Investigation on the Reasons for CO Overrun in the Return Air Corner of the Fully Mechanized Coal Mine Working Face
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Overview of the Mine
3. Coal Sample Tank Analysis Experiment
3.1. Experimental Conditions and Procedures
- 1.
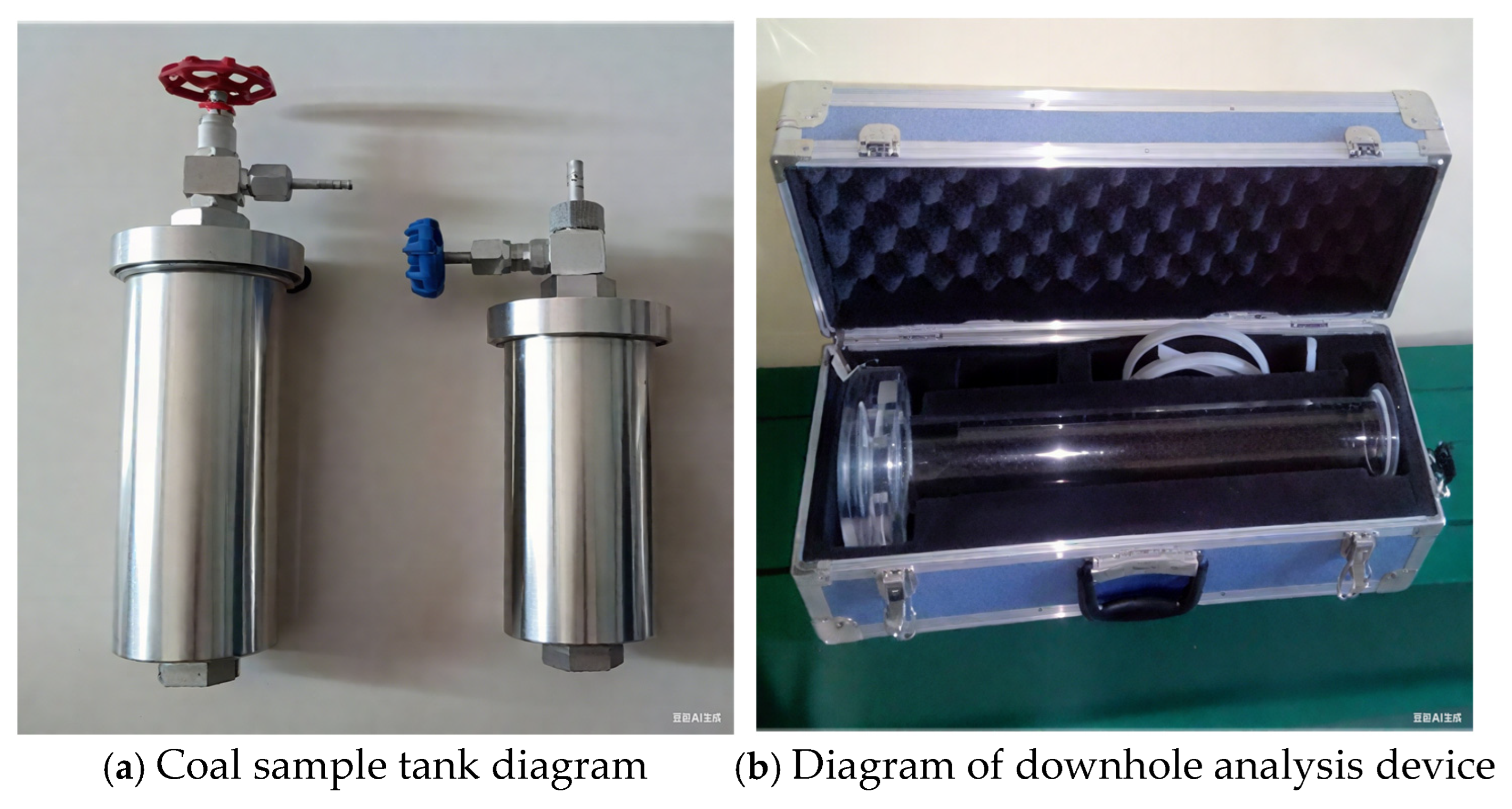
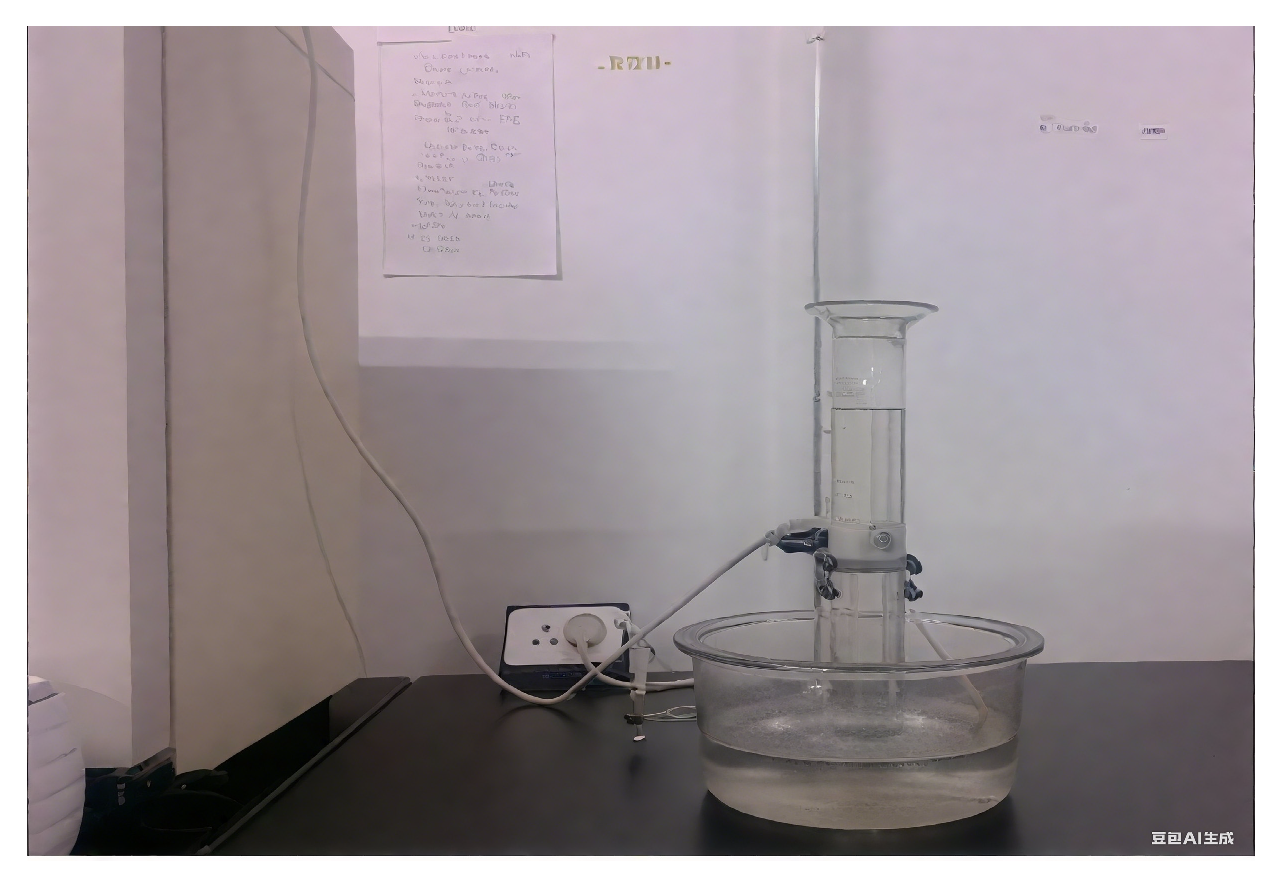
- Gas desorption device:
- 2.
- Desorption gas collection device:
- 3.
