A Fuzzy Five-Region Membership Model for Continuous-Time Vehicle Flow Statistics in Underground Mines
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Description of Time Membership Issues
2.1. Basic Definitions and Symbol System
2.2. Quantitative Analysis of Time Membership Discontinuity
2.3. Formal Definition of Fuzzy Time Membership
- 1.
- 2.
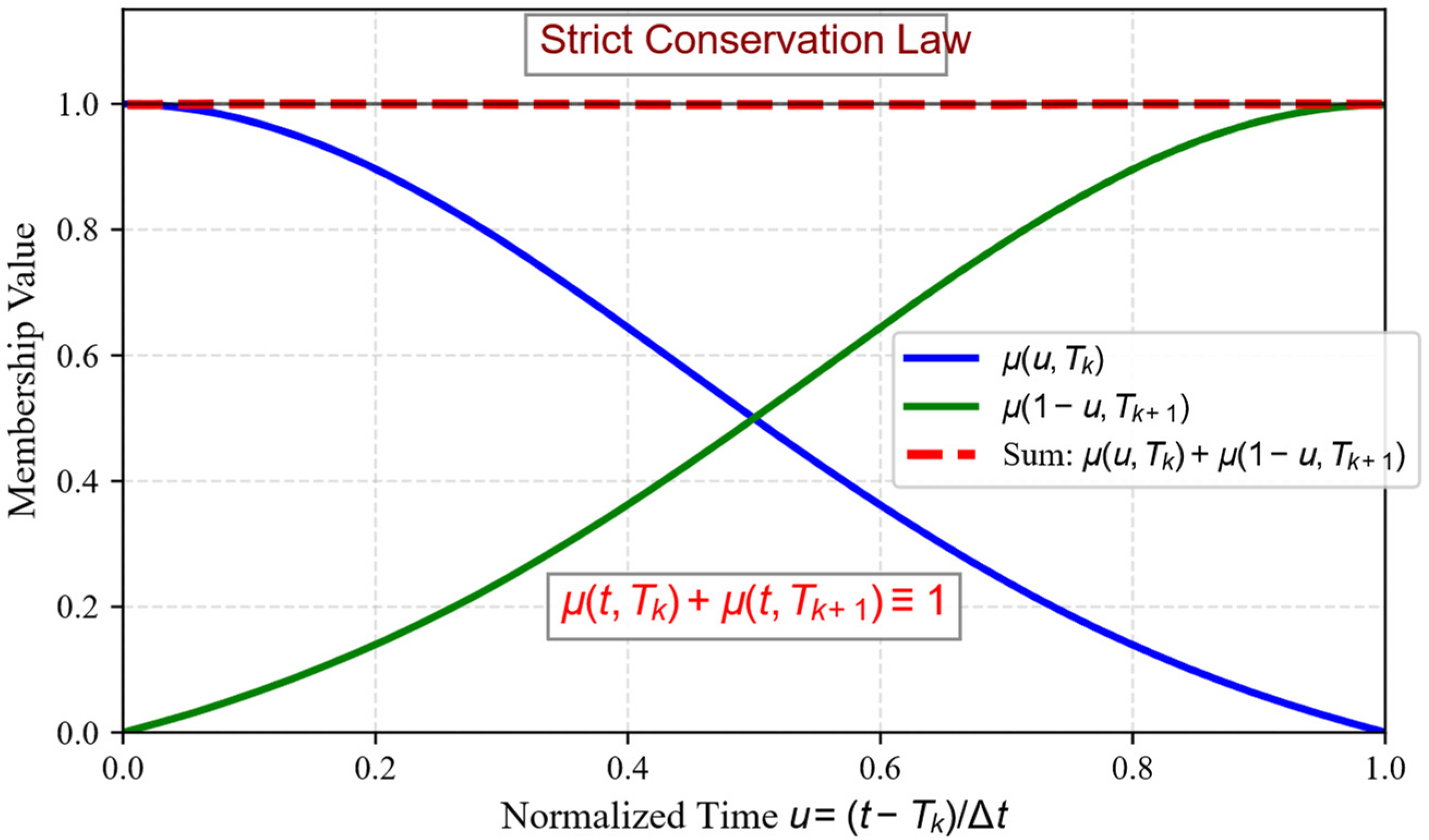
- Normalization Constraint: For any , . In the five-region model, this simplifies to , ensuring flow conservation.
