Abstract
The accurate estimation of methane reserves in closed coal mines is crucial for supporting clean energy recovery and reducing greenhouse gas emissions. This study addresses the technical challenges associated with complex geological conditions and limited post-closure data in China’s closed mines. Three mainstream estimation methods—the material balance, resource composition, and decline curve—are systematically reviewed and applied to a case study in the Huoxi Coalfield. Results indicate that the material balance method provides upper-bound estimates but is highly sensitive to incomplete historical data, whereas the resource composition method yields more conservative and geologically realistic values. Although the decline curve method is not applied in this case, it offers potential for forecasting when long-term monitoring data are available. A multi-method integration approach, supported by enhanced data archiving and uncertainty assessments, is recommended to improve the accuracy and reliability of methane reserve evaluations in post-mining environments.
1. Introduction
Over the past two decades, the global coal industry has undergone major shifts due to economic restructuring, decarbonization efforts, and resource depletion [1]. Methane emissions from closed mines now account for approximately 10% of anthropogenic methane emissions, according to the International Energy Agency (IEA) [2,3]. The accurate estimation and utilization of methane in closed coal mines are therefore crucial for both climate mitigation and clean energy development.
In China, the world’s largest coal producer and consumer, more than 5600 coal mines have been closed since the start of the 14th Five-Year Plan [4]. These closures have created extensive underground voids that still contain large volumes of untapped methane, leading to lost energy potential and ongoing safety and environmental risks [5]. China’s dual-carbon strategy has further elevated the importance of methane reuse in post-mining contexts [6]. To support this effort, it is essential to classify residual mine resources, their reuse pathways, and related risks. Table 1 summarizes these categories and challenges, offering a foundational framework for methane quantification and resource recovery in closed mines.

Table 1.
Closed coal mines: perspectives and reuse potentials [7,8].
Some countries, such as Germany, the United Kingdom, the United States, and Japan, have accumulated extensive experience in the reutilization of closed coal mines [9]. These mines have been transformed into museums, tourist attractions, and mining-themed towns [10]. Among them, the United States is the most successful in extracting and utilizing methane from abandoned coal mines. In contrast, China still faces many shortcomings in the utilization of residual resources from closed coal mines. In response, numerous studies have proposed reuse models and technical frameworks for these residual resources. Yuan et al. identified major scientific challenges and key enabling technologies for resource development in closed mines and proposed a green, low-carbon, and multi-energy complementary system aligned with China’s dual-carbon targets [11,12,13]. Feng et al. evaluated classification schemes for the graded utilization of closed or abandoned mines [14]. Yin et al. explored reuse models for coal mines in Hebei Province and developed a geological assessment framework for underground coal gasification [15,16]. Liang et al. investigated the emission mechanisms and monitoring techniques for residual methane and proposed targeted mitigation strategies [17]. Cheng et al. introduced a zoned approach to characterize mining-disturbed strata and proposed a new abandoned mine methane (AMM) evaluation method [18]. Li et al. developed the “gas trap” theory based on overburden deformation and methane migration patterns in mined-out areas [19].
Methane in closed coal mines primarily originates from coal seams, adjacent strata, and surrounding rock and occurs in three physical states: adsorbed, free, and dissolved [20]. Following mine closure, stress redistribution, ventilation cessation, and strata compaction significantly alter its spatial distribution and transport dynamics [21]. Methane tends to migrate and accumulate in structurally favorable zones [22]—such as fractured or caved zones—governed by factors including the roadway connectivity, overburden integrity, and groundwater inflow. Estimating methane reserves in abandoned coal mines remains challenging due to geological complexity and limited post-closure data. In China, three main methods are used: the material balance method, the resource composition method, and the decline curve method. However, existing studies rarely compare these approaches systematically or provide a unified framework for method selection.
This study reviews and compares the three methods in detail, analyzing their principles, data needs, and limitations. A case study from the Huoxi Coalfield illustrates their practical application and performance differences. Based on the findings, we suggest improvements such as integrating multiple methods, refining parameters through monitoring, and establishing a reliability assessment framework. This review aims to support researchers and engineers by consolidating current practices and offering practical guidance to improve methane reserve estimation in closed coal mines.
2. Methane Dynamics and Their Role in Reserve Estimation
2.1. Coal Mine Methane Sources and Occurrence in Closed Coal Mines
The accurate estimation of methane reserves in closed coal mines is essential for enabling effective recovery and utilization. Understanding the sources and occurrence characteristics of methane is critical for designing targeted development strategies. Similarly to active coal mines, methane in closed mines primarily originates from the coal seam itself, adjacent strata, and surrounding rocks. It exists in three forms: adsorbed, free, and dissolved states [23]. However, after a mine closure, substantial changes in underground conditions alter the relative proportions of these states, with free methane becoming increasingly dominant [24]. The collapse of mined-out areas typically leads to surface subsidence and the formation of the so-called “three zones” in the overburden: the caved zone, the fractured zone, and the bending zone. These structural zones play a key role in determining methane occurrence and migration. In particular, separation fractures within the fractured zone and tensile fractures oriented perpendicular to the strata serve as both storage spaces and migration pathways for free methane.
2.2. Methane Migration and Enrichment in Closed Coal Mine
- (1)
- Vertical migration and enrichment in a single goaf
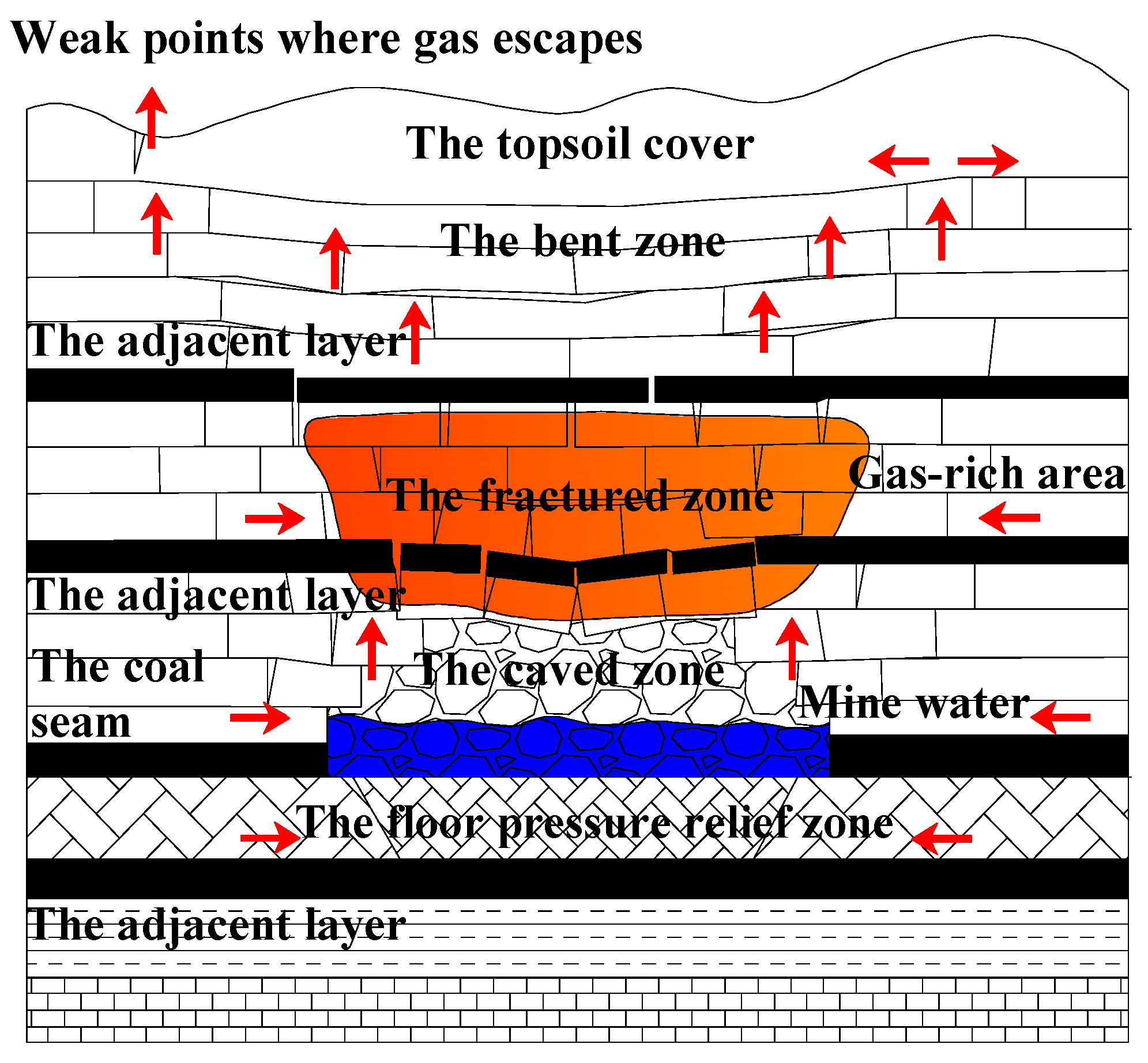
Mining-induced strata disturbance leads to the development of fractures throughout various zones. Methane stored in the caved and fractured zones migrates vertically into the goaf, driven by pressure gradients and concentration differences between these zones and the goaf. Simultaneously, methane stored in the pressure-relief zone of the floor migrates laterally under stress, eventually discharging into the goaf. In near-surface adjacent strata, the influence of the bending subsidence zone induces the formation of fractures that connect to the ground surface, allowing a portion of methane to escape directly into the atmosphere through these pathways [25]. As the gas pressure within the goaf gradually equilibrates, methane originating from the adjacent lower coal seams and the mined seam itself begins to migrate slowly into the goaf under the combined influence of concentration gradients and buoyancy, owing to methane’s lower density compared to air. Excluding the influence of residual mechanical ventilation that may exist in a few high-gas mines after closure, methane tends to first migrate vertically toward the upper regions of the goaf.
