Eudragit® S 100 Coating of Lipid Nanoparticles for Oral Delivery of RNA
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials
2.2. Preparation of Lipid Nanoparticles
2.3. mRNA Encapsulation
2.4. Differential Light Scattering (DLS) and Cryo-TEM Imaging
2.5. Gel Retardation and Nuclease Stability Assay
2.6. Cell Culture, Cytotoxicity and In Vitro Transfection
2.7. Macrophage Polarization of mRNA-LNPs
2.8. Preparation of Eu-Coated Lipid Nanoparticles (Eu-LNPs)
2.9. Eu-LNP In Vitro Transfection
2.10. Evaluation of Eu-LNPs Stability After Treatment with Simulated Gastric Fluid (SGF) and Transfection of the Particles Following Either SGF or Simulated Gastric Fluid (SIF) Treatment
2.11. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Characterization of LNPs
3.2. LNPs Encapsulate mRNA with Optimal Morphological Characteristics and Payload Retention
3.3. LNPs Protected the Nucleic Acid Load from RNase Degradation
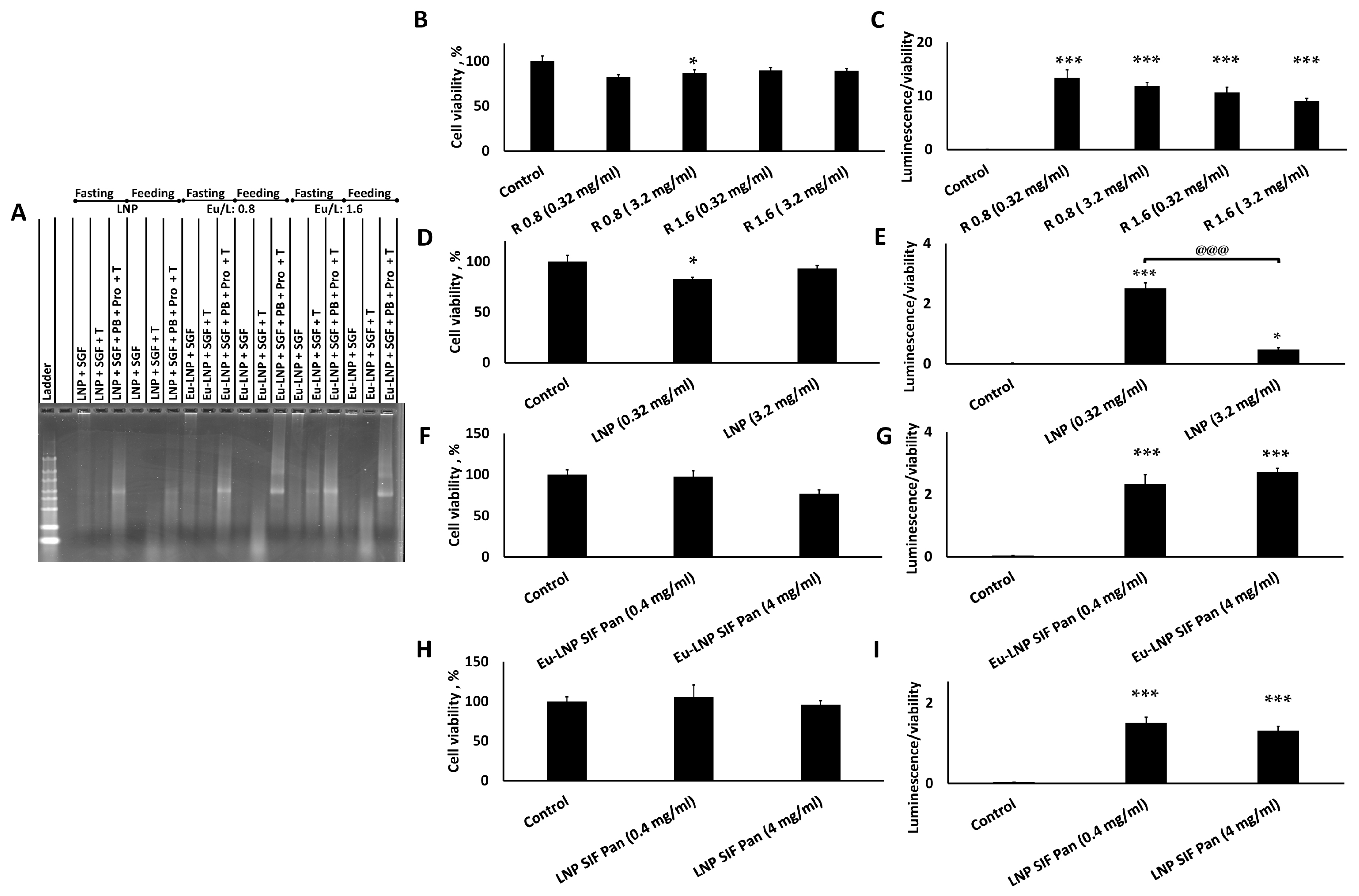
3.4. LNPs Demonstrated Limited Cytotoxicity and Inflammatory Response but Strong Transfection In Vitro
3.5. LNPs Were Released from Their Eu-Coating with Intact Nucleic Acid in a Neutral to Basic Environment
3.6. Eu-LNPs Produce Strong Transfection Following Eu Dissolution
3.7. Eu-LNPs Protected mRNA Against Simulated Gastric Fluids and Showed Significant Transfection After Treatment with SGF-Pep and SIF-Pan
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| LNPs | Lipid nanoparticles |
| Eu | Eudragit® |
| Eu-LNPs | Eudragit® coated LNPs |
| PB | Phosphate buffer at pH 8 |
| Arg-1 | Arginase-1 |
| iNOS | Inducible nitric oxide synthase |
| Eu/L | Eudragit® to lipid weight to weight ratio |
| WPB | With PB treatment |
| WTPB | Without PB treatment |
| SGF | Simulated gastric fluid |
| SIF | Simulated intestinal fluid |
| Pro | Protease inhibitor |
| Pep | Pepsin |
| Pan | Pancreatin |
| LFA | Lipofectamine |
| SEM | Standard error of the mean |
References
- Naeem, S.; Zhang, J.; Zhang, Y.; Wang, Y. Nucleic acid therapeutics: Past, present, and future. Mol. Ther. Nucleic Acids 2025, 36, 102440. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, M.M.; Bahal, R.; Rasmussen, T.P.; Manautou, J.E.; Zhong, X.B. The growth of siRNA-based therapeutics: Updated clinical studies. Biochem. Pharmacol. 2021, 189, 114432. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hald Albertsen, C.; Kulkarni, J.A.; Witzigmann, D.; Lind, M.; Petersson, K.; Simonsen, J.B. The role of lipid components in lipid nanoparticles for vaccines and gene therapy. Adv. Drug Deliv. Rev. 2022, 188, 114416. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lu, R.M.; Hsu, H.E.; Perez, S.; Kumari, M.; Chen, G.H.; Hong, M.H.; Lin, Y.S.; Liu, C.H.; Ko, S.H.; Concio, C.A.P.; et al. Current landscape of mRNA technologies and delivery systems for new modality therapeutics. J. Biomed. Sci. 2024, 31, 89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Haque, M.A.; Shrestha, A.; Mikelis, C.M.; Mattheolabakis, G. Comprehensive analysis of lipid nanoparticle formulation and preparation for RNA delivery. Int. J. Pharm. X 2024, 8, 100283. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nsairat, H.; Alshaer, W.; Odeh, F.; Esawi, E.; Khater, D.; Bawab, A.A.; El-Tanani, M.; Awidi, A.; Mubarak, M.S. Recent advances in using liposomes for delivery of nucleic acid-based therapeutics. OpenNano 2023, 11, 100132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suzuki, Y.; Ishihara, H. Difference in the lipid nanoparticle technology employed in three approved siRNA (Patisiran) and mRNA (COVID-19 vaccine) drugs. Drug Metab. Pharmacokinet. 2021, 41, 100424. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lim, S.A.; Cox, A.; Tung, M.; Chung, E.J. Clinical progress of nanomedicine-based RNA therapies. Bioact. Mater. 2022, 12, 203–213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, L.; Tang, C.; Yin, C. Oral delivery of shRNA and siRNA via multifunctional polymeric nanoparticles for synergistic cancer therapy. Biomaterials 2014, 35, 4589–4600. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hossian, A.; Mackenzie, G.G.; Mattheolabakis, G. miRNAs in gastrointestinal diseases: Can we effectively deliver RNA-based therapeutics orally? Nanomedicine 2019, 14, 2873–2889. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kang, S.H.; Revuri, V.; Lee, S.J.; Cho, S.; Park, I.K.; Cho, K.J.; Bae, W.K.; Lee, Y.K. Oral siRNA Delivery to Treat Colorectal Liver Metastases. ACS Nano 2017, 11, 10417–10429. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abramson, A.; Kirtane, A.R.; Shi, Y.; Zhong, G.; Collins, J.E.; Tamang, S.; Ishida, K.; Hayward, A.; Wainer, J.; Rajesh, N.U.; et al. Oral mRNA delivery using capsule-mediated gastrointestinal tissue injections. Matter 2022, 5, 975–987. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ball, R.L.; Bajaj, P.; Whitehead, K.A. Oral delivery of siRNA lipid nanoparticles: Fate in the GI tract. Sci. Rep. 2018, 8, 2178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suri, K.; Pfeifer, L.; Cvet, D.; Li, A.; McCoy, M.; Singh, A.; Amiji, M.M. Oral delivery of stabilized lipid nanoparticles for nucleic acid therapeutics. Drug Deliv. Transl. Res. 2025, 15, 1755–1769. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nikam, A.; Sahoo, P.R.; Musale, S.; Pagar, R.R.; Paiva-Santos, A.C.; Giram, P.S. A Systematic Overview of Eudragit® Based Copolymer for Smart Healthcare. Pharmaceutics 2023, 15, 587. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vollrath, A.; Schubert, S.; Windhab, N.; Biskup, C.; Schubert, U.S. Labeled Nanoparticles Based on Pharmaceutical EUDRAGIT® S 100 Polymers. Macromol. Rapid Commun. 2010, 31, 2053–2058. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khan, M.Z.; Prebeg, Z.; Kurjakovic, N. A pH-dependent colon targeted oral drug delivery system using methacrylic acid copolymers. I. Manipulation Of drug release using Eudragit L100-55 and Eudragit S100 combinations. J. Control. Release 1999, 58, 215–222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, S.H.; Back, S.Y.; Song, J.G.; Han, H.K. Enhanced oral delivery of insulin via the colon-targeted nanocomposite system of organoclay/glycol chitosan/Eudragit®S100. J. Nanobiotechnol. 2020, 18, 104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, S.; Guo, F.; Deng, T.; Zhu, S.; Liu, W.; Zhong, H.; Yu, H.; Luo, R.; Deng, Z. Eudragit S100-Coated Chitosan Nanoparticles Co-loading Tat for Enhanced Oral Colon Absorption of Insulin. AAPS PharmSciTech 2017, 18, 1277–1287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- De Leo, V.; Di Gioia, S.; Milano, F.; Fini, P.; Comparelli, R.; Mancini, E.; Agostiano, A.; Conese, M.; Catucci, L. Eudragit S100 Entrapped Liposome for Curcumin Delivery: Anti-Oxidative Effect in Caco-2 Cells. Coatings 2020, 10, 114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Catalan-Latorre, A.; Ravaghi, M.; Manca, M.L.; Caddeo, C.; Marongiu, F.; Ennas, G.; Escribano-Ferrer, E.; Peris, J.E.; Diez-Sales, O.; Fadda, A.M.; et al. Freeze-dried eudragit-hyaluronan multicompartment liposomes to improve the intestinal bioavailability of curcumin. Eur. J. Pharm. Biopharm. 