- 3.
- Locality Principle: as , limiting each segment’s influence to avoid distant timestamp associations. The threshold is dynamically adjusted for granularity.
- 4.
- Computational Complexity: Single-point membership calculation follows complexity. For timestamp and nearest segment , and are computed via closed-form expressions, meeting real-time scheduling requirements.
3. Five-Region Fuzzy Membership Model
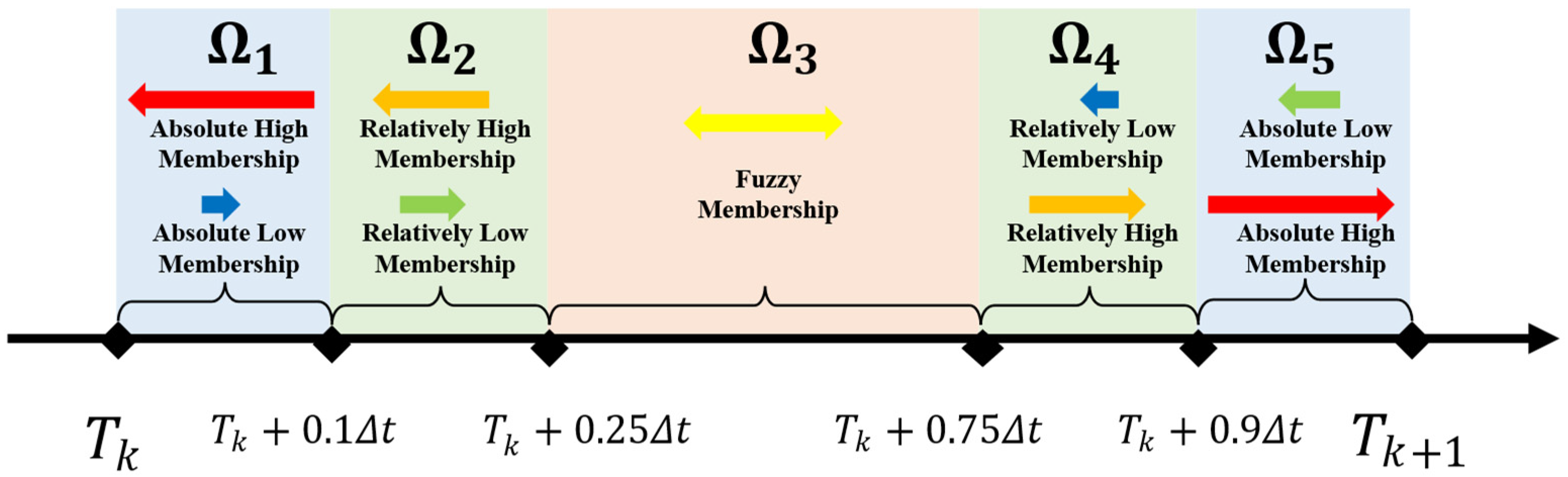
3.1. Theoretical Foundation of Region Division
- : Absolute Membership Zone
- : Linear Decay Zone
- : Nonlinear Transition Zone
- : Linear Increasing Zone
- : Absolute Membership Zone
3.2. Construction of Composite Membership Function
| Algorithm 1 Fuzzy Membership Assignment |
| ; |
| . |
| . |
| do |
| exists then |
| 8: else |
| for all k (boundary handling) |
| 10: end if |
| 11: end for |
3.3. Model Characteristics and Validation
3.3.1. Validation of the Five-Region Mapping Strategy
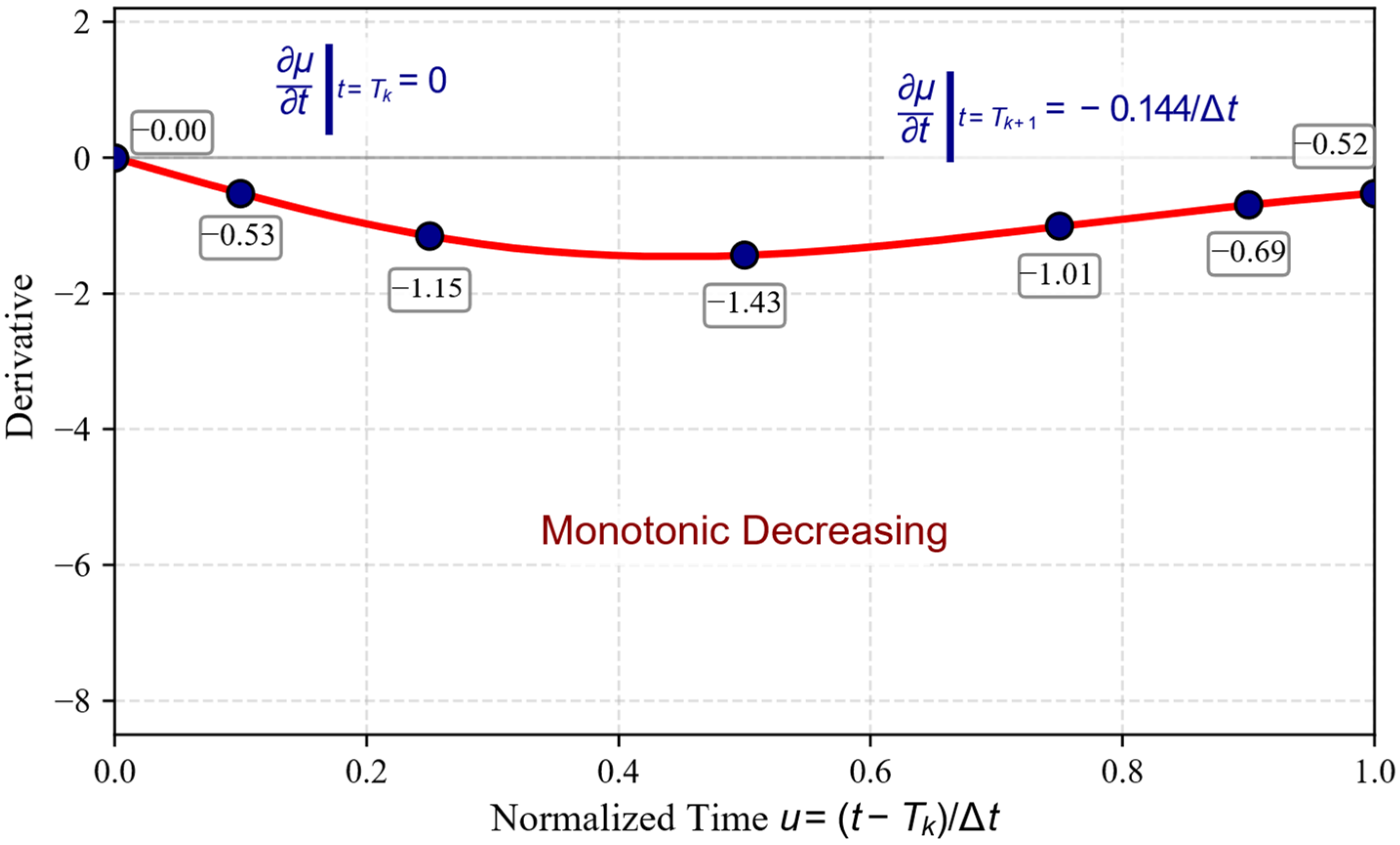
3.3.2. Derivative Continuity Analysis
3.3.3. Conservation Law Proof
3.3.4. Engineering Applicability
4. Case Study
4.1. Data Sources and Preprocessing
4.2. Evaluation Metrics
4.3. Experimental Results
5. Discussion
6. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Ali, M.A.M.; Sik, Y.H. Transportation Problem: A Special Case for Linear Programing Problems in Mining Engineering. Int. J. Min. Sci. Technol. 2012, 22, 371–377. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, N.; Wu, Y.; Ye, H.; Wang, L.; Wang, Q.; Jia, M. Scheduling Optimization of Underground Mine Trackless Transportation Based on Improved Estimation of Distribution Algorithm. Expert Syst. Appl. 2024, 245, 123025. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, M.; Bao, J.; Yuan, X.; Yin, Y.; Khalid, S. Research Status and Development Trend of Unmanned Driving Technology in Coal Mine Transportation. Energies 2022, 15, 9133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hou, J.; Li, G.; Chen, L.; Wang, H.; Hu, N. Optimization of Truck–Loader Matching Based on a Simulation Method for Underground Mines. Sustainability 2023, 15, 216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, J.; Chen, K.; Ding, Z.; Zhao, C.; Zhang, T.; Jiao, Z. A Multi-Mode Active Control Method for the Hydropneumatic Suspension of Auxiliary Transport Vehicles in Underground Mines. Appl. Sci. 2025, 15, 6871. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rahimdel, M.J.; Mohammadpour, R. Enhancing Mineral Transportation Systems in Underground Mines: A Framework for Capacity Analysis. Heliyon 2025, 11, e42708. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, M.; Xie, G.; Liu, L.; Wang, R.; Ruan, S.; Yang, P.; Fang, Z. Strengthening Mechanism of Granulated Blast-Furnace Slag on the Uniaxial Compressive Strength of Modified Magnesium Slag-Based Cemented Backfilling Material. Process Saf. Environ. Prot. 2023, 174, 722–733. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, H.; Zhang, X.; Yuan, H.; Wu, Z.; Zhou, M. A Lean Scheduling Framework for Underground Mines Based on Short Interval Control. Sustainability 2023, 15, 9195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Xue, Y.; Xiao, J.; Shi, D. Diffusion Characteristics of Airflow and CO in the Dead-End Tunnel with Different Ventilation Parameters after Tunneling Blasting. ACS Omega 2023, 8, 36269–36283. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, G.; Xu, Y.; Ren, H. Intelligent and Ecological Coal Mining as Well as Clean Utilization Technology in China: Review and Prospects. Int. J. Min. Sci. Technol. 2019, 29, 161–169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lasantha, L.; Karmakar, N.C.; Ray, B. Chipless RFID Sensors for IoT Sensing and Potential Applications in Underground Mining—A Review. IEEE Sens. J. 2023, 23, 9033–9048. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cavur, M.; Demir, E. RSSI-Based Hybrid Algorithm for Real-Time Tracking in Underground Mining by Using RFID Technology. Phys. Commun. 2022, 55, 101863. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gamache, M.; Basilico, G.; Frayret, J.-M.; Riopel, D. Real-Time Multi-Agent Fleet Management Strategy for Autonomous Underground Mines Vehicles. Int. J. Min. Reclam. Environ. 