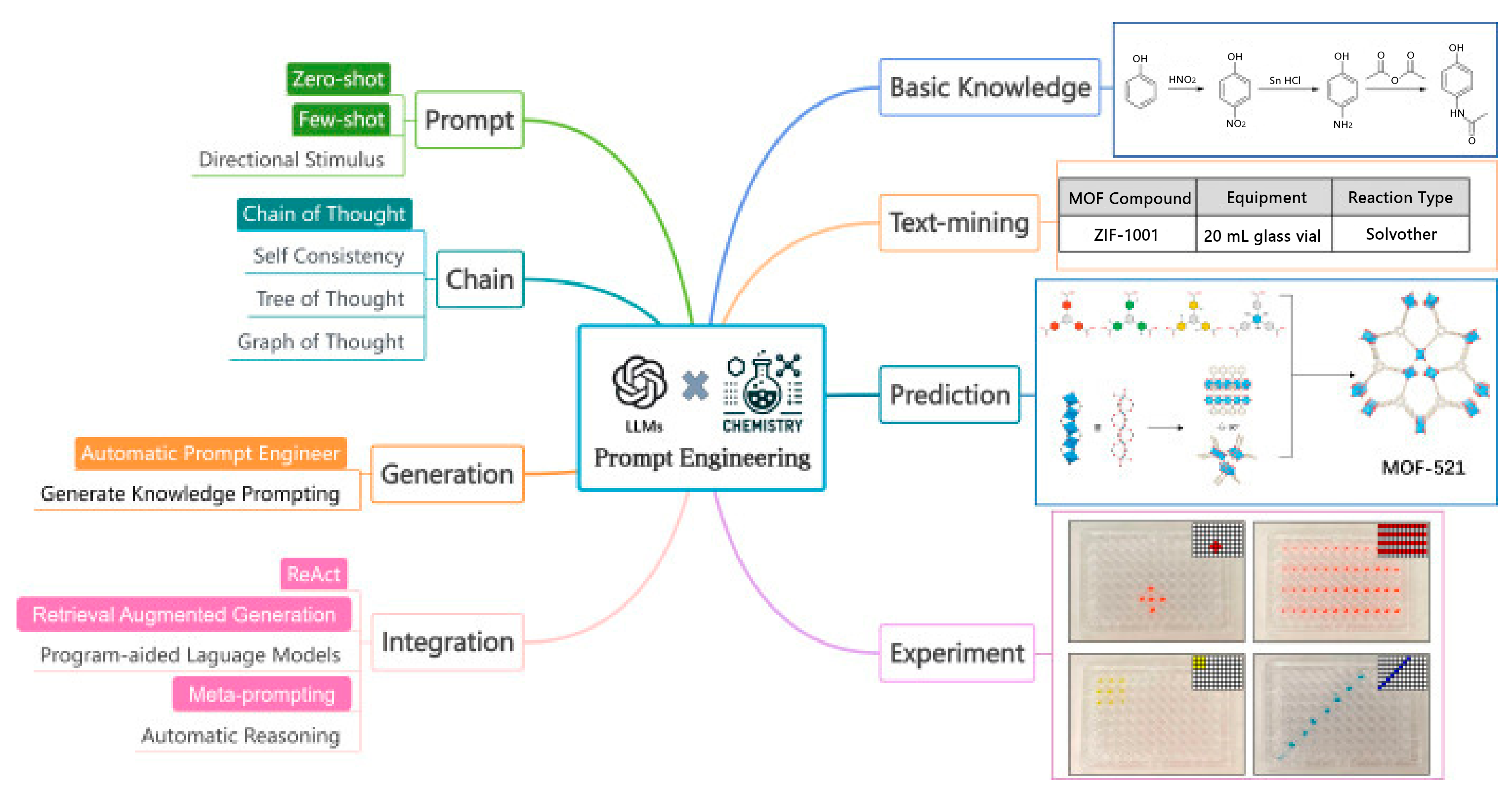
Abstract
This review provides a comprehensive overview of the evolution and application of artificial intelligence (AI) and large language models (LLMs) in engineering, with a specific focus on chemical engineering. The review traces the historical development of LLMs, from early rule-based systems and statistical models like N-grams to the transformative introduction of neural networks and transformer architecture. It examines the pivotal role of models like BERT and the GPT series in advancing natural language processing and enabling sophisticated applications across various engineering disciplines. For example, GPT-3 (175B parameters) demonstrates up to 87.7% accuracy in structured information extraction, while GPT-4 introduces multimodal reasoning with estimated token limits exceeding 32k. The review synthesizes recent research on the use of LLMs in software, mechanical, civil, and electrical engineering, highlighting their impact on automation, design, and decision-making. A significant portion is dedicated to the burgeoning applications of LLMs in chemical engineering, including their use as educational tools, process simulation and modelling, reaction optimization, and molecular design. The review delves into specific case studies on distillation column and reactor design, showcasing how LLMs can assist in generating initial parameters and optimizing processes while also underscoring the necessity of validating their outputs against traditional methods. Finally, the review addresses the challenges and future considerations of integrating LLMs into engineering workflows, emphasizing the need for domain-specific adaptations, ethical guidelines, and robust validation frameworks.
1. Introduction
The field of engineering has perpetually evolved through the adoption of new technologies that enhance design, analysis, and operational efficiency. From the slide rule to computer-aided design (CAD) and advanced simulation software, each technological leap has redefined the boundaries of what is possible. The field is undergoing a significant transition driven by advances in artificial intelligence (AI), particularly large language models (LLMs) [1]. These sophisticated models, capable of understanding and generating human-like text, are no longer confined to the realm of natural language processing but are emerging as powerful tools across a multitude of scientific and technical fields, including engineering [2].
This literature review explores the historical trajectory and contemporary applications of AI and LLMs within the broad landscape of engineering, with a specialized focus on their growing influence in chemical engineering. The objective is to provide a synthesized understanding of how these technologies have developed, from early expert systems to the current generation of powerful models like GPT-4, and how they are being practically applied to solve complex engineering problems. This review will navigate through the foundational concepts of LLMs and their general applications in diverse engineering disciplines and then delve deeply into their specific uses within chemical engineering, such as process design, simulation, and autonomous experimentation. Recent advances in AI-assisted engineering modelling further underscore this trend. For example, Peng et al. [3] developed a cognitive computing framework for predicting the flow status of a flexible rectifier, integrating data-driven learning with underlying physical principles to achieve high predictive accuracy under varying operating conditions. While this study does not involve an LLM, it illustrates how AI models can complement physics-based simulations in engineering—a capability that remains largely unexplored for LLMs and is identified in this review as a key research opportunity.
By examining key studies and emerging trends, this review aims to illuminate both the remarkable potential of LLMs to revolutionize engineering workflows and the inherent challenges that must be addressed. These challenges include issues of accuracy, the risk of over-reliance, and the ethical considerations surrounding their use. Ultimately, this review provides not only a synthesized and up-to-date overview of LLM applications across engineering domains but also a unique focus on how these models are currently transforming chemical engineering practice, an area less emphasized in prior reviews. By comparing general-purpose and domain-specific LLMs and evaluating their integration into simulation, reaction design, and autonomous experimentation, this paper offers a distinct perspective for chemical engineers seeking to adopt AI-driven methodologies.
2. Historical Development of Large Language Models (LLMs)
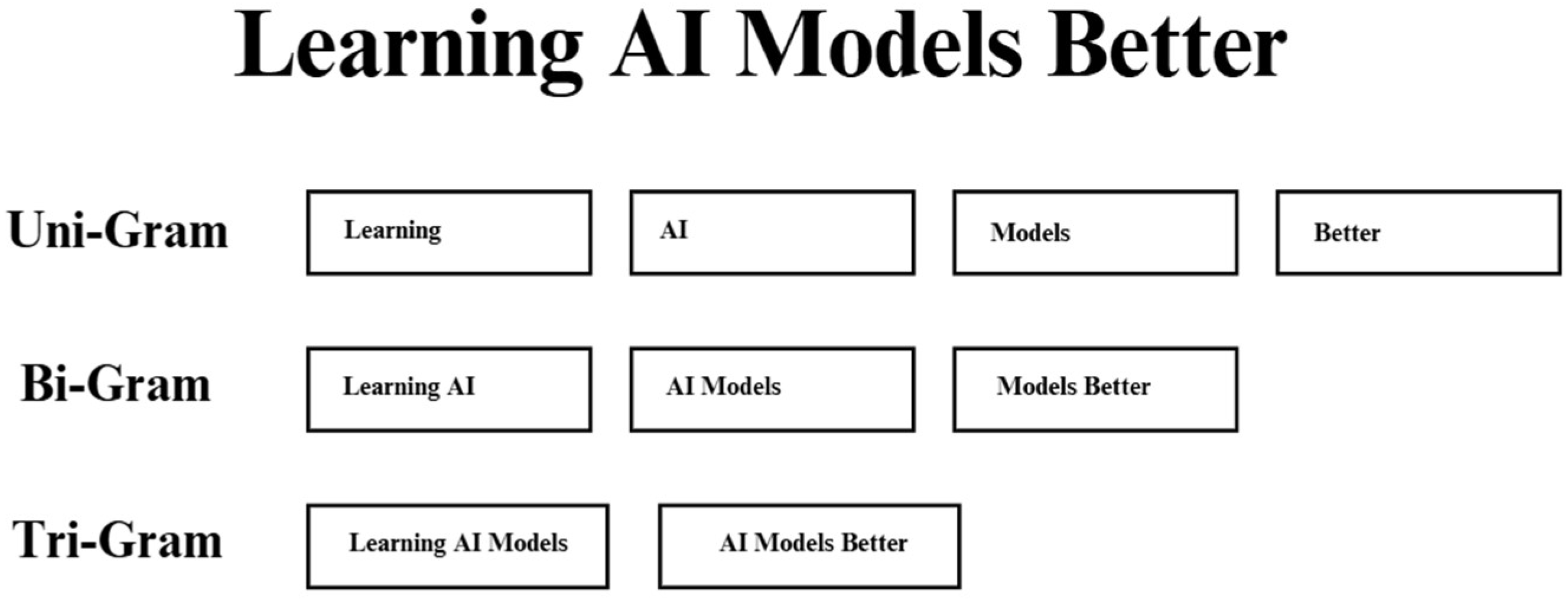
The significant advancements in large language models (LLMs) trace their roots to early natural language processing (NLP), which utilized rule-based and statistical models like N-grams, as illustrated in Figure 1, and Hidden Markov Models (HMMs). During the 1990s, statistical language models such as N-grams and HMMs were introduced, which used probability methods to predict word sequences based on training data. While these models improved performance on certain tasks, they still struggled with capturing long-range dependencies, as noted in various historical accounts [4].
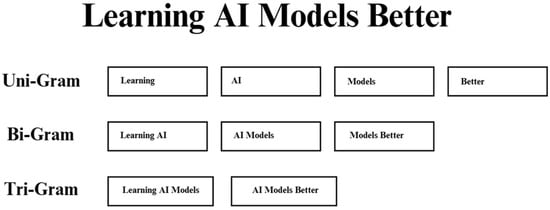
Figure 1.
Demonstration of N-grams.
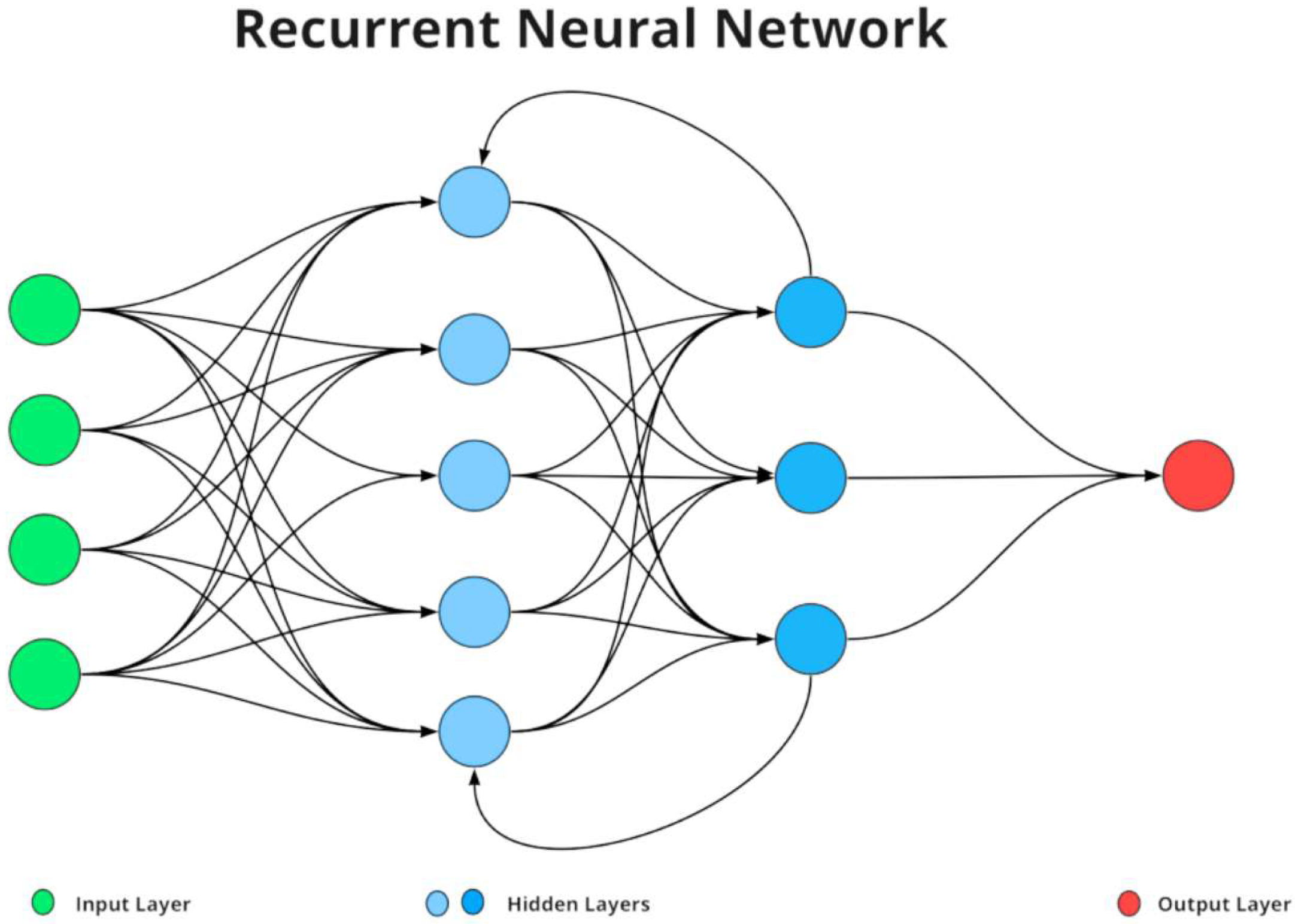
The emergence of neural networks in the 2010s marked a significant change in NLP. Word embedding techniques like Word2Vec and GloVe enabled the representation of words as dense vectors and capturing their semantic relationships [5]. Recurrent neural etworks (RNNs), as shown in Figure 2, and their variants such as Long Short-Term Memory (LSTM) networks allowed for the sequential processing of text and improving the handling of context over longer sequences. However, these models still faced challenges with parallelization and were computationally intensive for very long sequences, as detailed in timelines of LLM development.
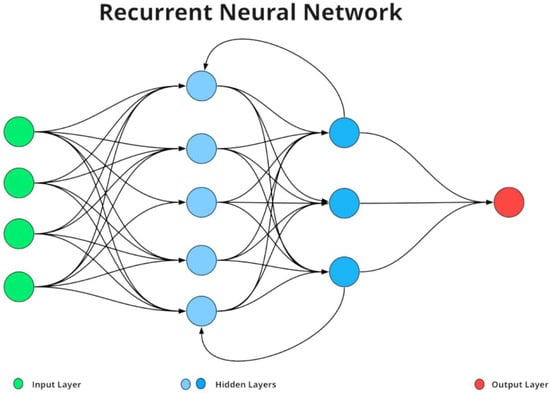
Figure 2.
Demonstration of recurrent neural network.
A pivotal moment came in 2017 with the introduction of the transformer architecture by Vaswani et al. [6]. This architecture later became the foundation for subsequent LLMs, allowing for the training of much larger models on vast amounts of data, as evidenced by the rapid adoption in subsequent years.
In 2018, Google released BERT (Bidirectional Encoder Representations from Transformers), which utilized the transformer encoder to achieve results on various NLP benchmarks through pre-training on large data and fine-tuning on specific tasks. A key innovation of BERT was its ability to understand context from both directions, which allowed it to analyze the words that came both before and after a given word to make more accurate predictions [7].
At the same time, OpenAI was developing its Generative Pre-trained Transformer (GPT) series, releasing GPT-1 in 2018, followed by GPT-2 in 2019, and then GPT-3 in 2020 [8]. These models employed the transformer decoder and were trained to predict the next word in a sequence, which enables them to generate coherent and contextually relevant text. GPT-3, with its 175 billion parameters, demonstrated remarkable few-shot learning capabilities, performing tasks with minimal examples and exhibiting emergent behaviors not seen in other smaller models, as detailed in its publication (Language Models are Few-Shot Learners) [9].
The trend of scaling-up model size continued with models like Google’s PaLM (540 billion parameters) and Meta’s OPT (175 billion parameters) in 2022 [10]. In 2023, OpenAI released GPT-4, as shown in Figure 3, which, although the exact parameter count is not publicly disclosed, is believed to be significantly larger than its predecessor, with estimates suggesting over a trillion parameters. GPT-4 showcased advanced reasoning, code generation, and multimodal capabilities, further pushing the boundaries of what LLMs can achieve [11].
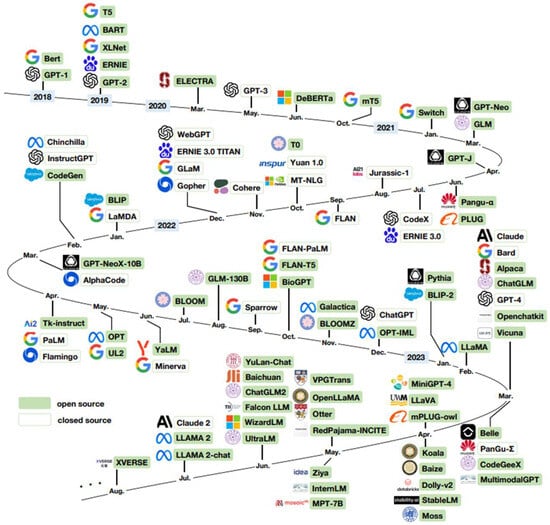
Figure 3.
History timeline of LLMs, multimodels and scientific models (open access) [12].
At the same time, the development of domain-specific LLMs has gained momentum. For instance, ChemLLM, introduced in 2024, which is fine-tuned on chemical databases to excel in chemistry-related tasks, demonstrated performance comparable to general-purpose models like GPT-4 in its domain [13]. This rapid progression underscores the exponential growth in model capacity and capability. Transforming LLMs from research tools into engines for language understanding and generation has multiple implications for various fields, including chemical engineering. The applications of these models in engineering contexts, particularly in chemical processes, are explored in this study.
2.1. Early Development of AI and NLP in Engineering
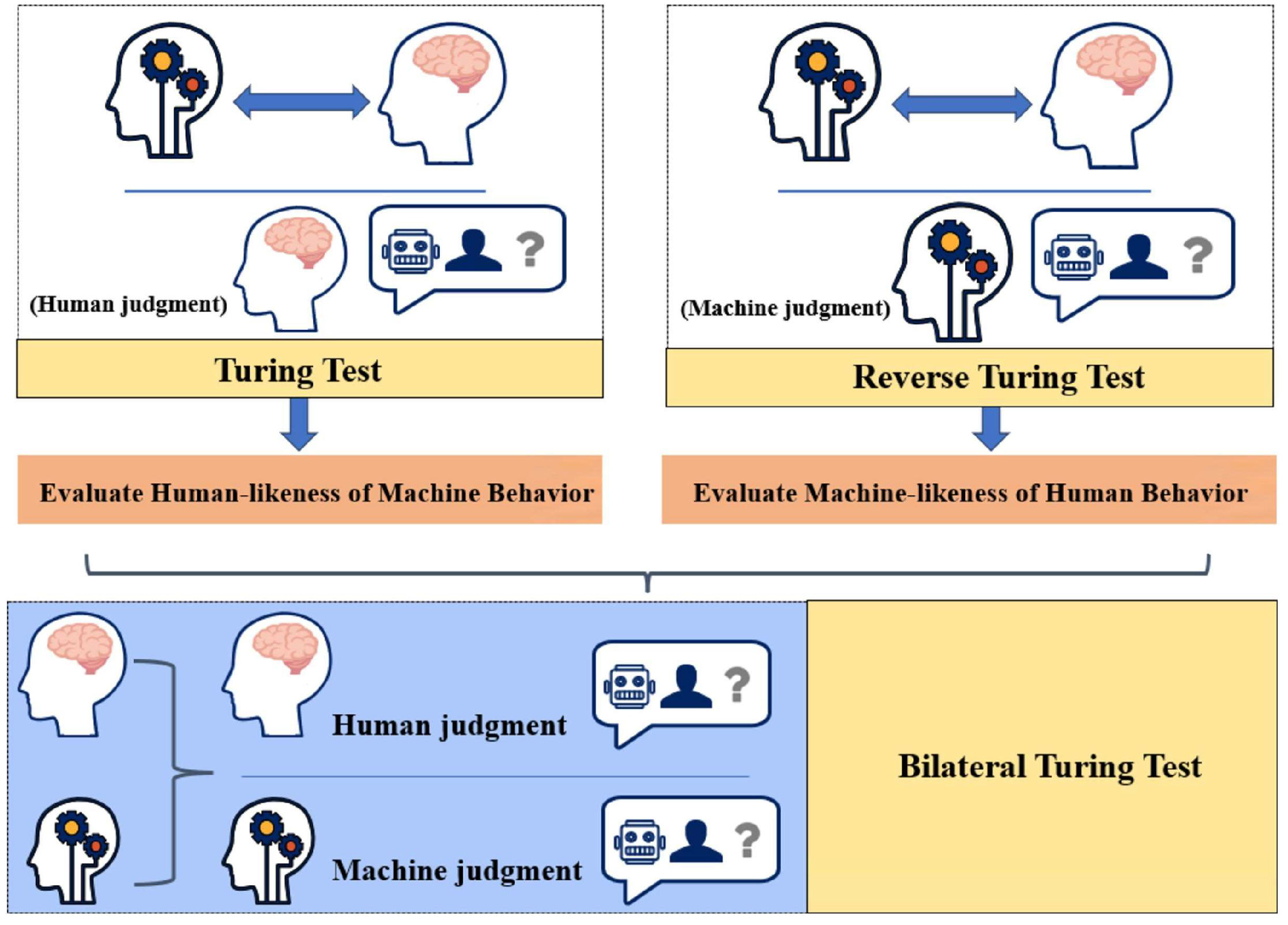
Artificial intelligence (AI) research began in the mid-20th century with foundational theoretical work by pioneers like Alan Turing in 1950, who proposed the idea of machines that could think and introduced the famous Turing Test [14]. The Turing Test, proposed by Alan Turing in 1950, is a method to evaluate a machine’s ability to exhibit intelligent behavior indistinguishable from a human, where a human judge interacts with a machine and a human via text and attempts to identify which is which. If the machine cannot be distinguished, it passes the test. The Bilateral Turing Test, as shown in Figure 4, was then introduced in the 2024 study by Wang et al. [15] and extends this concept to assess machine consciousness simulations by involving both humans and machines as judges in a mutual evaluation process, comparing their ability to recognize consciousness-related behaviors in each other, using the T-index to quantify how closely machine-simulated behaviors align with human consciousness, focusing on external behavior rather than internal mechanisms.