Upon reaching the roof zones of the goaf, the gas continues to ascend through fractures in the overlying strata, driven by persistent concentration differentials and pressure gradients, eventually approaching the top of the fractured zone. If the overlying bedrock above the fractured zone is sufficiently thick and possesses low permeability, and no large-scale open faults are present, methane becomes trapped, forming a vertically bounded high-concentration enrichment zone near the top of the fractured zone. The overall process of vertical methane migration and enrichment within a single goaf in a closed coal mine is illustrated in Figure 1.
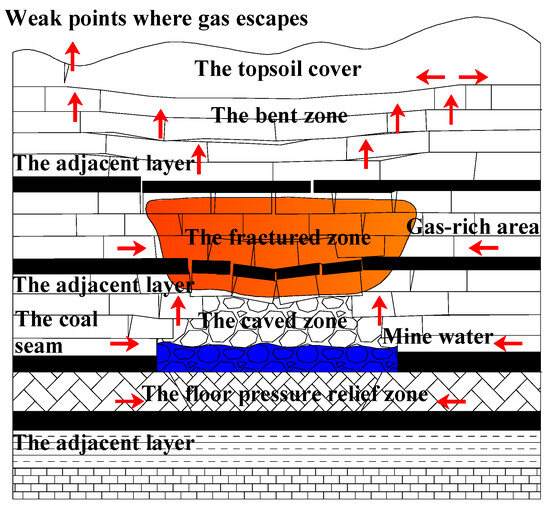
Figure 1.
Schematic diagram of methane vertical migration and enrichment in single goaf of closed coal mine.
- (2)
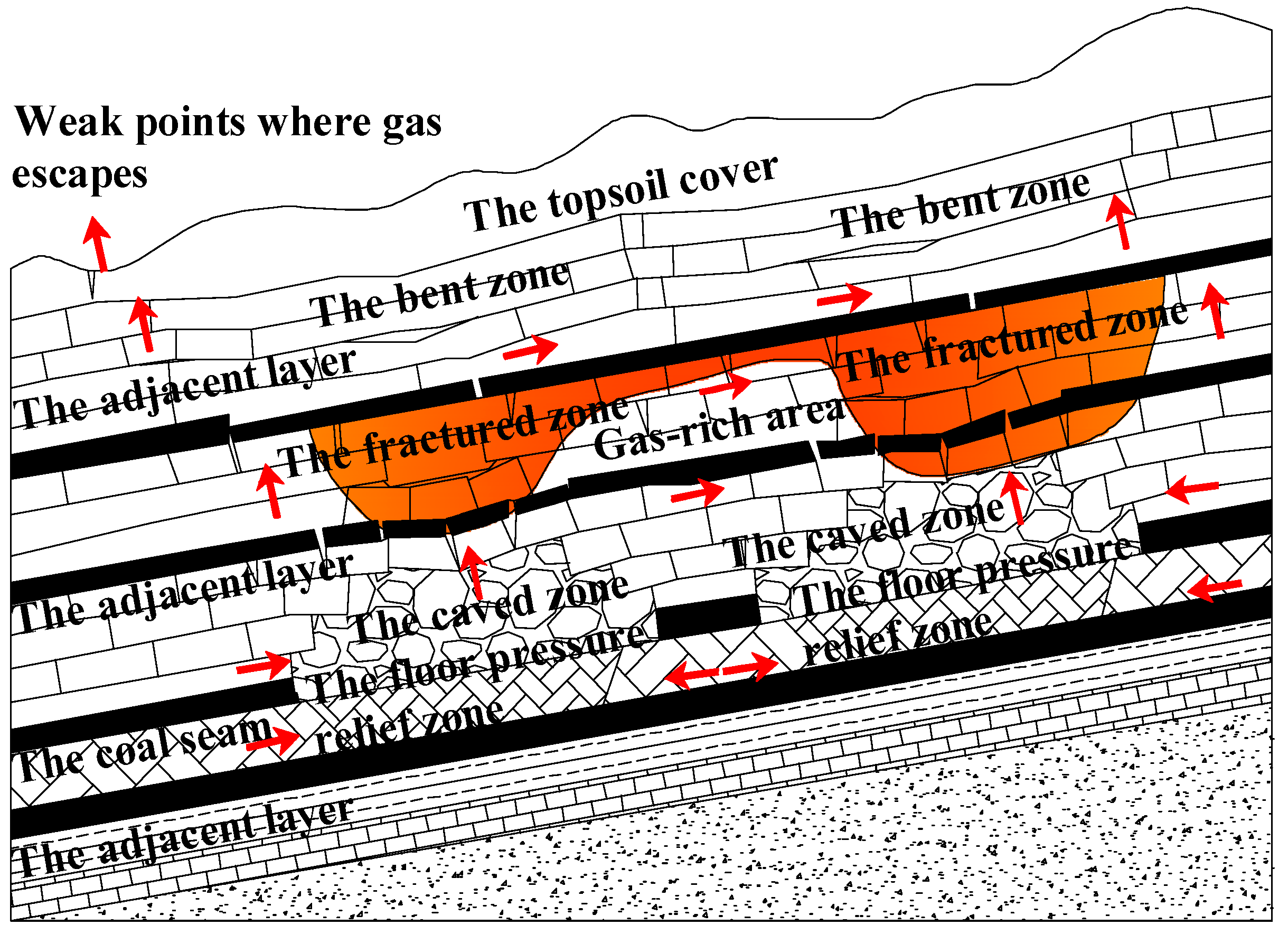
- Migration and enrichment in adjacent inclined goafs
When coal seams are mined using a downward (top-to-bottom) extraction sequence, the initial goaf typically develops a methane-enriched zone in its upper section, consistent with the vertical migration and enrichment pattern described previously for a single goaf. As mining progresses, desorbed methane migrates toward the newly formed goafs, where it accumulates. With the expansion of the goaf areas, the extent of the methane accumulation also increases. If the bending and fractured zones between adjacent goafs remain unconnected, two separate and independent methane-enriched zones are formed. However, once a significant overlap occurs between the two zones, the gas pathways become continuous. In this case, methane from the lower enrichment zone migrates upward into the upper zone, progressively merging into a single, larger methane accumulation area [25]. In multi-seam coal mining scenarios, particular attention should be given to the vertical spacing between coal seams in relation to the height of the overlying and underlying fracture zones. If the interlayer distance substantially exceeds the combined heights of the roof fracture zone in the lower seam and the floor failure zone in the upper seam, the vertical connectivity between seams is likely limited. Under such conditions, each seam can be considered as a relatively independent methane-bearing unit, and the estimation approach may follow the framework applied for single-seam conditions.