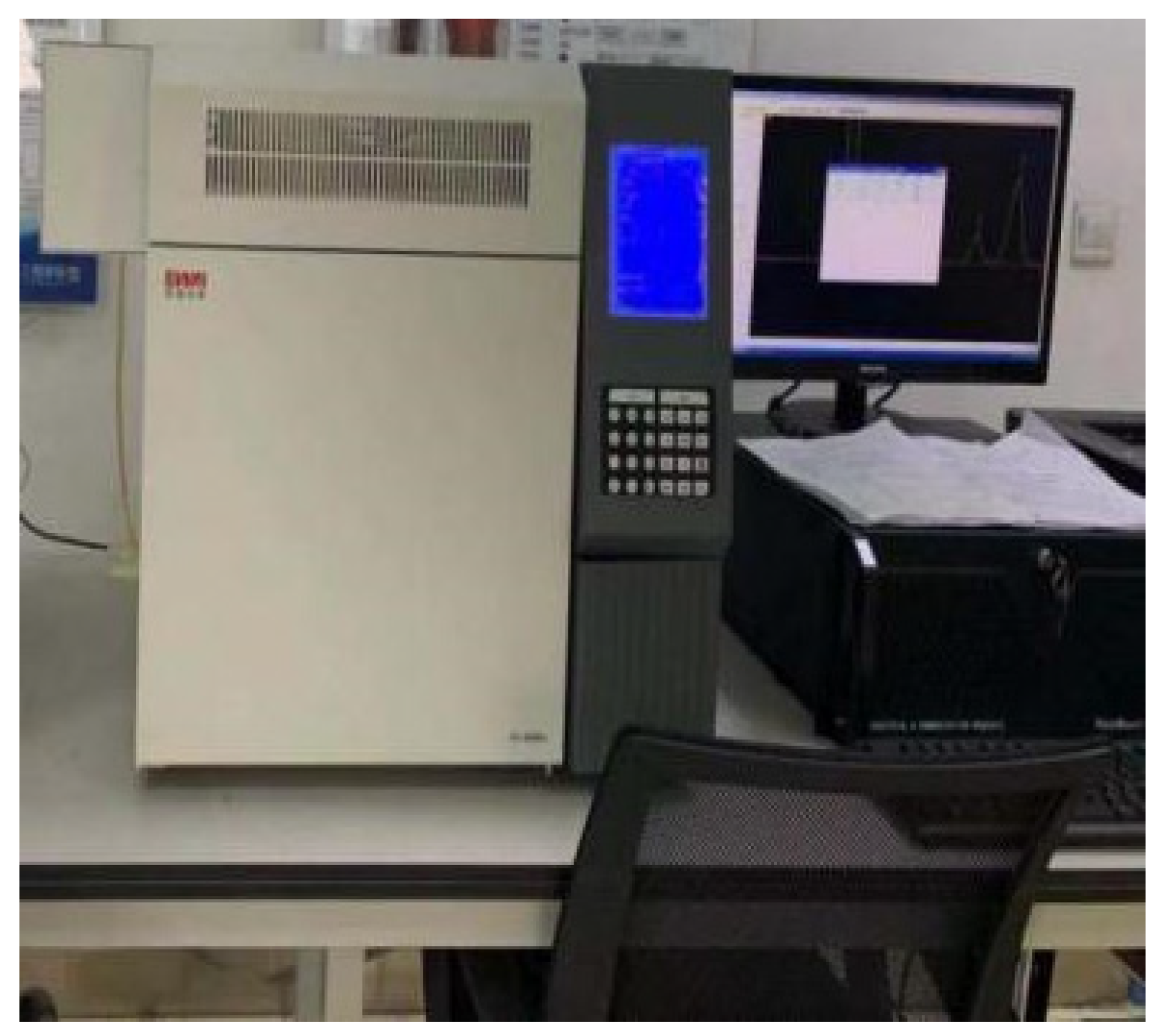
- Gas composition and concentration determination device:
3.2. Experimental Results and Analysis
- 1.
- Analysis of the results of gas downhole direct desorption experiments:
- 2.
- Analysis of the results of laboratory gas determination experiments:
4. Indoor Crushing Experiments
4.1. Experimental Conditions and Procedures
4.2. Experimental Results and Analysis
5. Cause Analysis of High CO in Return Air Corner
6. Prediction of the Dynamic Distribution of CO at the Return Air Corner Angle of the Fully Mechanized Working Face
6.1. Calculation Model of CO Concentration at the Return Air Corner of the Working Face
6.1.1. Goaf Air Leakage
- Air leakage intensity and air leakage volume:
6.1.2. The Amount of CO Produced
- Oxidation of CO from goaf area:
- 2.
