Study on the Synergistic Enhancement of Crude Oil Recovery by Bacillus Co-Culture Systems
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Chemicals and Reagents
2.2. Strains, Culture Conditions, and Preparation of Inoculums
2.3. Biosurfactant Activity Detection
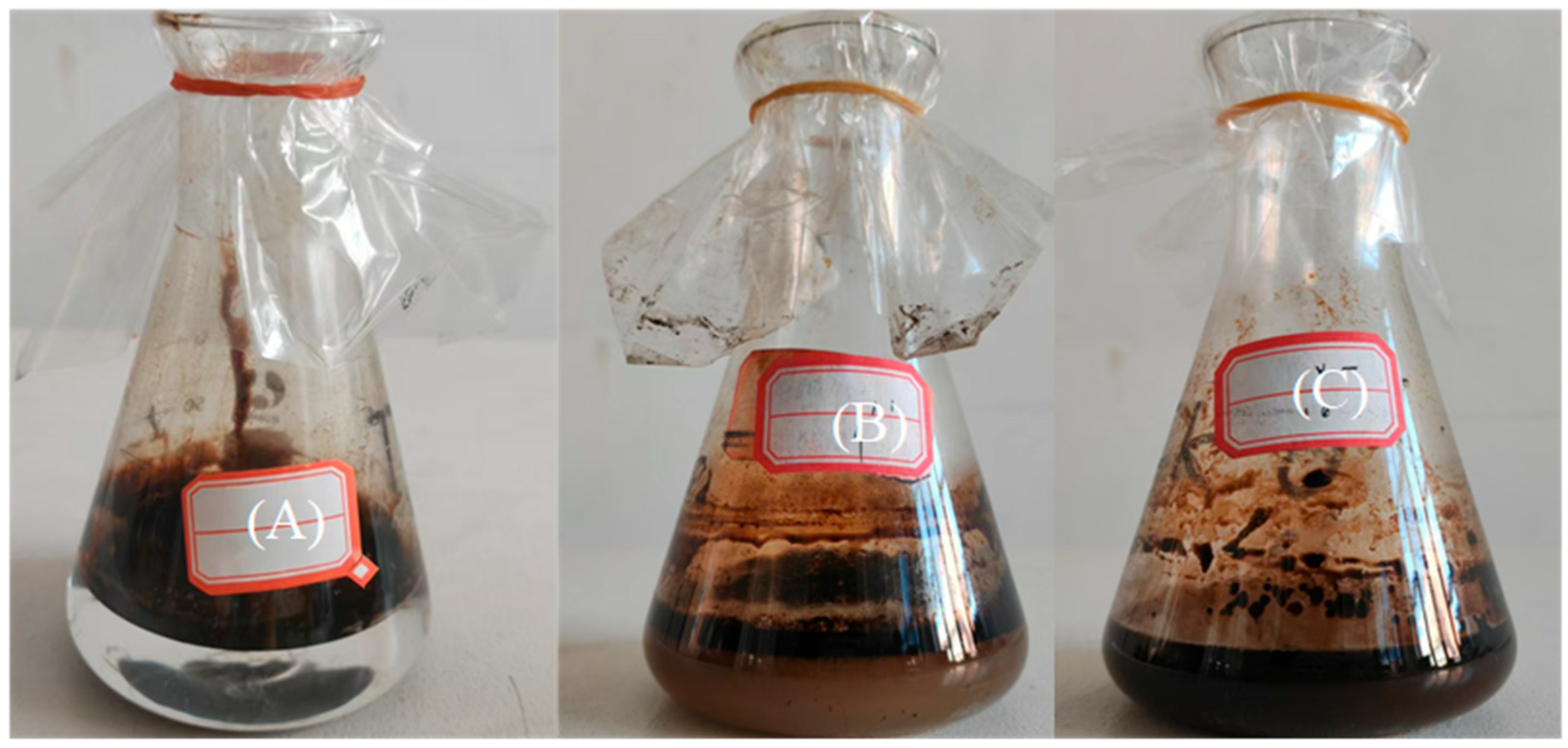
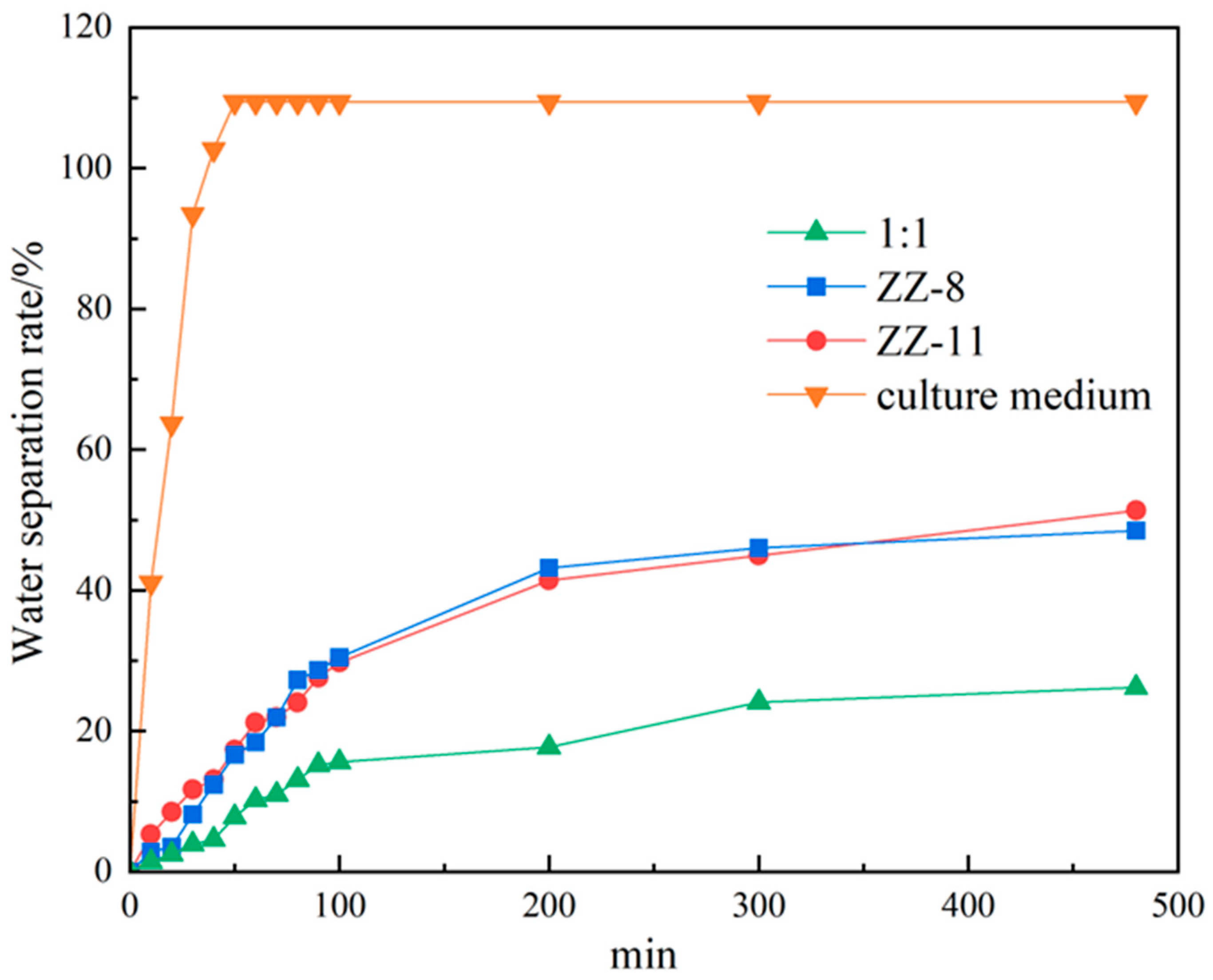
2.4. Water Separation Measurement
2.5. Oil Spreading Method
2.6. Contact Angle Measurement
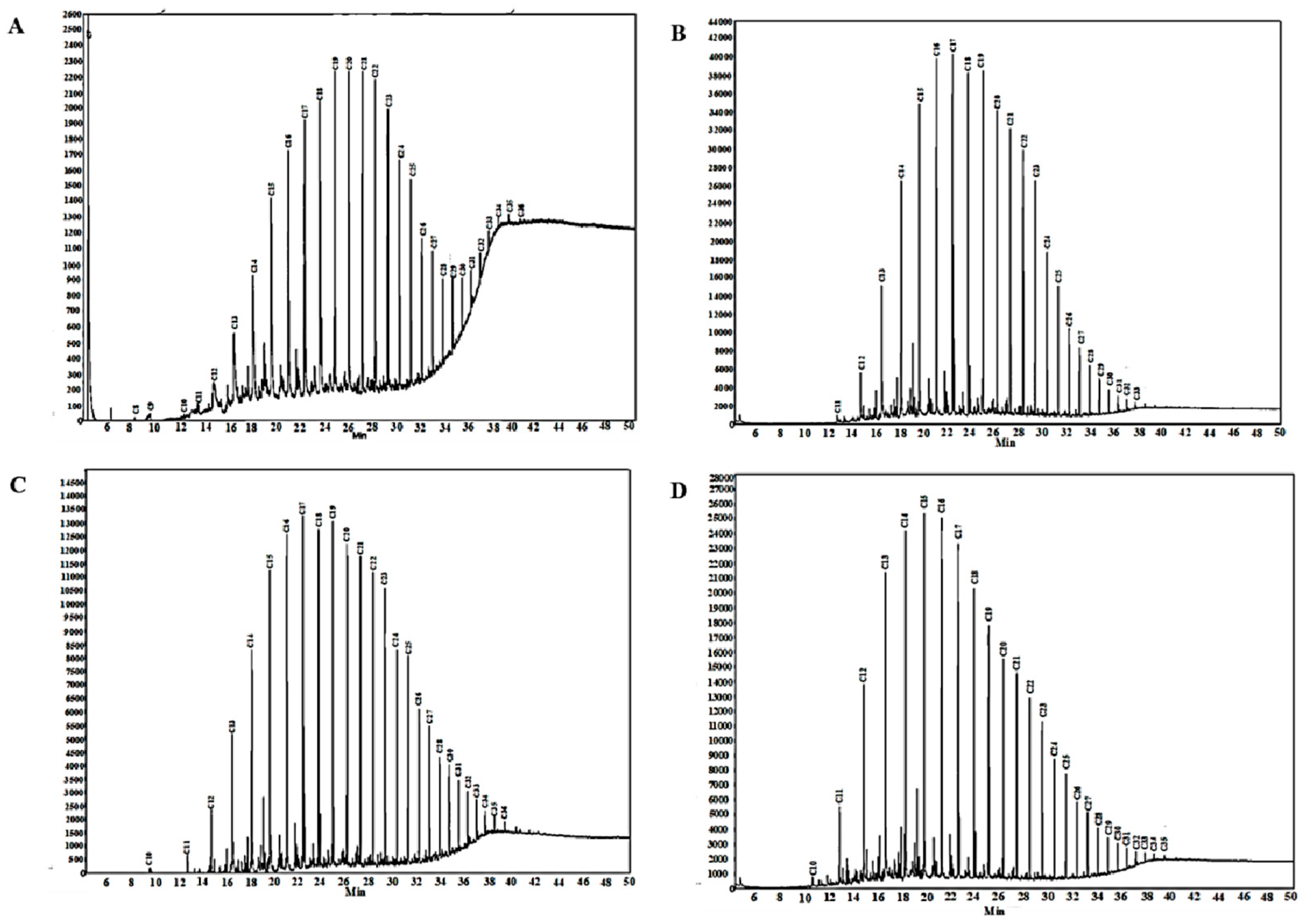
2.7. Gas Chromatographic Analysis of Saturated Hydrocarbons
2.8. Evaluation of the Oil Washing Efficiency
3. Results and Discussion
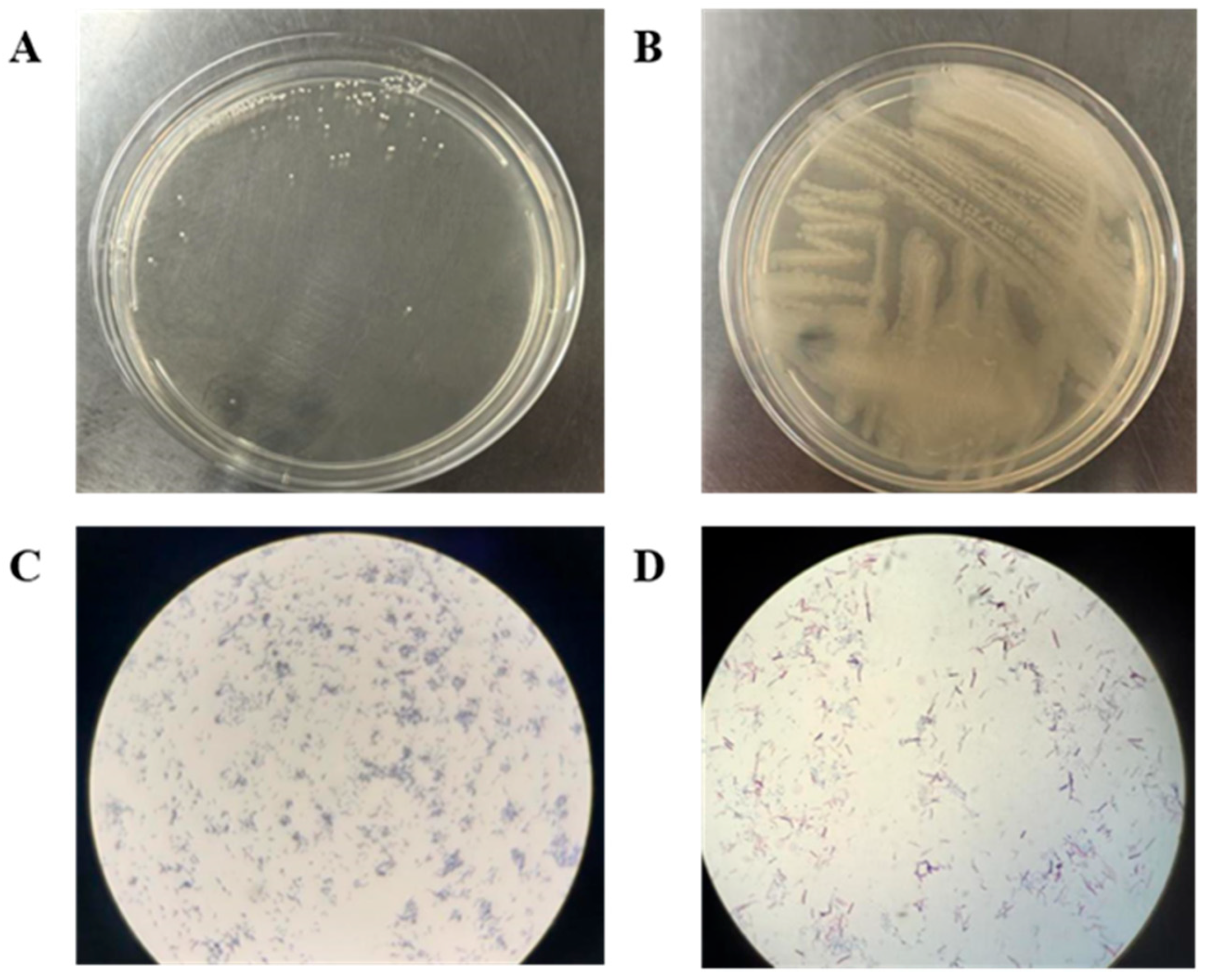
3.1. Strain Identification
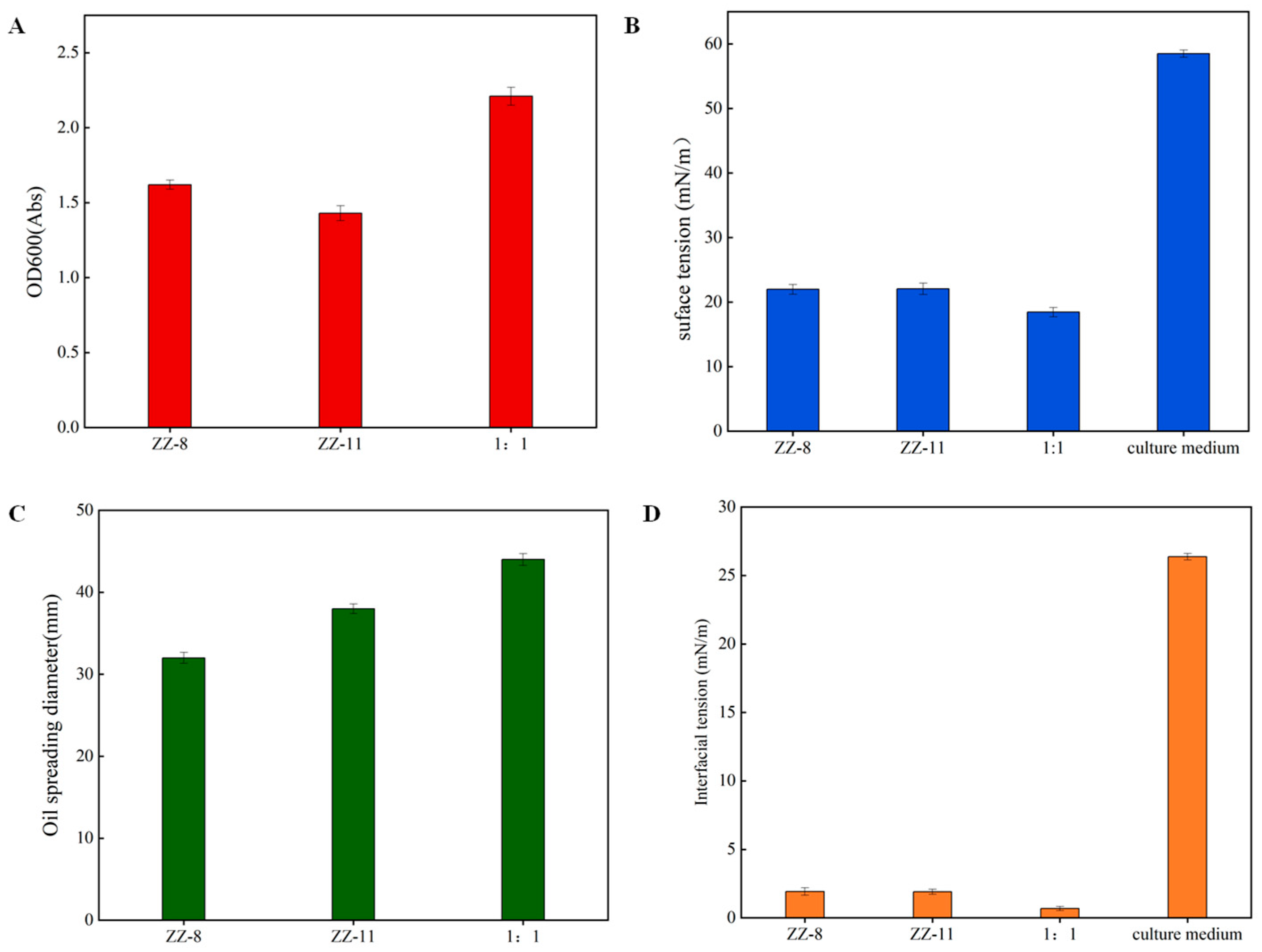
3.2. Biosurfactant Production
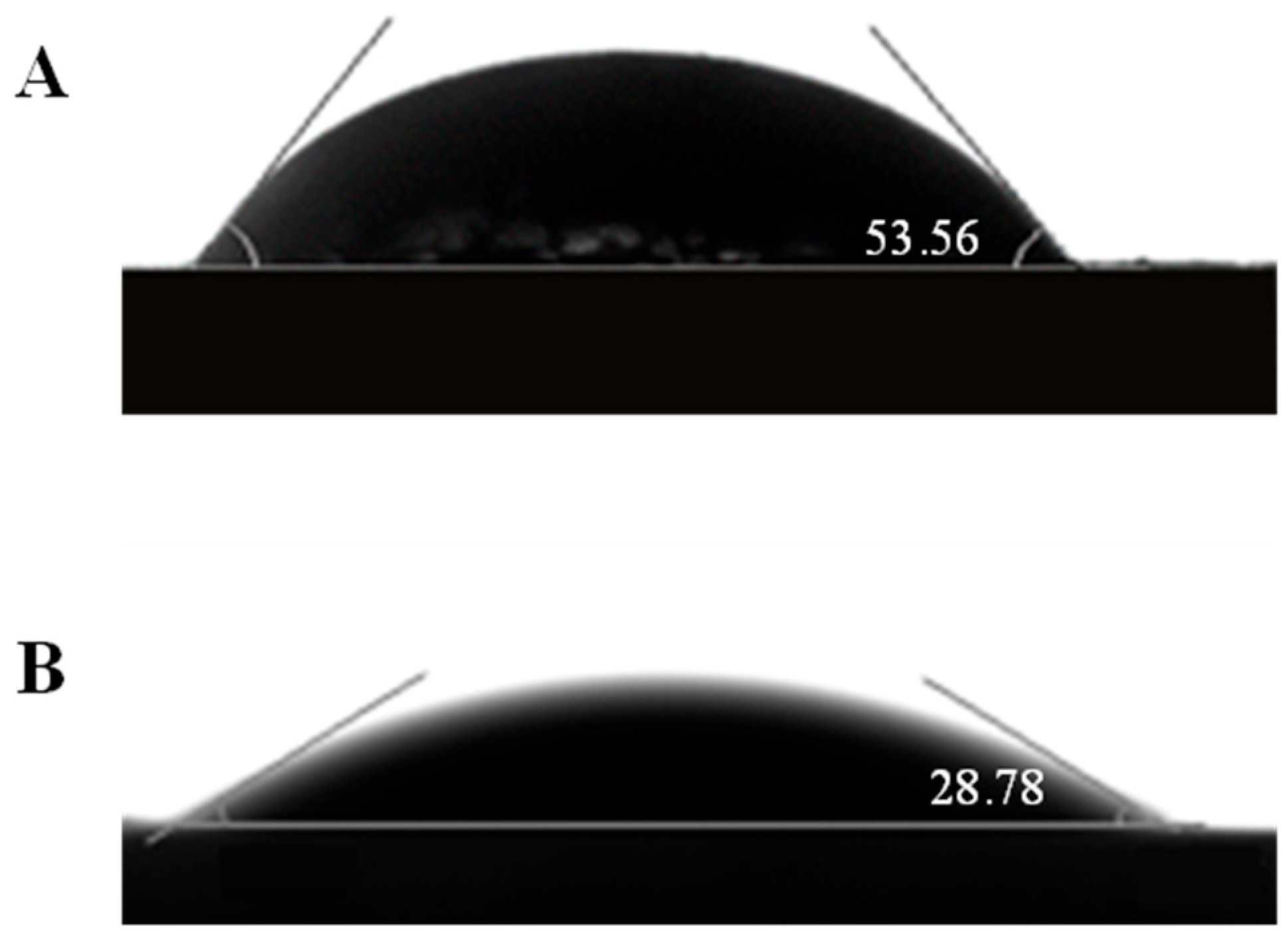
3.3. Contact Angle Measurement
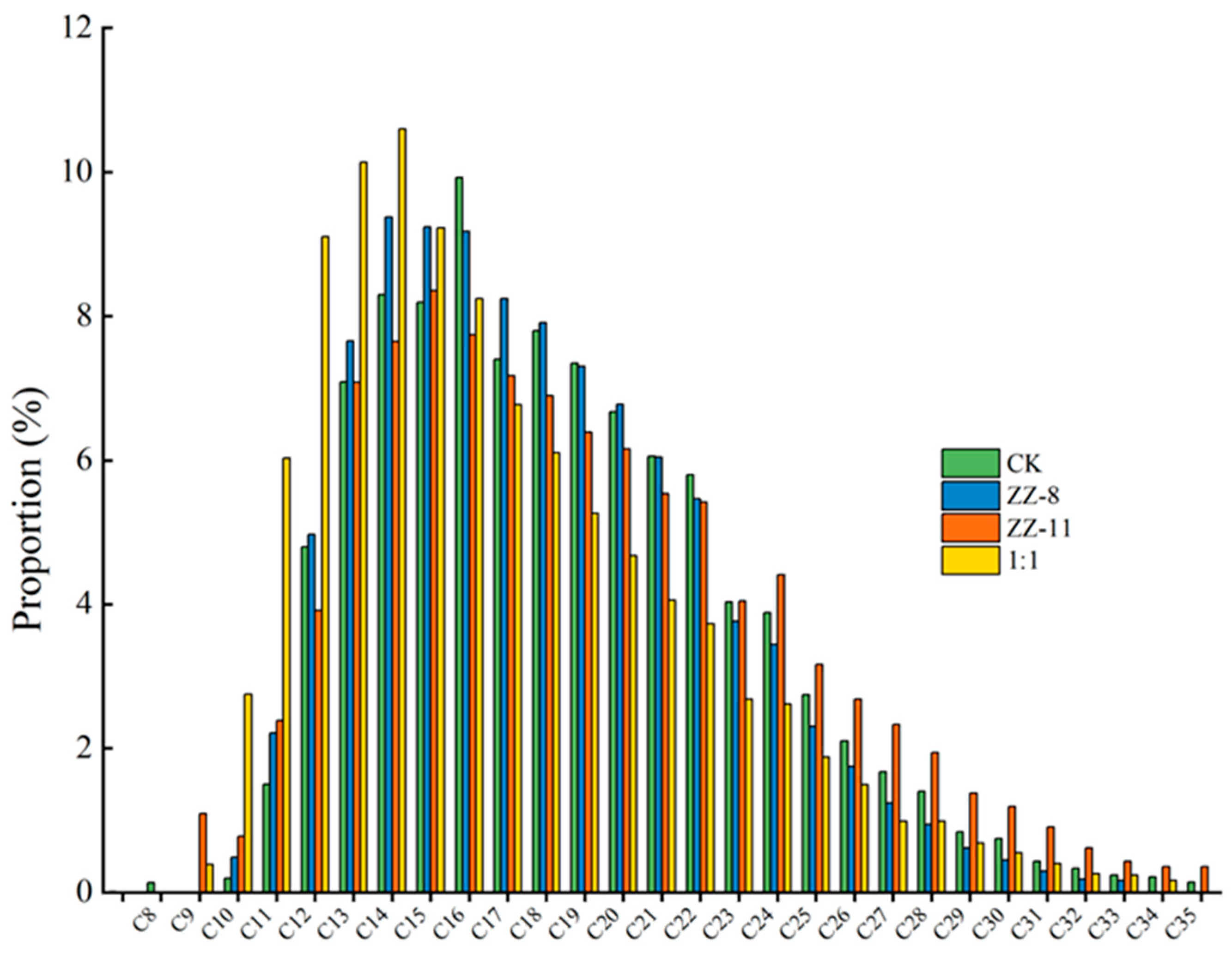
3.4. Gas Chromatographic Analysis Results of Crude Oil
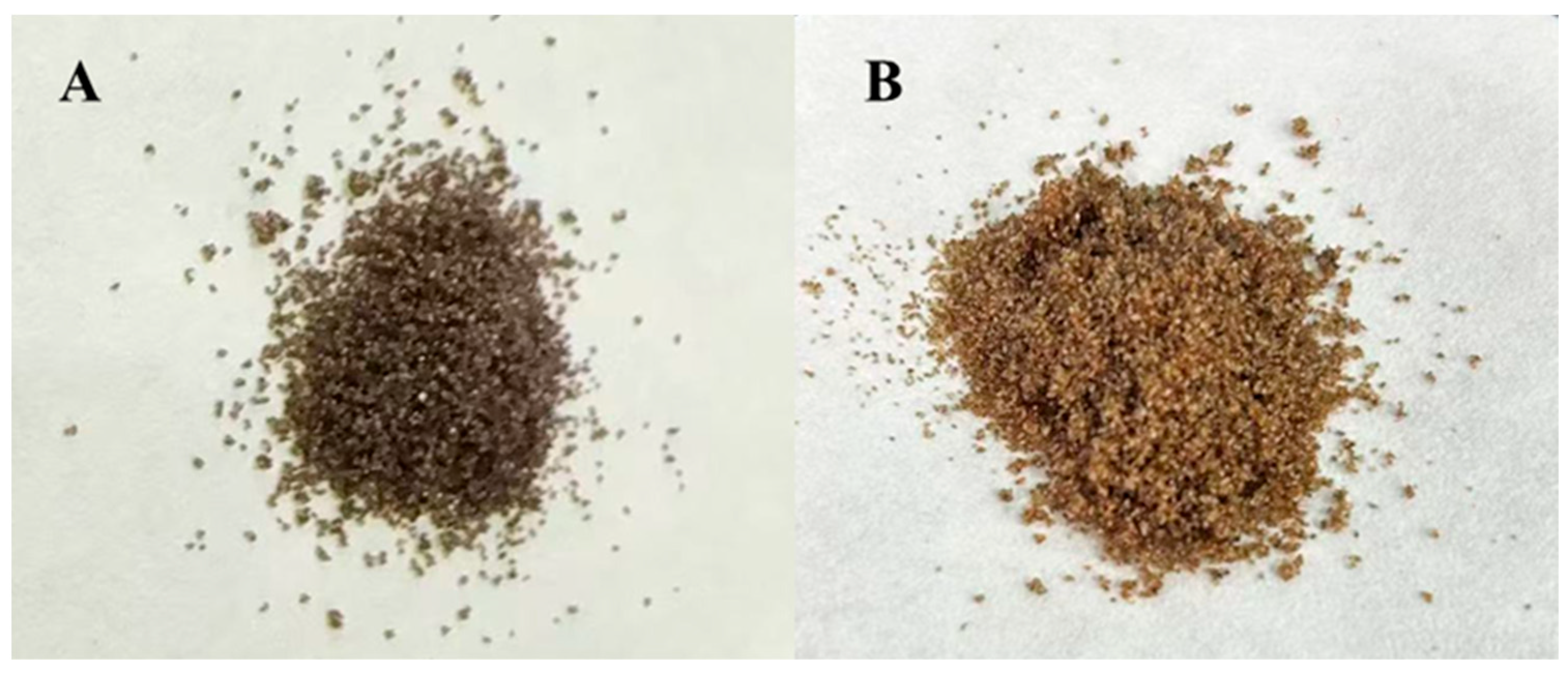
3.5. Oil Sand Washing Experiment
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Maleki, M.; Kazemzadeh, Y.; Dehghan Monfared, A.; Hasan-Zadeh, A.; Abbasi, S. Bio-enhanced oil recovery (BEOR) methods: All-important review of the occasions and challenges. Can. J. Chem. Eng. 2024, 102, 2364–2390. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saravanan, A.; Kumar, P.S.; Vardhan, K.H.; Jeevanantham, S.; Karishma, S.B.; Yaashikaa, P.R.; Vellaichamy, P. A review on systematic approach for microbial enhanced oil recovery technologies: Opportunities and challenges. J. Clean. Prod. 2020, 258, 120777. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiao, H.; Amir, Z.; Mohd Junaidi, M.U. Development of microbial consortium and its influencing factors for enhanced oil recovery after polymer flooding: A review. Processes 2023, 11, 2853. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beliaev, S.S.; Borzenkov, I.A.; Nazina, T.N.; Rozanova, E.P.; Glumov, I.F.; Ibatullin, R.R.; Ivanov, M.V. Use of Microorganisms in the Biotechnology for the Enhancement of Oil Recovery. Mikrobiologiia 2004, 73, 687–697. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yi, L.N.; Li, Z.P.; Liu, L.; Bi, Y.Q.; Wang, X.T.; Yi, J.P. Functional microbial stimulation for oil recovery enhancement based on microbial community analysis. Biotechnol. Biotechnol. Equip. 2018, 32, 1468–1476. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nikolova, C.; Gutierrez, T. Use of microorganisms in the recovery of oil from recalcitrant oil reservoirs: Current state of knowledge, technological advances and future perspectives. Front. Microbiol. 2020, 10, 2996. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Okoro, E.E.; Efajemue, E.A.; Sanni, S.E.; Olabode, O.A.; Orodu, O.D.; Ojo, T. Application of thermotolerant petroleum microbes at reservoir conditions for enhanced oil recovery. Petroleum 2023, 9, 223–236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ren, F.; Wang, Y.; Lin, T.; Liu, L.; Bin, M.; Du, H. Isolation and characterization of a hydrocarbon-degrading strain of Compostibacillus. Microbiol. China 2020, 47, 691–698. [Google Scholar]