Conversely, when the vertical spacing is small and the fracture zones overlap, an effective interconnection between seams is established. In such cases, methane released from the lower seam’s goaf can migrate upward under the influence of buoyancy and pressure gradients, ultimately accumulating within the upper seam’s goaf to form a secondary high-concentration enrichment zone. This cross-seam migration behavior has significant implications for defining reserve boundaries and developing gas extraction strategies.
The migration and enrichment pattern of methane along the inclined direction in closed coal mines is illustrated in Figure 2.
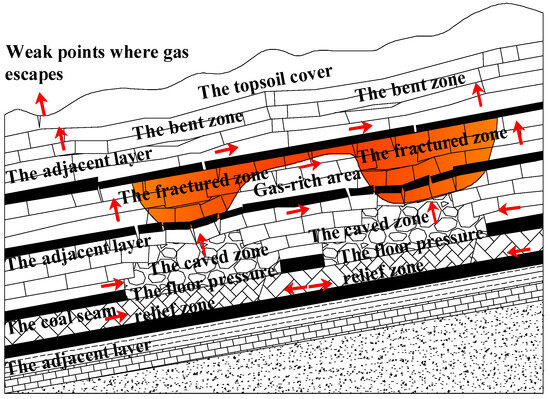
Figure 2.
Schematic diagram of methane migration and enrichment in adjacent inclined goafs of closed coal mine.
2.3. The Role of Methane Dynamics in Reserve Estimation
The identification of high-concentration methane enrichment zones, particularly those formed near the top of the fractured zone under effective sealing conditions, provides a critical spatial boundary for defining the methane reserve estimation domain. These zones represent areas with relatively stable gas accumulation and limited dissipation, making them suitable targets for reserve quantification. Conversely, methane that diffuses beyond the sealed strata or escapes through leakage pathways (e.g., degraded seals, residual fractures) contributes to unquantifiable losses and introduces uncertainty into reserve calculations. Therefore, accurately characterizing the methane migration and retention behavior is essential for selecting appropriate estimation methods and for minimizing errors associated with gas dissipation.
High-concentration methane enrichment zones serve as critical target areas for post-closure gas extraction in abandoned coal mines. Compared with low-concentration methane, high-concentration methane is not only more efficient to extract but also more suitable for purification, transportation, and subsequent utilization as an energy source. Therefore, accurately identifying these zones is essential for enhancing recovery efficiency and optimizing the economic viability of methane resource development.
Integrating migration dynamics with reserve assessment frameworks not only improves the precision of the resource evaluation but also enhances the reliability of subsequent utilization strategies.
2.4. Analysis of Factors Influencing Methane Migration in Closed Coal Mines
- (1)
- Connectivity of roadways in closed coal mines
The connectivity of roadways in closed coal mines plays a critical role in determining the patterns of methane migration and enrichment. In turn, the mine water inflow significantly influences this connectivity, thereby affecting the feasibility of secondary methane recovery [26]. In many mines outside China, mine water is typically directed to the lowest-level roadways during production and is pumped to the surface through designated drainage systems. After mine closure, residual inflows continue to accumulate in these lower roadways, while the main roadways often remain relatively dry or completely free of water [25]. This practice ensures better post-closure roadway connectivity, which facilitates the migration and accumulation of methane within the mine.
- (2)
- Coal mine closure and management methods
Following mine closure, wellheads must be sealed; however, the effectiveness of different sealing techniques varies significantly in terms of methane retention. Over time, the integrity of these seals tends to degrade, leading to substantial methane leakage. This not only results in resource loss but also hampers the potential for secondary methane recovery.
In summary, methane in closed coal mines exists in three states: adsorbed, free, and dissolved. It migrates from the pressure-relief zones in the floor toward the goaf, with the majority accumulating in the caved and fractured zones. A smaller portion escapes to the surface through interlayer fractures in weak sections of the overburden. In cases where multiple inclined goafs are vertically connected, methane from lower goafs can migrate upward under favorable connectivity conditions, eventually forming a unified enrichment zone. Enhancing the monitoring and control of methane in closed mines, along with improving sealing methods, can significantly reduce gas leakage. Additionally, conducting pre-closure interventions—such as clearing roadways and other connected pathways—can expand the effective gas storage space, facilitate methane migration and enrichment, and ultimately reduce the cost of extraction.
3. Research on Method for Estimation of Methane Reserves in Closed Coal Mines
The estimation and extraction methods for methane resources in closed coal mines differ significantly from those applied under conventional geological conditions. The mere presence of methane does not necessarily qualify it for inclusion in the reserve estimation of closed mines. Instead, it is essential to first delineate the resource area that can be feasibly developed using technologies specific to closed mine methane recovery. Only within this defined scope can an appropriate estimation method be selected to quantify the recoverable methane reserves.
3.1. Method for Determining the Estimation Scope of Methane Reserves
According to the results of previous studies in China, the estimation range of methane resources in closed coal mines can be divided into two dimensions: horizontal and vertical. Horizontally, the estimation can be guided by the “three zones” theory in conjunction with residual gas pressure profiles. The vertical cross-section of the estimation area is typically characterized by an asymmetric double-trapezoidal geometry, shaped by the redistribution of tectonic stress. With increasing distance from the primary coal seam, the width of the section expands, and the permeability tensor exhibits anisotropic behavior. Consequently, the mining influence angle can be introduced to define the relationship between the estimated gas-bearing area and its distance from the main seam [25]. Vertically, the extent of the estimation range can be determined based on the height of the pressure-relief and desorption zone, as defined in the “new three zones” theory [27]. This zone represents the region where the mining-induced pressure reduction causes the desorption of adsorbed methane and thus serves as a critical boundary for the vertical reserve evaluation.
3.2. Commonly Used Estimation Methods
3.2.1. Material Balance Method
The material balance method reflects the material balance of reservoir fluids [28], and its principle is to subtract the amount of methane that is desorbed and escapes during the mining process and the amount of methane lost during the period after the closure of the coal mine until the mining of the methane in the closed coal mine. The quantity of methane in closed coal mines can be calculated using Equation (1):
Here, QR is the volume of methane in the closed coal mine (m3), QA is the total methane volume within the area affected by coal mining activities (m3), Q1 is the amount of methane lost due to mining (m3), and Q2 is the amount of methane that escaped after the closure of the coal mine (m3).
The calculation steps for each parameter in the formula are as follows.
- (1)
- Before coal mining, methane mainly exists in the adsorbent, and the total methane volume can be calculated as follows (Equation (2)):
Here, A is the area (m2), H is the average thickness of coal seams (m), φf is the effective porosity of coal seams (%), Swfi is the flow water saturation (%), Bgi is the methane volume coefficient, D is the average density of coal seams (t/m3), fa is the average ash content of coal seams (%), K1 and K2 are conversion factors, and i is the number of coal seams.
- (2)
- The amount of methane lost in the process of coal mining for various reasons can be roughly regarded as composed of two categories: (1) the methane lost through the ventilation system in the coal mine and (2) the methane adsorbed in the mined coal. It can usually be calculated from the measured data pertaining to absolute and relative outflows (Equation (3)):
Here, qg is the relative methane emission rate (m3/t), and G is the mass of the coal produced (t).
