Cu/Bi-NC Composites Derived from Bimetallic MOFs for Efficient and Stable Capture of Multiform Iodine
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Experiment
2.1. Chemicals & Reagents
2.2. Preparation of the Cux/Bi10−x-MOF and Cux/Bi10−x-NC
2.3. Experiment of the Iodine Capture
2.3.1. Capture of Iodide Ions in Water
2.3.2. Capture of Iodine Vapor
2.3.3. Capture of Iodine in Cyclohexane
3. Results and Discussion
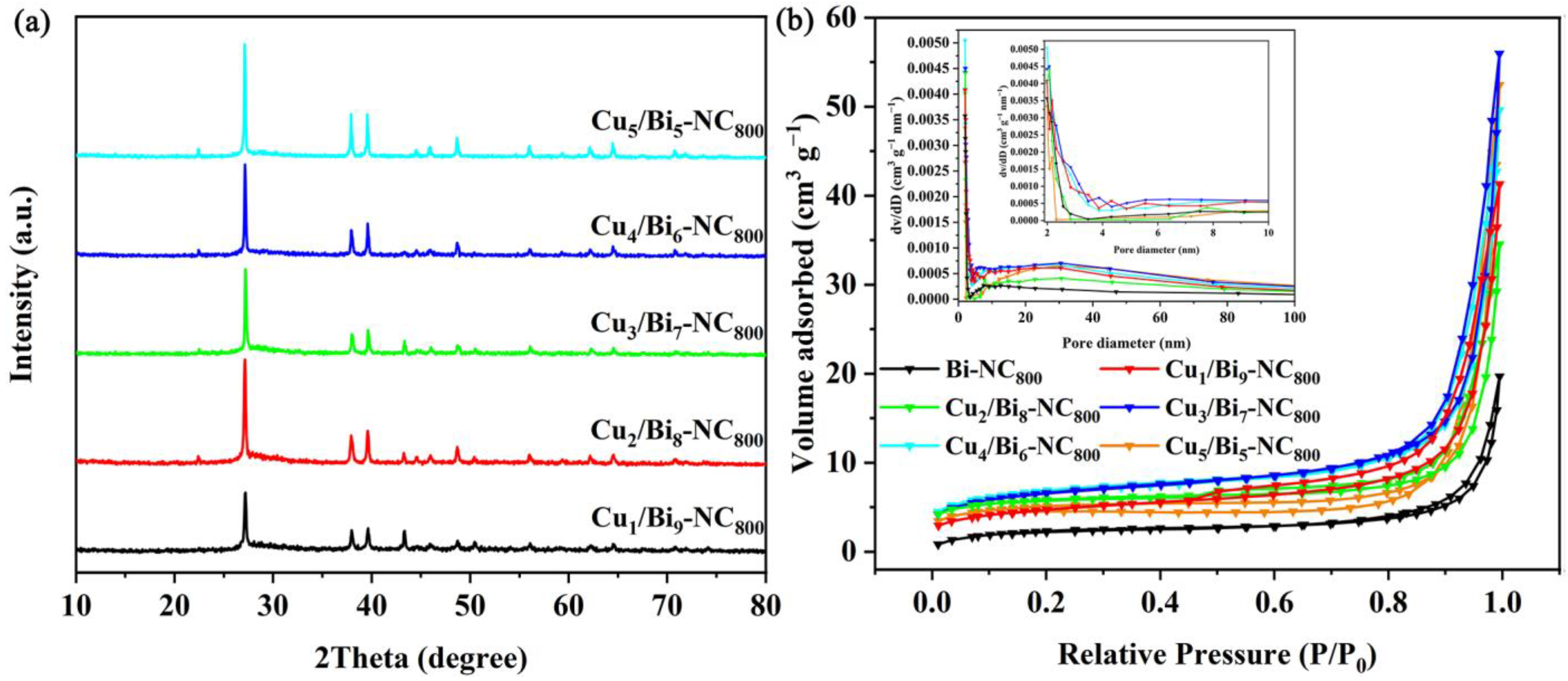
3.1. Characterization of the Cux/Bi10−x-NC
3.2. Capture Properties Evaluation of the Iodine Vapor
3.3. Capture Properties Evaluation of the Iodine in Cyclohexane
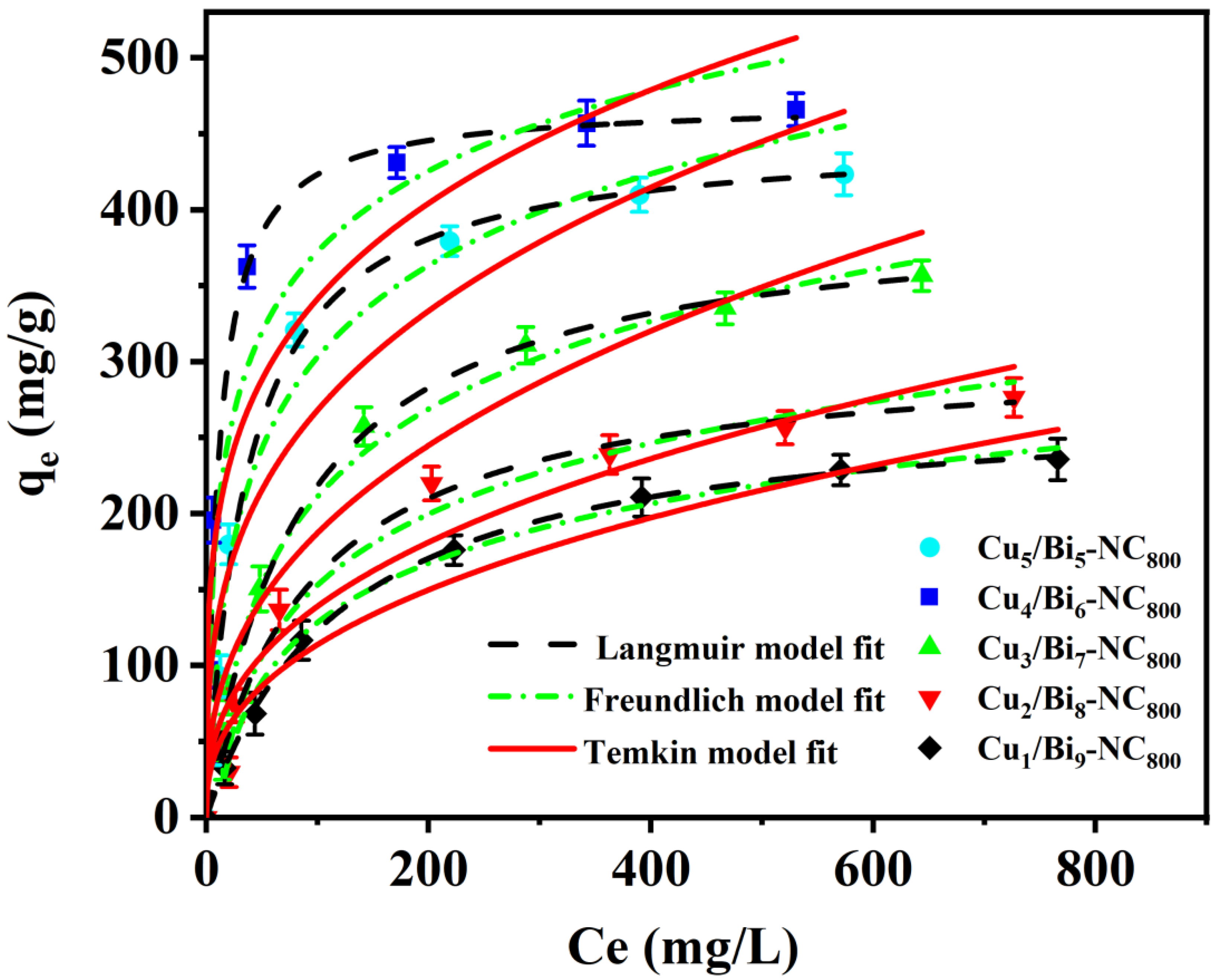
3.3.1. Adsorption Isotherms
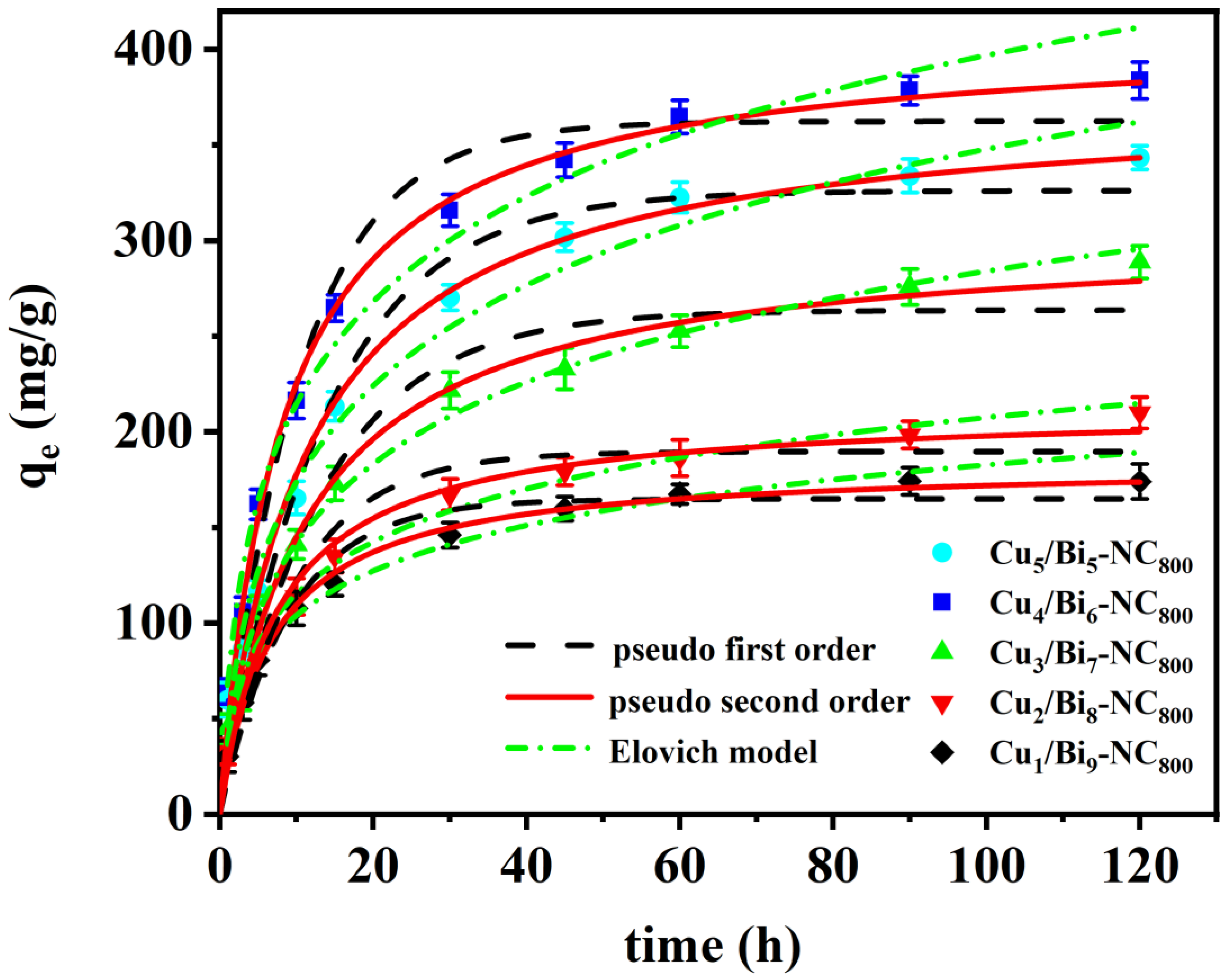
3.3.2. Adsorption Kinetics
3.4. Capture Mechanisms
3.5. Capture Properties Evaluation of the Iodine Ions
3.5.1. Adsorption Isotherms of the Iodine Ions
3.5.2. Adsorption Kinetics of the Iodine Ions
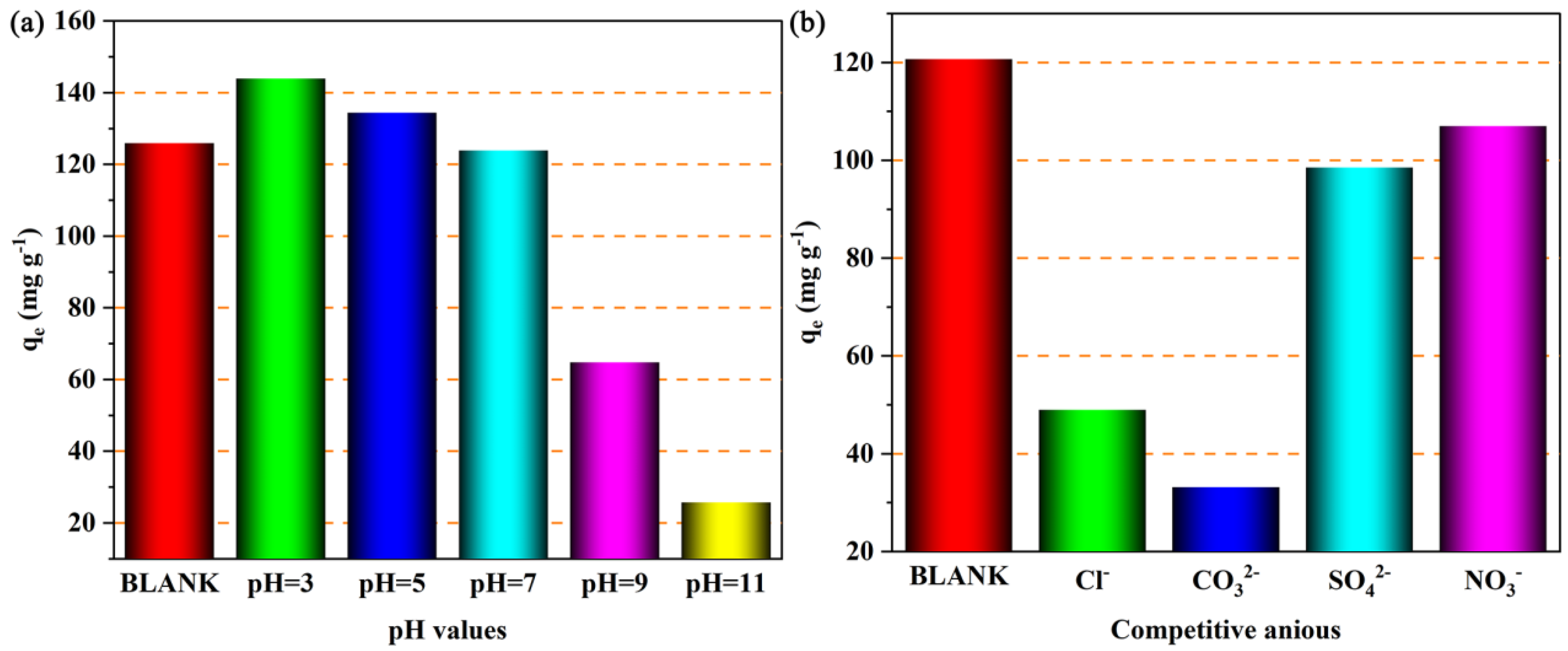
3.5.3. Influencing Factors of the Iodine Ion Adsorption
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Veliscek-Carolan, J. Separation of actinides from spent nuclear fuel: A review. J. Hazard. Mater. 2016, 318, 266–281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Robshaw, T.J.; Griffiths, S.M.; Canner, A.; Bezzina, J.P.; Waller, A.G.L.; Hammond, D.B.; van Meurs, S.; Ogden, M.D. Insights into the interaction of iodide and iodine with Cu(II)-loaded bispicolylamine chelating resin and applications for nuclear waste treatment. Chem. Eng. J. 2020, 390, 124647. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chapman, K.W.; Chupas, P.J.; Nenoff, T.M. Radioactive Iodine Capture in Silver-Containing Mordenites through Nanoscale Silver Iodide Formation. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2010, 132, 8897–8899. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, J.; Du, X.; Gao, F.; Ma, P.; Hao, X.; Guan, G.; Scialdone, O.; Li, J. Electrochemically triggered iodide-vacancy BiOI film for selective extraction of iodide ion from aqueous solutions. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2021, 259, 118120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, S.-H.; Takahashi, Y. Selective immobilization of iodide onto a novel bismuth-impregnated layered mixed metal oxide: Batch and EXAFS studies. J. Hazard. Mater. 2020, 384, 121223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, S.; Wang, N.; Zhang, Y.; Li, Y.; Han, Z.; Na, P. Efficient removal of radioactive iodide ions from water by three-dimensional Ag2O–Ag/TiO2 composites under visible light irradiation. J. Hazard. Mater. 2015, 284, 171–181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, J.; Gao, Q.; Zhang, X.; Liu, Y.; Wang, P.; Jiao, Y.; Yang, Y. Nanometer mixed-valence silver oxide enhancing adsorption of ZIF-8 for removal of iodide in solution. Sci. Total Environ. 2019, 646, 634–644. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.; Gu, P.; Zhou, S.; Li, X.; Zhang, G.; Dong, L. Enhanced removal of iodide ions by nano Cu2O/Cu modified activated carbon from simulated wastewater with improved countercurrent two-stage adsorption. Sci. Total Environ. 2018, 626, 612–620. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Gu, P.; Yang, Y.; Jia, L.; Zhang, M.; Zhang, G. Removal of radioactive iodide from simulated liquid waste in an integrated precipitation reactor and membrane separator (PR-MS) system. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2016, 171, 221–228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, Q.; Huang, B.; Du, X.; Zhang, J.; Fu, H.; Gao, H.; Liao, Y. Construction of N-loaded conjugated polymer for highly effective removal of iodine in organic solution. J. Environ. Chem. Eng. 2023, 11, 109125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, G.; Zhu, L.; Duan, T.; Zhang, L.; Liu, B.; Lei, J. Efficient