- The amount of CO oxidation produced by coal entering the goaf during the mining process:
- 3.
- The amount of CO produced by coal cutting, rubber-tired vehicles, and other reasons:
6.1.3. Mathematical Model for CO Concentration Calculation
6.2. On-Site Monitoring of CO Concentration at the Working Face
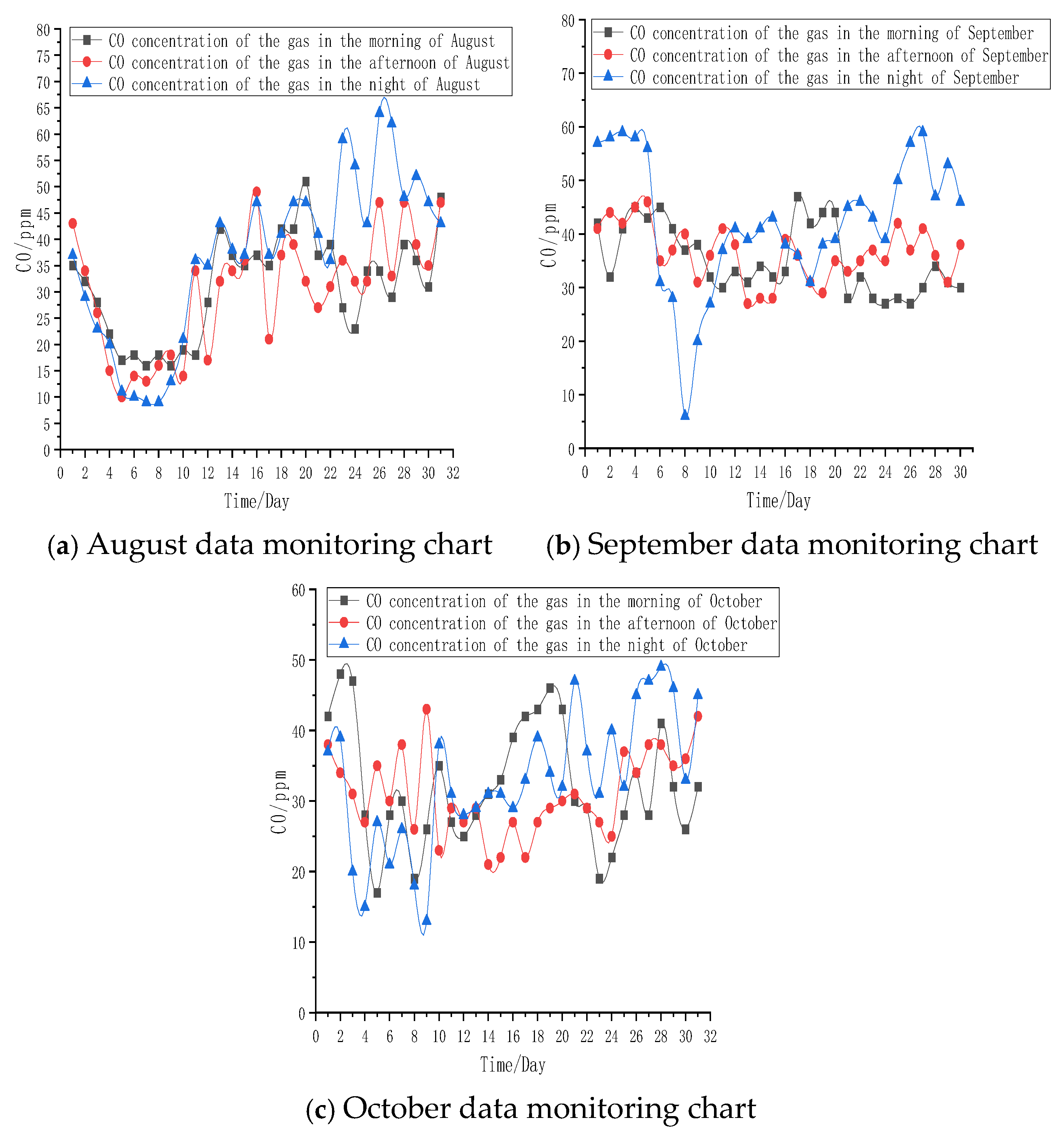
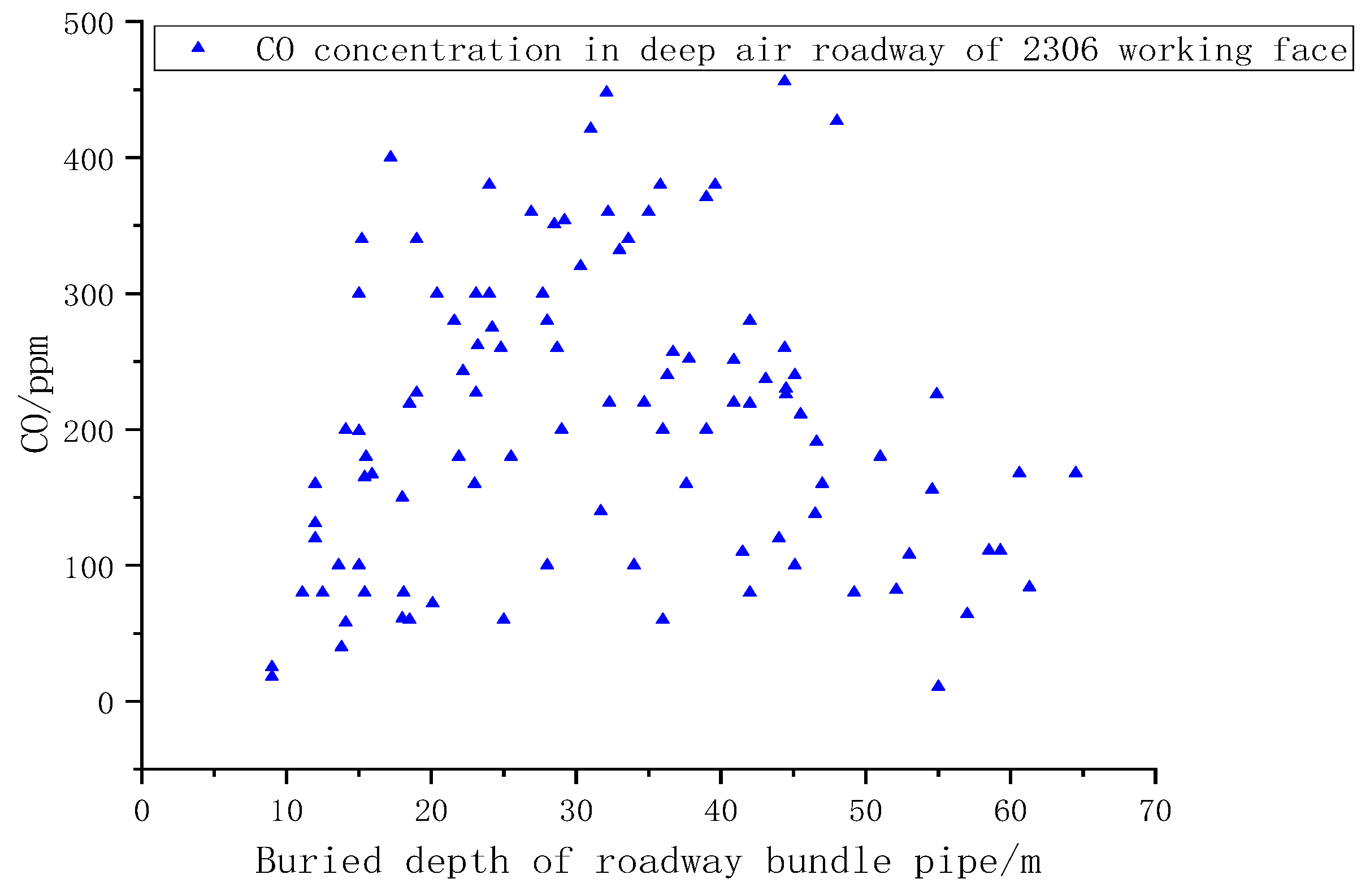
6.2.1. On-Site Monitoring of CO Concentration at the Return Air Corner of the Working Face
6.2.2. On-Site Monitoring of CO Concentration at the Return Air Corner of the Working Face
6.3. Dynamic Prediction of CO Concentration at the Return Air Corner of the Working Face
7. Discussion
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Shi, D.; Liu, X.; He, L. A review on mine fire prevention technology and theory based on bibliometric analysis. Sustainability 2023, 15, 16639. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Wen, H.; Chen, C.; Guo, J.; Jin, Y.; Zheng, X.; Cheng, X.; Li, D. Research status and development trend of coal spontaneous combustion fire and prevention technology in China: A review. ACS Omega 2024, 9, 21727–21750. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, Q.; Lu, Y.; Wang, Q.; Gu, W.; Wu, F. Research progress and development trend of coal spontaneous combustion prevention technology. Combust. Sci. Technol. 2024, 197, 3057–3084. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, S.