Abstract
Silver nanoparticles (AgNPs), iron oxide nanoparticles (Fe2O4NPs), and multiwalled carbon nanotubes (MWCNTs) are widely used in various applications, such as biomedicine, environmental remediation, and agriculture. In addition, these nanomaterials can affect the production of bioactive compounds in plants that have pharmacological activities. In the current study, the in vitro plant cultures of Chinese lobelia (Lobelia chinensis Lour.) were established in MS medium and treated with 0, 12.5, 25, 37.5, and 50 mg L−1 AgNPs or Fe2O4NPs, or MWCNTs. Initially, plants were grown for four weeks without any elicitors, and after that, the cultures were treated with nano-elicitors for one week. After five weeks, the effects of nano-elicitors were estimated on growth, total phenolic, flavonoids, polyacetylenes, and ABTS/DPPH/FRAP antioxidant activity was investigated. The results showed that lower levels of AgNPs (25 mg L−1), Fe2O4NPs (25 mg L−1), and MWCNTs (12.5 mg L−1) favored the accumulation of fresh and dry biomass. Whereas, 37.5 mg L−1 AgNPs, 25 mg L−1 Fe2O4NPs, and 37.5 mg L−1 MWCNTs enhanced the accumulation of total phenolics, flavonoids, specific phenolic compounds including chlorogenic acid, catechin, phloretic acid, coumaric acid, salicylic acid, naringin, myricetin, linarin, and polyacetylenes viz. lobetylonin and lobetyolin in higher concentrations. The plant extracts elicited by nanomaterials also depicted very good antioxidant activities according to ABTS, DPPH, and FRAP assays. These results suggest that specific nanomaterials, and at specific levels, could be used for the production of bioactive compounds from shoot cultures of Chinese lobelia.
1. Introduction
Chinese lobelia (Lobelia chinensis Lour.), is an important medicinal plant used in the Chinese, Oriental, and Japanese systems of medicine to cure malarial fever, edema, jaundice, diarrhea, and snake bites [1]. Phenolics, flavonoids, coumarins, polyacetylenes, terpenoids, and alkaloids are among the phytochemicals present in Chinese lobelia [1,2,3,4]. Chinese lobelia has anti-inflammatory [5], antioxidant [5,6], antiviral [3,7], anti-obesity [8], anti-tuberculosis [9], anticancer [3], and antitumor [10,11] pharmacological effects. Overuse of the plants has led to a decline in Chinese lobelia’s natural populations. Therefore, in vitro propagation methods have been developed using small-scale and bioreactor cultures [12,13,14].
A range of biotic and abiotic elicitors have been used to successfully increase the accumulation of bioactive compounds in the in vitro cultures [15,16,17]. In addition, nanoparticles (NPs) and nanomaterials (NMs) have also been used successfully as elicitors with in vitro cultures to enhance the accumulation of plant secondary metabolites [18]. For example, adding zinc and iron oxide nanoparticles at the proper concentration increased the production of hypericin and hyperforin in Hypericum perforatum in vitro cells [19]. Aluminum NPs have caused Nicotiana tabacum cell cultures to develop phenolics [20]. Chung et al. [21] used silver nanoparticles in a different study to boost phenolic production in hairy root cultures of Cucumis anguria. According to Kim et al. [22] and El-Temsah and Joner [23], iron NPs have a harmonic effect on plants, which means that higher quantities of NPs have a detrimental effect on growth while lower dosages have a positive effect. Similarly, Trigonella foenum-graecum hairy roots have effectively enhanced the trigonelline alkaloid using iron and zinc oxide nanoparticles [24].
According to our recent literature review, of the various metal NPs, AgNPs have been used extensively for elicitation and have resulted in increased phenolic production in a number of plant systems, including Cucumis anguria, Echinacea purpurea, Caralluma tuberculata, Fagonia indica, Lavandula angustifolia, and Linum usitatissimum callus/cell/hairy root/shoot cultures [18]. Of the many metal oxide nanoparticles, FeO4NPs have been tested on a variety of plants and have also been effectively employed in hairy root cultures of Hyoscyamus reticulatus to increase alkaloids production. Additionally, Salvia nemorosa cell cultures have been used to study MWCNTs. This analysis of the literature led to the selection of the effects of AgNPs, FeO4NPs, and MWCNTs on Chinese lobelia plant cultures.
The elicitation effect of yeast extract and salicylic acid has been recently studied by Bai et al. [25], and a stimulating effect on biomass and bioactive compounds has been reported in Chinese lobelia. To improve the production of bioactive phenolics and polyacetylenes, it is required to confirm the effects of NPs and NMs on Chinese lobelia plant cultures, as the influence of NPs/NMs on this plant has not been investigated. Thus, the main objectives of the present investigation were to ascertain the ways in which iron oxide (Fe2O4), silver (Ag), and multiwalled carbon nanotubes (MWCNTs) act as elicitors to promote the growth and accumulation of bioactive compounds in Lobelia chinensis plant cultures. We looked at the total phenolic and flavonoid content. Additionally, we used high-performance liquid chromatography (HPLC) to determine the quantity of various phenolics and polyacetylenes. We also assessed the antioxidant capacity of plant extracts induced by NPs and MWCNTs.
2. Results
2.1. Effects of AgNPs on Biomass Accumulation, Production of Bioactive Compounds, and Antioxidant Activity
2.1.1. Effect on Biomass Accumulation
The impact of AgNPs (0, 12.5, 25, 37.5, and 50 mg L−1) on the accumulation of fresh and dry biomass in Chinese lobelia is displayed in Table 1 and Figure 1. Fresh biomass increased to 216.4 g L−1, and dry biomass increased to 21.6 g L−1 with the addition of 25 mg L−1 AgNP treatment. In control cultures, the fresh and dry biomass values were 181.0 g L−1 and 17.6 g L−1, respectively. The increments in fresh and dry biomass were statistically significant according to DMRT at p ≤ 0.05. These results demonstrate that the addition of AgNPs boosts biomass. In contrast, fresh and dry biomass declined as concentrations of AgNPs rose (Table 1).

Table 1.
Effect of different concentrations of silver nanoparticles (AgNPs) on the growth of L. chinensis plantlets.

Figure 1.
Changes in plant biomass of in vitro grown Chinese lobelia in response to AgNP treatments.
2.1.2. Effect on Bioactive Compound Production
In the current study, cultures generated by the application of AgNPs produced an accumulation of total phenolics and total flavonoid content, which increased steadily as the concentration of AgNPs increased. The highest total phenolic content (3.38 mg GAE g−1 DW; Figure 2A) and the highest flavonoid content (22.59 mg CE g−1 DW; Figure 2B) were found in cultures treated with 37.5 mg L−1 AgNPs. These results were significant according to DMRT at p ≤ 0.05. However, treatment at higher doses (50 mg L−1) causes a reduction in phenolics and total flavonoids.
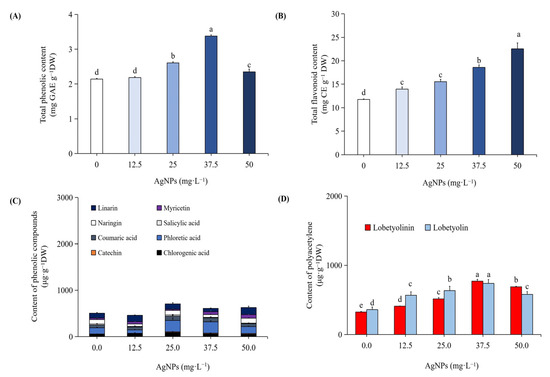
Figure 2.
Impact of varying AgNP concentrations on the total phenolic content (A), total flavonoid content (B), content of individual phenolics (C), and polyacetylenes (D). Different letters indicated significant (p < 0.05) differences.