capture of iodine by a polysulfide-inserted inorganic NiTi-layered double hydroxides. Chem. Eng. J. 2019, 378, 122181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, M.; Yang, L.; Li, X.; Chang, G. An indole-derived porous organic polymer for the efficient visual colorimetric capture of iodine in aqueous media via the synergistic effects of cation–π and electrostatic forces. Chem. Commun. 2020, 56, 1401–1404. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, J.; Wang, P.; Gong, C.; Sun, Y.; Zhu, B.; Yang, Y.; Liu, F. Bimetal ZIFs-derived Cu0 embedded in nitrogen-doped carbon framework activation of molecular oxygen for efficient iodide elimination. J. Environ. Chem. Eng. 2024, 12, 112235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, H.; Cao, L.; Cheng, X.; Ding, P.; Zhu, W.; Duan, T.; He, G.; Wei, Y.; Sun, D.; Zhou, Y.; et al. In-site interface growth of bismuth-based hydrothermal carbon using collagen fiber for selective removal of iodide ion from wastewater. Colloids Surf. A Physicochem. Eng. Asp. 2023, 664, 131177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Riley, B.J.; Chong, S.; Asmussen, R.M.; Bourchy, A.; Engelhard, M.H. Polyacrylonitrile Composites of Ag–Al–Si–O Aerogels and Xerogels as Iodine and Iodide Sorbents. ACS Appl. Polym. Mater. 2021, 3, 3344–3353. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, X.; Mao, P.; Jin, H.; Huang, W.; Gu, A.; Chen, K.; Yun, S.; Chen, J.; Yang, Y. Cu/Al2O3 aerogels for high-efficiency and rapid iodide elimination from water. J. Hazard. Mater. 2023, 443, 130349. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, J.; Gu, A.; Miensah, E.D.; Liu, Y.; Wang, P.; Mao, P.; Gong, C.; Jiao, Y.; Chen, K.; Yang, Y. Cu-Zn bimetal ZIFs derived nanowhisker zero-valent copper decorated ZnO nanocomposites induced oxygen activation for high-efficiency iodide elimination. J. Hazard. Mater. 