-L.; Liu, X. Study on multi-indicator quantitative risk evaluation methods for different periods of coal spontaneous combustion in coal mines. Combust. Sci. Technol. 2024, 196, 1628–1641. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, C.; Hu, P.; Sun, Y.; Yang, C. Study on CO source identification and spontaneous combustion warning concentration in the return corner of working face in shallow buried coal seam. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. Int. 2024, 31, 15050–15064. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Li, X.; Chen, S.; Cao, J.; Gao, F. Study on generation, migration and accumulation of CO in the mining goaf of shallow-buried close distance coal seam group. Sci. Rep. 2022, 12, 14424. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mao, X.; Zhou, Q.; Jia, B.; Chen, J.; Wang, D. Research on CO migration patterns in shallowly buried coal seam composite goafs. ACS Omega 2024, 9, 33710–33722. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, H.; Li, Z.; Li, J.; Yang, Y.; Zhang, Y. CO-based early warning threshold for coal spontaneous combustion. Mater. Chem. Phys. 2024, 313, 128730. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jia, X.; Qi, Q.; Zhao, Y.; Dong, Z.; Li, X. CO emission regularity and its influencing factors in a fully mechanized caving face. AIP Adv. 2021, 11, 075111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, W.; Zhong, X.; Wang, D.; Zhou, K.; Wang, Y.; Hou, F. CO release characteristics of coal spontaneous combustion in low-temperature oxygen-deficient environments: Coupling effects of temperature, oxygen concentration and time. J. Hazard. Mater. 