We carried out HPLC analysis of individual phenolic compounds with AgNPs-elicited plant cultures, and the results are presented in Figure 2C and Figure 3B. Eight different phenolics were detected, namely, chlorogenic acid, catechin, phloretic acid, coumaric acid, salicylic acid, naringin, myricetin, and linarin. The plant cultures which were elicited with 37.5 mg L−1 AgNPs showed increased concentrations of chlorogenic acid (99.99 µg g−1 DW), catechin (16.48 µg g−1 DW), phloretic acid (242.53 µg g−1 DW), coumaric acid (93.42 µg g−1 DW), naringin (97.88 µg g−1 DW), and linarin (117.26 µg g−1 DW), which are 55%, 166%, 84%, 57%, 6%, and 11% increments, respectively, when compared to non-elicited cultures. According to DMRT, these findings were significant at p ≤ 0.05. However, the amounts of salicylic acid (24.46 µg g−1 DW) and myricetin (25.04 µg g−1 DW) decreased by 2% and 24%, respectively. The values of polyacetylenes, viz. lobetyolinin (770.54 µg g−1 DW) and lobetyolin (737.62 µg g−1 DW), were also increased by 137% and 105%, respectively, with the 37.5 mg L−1 AgNPs-elicited cultures (Figure 2D and Figure 4B). These results were significant at p ≤ 0.05, according to DMRT.
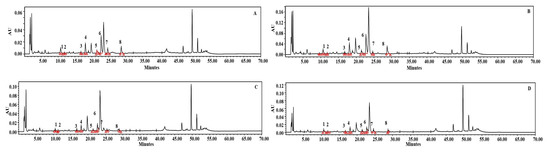
Figure 3.
HPLC chromatograms of the analysis of phenolics. Standard phenolics (A), in vitro plants elicited with 37.5 mg L−1 AgNPs (B), in vitro plants elicited with 25 mg L−1 Fe2O4NPs (C), in vitro plants elicited by 37.5 mg L−1 MWCNTs (D). 1. Chlorogenic acid, 2. Catechin, 3. Phloretic acid, 4. Coumaric acid, 5. Salicylic acid, 6. Naringin, 7. Myricetin, 8. Linarin.
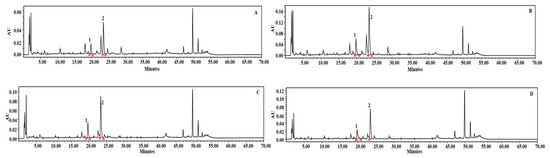
Figure 4.
HPLC chromatograms of the analysis of polyacetylenes. Standard polyacetylenes (A), in vitro plants elicited with 37.5 mg L−1 AgNPs (B), in vitro plants elicited with 25 mg L−1 Fe2O4NPs (C), in vitro plants elicited by 37.5 mg L−1 MWCNTs (D). 1. Lobetyolinin, 2. Lobetyolin.
2.1.3. Effect on Antioxidant Activities
Figure 5 shows the antioxidant activity of AgNPs-elicited plant cultures in comparison to non-elicited cultures according to ABTS (Figure 5A), DPPH (Figure 5B), and FRAP assays (Figure 5C). The phenolic and flavonoid levels were significantly higher in the AgNPs-elicited plants, which directly impact their antioxidant activity. ABTS radical scavenging was 98.30%, DPPH radical scavenging was 62.53%, and the FRAP activity was 58.75 Fe2+ mg g−1 DW with plant extracts which were from AgNPs-elicited cultures. According to DMRT, these findings were significant at p ≤ 0.05.
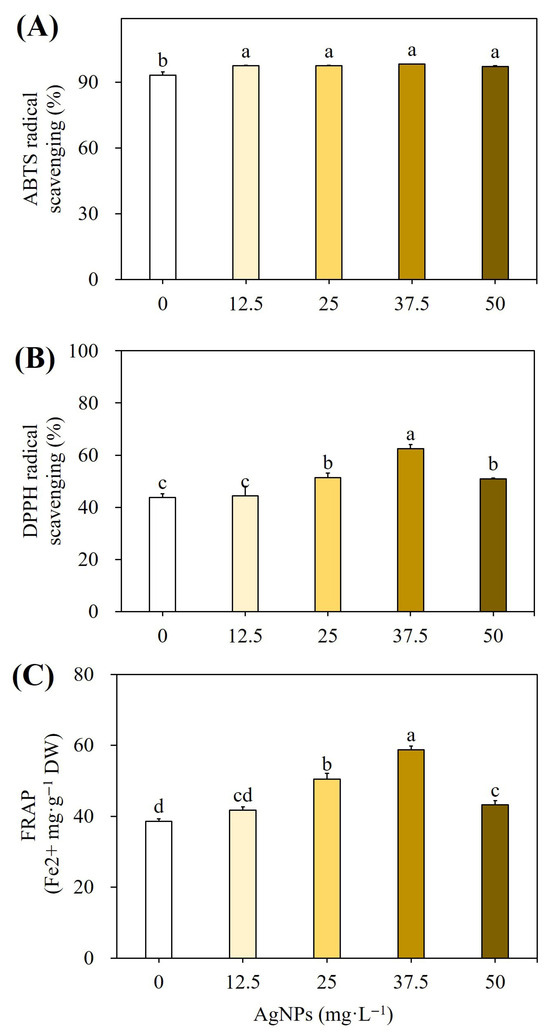
Figure 5.
Effect of different concentrations of AgNPs on ABTS free radical scavenging activity (A), DPPH scavenging activity (B), and FRAP activity (C). Different letters indicated significant (p < 0.05) differences.
2.2. Effects of Fe2O4NPs on Biomass Accumulation, Production of Bioactive Compounds, and Antioxidant Activity
2.2.1. Effect on Biomass Accumulation
The influence of Fe2O4NPs on the growth and biomass accumulation is presented in Table 2 and Figure 6. Fresh (230.0 g L−1) and dry biomass (23.4 g L−1) were higher in plant cultures evoked with 25 mg L−1 Fe2O4NPs than in control cultures. There was a 27% and 31% increment in fresh and dry biomass compared to non-elicited plant cultures. According to DMRT, the increase in fresh and dry biomass was statistically significant at p ≤ 0.05.

Table 2.
Effect of different concentrations of iron oxide nanoparticles (Fe2O4) on the growth of L. chinensis plantlets.

Figure 6.
Changes in plant biomass of in vitro grown Chinese lobelia in response to different concentrations of Fe2O4NPs as compared to control.
2.2.2. Effect on Bioactive Compound Production
The analysis of data showed that total phenolics and total flavonoids increased significantly with the addition of 25 mg L−1 Fe2O4NPs in the medium (Figure 7A,B). The content of total phenolics was 3.05 mg GAE g−1 DW, and total flavonoids were 18.98 mg CE g−1 DW in the plants treated with 25 mg L−1 Fe2O4NPs. These results were significant at p ≤ 0.05, according to DMRT. Furthermore, by adding 25 mg L−1 Fe2O4NPs in the medium, the individual phenolic content increased significantly (Figure 7C). The content of chlorogenic acid, coumaric acid, salicylic acid, myricetin, and linarin was increased by 17%, 528%, 26%, 22%, and 19%, respectively. According to DMRT, these findings were significant at p ≤ 0.05. However, the content of catechin, phloretic acid, and naringin was reduced by 37%, 8%, and 10%, respectively, with 25 mg L−1 Fe2O4NPs compared to non-elicited cultures (Figure 3C and Figure 7C). In the case of polyacetylenes, the highest content of lobetyolinin and lobetyolin was increased significantly, and about 37% and 98% higher than those of control plants (Figure 4C and Figure 7D). According to DMRT, these results were significant at p ≤ 0.05.
