Deformation, Failure Mechanism and Control Technology of Soft Rock Roadways Buried Under Coal Pillars: A Case Study
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Engineering Background
2.1. Working Face Overview
2.2. Original Support and Deformation Characteristics of the Roadway
3. Deformation Mechanisms of Underlying Soft Rock Roadways in Close-Distance Coal Seam Mining
3.1. Mechanical Analysis of the Surrounding Rock of Underlying Roadways in Close-Distance Coal Seam Mining
- The calculation formula for the abutment stress in the plastic zone of the upper coal seam floor is as follows:where σxsd is the horizontal stress of the advanced abutment stress in the plastic zone at point N of the coal seam 5# floor, MPa; σzsd is the vertical stress of the advanced abutment stress in the plastic zone at point N of the coal seam 5# floor, MPa; τxzsd is the shear stress of the advanced abutment stress in the plastic zone at point N of the coal seam 5# floor, MPa; and x0 is the range of the limit balance zone of the advanced abutment stress, m.
- The calculation formula for the abutment stress in the elastic zone of the upper coal seam floor is as follows:where σxtd is the horizontal stress of the advanced abutment stress in the elastic zone at point N of the upper coal seam floor, MPa; σztd is the vertical stress of the advanced abutment stress in the elastic zone at point N of the upper coal seam floor, MPa; τxztd is the shear stress of the advanced abutment stress in the elastic zone at point N of the upper coal seam floor, MPa; and x’ is the influence range of the advanced abutment stress, m.
- The calculation formula for the abutment stress in the in situ stress zone of the upper coal seam floor is as follows:where σxyd is the horizontal stress of the abutment stress in the in situ stress zone at point N of the upper coal seam floor, MPa; σzyd is the vertical stress of the abutment stress in the in situ stress zone at point N of the upper coal seam floor, MPa; and τxzyd is shear stress of the abutment stress in the in situ stress zone at point N of the upper coal seam floor, MPa.
3.2. Numerical Analysis of Surrounding Rock of Underlying Roadways in Close-Distance Coal Seam Mining
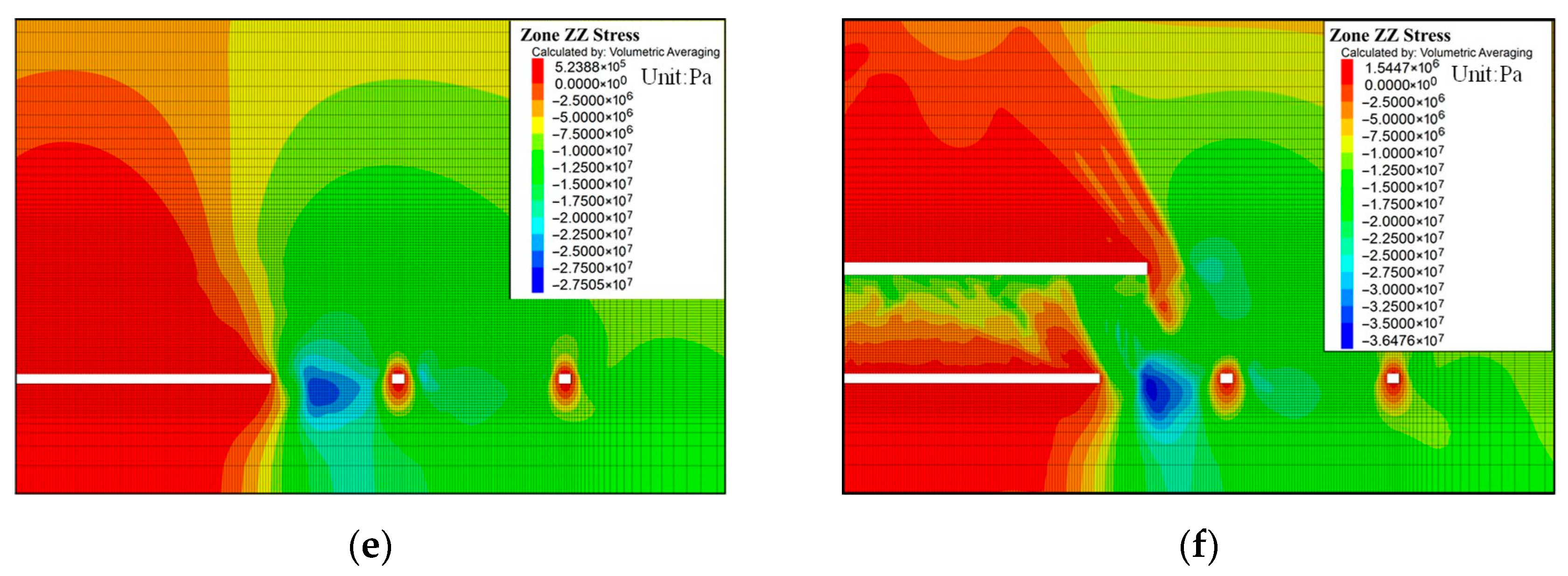
3.2.1. Vertical Stress Distribution of Surrounding Rock in the CTR Under Different Working Conditions
3.2.2. Vertical Displacement Distribution of Surrounding Rock in the CTR Under Different Working Conditions
3.3. The Influence of Roadway Section Size on Surrounding Rock
3.4. Analysis of the Main Controlling Factors for the Failure of Underlying Soft Rock Roadways in Close-Distance Coal Seam Mining
- (1)
- In situ stress
- (2)
- The properties of surrounding rock
- (3)
- Cross-section size
4. Research on Control Strategies for Underlying Soft Rock Roadways in Close-Distance Coal Seam Mining
4.1. Section Optimization Scheme for Soft Rock Roadways
4.2. Support Optimization Scheme for Soft Rock Roadways
4.3. Numerical Analysis of the Optimization Scheme
4.4. Monitoring Results of Deformation of Surrounding Rock
5. Conclusions