2021, 416, 126097. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reda, A.T.; Zhang, D.; Xu, X.; Xu, S. Highly stable iodine capture by pillared montmorillonite functionalized Bi2O3@g-C3N4 nanosheets. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2022, 292, 120994. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, Y.; Zeng, P.; Wang, D.; Li, T.-T.; Wu, L.-H.; Zheng, S.-R. A mixed-ligand Co(ii) MOF synthesized from a single organic ligand to capture iodine and methyl iodide vapour. Dalton Trans. 2023, 52, 7709–7717. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiong, Y.; Zhang, P.; Ren, W.; Li, S.; Jin, C. Rapid and selective removal of radioactive iodide ions from wastewater via bismuth-based metal-organic frameworks. J. Environ. Chem. Eng. 2024, 12, 111906. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, K.-W.; Gu, A.-T.; Zhou, X.-Y.; Wang, P.; Gong, C.-H.; Mao, P.; Jiao, Y.; Chen, K.; Yang, Y. Core-shell structured Bi2S3-ZnS@C derived from ZIF-8 for efficient capture and reliable storage of volatile radioactive iodine. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2023, 322, 124380. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dai, X.-J.; Chen, K.-W.; He, M.-L.; Chen, K.; Zhou, X.-Y.; Chen, Y.-T.; Gong, C.-H.; Wang, P.; Mao, P.; Yang, Y. Removal of radioactive iodine by Cu2O prepared with PVP as an active agent: Role of crystal facets and oxygen vacancy in adsorption mechanisms. Chem. Eng. J. 2024, 493, 152515. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liao, L.; Song, S.; Liang, G.; Wang, X.; Pan, N.; Lei, H.; Zhang, Y.; Zou, H.; Cheng, J.; Wen, J.; et al. Resource recovery from iodine-containing silver-loaded silica gel: Recycling of silver and immobilization of iodine. J. Hazard. Mater. 2025, 493, 138306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dai, X.-J.; Chen, K.-W.; He, M.-L.; Zhou, X.