- Najafi-Marghmaleki, A.; Kord, S.; Hashemi, A.; Motamedi, H. Experimental investigation of efficiency of MEOR process in a carbonate oil reservoir using Alcaligenes faecalis: Impact of interfacial tension reduction and wettability alteration mechanisms. Fuel 2018, 232, 27–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gudiña, E.J.; Pereira, J.F.; Costa, R.; Coutinho, J.A.; Teixeira, J.A.; Rodrigues, L.R. Biosurfactant-producing and oil-degrading Bacillus subtilis strains enhance oil recovery in laboratory sand-pack columns. J. Hazard. Mater. 2013, 261, 106–113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cui, Q.F.; Sun, S.S.; Luo, Y.J.; Yu, L.; Zhang, Z.Z. Comparison of in-situ and ex-situ microbial enhanced oil recovery by strain Pseudomonas aeruginosa WJ-1 in laboratory sand-pack columns. Pet. Sci. Technol. 2017, 35, 2044–2050. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, H.; Xia, W.; Dong, H.; She, Y.; Zhu, P.; Liang, K.; Zhang, Z.; Liang, C.; Song, Z.; Sun, S.; et al. Rhamnolipids produced by indigenous Acinetobacter junii from petroleum reservoir and its potential in enhanced oil recovery. Front. Microbiol. 2016, 7, 1710. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ng, Y.J.; Lim, H.R.; Khoo, K.S.; Chew, K.W.; Chan, D.J.C.; Bilal, M.; Munawaroh, H.S.H.; Show, P.L. Recent advances of biosurfactant for waste and pollution bioremediation: Substitutions of petroleum-based surfactants. Environ. Res. 2022, 212, 113126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Madani, M.; Zargar, G.; Takassi, M.A.; Daryasafar, A.; Wood, D.A.; Zhang, Z. Fundamental investigation of an environmentally-friendly surfactant agent for chemical enhanced oil recovery. Fuel 2019, 238, 