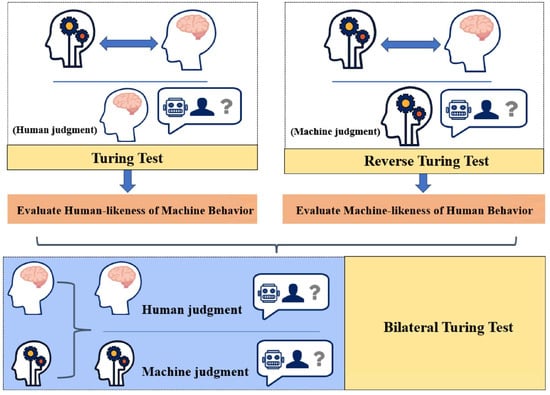
Figure 4.
Derivation of Bilateral Turing Test from Turing Test [15].
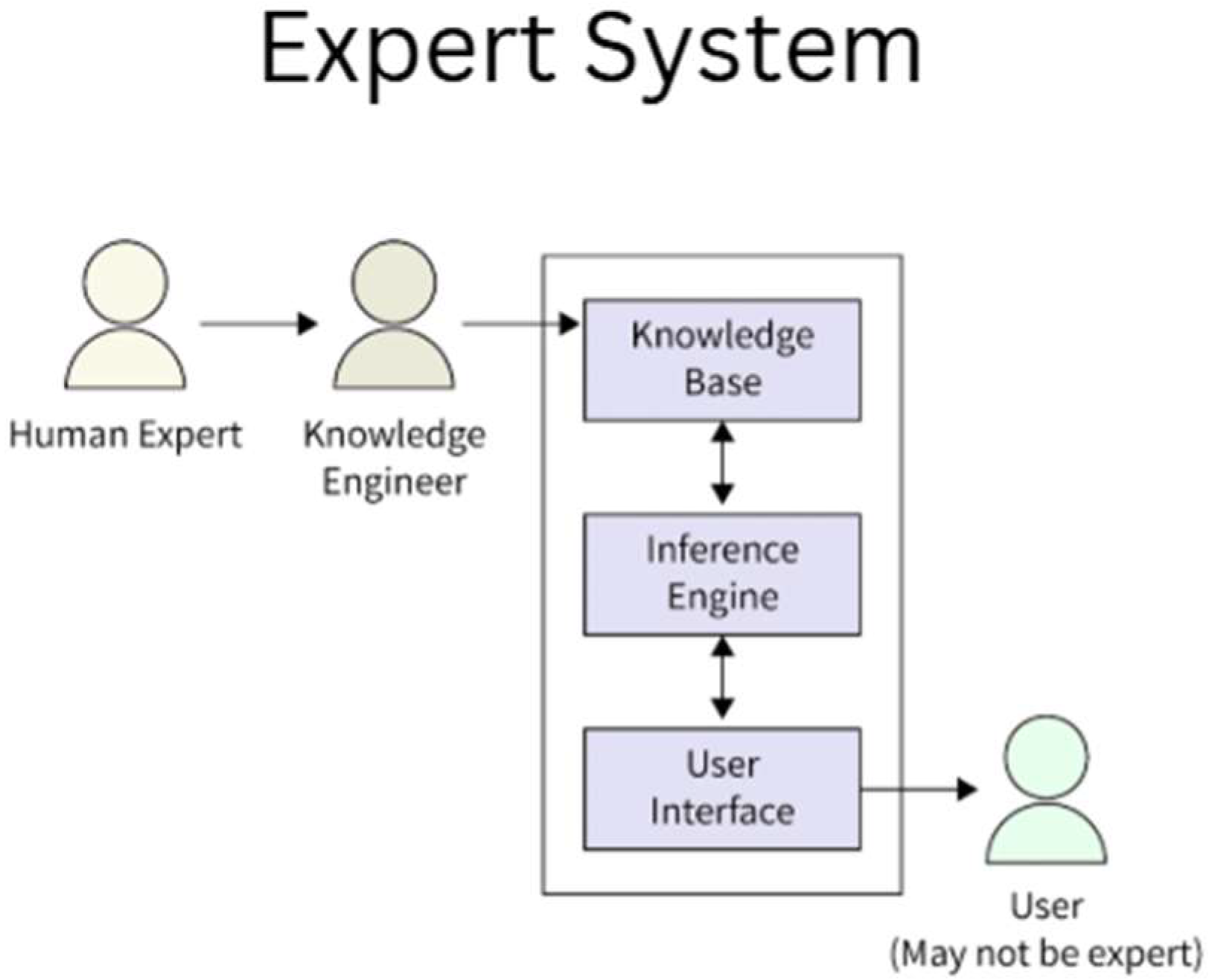
Early AI applications in the 1960s and 1970s were limited in scope and rarely targeted engineering problems, focusing instead on general problem-solving and knowledge representation. Notably, Newell and Simon’s development of the Logic Theorist and General Problem Solver in the 1950s demonstrated that computers could mimic some reasoning processes [16]. During this era, fields like engineering saw little direct AI application, aside from a few isolated efforts. Instead, the groundwork was laid by AI programs in other domains. Examples include MYCIN in medicine and PROSPECTOR in geology in the mid-1970s, which showed the power of rule-based expert systems for specialized problem-solving. These successes attracted interest in applying AI techniques to engineering tasks by the early 1980s [17]. By the 1980s, knowledge-based systems and expert systems (Figure 5) emerged as the dominant AI paradigm in engineering. Researchers began to encode expert knowledge in rule-based programs to assist in complex engineering decision-making. For instance, in chemical engineering, expert system prototypes were developed for process troubleshooting and design [18]. The first AIChE meeting on AI in process engineering was held in 1987, reflecting the growing activity in the field. Venkatasubramanian [19] notes that AI “started off with great promise in the early 1980s” in chemical engineering due to the expert system paradigm, leading to a new emergence of research activities in that decade. Similar enthusiasm was seen in other engineering disciplines: knowledge-based CAD systems for design and diagnostic systems for manufacturing and aerospace engineering were actively explored [20].
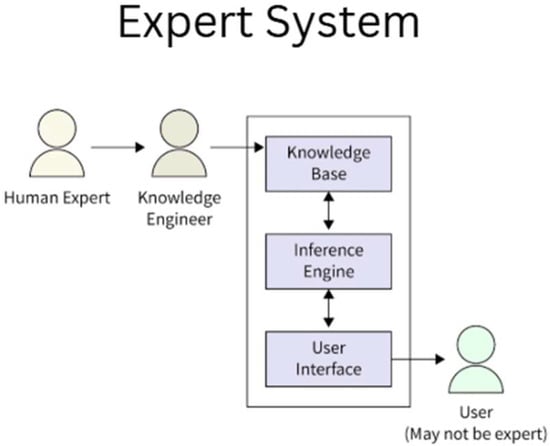
Figure 5.
Demonstration of the early expert system.
Academic groups at institutions like Carnegie Mellon (CMU), MIT, and Stanford spearheaded many such projects. A dedicated journal, AI in Engineering, was launched in 1986, and conferences on AI in Engineering proliferated. These systems were largely symbolic AI, manually encoding if–then rules and heuristics from human experts. They showed some success, for example, XCON, an expert system for configuring computer systems in DEC, and early chemical process advisors saved companies time and money by automating routine design decisions [21]. However, these expert systems were often brittle. They lacked the ability to learn or adapt beyond their fixed knowledge base. By the late 1980s, while a plethora of AI tools and shells (e.g., CLIPS, OPS5) became available to build expert systems, many engineering expert systems struggled to generalize or handle the full complexity of real-world engineering problems. This led to tempered expectations. Indeed, despite initial successes, AI did not fully live up to its promise in engineering through the 1990s, leading to what some termed the “AI winter” in expert systems [19].
Meanwhile, the field of natural language processing (NLP) had its own early milestones. In 1966, MIT’s ELIZA program demonstrated a simple conversational agent, though it was not specialized for engineering [22]. Through the 1970s and 1980s, NLP progressed via rule-based parsing and semantic networks, but engineering applications of NLP (such as understanding technical documents or patents) were very limited by the technology of that time. Some early attempts at knowledge-based engineering did incorporate some NLP interfaces, for example, allowing engineers to query databases in natural language, but these were constrained by the language understanding available. It was not until much later, with more robust NLP that language-based interfaces for engineering knowledge bases became practical. In summary, the early development of AI in engineering was characterized by the emergence of expert systems and rule-based approaches that captured human expertise in narrow inputs. This established a foundation and optimism that would influence later developments, even though true learning systems have not yet emerged in engineering practice.
2.2. Rise of Neural Networks and the Transformer Breakthrough
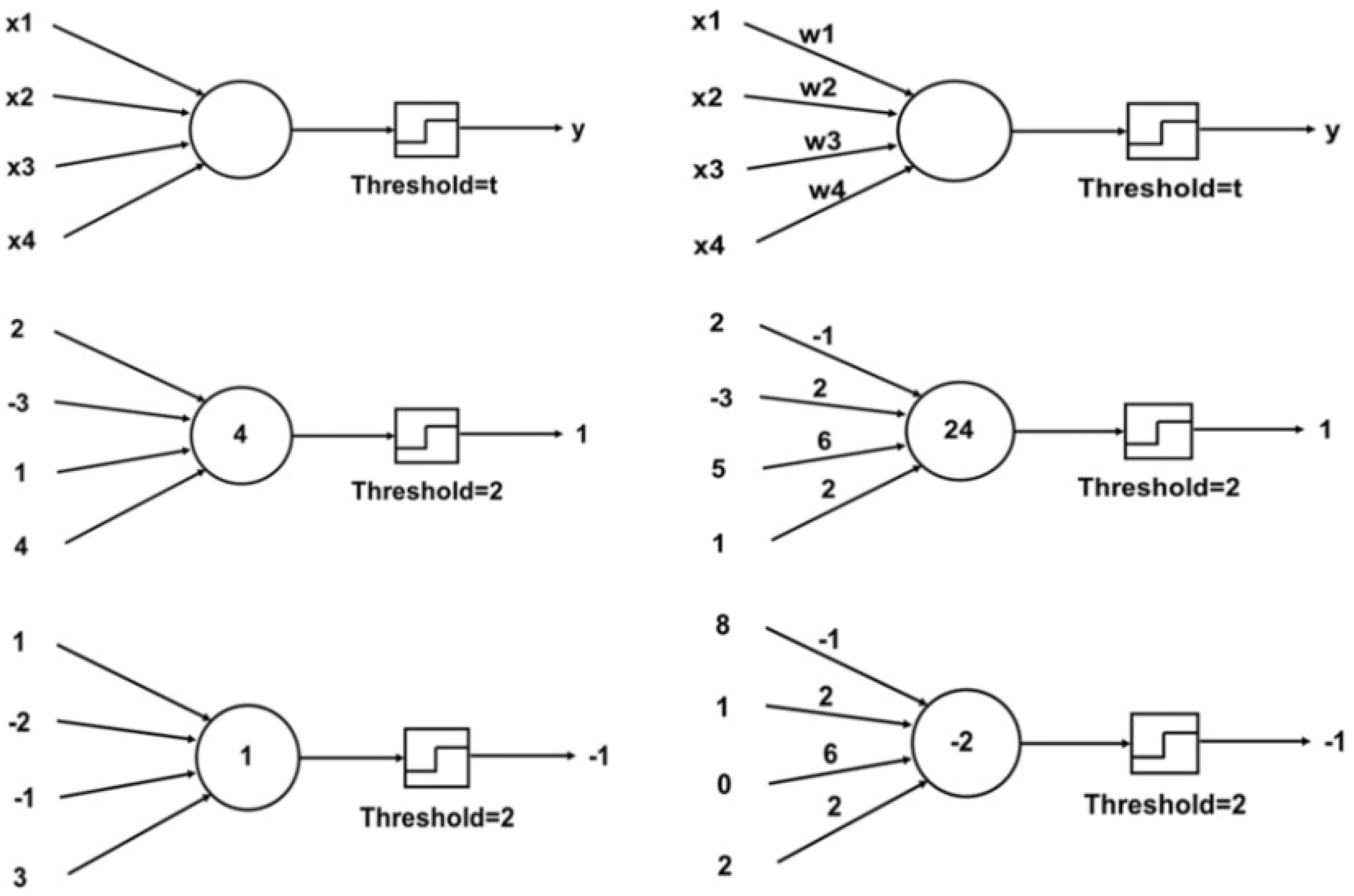
The limitations of purely rule-based AI led researchers to explore machine learning (ML) approaches in the 1990s and 2000s. Neural networks experienced a resurgence. The concept of artificial neural networks dates back to the 1940s and 1950s (e.g., McCulloch–Pitts’ neurons and Rosenblatt’s Perceptron in 1957), which can be seen in Figure 6. However, early networks could not solve complex engineering problems due to the limited computing power and the absence of effective training algorithms. In 1986, the re-discovery of the backpropagation algorithm by Rumelhart and colleagues enabled multi-layer neural networks to learn internal representations, rekindling interest in neural nets [23]. Through the 1990s, neural networks began to appear in the engineering literature, for instance, using feed-forward networks for process control modelling or using simple recurrent networks for system identification. However, these networks were relatively small (a few layers) and often treated as mathematical function approximators rather than general AI. They had some successes (such as in chemical engineering for nonlinear process modelling and fault detection) but also significant limitations in handling sequence data or complex combinatorial problems [24].
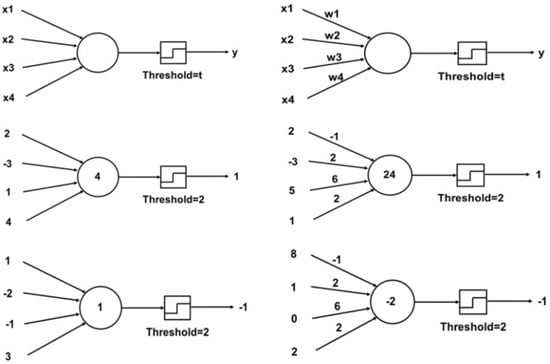
Figure 6.
Graphical representation of the McCulloch–Pitts neurons (left column) and Rosenblatt’s Perceptron (right column) (open access) [24].
A major shift came in the 2000s and early 2010s with the emergence of deep learning (DL). Breakthroughs outside the engineering field, such as the deep belief networks by Hinton [25], and the success of deep convolutional neural networks in image recognition demonstrated that much larger and deeper neural networks could be trained given enough data and computation [26]. Engineering domains then started to adopt these techniques for tasks like image-based inspection, predictive maintenance, and more sophisticated control strategies.
A key development in the field of natural language processing (NLP) was the invention of the transformer architecture. Proposed in the paper “Attention is All You Need” by Vaswani et al. [6], the transformer model revolutionized NLP. It introduced an architecture built exclusively on self-attention mechanisms and feed-forward layers, replacing the recurrent structures that had long dominated sequence learning. This innovative design allowed for much greater parallelization during training and enabled models to capture long-range dependencies in text more effectively than recurrent neural networks (RNNs). The transformer quickly outperformed older models on tasks like machine translation and became the foundational technology for a new generation of language models.
The growing use of neural networks in NLP and their application in engineering contexts are part of a broader trend away from symbolic AI and towards connectionist AI. With the transformer’s introduction, it became possible to scale-up NLP models significantly, using more data and building larger models. The architecture employs a technique called multi-head self-attention, which allows the model to weigh the relevance of different words in a sequence to each other. This was a crucial improvement in how machines process the context of language [4].
Large-scale models based on the transformer architecture began to appear almost immediately after 2017. A landmark model was BERT (Bidirectional Encoder Representations from Transformers), which was introduced by Devlin et al. [7] in 2018. BERT demonstrated how transformers could create deep, bi-directional representations of language, which dramatically improved performance on NLP tasks such as question answering and text classification. The success of BERT validated the power of pre-trained transformer models and paved the way for applying similar concepts in technical domains, such as the later development of SciBERT for scientific text.
At the same time, OpenAI’s Generative Pre-Trained Transformer (GPT) models showcased the effectiveness of transformer decoders for text generation. When GPT-2 was released in 2019 with 1.5 billion parameters, it stunned observers with its fluent and coherent text, leading to an initially limited release due to concerns about potential misuse [8]. This sequence of advances, from deep neural networks to attention mechanisms and transformer models, marked the shift to modern AI in engineering. Engineers now had models at their disposal that could learn from data and manage language and knowledge in ways that were not possible with the expert systems of the 1980s.
Crucially, the impact of these developments on engineering was not immediate but grew over time. Early adopters in engineering research started experimenting with DL for things like materials discovery (e.g., using neural nets to predict material properties) and with sequence models for analyzing sensor data or maintenance records [27]. The transformer breakthrough accelerated this by enabling the creation of large language models that could understand and generate technical text and code and even assist with the design rationale. By the late 2010s, there were trends of increasing computational power, large datasets, and advanced architectures. The stage was set for the emergence of true LLMs that would directly influence engineering practice.
It is also instructive to note how neural-network-based AI began to address long-standing challenges in engineering by building on earlier knowledge. Instead of relying on humans to encode every rule, the new method trained models on vast data to implicitly learn patterns. This data-driven approach started to yield superhuman performance in certain tasks. However, it also introduced new issues, such as the need for large training datasets and concerns about interpretability. Engineering, being a field that values safety, reliability, and clear reasoning, still struggled with these trade-offs. Neural networks offered powerful prediction and pattern-recognition capabilities, but their “black box” nature meant engineers had to be cautious in trust and validation [28]. Nonetheless, the success of neural networks and then general AI research paved the way for their adoption in engineering applications, effectively bridging a decades-long gap between what AI could achieve and what engineers needed.
2.3. Emergence of LLMs and Domain-Specific Adaptation
The period from 2018 onwards has seen the emergence of LLMs that utilize the transformer architecture to achieve huge performance in language understanding and generation. These models are characterized by their massive scale, billions of parameters, and their training on very large text data. A clear inflection point was OpenAI’s GPT-3, introduced in 2020 with 175 billion parameters, which demonstrated outstanding capabilities in generating human-like text and carrying out tasks with minimal task-specific training [9]. GPT-3 showcased the concept of “few-shot learning,” where an LLM can perform a new task given only a few examples in the prompt, thanks to the extensive knowledge it acquired during the pre-training. This represented a massive shift by showing that, rather than training separate models for each task, a single foundation model could be adapted to many tasks. The launch of GPT-3, and later refined models like GPT-3.5 and GPT-4, catalyzed widespread awareness of LLMs, including in engineering communities [29]. These models extended beyond natural-language conversation to generating programming code, reasoning through problems step by step, and summarizing or explaining complex documents—all highly valuable functions for engineering work. Different prompting strategies such as zero-shot, few-shot, chain-of-thought, and tree-of-thought learning methods illustrate how these models can be guided to improve reasoning and task performance [30].
A key development accompanying LLMs has been domain-specific adaptation. While GPT-3 and its ilk are trained on diverse internet text and thus possess broad knowledge, engineering disciplines often require deep domain knowledge and use specialized terminology (e.g., mechanical part specifications, chemical names, circuit nomenclature). Researchers recognized that fine-tuning or customizing these large models to specific domains could markedly improve their utility and accuracy in those areas. Early examples came from biomedicine and science; models like BioBERT and SciBERT took the BERT architecture and further trained it on the biomedical and scientific literature, respectively, yielding better performance on domain-specific NLP tasks than a general model. In the context of engineering and chemistry, analogous efforts have produced models such as ChemBERTa (a BERT model tuned on the chemical literature) and MatSciBERT (trained on materials science papers) [31,32]. These adaptations imply LLMs with vocabulary and knowledge unique to the domain, for instance, understanding that “PPM” likely means parts-per-million in a chemical engineering context or that “Young’s modulus” is a material property. Domain-specific LLMs significantly improve the relevance of outputs for engineers and reduce errors that a general model might make when encountering technical content.
Beyond fine-tuning, techniques like prompt engineering and in-context learning allow general LLMs to be guided for specialized tasks without modifying their weights. For example, prompting an LLM with a few examples of engineering unit conversions or failure analysis explanations can teach it to follow suit. Another approach is retrieval augmentation, where an LLM is connected to a database or knowledge graph of engineering data; the model first retrieves relevant facts (like a material property from a library) and then uses them to formulate its answer. This hybrid approach addresses one of the biggest issues with raw LLMs: the tendency to hallucinate incorrect facts by grounding them with verified data [33]. Researchers Pan et al. [34] discuss unifying LLMs with knowledge graphs, noting that LLMs alone often “fall short of capturing and accessing factual knowledge,” whereas knowledge graphs explicitly store vetted information; combining the two yields more reliable and interpretable systems. This kind of domain adaptation is crucial in engineering, where accuracy and factual correctness are paramount.
