± 0.03 c | 4.53 ± 0.45 d | 15.79 ± 0.03 d | 6.13 ± 0.14 a | 6.89 ± 0.02 a | 6.77 ± 1.19 a | 6.69 ± 0.51 a | 64.38 | 63.69 |
| 30% | 6713.08 ± 45.83 c | 1.53 ± 0.09 d | 664.53 ± 18.65 d | 103.59 ±0.66 cd | 67.06 ± 0.27 cd | 4.69 ± 0.16 c | 16.38 ± 0.06 c | 6.20 ± 0.01 a | 6.72 ± 0.03 a | 6.68 ± 0.83 a | 6.73 ± 0.86 a | 61.22 | 60.97 |
| 40% | 7003.65 ± 12.92 b | 1.07 ± 0.06 e | 570.17 ± 15.32 e | 111.26 ±0.78 b | 66.51 ± 0.65 cd | 4.97 ± 0.35 ab | 16.98 ± 0.25 ab | 6.11 ± 0.05 a | 6.78 ± 0.07 a | 6.61 ± 0.77 a | 6.98 ± 1.11 a | 38.61 | 41.48 |
| 50% | 8588.7 ± 47.91 a | 0.57 ± 0.01 f | 504.74 ± 5.86 f | 134.79 ± 0.91 a | 66.02 ± 0.14 e | 5.03 ± 0.11 a | 17.02 ± 0.44 a | 6.09 ± 0.08 a | 6.54 ± 0.05 a | 6.52 ± 1.47 a | 6.72 ± 0.73 a | 57.21 | 57.51 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Wang, F.; Shen, H.; Shen, X.; Wang, Y.; Zhao, R.; Li, Z.; Yao, X. Glycemic Response to White Kidney Beans as Part of a Rice Meal: A Thermal Processing Method. Processes 2025, 13, 2977. https://doi.org/10.3390/pr13092977
Wang F, Shen H, Shen X, Wang Y, Zhao R, Li Z, Yao X. Glycemic Response to White Kidney Beans as Part of a Rice Meal: A Thermal Processing Method. Processes. 2025; 13(9):2977. https://doi.org/10.3390/pr13092977
Chicago/Turabian StyleWang, Fei, Huifang Shen, Xinting Shen, Yao Wang, Rui Zhao, Zhebin Li, and Xinmiao Yao. 2025. "Glycemic Response to White Kidney Beans as Part of a Rice Meal: A Thermal Processing Method" Processes 13, no. 9: 2977. https://doi.org/10.3390/pr13092977
APA StyleWang, F., Shen, H., Shen, X., Wang, Y., Zhao, R., Li, Z., & Yao, X. (2025). Glycemic Response to White Kidney Beans as Part of a Rice Meal: A Thermal Processing Method. Processes, 13(9), 2977. https://doi.org/10.3390/pr13092977