- (3)
- The amount of methane reserves lost due to natural dissipation after the closure of the coal mine (Q2) needs to be determined by monitoring and calculating the methane emitted post-closure. Initially, detailed measurements of the methane content and flow must be conducted before the closure of the mine to establish baseline data for methane emissions. Subsequently, methane monitoring equipment, such as methane sensors and flow meters, should be installed to continuously monitor the methane concentration and flow within the mine and at its ventilation outlets. Finally, the total volume of methane released through the mine ventilation system or natural fractures during a specified period is calculated using the data from the flow meters.
3.2.2. Resource Composition Method
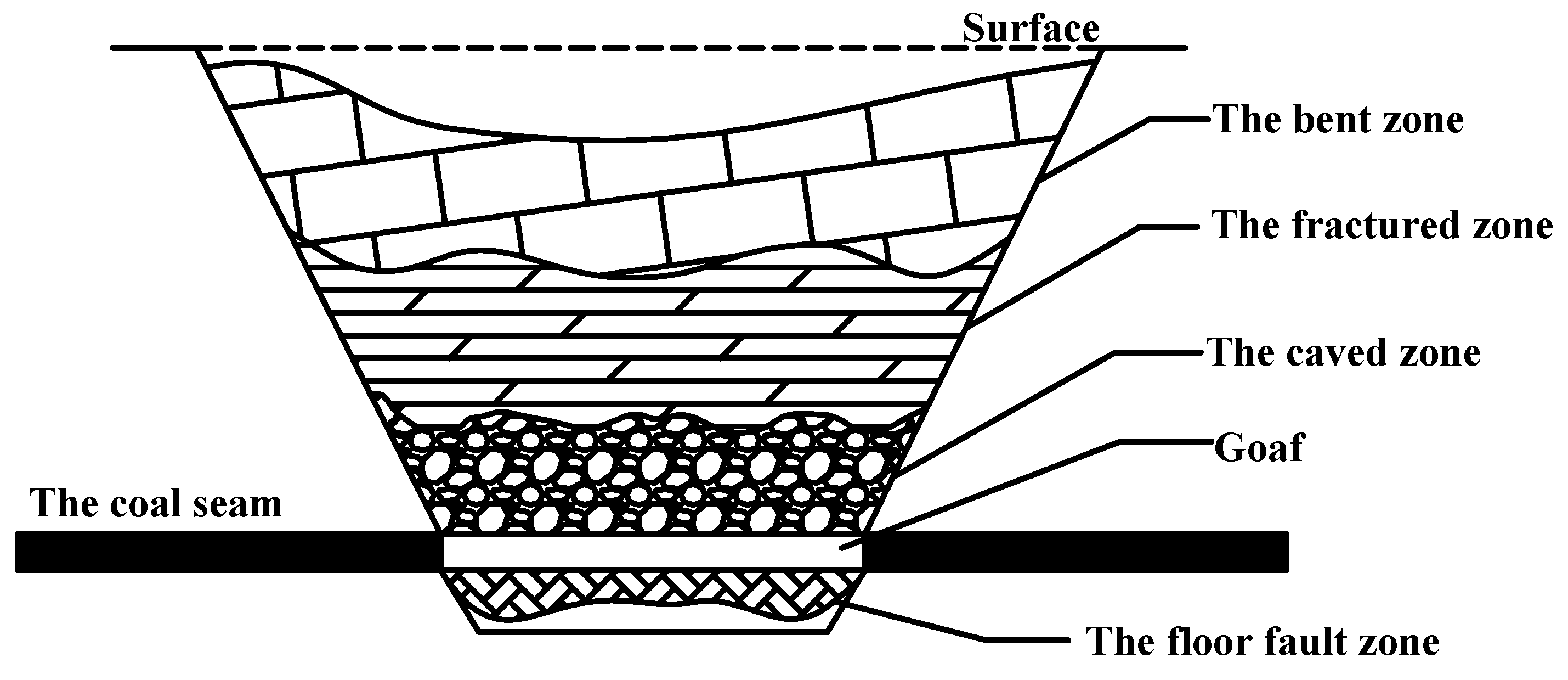
The methane reserves of closed coal mines are mainly free methane and methane adsorbed on the residual coal, and the methane volumes in closed coal mines are estimated by the resource composition method by calculating the volumes of the free and adsorbed methane separately and then adding them [29]. The estimated range is shown in Figure 3.
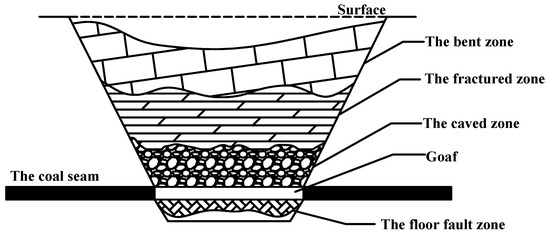
Figure 3.
Distribution range of coalbed methane.
- (i)
- Calculation of free methane volume
(1) Goafs
Here, Qyl is the free methane volume in goafs (m3), V is the volume of the goaf (m3), and gyl is the free methane concentration in the goaf (%).
(2) Caved zone
① Pore volume of rock mass in caved zone
The height of the caved zone can be calculated using Equation (5):
Here, Hm is the height of the caved zone (m), M is the coal mining height (m), θ is the inclination of the coal seam (°), and kp is the rock fragmentation coefficient. The rock fragmentation coefficient is not constant, and its value is related to the stratigraphic structure and rock properties of the overlying rock layer [30].
The pore volume of the caved zone can be calculated using Equation (6):
Here, L1 is the length of the work face in the direction of inclination (m); L2 is the length of the face along the strike (m); a1 is the length of the side at the top of the falling band in the inclined direction (m), and a1 = L1 − 2Hmcotφ, where φ is the fracture angle of the rock formation (°); and b1 is the length of the top of the caved zone along the strike side (m), and b1 = L2-2Hmcotφ [31], where K1 is the porosity of rocks in the caved zone.
② Methane reserves in caved zone
The methane volume in caved zone is calculated as follows:
Here, Q4 is the amount of free methane in the caved zone (m3), Vm is the pore volume of the caved zone (m3), and η1 is the volume fraction of methane in the caved zone.
(3) Fractured zone
① Volume of pores of rock mass in fractured zone
The height of the fractured zone (H1) can be calculated using Equation (8):
② Volume of pores in fractured zone
The volume of pores can be calculated using Equation (9):
③ Methane reserves in the fractured zone
The methane volume in the fractured zone can be calculated as follows:
Here, Q5 is the amount of free methane in the fractured zone (m3), Vn is the pore volume of the fractured zone (m3), η2 is the volume fraction of methane in the fractured zone (%), and K2 is the rock porosity in the fractured zone (%).
(4) Floor fault zone
The pore volume of the rock mass in the floor fault zone is calculated as follows:
Here, V3 is the pore volume of the floor fractured zone (m3); h1 is the maximum depth of failure of the rock mass at the bottom of the coal seam (m); and L3 and L4 are the lengths of the failure zone of the floor along the strike and incline of the working face (m), respectively, and can be calculated according to the literature [32]; L5 and L6 are the lengths of the strike and incline minus the distance between the maximum depth of failure of the coal seam floor rock mass and the end of the working face (m); and K3 is the porosity of the rock during compaction (%).
The free methane volume in the floor fault zone (Q6) can be calculated using Equation (12).
Here, V3 is the pore volume in the floor fractured zone (m3), and η3 is the volume fraction of methane in the floor fault zone (%).
- (ii)
- Estimation of adsorbed methane volume
(1) Residual coal
After the closure of the coal mine, some amount of methane remains adsorbed on the residual coal and continues to desorb from the coal. Therefore, the original methane content cannot be used for calculations. The adsorbed methane in the residual coal includes both desorbable and non-desorbable components [33]. The amount of methane in the residual coal (Qy) can be calculated using Equation (13).
Here, My is the total amount of coal left in the goaf (t), qc is the residual methane content from the coal in the goaf (m3/t), and Xb is the non-desorbable methane content (m3/t).
(2) Coal pillars
The amount of methane reserves in the coal pillars of closed coal mines can be calculated using Equation (14):
Here, Qm is the volume of the residual methane in coal pillars (m3), M1 is the mass of the remaining coal (t), and q2 is the residual methane content of coal pillars in mining seams (m3/t).