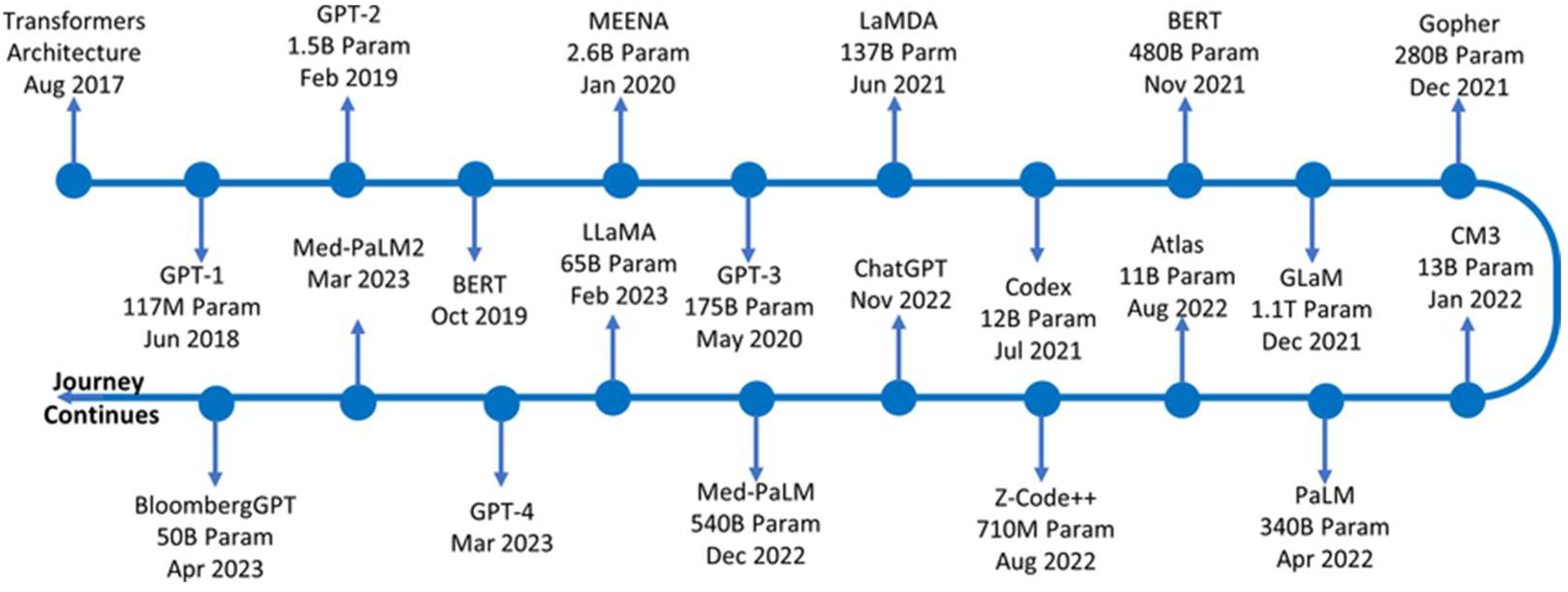
By the early 2020s, the emergence of foundation models, a term popularized by Bommasani et al. [35] to describe large models like LLMs that can be adapted to various downstream tasks, has influenced engineering software and research tools. Large tech companies and research institutions have released their own LLMs (e.g., Google’s PaLM, Meta’s LLaMA, the open-source BLOOM model), and some are trained in technical content. Notably, BloombergGPT was released in 2023 as a finance-domain LLM trained on financial data [36], an example that could be parallel in engineering with models trained on years of CAD drawings and simulation reports. While a dedicated public LLM for “engineering” at large does not yet exist, some preliminary steps have already been implemented. For instance, GPT-4 has been evaluated on engineering knowledge problems and even exam questions [11], and custom models are being built behind corporate firewalls using engineering data. Figure 7 shows the timeline of significant LLMs released after the transformer architecture was published.
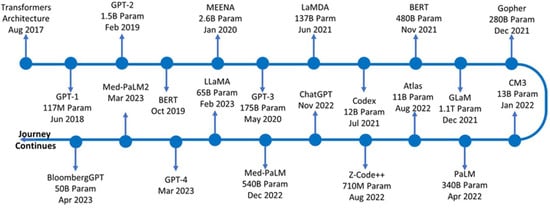
Figure 7.
Release of LLMs based on timeline (open access) [37].
It is important to emphasize how domain-specific LLM adaptation can address knowledge gaps that general models have. Engineering often involves constrained problems (adhering to physical laws or standards) and data that may be lacking in the general web text. By training or fine-tuning on technical papers, standards, textbooks, and legacy data, an LLM can learn [38], for example, the typical steps to size a distillation column or the safety regulations for a pressure vessel. This not only improves performance but also helps build trust among engineers who might be skeptical of a generic AI that was not designed with their domain in mind. Indeed, early experiments have shown that a model like SciBERT can outperform generic BERT on scientific information extraction, and similarly, one can expect a properly tuned engineering LLM to outperform a generic model on engineering Q&A tasks [32].
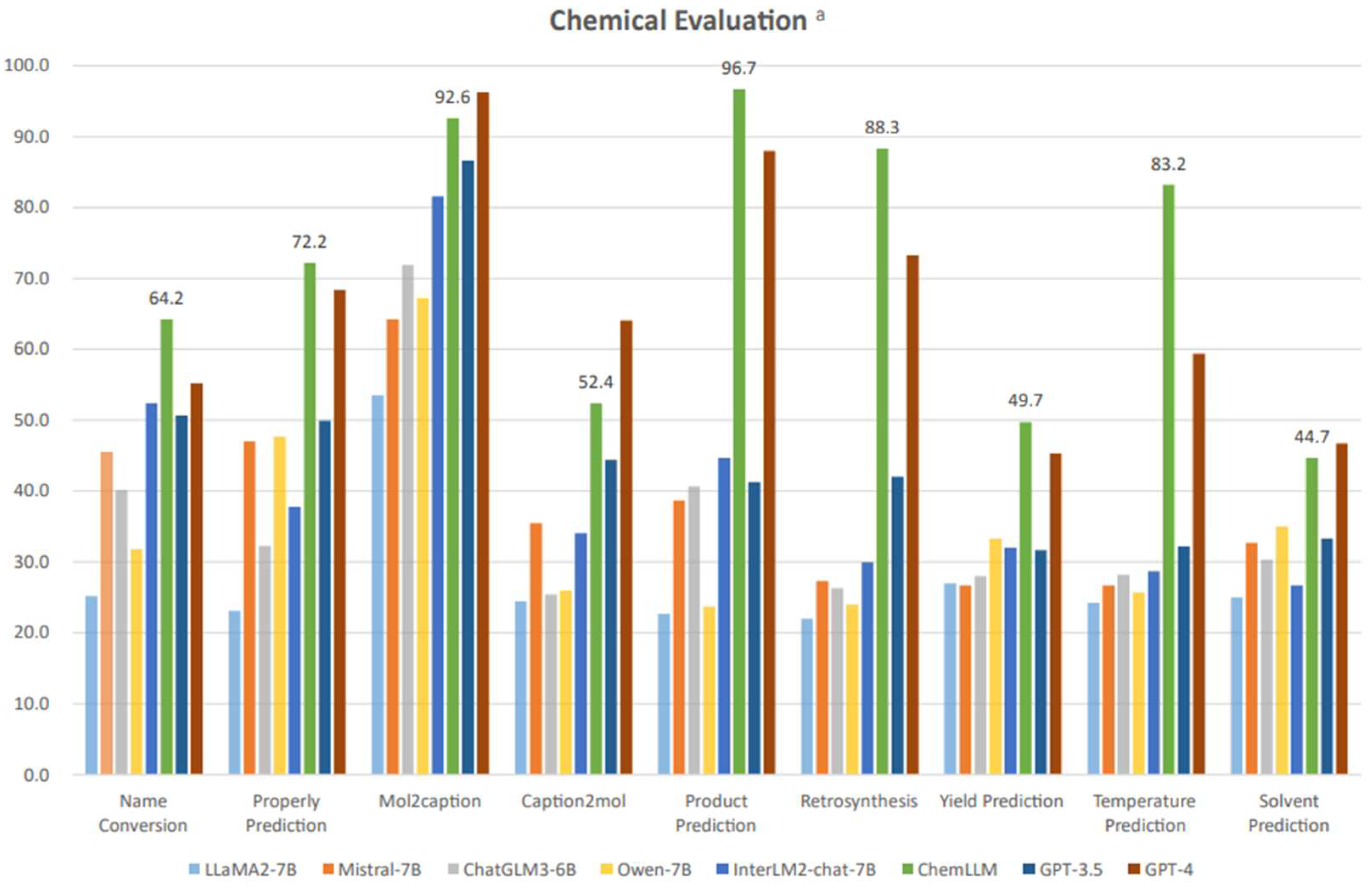
Recent benchmark results by Zhang et al. [13], illustrated in Figure 8, compare multiple large language models, including GPT-3.5, GPT-4, and the domain specific LLM ChemLLM across nine chemical engineering-related tasks: name conversion, property prediction, Mol2Caption, Caption2Mol, product prediction, retrosynthesis, yield prediction, temperature prediction, and solvent prediction. The quantitative results show clear task-dependent performance differences. For example, ChemLLM achieves 88.3% accuracy in retrosynthesis prediction, outperforming GPT-4 by approximately 15 percentage points. In temperature prediction, ChemLLM records 83.2%, exceeding GPT-4’s score by over 20 percentage points. ChemLLM also leads in property prediction (72.2% vs. ~66.0%) and yield prediction (49.7% vs. ~45.0%). By contrast, GPT-4 outperforms ChemLLM in Mol2Caption (~96.7% vs. 92.6%) and Caption2Mol, where its broader training appears advantageous.
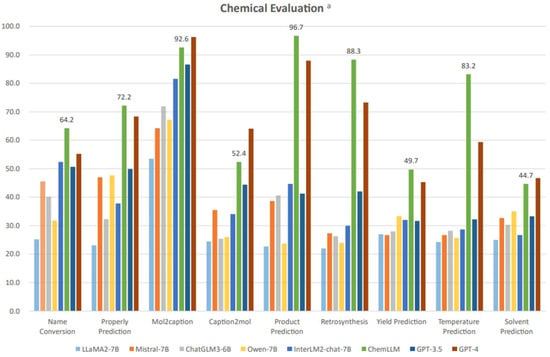
Figure 8.
Comparative accuracy of multiple large language models, including ChemLLM and GPT-4, across nine chemical engineering-related tasks (open access) [13]. The superscript “a” indicates that the results are evaluated in a 5-shot manner.
These results indicate that model choice should be guided by the nature of the task. For domain-specific chemical informatics, particularly retrosynthesis, temperature prediction, and property prediction, ChemLLM could offer higher accuracy and may reduce computational overhead compared to GPT-4. Conversely, for generative or multimodal tasks, GPT-4’s broader knowledge base enables superior performance. In engineering practice, especially for safety-critical workflows, a hybrid approach could be optimal, such as deploying ChemLLM for specialized, high-accuracy predictions and GPT-4 for integrative reasoning or cross-disciplinary problem-solving.
In summary, the historical development of AI and NLP in engineering has progressed from early symbolic systems to the powerful data-driven LLMs of today. Over roughly four decades, AI moved from manually encoding a few hundred rules in an expert system to training models with billions of connections that implicitly encode knowledge drawn from millions of documents. The transformer breakthrough enabled this scaling, and the current wave of LLMs offers new opportunities to integrate AI in engineering practice. Equally, it raises new challenges: engineers now must consider how to adapt and govern these models, fine-tuning them to domain needs, ensuring they remain accurate and ethical, and combining them with traditional engineering software. The next chapters will explore how these LLMs are being applied across engineering domains and specifically in chemical engineering, including the benefits realized and the open issues that remain.
Table 1 below summarizes the important milestones of LLMs development into one comprehensive table.

Table 1.
Important milestones in LLM development.
3. Applications of AI and LLMs
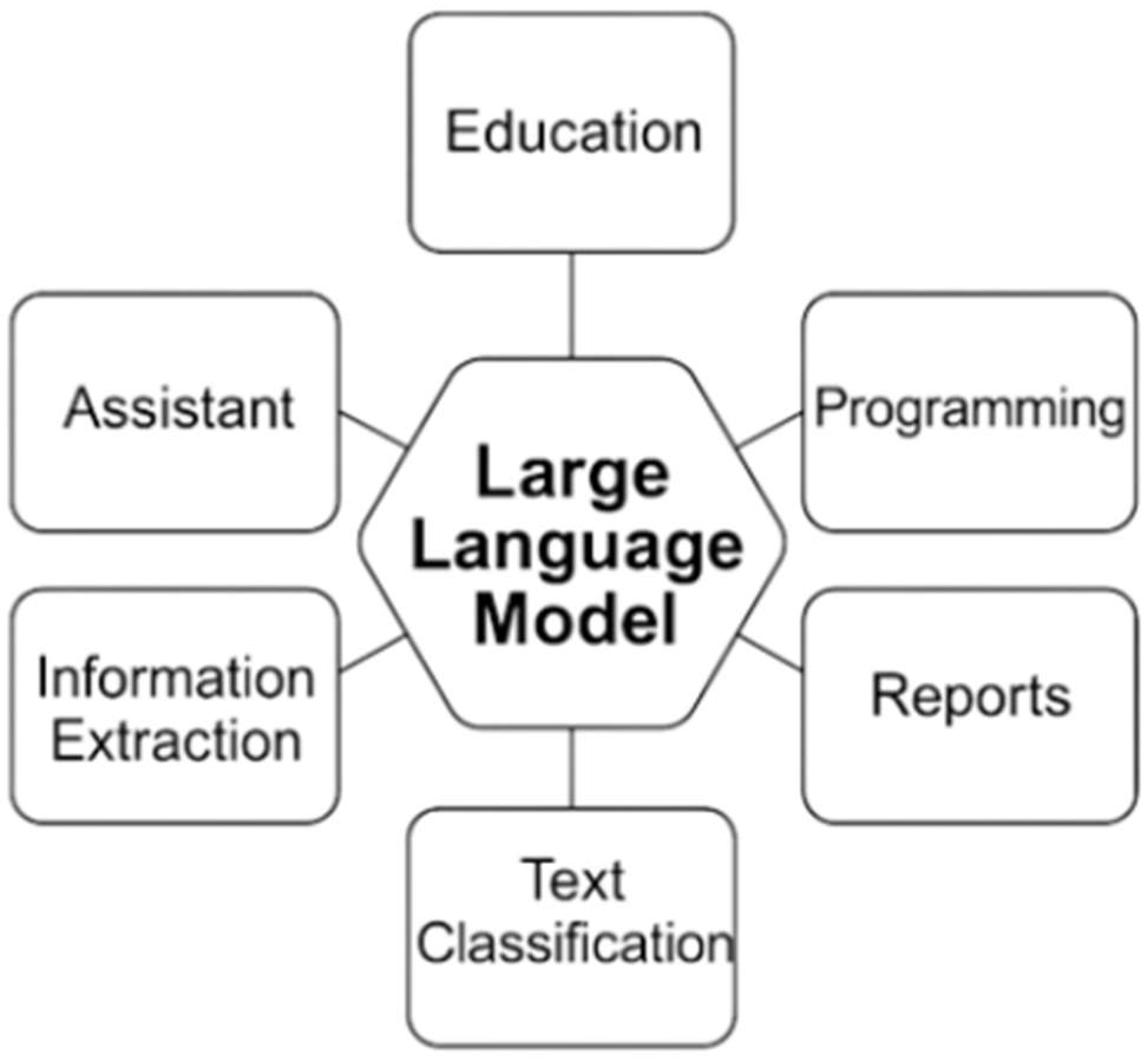
Large language models (LLMs) have emerged as transformative tools in various engineering disciplines, showcasing their versatility in applications such as education, programming, and information extraction, as depicted in Figure 9, which outlines key LLM applications, including education, programming, information extraction, text classification, reports, and assistant roles. In pathology, a subfield of bioengineering, LLMs like ChatGPT-4 and BERT (Sentence–BERT) are utilized to enhance educational experiences by generating curricula, case scenarios, and interactive learning materials tailored to individual needs, such as creating multiple-choice questions or summarizing complex topics like hyperlipidemia management [2]. However, their educational applications are not without flaws, as studies reveal inconsistent performance; for instance, ChatGPT-4 scored only 56.98% on the 2022 American Society for Clinical Pathology resident question bank, highlighting the need for validation against reputable sources due to potential inaccuracies [40].
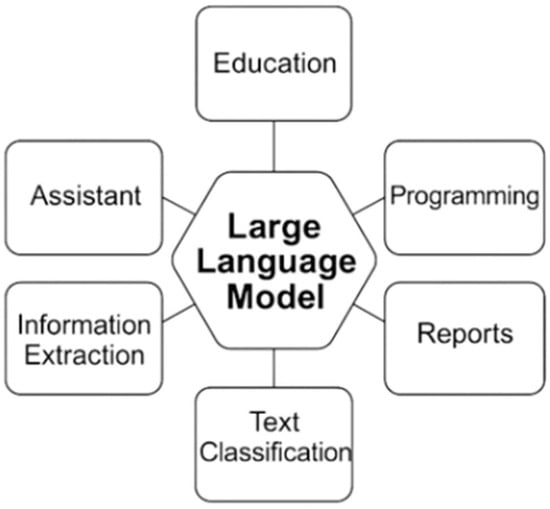
Figure 9.
Application of AI in general engineering.
Beyond education, LLMs significantly contribute to programming and software development within engineering contexts, particularly in pathology informatics, where they enable pathologists with minimal coding experience to develop software for tasks like tiling whole-slide images into smaller segments [2]. This capability, also illustrated in Figure 9 under the “Programming” segment, underscores LLMs’ role in increasing productivity, automating tasks, and reducing errors in coding, with applications extending to data visualization and AI software development using languages like Python 3.13. However, human validation remains essential, as LLM-generated code can contain errors, and studies emphasize the importance of oversight to ensure functionality, especially when translating legacy code or adapting deep learning frameworks [41].
In terms of information extraction, LLMs offer substantial benefits in bioengineering, particularly in pathology, by automating the extraction of structured data from unstructured pathology reports, as highlighted in Figure 9. For example, research demonstrates that LLMs like GPT-3.5 can extract clinical information such as tumor location and histologic grade from pathology reports with an accuracy of 87.7%, significantly reducing time and cost compared to manual methods, though manual supervision is still required due to potential errors [42]. Moreover, fine-tuned BERT models have achieved high precision (0.927) and recall (0.939) in extracting concepts from breast cancer reports, showcasing LLMs’ ability to handle complex unstructured data and improve efficiency in cancer registries and research studies [43].
3.1. LLMs for Complex Problem Solving and Ideation
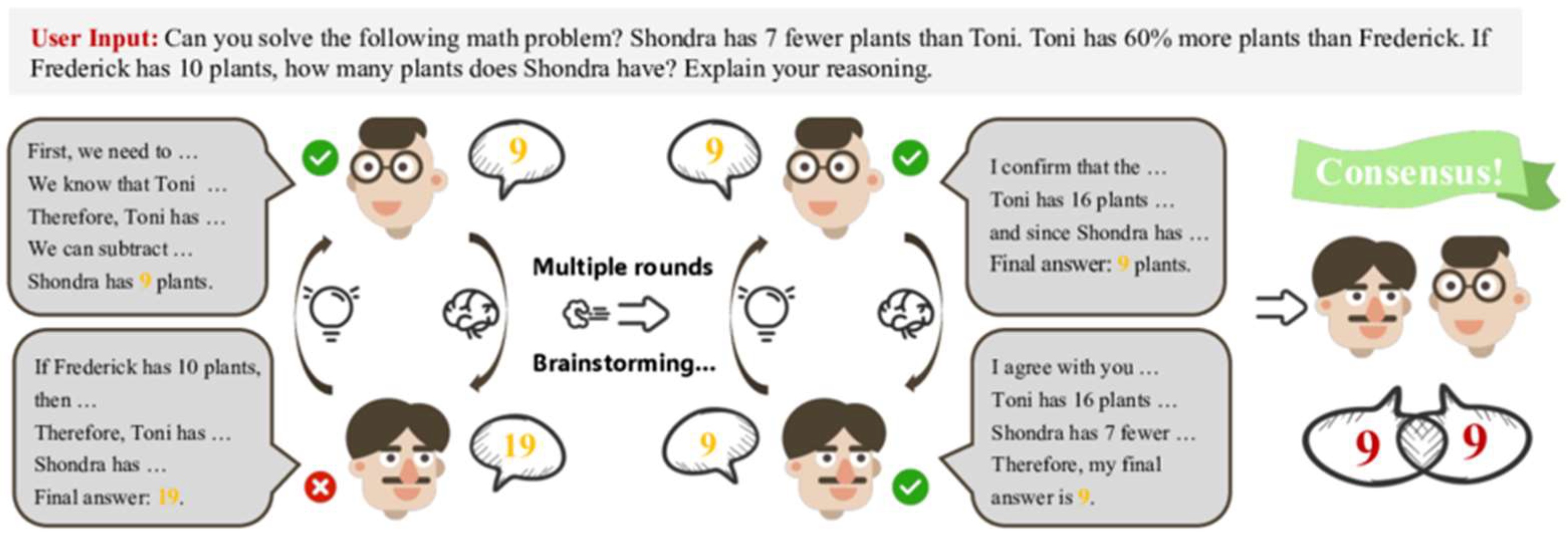
One of the most immediate ways LLMs have been adopted in engineering is as intelligent assistants for problem solving and design ideation. Engineering problems often require creative thinking, synthesis of knowledge, and consideration of multiple solution options. LLMs like ChatGPT (based on GPT-3.5/-4) have demonstrated an ability to generate ideas and approaches, which engineers can use as a form of brainstorming partner [44]. A simple illustration of this idea is shown in Figure 10.
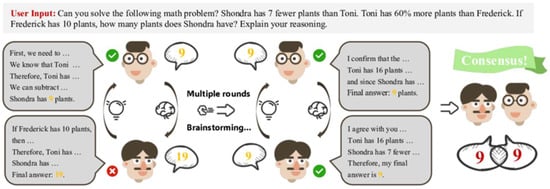
Figure 10.
An illustration of LLMs as a brainstorming partner (open access) [44].
This kind of idea generation is valuable in the conceptual phase of projects. It expands the engineer’s view by bringing in ideas that the engineer may not immediately think of, including some cross-domain solutions. As an illustrative case, students using ChatGPT (GPT-3.5/-4) for a design brainstorming exercise (designing a semi-autonomous robot) found that the AI could indeed contribute novel suggestions. In a study by Shah et al. [45], first-year engineering students engaged ChatGPT (GPT-3.5/-4) during brainstorming and it provided numerous solution concepts; however, the students often treated it as a search engine, sometimes asking for “the best solution” outright. This indicates that while LLMs can generate diverse ideas, users must employ them effectively to explore the design space.
Experienced engineers have also reported success in using LLMs to troubleshoot problems or perform rapid calculations in the early stages of problem solving. For instance, if an engineer is evaluating different algorithms or formulas to apply, they might query the LLM for comparisons. An LLM can outline the pros and cons of using a PID controller versus a state-space controller for a given scenario or compare two design standards, helping the engineer quickly gather insights. ChatGPT-4 can provide “quick responses to complex technical problems,” essentially serving as a knowledgeable colleague who is always available. Of course, the accuracy is not guaranteed, so these responses serve as guidance or brainstorming rather than final authority. Even so, this use of LLMs accelerates the problem-solving cycle by providing immediate informative suggestions. Qin et al. [44] observes that engineers who know how to use AI as a tool will have an edge over those who do not, as they can offload some cognitive load to the AI and focus on higher-level evaluation.
It is important to note that the value of LLMs in ideation is not in providing final answers but in expanding the set of possibilities. Engineers must then apply critical thinking to evaluate which ideas are viable. In many cases, the LLM’s output may need refinement or further inquiry [33]. The iterative dialogue capabilities of LLMs support this; an engineer can ask follow-up questions, request clarifications, or detail specific constraints, and the LLM will adjust its suggestions accordingly. This iterative Q&A can resemble the Socratic method, helping engineers to refine their problem understanding. For instance, one might start with a broad prompt and then narrow down, using the LLM’s outputs to identify missing information or new angles to examine [38].