186–197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Darvishi, P.; Ayatollahi, S.; Mowla, D.; Niazi, A. Biosurfactant production under extreme environmental conditions by an efficient microbial consortium, ERCPPI-2. Colloids Surf. B Biointerfaces 2011, 84, 292–300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al-Bahry, S.N.; Al-Wahaibi, Y.M.; Elshafie, A.E.; Al-Bemani, A.S.; Joshi, S.J.; Al-Makhmari, H.S.; Al-Sulaimani, H.S. Biosurfactant production by Bacillus subtilis B20 using date molasses and its possible application in enhanced oil recovery. Int. Biodeterior. Biodegrad. 2013, 81, 141–146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Xue, S.; He, C.; Qi, H.; Chen, F.; Ma, Y. Effect of exogenous inoculants on enhancing oil recovery and indigenous bacterial community dynamics in long-term field pilot of low permeability reservoir. World J. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2018, 34, 53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yin, J.; Wei, X.; Hu, F.; Cheng, C.; Zhuang, X.; Song, M.; Zhuang, G.; Wang, F.; Ma, A. Halotolerant Bacillus velezensis sustainably enhanced oil recovery of low permeability oil reservoirs by producing biosurfactant and modulating the oil microbiome. Chem. Eng. J. 2023, 453, 139912. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kang, D.; Lin, H.; Li, Q.; Su, N.; Cheng, C.; Luo, Y.; Zhang, Z.; Zhang, Z. Enhanced Oil Recovery in a Co-Culture System of Pseudomonas aeruginosa and Bacillus subtilis. Microorganisms 2024, 12, 2343. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Song, B.; Springer, J. Determination of interfacial tension from the profile of a pendant drop using computer-aided image processing: 2. Experimental. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 1996, 184, 77–91. [Google Scholar]