(3) Adjacent layers
Here, Ql1 is the methane reserves in adjacent layers (m3), QL is the original methane reserves (disregard methane dispersion) in adjacent layers (m3), mi is the thickness of the ith adjacent coal seam (m), M is the mining height of the working face (m), ηi is the methane emission rate of the ith adjacent layer (%), Woi is the original methane content of the coal seam in the ith adjacent seam (m3/t), and Ml is the coal reserves in adjacent layers (t).
The sum of the abovementioned methane volumes is the estimated total amount of methane (QB) in closed coal mines.
3.2.3. Decline Curve Method
In the decline curve method, the amount of methane is calculated mathematically on the basis of the plot of the rate and time of the methane desorption. In a previous study, through the analysis of the data pertaining to the on-site desorption from a borehole coal core, which refers to the sample of coal extracted from a coal seam during drilling operations, researchers concluded that the plot of the desorption rate of methane versus time is a hyperbola. By fitting these data, the decline curve (describes how the rate of methane emission from coal decreases over time after mining activities have stopped) of the methane emission velocity versus time can be obtained, and the methane reserves of the closed coal mine can then be determined by integrating the curve from the time of the desorption from the borehole coal core to infinity [34].
Here, q is the velocity of methane gushing out at time t (m3/day), qi is the initial methane outburst velocity (m3/day), b is the hyperbolic index, Di is the initial decline rate (year−1), and T is the time that has passed since the mine was closed (years). Furthermore, b and Di can be obtained by the on-site monitoring of the fugitive data pertaining to the methane in the closed coal mine and fitting by using the above formula.
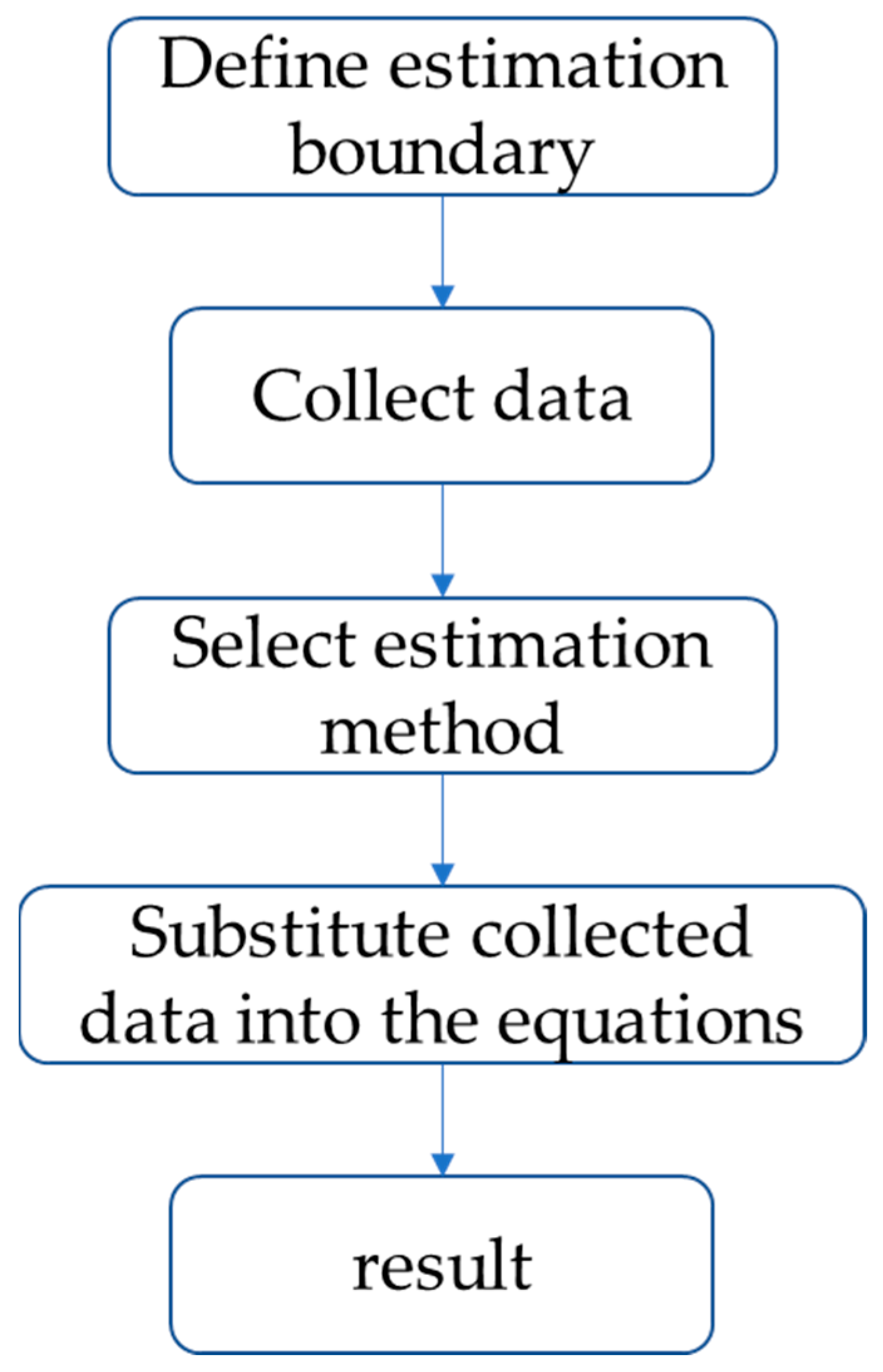
3.3. Estimation Workflow for Methane Reserves
The estimation of methane reserves begins with defining the assessment boundary, primarily focusing on the goaf area and the “three zones”. This is based on parameters such as the goaf area, the coal seam thickness, and the height of the “three zones”. The next step involves data collection, typically sourced from mine records. However, in China, documentation is often incomplete following mine closure, making data quality a critical factor that directly influences both the feasibility and accuracy of the estimation. An appropriate estimation method is then selected based on the type and availability of data, as each method has different input requirements. Finally, the collected parameters are substituted into the selected equations to calculate the reserve. The overall procedure is illustrated in Figure 4.
Figure 4.
Estimation workflow for methane reserve.
4. Case Study on Methane Reserve Estimation
4.1. An Illustrative Example of the Estimation Methods
An illustrative example from a closed coal mine in the Huoxi Coalfield is used to estimate methane reserves and compare the applicability of the aforementioned estimation methods. In Seam No. 2, a total of 30 goafs are present, covering an area of approximately 11.18 km2. Seam No. 5 contains two goafs with a combined area of about 0.19 km2, and Seam No. 6 also has two goafs totaling approximately 0.24 km2. Seam No. 9 contains 17 goafs, covering roughly 3.24 km2, while Seam No. 10 has 34 goafs with a total area of 4.44 km2. Lastly, Seam No. 11 includes 39 goafs, covering about 3.01 km2.
The average thicknesses of Seams No. 2, 2-Sub, 4, 5, 6, 7, 9, 10, and 11 are 3.39 m, 0.75 m, 0.52 m, 0.84 m, 0.89 m, 0.44 m, 0.90 m, 2.48 m, and 1.71 m, respectively. Based on calculations, the total remaining recoverable coal reserves in these seams amount to 53.17 million tons. Seam No. 2 contains only coal pillar reserves and thus has no recoverable resources. The remaining recoverable reserves in Seams No. 2-Sub, 4, 5, 6, 7, 9, 10, and 11 are estimated at 0.4, 0.43, 7.05, 7.63, 0.51, 10.76, 13.06, and 13.34 million tons, respectively. The detailed information on the goaf distribution and characteristics in each seam is provided in Table 2.

Table 2.
Table of goaf parameters [35,36].