2025, 495, 139073. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, S.; Gao, D.; Liu, Y.; Chai, J.; Chen, J. Distribution law of coal spontaneous combustion hazard area in composite goaf of shallow buried close distance coal seam group. Combust. Sci. Technol. 2023, 195, 1960–1980. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Jiang, M.; Jing, Z. Prediction Model of Spontaneous Combustion of Lignite in Zhalainuoer Mining Area. ACS Omega 2024, 9, 31765–31775. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, Y.; Shu, L.; Song, X.; Gong, H. Study on Air Injection to Enhance Coalbed Gas Extraction. Processes 2025, 13, 1882. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, Y.; Yang, Y.; Guo, S.; Tian, F.; Wang, S. Combustion mechanism and control approaches of underground coal fires: A review. Int. J. Coal Sci. Technol. 2023, 10, 24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Zhang, J.; Ren, X.; Liu, Y.; Zhou, C.; Li, T. Study on condition analysis and temperature prediction of coal spontaneous combustion based on improved genetic algorithm. AIP Adv. 2022, 12, 115128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- GB/T 44819-2024; Method for Determining the Spontaneous Combustion Indicator Gas and Critical Value in Coal Seams. State Administration of Market Supervision and Administration, National Standardization Management Committee Publisher: Beijing, China, 2024.