- Shu, Y. Effect of emulsification by surfactant flooding on enhanced oil recovery. Chem. Eng. Des. Commun. 2023, 49, 44–46. [Google Scholar]
- Jaysree, R.C.; Subham, B.; Priyanka, P.S.; Twinkle, G.; Pragya, A.P.; Yekala, K.; Rajendran, N. Isolation of biosurfactant producing bacteria from environmental samples. Pharmacol. Online 2011, 63, 1427–1433. [Google Scholar]
- Al-Sulaimani, H.; Al-Wahaibi, Y.; Al-Bahry, S.; Elshafie, A.; Al-Bemani, A.; Joshi, S.; Ayatollahi, S. Residual-oil recovery through injection of biosurfactant, chemical surfactant, and mixtures of both under reservoir temperatures: Induced-wettability and interfacial-tension effects. SPE Reserv. Eval. Eng. 2012, 15, 210–217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.B.; Chi, C.Q.; Nie, Y.; Tang, Y.Q.; Tan, Y.; Wu, G.; Wu, X.L. Degradation of petroleum hydrocarbons (C6–C40) and crude oil by a novel Dietzia strain. Bioresour. Technol. 2011, 102, 7755–7761. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, M.; Kang, W.; Li, Z.; Yang, H.; Jia, R.; He, Y.; Kang, X.; Zheng, Z.; Wang, Y.; Sarsenbekuly, B.; et al. Stability of oil-in-water (O/W) nanoemulsions and its oil washing performance for enhanced oil recovery. Phys. Fluids 2021, 33, 072002. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, G.S.; Li, D.; Chen, X.; Wang, X.; Zhang, Z.H. Study on oil washing efficiency based on different surfactants. Chem. Eng. 2021, 6, 73–76. [Google Scholar]