As of the mine closure, the cumulative verified coal resource in the entire mining field was 2.9 × 108 t, with an in situ resource reserve of 2.19 × 108 t, including approximately 1.5 × 108 t safeguarded within protective coal pillars. Field measurements indicated an initial methane content of 7.1 m3/t, with absolute and relative methane emission rates of 2.54 m3/min and 1.09 m3/t, respectively. The residual methane content was determined to be 5.106 m3/t.
The methane resource estimation was first conducted using the material balance method. It should be noted that due to incomplete data availability, the total methane resource was approximated by multiplying the coal resource quantity by the initial methane content. Subsequently, these data were substituted into Equation (3) to calculate the volume of methane lost during mining operations. The total methane resource prior to mining (QA) was estimated to be approximately 2.06 × 109 m3, while the methane loss during coal extraction (Q1) was approximately 7.7 × 107 m3. In the absence of measured data on methane emissions following the mine closure, this value was conservatively estimated as 2% of the total resource, yielding Q2 = 4.12 × 107 m3. This assumption is consistent with the lower bound (1–2%) of post-closure methane loss factors reported for abandoned coal mines with good sealing or water-flooded conditions and falls within the range observed in Chinese AMM inventories [37]. Finally, substituting these estimates into Equation (1) resulted in an estimated methane resource of approximately 1.94 × 109 m3 remaining in the closed mine.
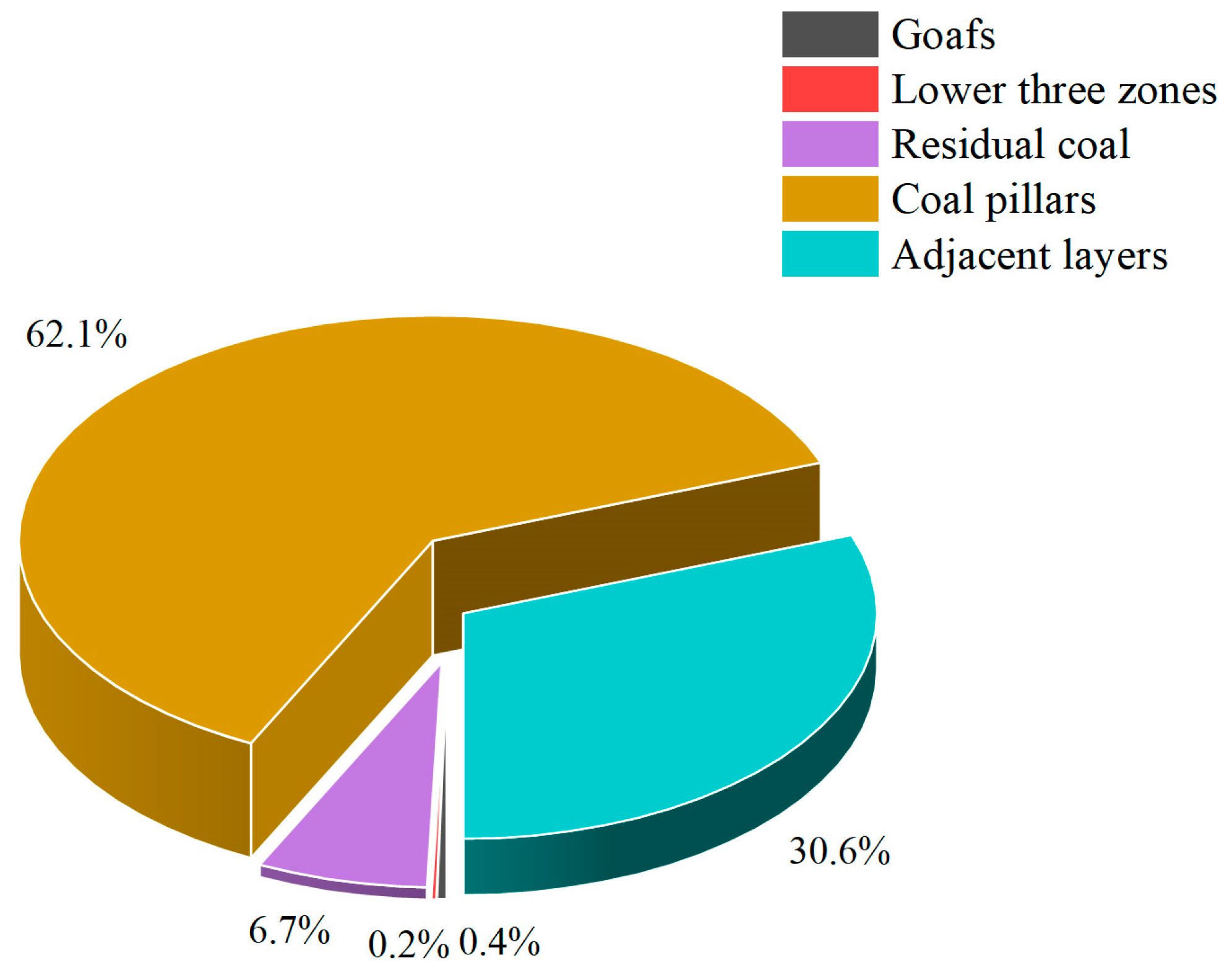
Subsequently, the methane resource was also estimated using the resource composition method. The total amount of coal remaining in the protective coal pillars and goaf areas was 1.66 × 108 t. By multiplying this coal mass with the residual methane content, the adsorbed methane resource within the goaf was estimated to be 8.49 × 108 m3. The result was derived based on the calculation from Equations (13) and (14). Additionally, the coal resource in adjacent seams was approximately 5.32 × 107 t, corresponding to an adsorbed methane volume of 3.78 × 108 m3, as calculated using Equation (2). Field measurements indicated that the free methane concentration in different goafs varied, generally ranging between 6% and 10%. For calculation convenience and to ensure data representativeness, a concentration of 8% was assumed in the estimation. The total volume of the goaf was approximated by summing the products of the goaf area and the thickness for each coal seam, yielding an estimated goaf volume of 5.73 × 107 m3. Therefore, the volume of free methane in the goaf can be calculated using Equation (4), yielding a result of approximately 4.58 × 106 m3. The collapsed zone, fractured zone, and floor fault zone—collectively referred to as the “lower three zones”—were also considered. Their pore volumes were estimated at 8.59 × 106 m3, 1.43 × 107 m3, and 5.73 × 106 m3, respectively, with corresponding methane volume fractions of 8%, 10%, and 8%. The total free methane resource in the lower three zones was thus calculated to be 2.29 × 106 m3, as calculated using Equations (7), (10), and (12). As the preserved mine data contain the volumes of the “lower three zones”, it is unnecessary to calculate their heights separately; if required, the formulas provided above can be used for the calculation. By summing the methane volumes from all these components, the total methane resource estimated using the resource composition method was approximately 1.23 × 109 m3. The composition of various methane resources is illustrated in Figure 5.
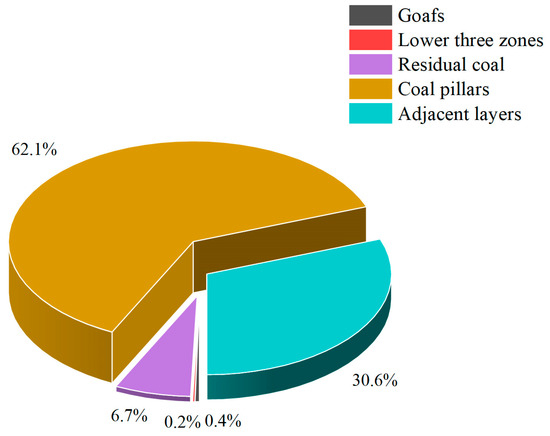
Figure 5.
Composition of methane resources.
As shown in Figure 5, methane in closed coal mines predominantly exists in the adsorbed state within the coal matrix, while the proportion of free methane is relatively low. Among the various sources, coal pillars contain the largest share of the total methane reserves.
In China, research on the decline curve method has been conducted mainly at the theoretical level. Due to factors such as the relatively simple closure procedures of coal mines and insufficient on-site monitoring, this method has rarely been applied in practice, which is the main reason it could not be used for estimation in this study. Nevertheless, from a theoretical perspective, the method is feasible and represents a key direction for future research on methane reserve estimation in closed coal mines.