2023, 37, 649–666. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wan, M.; Li, H.; Wang, H.; Hou, J. Scheduling Optimization of Electric Rubber-Tired Vehicles in Underground Coal Mines Based on Constraint Programming. Sensors 2025, 25, 3435. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gu, J.; Li, M.; Yu, L.; Li, S.; Long, K. Analysis on Link Travel Time Estimation Considering Time Headway Based on Urban Road RFID Data. J. Adv. Transp. 2021, 2021, 8876626. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, W.; Yang, G.; Xiong, Z.; Zhu, X.; Ma, X. A Traffic Flow Prediction Model Based on Dynamic Graph Convolution and Adaptive Spatial Feature Extraction. Symmetry 2025, 17, 1007. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Skripnik, I.; Savelev, D.; Kaverzneva, T.; Rumyantseva, N. Implementation of a Risk-Based OHS Management System at IMC Mining Company. E3S Web Conf. 2023, 376, 05031. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gmira, M.; Gendreau, M.; Lodi, A.; Potvin, J.-Y. Tabu Search for the Time-Dependent Vehicle Routing Problem with Time Windows on a Road Network. Eur. J. Oper. Res. 2021, 288, 129–140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Coifman, B.; Cassidy, M. Vehicle Reidentification and Travel Time Measurement on Congested Freeways. Transp. Res. Part A Policy Pract. 2002, 36, 899–917. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sam, D.; Velanganni, C.; Evangelin, T.E. A Vehicle Control System Using a Time Synchronized Hybrid VANET to Reduce Road Accidents Caused by Human Error. Veh. Commun. 2016, 6, 17–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Z.; Shang, W.-L.; Zhang, H.; Garg, H.; Han, C. Assessing the Green Distribution Transformer Manufacturing Process Using a Cloud-Based q-Rung Orthopair Fuzzy Multi-Criteria Framework. Appl. Energy 2022, 311, 118687. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sustainability Assessment of Regional Transportation: An Innovative Fuzzy Group Decision-Making Model. Available online: https://ieeexplore.ieee.org/abstract/document/10144475 (accessed on 19 July 2025).