- Wei, D.; Du, C.; Lei, B.; Lin, Y. Prediction and prevention of spontaneous combustion of coal from goafs in workface: A case study. Case Stud. Therm. Eng. 2020, 21, 100668. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yılmaz, A.; Bilen, M.; Rasskazova, A. Determination of Gas Contents and Spontaneous Combustion Liabilities of Zonguldak Coals. Solid Fuel Chem. 2025, 59, 97–103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, S.; Tang, M.; Luo, X.; Zhou, L.; Qiu, J.; Zhang, R. Dynamic simulation study on space-time evolution law of coal spontaneous combustion hazardous zone and high-temperature points in goaf. Int. J. Heat Mass Transf. 2025, 251, 127321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, Z.; Qin, B.; Shi, Q.; Zhu, T.; Chen, X.; Liu, H. The location analysis and efficient control of hidden coal spontaneous combustion disaster in coal mine goaf: A case study. Process Saf. Environ. Prot. 2024, 184, 66–78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Li, J.; Wang, T.; Liu, G.; He, Z.; Li, C.; Xie, H. Key techniques for precise measuring gas content in deep coal mine: In-situ pressure-and gas-preserved coring. Int. J. Min. Sci. Technol. 2025, 35, 589–607. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deng, J.; Li, X.; Wang, K.; Wang, C.; Ren, L.; Qu, G.; Li, Q. Advances and Prospects in the Risk Prediction and Early Warning Technology for the compound disaster of coal spontaneous combustion and gas explosion. Process Saf. Environ. Prot. 2025, 201, 107489. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, J.; Ma, Y.; Lu, W.; Liu, G.; Cai, F. Using inverting CO critical value to predict coal spontaneous combustion severity in mine gobs with considering air leakages–A case study. Process Saf. Environ. Prot. 2022, 167, 45–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.; Cheng, X.; Wen, H.; Wang, W. Prediction and control of coal spontaneous combustion in a multi-fault fully mechanized top coal caving face at the mine field boundary. Combust. Sci. Technol. 2022, 194, 1895–1913. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, F.; Shi, S.; Lu, Y.; Shao, S.; Wu, X.; Gu, W. Analysis of CO source and prediction model of gushing concentration at the return air corner of working face in shallow coal seam mine. Combust. Sci. Technol. 2024, 196, 4204–4219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, X.; Song, C.; Zhang, Z. The Influence of the Fire Point on the Thermal Dynamic Disaster in the Goaf. Fire 2024, 7, 270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Zhou, C.; Wang, J.; Wu, J.; Ren, T. Study of CO sources and early-warning concentration of spontaneous combustion at air return corner in fully mechanized mining faces. Combust. Sci. Technol. 2021, 193, 1587–1604. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kursunoglu, N.; Ankara, H. Application of statistical process control to monitor underground coal mine fires based on CO emissions. Combust. Sci. Technol. 2024, 196, 142–159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lei, C.; Zhu, Y.; Feng, Q.; Ma, L.; Zhao, J.; Cui, C.; Deng, C. Migration characteristics and prediction of high temperature points in coal spontaneous combustion. Energy 2025, 326, 136288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, L.; Zhang, W.; Zhao, Q.; Wei, G.; Guo, Y.; Lou, F.; Jin, S.; Tuo, L. Dangerous area evolution and coal spontaneous combustion prevention method induced by air leakage in Goaf of ultra-long working face. Combust. Sci. Technol. 2025, 57, 1–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]




| Title | Date |
|---|---|
| Coal mining face | 2306 |
| Mining methods | Fully mechanized mining top coal |
| Working face length | 180 m |
| Air volume of the working face | 1476 m3/min |