A practical example reported by NASA researchers Pierson and Ha [46] involves using ChatGPT-4 to develop an engineering tool: they prompted ChatGPT-4 to generate a Python script for visualizing fluid flow data (boundary layer profiles). ChatGPT-4 provided a working starting point for the code, effectively solving a sub-problem (creating an interactive plot) that saved the engineers’ time. This demonstrates problem-solving at a micro level, using LLMs to handle well-defined tasks like coding or data parsing as part of the larger engineering problem [46]. On a macro level, LLMs have been used to suggest overall approaches to engineering challenges. For a given problem description, ChatGPT-4 can outline steps an engineer might take (e.g., “1. Gather requirements, 2. Apply formula X, 3. Simulate using tool Y, 4. Evaluate against criterion Z”), functioning almost like a tutor or advisor that structures the problem-solving process. Such outlines can help ensure no key step is overlooked in the early planning phase.
In terms of productivity and efficiency, utilizing LLMs for ideation can significantly reduce the time spent on literature searches or recalling offhand knowledge (Figure 11 shows graphical demonstration steps). Instead of flipping through textbooks or manuals for brainstorming, an engineer can obtain a synthesized answer in seconds. One reported benefit is time saved on unskilled tasks, allowing engineers to focus on critical analysis. For example, generating a first draft of a design rationale document or a list of potential failure modes via an LLM frees the engineer to concentrate on evaluating those failure modes or refining the design rationale [47].
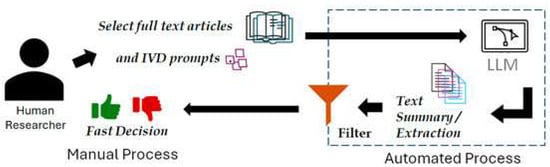
Figure 11.
LLM-assisted application of literature review overview (open access) [47].
Of course, there are challenges and best practices emerging alongside these applications. Engineers have learned that the quality of prompts greatly influences the usefulness of LLM outputs. A well-crafted prompt that clearly specifies the problem and requests multiple ideas or a rationale will yield more relevant and diverse solutions. An overly vague prompt might result in generic answers, while an extremely detailed prompt might unnecessarily constrain the AI’s creativity. The concept of prompt engineering has thus become a skill, i.e., knowing how to ask the AI in a way that draws out helpful responses. As Pierson and Ha [46] note, “if a prompt is well-crafted, the user is much more likely to successfully achieve their objective”, whereas poorly specified requests can lead to less useful outputs. Over time, engineers will likely develop standardized prompt templates for common tasks. In fact, some resources are already sharing these prompt strategies for problem solving.
In conclusion, LLMs are proving to be powerful aids for engineering problem solving and idea creation by providing quick knowledge-based suggestions, creative ideas from cross-input analogies, and even partial solutions like code or calculations. They act as intelligent collaborators, an engineer’s brainstorm partner. The use of LLMs in this capacity is still in its early stages, and best practices for maximizing their utility while minimizing their pitfalls (like the risk of incorrect suggestions) are actively being developed. As engineers become more adept at working with LLMs, we can expect these models to be integrated into standard engineering workflows for brainstorming, much like how calculators and CAD tools are integral today. The key is maintaining a critical eye, treating the LLM as an assistant whose suggestions must be verified and validated through engineering judgment, testing, and analytical proof.
3.2. Educational Applications of Large Language Models
Large language models (LLMs) are changing the landscape of engineering education by acting as powerful tutoring tools that promote personalized learning. Models like ChatGPT-4 can offer explanations of complex topics, such as Bernoulli’s principle in fluid dynamics, that are tailored to an individual student’s needs, using either formal language or simple analogies. Studies have shown that LLMs can function as “personalized tutors” by providing customized feedback and step-by-step guidance on tasks like solving beam bending problems. This approach effectively mimics one-on-one tutoring, a method known to be highly effective for student education [48,49].
Educators are also harnessing LLMs to generate practice problems and solutions, which frees them to concentrate on more complex teaching duties. For example, an instructor can ask an LLM for several variations of a problem along with detailed solutions, thereby expanding the available practice materials. LLMs also benefit students by providing instant answers to their questions outside of class hours, offering help with assignments. This new capability, however, raises concerns about academic integrity, as unsupervised use of LLMs could allow students to bypass the learning process. The paper by Bernabei et al. [50] highlights the “academic hypocrisy” of banning students from using AI while educators use it for their own lecture preparation. As a result, the trend is shifting from outright prohibition to integrating LLMs into the curriculum. This approach involves teaching students how to use AI ethically and designing assessments that either permit AI use with proper citation or focus on higher-order skills like creative design and lab experiments that LLMs cannot easily replicate.
When it comes to programming and simulation, LLMs such as GitHub Copilot are valuable aids for students, offering suggestions for code snippets or help with debugging tasks like MATLAB R2025a scripts for control systems. This support can lower the barrier to learning programming, which helps students who are struggling to keep up while enabling those who are more advanced to tackle complex ideas. A study by Shah et al. [45] notes that students tend to underutilize these tools by asking simple questions, which highlights the need to train them in better prompting strategies and the importance of verifying the LLM’s output. As a result, assignments can be structured to require students to generate solutions with an LLM and then critically improve them, a process that fosters both AI literacy and sound engineering judgment [50].
In summary, LLMs enrich the engineering education experience through personalized tutoring, content generation, and coding assistance. The key challenge is to ensure these tools are integrated ethically in a way that complements, rather than replacing, critical thinking, thereby preparing students to effectively leverage AI as part of their professional skillset.
4. General Engineering Applications for Large Language Models
Large language models (LLMs) like GPT-3, GPT-4, and Claude have revolutionized natural language processing by using massive text databases to comprehend and produce text that reads as if a human wrote it. These models are constructed on transformer architectures and excel at tasks involving language comprehension, reasoning, and generation, which makes them highly versatile tools for many professional fields. Within engineering, LLMs are being used more and more to automate complicated tasks, improve design workflows, and support better decision-making. This part of the literature review synthesizes current research on LLM applications in general engineering areas, including software, mechanical, civil, and electrical engineering. It delves into how they help optimize workflows, the methodologies used, and the challenges that arise with their adoption, offering a thorough overview of their effect on engineering practices.
4.1. LLMs in Software Engineering
In the field of software engineering, LLMs have made a significant impact by automating a variety of development tasks. A systematic literature review conducted by Hou et al. [51] examined 395 research articles from January 2017 to January 2024, classifying the use of LLMs like GPT-3 and CodeBERT in software engineering applications. The review pinpoints several key uses, such as code generation, bug fixing, automated testing, and documentation. Tools like GitHub Copilot, for example, use LLMs to suggest snippets code, thereby shortening development time. To improve the performance of these models, the study highlights the importance of using well-curated datasets and preprocessing techniques like tokenization and prompt engineering. However, human supervision is still necessary to address challenges, such as instances where the models generate code that is syntactically correct but semantically flawed.
4.2. LLMs in Mechanical Engineering
In mechanical engineering, LLMs are applied to solve complex mechanical problems, automate design processes, and enhance educational content. A survey shows emerging applications in mechanics, product design, and manufacturing [52]. Key uses include boosting the intelligence of digital twins, which are virtual replicas of physical systems, and facilitating inverse mechanics, where LLMs infer material properties from observed behaviors. In product design, LLMs work with generative models to support conceptual design, prototyping, and knowledge discovery to foster creativity. In manufacturing, they advance intelligent process planning and maintenance. Another study introduces the MechAgents framework, where GPT-4-powered agents collaborate to solve elasticity problems, employing roles like planner, scientist, and engineer, achieving high accuracy with minimal human intervention [53]. Additionally, LLMs have been used to generate educational modules for mechanical engineering, reducing content creation time from hours to minutes [54].
4.3. LLMs in Civil Engineering
LLMs are transforming civil engineering by addressing data management and designing automation challenges. A book chapter examines LLMs in construction facilities’ lifecycle data management, employing methods like Retrieval-Augmented Generation (RAG) for unstructured data and Knowledge Maps for sensitive data. Testing showed RAG’s effectiveness in retrieving information, reducing errors in project management [55]. Another source discusses practical applications, including understanding contracts, supporting expert witnesses, extracting knowledge from thousands of documents, and automating design workflows [56]. These applications enhance efficiency in handling the fragmented data typical of construction projects. Seminars further educate professionals on integrating LLMs into civil engineering practices, emphasizing their role in processing complex documentation.
4.4. LLMs in Electrical Engineering
In the field of electrical engineering, large language models (LLMs) provide support to power engineers for both operational and safety-related tasks. A study that explored the capabilities of LLMs in the electric energy sector focused on their application in areas like correlation analysis, identifying wildfire risks, detecting equipment damage, recognizing on-site hazards, analyzing documents, and forecasting energy loads and prices [57]. The research found that fine-tuning these LLMs resulted in a significant improvement in forecasting accuracy, demonstrated by a drop in load forecast errors. Furthermore, a proposed method called Meta In-Context Learning (M-ICL) can classify time series electrical data, which reduces the need for large, extensively annotated datasets [58]. These applications showcase the potential for LLMs to improve both the efficiency and safety of critical infrastructure.
The various applications of LLMs across different engineering disciplines are compiled in Table 2, which presents key areas, their descriptions, and the relevant references.

Table 2.
Applications of LLMs in different branches of engineering.
4.5. Integration of LLMs with Simulation and Programming Tools
Beyond simply being used for brainstorming and answering questions, a new frontier for large language models (LLMs) in engineering is their integration with simulation software and programming workflows. Engineering work often relies on specialized software tools to model physical systems, run complex simulations like FEA and CFD, or program custom scripts for analysis. LLMs can act as a natural language interface or even an automation agent for these tools, helping to streamline complex workflows that have traditionally required significant programming knowledge or manual setup.
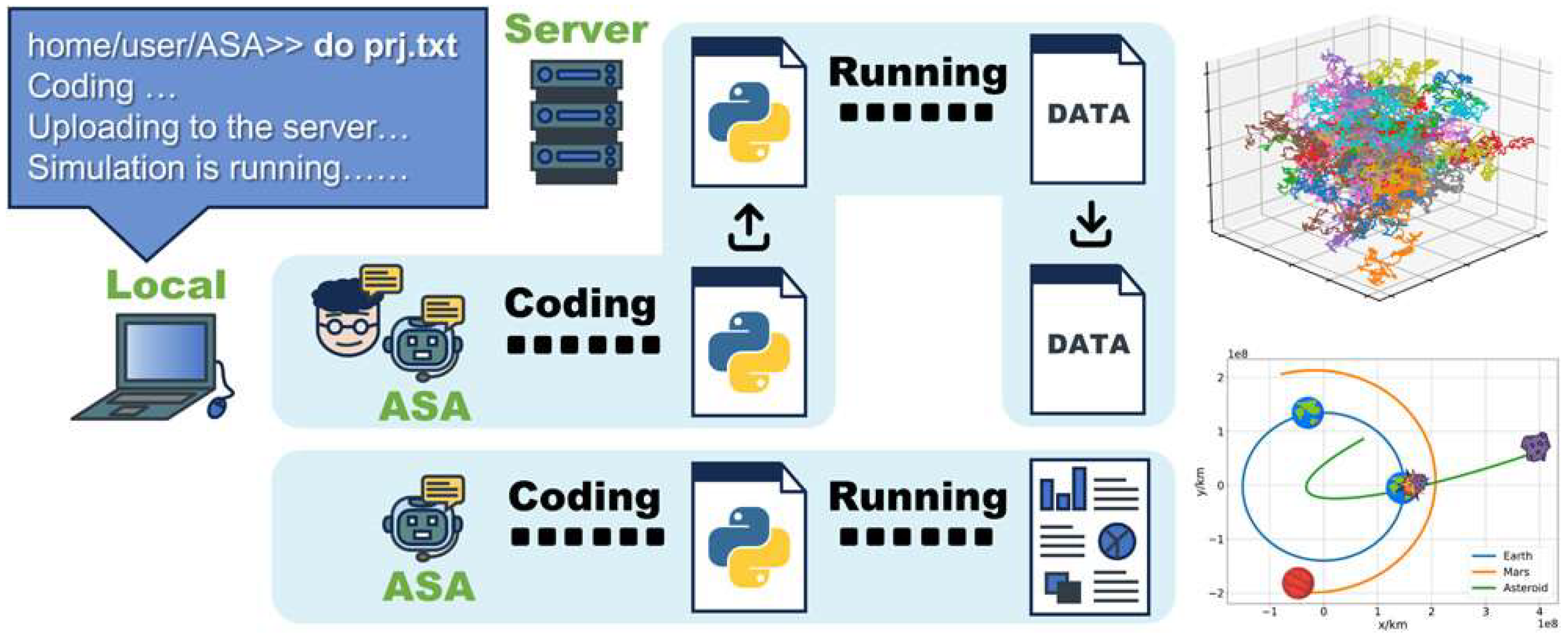
One clear example of using LLMs to automate simulation research is the creation of an Autonomous Simulation Agent (ASA), a concept described by Liu, Chai and Li [59]. Typically, an engineer conducting a finite element analysis (FEA) for a new component has to manually define its geometry, material properties, boundary conditions, and other parameters through a graphical user interface (GUI) or a specific scripting language. With an LLM-powered ASA, however, the engineer could simply describe the simulation requirements in plain language, with a prompt like: “Simulate a cantilever beam of length 2 m, rectangular cross-section 0.1 m by 0.2 m, made of aluminium, fixed at one end, with a 500N downward point load at the free end. Provide the stress distribution and maximum deflection”. The ASA, using prompt engineering and an API automation program, would then interpret this request, generate the required simulation code, configure the model, apply the correct properties and conditions from a library, and run the entire process to analyze the results. The ASA could then compile a comprehensive report summarizing the stress distribution and maximum deflection, all without human intervention, demonstrating the potential to streamline complex simulation workflows. Figure 12 shows the schematic diagram demonstrating how ASAs assist in automated simulation.
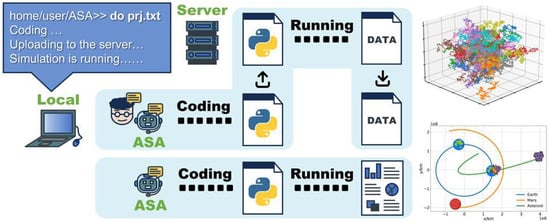
Figure 12.
Schematic diagram of ASA assisting in automated simulation [59].
While this scenario is aspirational, it is seeing steps toward it. The NASA study by Pierson and Ha [46] demonstrated ChatGPT-4’s capability in interacting with an engineering tool; they attempted to have ChatGPT-4 write a script to automate a process in Ansys Workbench (https://www.ansys.com/products/fluids/ansys-fluent, accessed on 3 July 2025). The attempt revealed both potential and pitfalls. ChatGPT-4 could generate the script and explain its logic, but due to the complexity and specific context needed, the automation did not fully succeed without further human refinement.
Another rapidly developing integration is with programming tools and computational notebooks used by engineers (like MATLAB R2025a, Python notebooks, or domain specific languages). LLM-powered code assistants (e.g., CoPilot, ChatGPT-4’s code interpreter mode) can generate boilerplate code for calculations, help debug errors, or translate a massive of code from one language to another. Engineers spend a lot of time programming tasks such as data processing, running custom algorithms, or connecting different software via scripts. LLMs can interpret a natural-language goal and produce working code to achieve it. Pierson and Ha [46] used ChatGPT-4 to write Python code for design optimization and data sampling, integrating with tools like scikit-learn for surrogate modelling. The result was an optimization workflow for a turbine blade where ChatGPT-4’s contributions helped link together geometry generation, meshing, and a neural network surrogate model.
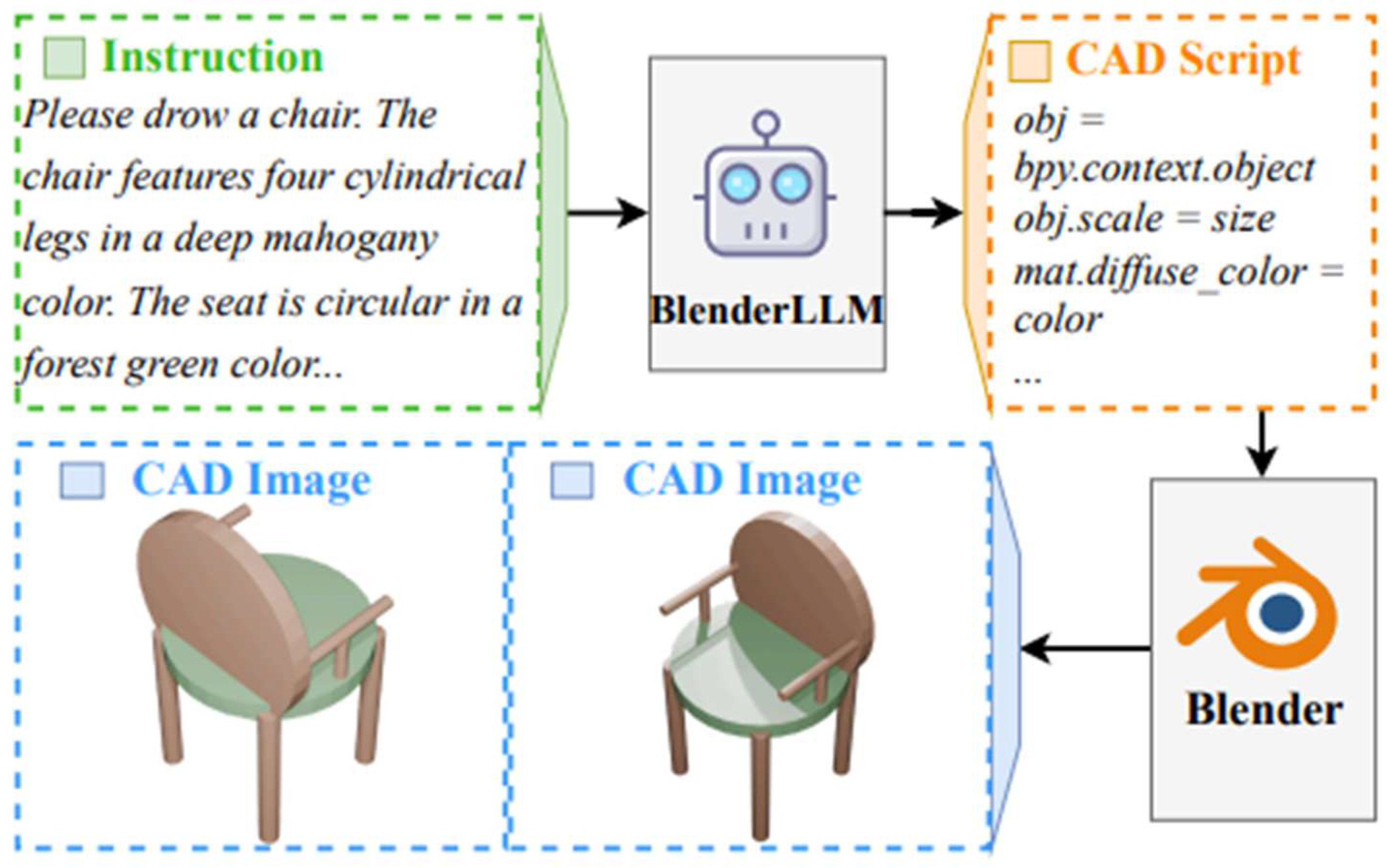
Engineers are also integrating LLMs with CAD software for design automation. Some experimental plugins allow one to describe changes to a 3D model in words (e.g., “make this flange 10% thicker and add 4 bolt holes equally spaced on the perimeter”), and the LLM will attempt to execute those changes using the CAD API [60]. While still newly emerging, this points to a future where routine CAD modifications or repetitive design tasks can be offloaded to an AI agent, speeding up the design iteration loop. Figure 13 shows how LLMs can turn a simple instruction into a CAD drawing using Blender LLM, an LLM specifically trained for CAD tasks.
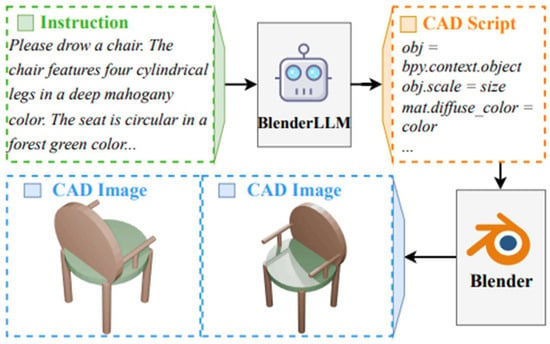
Figure 13.
CAD design generation using large language models (open access) [60].
However, integrating LLMs with engineering tools comes with challenges. One major issue is ensuring accuracy and maintaining constraints. Engineering software deals with strict rules (geometric constraints, meshing requirements, convergence criteria). An LLM’s generated script or command must respect these, or the result may fail or, worse, produce subtly wrong outcomes There is active research on combining LLMs with constraint solvers or validation layers that check the AI’s outputs against engineering rules. For example, if an LLM suggests a material or component that does not exist in the database, the system should catch that. NASA’s experiments noted that ChatGPT-4 confidently generates code or commands that look plausible but does not perfectly match the software’s API or context, requiring human debugging. Thus, these integrations often follow a human-in-the-loop paradigm currently; the LLM performs the drafting of code or commands, and the engineer reviews and corrects as needed [60]. Even with that, the productivity boost is significant.
Another challenge is security and versioning. Many engineering tools and codes are proprietary, and giving LLM access to them means dealing with data privacy. Solutions like on-premises LLMs or those fine-tuned on internal code (to avoid sending data to external servers) are being considered. On the versioning front, engineering software changes, and an LLM might have been trained on older versions. It might suggest commands that are incorrect [61]. This again underscores the need for continuous updating of the AI or dynamic documentation linking.
Nonetheless, the direction is clear: the world is moving towards a scenario where an engineer can speak or write in natural language to control engineering software, effectively instructing the computer at a high level of abstraction and letting the AI handle the low-level details. Generative AI models are enhancing solution methodologies within process systems engineering, as Decardi-Nelson et al. [62] highlight in their review.
To conclude, integrating LLMs with simulation and programming tools is unlocking a new level of automation and accessibility in engineering workflows. By bridging the gap between human intent and machine execution by allowing engineers to command complex software environments through language. This approach democratizes access to innovation and accelerates progress in the engineering field. As with any powerful tool, careful oversight is needed. The trend points to engineers increasingly working side by side with AI agents that prepare models, run analyses, and even make preliminary interpretations. Such synergy could free engineers to focus on innovation and higher-level decision-making, with routine or laborious aspects handled by their digital assistant. The case studies so far (like the ones from NASA and others) are encouraging, showing that even with current LLM capabilities, meaningful integration is possible and beneficial. Future developments in this area will likely refine the reliability of these AI assistants and broaden the scope of tasks they can perform autonomously under an engineer’s guidance.