- Shang, W.-L.; Song, X.; Xiang, Q.; Chen, H.; Elhajj, M.; Bi, H.; Wang, K.; Ochieng, W. The Impact of Deep Reinforcement Learning-Based Traffic Signal Control on Emission Reduction in Urban Road Networks Empowered by Cooperative Vehicle-Infrastructure Systems. Appl. Energy 2025, 390, 125884. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, Q.; Tang, J.; Shang, W.-L.; Li, C.; Ren, Y.; Quddus, M.; Ochieng, W. Optimization of Passenger Flow Control and Parallel Bus Bridging in Urban Rail Transit Based on Intelligent Transport Infrastructure. Available online: https://doi.org/10.1111/mice.13460 (accessed on 1 July 2025).
- Control a Mobile Robot in Social Environments by Considering Human as a Moving Obstacle. Available online: https://ieeexplore.ieee.org/document/8657641 (accessed on 19 July 2025).
- Hamzeh, F.; Fathollahi Dehkordi, S.; Naeimifard, A.; Abyaz, A. Continuously Variable Geometry Quadrotor: Robust Control via PSO-Optimized Sliding Mode Control. Actuators 2025, 14, 308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ren, X.; Guo, H.; Sheng, K.; Mao, G. Real-Time Path Planning of Driverless Mining Trains with Time-Dependent Physical Constraints. Appl. Sci. 2023, 13, 3729. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duan, L.; Yu, F.; Pedrycz, W.; Wang, X.; Yang, X. Time-Series Clustering Based on Linear Fuzzy Information Granules. Appl. Soft Comput. 2018, 73, 1053–1067. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nguyen, K.A.; Wang, Y.; Li, G.; Luo, Z.; Watkins, C. Realtime Tracking of Passengers on the London Underground Transport by Matching Smartphone Accelerometer Footprints. Sensors 2019, 19, 4184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bao, H.; Zhang, R. Study on Optimization of Coal Truck Flow in Open-Pit Mine. Adv. Civ. Eng. 2020, 2020, 8848140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, J.-F.; Lo, S.-K.; Do, Q.H. Forecasting Short-Term Traffic Flow by Fuzzy Wavelet Neural Network with Parameters Optimized by Biogeography-Based Optimization Algorithm. Comput. Intell. Neurosci. 2018, 2018, 5469428. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, S.; Gao, X.; Ma, W.; Lu, H.; Lv, T.; Xu, S.; Zhu, X.; Sun, H.; Wang, Y. Derivation and Verification of Three-Dimensional Wake Model of Multiple Wind Turbines Based on Super-Gaussian Function. Renew. Energy 2023, 215, 118968. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alacoque, L.; James, K.A. Topology Optimization with Variable Loads and Supports Using a Super-Gaussian Projection Function. Struct Multidisc Optim 2022, 65, 50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Romero, J.L.; Ulanovskii, A.; Zlotnikov, I. Sampling in the Shift-Invariant Space Generated by the Bivariate Gaussian Function. J. Funct. Anal. 2024, 287, 110600. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tolga, A.C.; Parlak, I.B.; Castillo, O. Finite-Interval-Valued Type-2 Gaussian Fuzzy Numbers Applied to Fuzzy TODIM in a Healthcare Problem. Eng. Appl. Artif. Intell. 2020, 87, 103352. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
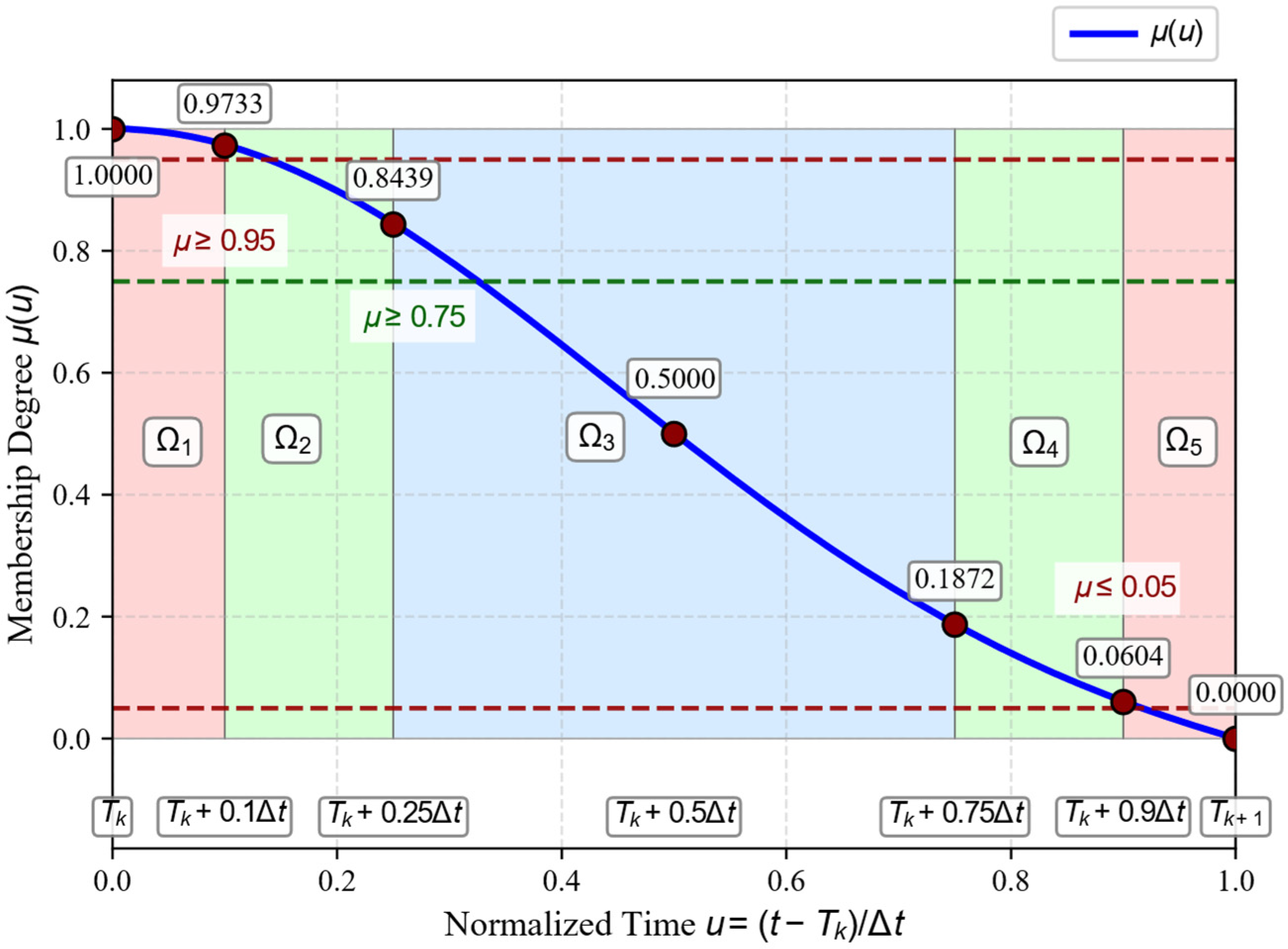
| Region | Position t | Theoretical Requirement | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Start | 1.0000 | 1.0 | |
| 0.9792 | >0.95 | ||
| 0.8364 | [0.75, 0.95) | ||
| 0.5000 | [0.25, 0.75] | ||
| 0.0657 | (0.05, 0.25] | ||
| 0.0163 | <0.05 | ||
| End | 0.0000 | 0.0 |
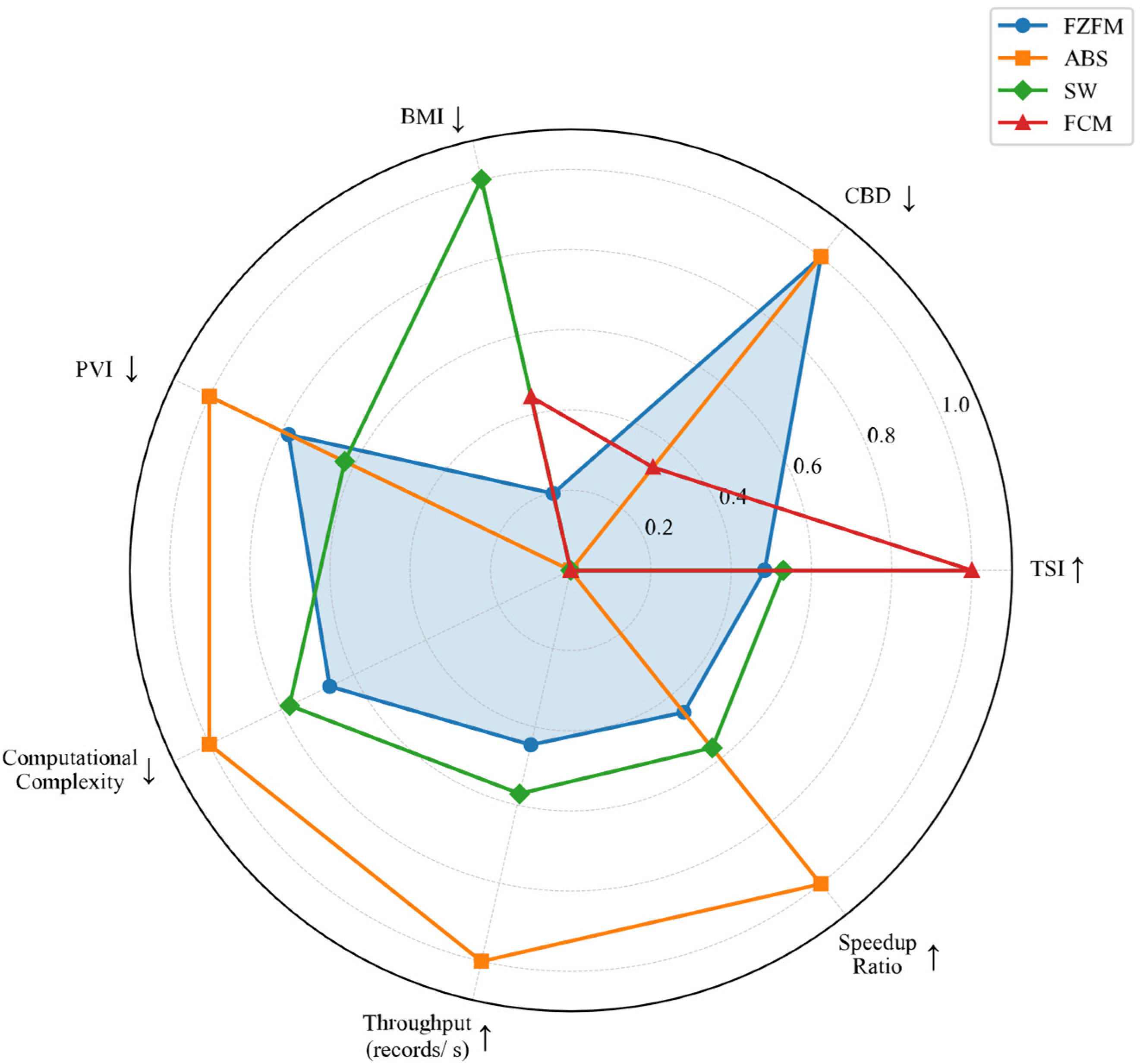
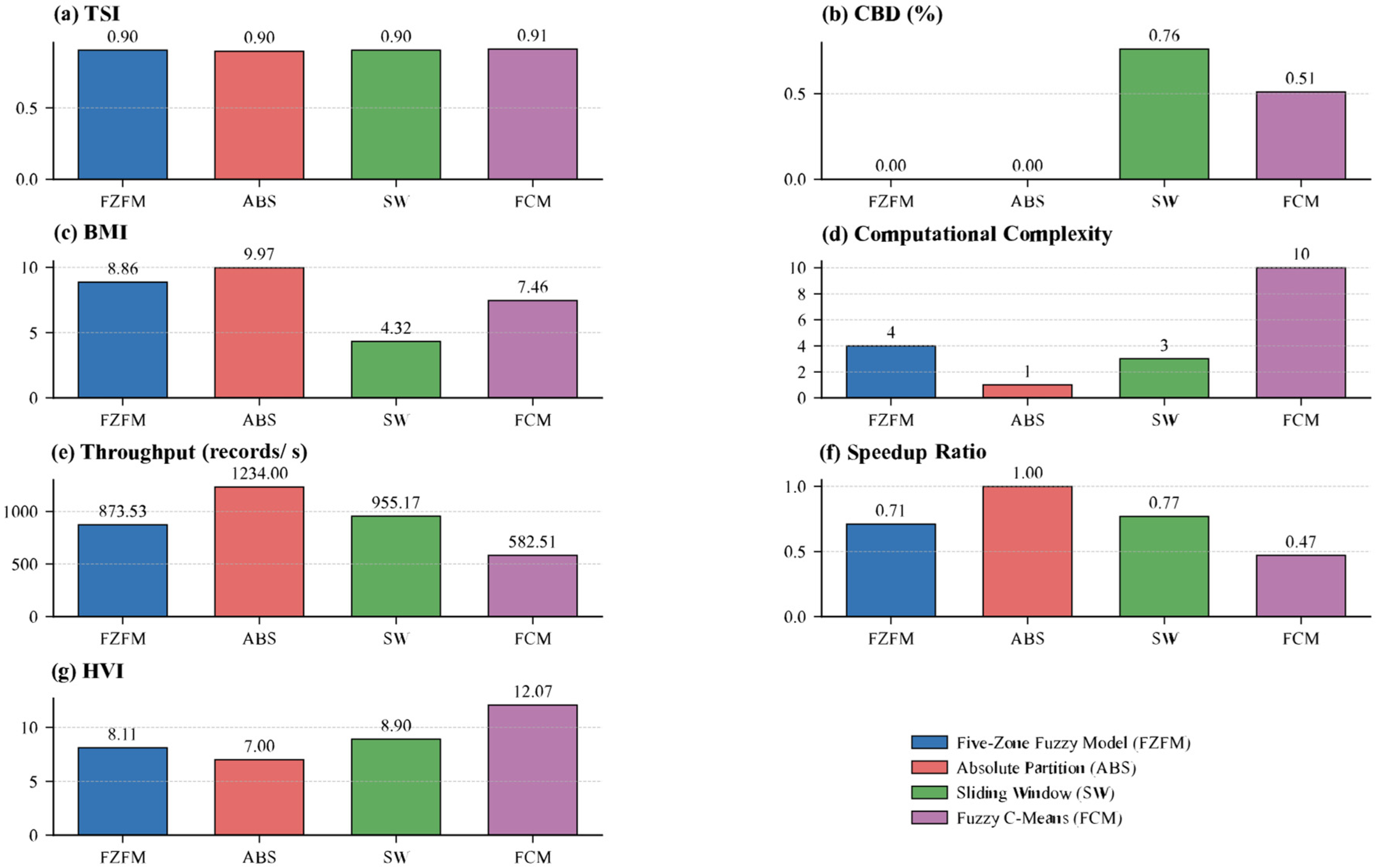
| Indicator | FZFM | ABS | SW | FCM | Optimal Direction |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| TSI | 0.9036 | 0.8963 | 0.9043 | 0.9114 | maximize |