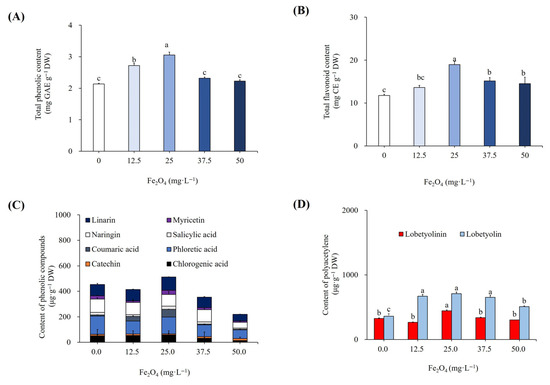
Figure 7.
Effect of different concentrations of Fe2O4NPs on total phenolic content (A), total flavonoid content (B), content of individual phenolics (C), and polyacetylenes (D). Different letters indicated significant (p < 0.05) differences.
2.2.3. Effect on Antioxidant Activities
Plant extracts treated with Fe2O4NPs had higher DPPH and ABTS radical scavenging activities than the control group, with respective values of 98.13% and 53.75% (Figure 8A,B). Additionally, the extract from Fe2O4NPs-elicited cells had more potent FRAP activity (47.06 Fe2+ mg g−1 DW) than the control (Figure 8C). According to DMRT, these findings were significant at p ≤ 0.05.
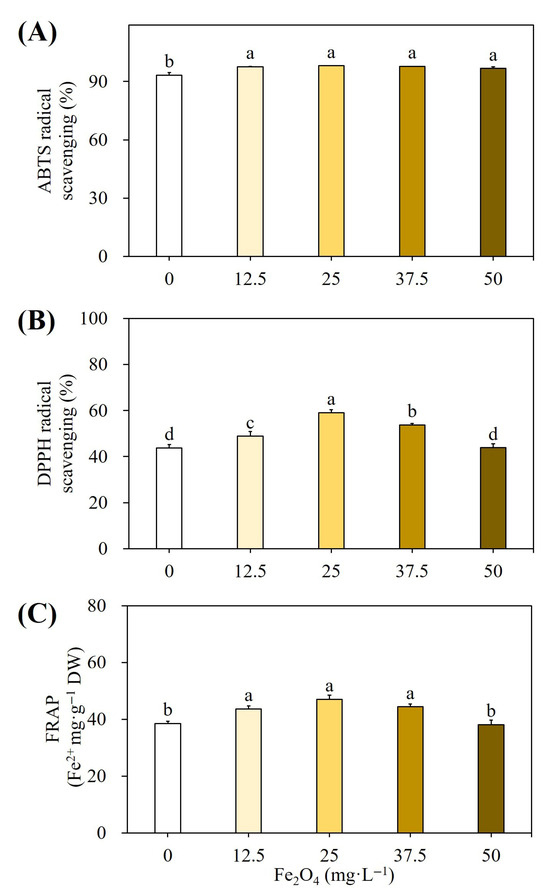
Figure 8.
Effect of different concentrations of Fe2O4NPs on ABTS free radical scavenging activity (A), DPPH scavenging activity (B), and FRAP activity (C). Different letters indicated significant (p < 0.05) differences.
2.3. Effects of MWCNTs on Biomass Accumulation, Production of Bioactive Compounds, and Antioxidant Activity
2.3.1. Effect on Biomass Accumulation
In the current studies, we treated the plant cultures of Chinese lobelia with 12.5, 25, 25, 37.5, and 50 mg L−1 MWCNTs and compared their response with non-elicited cultures. As presented in Table 3, the lower concentration of MWCNTs (12.5 mg L−1) stimulated the growth of in vitro plants and was responsible for an increment in both fresh (240.6 g L−1) and dry (22.6 g L−1) biomass (Figure 9). The increment in fresh and dry biomass was 20% and 18%, respectively. These results were significant at p ≤ 0.05, according to DMRT.

Table 3.
Effect of different concentrations of multiwalled carbon nanotubes (MWCNTs) on the growth of L. chinensis plantlets.

Figure 9.
Changes in plant biomass of in vitro grown Chinese lobelia in response to different concentrations of MWCNTs as compared to control.
2.3.2. Effect on Bioactive Compound Production
Treatments with increasing concentrations of MWCNTs led to an accumulation of total phenolics, flavonoids, and specific phenolic compounds. The optimal results were observed with the treatment of 37.5 mg L−1 MWCNT-elicited cultures, which accumulated 2.84 mg GAE g−1 DW of phenolics (Figure 10A) and 19.48 mg CE g−1 DW of flavonoids (Figure 10B). According to DMRT, these findings were significant at p ≤ 0.05 compared to non-elicited cultures. These cultures were also involved in the hyperaccumulation of individual phenolics, viz. 28.02 mg g−1 DW catechin, 203.30 mg g−1 DW phloretic acid, and 34.09 mg g−1 DW salicylic acid, and they were 150%, 54% and 36% higher than the non-elicited cultures (Figure 3D and Figure 10C). However, there were 10%, 76%, 20%, 10%, and 20% reductions in chlorogenic acid, coumaric acid, naringin, myricetin, and linarin compared with the elicited cultures. The polyacetylenes, lobetyolinin (464.57 mg g−1 DW), and lobetyolin (744.75 mg g−1 DW) contents were also enhanced by 43% and 107% with the elicitation of 37.5 mg L−1 MWCNTs (Figure 4D and Figure 10D). According to DMRT, these results were considered significant at p ≤ 0.05.
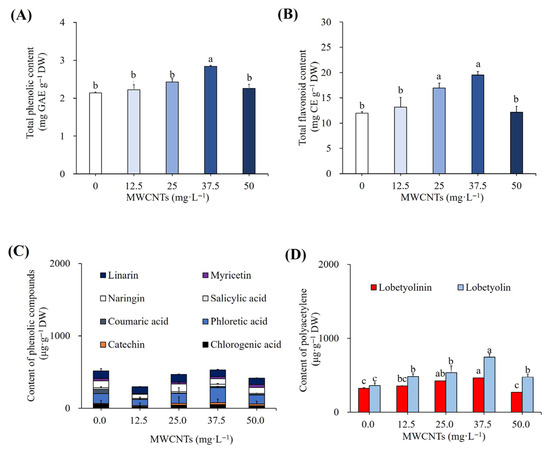
Figure 10.
Impact of varying MWCNT concentrations on the total phenolic content (A), total flavonoid content (B), content of individual phenolics (C), and polyacetylenes (D). Different letters indicated significant (p < 0.05) differences.
2.3.3. Effect on Antioxidant Activities
The results of the antioxidant activity of MWCNT-elicited cultures were compared with non-elicited cultures using ABTS, DPPH, and FRAP assays, and the results are presented in Figure 11. The plant extracts, which were elicited using 37.5 mg L−1 MWCNTs, showed 98.60% ABTS radical scavenging (Figure 11A), 61.66% DPPH radical scavenging (Figure 11B), and 51.23 Fe2+ mg g−1 DW of FRAP activity (Figure 11C). Thus, the ABTS, DPPH, and FRAP antioxidant activity of Chinese lobelia plant cultures treated by MWCNTs was significantly enhanced according to DMRT at p ≤ 0.05.