-Y.; Chen, Y.-T.; Li, S.-X.; Gong, C.-H.; Wang, P.; Mao, P.; Lu, J.-G.; et al. Efficient removal of radioactive iodine anions using δ-Bi2O3/MOF-808 through photo-oxidation and adsorption: Performance evaluation and investigation of synergistic mechanisms. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2025, 360, 130973. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, L.-W.; Chen, K.-W.; Dai, X.-J.; He, M.-L.; Wang, P.; Gong, C.-H.; Gu, A.-T.; Lu, J.-G.; Yang, Y. Tunable Cu(0)/Cu(I) hybrids derived from Cu-MOF for enhanced removal of iodide anions. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2025, 357, 130046. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, S.; Um, W.; Kim, W.-S. Development of bismuth-functionalized graphene oxide to remove radioactive iodine. Dalton Trans. 2019, 48, 478–485. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kamal, S.; Khalid, M.; Khan, M.S.; Shahid, M.; Ahmad, M. A bifunctionalised Pb-based MOF for iodine capture and dye removal. Dalton Trans. 2023, 52, 4501–4516. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Agarwal, R.A. Selective and Reversible Capture of Volatile I2 Modifying As-Synthesized 2D Cd-MOF to 3D. Cryst. Growth Des. 2021, 21, 2046–2055. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaneti, Y.V.; Tang, J.; Salunkhe, R.R.; Jiang, X.; Yu, A.; Wu, K.C.W.; Yamauchi, Y. Nanoarchitectured Design of Porous Materials and Nanocomposites from Metal-Organic Frameworks. Adv. Mater. 2017, 29, 1604898. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, K.-W.; Zhou, X.-Y.; Chen, Y.-T.; Dai, X.-J.; Li, S.-X.; Gu, A.-T.; Gong, C.-H.; Wang, P.; Mao, P.; Lu, J.-G.; et al. Tunable sulfur vacancies in amorphous-crystalline AC-Bi2S3−x@C derived from CAU-17 for efficient capture of radioiodine: Comparison of sulfur vacancies in amorphous and crystalline structures. Chem. Eng. J. 2024, 499, 156002. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nguyen, V.H.; Pham, A.L.H.; Nguyen, V.-H.; Lee, T.; Nguyen, T.D. Facile synthesis of bismuth(III) based metal-organic framework with difference ligands using microwave irradiation method. Chem. Eng. Res. Des. 2022, 177, 321–330. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, Q.; Jiang, X.; Cheng, Z.; Liao, Y.; Pu, Q.; Duan, M. Millimeter-sized Bi2S3@polyacrylonitrile hybrid beads for highly efficient iodine capture. New J. Chem. 2020, 44, 16759–16768. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choudhary, M.; Kumar, R.; Neogi, S. Activated biochar derived from Opuntia ficus-indica for the efficient adsorption of malachite green dye, Cu+2 and Ni+2 from water. J. Hazard. Mater. 2020, 392, 122441. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nekouei, F.; Nekouei, S.; Tyagi, I.; Gupta, V.K. Kinetic, thermodynamic and isotherm studies for acid blue 129 removal from liquids using copper oxide nanoparticle-modified activated carbon as a novel adsorbent. J. Mol. Liq. 2015, 201, 124–133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choung, S.; Um, W.; Kim, M.; Kim, M.G. Uptake mechanism for iodine species to black carbon. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2013, 47, 10349–10355. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Yang, Z.; Wang, J. Fenton-like degradation of sulfamethoxazole in Cu-0/Zn-0-air system over a broad pH range: Performance, kinetics and mechanism. Chem. Eng. J. 2021, 403, 126320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, H.; Tang, L.; Tang, J.; Zeng, G.; Dong, H.; Deng, Y.; Wang, L.; Liu, Y.; Ren, X.; Zhou, Y. Cu-Doped Fe@Fe2O3 core-shell nanoparticle shifted oxygen reduction pathway for high-efficiency arsenic removal in smelting wastewater. Environ. Sci. Nano 2018, 5, 1595–1607. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, H.