| CBD (%) | 0 | 0 | 0.76 | 0.51 | minimize |
| BMI | 8.86 | 9.97 | 4.32 | 7.46 | minimize |
| Computational Complexity | 4 | 1 | 3 | 10 | minimize |
| Throughput (records/s) | 873.53 | 1234.00 | 955.17 | 582.51 | maximize |
| Speedup Ratio | 0.71 | 1.00 | 0.77 | 0.47 | maximize |
| PVI | 8.11 | 7.00 | 8.90 | 12.07 | minimize |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Wang, H.; Wan, M.; Gong, H.; Hou, J. A Fuzzy Five-Region Membership Model for Continuous-Time Vehicle Flow Statistics in Underground Mines. Processes 2025, 13, 2434. https://doi.org/10.3390/pr13082434
Wang H, Wan M, Gong H, Hou J. A Fuzzy Five-Region Membership Model for Continuous-Time Vehicle Flow Statistics in Underground Mines. Processes. 2025; 13(8):2434. https://doi.org/10.3390/pr13082434
Chicago/Turabian StyleWang, Hao, Maoqua Wan, Hanjun Gong, and Jie Hou. 2025. "A Fuzzy Five-Region Membership Model for Continuous-Time Vehicle Flow Statistics in Underground Mines" Processes 13, no. 8: 2434. https://doi.org/10.3390/pr13082434
APA StyleWang, H., Wan, M., Gong, H., & Hou, J. (2025). A Fuzzy Five-Region Membership Model for Continuous-Time Vehicle Flow Statistics in Underground Mines. Processes, 13(8), 2434. https://doi.org/10.3390/pr13082434