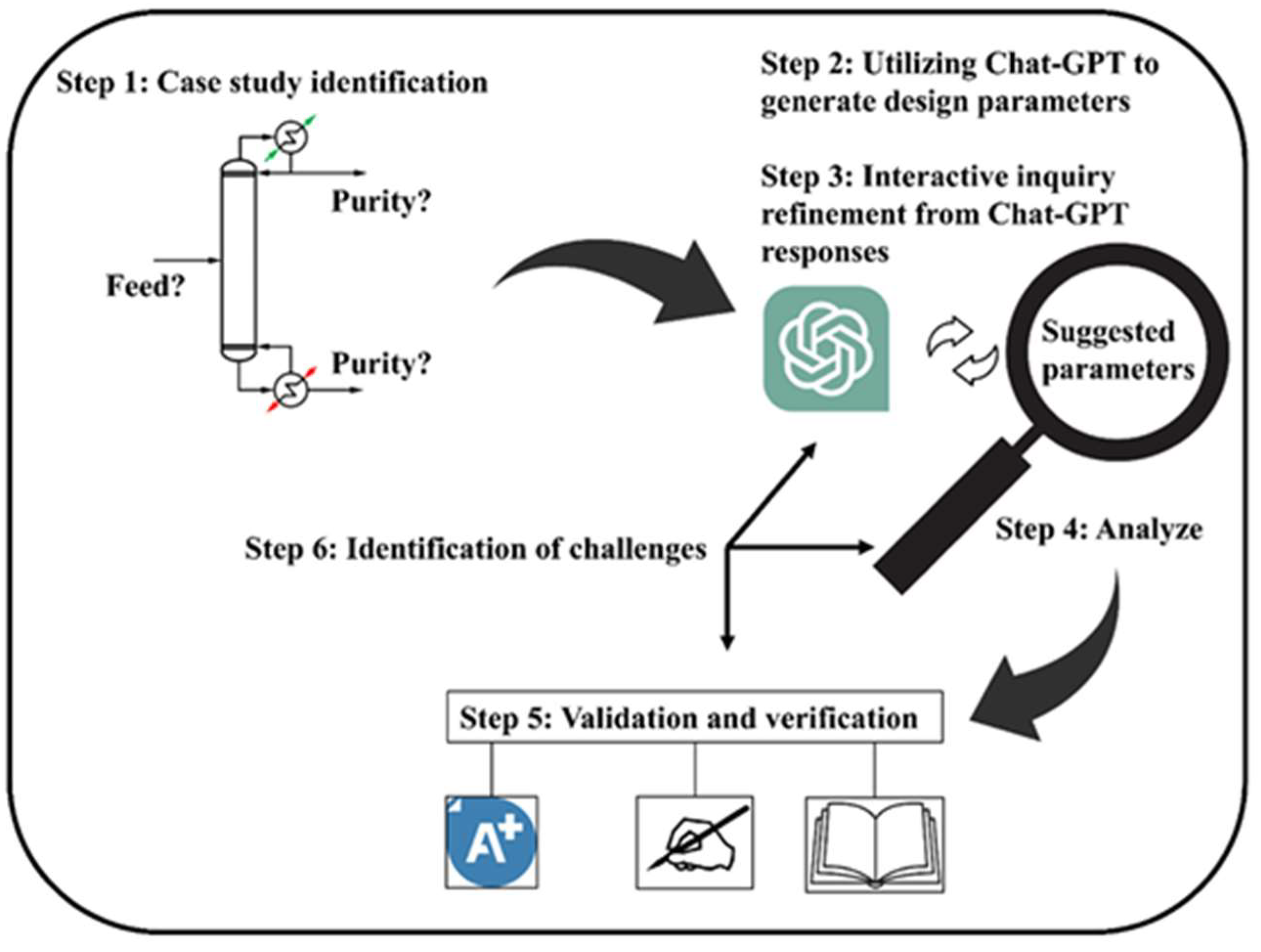
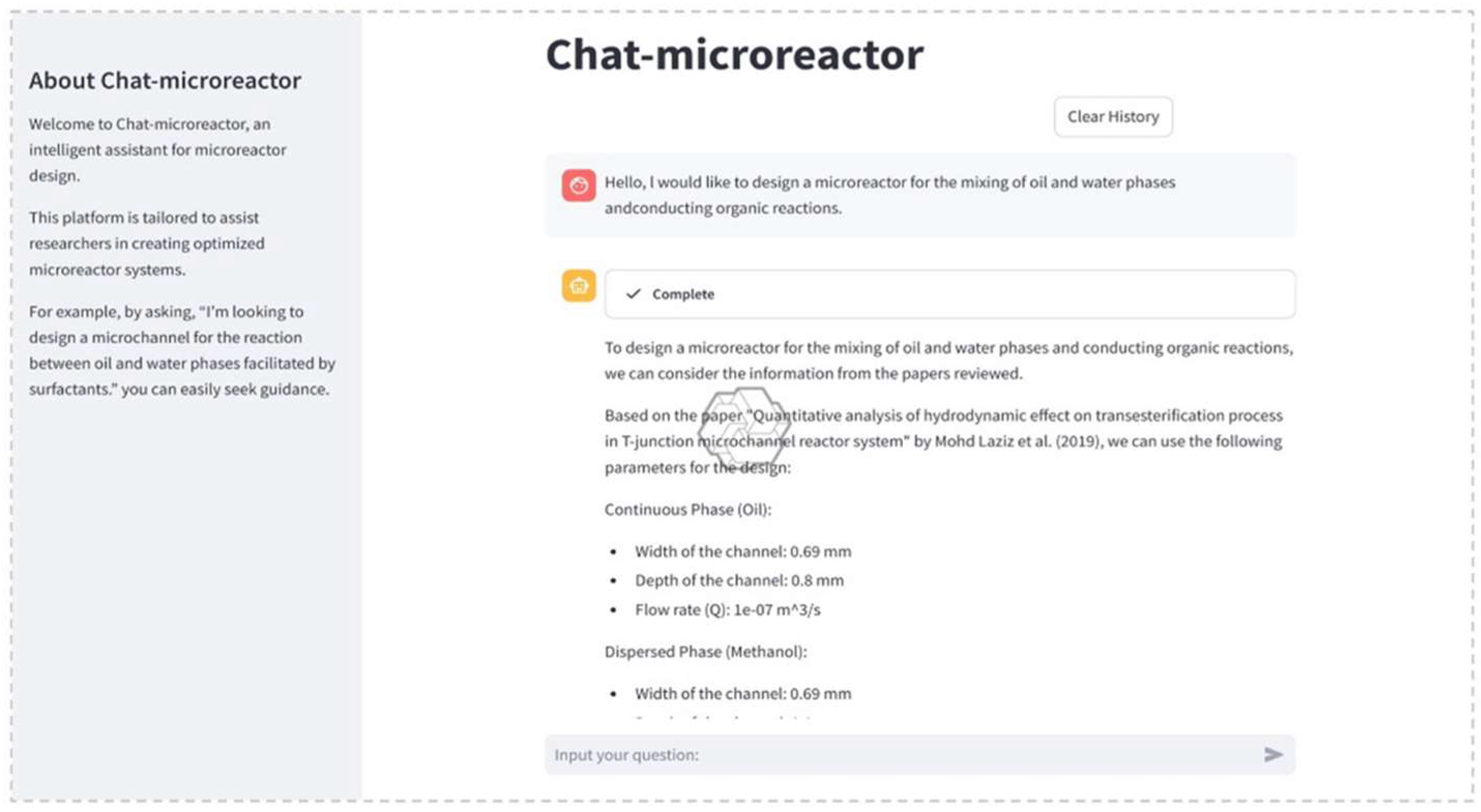
5. Applications of LLMs in Chemical Engineering
LLMs are a class of AI systems, often based on transformer architectures, trained on massive text corpora to generate human-like language. In recent years, LLMs such as GPT-3 and GPT-4 have demonstrated remarkable capabilities across domains, from natural language processing to programming, and they are beginning to impact scientific fields like chemistry and chemical engineering [63]. Chemical engineering, traditionally reliant on first-principles modelling and experimental data, is now witnessing a surge in interest in applying LLM-driven techniques to complex problems [39]. Early successes have shown that LLMs can capture domain knowledge and reasoning patterns, enabling new approaches to simulation, design, and decision-making. Crucially, LLMs can interface with other tools and data, serving as intelligent assistants that automate labor-intensive tasks or provide insights beyond human intuition [63,64].
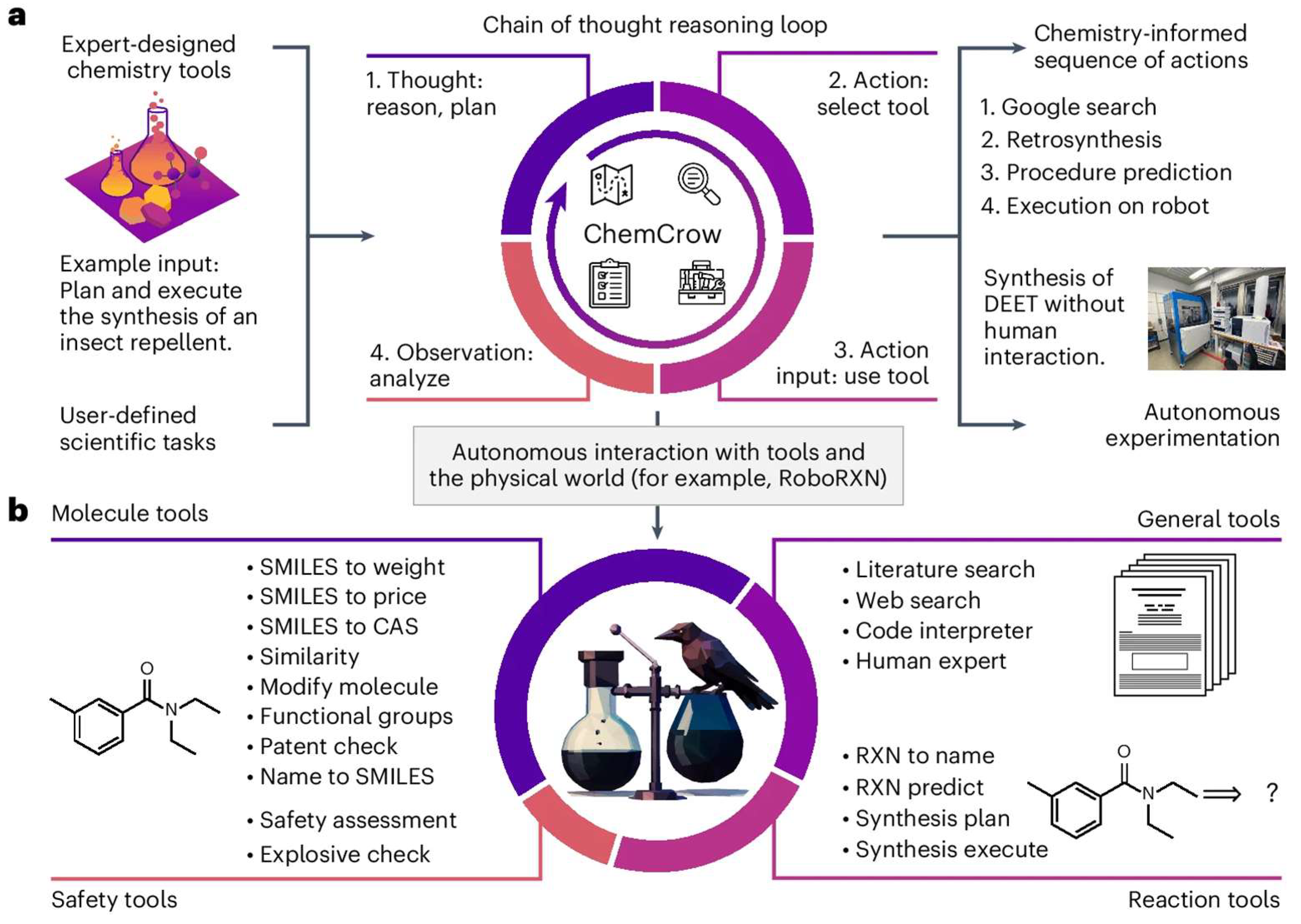
This chapter provides a literature review of LLM applications in chemical engineering, drawing on recent academic research and selected industrial case studies. It surveys a range of subtopics, from chemical engineer education to distillation/reactor modelling and process control systems. In each part, it also highlights how LLMs are used to solve problems more efficiently or creatively than conventional methods. Figure 14 illustrates one example of an LLM-based chemistry agent (“ChemCrow”) that integrates multiple specialized tools to plan and execute experiments autonomously [65]. Such integrations underscore the transformative potential of LLMs when coupled with chemical engineering knowledge and resources.
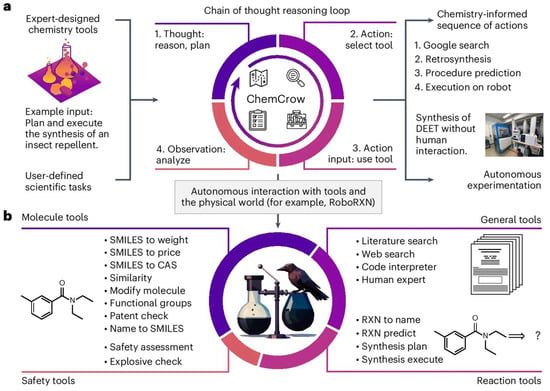
Figure 14.
An example of an LLM-powered autonomous chemistry agent (ChemCrow) using a chain-of-thought reasoning loop with integrated tools to plan and execute a synthesis task (open access) [65].
5.1. LLMs in Chemical Engineering Education
The use of large language models (LLMs) in chemical engineering education is built upon a strong foundation of research into artificial intelligence (AI) applications within academic settings. A cornerstone was laid by Brown et al. [9] with the development of GPT-3, which demonstrated an ability to handle complex tasks with minimal instruction and paved the way for LLMs like ChatGPT-4 to be used in education. Ouyang et al. [66] furthered this work by incorporating human feedback to fine-tune the models, which produced more reliable and human-like responses, a crucial feature for educational applications where accuracy is essential. These advancements highlight the potential for LLMs to transform problem-solving in chemical engineering by automating tasks like code generation and the construction of virtual models, although the need to critically verify their outputs remains a key consideration.
Further research from other fields shows the versatility of LLMs, with applications in journalism, medical education, and translation [67,68]. Within education, Bai Doo-Anu and Owusu Ansah [69] emphasize the challenges LLMs pose to academic integrity, which calls for innovative assessment methods and a focus on fostering critical evaluation skills in students. New developments like multimodal LLMs [70] and prompt engineering [71] are expanding the use of LLMs for visual and analytical tasks in engineering education. However, Weidinger et al. [72] also warn against ethical risks such as misinformation, stressing the importance of a rigorous approach to evaluating any LLM-generated content to ensure its reliability in technical applications.
Despite these advancements, the literature points to persistent challenges in the reliability and interpretability of LLMs, particularly in fields that require precise calculations. Evans et al. [73] advocate for trustworthy AI outputs and stress that users must have strong foundational knowledge to identify and correct errors in models generated by LLMs. This supports the view that LLMs enhance efficiency but do not replace the need for a deep understanding of the subject matter. By synthesizing theoretical progress with practical applications in areas like thermodynamics and process modelling, this review positions LLMs as transformative tools in chemical engineering education while also acknowledging the ongoing need to address their limitations through critical engagement and thoughtful pedagogical strategies.
5.2. LLMs in Process Simulation and Modelling
Process simulation is fundamental in chemical engineering for designing and optimizing unit operations and complete process flowsheets. Traditionally, engineers use physics-based simulators (e.g., Aspen Plus V14, COMSOL 6.3), which require expert knowledge to set up models and significant computational effort for complex systems. LLMs are beginning to assist in two main ways: (i) by serving as surrogate models that emulate detailed simulations at a fraction of the cost, and (ii) by generating simulation code or models from natural-language descriptions, thus streamlining model development.
5.2.1. Surrogate Modelling
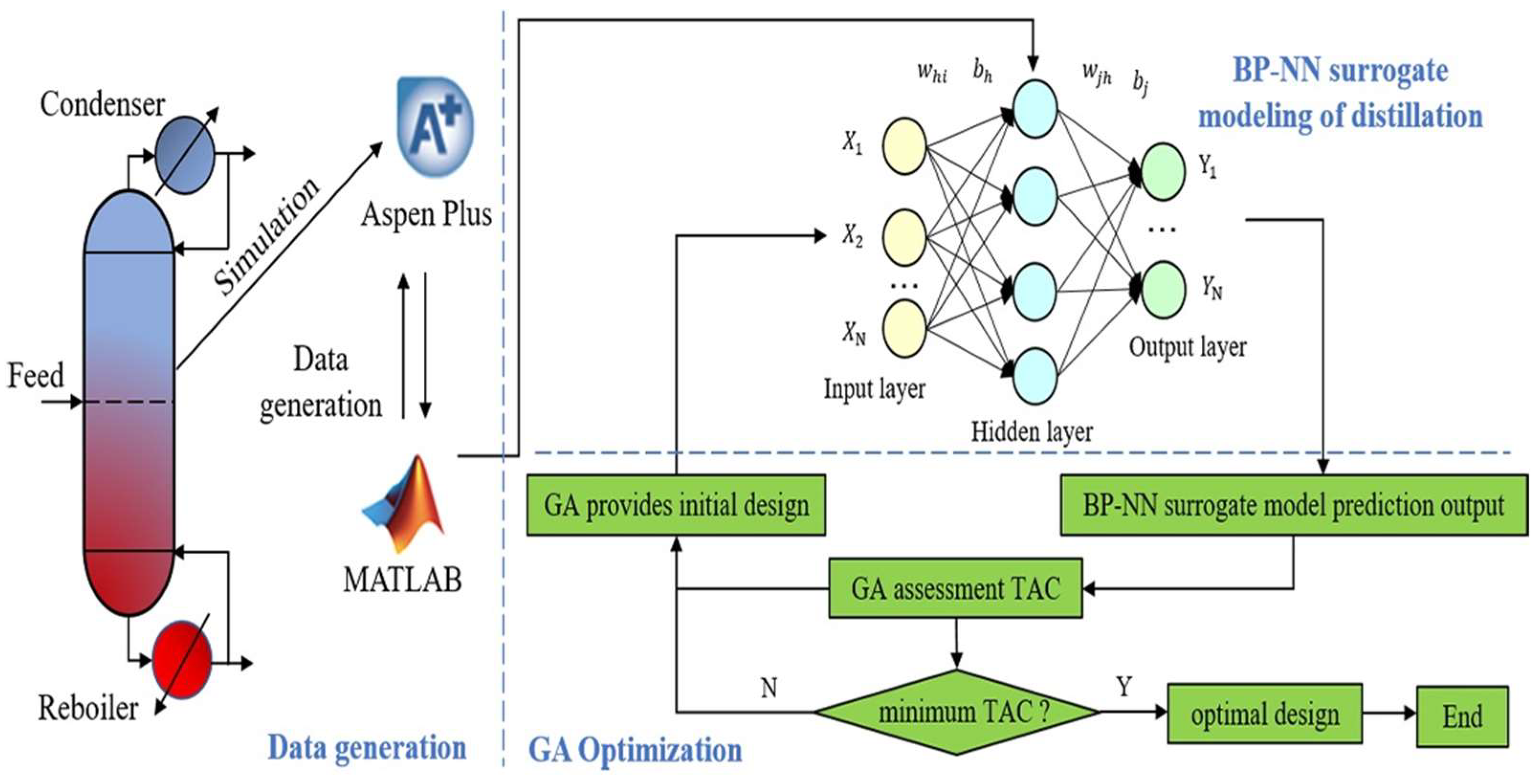
Recent studies show that deep learning models can approximately process behavior, enabling rapid what-if analyses and optimization. For instance, Ye et al. [74] developed a surrogate model of a propylene distillation column using a back-propagation neural network trained on data from rigorous simulations (Figure 15). This surrogate, combined with a genetic algorithm, optimized the column design (plates, feed location, reflux ratio, etc.), finding a solution that matched the simulator’s accuracy within a <0.7% error. While Ye et al.’s model is not an LLM, it demonstrates the efficacy of data-driven models in process design. Building on this, one can envision LLM-based surrogates that incorporate not only numeric data but also textual knowledge (e.g., operating guidelines, equipment descriptions) to improve fidelity. Ramos et al. [39] note that LLMs fine-tuned on technical text can capture domain correlations without manual feature engineering, opening doors to broader use by domain experts. In fact, Van Herck et al. [75] showed that converting simulation datasets into a text question–answer format for LLM training is straightforward and yields accurate predictive models even with limited data. This suggests an opportunity to treat simulation results as language and use LLMs as universal surrogates that “learn” process behavior through fine-tuning.
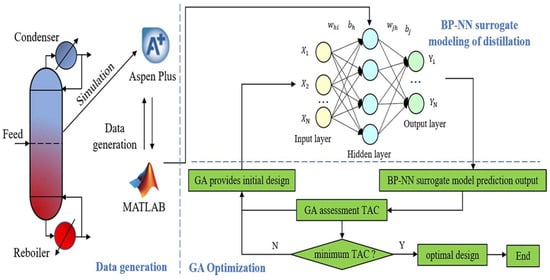
Figure 15.
Demonstration of surrogate model of a propylene distillation column using a back-propagation neural network (open access) [74].
5.2.2. Code Generation for Models
A notable development is using LLMs to automatically generate process models or code, accelerating the model-building phase. Rupprecht et al. [76] explored a Text2Model approach where an LLM was fine-tuned to produce dynamic reactor models (in Modelica language) from textual descriptions of the reactor system. Their fine-tuned 8-billion parameter model could translate a user’s description (e.g., “CSTR with first-order exothermic reaction and cooling jacket”) into syntactically correct and semantically meaningful Modelica code, outperforming the base model and approaching GPT-4’s correctness on seen scenarios. This approach lowers the barrier for engineers who may not be fluent in a simulator’s programming language—the engineer can simply describe the process in natural language and let the LLM draft the simulation code. While generalization to completely novel scenarios remain a challenge (the fine-tuned model struggled with unseen cases compared to GPT-4), this indicates a path forward for AI-assisted model development. Similarly, M. Bran et al. [65] reports that LLM-based agents can interface with process simulation software by generating input files or analyzing outputs as part of their toolset. By leveraging chain-of-thought prompting and external calculators, an LLM agent can adjust simulation parameters iteratively to achieve target conditions, much like an engineer would.