2016, 107, 49–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alghurabi, H.; Tagami, T.; Ogawa, K.; Ozeki, T. Preparation, Characterization and In Vitro Evaluation of Eudragit S100-Coated Bile Salt-Containing Liposomes for Oral Colonic Delivery of Budesonide. Polymers 2022, 14, 2693. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barea, M.J.; Jenkins, M.J.; Gaber, M.H.; Bridson, R.H. Evaluation of liposomes coated with a pH responsive polymer. Int. J. Pharm. 2010, 402, 89–94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Barea, M.J.; Jenkins, M.J.; Lee, Y.S.; Johnson, P.; Bridson, R.H. Encapsulation of Liposomes within pH Responsive Microspheres for Oral Colonic Drug Delivery. Int. J. Biomater. 2012, 2012, 458712. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chander, N.; Basha, G.; Yan Cheng, M.H.; Witzigmann, D.; Cullis, P.R. Lipid nanoparticle mRNA systems containing high levels of sphingomyelin engender higher protein expression in hepatic and extra-hepatic tissues. Mol. Ther. Methods Clin. Dev. 2023, 30, 235–245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Leung, A.K.; Hafez, I.M.; Baoukina, S.; Belliveau, N.M.; Zhigaltsev, I.V.; Afshinmanesh, E.; Tieleman, D.P.; Hansen, C.L.; Hope, M.J.; Cullis, P.R. Lipid Nanoparticles Containing siRNA Synthesized by Microfluidic Mixing Exhibit an Electron-Dense Nanostructured Core. J. Phys. Chem. C Nanomater. Interfaces 2012, 116, 18440–18450. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Larson, N.R.; Hu, G.; Wei, Y.; Tuesca, A.D.; Forrest, M.L.; Middaugh, C.R. pH-Dependent Phase Behavior and Stability of Cationic Lipid-mRNA Nanoparticles. J. Pharm. Sci. 2022, 111, 690–698. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheung, C.C.L.; Al-Jamal, W.T. Sterically stabilized liposomes production using staggered herringbone micromixer: Effect of lipid composition and PEG-lipid content. Int. J. Pharm. 2019, 566, 687–696. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cui, L.; Renzi, S.; Quagliarini, E.; Digiacomo, L.; Amenitsch, H.; Masuelli, L.; Bei, R.; Ferri, G.; Cardarelli, F.; Wang, J.; et al. Efficient Delivery of DNA Using Lipid Nanoparticles. Pharmaceutics 2022, 14, 1698. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Belliveau, N.M.; Huft, J.; Lin, P.J.; Chen, S.; Leung, A.K.; Leaver, T.J.; Wild, A.W.; Lee, J.B.; Taylor, R.J.; Tam, Y.K.; et al. Microfluidic Synthesis of Highly Potent Limit-size Lipid Nanoparticles for In Vivo Delivery of siRNA. Mol. Ther. Nucleic Acids 2012, 1, e37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lokugamage, M.P.; Vanover, D.; Beyersdorf, J.; Hatit, M.Z.C.; Rotolo, L.; Echeverri, E.S.; Peck, H.E.; Ni, H.; Yoon, J.K.; Kim, Y.; et al. Optimization of lipid nanoparticles for the delivery of nebulized therapeutic mRNA to the lungs. Nat. Biomed. Eng. 2021, 5, 1059–1068. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blakney, A.K.; McKay, P.F.; Yus, B.I.; Aldon, Y.; Shattock, R.J. Inside out: Optimization of lipid nanoparticle formulations for exterior complexation and in vivo delivery of saRNA. Gene Ther. 2019, 26, 363–372. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hossian, A.; Jois, S.D.; Jonnalagadda, S.C.; Mattheolabakis, G. Nucleic Acid Delivery with alpha-Tocopherol-Polyethyleneimine-Polyethylene Glycol Nanocarrier System. Int. J. Nanomed. 2020, 15, 6689–6703. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, H.; Huang, N.; Zhu, W.; Wu, J.; Yang, X.; Teng, W.; Tian, J.; Fang, Z.; Luo, Y.; Chen, M.; et al. Modulation the crosstalk between tumor-associated macrophages and non-small cell lung cancer to inhibit tumor migration and invasion by ginsenoside Rh2. BMC Cancer 2018, 18, 579. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, S.; Wang, L.; Liu, W.; Wu, Y.; Yuan, Z. The synergistic effect of homocysteine and lipopolysaccharide on the differentiation and conversion of raw264.7 macrophages. J. Inflamm. 2014, 11, 13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, S.; Saeed, A.; Liu, Q.; Jiang, Q.; Xu, H.; Xiao, G.G.; Rao, L.; Duo, Y. Macrophages in immunoregulation and therapeutics. Signal Transduct. Target. Ther. 2023, 8, 207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mirzaeei, S.; Taghe, S.; Alany, R.G.; Nokhodchi, A. Eudragit® L100/Polyvinyl Alcohol Nanoparticles Impregnated Mucoadhesive Films as Ocular Inserts for Controlled Delivery of Erythromycin: Development, Characterization and In Vivo Evaluation. Biomedicines 2022, 10, 1917. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Leo, V.; Milano, F.; Mancini, E.; Comparelli, R.; Giotta, L.; Nacci, A.; Longobardi, F.; Garbetta, A.; Agostiano, A.; Catucci, L. Encapsulation of Curcumin-Loaded Liposomes for Colonic Drug Delivery in a pH-Responsive Polymer Cluster Using a pH-Driven and Organic Solvent-Free Process. Molecules 2018, 23, 739. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mudie, D.M.; Amidon, G.L.; Amidon, G.E. Physiological parameters for oral delivery and in vitro testing. Mol. Pharm. 2010, 7, 1388–1405. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Carrasco, M.J.; Alishetty, S.; Alameh, M.G.; Said, H.; Wright, L.; Paige, M.; Soliman, O.; Weissman, D.; Cleveland, T.E.; Grishaev, A.; et al. Ionization and structural properties of mRNA lipid nanoparticles influence expression in intramuscular and intravascular administration. Commun. Biol. 2021, 4, 956. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Takanashi, A.; Pouton, C.W.; Al-Wassiti, H. Delivery and Expression of mRNA in the Secondary Lymphoid Organs Drive Immune Responses to Lipid Nanoparticle-mRNA Vaccines after Intramuscular Injection. Mol. Pharm. 2023, 20, 3876–3885. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schoenmaker, L.; Witzigmann, D.; Kulkarni, J.A.; Verbeke, R.; Kersten, G.; Jiskoot, W.; Crommelin, D.J.A. mRNA-lipid nanoparticle COVID-19 vaccines: Structure and stability. Int. J. Pharm. 2021, 601, 120586. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Philipp, J.; Dabkowska, A.; Reiser, A.; Frank, K.; Krzyszton, R.; Brummer, C.; Nickel, B.; Blanchet, C.E.; Sudarsan, A.; Ibrahim, M.; et al. pH-dependent structural transitions in cationic ionizable lipid mesophases are critical for lipid nanoparticle function. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2023, 120, e2310491120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hassett, K.J.; Benenato, K.E.; Jacquinet, E.; Lee, A.; Woods, A.; Yuzhakov, O.; Himansu, S.; Deterling, J.; Geilich, B.M.; Ketova, T.; et al. Optimization of Lipid Nanoparticles for Intramuscular Administration of mRNA Vaccines. Mol. Ther. Nucleic Acids 2019, 15, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jürgens, D.C.; Deßloch, L.; Porras-Gonzalez, D.; Winkeljann, J.; Zielinski, S.; Munschauer, M.; Hörner, A.L.; Burgstaller, G.; Winkeljann, B.; Merkel, O.M. Lab-scale siRNA and mRNA LNP manufacturing by various microfluidic mixing techniques—An evaluation of particle properties and efficiency. OpenNano 2023, 12, 100161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sanghani, A.; Kafetzis, K.N.; Sato, Y.; Elboraie, S.; Fajardo-Sanchez, J.; Harashima, H.; Tagalakis, A.D.; Yu-Wai-Man, C. Novel PEGylated Lipid Nanoparticles Have a High Encapsulation Efficiency and Effectively Deliver MRTF-B siRNA in Conjunctival Fibroblasts. Pharmaceutics 2021, 13, 382. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roces, C.B.; Lou, G.; Jain, N.; Abraham, S.; Thomas, A.; Halbert, G.W.; Perrie, Y. Manufacturing Considerations for the Development of Lipid Nanoparticles Using Microfluidics. Pharmaceutics 2020, 12, 1095. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Somu Naidu, G.; Rampado, R.; Sharma, P.; Ezra, A.; Kundoor, G.R.; Breier, D.; Peer, D. Ionizable Lipids with Optimized Linkers Enable Lung-Specific, Lipid Nanoparticle-Mediated mRNA Delivery for Treatment of Metastatic Lung Tumors. ACS Nano 2025, 19, 6571–6587. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Massaro, M.; Wu, S.; Baudo, G.; Liu, H.; Collum, S.; Lee, H.; Stigliano, C.; Segura-Ibarra, V.; Karmouty-Quintana, H.; Blanco, E. Lipid nanoparticle-mediated mRNA delivery in lung fibrosis. Eur. J. Pharm. Sci. 2023, 183, 106370. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kong, W.; Wei, Y.; Dong, Z.; Liu, W.; Zhao, J.; Huang, Y.; Yang, J.; Wu, W.; He, H.; Qi, J. Role of size, surface charge, and PEGylated lipids of lipid nanoparticles (LNPs) on intramuscular delivery of mRNA. J. Nanobiotechnol. 2024, 22, 553. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rampado, R.; Naidu, G.S.; Karpov, O.; Goldsmith, M.; Sharma, P.; Ezra, A.; Stotsky, L.; Breier, D.; Peer, D. Lipid Nanoparticles with Fine-Tuned Composition Show Enhanced Colon Targeting as a Platform for mRNA Therapeutics. Adv. Sci. 2025, 12, e2408744. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Miki, S.; Suzuki, J.I.; Takashima, M.; Ishida, M.; Kokubo, H.; Yoshizumi, M. S-1-Propenylcysteine promotes IL-10-induced M2c macrophage polarization through prolonged activation of IL-10R/STAT3 signaling. Sci. Rep. 2021, 11, 22469. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
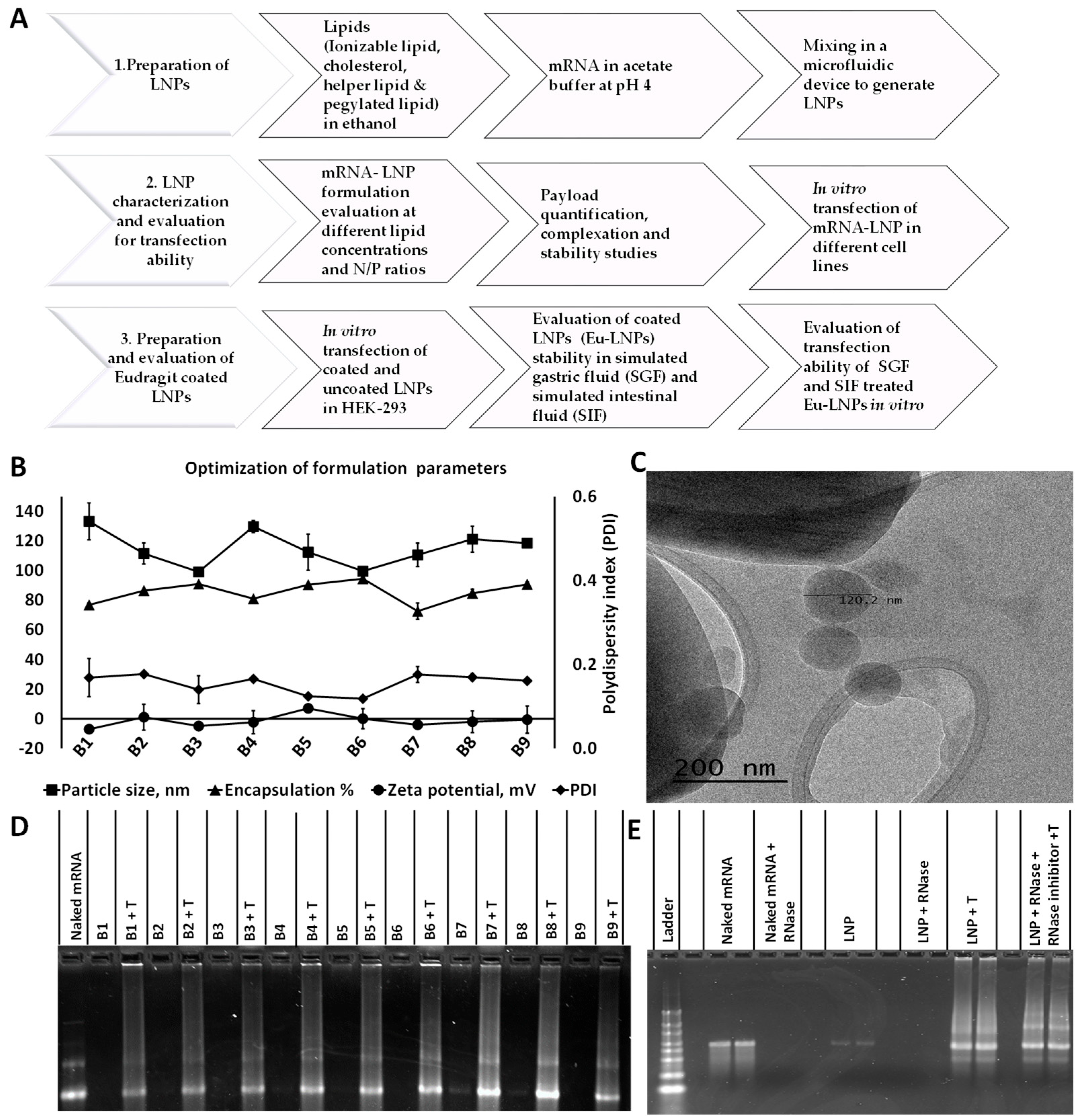
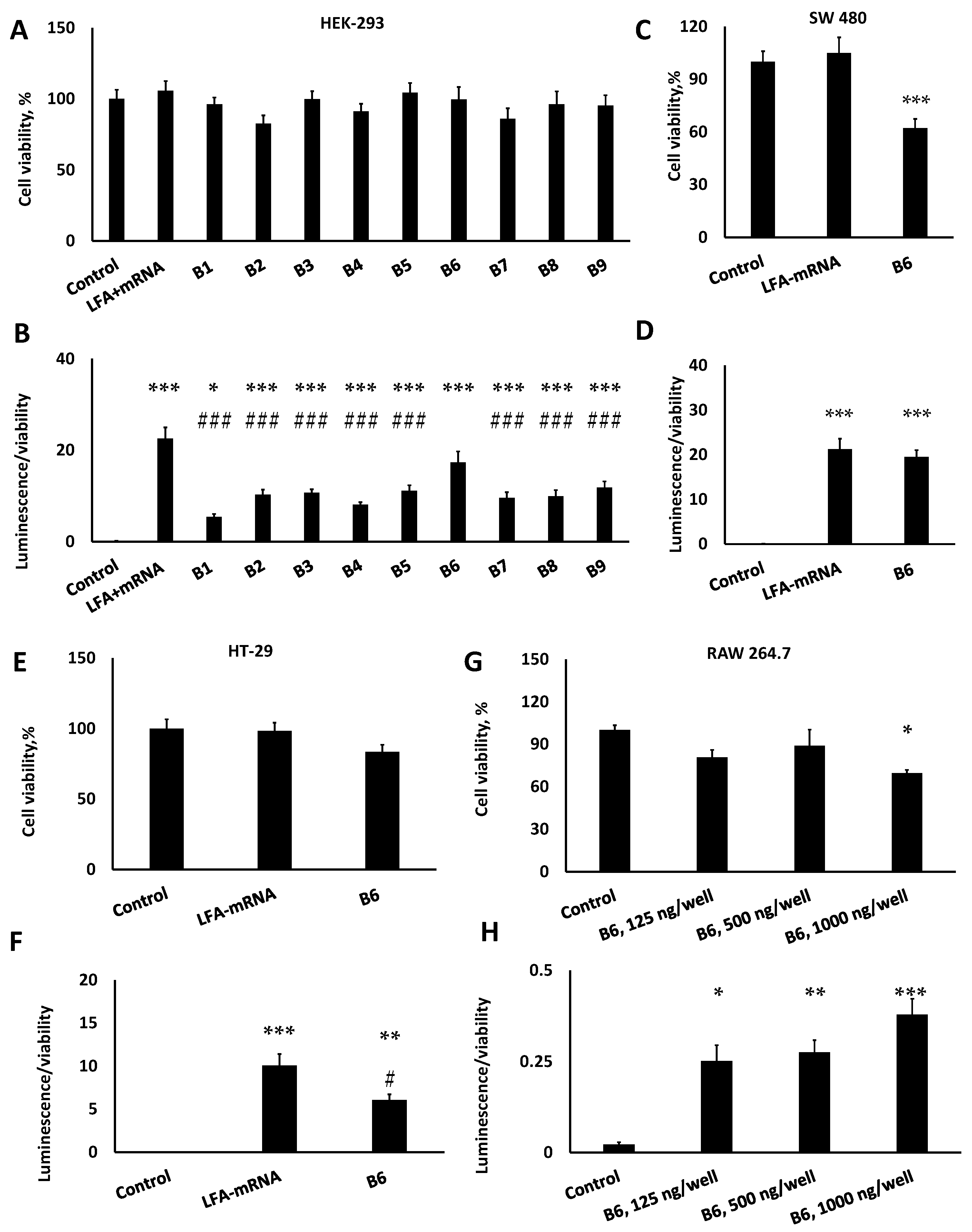
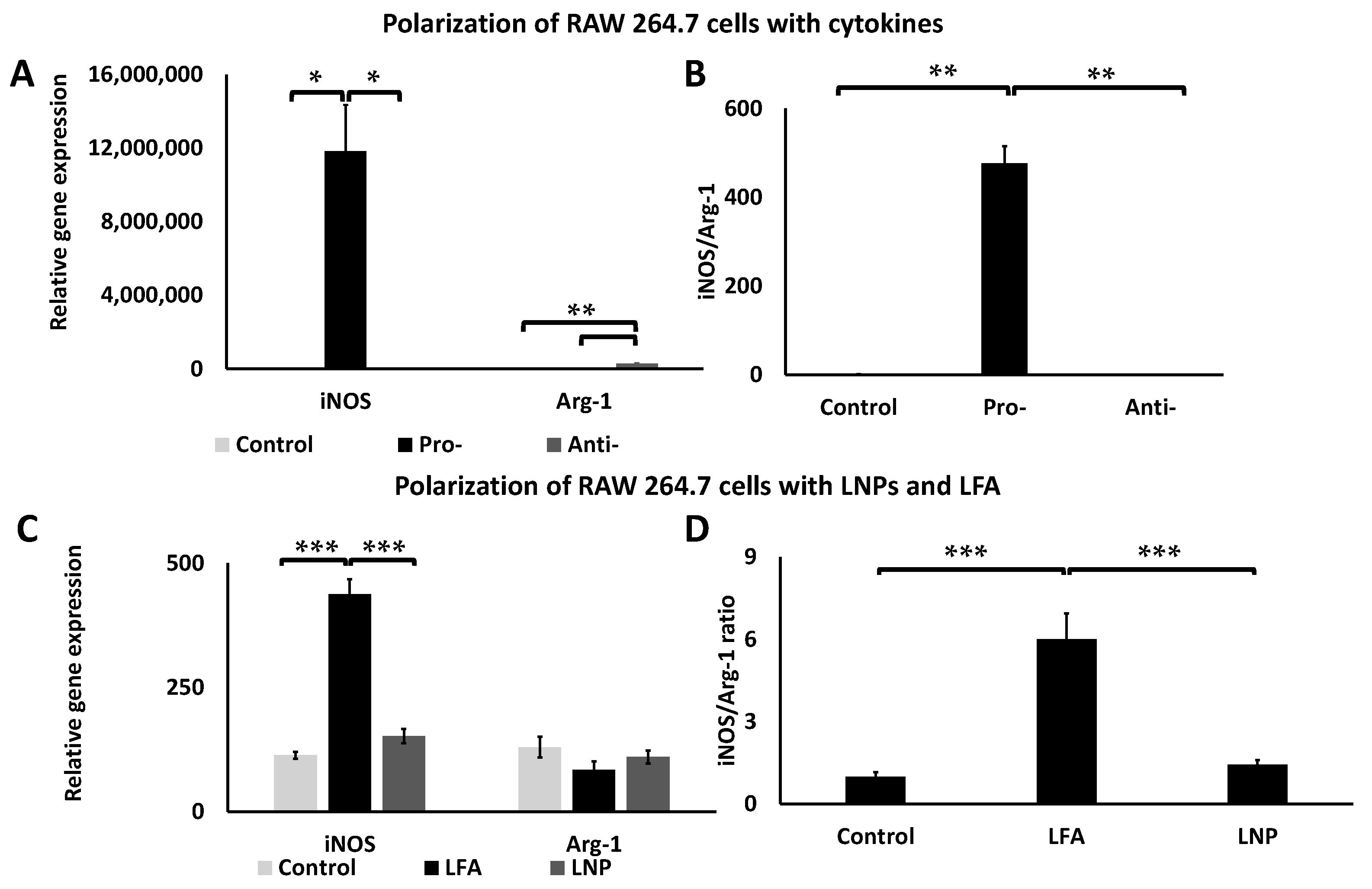
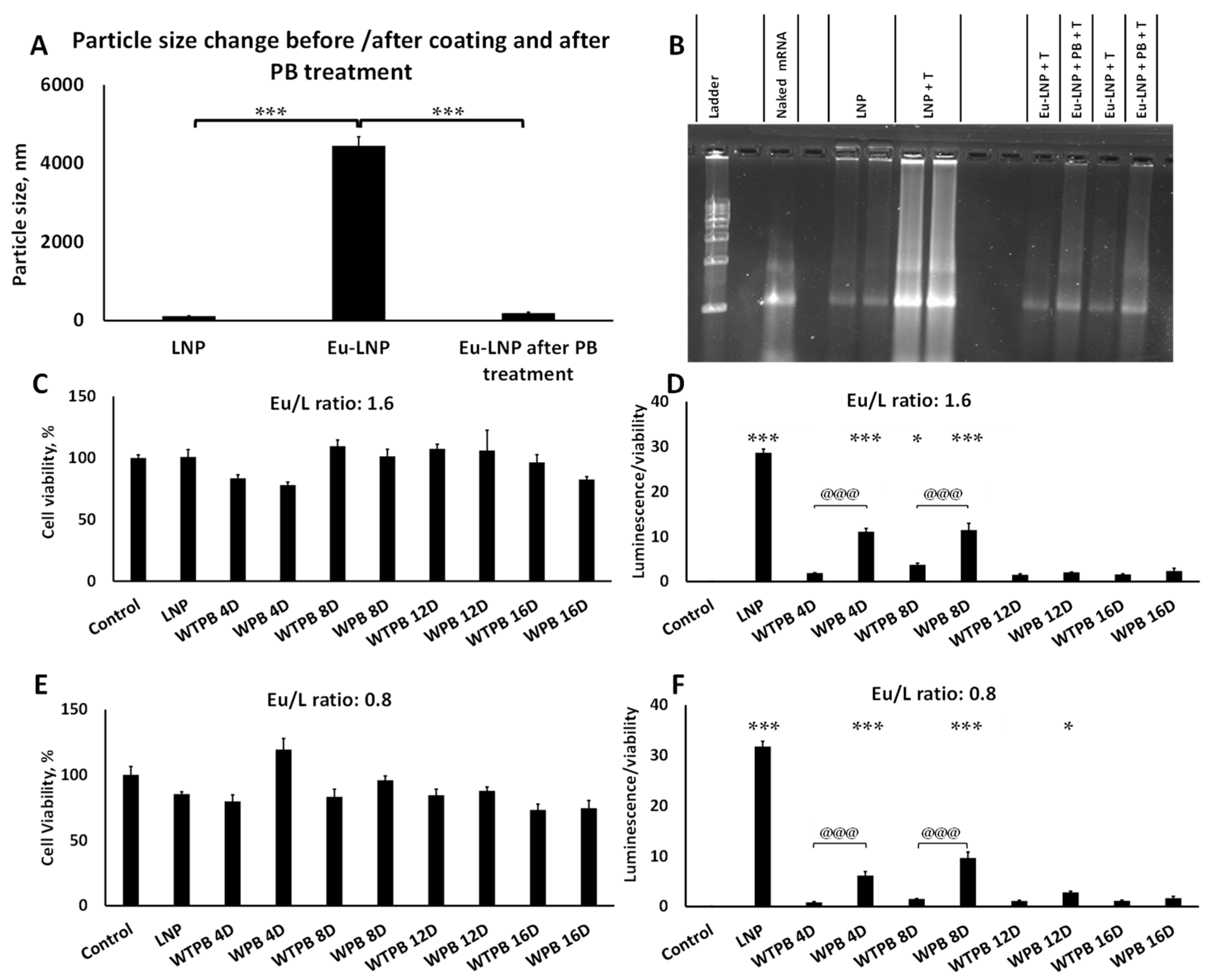
| Batch No. | Identification | Nitrogen-to-Phosphate (N/P) Ratio | Total Lipid Concentration (TLC), mg/mL | Total Lipid/mRNA Ratio, w/w |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| B1 | NP 3/TLC 1.5 | 3 | 1.5 | 10.4 |
| B2 | NP 6/TLC 1.5 | 6 | 1.5 | 20.9 |
| B3 | NP 10/TLC 1.5 | 10 | 1.5 | 34.4 |
| B4 | NP 3/TLC 1.8 | 3 | 1.8 | 10.4 |
| B5 | NP 6/TLC 1.8 | 6 | 1.8 | 20.9 |
| B6 | NP 10/TLC 1.8 | 10 | 1.8 | 34.4 |