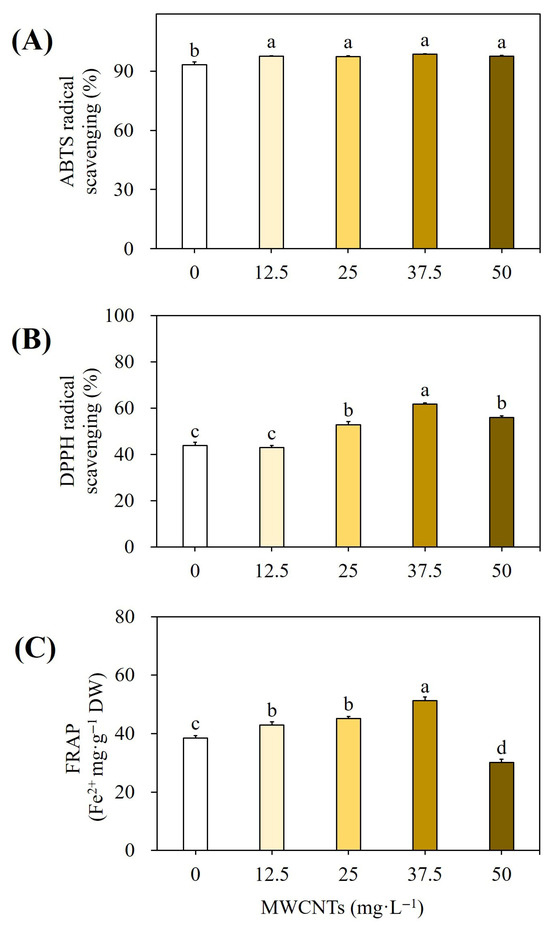
Figure 11.
Effect of different concentrations of MWCNTs on ABTS free radical scavenging activity (A), DPPH activity (B), and FRAP activity (C). Different letters indicated significant (p < 0.05) differences.
3. Discussion
Plant cell, tissue, and organ cultures provide an excellent alternative to field cultivation for large-scale biomass and phytochemical production [26]. Cell and organ cultures have been used to produce a variety of phytochemicals, such as natural colorants, medicinal compounds, flavors, and fragrances [26]. Furthermore, several biotic and abiotic elicitors have been introduced to cell and organ cultures, resulting in an increased accumulation of bioactive chemicals [15]. Similarly, nanomaterials like carbon-based nanomaterials and metal or metal oxide nanoparticles have been effectively employed to boost the in vitro synthesis of bioactive chemicals [18]. Chinese lobelia plants cultivated in vitro were used to examine the effects of nanomaterials, including AgNPs (particle size < 100 nm), Fe2O4NPs (particle size 50–100 nm), and MWCNTs (diameter 50–90 nm), on growth performance and metabolite accumulation. The results are discussed below.
3.1. Effect of Nanomaterials on the Growth Performance of Chinese Lobelia Plants In Vitro
Among the varied concentrations of AgNPs (0, 12.5, 25, 37.5, and 50 mg L−1) used, enhanced fresh biomass of 216.4 g L−1 and dry biomass of 21.6 g L−1 were observed with the addition of 25 mg L−1 AgNP treatment. Similarly, the application of 25 mg L−1 Fe2O4NPs showed an increase in fresh (230.0 g L−1) and dry biomass (23.4 g L−1). There was a 27% and 31% increment in fresh and dry biomass compared to non-elicited plant cultures. However, higher concentrations of AgNPs/Fe2O4NPs had a detrimental effect on biomass accumulation. Various studies have reported that the interaction of NMs with plants varies with plant species, and it also depends on the size and concentration of NMs as well as their nature [27]. Varied phytochemicals such as phenolics, flavonoids, and amines indirectly play a physiological role and may be able to affect plant cell growth [28]. It has been shown by other researchers that elicitation of cell and organ cultures showed improvement of biomass at specific concentrations of AgNP treatment; however, increased concentrations lead to a decrease in biomass as shown with cell cultures of Arabidopsis thaliana [29] and Brassica rapa [30]. Similarly, reports are also on record with the treatment of FeNPs in Stevia rebaudiana plant cultures [31].
As presented in Table 3, the lower concentration of MWCNTs at 12.5 mg L−1 stimulated the growth of in vitro grown Chinese lobelia plants and was responsible for an increment in both fresh (240.6 g L−1) and dry (22.6 g L−1) biomass. The increment in fresh and dry biomass was 20% and 18%, respectively. The elicitation of MWCNTs in Satureja khuzestanica at lower concentrations (25, 50, and 100 µg mL−1) is comparable to the current findings [32]. Similar results showing that adding carbon nanotubes at a certain concentration aid in biomass growth have also been reported for Brassica napus [33], Hibiscus sabdariffa [34], and Catharanthus roseus [35].
According to Dilshad et al. [36] and Yousaf et al. [37], adequate uptake of water and nutrients from the culture medium, which is in charge of growth and plant cellular metabolism, is responsible for the increase in growth of cells and tissues grown in vitro. Previously, Quian et al. [38] and Maurel et al. [39] proposed that NMs activate the water channels, like aquaporins, that are found in cell membranes. In addition to facilitating the passage of water across cell membranes and maintaining water homeostasis, activated aquaporins also aid in the uptake of nutrients and gases, including carbon dioxide, which promotes cell growth and division. Additionally, earlier research showed that specific concentrations of carbon NMs and silver NPs stimulated the expression of aquaporin genes in Arabidopsis thaliana seedlings and Lycopersicon esculentum roots, respectively [38,40].
Numerous studies have documented the more pronounced negative impacts of increased NM concentrations on plant growth [41,42,43]. According to reports, higher NP/NM concentrations cause the synthesis of ethylene, which raises the activity of several different enzymes, including chlorophyllase. This may have damaged the internal chloroplast membrane and impeded development parameters [44].
3.2. Effect of Nanomaterials on the Accumulation of Bioactive Compounds and Antioxidant Activities in Chinese Lobelia Plant Cultures
Plants treated with 37.5 mg L−1 AgNPs had the highest levels of flavonoids (22.59 mg CE g−1 DW) and total phenolic content (3.38 mg GAE g−1 DW). Chlorogenic acid (99.99 µg g−1 DW), catechin (16.48 µg g−1 DW), phloretic acid (242.53 µg g−1 DW), coumaric acid (93.42 µg g−1 DW), naringin (97.88 µg g−1 DW), and linarin (117.26 µg g−1 DW) were all found to be 55%, 166%, 84%, 57%, 6%, and 11% increments, respectively, in the plants that were elicited with 37.5 mg L−1 AgNPs. Additionally, the 37.5 mg L−1 AgNPs-elicited cultures elevated the levels of polyacetylenes, specifically lobetyolinin (770.54 µg g−1 DW) and lobetyolin (737.62 µg g−1 DW), by 137% and 105%, respectively. Similarly, the elicitation of callus cultures of Prunella vulgaris [45] and Fagonia indica [46] increased the total phenolic and flavonoid contents with AgNP treatment. Similarly, AgNPs induced the production of hydroxybenzoic acids, hydroxycinnamic acids, and flavanols, which was evident with cell suspension cultures of Momordica charantia [47]. The cultures treated with 37.5 mg L−1 AgNPs also showed higher levels of antioxidant activities as assessed by ABTS, DPPH, and FRAP assays. The cultures treated with AgNPs have higher levels of total phenolics and flavonoids, which are accountable for higher antioxidant activities. Consistently, AgNPs-elicitation stimulated the antioxidant system and a significant amount of taxol production in cell cultures of Corylus avellana [48]. Correspondingly, higher antioxidant enzyme activity was demonstrated in AgNPs-treated seedlings of Bacopa monnieri [49].
Applying 25 mg L−1 Fe2O4NPs to the medium promoted the accumulation of total phenolics (3.05 mg GAE g−1 DW) and total flavonoids (18.98 mg CE g−1 DW) in regenerated Chinese lobelia plants. It was also the cause of an increase in the content of certain phenolics, such as chlorogenic acid, coumaric acid, salicylic acid, myricetin, and linarin, which increased by 17%, 528%, 26%, 22%, and 19%, respectively. Lobetyolinin and lobetyolin were significantly higher (37% and 98%) with Fe2O4NP elicitation when compared to non-elicited plants. According to Taghizadeh et al. [50], the content of total phenolics, flavonoids, and anthocyanins was significantly enhanced in the suspension cultures of Dracocephalum polychaetum treated with FeONPs. The application of 25 mg L−1 Fe2O4NPs has also shown very good antioxidant activities with the Chinese lobelia plants, and these findings support those of Khan et al. [31], who previously showed that FeNPs enhanced Stevia rebaudina’s capacity to produce polyphenols and DPPH free radical scavenging activity.