5.2.3. Digital Twins and Data Integration
In industrial settings, digital twins of chemical plants generate vast amounts of data (sensor readings, operational logs). LLMs trained on this operational data can act as advanced analytics engines. For example, SymphonyAI and Microsoft have collaborated on an “Industrial LLM” specialized for manufacturing processes, trained on sensor data, maintenance logs, and process parameter [77]. This industrial LLM is reported to provide clear explanations for shop-floor issues and answer complex operational questions by tapping into historical data and a knowledge graph of the plant. Early case studies suggest that such models can help predict equipment failures or recommend process adjustments in real time, effectively bringing AI into the loop of process control [78]. While rigorous peer-reviewed studies of industrial LLM deployments are still emerging, the trend is clear: by merging data-driven insights with language understanding, LLMs enable more intuitive interactions with process simulations and plant data. Engineers can ask a digital twin “What is causing the drop in distillate purity?” and receive an answer that draws on both numerical simulation and documented domain knowledge, which is a task that previously required hours of manual analysis.
5.2.4. Soft Sensors and Advanced Process Control
Beyond simulation and modelling, AI-based data-driven models have gained significant traction in chemical process plants for developing soft sensors, virtual measurement tools that estimate hard-to-measure or costly variables in real time. These models, typically built on machine learning techniques such as neural networks or support vector regression, use readily available process measurements (e.g., temperature, pressure, flow rate) to infer unmeasured states like composition or reaction conversion [79]. When integrated into advanced process control (APC) frameworks, AI-driven soft sensors enable more responsive and precise control strategies, improving set-point tracking, disturbance rejection, and fault detection [80].
For example, in distillation control, a soft sensor can estimate tray compositions from temperature profiles, allowing the APC system to adjust reflux and boil-up rates dynamically, thereby optimizing both energy consumption and product purity. While most current soft sensor implementations do not use LLMs directly, there is potential for future integration. The synergy between LLM-based reasoning and traditional AI soft sensors could provide not only quantitative predictions but also contextual, human-readable explanations for control actions in real time, enhancing both operator trust and decision-making [80].
5.2.5. LLM-Integrated Design and Simulation Systems
Recent developments highlight the potential of large language models (LLMs) to be embedded into specialized engineering decision-support tools, particularly in domains requiring multi-physics process optimization. A notable example is the intelligent design and simulation aid system for heat treatment processes, named Chat-IMSHT, proposed by Sun et al. [81]. This system integrates a domain-adapted LLM, specifically Qwen2.5:32b, enhanced via Retrieval-Augmented Generation (RAG) with a curated knowledge base derived from heat treatment manuals, experimental data, and the relevant literature. This setup enables the LLM to generate tailored process design schemes from natural-language textual prompts, retrieve and incorporate domain-specific knowledge for accurate responses, and facilitate simulation of candidate process routes. The RAG approach ensures that model outputs are grounded in verified metallurgical and thermal treatment data, significantly improving reliability and reducing hallucinations compared to generic LLM responses. Additionally, the framework employs a lighter LLM, ChatGLM3-6b, to extract structured parameters from natural-language outputs and generate executable input files (e.g., POS for processes and DAT for material properties) for finite element simulation software like COSMAP v1.4. It also incorporates an iterative reasoning loop, where generated process parameters (e.g., temperature, time, and carbon potential across heating, carburizing, diffusion, and insulation stages) are validated through simulations and refined based on deviations from target specifications, such as surface hardness or carburization depth.
Beyond their application in materials engineering, this study exemplifies a broader trend in leveraging LLMs not merely as conversational assistants but as interactive co-pilots that bridge natural language processing with domain-specific simulation environments. By enabling engineers to specify complex requirements in plain language, receive knowledge-grounded recommendations, and obtain automated simulation setups, such systems reduce the need for manual navigation of specialized software tools. While the case study focuses on steel heat treatment, the underlying principles of domain-tuned RAG for knowledge retrieval, LLM-driven parameter extraction, simulation integration, and closed-loop refinement hold significant promise for adaptation to chemical engineering tasks.
5.3. LLMs in Reaction Optimization and Autonomous Experimentation
One of the most exciting applications of LLMs in chemical engineering is in reaction engineering, specifically, optimizing reaction conditions and even planning experiments autonomously. Traditionally, chemists and process engineers would rely on experience or design of experiments to find optimal reaction parameters (catalysts, temperatures, solvents) for yield or selectivity. Now, LLM-driven systems are showing the ability to read the literature, propose conditions, and iteratively improve reactions with minimal human intervention.
5.3.1. Autonomous Labs and Agents
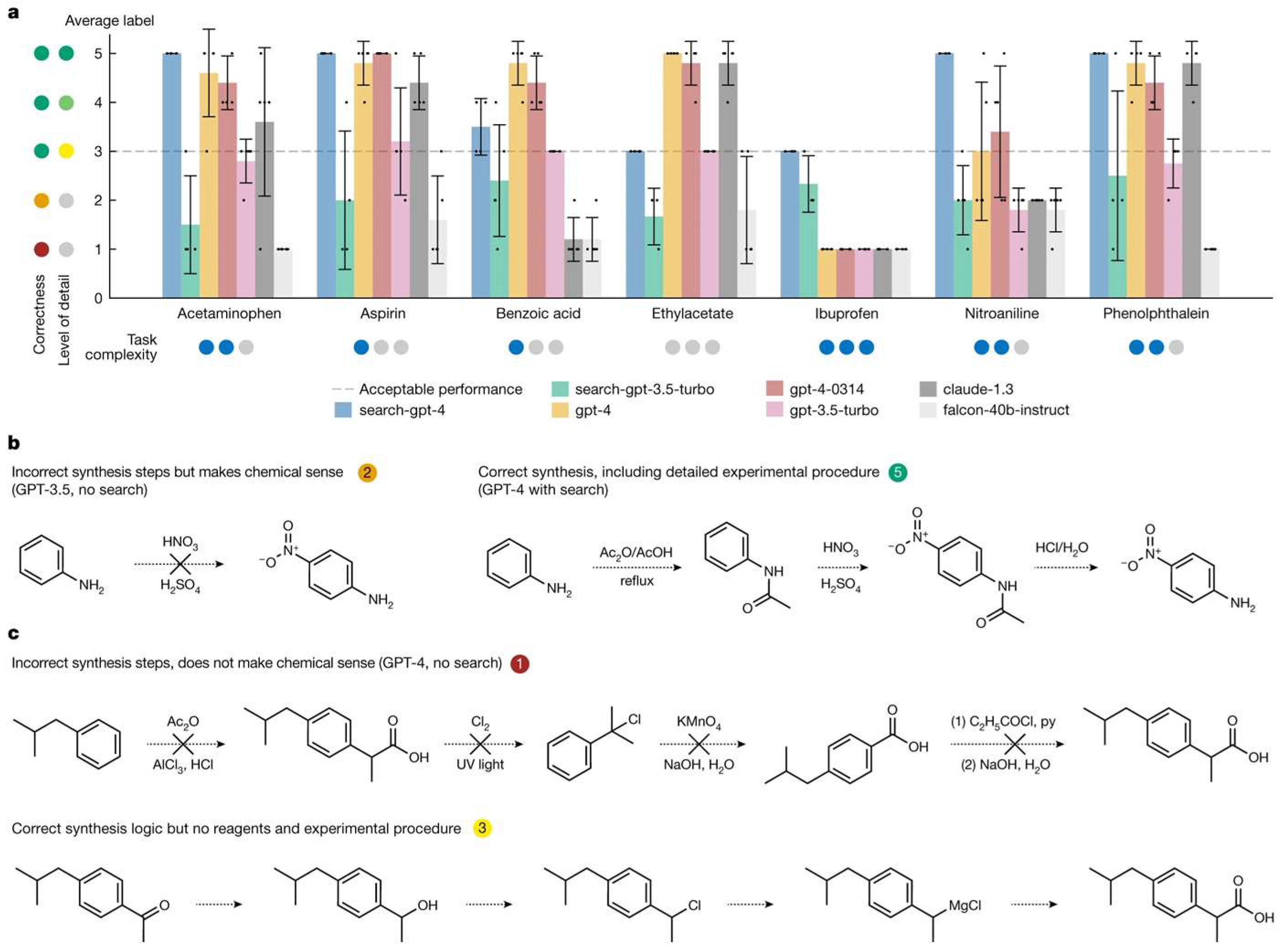
A landmark example in the field of autonomous labs is the work by Boiko et al. [63], who introduced an AI system named “Coscientist.” Driven by GPT-4, Coscientist is capable of autonomously designing, planning, and executing experiments. In a significant demonstration, Coscientist successfully optimized a palladium-catalyzed cross-coupling reaction both in simulation and in a physical lab, identifying improved conditions for the reaction’s yield. The GPT-4 model was enhanced with tools for literature searches and experimental control, which allowed it to select reagents and modify conditions based on experimental results. This represents a new model for “self-driving laboratories,” where LLMs act as the “brain” orchestrating robotic experiment platforms. The capabilities of Coscientist in planning chemical production routes using various LLMs are shown in Figure 16.
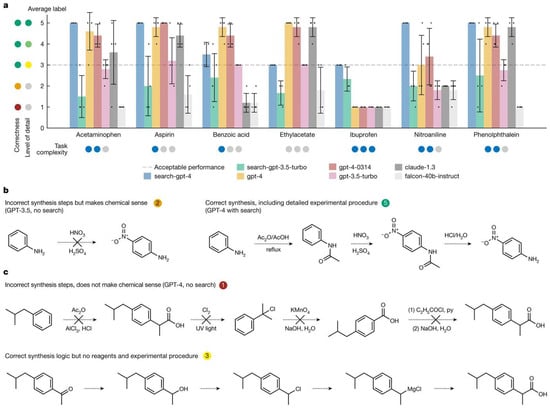
Figure 16.
Coscientist’s capabilities in planning routes of chemical production based on different LLMs (a) Performance comparison of different LLMs on compound synthesis benchmarks, with error bars showing standard deviations. (b) Two illustrative examples of model-generated synthesis routes for nitroaniline. (c) Two illustrative examples of model-generated synthesis routes for ibuprofen. UV, ultraviolet (open access) [63].
Similarly, Ruan et al. [82] created an end-to-end reaction development framework (LLM-RDF) that employs GPT-4 agents to oversee each stage of synthesis development. Their system was composed of specialized agents that communicated in natural language, including a “Literature Scouter” to find prior knowledge, an “Experiment Designer” to propose tests, and a “Result Interpreter” to analyze data. In a case study on aerobic alcohol oxidation, the LLM-based agents were able to plan screening experiments, recommend the best catalysts and conditions, scale-up the reaction, and provide instructions on purification steps like distillation or separation. This automated cycle completed a process that would typically take weeks or months in days, showcasing the efficiency that can be gained from LLM orchestration.
5.3.2. Prompt-Driven Reaction Optimization
Even without full automation, LLMs can assist human researchers by quickly querying chemical knowledge and suggesting conditions. Jablonka et al. [64] showed that a GPT-3 model, when fine-tuned on a database of reactions, could answer questions about expected yields and recommend reagents for various reactions. Remarkably, their fine-tuned LLM matched or outperformed task-specific ML models in predicting reaction outcomes, especially in low-data regimes. In one example, the model was asked (in plain English) how to improve the yield of a given organic reaction; it responded with a set of condition changes that aligned with expert knowledge (e.g., slightly raising temperature and adding a base), which were later confirmed experimentally. The ability to invert questions was also powerful; by phrasing prompts like “What substrate and catalyst would give a >90% yield for X product?” the LLM effectively performed inverse design of reactions. This suggests that LLMs can function as virtual reaction advisors, rapidly mining prior data to guide experimentalists. Luo et al. [83] emphasize that careful prompt engineering is crucial in such scenarios; by structuring queries to include context (e.g., known mechanisms or solvent constraints), LLM suggestions become significantly more reliable and chemically valid. In their outlook, Luo and colleagues argue that domain-specific prompt templates (incorporating units, safety checks, etc.) can enhance LLM accuracy and thus accelerate reaction optimization efforts. Figure 17 shows an illustration of LLMs aiding in chemical research.
Figure 17.
Demonstration of using LLM models for predictive chemistry (open access) [83].
5.3.3. LLM-Powered Synthesis Planning
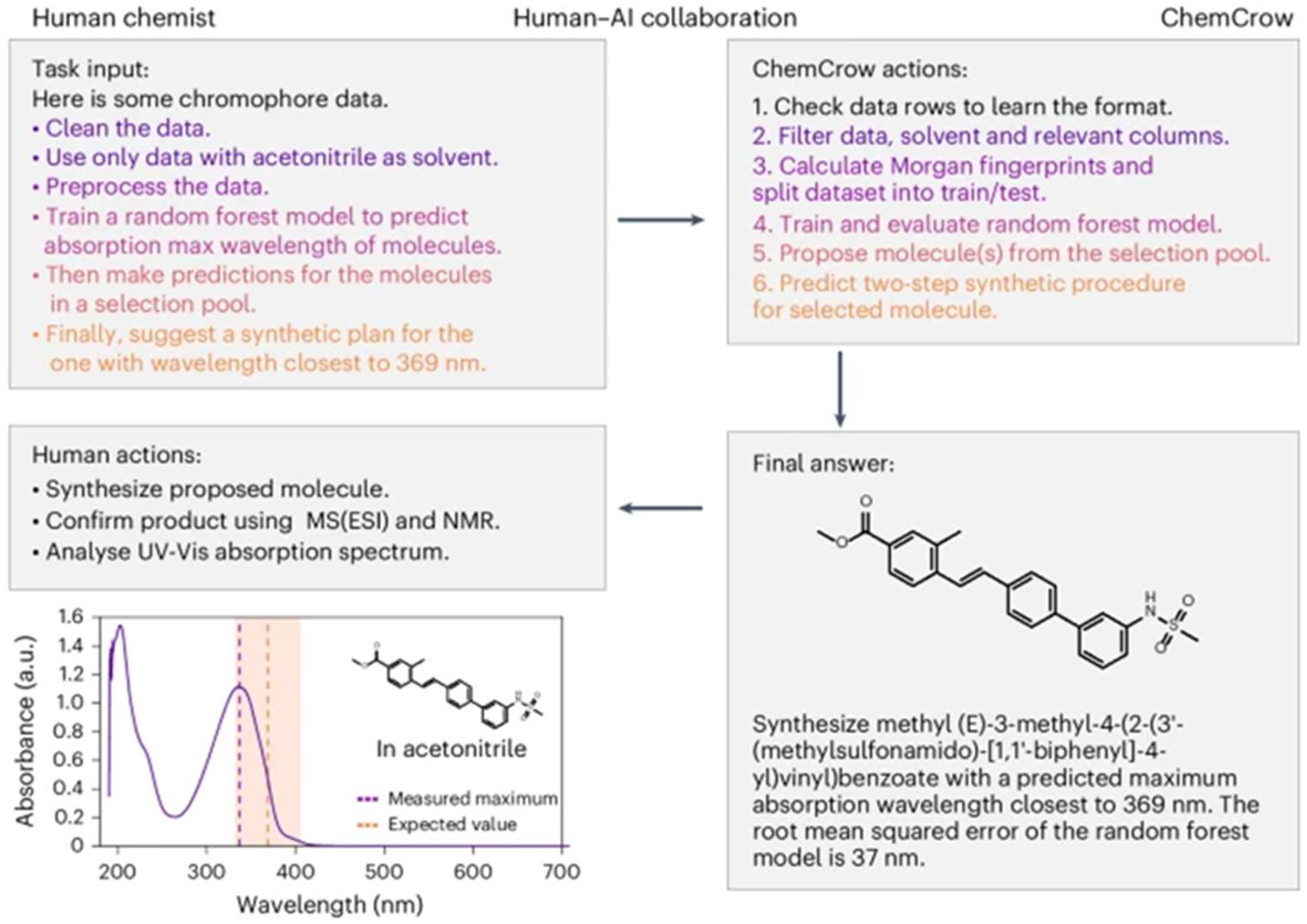
LLMs have also made development in retrosynthesis and synthesis planning, tasks at the interface of chemistry and process design. Modern transformer models can translate target molecules into suggested synthesis routes (sequence of reactions). While early tools like IBM’s RXN system and Schwaller’s retrosynthesis model are not fully-fledged LLMs in the interactive sense, newer systems integrate them into an LLM agent. For instance, ChemCrow is an agent that uses GPT-4 with a suite of chemistry tools to plan syntheses and even execute them on automated platforms [65]. ChemCrow can take a user request such as “Find a catalyst for a Diels–Alder reaction and provide a synthesis plan for it” and perform the following steps autonomously: literature search for candidate catalysts, selection of a promising catalyst, planning of a multi-step synthesis for that catalyst, and then execution of those steps using a robotic system, as shown in Figure 18. Impressively, ChemCrow was able to synthesize an insect repellent (DEET) and several organocatalysts without human intervention by iteratively using tools for each subtask.
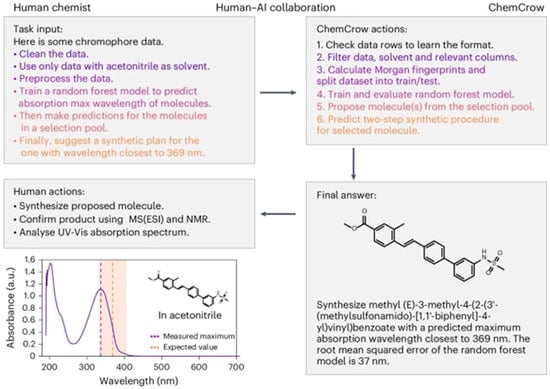
Figure 18.
ChemCrow model used to discover new chromophore by processing user input (open access) [65].
The outcomes of these autonomous runs were successful. The intended products were obtained in each case. ChemCrow’s approach highlights how LLMs can combine textual reasoning (e.g., reading safety instructions, checking compatibility of reagents) with experimental action.
From these examples, LLMs are revolutionizing reaction optimization by accelerating knowledge retrieval, enabling autonomous experimentation, and facilitating creative problem-solving. Early adopters in industry are also experimenting with these capabilities. A 2023 report in Nature Biotechnology noted that some pharmaceutical companies have customized ChatGPT-4 to interface with their internal reaction databases, allowing chemists to query, “How can I optimize this API synthesis?” and receive detailed suggestions backed by both the literature and in-house data [84]. However, issues of accuracy and trust remain. ChatGPT-4 and similar models can sometimes confidently suggest incorrect or unsafe actions. The incorporation of domain constraints and verification tools is mitigating these concerns [85]. The future of reaction engineering may feature LLMs as co-pilots in the lab, suggesting experiments, running them via robots, and learning from the results, thereby continually refining the process design. All these points toward more efficient development cycles in chemical manufacturing, where optimal conditions are reached with far fewer experimental runs than previously thought possible.
5.4. LLMs in Molecular Design and Discovery
Chemical engineering often overlaps with molecular science when designing catalysts, solvents, polymers, or pharmaceuticals. Here, the application of LLMs has largely focused on generative design and property prediction for molecules and materials. By treating chemical representations (like SMILES strings, InChI, or even polymer text descriptors) as a language, researchers have trained LLMs to “speak” chemistry to generate novel molecular structures with desired properties or predicting properties from structure, all in a data-driven manner [86].
5.4.1. Chemical Language Models
An emerging concept is that molecules have a “language” that AI can learn. Mswahili and Jeong [86] provide a comprehensive review of transformer-based models for chemical sequences, noting that “chemical language models” have reached state-of-the-art performance at the beginning of molecular design. These models are inspired by NLP architectures and are capable of generating chemically valid structures and exploring vast chemical spaces more efficiently than brute-force methods. For example, an LLM-based generator can be tasked with creating a molecule that maximizes some score (e.g., drug likeness or octane number) and, through iterative sampling or reinforcement learning, produce candidates that meet the criteria.
Noutahi et al. [87] introduced MolGPT, a GPT-based decoder that learns the syntax of SMILES strings and can propose new drug-like molecules; it demonstrated the ability to generate novel compounds that passed medicinal chemistry filters and even suggested alternatives to known drugs. Transformer models excel at capturing context in sequences, which for chemistry means understanding that, say, “COOH” is a carboxyl group or that certain substructures are likely to appear together. The review by Mswahili and Jeong [86] highlights multiple transformer implementations, from ChemBERTa (an encoder for property prediction) to SMILES transformer models for molecule generation and discusses their advantages and limitations. One key takeaway is that transformer LLMs can generalize in chemical space, generating molecules that are unlike those in the training set yet are chemically plausible, indicating they learn an abstract representation of chemistry rules.
5.4.2. Accelerating Materials Discovery
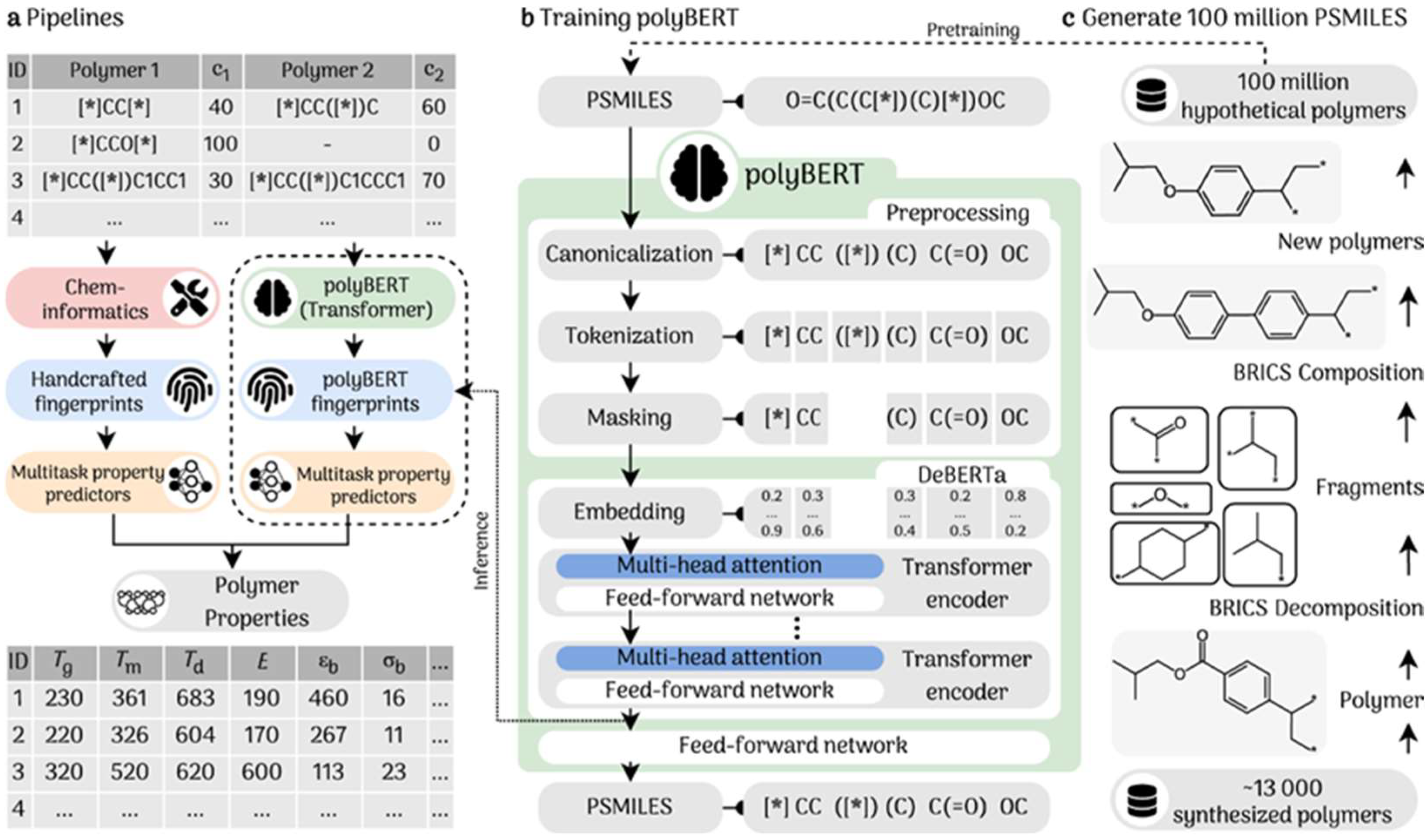
LLMs have shown particular promise in polymer and materials design, where the search spaces are enormous. Kuenneth and Ramprasad [88] developed polyBERT, a BERT-like model that generates polymer fingerprints (embeddings) from textual polymer representations, enabling ultrafast property predictions. The polyBERT pipeline treats polymers as “sentences” of monomer codes and learns to map them to properties such as glass transition temperature or tensile strength. Remarkably, polyBERT-based predictions were two orders of magnitude faster than traditional simulations or even group-contribution methods while retaining comparable accuracy. This allowed for a rapid screening of millions of hypothetical polymers to identify promising candidates for specific applications.