4.2. Results and Discussion
The results derived from the equations described above are summarized in Table 3.

Table 3.
Results of methane reserve estimation using different equations.
The results derived from the material balance and resource composition methods show substantial differences in estimated methane reserves for the Huoxi Coalfield. The material balance method yielded an estimate of 1.94 × 109 m3, while the resource composition method produced a lower value of 1.23 × 109 m3. This discrepancy reflects differing assumptions and boundary definitions: the material balance method estimates the total remaining methane based on pre- and post-mining losses, potentially overestimating reserves when post-closure losses are poorly constrained. In contrast, the resource composition method focuses on physically defined volumes and separates adsorbed and free methane, providing a more conservative and geologically realistic result. The majority of the estimated methane (over 90%) exists in an adsorbed form, primarily within coal pillars and residual coal seams. Free methane in the goaf and fractured zones contributes less than 1% of total reserves. This indicates that any future recovery strategy must focus on the desorption from the residual coal, requiring effective stimulation and drainage techniques.
The comparison also highlights the sensitivity of reserve estimates to key input parameters. For example, the assumed post-closure loss rates, gas content in residual coal, and porosity values in disturbed zones can significantly impact the outcome.
Each method presents different strengths and limitations. The material balance method is more suitable for recently closed mines with reliable data; the resource composition method offers better applicability to long-closed or poorly documented sites due to its reliance on spatial and geological parameters. The decline curve method, although not applied here due to limited monitoring data, could complement the other methods by enabling production forecasting when continuous methane emission records exist.
These findings support the adoption of a multi-method approach for methane reserve estimation in closed coal mines. Cross-validation among methods enhances the confidence in the estimates, while a sensitivity analysis helps prioritize data collection for parameters with the largest influence on the uncertainty.
4.3. Comparative Analysis of Advantages and Limitations
All three of the aforementioned methods are theoretically applicable for estimating methane reserves in closed coal mines; however, they differ significantly in principles, data requirements, and applicability. Each method has its own strengths and limitations. A detailed comparison is provided in Table 4.

Table 4.
Comparison for three estimation methods [38,39,40].
The material balance method is conceptually straightforward and provides a theoretical upper bound for methane reserves. It is suitable for mines that have been closed for a short period and retain comprehensive operational records. However, it requires the accurate quantification of methane losses during both the mining and post-closure phases. For mines that have been abandoned for extended periods, key parameters are often missing or unreliable, reducing the method’s accuracy. Therefore, it is more appropriate for macro-level planning and total resource assessments.
The resource composition method is systematic, with clearly defined parameters that are relatively accessible [40]. It differentiates between adsorbed and free methane, offering estimates that better reflect geological realities and extractable conditions. However, it requires detailed data on residual methane in coal pillars and adjacent strata, making it heavily dependent on the completeness of geological and mining records. This method is best suited for project-level development planning and risk assessment.
The decline curve method requires only a limited amount of historical data to predict total reserves and is operationally simple [41]. However, it does not account for un-desorbed adsorbed methane or dissolved methane and relies on the long-term monitoring of emission rates. The accuracy of the curve fitting can be significantly affected by incomplete or noisy datasets. This method is best suited for mines with abundant historical methane extraction records and can support mid- to long-term production forecasting [42,43].
To improve the scientific rigor and credibility of methane reserve evaluations, it is recommended that multiple methods be applied in parallel, with the cross-validation of results to enhance the robustness of resource assessments.
5. Conclusions
This study reviewed three mainstream methods for estimating methane reserves in closed coal mines in China and applied them to a case study from the Huoxi Coalfield. The following conclusions can be drawn:
- (1)
- Method selection matters: The material balance method provides an upper-bound estimate but is sensitive to missing historical data. The resource composition method yields more conservative and realistic results by defining physical boundaries and gas occurrence states. The decline curve method can support production forecasting but requires long-term monitoring data.
- (2)
- Adsorbed methane dominates: Most of the methane in closed coal mines exists in the adsorbed form, primarily in coal pillars and residual seams. Free methane contributes a minor share but can serve as an early-stage target for drainage.
- (3)
- Data quality is critical: Reserve estimates are highly sensitive to parameters such as the residual gas content, post-closure loss rates, and porosity assumptions. Data incompleteness is a key limitation, especially in older mines.
Future research priorities include the following:
- Mandatory data archiving policies before mine closures, including the gas content, seam geometry, and emission logs.
- The improved post-closure characterization of the “three zones”, especially the fracture connectivity across goafs.
- The development of a reliability assessment framework for reserve estimation, incorporating an uncertainty and cross-method comparison.
Author Contributions
Formal analysis, investigation, writing—original draft preparation, F.Z. and Y.H.; resources, data curation, super vision, project administration, funding acquisition, F.Z. and C.W.; writing—review and editing, F.Z., Q.L. and Y.H. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research was supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (Nos. 51974108 and 51404093), the Scientific and Technological Project of Henan Province (242102320213), the Natural Science Foundation of Henan Province (No. 232300420077), the Fundamental Research Funds for the Universities of Henan Province (No. NSFRF240638), the Post-doctoral Research Project in Henan Province (No. 001701014).
Data Availability Statement
The original contributions presented in this study are included in the article. Further inquiries can be directed to the corresponding author.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
- Pavloudakis, F.; Roumpos, C.; Spanidis, P.M. Planning the Closure of Surface Coal Mines Based on Circular Economy Principles. Circ. Econ. Sustain. 2024, 4, 75–96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.; Li, J.R. Recovery of greenhouse gas as cleaner fossil fuel contributes to carbon neutrality. Green Energy Environ. 2023, 8, 351–353. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Q.C.; Wu, J.J.; Li, Q.; Wang, F.; Cheng, Y.F. Sediment Instability Caused by Gas Production from Hydrate-bearing Sediment in Northern South China Sea by Horizontal Wellbore: Sensitivity Analysis. Nat. Resour. Res. 2025, 34, 1667–1699. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- National Energy Administration of China. Outline of the 14th Five-Year Plan for Energy Development (2021–2025). Available online: http://www.nea.gov.cn/ (accessed on 13 November 2022).