-P.; Yeager, C.M.; Brinkmeyer, R.; Zhang, S.; Ho, Y.-F.; Xu, C.; Jones, W.L.; Schwehr, K.A.; Otosaka, S.; Roberts, K.A.; et al. Bacterial production of organic acids enhances H2O2-dependent iodide oxidation. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2012, 46, 4837–4844. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Changani, Z.; Razmjou, A.; Taheri-Kafrani, A.; Warkiani, M.E.; Asadnia, M. Surface modification of polypropylene membrane for the removal of iodine using polydopamine chemistry. Chemosphere 2020, 249, 126079. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, W.; Chen, C.; Zhu, J.; Zhou, L.; Lan, Y. Efficient removal of aniline by micro-scale zinc-copper (mZn/Cu) bimetallic particles in acidic solution: An oxidation degradation mechanism via radicals. J. Hazard. Mater. 2019, 366, 482–491. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mao, P.; Qi, L.; Liu, X.; Liu, Y.; Jiao, Y.; Chen, S.; Yang, Y. Synthesis of Cu/Cu2O hydrides for enhanced removal of iodide from water. J. Hazard. Mater. 2017, 328, 21–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiao, H.; Li, Y.; Gao, K.; Zhao, J.; Wang, C.; Li, M.; Na, P. Efficient removal of radioactive iodide by three-dimensional Cu@Cu2O: An adsorption and electrocatalytic oxidation coupling process. Colloids Surf. A-Physicochem. Eng. Asp. 2020, 602, 124964. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, J.; Gu, A.; Miensah, E.D.; Liu, Y.; Wang, P.; Mao, P.; Gong, C.; Jiao, Y.; Chen, K.; Zhang, Z.; et al. Core-shell ZnO@Cu2O encapsulated Ag NPs nanocomposites for photooxidation-adsorption of iodide anions under visible light. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2021, 262, 118328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seon, J.; Hwang, Y. Cu/Cu2O-immobilized cellulosic filter for enhanced iodide removal from water. J. Hazard. Mater. 2021, 409, 124415. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]