Figure 19 illustrates a comprehensive workflow for polymer property prediction using machine learning. Panel (a) contrasts two prediction pipelines: the left uses traditional cheminformatics tools with handcrafted fingerprints to predict properties like glass transition temperature (Tg), melting temperature (Tm), degradation temperature (Td), Young’s modulus (E), elongation at break (ϵb), and tensile strength at break (σb) for polymers (e.g., ID1, ID3 as copolymers, ID2 as a homopolymer), while the right employs polyBERT, an end-to-end machine-driven predictor that processes polymer data directly. Panel (b) details polyBERT’s training, where Polymer Simplified Molecular-Input Line-Entry System (PSMILES) strings are canonicalized, tokenized, and masked and then fed into the DeBERTa model with 12 transformer encoders (each with 12 attention heads) to generate polymer fingerprints via sentence averaging, enabling property prediction. Panel (c) describes the generation of 100 million hypothetical polymers by decomposing 13,766 known polymers into 4424 fragments using the BRICS method and then reassembling these fragments randomly to create new polymer structures for further study [88].
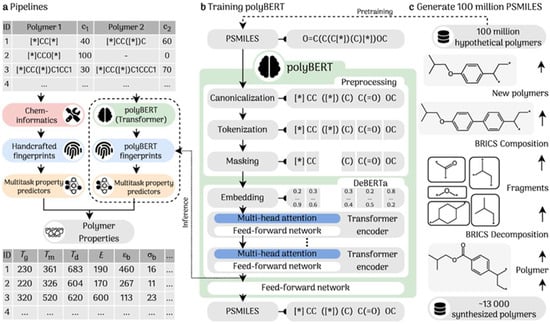
Figure 19.
Workflow for polymer property prediction and generation using polyBERT and BRICS decomposition (open access) [88].
In another study, an LLM fine-tuned on metal–organic framework (MOF) data was used to generate new MOF linker candidates with potential for carbon capture, some of which were later synthesized and found to have excellent CO2 uptake [75]. These examples illustrate how LLMs can drive a shift from trial-and-error synthesis to AI-guided molecular engineering, where computers propose what to make next. The ability of LLMs to perform inverse design (asking for structures that yield a target property) is especially powerful, essentially solving a problem that is traditionally very challenging in materials science.
5.4.3. Property Prediction and Knowledge Extraction
Besides generation, LLMs are being used to predict properties or assess molecular feasibility. Fine-tuning large models on curated datasets (e.g., toxicity data, solubility measurements) yields predictors that take a molecule’s name or formula as input and output an estimated property. Jablonka et al. [64] found that a GPT-3 model fine-tuned on a small thermodynamics dataset could answer questions like “What is the flash point of ethanol?” or “Is compound X likely to be biodegradable?” with surprising accuracy, often within the range of error of experimental methods. Because the model was trained in a QA format, it effectively encodes the mapping from chemical description to property in its weights, bypassing the need for explicit descriptors or equations. One advantage highlighted by Van Herck et al. [75] is that using natural-language input for such models removes the requirement for expert-crafted features (like Morgan fingerprints or Coulomb matrices). Moreover, LLMs can incorporate contextual knowledge; an LLM might know that “toluene” is flammable and infer a flash point range even if data is sparse by analogizing to benzene or xylene (this kind of reasoning is harder for a standard regression model). An LLM might also pick up misleading correlations from its text pre-training (e.g., overestimating a property based on seeing it in a patent that exaggerates performance). Thus, rigorous fine-tuning and validation are needed for critical applications.
A related use of LLMs is in retrosynthesis planning is shown in Figure 20, which, while a chemistry problem, strongly intersects with chemical engineering in process development [89]. Transformer models like MIT-IBM RXN [90] showed that sequence-to-sequence models can predict reaction outcomes and even multi-step syntheses by learning from millions of reaction examples. Now, with larger language models, the trend is toward interactive planning; an LLM can propose a route, and if one step looks infeasible (perhaps flagged by a chemist or another AI tool), the LLM can revise the plan. M. Bran et al. [65] and Ramos, Collison, and White [39] both survey how LLM-based agents are used for synthesis planning. These agents can perform things like scrape the literature for similar molecules to see what reactions were used or use a “retro-analysis” tool to break down a target into precursors and then ask the LLM to find suppliers or suggest conditions for each step.
Figure 20.
LLMs in retrosynthesis planning (open access) [89].
5.5. LLMs in Process Design and Operations
Large language models (LLMs) are proving to be transformative tools in chemical engineering, changing traditional methods for process design and operations. Trained on vast amounts of technical literature and engineering data, these models can help with tasks like creating initial process designs, planning experiments, optimizing reactors, and diagnosing operational problems. Because of their ability to understand context, synthesize specialized knowledge, and work through chains of reasoning, they are becoming intelligent co-pilots in design scenarios that previously depended on manual calculations and simulation tools like Aspen Plus V14.
This literature review examines how LLMs are being applied in chemical process design and operations, with a special focus on designing distillation columns and reactors. It looks at their roles in predicting parameters, optimizing workflows, planning experiments, and providing operational support, drawing from case studies by Kong et al. [1], Boiko et al. [63], Ruan et al. [82], and Pan et al. [91]. The review also explores the challenges and future directions for this technology, highlighting the potential for LLMs to improve efficiency and automation in chemical engineering while also emphasizing the need for proper validation and advancements specific to the domain.
5.5.1. LLMs in Distillation Column Design
Large language models (LLMs), such as ChatGPT-3.5, are showing potential as useful assistants in the design of distillation columns, particularly in providing initial design parameters and facilitating a more iterative design process. A pivotal study by Kong et al. [1] details a method for using ChatGPT-3.5 to suggest key parameters like feed stage location, the number of trays, reflux ratio, and reboiler duty for separating binary mixtures, such as propane/isobutane.
The methodology involves a few key steps: First, identifying relevant case studies from literature and then using ChatGPT-3.5 to propose a design from scratch without any initial parameters. This is followed by refining the design through iterative inquiries, analyzing the calculations provided by ChatGPT-3.5, and finally, validating the results using professional tools like Aspen Plus (version not specified) and manual techniques like the McCabe–Thiele method. The workflow from the Kong et al. paper is illustrated in Figure 21. This approach highlights the ability of LLMs to provide initial insights and rules of thumb, though their computational instability necessitates rigorous validation due to potential inaccuracies in complex calculations. The study emphasizes that LLMs serve as auxiliary tools, enhancing efficiency by reducing initial design time while requiring human oversight to ensure reliability.
Figure 21.
Methodology of distillation column designed by LLMs [1].
5.5.2. LLMs in Experiment Design for Reactors
In the initial stages of reactor design, large language models (LLMs) are increasingly being used to help with the planning and design of experiments. A key example is the Coscientist system, developed by Boiko et al. [63], which uses GPT-4 to autonomously plan and design complex chemical experiments, including those that involve reactors. Based on the requirements of a reaction, Coscientist can search through the relevant literature, propose reaction conditions, and even suggest appropriate reactor configurations. In one demonstration, it streamlined the design process by planning a Suzuki–Miyaura coupling reaction, where it selected the necessary reagents, solvents, and a suitable reactor setup.
Similarly, the LLM-RDF framework from Ruan et al. [82] utilizes LLMs to guide the entire process of synthesis development, which includes setting up reactors for scale-up. For instance, it proposed modifications for a reactor used in a copper-/TEMPO-catalyzed aerobic alcohol oxidation reaction to ensure efficiency at larger scales. These examples show how LLMs can reduce the reliance on manual literature reviews and trial-and-error, allowing engineers to iterate on reactor designs much more quickly.
Pan et al. [91] have advanced this field even further with their “Chat-microreactor” tool, whose interface can be observed through Figure 22, which uses LLMs to extract key information from the scientific literature to help design continuous flow systems. This tool combines neural network classifiers with text vectorization to identify important parameters like density, flow rate, and surface tension. It has achieved an F1 score of over 70% for classifying flow patterns and has reduced the time it takes to process a paragraph of text from 24 to 16 s. While this method is focused on microreactors, it is highly relevant to the design of reactor experiments in general, as it can extract reaction conditions and fluid dynamics data from the literature that could inform the design of both batch and continuous systems. Such capabilities could also be extended to designing experiments for reactors that are integrated with other processes like distillation, which would lead to greater automation in chemical engineering. Moreover, LLMs can predict how reaction conditions may need to be adjusted when scaling-up from a laboratory to an industrial reactor. By analyzing data from small-scale experiments, LLMs can suggest modifications to reactor parameters like heat transfer, mixing, and mass transfer rates. For example, within the LLM-RDF framework, an “Experiment Designer” agent used LLMs to propose sampling schedules and scale-up strategies, which helped to maintain reaction efficiency across different reactor sizes. This capability not only speeds up the design process but also bridges the gap between laboratory research and industrial application, making LLMs invaluable for reactor design.
Figure 22.
Chat-microreactor interface (open access) [91].
Additionally, LLMs can manage more complex reactor systems, such as those used for flow chemistry or continuous processing. They can generate code for these systems to regulate parameters like flow rates, pressures, and temperatures in real time, thereby optimizing the reactor’s performance. For instance, Yoshikawa et al. [92] demonstrated that LLMs can translate natural-language instructions into executable plans for robotic systems in self-driving labs, including reactor setups. This allows chemists to describe experiments in plain language, with the LLM translating their words into precise commands for the reactor hardware. Advancements like these make reactor operation more accessible and efficient, especially for non-experts, while also ensuring the systems are scalable and configurable.
5.5.3. Optimization of Reactor Conditions
Optimizing the conditions inside a chemical reactor is essential for achieving high yields, selectivity, and energy efficiency. Large language models (LLMs) contribute to this by analyzing experimental data and suggesting the best parameters. For instance, the Coscientist system was able to optimize conditions for Pd-catalyzed transformations by using datasets from previous studies; it identified the best combination of catalysts, solvents, and temperatures through iterative experimentation to maximize the reaction’s efficiency. Similarly, the “Result Interpreter” agent in the LLM-RDF framework fits kinetic models to experimental data, which provides insights into reaction mechanisms and helps suggest adjustments to the reactor conditions. This data-driven approach reduces the number of experiments that need to be run, saving both time and resources.
Pan et al. [91] have advanced this capability by using LLMs to build vectorized databases from the scientific literature, which allows for the rapid use of machine learning models for parameter optimization in microreactors. Their tool was able to achieve an F1 score of 80% in new reactor systems, showing its efficiency in finding optimal flow conditions. This method could be adapted to optimize conditions in larger reactor systems by extracting thermodynamic and kinetic parameters to help in fine-tuning temperature, pressure, and flow rates.
Table 3 offers a summary of the LLMs discussed previously, detailing their applications in process design and operations.

Table 3.
Summary of LLM applications in process design and operations.
5.5.4. Operational Support
LLMs can enhance distillation column monitoring and control by providing high-level insights from operation logs and operator notes. Modern distillation columns are equipped with sensors measuring temperatures, pressures, and flow rates, managed by advanced control strategies like model-predictive control. LLMs can complement these systems by analyzing textual data, such as an operator note stating, “Experiencing foaming in column 3, possibly due to impurity buildup.” This guidance, drawn from textual databases, enhances numeric control systems. Devarapalli [78] suggests that LLM-based virtual assistants improve decision-making in plant operations by providing real-time contextual reasoning and information retrieval. For instance, in a distillation unit, an LLM might address a query like “Why has the differential pressure spiked?” by correlating sensor trends, maintenance logs, and past events, responding: “The pressure rise could indicate flooding, historically this column floods when throughput exceeds 120% or when condenser duty drops. Current data shows throughput at 130%, so flooding is likely”.
Pan et al. [91] support this vision by demonstrating how LLMs can process the literature to provide operational insights for continuous flow systems. Their Chat microreactor tool could be adapted to analyze operational logs for distillation columns, identifying patterns in parameters like flow rates or pressures to suggest maintenance or adjustment strategies. While direct control of distillation columns via LLMs is not advisable due to safety-critical constraints, LLMs can enhance human operators’ understanding and speed up troubleshooting. Additionally, LLMs can serve as training tools, allowing new engineers to query scenarios like “What happens if reflux is cut in half?” and receive pedagogical answers referencing distillation principles, facilitating on-the-job learning [38].
5.6. Challenges and Future Considerations for LLMs in Chemical Engineering
The integration of large language models into chemical engineering offers transformative potential but is accompanied by significant challenges. A primary limitation is their probabilistic inference, which can produce scientifically plausible but technically inaccurate suggestions, particularly in precision-critical tasks like distillation column and reactor design [33]. For example, Kong et al. [1] found that ChatGPT-3.5’s suggestions for distillation parameters often required multiple iterations and verification due to computational instability, with deviations in purity or energy demands. Similarly, in reactor design, LLMs must be rigorously validated to ensure accuracy in parameters like reactor size or reaction kinetics [63,82]. This necessitates the use of traditional methods, such as manual calculations and simulation software like Aspen Plus V14, to ensure safety and reliability.
Ethical and educational concerns further complicate LLM adoption. Overreliance risks deskilling students and junior engineers, potentially undermining critical thinking skills essential for engineering innovation. Ethical issues, including bias, data privacy, and misinformation, require clear governance standards to ensure responsible use [19]. Educators must integrate LLMs into curricula thoughtfully, training students to critically evaluate outputs and maintain accountability for their designs.
Another important consideration for future LLM adoption in chemical engineering is the quality of the underlying information sources. Since LLMs are trained on vast corpora that may include low-quality or unverified publications, there is a risk of propagating inaccurate or misleading information into engineering decisions. This is particularly relevant given the increasing prevalence of predatory journals and hastily published technical reports. To mitigate this, future research should focus on curating domain-specific, peer-reviewed datasets and incorporating automated quality assessment mechanisms, such as weighting sources based on publisher reputation, citation impact, and verification against established engineering standards. Integrating explainable AI methods that can trace outputs back to their source material will also help engineers critically assess the trustworthiness of AI-generated recommendations. Such measures will be essential to ensure that LLM-assisted workflows are grounded in high-quality, reliable engineering knowledge.
Looking ahead, addressing these challenges requires innovative solutions. Developing hybrid physics-informed LLM architectures that embed fundamental laws, such as mass and energy balances, phase equilibria, and reaction kinetics, could enhance reliability for safety-critical processes. Pan et al. [91] demonstrate progress by combining LLMs with machine learning for literature extraction, suggesting that similar approaches could integrate thermodynamic models for distillation and reactor design. Fine-tuning domain-specific LLMs on curated datasets, such as simulation outputs and plant operation logs, is another critical direction. Initiatives like ChemLLM and industry-specific models, such as Dow’s AI assistant, show improved performance for specialized tasks [39].
In practical chemical engineering workflows, fine-tuning and hybrid LLM approaches can be integrated by linking the models to existing process data and engineering knowledge infrastructure. Historical data from process simulations (e.g., Aspen HYSYS: https://www.aspentech.com/en/products/engineering/aspen-hysys, accessed on 3 July 2025), laboratory experiments, and plant historians can be pre-processed to create high-quality, domain-specific training datasets. These datasets enable supervised fine-tuning so that the LLM learns operational constraints, common process faults, and efficiency–yield trade-offs relevant to the plant’s context. Retrieval-augmented generation (RAG) [55] can connect the LLM to curated repositories such as process flow diagrams (PFDs), piping and instrumentation diagrams (P&IDs), safety data sheets, and thermodynamic property databases, allowing it to generate responses grounded in authoritative sources. Knowledge graphs representing process equipment interconnections, material properties, and operating rules can be queried in real time to constrain the LLM’s outputs, ensuring compliance with mass and energy balances. In deployment, the LLM can be embedded within engineering dashboards or control room interfaces, functioning as an interactive co-pilot that proposes design modifications, recommends operational setpoints, and explains decisions by referencing the linked datasets, thus bridging advanced AI reasoning with safety-critical engineering practice.
Autonomous process design agents represent a promising future, capable of generating preliminary designs with heat and mass balances, equipment lists, and control logic in coordination with simulators like Aspen Plus V14, reducing design timelines for pharmaceuticals and sustainable fuels. However, robust human-in-the-loop frameworks are essential to ensure safety, regulatory compliance, and transparent reasoning. In education, fostering AI literacy is crucial, equipping engineers to validate and challenge LLM outputs. Collaborative benchmarking initiatives, evaluating LLM performance on standardized problems like azeotropic distillation or reactor scale-up can facilitate best practices and objective metrics.
In addition to current advancements, several research gaps remain that warrant systematic investigation. First, there is a lack of standardized benchmarking frameworks for quantitatively evaluating LLM performance against domain-specific engineering metrics, which limits reproducibility and comparability across studies. Second, although domain-specific fine-tuning has shown promise, secure adaptation using proprietary industrial datasets is still in its infancy, with unresolved challenges in data governance and catastrophic forgetting. Third, most current LLM deployments in chemical engineering operate as “black-box” systems with limited interpretability, constraining their adoption in safety-critical or regulatory contexts. Finally, ethical and societal considerations, including bias mitigation, accountability for AI-driven engineering decisions, and workforce upskilling, are rarely addressed in technical studies. Future research should prioritize the development of domain-specific benchmarks, privacy-preserving fine-tuning protocols, explainability frameworks tailored for engineering workflows, and longitudinal studies on the socio-technical impact of LLM adoption in the profession.
A particularly critical and underexplored gap lies in the integration of LLMs with physics-based and first-principles models that underpin modern engineering simulations. While conceptual approaches have been proposed, typically via API or scripting interfaces allowing LLMs to generate model inputs, execute simulations, and interpret outputs, there are few documented case studies in real industrial environments. This lack of empirical validation raises questions about input validity, compliance with physical constraints, error propagation, and the computational overhead of high-fidelity models. Future work should therefore design and test reproducible integration frameworks, supported by rigorous benchmarking protocols to evaluate both technical accuracy and efficiency gains. Demonstrating robust LLM–simulation coupling with tools such as Aspen HYSYS, ANSYS Fluent, and COMSOL Multiphysics would represent a major advance, enabling AI to act as a true co-pilot for modelling and design tasks rather than a stand-alone advisor.
5.7. Limitations of LLMs in Safety-Critical Engineering Contexts
Despite their promise, LLMs face significant constraints when deployed in safety-critical engineering environments. A key concern is hallucination, where models produce outputs that are syntactically correct but factually inaccurate, often with high confidence [94]. In engineering contexts, such errors could propagate into flawed designs, inaccurate simulations, or unsafe operating conditions if not rigorously verified. Interpretability is another critical challenge; most transformer-based models operate as black boxes, making it difficult to trace the reasoning behind a given recommendation [95]. This lack of transparency limits trust, particularly in regulated sectors where decision-making must be auditable. Bias in training datasets also poses risks, as over-representation of specific standards, materials, or geographic practices can lead to outputs that are unsuitable or non-compliant in other jurisdictions [96]. These risks are amplified in chemical engineering applications where safety margins are tight and errors may result in hazardous consequences.
Furthermore, the computational cost of state-of-the-art LLMs presents both economic and operational limitations. High-parameter models such as GPT-4 require substantial processing resources for inference, often necessitating cloud-based deployment, which can introduce latency and raise data security concerns. This makes real-time application in control systems challenging, particularly for facilities with strict on-premises data requirements. Smaller domain-specific models (e.g., ChemBERTa, SciBERT) offer faster inference and reduced hardware demands but may sacrifice general reasoning capabilities [32]. In safety-critical engineering, mitigating these limitations requires the integration of robust validation pipelines, adoption of explainable AI (XAI) methods tailored for engineering workflows, and development of lightweight, physics-informed LLMs that can operate reliably under constrained resources [95]. Such measures will be essential to ensure that the adoption of LLMs enhances, rather than undermines, the safety, reliability, and compliance of engineering operations.
6. Conclusions
The rapid advancement of artificial intelligence, particularly large language models (LLMs), is reshaping the engineering profession by introducing new paradigms for design, simulation, optimization, and decision-making. In the near future, AI is expected to become a standard component of engineering workflows, enabling faster problem-solving, enhanced predictive capabilities, and more efficient integration of multidisciplinary knowledge. LLMs have the potential to bridge the gap between human expertise and computational tools, providing engineers with context-aware insights that are both technically rigorous and intuitively accessible.
However, the adoption of AI in engineering also demands careful attention to several critical aspects. Accuracy and reliability remain paramount, as AI-generated outputs can suffer from bias, overgeneralization, or “hallucinations” that may lead to unsafe or suboptimal decisions. Transparency and explainability must be prioritized to ensure that engineers and stakeholders can trust AI-assisted recommendations. Ethical considerations, including data privacy, intellectual property protection, and accountability for AI-driven decisions, must be addressed through clear guidelines and governance frameworks.
To mitigate the risk of wrong predictions, several measures should be prioritized. Rigorous validation and cross-verification of AI outputs against experimental data, pilot-scale results, or established physics-based models must be conducted before deployment in safety-critical contexts. Hybrid modelling frameworks that embed domain-specific constraints can help ensure predictions remain physically consistent and feasible. Human-in-the-loop supervision should remain standard practice, allowing engineers to review and override AI recommendations where necessary. Continuous retraining and model updating using recent operational and experimental data can reduce performance drift, while explainability and uncertainty quantification can provide transparency into the reasoning behind predictions and help engineers assess their reliability.