The present study also demonstrates that elicitation of Chinese lobelia plant cultures with 37.5 mg L−1 MWCNT was involved in the accumulation of higher total phenolics (2.84 mg GAE g−1 DW) and total flavonoids (19.48 mg CE g−1 DW). Such treatment was also responsible for an increase in catechin, phloretic acid, and salicylic acid by 150%, 54%, and 36% when compared to non-elicited cultures. In addition, an increment in lobetyolinin (43%) and lobetyolin (107%) was also recorded with 37.5 mg L−1 MWCNT elicitation. ABTS, DPPH, and FRAP assay data also depicted higher antioxidant activity with the plant extracts, which were elicited by 37.5 mg L−1 MWCNT. The above results are concurrent with reports of Ghorbanpour and Hadin [32] who demonstrated that the elicitation of callus cultures of Satureja khuzestanica with 25, 50, and 100 µg mL−1 led to the accumulation of total phenolics and flavonoids. An extract of callus with such treatments also reported higher antioxidant potential. Similar findings have also been documented in Brassica napus [33], Hibiscus sabdariffa [34], and Catharanthus roseus [35] tissue cultures.
The mechanism by which NPs and NMs activate the elicitation process has not been fully understood. However, some evidence suggests that when NMs come into contact with plant cells, a series of processes take place that result in oxidative outburst and the formation of reactive oxygen species (ROS) near the plant cells [51]. Second messengers such as nitric oxide, brassinosteroids, and jasmonic acid express genes related to secondary metabolism as a result of ROS-mediated signaling events [52,53,54]. Various researchers have demonstrated the expression of genes involved in the phenolic biosynthetic pathway in response to the NM treatment. For example, Thiruvengadam et al. [30] showed the expression of phenylalanine ammonia-lyase (PAL), anthocyanin synthase (ANS), and production of anthocyanin pigment-1 (PAP1) genes with AgNP treatment in Brassica rapa ssp. rapa seedlings. In a similar vein, Drococephalum kotschyi hairy roots treated with iron-oxide NPs showed increased expression of the PAL and rosmarinic acid synthase (RAS) genes, according to Nourozi et al. [55]. After being exposed to 100 and 200 µg mL−1 MWCNTs, Ghorbanpur and Hadian [32] showed phenolic biosynthesis, which they associated with the highest PAL activity. This study supports the notion that NPs/NMs, which are used as elicitors in plant cell and organ cultures, are responsible for triggering the antioxidant system and, in turn, gene expression, which in turn drives secondary metabolism.
Plants with the treatment of NPs or NMs may bioaccumulate nanoparticles, which could affect growth, photosynthesis, primary and secondary metabolism, and other processes in both good and negative ways. This implies that the effects differ according to plant species, development stage, size, charge, and concentration [56]. The scientific community should conduct a detailed evaluation of the effects of bioaccumulation of NPs or NMs in vivo or plants cultivated in vitro.
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Establishment of In Vitro Culture
The experimental material used in this study, Lobelia chinensis, was derived from axenic cultures. L. chinensis shoots were maintained in MS medium [57] enriched with 3% sucrose and 7 g L−1 agar by routinely cultivating stem segments with nodes once every four weeks. The pH of the medium was adjusted to 5.8 before autoclaving. The cultures were kept at 25 ± 2 °C, 70% relative humidity, and 40 µmol m−2 s−1 light intensity (using fluorescent lights) for a 16 h day/night photoperiod.
4.2. Elicitation
Five hundred mL capacity culture jars (Cat. No 310123, 120 × 80 mm plant tissue culture jars, SPL Life Sciences, Pocheon-si, Republic of Korea) with 100 mL of MS medium containing 3% sucrose were used to establish the cultures. Three g L−1 explants, which are 1.5 cm long stem segments with two nodes and alternate leaves, without roots, were used to establish cultures. Cultures were maintained on a rotary shaker set at 100 rpm (OS 4000 orbital shaker, Jeio Tech, Daejon, Republic of Korea). Using red, blue, and green light-emitting diodes (LEDs, Itswell Co., Incheon, Republic of Korea), the cultures were kept at 25 ± 2 °C, 70% relative humidity, and 60 µmol m−2 s−1 light intensity. The elicitation effects of iron oxide NPs (Fe2O4NPs, 50–100 nm particle size, Code #637106, Sigma, St. Louis, MO, USA), silver NPs (AgNPs, <100 nm particle size, Code #576832, Sigma, St. Louis, MO, USA), and multiwalled carbon nanotubes (MWCNTs, 50–90 nm diameter, Code #901019, Sigma, St. Louis, MO, USA) at concentrations of 0, 12.5, 25, 37.5, and 50 mg L−1 were assessed after four weeks of culture establishment. The stock solutions were prepared by using sterile distilled water and then added to the medium. The cultures were then maintained for an additional week as previously mentioned. The plants were harvested after five weeks, their fresh and dry biomass was measured, and the content of secondary metabolites that had accumulated in the regenerated plants was estimated.
4.3. Biomass Estimation
The biomass from the plants was gathered after five weeks of cultivation, the medium was washed off with tap water, and the surface water was wiped off with tissue paper. An estimate was made of the fresh biomass/fresh weight (FW). After the biomass was dried for 72 h at 50 °C, the dry biomass/dry weight (DW) was calculated. The growth ratio was calculated using the formula [harvested dry weight (g)—inoculated dry weight (g)/inoculated dry weight].
4.4. Plant Extract Preparation
Using 80% ethanol and an ultrasonic extractor (Model SD-D250H; Sungdong Ultrasonics, Seoul, Republic of Korea, 40 kHz, 150 W), one gram of dried and powdered plant material was extracted for one hour at 80 °C. The extract was filtered through a qualitative cellulose filter paper (Grade 2; Whatman, Cytiva, Marlborough, MA, USA; average pore size 8 µm, thickness 190 µm, basis weight 97 g/m2). Using a vacuum pump (Model 2546C-10; Welch, Gardner Denver, Niles, IL, USA), vacuum filtering was carried out on this qualitative filter paper, which is of the non-membrane type.
4.5. Quantification of Phenolic Content
The Folin-Ciocalteu reagent method was used for determining the total phenolic content [58]. In summary, 0.1 mL of 2 N Folin-Ciocalteu reagent was added to a known volume of plant extract that had been raised up to 3 mL with distilled water. Following a 6 min incubation period, 0.5 mL of 20% Na2CO3 was added to each tube. After the tubes were incubated in warm water for half an hour, the absorbance at 760 nm was measured with a UV-visible spectrophotometer (Libra S22, Biochrome Ltd., Cambridge, UK). The standard chemical that was used was gallic acid. The results are expressed in milligrams of gallic acid equivalents (GAE) per gram of dry weight (DW). R2 was 0.9985, and the calibration curve’s equation was y = 0.0023x + 0.0022.
4.6. Quantification of Flavonoid Content
To assess the extracts’ flavonoid concentration, the Harborne [58] technique was employed. After mixing 0.1 mL of extract, 0.15 mL of 10% AlCl3, and 2 mL of 1 M NaOH, the final volume was adjusted with distilled water to 3 mL. At room temperature, the solution was incubated for five minutes. Following the vortexing of the solutions, a spectrophotometer (Libra S22, Biochrome Ltd., Cambridge, UK) was used to detect absorbance at 510 nm. The norm was catechin. In milligrams of catechin equivalents (CE) per gram of dry weight (DW), the final data is shown. The calibration curve’s equation was y = 0.0024x + 0.0562, with R2 = 0.995.