- Liu, H.; Yang, Y.; Jiao, W.; Wang, S.; Cheng, F. A New Assessment Method for the Redevelopment of Closed Coal Mine—A Case Study in Shanxi Province in China. Sustainability 2022, 14, 9759. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, C.; Li, G.; Yu, C. Methods for the Geophysical Exploration and Sustainable Utilisation of Coalbed Methane Resources in Abandoned Mines of Shanxi, China. Sustainability 2024, 16, 2677. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Z.; Zhang, C.; Su, P.; Zhao, G.; Wang, Z.; Li, Y.; Li, Y.; Wang, M.; Qiao, P.; Guo, J.; et al. The feasibility and prospects of coal mine water as a cooling medium for data centers. J. Environ. Chem. Eng. 2025, 13, 117365. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sechman, H.; Kotarba, M.; Kędzior, S.; Kochman, A.; Twaróg, A. Fluctuations in methane and carbon dioxide concentrations in the near-surface zone and their genetic characterization in abandoned and active coal mines in the SW part of the Upper Silesian Coal Basin, Poland. Int. J. Coal Geol. 2020, 227, 103529. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krzemień, A.; Sánchez, A.S.; Fernández, P.R.; Zimmermann, K.; Coto, F.G. Towards sustainability in underground coal mine closure contexts: A methodology proposal for environmental risk management. J. Cleaner Prod. 2016, 139, 1044–1056. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kivinen, S. Sustainable Post-Mining Land Use: Are Closed Metal Mines Abandoned or Re-Used Space? Sustainability 2017, 9, 1705. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuan, L.; Jiang, Y.; Wang, K.; Zhao, Y.; Hao, X.; Chao, X.U. Precision exploitation and utilization of closed/abandoned mine resources in China. J. China Coal Soc. 2018, 43, 14–20. [Google Scholar]
- Yuan, L.; Yang, K. Further discussion on the scientific problems and countermeasures in the utilization of abandoned mines. J. China Coal Soc. 2021, 46, 16–24. [Google Scholar]
- Yuan, L.; Zhang, T.; Zhang, Q.; Jiang, B.; Lü, X.; Li, S.; Fu, Q. Construction of green, low-carbon and multi-energy complementary system for abandoned mines under global carbon neutrality. J. China Coal Soc. 2022, 47, 2131–2139. [Google Scholar]
- Feng, F.S.; Zhang, J.Q.; Wang, Y. Classified utilization and grade evaluation of closed/abandoned mines in China. Sci. Technol. Rev. 2022, 40, 105–112. [Google Scholar]
- Yin, Q.Z.; Chen, Z.; Feng, Q.; Geng, L.; Lian, L.; Li, F.; Liu, N. Discussion on the recommended models for resource reuse of closed coal mines in main mining areas of Hebei Province. Coal Geol. Explor. 2021, 49, 113–120. [Google Scholar]
- Yin, Q.; Chen, Z.; Hou, T.; Liang, J.; Geng, L.; Li, B.; Liang, J.; Song, P. Construction and practice of geological condition e valuation system for underground coal gasification in closed coal mines. Saf. Coal Mines 2023, 54, 43–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, Y.; Li, Z.; Zhu, S.; Chen, Q.; Wang, X.; Qin, C. Research status and reduction strategies of methane emissions from closed/abandoned coal mines. J. China Coal Soc. 2023, 48, 1645–1660. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, M.; Fu, X.; Chen, Z.; Liu, T.; Zhang, M.; Kang, J. A new approach to evaluate abandoned mine methane resources based on the zoning of the mining-disturbed strata. Energy 2023, 274, 127307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, D.; Su, X.B.; Su, L.N. Theory of gas traps in stope and its application in ground extraction of abandoned mine gas: Part 1—Gas trap in stope and resources estimation. J. Pet. Sci. Eng. 2021, 207, 109285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adsul, T.; Ghosh, S.; Kumar, S.; Tiwari, B.; Dutta, S.; Varma, A.K. Biogeochemical Controls on Methane Generation: A Review on Indian Coal Resources. Minerals 2023, 13, 695. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karacan, C.Ö.; Warwick, P.D. Assessment of coal mine methane (CMM) and abandoned mine methane (AMM) resource potential of longwall mine panels: Example from Northern Appalachian Basin, USA. Int. J. Coal Geol. 2019, 208, 37–53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Q.; Li, Q.C.; Wang, F.; Ning, X.; Wang, Y.L.; Bai, B.J. Settling behavior and mechanism analysis of kaolinite as a fracture proppant of hydrocarbon reservoirs in CO2 fracturing fluid. Colloids Surf. A: Physicochem. Eng. Asp. 2025, 724, 137463. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, J.G.; Mao, J.R. Research progress on gas resource evaluation, extraction and utilization in abandoned coal mines in China. Saf. Coal Mines 2021, 52, 162–169. [Google Scholar]
- Li, Q.; Cheng, Y.; Zhang, H.; Yan, C.; Liu, Y. Simulating the effect of hydrate dissociation on wellhead stability during oil and gas development in deepwater. J. Ocean. Univ. China 2018, 17, 35–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, H.D. Study on Distribution and Evaluation Methodology of CBM (Coal Mine Gas) Resources in Coal Resource Depleting Mine; China University of Mining and Technology: Xuzhou, China, 2015. [Google Scholar]
- Hu, W.Y.; Li, Z.M.; Wang, C.X. Geological environmental hazards caused by abandoned mine. Coal Geol. Explor. 2002, 30, 33–35. [Google Scholar]
- Han, B.S.; Zhang, X.M.; Zhang, Q. Theoretical study on calculation limits of CBM resource of abandoned coal mine. Coal Geol. Explor. 2004, 32, 29–31. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, J.; Wang, Z.M. Application of material balance method to productivity forecast in coalbed methane reservoir. Coal Geol. Explor. 2009, 37, 23–26. [Google Scholar]
- Li, X.M. Assessment Method and Application of Gas Resources in Abandoned Mine. Min. Res. Dev. 2019, 39, 101–104. [Google Scholar]
- Meng, Z.P.; Shi, X.C.; Liu, S.S.; Tian, Y.D.; Li, C. Evaluation model of CBM resources in abandoned coal mine and its application. J. China Coal Soc. 2016, 41, 537–544. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, G.X. Rock Fragmentation Law of Roof Cutting and Pressure Releasing in Medium-thick Deep Coal Seam. Coal Eng. 2019, 51, 118–121. [Google Scholar]
- Li, D. Calculation of Coalbed Methane Resources in Mining Stability Zone Based on Gas Emission. Saf. Coal Mines 2020, 51, 162–166. [Google Scholar]
- Yuan, M. Experimental Study of the influence of Solidity Coefficient on Permeability of Coal Containing Gas. Min. Res. Dev. 2012, 32, 39–42. [Google Scholar]
- Han, B.S.; Li, J.W.; Dong, M.T. Estimation of Abandoned Mine CBM Resources through Drop-Down Curves. Coal Geol. China 2005, 17, 37–39+46. [Google Scholar]
- Yi, X.; Zhang, M.; Deng, J.; Xiao, Y.; Chen, W.; Heris, S.Z. Effects on environmental conditions and limiting parameters for spontaneous combustion of residual coal in underground goaf. Process Saf. Environ. Prot. 2024, 187, 1378–1389. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tao, Y.; Luo, X.; Zhou, J.; Wu, Y.; Zhang, L.; Liu, Y. Site selection for underground pumped storage plant using abandoned coal mine through a hybrid multi-criteria decision-making framework under the fuzzy environment: A case in China. J. Energy Storage. 2022, 56, 105957. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Innovative Green Development Program. China Coal Mine Methane Emissions: Current Status and Policy Options. 2022. Available online: https://www.igdp.cn/wp-content/uploads/2023/01/2022-10-IGDP-Policy-Brief-CN-Methane-Reduction-in-Coal-Mines-in-China.pdf (accessed on 8 August 2023).
- Hua, X.; Qin, H.; Hao, D.; Shi, B.; Lin, B.; Zhao, Z.; Zhang, M. Research status and prospect of gas extraction in abandoned/closed coal mines in China. Coal Sci. Technol. 2025, 53, 15–28. [Google Scholar]
- Kim, Y.; Park, S.; Lee, H.P.; Sun, W.; Ouchi, H.; Jeong, H. Estimation of CO2 storage capacities in saline sandstone aquifers using material balance considering CO2 dissolution trapping. Fuel 2026, 404, 136143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pratama, M.A.; Al Qoroni, O.; Rahmatullah, I.K.; Jameel, M.F.; Weijermars, R. Probabilistic production forecasting and reserves estimation: Benchmarking Gaussian decline curve analysis against the traditional Arps method (Wolfcamp shale case study). Geoenergy Sci. Eng. 2024, 232, 212737. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Q.; Wang, F.; Wang, Y.; Zhang, J.; Yu, X.; Zhao, M.; Zhou, C.; Forson, K.; Shi, S.; Zhao, Y.; et al. Influence of organoboron cross-linker and reservoir characteristics on filtration and reservoir residual of guar gum fracturing fluid in low-permeability shale gas reservoirs. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2022, 29, 82975–82985. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Q. Reservoir Science: A Multi-Coupling Communication Platform to Promote Energy Transformation, Climate Change and Environmental Protection. Reserv. Sci. 2025, 1, 1–2. [Google Scholar]
- Li, Q.; Wang, Y.; Wang, X.; Yu, H.; Li, Q.; Wang, F.; Bai, H.; Kobina, F. An application of thickener to increase viscosity of liquid CO2 and the assessment of the reservoir geological damage and CO2 utilization. Energy Sources Part A Recovery Util. Environ. Eff. 2019, 41, 368–377. [Google Scholar]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).