Looking ahead, the most effective use of AI in engineering will likely emerge from hybrid approaches that combine physics-based models, domain-specific knowledge, and AI-driven reasoning. Continuous human oversight, rigorous validation, and adaptive learning mechanisms will be essential to ensure that AI tools serve as reliable collaborators rather than unquestioned authorities. By balancing innovation with caution, the engineering profession can harness AI’s transformative potential while safeguarding the quality, safety, and integrity of its outcomes.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, T.S.L.; Writing—Original Draft Preparation, T.L.K.; Writing—Review and Editing, T.L.K. and T.S.L.; Supervision, T.S.L. and S.-T.B.; Project Administration, Y.-Y.Z., C.M. and S.-T.B. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research received no external funding except APC is funded by solely Universiti Tunku Abdul Rahman.
Data Availability Statement
The original contributions presented in this study are included in the article. Further inquiries can be directed to the corresponding author.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
- Kong, Z.Y.; Adi, V.S.K.; Segovia-Hernández, J.G.; Sunarso, J. Complementary role of large language models in educating undergraduate design of distillation column: Methodology development. Digit. Chem. Eng. 2023, 9, 100126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, J. Applications of Large Language Models in Pathology. Bioengineering 2024, 11, 342. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peng, Y.; Yang, X.; Li, D.; Ma, Z.; Liu, Z.; Bai, X.; Mao, Z. Predicting flow status of a flexible rectifier using cognitive computing. Expert Syst. Appl. 2025, 264, 125878. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hadi, M.U.; Tashi, Q.A.; Qureshi, R.; Shah, A.; Muneer, A.; Irfan, M.; Zafar, A.; Shaikh, M.B.; Akhtar, N.; Hassan, S.Z.; et al. Large Language Models: A Comprehensive Survey of Its Applications, Challenges, Limitations, and Future Prospects 2025. TechRxiv 2025. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Biswas, R.; De, S. A Comparative Study on Improving Word Embeddings Beyond Word2Vec and GloVe. In Proceedings of the 2022 Seventh International Conference on Parallel, Distributed and Grid Computing (PDGC), Solan, Himachal Pradesh, India, 25–27 November 2022; IEEE: New York City, NY, USA, 2022; pp. 113–118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vaswani, A.; Shazeer, N.; Parmar, N.; Uszkoreit, J.; Jones, L.; Gomez, A.N.; Kaiser, Ł.; Polosukhin, I. Attention is All you Need. In Advances in Neural Information Processing Systems; Curran Associates, Inc.: Red Hook, NY, USA, 2017; Available online: https://proceedings.neurips.cc/paper_files/paper/2017/hash/3f5ee243547dee91fbd053c1c4a845aa-Abstract.html (accessed on 23 April 2025).
- Devlin, J.; Chang, M.-W.; Lee, K.; Toutanova, K. BERT: Pre-training of Deep Bidirectional Transformers for Language Understanding. arXiv 2018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yenduri, G.; Ramalingam, M.; Selvi, G.C.; Supriya, Y.; Srivastava, G.; Maddikunta, P.K.R.; Raj, G.D.; Jhaveri, R.H.; Prabadevi, B.; Wang, W.; et al. GPT (Generative Pre-Trained Transformer)—A Comprehensive Review on Enabling Technologies, Potential Applications, Emerging Challenges, and Future Directions. IEEE Access 2024, 12, 54608–54649. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brown, T.B.; Mann, B.; Ryder, N.; Subbiah, M.; Kaplan, J.; Dhariwal, P.; Neelakantan, A.; Shyam, P.; Sastry, G.; Askell, A.; et al. Language Models are Few-Shot Learners. arXiv 2020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Voicebot.ai. Timeline History of Large Language Models. Available online: https://voicebot.ai/large-language-models-history-timeline/ (accessed on 23 April 2025).
- OpenAI; Achiam, J.; Adler, S.; Agarwal, S.; Ahmad, L.; Akkaya, I.; Aleman, F.L.; Almeida, D.; Altenschmidt, J.; Altman, S.; et al. GPT-4 Technical Report. arXiv 2023. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, K.; He, S.; He, Z.; Lin, J.; Pei, Q.; Shao, J.; Zhang, W. Examining User-Friendly and Open-Sourced Large GPT Models: A Survey on Language, Multimodal, and Scientific GPT Models. arXiv 2023. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, D.; Liu, W.; Tan, Q.; Chen, J.; Yan, H.; Yan, Y.; Li, J.; Huang, W.; Yue, X.; Ouyang, W.; et al. ChemLLM: A Chemical Large Language Model. arXiv 2024. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Muggleton, S. Alan Turing and the development of Artificial Intelligence. Eur. J. Artif. Intell. 2014, 27, 3–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, G.; Li, X.; Xie, S. Bilateral Turing Test: Assessing machine consciousness simulations. Cogn. Syst. Res. 2024, 88, 101299. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gugerty, L. Newell and Simon’s Logic Theorist: Historical Background and Impact on Cognitive Modeling. Proc. Hum. Factors Ergon. Soc. Annu. Meet. 2006, 50, 880–884. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pollitzer, E.; Jenkins, J. Expert knowledge. expert systems and commercial interests. Omega 1985, 13, 407–418. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rich, S.H.; Venkatasubramanian, V. Model-based reasoning in diagnostic expert systems for chemical process plants. Comput. Chem. Eng. 1987, 11, 111–122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Venkatasubramanian, V. The promise of artificial intelligence in chemical engineering: Is it here. finally? AIChE J. 2019, 65, 466–478. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sriram, D.; Stephanopoulos, G.; Logcher, R.; Gossard, D.; Groleau, N.; Serrano, D.; Navinchandra, D. Knowledge-Based System Applications in Engineering Design: Research at MIT. AI Mag. 1989, 10, 79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sriram, R.D. Artificial Intelligence in Engineering: Personal Reflections. NIST 2006. preprint. Available online: https://www.nist.gov/publications/artificial-intelligence-engineering-personal-reflections (accessed on 23 April 2025).
- Shrager, J. ELIZA Reinterpreted: The world’s first chatbot was not intended as a chatbot at all. arXiv 2024. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rumelhart, D.E.; Hinton, G.E.; Williams, R.J. Learning representations by back-propagating errors. Nature 1986, 323, 533–536. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sánchez Fernández, I.; Peters, J.M. Machine learning and deep learning in medicine and neuroimaging. Ann. Child Neurol. Soc. 2023, 1, 102–122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hinton, G. Deep belief networks. Scholarpedia 2009, 4, 5947. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krizhevsky, A.; Sutskever, I.; Hinton, G.E. ImageNet classification with deep convolutional neural networks. Commun. ACM 2017, 60, 84–90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Zhao, T.; Ju, W.; Shi, S. Materials discovery and design using machine learning. J. Mater. 2017, 3, 159–177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Benitez, J.M.; Castro, J.L.; Requena, I. Are artificial neural networks black boxes? IEEE Trans. Neural Netw. 1997, 8, 1156–1164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rosoł, M.; Gąsior, J.S.; Łaba, J.; Korzeniewski, K.; Młyńczak, M. Evaluation of the performance of GPT-3.5 and GPT-4 on the Polish Medical Final Examination. Sci. Rep. 2023, 13, 20512. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, S.; Otake, Y.; Mizutani, D.; Liu, C.; Asano, K.; Sato, N.; Saito, T.; Baba, H.; Fukunaga, Y.; Higo, Y.; et al. Future-proofing geotechnics workflows: Accelerating problem-solving with large language models. Georisk Assess. Manag. Risk Eng. Syst. Geohazards 2024, 19, 307–324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, J.; Yoon, W.; Kim, S.; Kim, D.; Kim, S.; So, C.H.; Kang, J. BioBERT: A pre-trained biomedical language representation model for biomedical text mining. arXiv 2019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beltagy, I.; Lo, K.; Cohan, A. SciBERT: A Pretrained Language Model for Scientific Text. arXiv 2019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cleti, M.; Jano, P. Hallucinations in LLMs: Types, Causes, and Approaches for Enhanced Reliability. 2024. Available online: https://www.researchgate.net/profile/Meade-Cleti/publication/385085962_Hallucinations_in_LLMs_Types_Causes_and_Approaches_for_Enhanced_Reliability/links/6715051009ba2d0c760eabb8/Hallucinations-in-LLMs-Types-Causes-and-Approaches-for-Enhanced-Reliability.pdf (accessed on 3 July 2025). [CrossRef]
- Pan, S.; Luo, L.; Wang, Y.; Chen, C.; Wang, J.; Wu, X. Unifying Large Language Models and Knowledge Graphs: A Roadmap. arXiv 2023. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bommasani, R.; Hudson, D.A.; Adeli, E.; Altman, R.; Arora, S.; von Arx, S.; Bernstein, M.S.; Bohg, J.; Bosselut, A.; Brunskill, E.; et al. On the Opportunities and Risks of Foundation Models. arXiv 2021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, S.; Irsoy, O.; Lu, S.; Dabravolski, V.; Dredze, M.; Gehrmann, S.; Kambadur, P.; Rosenberg, D.; Mann, G. BloombergGPT: A Large Language Model for Finance. arXiv 2023. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohamadi, S.; Mujtaba, G.; Le, N.; Doretto, G.; Adjeroh, D.A. ChatGPT in the Age of Generative AI and Large Language Models: A Concise Survey. arXiv 2023. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsai, M.-L.; Ong, C.W.; Chen, C.-L. Exploring the use of large language models (LLMs) in chemical engineering education: Building core course problem models with Chat-GPT. Educ. Chem. Eng. 2023, 44, 71–95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramos, M.C.; Collison, C.J.; White, A.D. A review of large language models and autonomous agents in chemistry. Chem. Sci. 2025, 16, 2514–2572. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Geetha, S.D.; Khan, A.; Khan, A.; Kannadath, B.S.; Vitkovski, T. Evaluation of ChatGPT pathology knowledge using board-style questions. Am. J. Clin. Pathol. 2024, 161, 393–398. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Poldrack, R.A.; Lu, T.; Beguš, G. AI-assisted coding: Experiments with GPT-4. arXiv 2023. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choi, H.S.; Song, J.Y.; Shin, K.H.; Chang, J.H.; Jang, B.-S. Developing prompts from large language model for extracting clinical information from pathology and ultrasound reports in breast cancer. Radiat. Oncol. J. 2023, 41, 209–216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, X.; Zhang, Y.; Zhang, Q.; Ren, Y.; Qiu, T.; Ma, J.; Sun, Q. Extracting comprehensive clinical information for breast cancer using deep learning methods. Int. J. Med. Inform. 2019, 132, 103985. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qin, Z.; Wang, C.; Qin, H.; Jia, W. Brainstorming Brings Power to Large Language Models of Knowledge Reasoning. arXiv 2024. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reeping, D.; Shah, A. Work-in-Progress: Students’ Prompting Strategies When Solving an Engineering Design Task. In Proceedings of the 2024 IEEE Frontiers in Education Conference (FIE), Washington, DC, USA, 13–16 January 2024; pp. 1–5. [Google Scholar]
- Pierson, K.C.; Ha, M.J. Usage of ChatGPT for Engineering Design and Analysis Tool Development. In Proceedings of the AIAA SCITECH 2024 Forum, Orlando, FL, USA, 8–12 January 2024. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ye, A.; Maiti, A.; Schmidt, M.; Pedersen, S.J. A Hybrid Semi-Automated Workflow for Systematic and Literature Review Processes with Large Language Model Analysis. Future Internet 2024, 16, 167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, S.; Xu, T.; Li, H.; Zhang, C.; Liang, J.; Tang, J.; Yu, P.S.; Wen, Q. Large Language Models for Education: A Survey and Outlook. arXiv 2024. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guizani, S.; Mazhar, T.; Shahzad, T.; Ahmad, W.; Bibi, A.; Hamam, H. A systematic literature review to implement large language model in higher education: Issues and solutions. Discov. Educ. 2025, 4, 35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bernabei, M.; Colabianchi, S.; Falegnami, A.; Costantino, F. Students’ use of large language models in engineering education: A case study on technology acceptance, perceptions, efficacy, and detection chances. Comput. Educ. Artif. Intell. 2023, 5, 100172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hou, X.; Zhao, Y.; Liu, Y.; Yang, Z.; Wang, K.; Li, L.; Luo, X.; Lo, D.; Grundy, J.; Wang, H. Large Language Models for Software Engineering: A Systematic Literature Review. arXiv 2023. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, Y.; Zhao, Y.; Zheng, H.; Li, Z.; Tan, J. Data-driven product design toward intelligent manufacturing: A review. Int. J. Adv. Robot. Syst. 2020, 17, 172988142091125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ni, B.; Buehler, M.J. MechAgents: Large language model multi-agent collaborations can solve mechanics problems, generate new data, and integrate knowledge. Extrem. Mech. Lett. 2024, 67, 102131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bermudez-Viramontes, L. Leveraging Large Language Models for the Development of Educational Modules in Mechanical Engineering. 2024. Available online: https://escholarship.org/uc/item/7d9871hb (accessed on 3 July 2025).
- Xu, K.; Zhang, K.; Li, J.; Huang, W.; Wang, Y. CRP-RAG: A Retrieval-Augmented Generation Framework for Supporting Complex Logical Reasoning and Knowledge Planning. Electronics 2024, 14, 47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Taboada, I.; Daneshpajouh, A.; Toledo, N.; De Vass, T. Artificial Intelligence Enabled Project Management: A Systematic Literature Review. Appl. Sci. 2023, 13, 5014. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Majumder, S.; Dong, L.; Doudi, F.; Cai, Y.; Tian, C.; Kalathil, D.; Ding, K.; Thatte, A.A.; Li, N.; Xie, L. Exploring the capabilities and limitations of large language models in the electric energy sector. Joule 2024, 8, 1544–1549. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, M.; Li, F.; Zhang, F.; Zheng, J.; Ma, Q. Meta In-Context Learning: Harnessing Large Language Models for Electrical Data Classification. Energies 2023, 16, 6679. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Z.; Chai, Y.; Li, J. Toward Automated Simulation Research Workflow through LLM Prompt Engineering Design. J. Chem. Inf. Model. 2025, 65, 114–124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Du, Y.; Chen, S.; Zan, W.; Li, P.; Wang, M.; Song, D.; Li, B.; Hu, Y.; Wang, B. BlenderLLM: Training Large Language Models for Computer-Aided Design with Self-improvement. arXiv 2024. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yao, Y.; Duan, J.; Xu, K.; Cai, Y.; Sun, Z.; Zhang, Y. A survey on large language model (LLM) security and privacy: The Good, The Bad, and The Ugly. High-Confid. Comput. 2024, 4, 100211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Decardi-Nelson, B.; Alshehri, A.S.; Ajagekar, A.; You, F. Generative AI and process systems engineering: The next frontier. Comput. Chem. Eng. 2024, 187, 108723. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boiko, D.A.; MacKnight, R.; Kline, B.; Gomes, G. Autonomous chemical research with large language models. Nature 2023, 624, 570–578. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jablonka, K.M.; Schwaller, P.; Ortega-Guerrero, A.; Smit, B. Leveraging large language models for predictive chemistry. Nat. Mach. Intell. 2024, 6, 161–169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bran, A.M.; Cox, S.; Schilter, O.; Baldassari, C.; White, A.D.; Schwaller, P. Augmenting large language models with chemistry tools. Nat. Mach. Intell. 2024, 6, 525–535. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ouyang, L.; Wu, J.; Jiang, X.; Almeida, D.; Wainwright, C.L.; Mishkin, P.; Zhang, C.; Agarwal, S.; Slama, K.; Ray, A.; et al. Training language models to follow instructions with human feedback. arXiv 2022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiao, W.; Wang, W.; Huang, J.; Wang, X.; Shi, S.; Tu, Z. Is ChatGPT a Good Translator? Yes with GPT-4 as the Engine. arXiv 2023. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kung, T.H.; Cheatham, M.; Medenilla, A.; Sillos, C.; De Leon, L.; Elepaño, C.; Madriaga, M.; Aggabao, R.; Diaz-Candido, G.; Maningo, J.; et al. Performance of ChatGPT on USMLE: Potential for AI-assisted medical education using large language models. PLoS Digit. Health 2023, 2, e0000198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baidoo-Anu, D.; Owusu Ansah, L. Education in the Era of Generative Artificial Intelligence (AI): Understanding the Potential Benefits of ChatGPT in Promoting Teaching and Learning. J. AI 2023, 7, 52–62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, S.; Dong, L.; Wang, W.; Hao, Y.; Singhal, S.; Ma, S.; Lv, T.; Cui, L.; Mohammed, O.K.; Patra, B.; et al. Language Is Not All You Need: Aligning Perception with Language Models. arXiv 2023. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- White, J.; Fu, Q.; Hays, S.; Sandborn, M.; Olea, C.; Gilbert, H.; Elnashar, A.; Spencer-Smith, J.; Schmidt, D.C. A Prompt Pattern Catalog to Enhance Prompt Engineering with ChatGPT. arXiv 2023. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weidinger, L.; Uesato, J.; Rauh, M.; Griffin, C.; Huang, P.-S.; Mellor, J.; Glaese, A.; Cheng, M.; Balle, B.; Kasirzadeh, A.; et al. Taxonomy of Risks posed by Language Models. In Proceedings of the 2022 ACM Conference on Fairness, Accountability, and Transparency, Seoul, Republic of Korea, 21–24 June 2022; pp. 214–229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Evans, O.; Cotton-Barratt, O.; Finnveden, L.; Bales, A.; Balwit, A.; Wills, P.; Righetti, L.; Saunders, W. Truthful AI: Developing and governing AI that does not lie. arXiv 2021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ye, L.; Zhang, N.; Li, G.; Gu, D.; Lu, J.; Lou, Y. Intelligent Optimization Design of Distillation Columns Using Surrogate Models Based on GA-BP. Processes 2023, 11, 2386. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Herck, J.; Gil, M.V.; Jablonka, K.M.; Abrudan, A.; Anker, A.S.; Asgari, M.; Blaiszik, B.; Buffo, A.; Choudhury, L.; Corminboeuf, C.; et al. Assessment of fine-tuned large language models for real-world chemistry and material science applications. Chem. Sci. 2025, 16, 670–684. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rupprecht, S.; Hounat, Y.; Kumar, M.; Lastrucci, G.; Schweidtmann, A.M. Text2Model: Generating dynamic chemical reactor models using large language models (LLMs). arXiv 2025. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- SymphonyAI. Industrial LLM-Symphony (No Date). Available online: https://www.symphonyai.com/industrial/industrial-llm/ (accessed on 24 April 2025).
- Devarapalli, V.N. How LLM-Based Virtual Assistants Can Benefit the Digitalization of the Process Industry Plant Operations. Int. Res. J. Sci. Eng. Technol. 2025, 12, 1–8. Available online: https://www.researchgate.net/publication/388284659_How_LLM-Based_Virtual_Assistants_Can_Benefit_the_Digitalization_of_the_Process_Industry_Plant_Operations (accessed on 24 April 2025).
- Kadlec, P.; Gabrys, B.; Strandt, S. Data-driven Soft Sensors in the process industry. Comput. Chem. Eng. 2009, 33, 795–814. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yin, S.; Li, X.; Gao, H.; Kaynak, O. Data-Based Techniques Focused on Modern Industry: An Overview. IEEE Trans. Ind. Electron. 2015, 62, 657–667. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, Y.; Li, X.; Liu, C.; Deng, X.; Zhang, W.; Wang, J.; Zhang, Z.; Wen, T.; Song, T.; Ju, D. Development of an intelligent design and simulation aid system for heat treatment processes based on LLM. Mater. Des. 2024, 248, 113506. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ruan, Y.; Lu, C.; Xu, N.; He, Y.; Chen, Y.; Zhang, J.; Xuan, J.; Pan, J.; Fang, Q.; Gao, H.; et al. An automatic end-to-end chemical synthesis development platform powered by large language models. Nat. Commun. 2024, 15, 10160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Luo, F.; Zhang, J.; Wang, Q.; Yang, C. Leveraging Prompt Engineering in Large Language Models for Accelerating Chemical Research. ACS Cent. Sci. 2025, 11, 511–519. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Savage, N. Drug discovery companies are customizing ChatGPT: Here’s how. Nat. Biotechnol. 2023, 41, 585–586. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xuan, J.; Daniel, T. The Future of Chemical Engineering in the Era of Generative AI. 2023. Available online: https://www.thechemicalengineer.com/features/the-future-of-chemical-engineering-in-the-era-of-generative-ai/ (accessed on 24 April 2025).
- Mswahili, M.E.; Jeong, Y.-S. Transformer-based models for chemical SMILES representation: A comprehensive literature review. Heliyon 2024, 10, e39038. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Noutahi, E.; Gabellini, C.; Craig, M.; Lim, J.S.C.; Tossou, P. Gotta be SAFE: A New Framework for Molecular Design. arXiv 2023. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kuenneth, C.; Ramprasad, R. polyBERT: A chemical language model to enable fully machine-driven ultrafast polymer informatics. Nat. Commun. 2023, 14, 4099. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, Q.; Zhou, Y.; Li, J. Automated Retrosynthesis Planning of Macromolecules Using Large Language Models and Knowledge Graphs. Macromol. Rapid Commun. 2025, 2500065. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schwaller, P.; Laino, T.; Gaudin, T.; Bolgar, P.; Hunter, C.A.; Bekas, C.; Lee, A.A. Molecular Transformer: A Model for Uncertainty-Calibrated Chemical Reaction Prediction. ACS Cent. Sci. 2019, 5, 1572–1583. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pan, Y.; Xiao, Q.; Zhao, F.; Li, Z.; Liu, J.; Ullah, S.; Lim, K.H.; Huang, T.; Yu, Z.; Li, C.; et al. Chat-microreactor: A large-language-model-based assistant for designing continuous flow systems. Chem. Eng. Sci. 2025, 311, 121567. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yoshikawa, N.; Skreta, M.; Darvish, K.; Arellano-Rubach, S.; Ji, Z.; Bjørn Kristensen, L.; Li, A.Z.; Zhao, Y.; Xu, H.; Kuramshin, A.; et al. Large language models for chemistry robotics. Auton. Robot. 2023, 47, 1057–1086. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hirtreiter, E.; Schulze Balhorn, L.; Schweidtmann, A.M. Toward automatic generation of control structures for process flow diagrams with large language models. AIChE J. 2024, 70, e18259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ji, Z.; Lee, N.; Frieske, R.; Yu, T.; Su, D.; Xu, Y.; Ishii, E.; Bang, Y.J.; Madotto, A.; Fung, P. Survey of Hallucination in Natural Language Generation. ACM Comput. Surv. 2023, 55, 1–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rai, A. Explainable AI: From black box to glass box. J. Acad. Mark. Sci. 2020, 48, 137–141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mehrabi, N.; Morstatter, F.; Saxena, N.; Lerman, K.; Galstyan, A. A Survey on Bias and Fairness in Machine Learning. ACM Comput. Surv. 2022, 54, 1–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).