4.7. Analysis of Phenolics Using HPLC
Phenolic compounds were extracted and analyzed using the Burin et al. [59] technique. A total of 2.0 mL of 70% methanol with 2% formic acid was used to dissolve 0.1 g of material. The samples were then centrifuged at 10,000× g for 10 min at 4 °C. Before analysis, the supernatant was filtered through 0.22 µm syringe filters. HPLC analysis was conducted in triplicate using a Shimadzu (Kyoto, Japan) liquid chromatography system equipped with a 20 µL loop injector (Rheodyne), quaternary pump LC-10AT, UV-vis detector (SPD-10AV), and vacuum degasser (DGU-14A) (Shimadzu, Kyoto, Japan). The gradient settings, UV-vis, and data gathering were managed by the CLASS-V application (version 6.1). A 4.6 × 250 mm C18 reverse-phased column with a 5 µm particle size was used. Acetic acid in filtered Milli-Q water with a pH of 2.6 was used as solvent A in the mobile phase, while 20% of solution A in 80% acetonitrile served as solvent B. The flow rate was 1.2 mL/min. To identify phenolic compounds, the retention time and UV spectra were compared with authentic standards (Sigma-Aldrich, St. Louis, MO, USA).
4.8. Analysis of Polyacetylenes Using HPLC
The extraction of the polyacetylenes (lobetyolin and lobtyolinin) was carried out according to the method of Qiao et al. [60]. For HPLC analysis, a Shimadzu liquid chromatography system (Kyoto, Japan) equipped with a C18 column (4.65 × 250 mm, 5 µM) was utilized. The column’s temperature was set to 20 °C. Acetonitrile and water comprised the mobile phase. It was applied in 25 and 35 min, respectively, using linear gradient elution from 10% to 40% and then to 100% acetonitrile. The detection wavelengths were 267 and 295 nm. Standards were procured from Sigma-Aldrich, St. Louis, MO, USA.
4.9. Antioxidant Activity Assays
4.9.1. DPPH Assay
A 0.1 mM DPPH solution prepared in ethanol (1.9 mL) was added to 0.1 mL of plant extract. After vortexing the tubes, the solution was left in the dark for fifteen minutes. A UV-visible spectrophotometer (Libra S22, Biochrome Ltd., Cambridge, UK) was used to evaluate the discoloration of DPPH solution at 517 nm using DPPH solution without plant extract as a blank. The activity of the extracts was expressed as mg gallic acid equivalent (GAE)/g extract, with gallic acid serving as the reference [61].
4.9.2. ABTS Assay
The ABTS solution was prepared using a 1:1 mixture of 7 mM ABTS and 2.45 mM potassium persulfate, and it was then left in the dark for a full day. To obtain the value of 0.70 at 732 nm, the ABTS solution was diluted with phosphate buffer (pH 7.3) at the time of analysis. Then, 50 µL of the extract was added to 950 µL of diluted ABTS solution, and the combination was left in the dark for 10 min before the absorbance was measured at 732 nm using UV-visible spectrophotometry (Libra S22, Biochrome Ltd., Cambridge, UK). The antioxidant activity as a percentage was represented by the formula = absorbance of control solution-absorbance of sample solution/absorbance of control solution × 100 [61].
4.9.3. FRAP Assay
To make the FRAP reagent, a 20 mM FeCl2·6H2O solution, 300 mM acetate buffer (pH 3.6), and a 10 mM 2,4,6-tripyridyl-s-triazine (TPTZ) solution in 40 mM HCl were added. Their combo had a 1:10:1 ratio. After adding 2 mL of extract and 3 mL of FRAP reagent, the tubes were vortexed and allowed to stand for six minutes at room temperature. A UV-visible spectrophotometer (Libra S22, Biochrome Ltd., Cambridge, UK) was used to measure the absorbance at 593 nm. Activity is measured as mg ascorbic acid equivalent (AAE)/g extract, with ascorbic acid serving as the reference [61]. The equation for the calibration curve was y = 0.0028x + 0.5795, with R2 = 0.7853.
4.10. Statistical Analysis
A completely randomized design was used to set up each study, and three replications were used to collect data. A one-way analysis of variance (ANOVA) was employed to identify significant differences among each treatment. Duncan’s multiple range test was used to determine whether the mean value differences were statistically significant at p ≤ 0.05.
5. Conclusions
The production of target bioactive compounds can be improved by using plant cell and organ cultures, and elicitation is a practical method for increasing the accumulation of secondary metabolites. The effects of AgNPs, Fe2O4NPs, and MWCNTs on plant growth and bioactive chemical accumulation in vitro were investigated in the current work. Application-specific concentrations of 37.5 mg L−1 AgNPs, 25 mg L−1 Fe2O4NPs, and 37.5 mg L−1 MWCNTs were useful for the production of phenolics, flavonoids, and polyacetylenes in the shoot cultures of Chinese lobelia. Of the several NP/NM treatments, elicitation of Chinese lobelia plant cultures with 37.5 mg L−1 AgNPs is highly beneficial as it accounts for higher levels of chlorogenic acid (55%), catechin (166%), phloretic acid (84%), coumaric acid (57%), naringin (6%), linarin (11%), lobetyolinin (137%), and lobetyolin (105%) when compared to non-elicited cultures. These results are useful for the large-scale production of phenolics and polyacetylenes in Chinese lobelia through the use of bioreactor cultures.
Author Contributions
X.B. conducted the experiments; H.-S.L. helped in the analysis; J.-E.H. helped in the analysis; H.N.M. was involved in the analysis of data and writing; S.-Y.P. was involved in conceptualization, procuring funding, and guiding the students. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This work was supported by the Industrial Strategic Technology Development Program (Grant No. P0018148) funded by the Ministry of Trade, Industry and Energy, Republic of Korea. The National Research Foundation, Republic of Korea’s “Brain Pool” (Grant No. 2022H1D3A2A02056665) is gratefully acknowledged by Hosakatte Niranjana Murthy.