| Coal mining thickness | 10.3 m |
| Advance speed | 3.2 m/d |
| Recovery rate | 93% |
| Air leakage | 10 m3/min |
| Time/Min | The Amount of Resolution/cm3 |
|---|---|
| 1 | 20 |
| 2 | 10 |
| 3 | 2 |
| 4 | 2 |
| 5 | 2 |
| 6 | 2 |
| 7 | 2 |
| 8 | 2 |
| 9 | 1 |
| 10 | 1 |
| 11 | 1 |
| 12 | 1 |
| 13 | 1 |
| 14 | 1 |
| 15 | 0 |
| 16 | 0 |
| Serial Number | O2 (%) | N2 (%) | CO (ppm) | CO2 (%) | CH4 (%) | C2H6 (%) | C2H4 (%) | C2H2 (%) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 15.2303 | 77.7886 | 9 | 0.3291 | 6.6456 | 0.0055 | 0.0000 | 0.0000 |
| 2 | 15.4325 | 77.1314 | 11 | 0.3894 | 7.0409 | 0.0047 | 0.0000 | 0.0000 |
| 3 | 14.9256 | 77.7855 | 8 | 0.3380 | 6.9451 | 0.0050 | 0.0000 | 0.0000 |
| Average | 15.1961 | 77.5685 | 9 | 0.3522 | 6.8772 | 0.0051 | 0.0000 | 0.0000 |
| Serial Number | O2 (%) | N2 (%) | CO (ppm) | CO2 (%) | CH4 (%) | C2H6 (%) | C2H4 (%) | C2H2 (%) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 16.2346 | 77.3082 | 10 | 0.2572 | 6.1952 | 0.0038 | 0.0000 | 0.0000 |
| 2 | 16.5426 | 77.2783 | 9 | 0.2742 | 5.8991 | 0.0049 | 0.0000 | 0.0000 |
| Average | 16.3886 | 77.2933 | 10 | 0.2657 | 6.0472 | 0.0044 | 0.0000 | 0.0000 |
| Serial Number | O2 (%) | N2 (%) | CO (ppm) | CO2 (%) | CH4 (%) | C2H6 (%) | C2H4 (%) | C2H2 (%) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| N2 No.1 | 15.7032 | 84.3160 | 0 | 0.0528 | 0.0280 | 0.0000 | 0.0000 | 0.0000 |
| N2 No.2 | 13.3300 | 86.6083 | 0 | 0.0414 | 0.0204 | 0.0000 | 0.0000 | 0.0000 |
| air No.1 | 21.4732 | 78.3863 | 3 | 0.0719 | 0.0681 | 0.0001 | 0.0000 | 0.0000 |
| air No.2 | 21.8240 | 78.1200 | 0 | 0.0483 | 0.0076 | 0.0000 | 0.0000 | 0.0000 |
| Serial Number | O2 (%) | N2 (%) | CO (ppm) | CO2 (%) | CH4 (%) | C2H6 (%) | C2H4 (%) | C2H2 (%) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| N2 No.1 | 16.8411 | 83.1131 | 0 | 0.0450 | 0.0009 | 0.0000 | 0.0000 | 0.0000 |
| N2 No.2 | 15.1562 | 84.8000 | 0 | 0.0434 | 0.0003 | 0.0000 | 0.0000 | 0.0000 |
| air No.1 | 21.8165 | 78.1309 | 6 | 0.0520 | 0.0000 | 0.0000 | 0.0000 | 0.0000 |
| air No.2 | 22.4956 | 77.4533 | 0 | 0.0511 | 0.0000 | 0.0000 | 0.0000 | 0.0000 |
| Title | Date |
|---|---|
| Width of the goaf oxide zone | 31.35 m |
| The width of the goaf heat dissipation zone | 12.4 m |
| The oxidation correction coefficient of residual coal in the oxidation zone (α) | 0.3 |
| The correction coefficient of the oxidation of the residual coal in the heat dissipation zone(β) | 0.5 |
| On-site monitoring value of CO concentration at the corner of the return air | 6–64 ppm |
| Calculated value of CO concentration prediction at the corner of the return air corner | 11–66 ppm |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Liu, W.; Qi, C.; Jin, Y.; Cheng, X.; Li, Y.; Li, C.; Zhang, L.; Hui, J. Investigation on the Reasons for CO Overrun in the Return Air Corner of the Fully Mechanized Coal Mine Working Face. Processes 2025, 13, 2869. https://doi.org/10.3390/pr13092869
Liu W, Qi C, Jin Y, Cheng X, Li Y, Li C, Zhang L, Hui J. Investigation on the Reasons for CO Overrun in the Return Air Corner of the Fully Mechanized Coal Mine Working Face. Processes. 2025; 13(9):2869. https://doi.org/10.3390/pr13092869
Chicago/Turabian StyleLiu, Wenyong, Chenyang Qi, Yongfei Jin, Xiaojiao Cheng, Yixin Li, Changsheng Li, Lei Zhang, and Jing Hui. 2025. "Investigation on the Reasons for CO Overrun in the Return Air Corner of the Fully Mechanized Coal Mine Working Face" Processes 13, no. 9: 2869. https://doi.org/10.3390/pr13092869
APA StyleLiu, W., Qi, C., Jin, Y., Cheng, X., Li, Y., Li, C., Zhang, L., & Hui, J. (2025). Investigation on the Reasons for CO Overrun in the Return Air Corner of the Fully Mechanized Coal Mine Working Face. Processes, 13(9), 2869. https://doi.org/10.3390/pr13092869