| B7 | NP 3/TLC 2.2 | 3 | 2.2 | 10.4 |
| B8 | NP 6/TLC 2.2 | 6 | 2.2 | 20.9 |
| B9 | NP 10/TLC 2.2 | 10 | 2.2 | 34.4 |
| LNPs | Parent LNP Batch |
|---|---|
| WTPB 4D | 4 times dilution in complete media without PB treatment |
| WPB 4D | 4 times dilution (1:1 initial dilution with PB, followed by 1:2 complete media dilution) |
| WTPB 8D | 8 times dilution in complete media without PB treatment |
| WPB 8D | 8 times dilution (1:1 initial dilution with PB, followed by 1:4 complete media dilution) |
| WTPB 12D | 12 times dilution in complete media without PB treatment |
| WPB 12D | 12 dilutions (1:1 initial dilution with PB, followed by 1:6 complete media dilution) |
| WTPB 16D | 16 times dilution in complete media without PB treatment |
| WPB 16D | 16 times dilution (1:1 initial dilution with PB, followed by 1:8 complete media dilution) |
| Average ± SEM | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| LNP Formulations | Encapsulation, % | Zeta Potential, mV | Particle Size, nm | PDI |
| B1 | 76.9 ±1.4 | −7.11 ± 2.7 | 133.3 ± 12.44 | 0.169 ± 0.05 |
| B2 | 86.5 ± 0.32 | 1.05 ± 8.72 | 111.6 ± 7.14 | 0.177 ± 0.00 |
| B3 | 91 ± 0.26 | −4.93 ± 0.42 | 99.2 ± 2.53 | 0.140± 0.03 |
| B4 | 81 ± 0.07 | −2.4 ± 7.79 | 129.8 ± 3.97 | 0.166 ± 0.00 |
| B5 | 90.5 ± 0.43 | 7.02 ± 2.66 | 112.5 ± 12.19 | 0.124 ± 0.01 |
| B6 | 94.5± 0.22 | 0.0 ± 6.73 | 99.7 ± 2.0 | 0.119± 0.00 |
| B7 | 72.6 ± 5.53 | −4.09 ± 2.76 | 110.7 ± 7.94 | 0.176 ± 0.02 |
| B8 | 84.7 ± 2.82 | −2.08 ± 7.27 | 121.3 ± 8.79 | 0.170 ± 0.01 |
| B9 | 90.8 ± 1.53 | −0.61 ± 9.21 | 118.6 ± 0.21 | 0.161 ± 0.01 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Haque, M.A.; Shrestha, A.; Mattheolabakis, G. Eudragit® S 100 Coating of Lipid Nanoparticles for Oral Delivery of RNA. Processes 2025, 13, 2477. https://doi.org/10.3390/pr13082477
Haque MA, Shrestha A, Mattheolabakis G. Eudragit® S 100 Coating of Lipid Nanoparticles for Oral Delivery of RNA. Processes. 2025; 13(8):2477. https://doi.org/10.3390/pr13082477
Chicago/Turabian StyleHaque, Md. Anamul, Archana Shrestha, and George Mattheolabakis. 2025. "Eudragit® S 100 Coating of Lipid Nanoparticles for Oral Delivery of RNA" Processes 13, no. 8: 2477. https://doi.org/10.3390/pr13082477
APA StyleHaque, M. A., Shrestha, A., & Mattheolabakis, G. (2025). Eudragit® S 100 Coating of Lipid Nanoparticles for Oral Delivery of RNA. Processes, 13(8), 2477. https://doi.org/10.3390/pr13082477