Data Availability Statement
Raw data is available from Prof. So-Young Park, Department of Horticulture, Chungbuk National University, Cheongju 28644, Republic of Korea.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Abbreviations
The abbreviations listed below are utilized in this manuscript:
| ABTS | 2,2′-azino-bis (3-ethybenzothiazoline-6-sulphonic acid |
| AgNPs | Silver nanoparticles |
| AAE | Ascorbic acid equivalent |
| CE | Catechin equivalent |
| DPPH | 2,2 Diphenyl 1 picrylhydrazyl |
| DW | Dry weight |
| FRAP | Ferric reducing antioxidant power |
| Fe2O4NPs | Iron oxide nanoparticles |
| FW | Fresh weight |
| HPLC | High-performance liquid chromatography |
| LEDs | Light-emitting diodes |
| NP | Nanoparticle |
| NM | Nanomaterial |
| MWCNTs | Multiwalled carbon nanotubes |
| MS | Murashige and Skoog medium |
| UV | Ultraviolet light |
References
- Li, S. The Ben Cao Gang Mu, 1st ed.; University of California Press: Oakland, CA, USA, 2016; p. 625. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Kuo, P.C.; Hwang, T.L.; Lin, Y.T.; Kuo, Y.C.; Leu, Y.L. Chemical constituents from Lobelia chinensis and their anti-virus and anti-inflammatory bioactivates. Arch. Pharmacal Res. 2011, 34, 715–722. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, M.S.; Chen, W.R.; Zhang, J.M.; Long, X.Y.; Wang, Y.T. Lobelia chinesnis: Chemical constituents and anticancer activity perspective. Chin. J. Nat. Med. 2014, 12, 103–107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, S.; Shen, T.; Zhao, L.J.; Li, C.; Zhang, Y.; Lou, H.X.; Ren, D.M. Chemical constituents of Lobelia chinensis. Fitoterapia 2014, 93, 168–174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, K.C.; Ho, Y.L.; Huang, G.J.; Chang, Y.S. Anti-oxidative and anti-inflammatory effects of Lobelia chinensis in vitro and in vivo. Am. J. Chin. Med. 2015, 43, 269–287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, L.; Reddy, N.; Khoo, C.; Koyyalamudi, S.R.; Jones, C.E. Antioxidant and immunomodulatory activities and structural characterization of polysaccharides isolated from Lobelia chinensis Lour. Pharmacologia 2018, 9, 157–168. [Google Scholar]
- Kuo, Y.C.; Lee, Y.C.; Leu, Y.L.; Tsai, W.J.; Chang, S.C. Efficacy of orally administered Lobelia chinensis extracts on herpes simplex virus type 1 infection in BALB/c mice. Antivir. Res. 2008, 80, 206–212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, X.; Hu, P.; Zhang, X.; Li, X. Chemical structure elucidation of an inulin-type fructan isolated from Lobelia chinensis Lour. with anti-obesity on diet-induced mice. Carbohydr. Polym. 2020, 240, 116357. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Choi, W.H.; Lee, I.A. The anti-tubercular activity of Melia azedarach L. and Lobelia chinensis Lour. and their potential as effective anti-Mycobacterium tuberculosis candidate agents. Asian Pac. J. Trop. Biomed. 2016, 6, 830–835. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shao, J.H.; Zhang, H. Influence of Lobelia chinses Lour. Decoction on expression of C-erbB-2 and P53 on H22 tumor-bearing mice. Chin. J. Clin. Pharm. 2010, 19, 372–375. [Google Scholar]
- Santosa, M.H.; Herzog, R.; Voelter, W. Antitumor activity of the hot water extract of Lobelia chinensis. Planta Med. 1986, 6, 555. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bai, X.; Lee, H.S.; Murthy, H.N.; Kwon, H.J.; Yeon, S.H.; Ju, J.Y.; Park, S.Y. Micropropagation of Lobelia chinensis Lour.: Influence of medium parameters on plant regeneration, antioxidant activity and secondary metabolite accumulation. Korean J. Plant Res. 2024, 37, 225–234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bai, X.; Lee, H.S.; Han, E.J.; Murthy, H.N.; Paek, K.Y.; Park, S.Y. Stimulating synthesis of phenolics and polyacetylenes in Lobelia chinensis Lour. Plantlets using various bioreactor systems: A comparison of parameter effects. Plant Cell Tissue Organ Cult. 2024, 16, 36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bai, X.L.; Murthy, H.N.; Park, S.Y. In vitro propagation of Lobelia chinensis Lour. under different LED lights. Rom. Biotechnol. Lett. 2023, 28, 3942–3949. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramirez-Estrda, K.; Limon, H.V.; Hidalgo, D.; Moyano, E.; Golenioswki, M.; Cudio, R.M.; Palazon, J. Elicitation, an effective strategy for the biotechnological production of bioactive high-added value compounds in plant cell factories. Molecules 2016, 21, 182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Murthy, H.N.; Joseph, K.S.; Paek, K.Y.; Park, S.Y. Production of specialized metabolites in plant cell and organo-cultures: The role of gamma radiation in eliciting secondary metabolism. Int. J. Rad. Biol. 2024, 100, 678–688. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Murthy, H.N.; Joseph, K.S.; Paek, K.Y.; Park, S.Y. Light as an elicitor for enhanced production of secondary metabolites in plant cell, tissue, and organ cultures. Plant Growth Regul. 2024, 104, 31–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Murthy, H.N.; Joseph, K.S.; Paek, K.Y.; Park, S.Y. Nanomaterials as novel elicitors of pharmacologically active plant specialized metabolites in cell and organ cultures: Current status and future outlooks. Plant Growth Regul. 2024, 104, 5–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharafi, E.; Khayam Nekoei, S.M.; Fotokian, M.H.; Davoodi, D.; Hadavand Mirzaei, H.; Hsanloo, T. Improvement of hypericin and hyperforin production using zinc and iron nano-oxides as elicitors in cell suspension culture of St. John’s wort (Hypericum perforatum L.). J. Med. Plants By-Prod. 2013, 2, 177–184. [Google Scholar]
- Poboilova, Z.; Opatrilova, R.; Babula, P. Toxicity of aluminum oxide nanoparticles demonstrated using a BY-2 plant cell suspension culture model. Environ. Exp. Bot. 2013, 91, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chung, I.M.; Rajakumar, G.; Thiruvengadam, M. Effect of silver nanoparticles on phenolic compounds production and biological activities in hairy root cultures of Cucumis anguria. Acta Biol. Hung. 2018, 69, 97–109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, J.H.; Oh, Y.; Yoon, H.; Hwang, I.; Chang, Y.S. Iron nanoparticle-induced activation of plasma membrane H+-ATPase promotes stomatal opening in Arabidopsis thaliana. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2015, 49, 1113–1119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- El-Temsah, Y.S.; Joner, E.J. Impact of Fe and Ag nanoparticles on seed germination and differences in bioavailability during exposure in aqueous suspension and soil. Environ. Toxicol. 2012, 27, 42–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tariverdizadeh, N.; Mohebodini, M.; Chamani, E.; Ebadi, A. Iron and zinc oxide nanoparticles: An efficient elicitor to enhance trigonelline alkaloid production in hairy roots of fenugreek. Ind. Crops Prod. 2021, 162, 113240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bai, X.; Lee, H.S.; Han, J.E.; Murthy, H.N.; Park, S.Y. Enhancement of phenolic and polyacetylene accumulation in Lobelia chinensis (Chinese lobelia) plantlet cultures through yeast extract and salicylic acid elicitation. Horticulturae 2025, 11, 612. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wilson, S.A.; Roberts, S.C. Recent advances towards development and commercialization of plant cell culture processes for synthesis of biomolecules. Plant Biotechnol. J. 2012, 10, 249–268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Khodakovskaya, M.V.; De-silva, K.; Nedosekin, D.A.; Dervishi, A.; Biris, A.S.; Shashkov, E.V.; Galnzha, E.V.; Galanzha, E.J.; Zharov, V.P. Complex genetic, photochemical, and photacoustic analysis of nanoparticle-plant interactions. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2011, 108, 1028–1033. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yoshioka, T.; Inokuchi, T.; Fujioka, S.; Kimura, Y. Phenolic compounds and flavonoids as plant growth regulators from fruit and leaf of Vitex rotundifolia. Z. Naturforschung C 2004, 59, 509–514. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaveh, R.; Li, Y.S.; Ranjbar, S.; Tehrani, R.; Brueck, C.L.; Aken, B.V. Changes in Arabidopsis thaliana gene expression in response silver nanoparticles and silver ions. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2013, 47, 10637–10644. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thiruvengadam, M.; Gurunathn, S.; Chung, I.M. Physiological, metabolic, and transcriptional effects of biologically-synthesized silver nanoparticles in turnip (Brassica rapa ssp. rapa L.). Protoplasma 2015, 252, 1031–1046. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khan, M.A.; Ali, A.; Mohammed, S.; Ali, H.; Khan, T.; Mashwani, Z.R.; Jan, A.; Ahmad, P. Iron nono modulated growth and biosynthesis of steviol glycosides in Stevia rebaudiana. Plant Cell Tissue Organ Cult. 2020, 143, 121–130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghorbanpour, M.; Hadin, J. Multi-walled carbon nanotubes stimulate callus induction, secondary metabolites biosynthesis and antioxidant capacity in medicinal plant Satureja khuzestanica grown in vitro. Carbon 2015, 94, 749–759. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, G.; Zhao, Y.; Lou, W.; Su, J.; Wei, S.; Yang, X.; Wang, R.; Guan, R.; Pu, H.; Shen, W. Nitrate reductase-dependent nitric oxide is crucial for multi-walled carbon nanotube-induced plant tolerance against salinity. Nanoscale 2019, 11, 10511–10523. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sareea Al-Rekaby, L. Influence of multiwalled carbon nanotubes and biostimulators on growth and content of bioactive constituents of karkade (Hibiscus sabadariffa L.). J. Bot. 2018, 2018, ID9097363. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghasempour, M.; Iranbakhsh, A.; Ebadi, M.; Oraghi Aardebili, Z. Multi-walled carbon nanotubes improved growth, anatomy, physiology, secondary metabolism, and callus performance in Catharanthus roseus: An in vitro study. Biotech 2019, 9, 404. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dilshad, E.; Ismail, H.; Khan, M.A.; Cusido, R.M.; Mirza, B. Metabolite profiling of Artemisia carvifolia Buch. transgenic plants and estimation of their anticancer and antidiabetic potential. Bioctal. Agric. Biotechnol. 2020, 25, 101539. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yousaf, R.; Khan, M.A.; Ullah, N.; Khan, I.; Hayat, O.; Shehzad, M.A.; Khan, I.; Taj, F.; Ud Din, N.; Khan, A. Biosynthesis of anti-leishmanial natural products in callus cultures of Artemisia scoparia. Artif. Cells Nanomed. Biotechnol. 2019, 47, 1122–1131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Qian, H.; Peng, X.; Han, X.; Ren, J.; Sun, L.; Fu, Z. Comparison of the toxicity of silver nanoparticles and silver ions on the growth of terrestrial plant model Arabidopsis thaliana. J. Environ. Sci. 2013, 25, 1947–1956. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maurel, C.; Boursiac, Y.; Luu, D.T.; Santoni, V.; Shahzad, Z.; Verdoucq, L. Aquaporins in plants. Physiol. Rev. 2015, 95, 1321–1358. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Villagarcia, H.; Dervishi, E.; de Silva, K.; Biris, A.S.; Khodakovskaya, M.V. Surface chemistry of carbon nanotubes impacts the growth and expression of water channel protein in tomato plants. Small 2012, 8, 2328–2334. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Keller, A.A.; Lazareva, A. Predicted releases of engineered nano-materials: From global to regional to local. Environ. Sci. Technol. Lett. 2014, 1, 65–70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pokhrel, L.R.; Dubey, B. Evaluation of developmental responses of two crop plants exposed to silver and zinc oxide nanoparticles. Sci. Total Environ. 2013, 452, 321–332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zuverza-Mena, N.; Armendariz, R.; Peralta-Videa, J.R.; Gardea-Torresdey, J.L. Effects of silver nanoparticles on radish sprouts: Root growth reduction and modifications in the nutritional value. Front. Plant Sci. 2016, 7, 90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Khan, M.A.; Riaz, M.S.; Ullah, N.; Alid, H.; Nadhmane, A. Plant cell nanomaterials interaction: Growth, physiology and secondary metabolism. Analysis, fate, and toxicity of engineered nanomaterials in plants. Compr. Anal. Chem. 2019, 84, 23–54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fazal, H.; Abbaisi, B.H.; Ahmad, N.; Ali, M. Elicitation of medicinally important antioxidant secondary metabolites with silver and gold nanoparticles in callus cultures of Prunella vulgaris L. Appl. Biochem. Biotechnol. 2016, 180, 1076–1092. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Begaum, S.; Zahid, A.; Khan, T.; Khan, N.Z. Comparative analysis of the effects of chemically and biologically synthesized silver nanoparticles on biomass accumulation and secondary metabolism in callus cultures of Fagonia indica. Physiol. Mol. Biol. Plants 2020, 26, 1739–1750. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chung, I.M.; Rekha, K.; Rajakumar, G.; Thiruvengadam, M. Elicitation of silver nanoparticles enhanced the secondary metabolites and pharmacological activities in cell suspension cultures of bitter gourd. 3 Biotech 2018, 8, 412. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jamshidi, M.; Ghanati, F.; Rezaei, A.; Bemani, E. Change of antioxidant enzymes activity of hazel (Corylus avellana L.) cells by AgNPs. Cytotechnology 2016, 68, 525–530. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krishnaraj, C.; Jagan, G.; Ramachandran, R.; Abirami, S.M.; Mohan, N.; Kalaichelvan, P.T. Effect of biologically synthesized silver nanoparticles on Bacopa monnieri L. Wettst. plant growth metabolism. Process Biochem. 2012, 47, 651–658. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Taghizadeh, M.; Nasibi, F.; Kalntari, K.M.; Ghanati, F. Evaluation of secondary metabolites and antioxidant activity in Dracocephalum polychaetum Bornm. cell suspension culture under magnetite nanoparticles and static magnetic field cultivation. Plant Cell Tissue Organ Cult. 2019, 136, 489–498. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marslin, G.; Sheeba, C.J.; Fraklin, G. Nanoparticles alter secondary metabolism in plants via ROS burst. Front. Plant Sci. 2017, 8, 832. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lindermayr, C.; Durner, J. Interplay of reactive oxygen species homeostasis. Plant Physiol. 2015, 167, 1209–1210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xia, X.J.; Wang, Y.J.; Zhou, Y.H.; Tao, Y.; Mao, W.H.; Shi, K.; Asami, T.; Chen, Z.; Yu, J.Q. Reactive oxygen species are involved in barassinosteroid-induced stress tolerance in cucumber. Plant Physiol. 2009, 150, 801–814. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, H.; Li, A.; Zhang, Z.; Huang, Z.; Lu, P.; Zhang, D.; Liu, X.; Zhang, Z.F.; Huang, R. Ethylene response factor TREF1, regulated by ETHYLEND-RESPONSE3-like factors, functions in reactive oxygen species (ROS) scavenging in tobacco (Nicotiana tabacum L.). Sci. Rep. 2016, 6, 29948. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nourozi, E.; Hosseini, B.; Maleki, R.; Abdollahi Mandoulakani, B.A. Iron oxide nanoparticles: A novel elicitor to enhance anticancer flavonoid production and gene expression in Dracocephalum kotschyi hairy-root cultures. J. Sci. Food Agric. 2019, 99, 6418–6430. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Djanaguiraman, M.; Anbazhagn, V.; Dhankher, O.M.; Vara Prasad, P.V. Uptake, tranlocaiton, toxicity, and impact of nanoparticles on plant physiological processes. Plants 2024, 13, 3137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Murashige, T.; Skoog, F. A revised medium for rapid growth and bioassays with tobacco tissue cultures. Physiol. Plant. 1962, 15, 373–497. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harborne, A.J. Phytochemical Methods: A Guide to Modern Techniques of Plant Analysis; Springer: Dordrecht, The Netherlands, 1994. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Burin, V.M.; Arari, S.G.; Costa, L.L.F.; Bordingon-Luiz, A.M.T. Determination of some phenolic compounds in red wind by RP-HPLC: Method development and validation. J. Chromatogr. Sci. 2011, 49, 647–651. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qiao, C.F.; He, Z.D.; Han, Q.B.; Hu, H.X.; Jiang, R.W.; Li, S.L.; Zhang, Y.B.; But, P.P.H.; Shaw, P.C. The use of lobetyolin and HPLC-UV fingerprints for quality assessment of radix codonopsis. J. Food Drug. Anal. 2007, 15, 258–264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Munteanu, I.G.; Apetrei, C. Analytical methods used in determining antioxidant activity: A review. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 22, 3380. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).