- By considering the engineering geological conditions of the Danhou coal mine, a mechanical model of advance abutment stress transfer along the goaf floor was established. The theoretical analytical solution for vertical stress and horizontal stress at any point of the floor under the influence of advance abutment stress in close-distance coal seam mining was provided.
- The increase in abutment stress of the floor due to advance abutment stress transfer along the floor of the 5# coal seam resulted in further stress concentration of the surrounding rock of CTR in the 1# coal seam, leading to floor bulging and significant deformation on both sides.
- Numerical simulation results revealed significant changes in the stress and deformation of the surrounding rock with increasing distance between CTR and the goaf. The stress distribution exhibited an asymmetric–symmetric–asymmetric pattern, while the deformation showed an asymmetric distribution pattern that gradually decreased.
- The monitoring results of surrounding rock deformation demonstrated a 63.4% reduction in average deformation on both sides of CTR and a 93% decrease in average floor heave after implementing the new support scheme. This indicates that the technology effectively controls the deformation of the surrounding rock in soft rock roadways.
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Kang, H.; Yang, J.; Jiang, P.; Gao, F.; Li, W.; Li, J.; Chen, H. Theory, technology and application of grouted bolting in soft rock roadways of deep coal mines. Int. J. Miner. Met. Mater. 2024, 31, 1463–1479. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, K.; Zhao, E.; Guo, Y.; Du, F.; Ding, K. Effect of loading rate on the mechanical and seepage characteristics of gas-bearing coal–rock and its mechanical constitutive model. Phys. Fluids 2024, 36, 026606. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, Y.; Liu, X.; Li, W.; Du, F.; Ma, J.; Qian, R.; Huo, N. Research on abutment stress distribution of roof–cutting coalface: Numerical simulation and field measurement. Geomech. Geophys. Geo-Energy Geo-Resour. 2024, 10, 86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, Z.; Li, W.; He, M.; You, J.; Li, Y. Model test on failure mechanisms of deep high-stress soft rock roadways based on excavation compensation method. Eng. Fail. Anal. 2024, 160, 108161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, G.; Ma, F.; Guo, J.; Zhao, H. Experimental research on deformation failure process of roadway tunnel in fractured rock mass induced by mining excavation. Environ. Earth Sci. 2022, 81, 243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tian, M.; Gao, X.; Zhang, A.; Han, L.; Xiao, H. Study on the deformation failure mechanism and coupling support technology of soft rock roadways in strong wind oxidation zones. Eng. Fail. Anal. 2023, 156, 107840. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, Y.; Wang, K.; Du, F.; Guo, H.; Li, K.; Wang, Y. Mechanical-permeability characteristics of composite coal rock under different gas pressures and damage prediction model. Phys. Fluids 2024, 36, 0199545. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ru, W.; Hu, S.; Ning, J.; Wang, J.; Gu, Q.; Guo, Y.; Zuo, J.; Wu, B. Study on the Rheological Failure Mechanism of Weakly Cemented Soft Rock Roadway during the Mining of Close-Distance Coal Seams: A Case Study. Adv. Civ. Eng. 2020, 2020, 8885849. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.; Zhuo, Q.; Yang, S.; Yang, T.; Wang, B.; Bai, W.; Wu, J.; Xie, S. Study on the Coal Pillar Weakening Technology in Close Distance Multi-Coal Seam Goaf. Energies 2022, 15, 6532. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Z.; Deng, M.; Bai, J.; Yan, S.; Yu, X. Stability control of gob-side entry retained under the gob with close distance coal seams. Int. J. Min. Sci. Technol. 2021, 31, 321–332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, C.; Yao, H.; Huang, Y. Stability control of goaf-driven roadway surrounding rock under interchange remaining coal pillar in close distance coal seams. Energy Sci. Eng. 2024, 12, 2553–2567. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, S.L.; Li, Q.; Yue, H.; Kong, D.Z.; Wu, G.Y.; Liu, F.Q. Study on Roof Deformation and Failure Law of Close Distance Coal Seams Mining Based on Digital Image Correlation. Exp. Tech. 2024, 48, 1005–1026. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, X.-X.; Zhao, Z.-Q.; Wang, Y.-W.; Wang, X.-H.; Hui, Z.-L. Study on the law of stress distribution in the presence of remaining coal pillar in a close-distance coal seam and the reasonable location of the roadway. Sci. Rep. 2025, 15, 8737. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seki, S.; Kaise, S.; Morisaki, Y.; Azetaka, S.; Jiang, Y. Model experiments for examining heaving phenomenon in tunnels. Tunn. Undergr. Space Technol. 2008, 23, 128–138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nunes, M.; Meguid, M. A study on the effects of overlying soil strata on the stresses developing in a tunnel lining. Tunn. Undergr. Space Technol. 2009, 24, 716–722. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, J.; Jiao, J.; Zhou, S. Controlling large deformations in soft rock roadways with integrated anchor shotcrete and grouting techniques. Sci. Rep. 2024, 14, 28339. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Qiu, W.; Duan, D. Using Energy-Absorbing Dampers to Solve the Problem of Large Deformation in Soft-Rock Tunnels: A Case Study. Energies 2022, 15, 1916. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, W.; Zhao, T.-B.; Zhang, X.-T. Stability analysis and deformation control method of swelling soft rock roadway adjacent to chambers. Géoméch. Geophys. Geo-Energy Geo-Resour. 2023, 9, 91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sakhno, I.; Sakhno, S. Numerical studies of floor heave mechanism and the effectiveness of grouting reinforcement of roadway in soft rock containing the mine water. Int. J. Rock Mech. Min. Sci. Géoméch. Abstr. 2023, 170, 105484. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Yang, S.; Han, L.; Liu, Y.; Xue, B.; Li, J. Application research on composite support technology of concrete-filled steel tube support in high stress and large deformation soft rock roadway: A case study. Structures 2024, 60, 105814. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, W.; Guo, Y.; Liu, X.; Du, F.; Li, G.; Ma, Q. Failure mechanisms and reinforcement support of roadway in deep coal seam: A case study. Eng. Fail. Anal. 2024, 165, 108745. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Z.-Q.; He, C.; Wang, J.; Ma, C.-C. Time-dependent squeezing deformation mechanism of tunnels in layered soft-rock stratum under high geo-stress. J. Mt. Sci. 2021, 18, 1371–1390. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, D.; Wang, F.; Hu, Q.; Huang, H.; Zuo, J.; Tian, C.; Zhang, D. Structural responses and treatments of shield tunnel due to leakage: A case study. Tunn. Undergr. Space Technol. 2020, 103, 103471. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suchowerska, A.; Merifield, R.; Carter, J. Vertical stress changes in multi-seam mining under supercritical longwall panels. Int. J. Rock Mech. Min. Sci. Géoméch. Abstr. 2013, 61, 306–320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, Z.; Li, W.; Yin, S.; Yang, D.; Ma, Z. An Innovative Technology for Monitoring the Distribution of Abutment Stress in Longwall Mining. Energies 2021, 14, 475. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, S.; Sun, H.; Zhang, D.; Yang, K.; Li, X.; Wang, D.; Li, Y. Experimental study of effect of liquid nitrogen cold soaking on coal pore structure and fractal characteristics. Energy 2023, 275, 127470. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bai, Y.; Xin, H.; Xie, B.; Shen, K.; Yan, Y. Research on the interfacial bonding performance of novel composite L-shaped concrete-filled steel tubes. Struct. Des. Tall Spéc. Build. 2024, 33, e2108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, W.; Meng, L.; Li, S.; Xu, Y.; Wang, L.; Zhang, P.; Dou, S.; Sun, H. Study on progressive failure behavior and mechanical properties of tunnel arch support structures. Tunn. Undergr. Space Technol. 2023, 140, 105285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, W.; Wang, M.; Zhou, Z.; Li, L.; Yuan, Y.; Gao, C. A true triaxial geomechanical model test apparatus for studying the precursory information of water inrush from impermeable rock mass failure. Tunn. Undergr. Space Technol. 2019, 93, 105285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kusui, A.; Villaescusa, E.; Funatsu, T. Mechanical behaviour of scaled-down unsupported tunnel walls in hard rock under high stress. Tunn. Undergr. Space Technol. 2016, 60, 30–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Q.; Liu, C.; Duan, K.; Zhang, Z.; Xiang, W. True Three-Dimensional Geomechanical Model Tests for Stability Analysis of Surrounding Rock During the Excavation of a Deep Underground Laboratory. Rock Mech. Rock Eng. 2019, 53, 517–537. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, G.-Q.; Feng, X.-T.; Zhou, Y.-Y.; Li, Z.-W.; Fu, L.-J.; Xiong, Y.-R. Physical Model Experimental Study on Spalling Failure Around a Tunnel in Synthetic Marble. Rock Mech. Rock Eng. 2019, 53, 909–926. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, S.-Q.; Chen, M.; Fang, G.; Wang, Y.-C.; Meng, B.; Li, Y.-H.; Jing, H.