- Ron, E.Z.; Rosenberg, E. Biosurfactants and oil bioremediation. Curr. Opin. Biotechnol. 2002, 13, 249–252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gao, C.H.; Cao, H.; Cai, P.; Sørensen, S.J. The initial inoculation ratio regulates bacterial coculture interactions and metabolic capacity. ISME J. 2021, 15, 29–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jin, C.; Nie, C.J.; Guo, Y.J.; Liang, Y.; Hu, J.; Li, J.; Xiong, Q.Y. Research on the properties of in situ emulsified active associative polymer with low molecular weight based on low permeability oil reservoirs. Colloid Polym. Sci. 2024, 302, 679–694. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kowalewski, E.; Rueslatten, I.; Steen, K.H.; Bodtker, G.; Torsaeter, O. Microbial improved oil recovery- bacterial induced wettability and interfacial tension effects on oil production. J. Pet. Sci. Eng. 2006, 52, 275–286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dabiri, A.; Honarvar, B. Investigation of Interfacial Tension Reduction, Wettability Alteration, and Oil Recovery Using a New Non-ionic Oil-Based Surfactant from Gemini Surfactants Family Coupled with Low-Salinity Water: Experimental Study on Oil-Wet Carbonate Rock. J. Surfactants Deterg. 2020, 23, 821–829. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alvarez, V.M.; Guimarães, C.R.; Jurelevicius, D.; de Castilho, L.V.A.; de Sousa, J.S.; da Mota, F.F.; Freire, D.M.G.; Seldin, L. Microbial enhanced oil recovery potential of surfactin-producing Bacillus subtilis AB2. 0. Fuel 2020, 272, 117730. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Joshi, S.J.; Al-Wahaibi, Y.M.; Al-Bahry, S.N.; Elshafie, A.E.; Al-Bemani, A.S.; Al-Bahri, A.; Al-Mandhari, M.S. Production, characterization, and application of Bacillus licheniformis W16 biosurfactant in enhancing oil recovery. Front. Microbiol. 2016, 7, 1853. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al-Wahaibi, Y.; Joshi, S.; Al-Bahry, S.; Elshafie, A.; Al-Bamani, A.; Shibulal, B. Biosurfactant production by Bacillus subtilis B30 and its application in enhancing oil recovery. Colloids Surf. B 2014, 114, 324–333. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, H.; Kang, W.; Yang, H.; Zhang, H.; Zhu, T.; Wang, F.; Li, X.; Zhou, B.; Sarsenbekuly, B.; Aidarova, S.; et al. Imbibition enhancing oil recovery mechanism of the two surfactants. Phys. Fluids 2020, 32, 047103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mu, B.; Wu, Z.; Chen, Z.; Wang, X.; Ni, F.; Zhou, J. Wetting behavior on quartz surfaces by the microbial metabolism and metabolic products. In Proceedings of the 7th International Symposium on Wettability and Its Effects on Oil Recovery, Tasmania, Australia, 12–14 March 2002; pp. 12–14. [Google Scholar]
- Li, C.; Zhou, Z.-X.; Jia, X.-Q.; Chen, Y.; Liu, J.; Wen, J.-P. Biodegradation of crude oil by a newly isolated strain Rhodococcus sp. JZX-01. Appl. Biochem. Biotechnol. 2013, 171, 1715–1725. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pi, Y.; Chen, B.; Bao, M.; Fan, F.; Cai, Q.; Ze, L.; Zhang, B. Microbial degradation of four crude oil by biosurfactant producing strain Rhodococcus sp. Bioresour. Technol. 