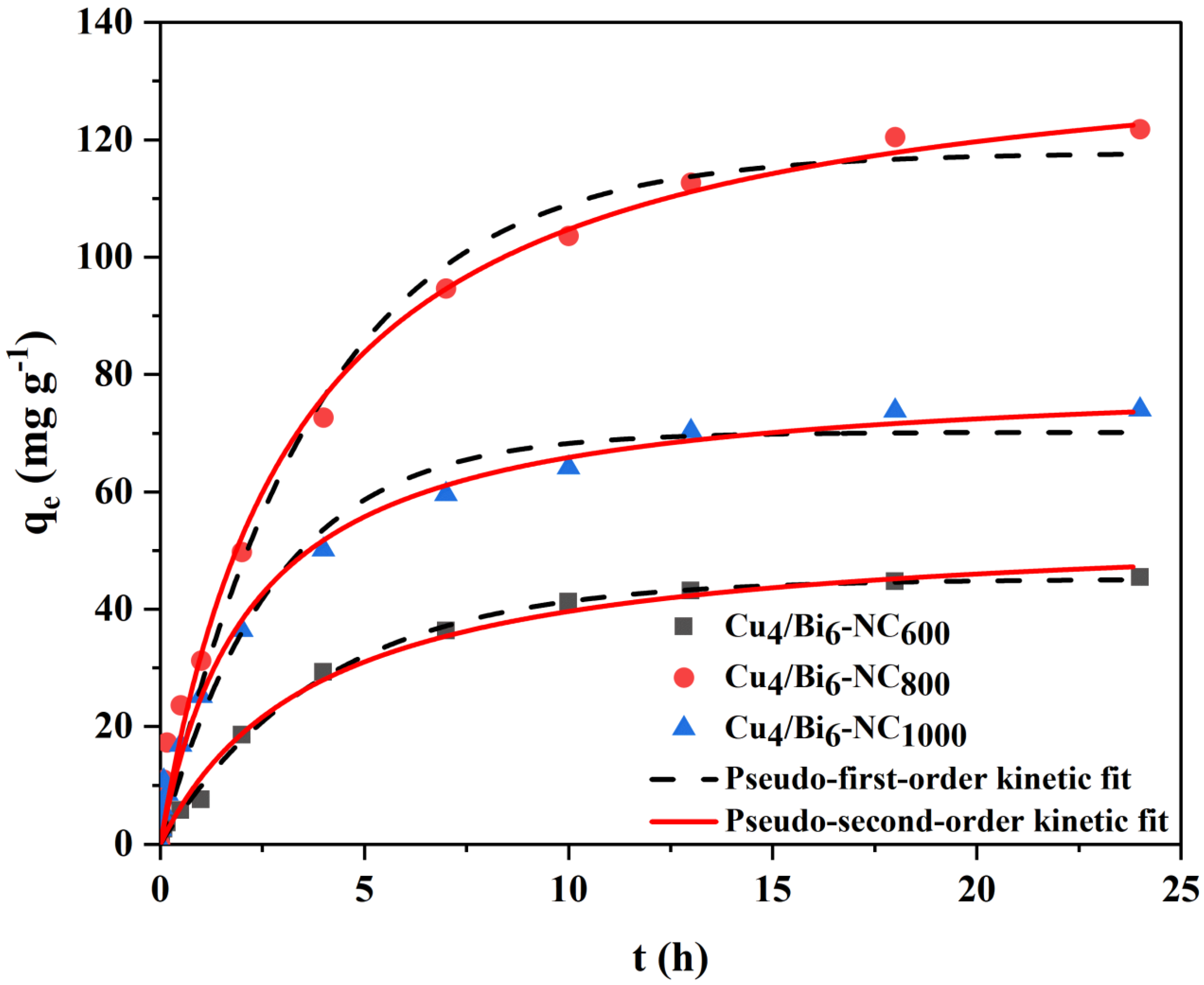
| Adsorbents | Langmuir Model | Freundlich Model | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Qm (mg g−1) | KL (L mg−1) | R2 | KF | 1/n | R2 | |
| Cu4/Bi6-NC600 | 70.3 | 0.018 | 0.984 | 10.2 | 0.363 | 0.971 |
| Cu4/Bi6-NC800 | 167.3 | 0.006 | 0.982 | 6.9 | 0.608 | 0.973 |
| Cu4/Bi6-NC1000 | 97.5 | 0.011 | 0.989 | 4.3 | 0.463 | 0.982 |
| Adsorbents | First-Order Kinetic Equation | Second-Order Kinetic Equation | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| qe (mg g−1) | K1 | R2 | qe (mg g−1) | K2 | R2 | |
| Cu4/Bi6-NC600 | 45.1 | 0.248 | 0.996 | 54.8 | 4.75 × 10−3 | 0.994 |
| Cu4/Bi6-NC800 | 117.8 | 0.259 | 0.982 | 139.6 | 2.15 × 10−3 | 0.986 |
| Cu4/Bi6-NC1000 | 70.2 | 0.361 | 0.974 | 80.5 | 5.60 × 10−3 | 0.987 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Ren, J.; Gu, A.; Wang, P.; Gong, C.; Chen, K.; Mao, P.; Jiao, Y.; Chen, K.; Yang, Y. Cu/Bi-NC Composites Derived from Bimetallic MOFs for Efficient and Stable Capture of Multiform Iodine. Processes 2025, 13, 2678. https://doi.org/10.3390/pr13092678
Ren J, Gu A, Wang P, Gong C, Chen K, Mao P, Jiao Y, Chen K, Yang Y. Cu/Bi-NC Composites Derived from Bimetallic MOFs for Efficient and Stable Capture of Multiform Iodine. Processes. 2025; 13(9):2678. https://doi.org/10.3390/pr13092678
Chicago/Turabian StyleRen, Jie, Aotian Gu, Peng Wang, Chunhui Gong, Kaiwei Chen, Ping Mao, Yan Jiao, Kai Chen, and Yi Yang. 2025. "Cu/Bi-NC Composites Derived from Bimetallic MOFs for Efficient and Stable Capture of Multiform Iodine" Processes 13, no. 9: 2678. https://doi.org/10.3390/pr13092678
APA StyleRen, J., Gu, A., Wang, P., Gong, C., Chen, K., Mao, P., Jiao, Y., Chen, K., & Yang, Y. (2025). Cu/Bi-NC Composites Derived from Bimetallic MOFs for Efficient and Stable Capture of Multiform Iodine. Processes, 13(9), 2678. https://doi.org/10.3390/pr13092678