-W. Physical experiment and numerical modelling of tunnel excavation in slanted upper-soft and lower-hard strata. Tunn. Undergr. Space Technol. 2018, 82, 248–264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, L.; Shang, C.; Chu, K.; Zhou, Z.; Song, S.; Liu, Z.; Chen, Y. Large-scale geo-mechanical model tests for stability assessment of super-large cross-section tunnel. Tunn. Undergr. Space Technol. 2021, 109, 103756. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, G.; Wang, B.; Ma, G.; Du, J.; Chen, X.; Hou, Z. Study on the damage evolutional process of secondary tunnel lining under rheological effect of surrounding rock. Eng. Fail. Anal. 2022, 142, 103756. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]





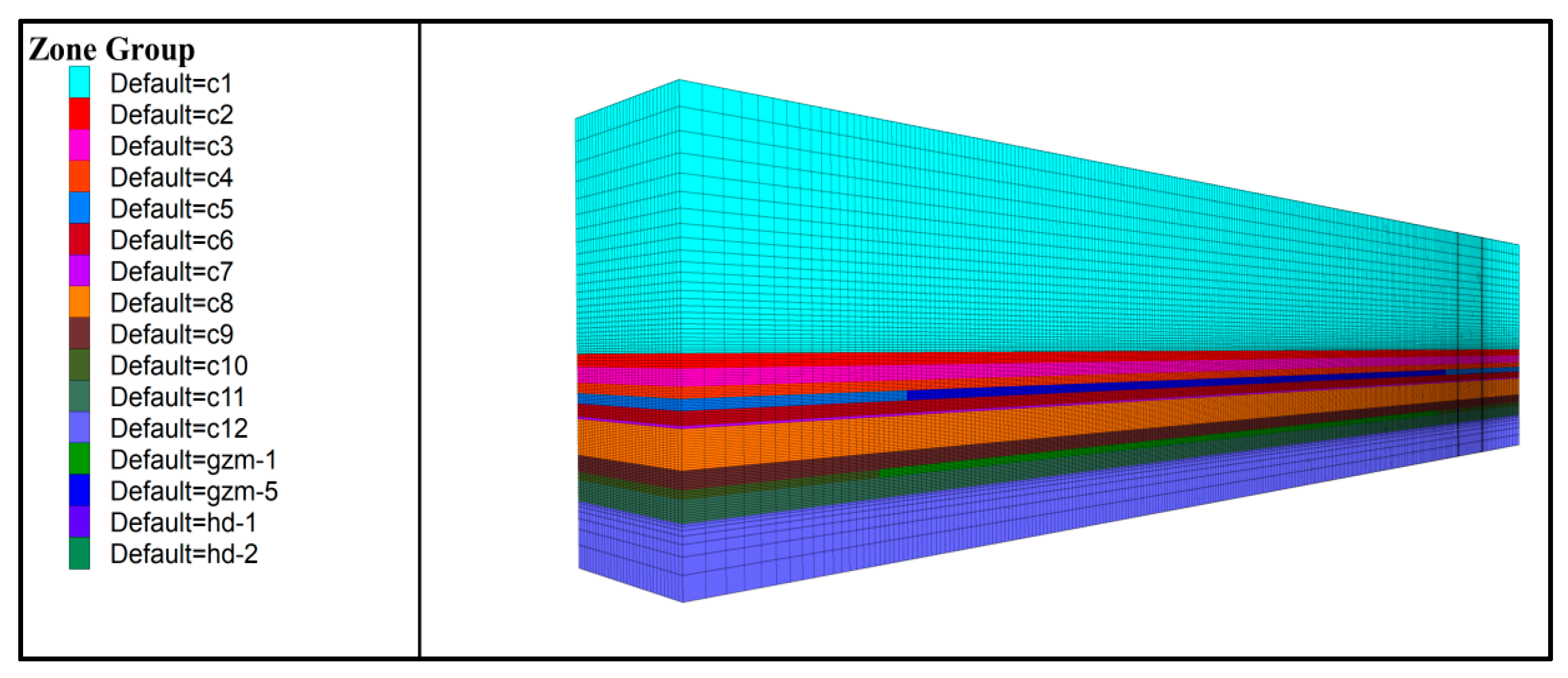








| Lithology | Thickness/m | Density/kg/m3 | E/GPa | µ | K/GPa | G/GPa | T/MPa | C/MPa | φ/° |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Mudstone | 4.4 | 2550 | 3.08 | 0.2 | 1.71 | 1.28 | 0.58 | 1.56 | 26.9 |
| Siltstone | 5.6 | 2540 | 5.22 | 0.22 | 3.11 | 2.14 | 1.05 | 3.12 | 22.3 |
| Mudstone | 1.4 | 2550 | 3.56 | 0.2 | 1.98 | 1.48 | 0.54 | 1.58 | 19.9 |
| Coal seam 4 | 1.1 | 1400 | 2.18 | 0.25 | 1.45 | 0.87 | 0.56 | 1.19 | 26.9 |
| Mudstone | 16.0 | 2550 | 3.29 | 0.23 | 2.03 | 1.34 | 0.59 | 1.57 | 23.16 |
| Siltstone | 2.2 | 2540 | 5.02 | 0.22 | 2.99 | 2.06 | 1.21 | 3.25 | 27.6 |
| Mudstone | 4.6 | 2550 | 3.20 | 0.2 | 1.78 | 1.33 | 0.57 | 1.51 | 22.5 |
| Siltstone | 0.6 | 2540 | 5.45 | 0.22 | 3.24 | 2.23 | 1.39 | 3.03 | 30.5 |
| Coal seam 1 | 3.2 | 1400 | 2.07 | 0.25 | 1.38 | 0.83 | 0.52 | 1.15 | 27.7 |
| Mudstone | 9.3 | 2550 | 1.96 | 0.2 | 1.09 | 0.82 | 0.5 | 1.54 | 21.8 |
| Limestone | 20.0 | 2100 | 9.98 | 0.29 | 7.92 | 3.87 | 2.11 | 5.06 | 27.6 |
| Conditions | Coal Seam Spacing Z0/m | Depth H/m | Lateral Pressure Coefficient/λ | Horizontal Distance L0/m | Remarks | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 1-1 | 35 | 400 | 1.8 | 6 | Coal seam 5# has not been mined |
| 1-2 | 35 | 400 | 1.8 | 16 | ||
| 1-3 | 35 | 400 | 1.8 | 26 | ||
| 2 | 2-1 | 35 | 400 | 1.8 | 6 | Coal seam 5# has been mined |
| 2-2 | 35 | 400 | 1.8 | 16 | ||
| 2-3 | 35 | 400 | 1.8 | 26 | ||
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Bi, Y.; Li, Y.; Xu, F.; Zhu, L. Deformation, Failure Mechanism and Control Technology of Soft Rock Roadways Buried Under Coal Pillars: A Case Study. Processes 2025, 13, 2570. https://doi.org/10.3390/pr13082570
Bi Y, Li Y, Xu F, Zhu L. Deformation, Failure Mechanism and Control Technology of Soft Rock Roadways Buried Under Coal Pillars: A Case Study. Processes. 2025; 13(8):2570. https://doi.org/10.3390/pr13082570
Chicago/Turabian StyleBi, Yewu, Yichen Li, Feng Xu, and Lihua Zhu. 2025. "Deformation, Failure Mechanism and Control Technology of Soft Rock Roadways Buried Under Coal Pillars: A Case Study" Processes 13, no. 8: 2570. https://doi.org/10.3390/pr13082570
APA StyleBi, Y., Li, Y., Xu, F., & Zhu, L. (2025). Deformation, Failure Mechanism and Control Technology of Soft Rock Roadways Buried Under Coal Pillars: A Case Study. Processes, 13(8), 2570. https://doi.org/10.3390/pr13082570