2017, 232, 263–269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Geetha, S.J.; Banat, I.M.; Joshi, S.J. Biosurfactants: Production and potential applications in microbial enhanced oil recovery (MEOR). Biocatal. Agric. Biotechnol. 2018, 14, 23–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lv, J.Q.; Ying, X.G.; Zhang, Y.L.; Liu, B.; Yang, X.J.; Li, X. Investigation of degradation characteristics of complex petroleum hydrocarbons by Bacillus cereus LY-1. Chem. Pap. 2022, 76, 6753–6765. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


| Fermentation Solution | Oil Washing Efficiency/% |
|---|---|
| ZZ-8 | 40.83 |
| ZZ-11 | 34.32 |
| Culture medium | 8.60 |
| 1:1 | 84.39 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Wang, M.; Yu, C.; Zhao, X.; Liu, J.; Zhai, H.; Qi, M.; Zhang, X.; Liu, Y. Study on the Synergistic Enhancement of Crude Oil Recovery by Bacillus Co-Culture Systems. Processes 2025, 13, 2854. https://doi.org/10.3390/pr13092854
Wang M, Yu C, Zhao X, Liu J, Zhai H, Qi M, Zhang X, Liu Y. Study on the Synergistic Enhancement of Crude Oil Recovery by Bacillus Co-Culture Systems. Processes. 2025; 13(9):2854. https://doi.org/10.3390/pr13092854
Chicago/Turabian StyleWang, Min, Chunjing Yu, Xiaoyu Zhao, Junhao Liu, Haochen Zhai, Meng Qi, Xiumei Zhang, and Yinsong Liu. 2025. "Study on the Synergistic Enhancement of Crude Oil Recovery by Bacillus Co-Culture Systems" Processes 13, no. 9: 2854. https://doi.org/10.3390/pr13092854
APA StyleWang, M., Yu, C., Zhao, X., Liu, J., Zhai, H., Qi, M., Zhang, X., & Liu, Y. (2025). Study on the Synergistic Enhancement of Crude Oil Recovery by Bacillus Co-Culture Systems. Processes, 13(9), 2854. https://doi.org/10.3390/pr13092854





