Abstract
Since dust aerosols are one of the major pollutants in Georgia, it is important to study the aeolian desert dust (ADD) invasion to Georgia from the neighboring deserts to find out its contribution to the dust pollution problem. Therefore, the main objective of this study is to investigate the history, frequency and routes of ADD invasions to the Caucasus (Georgia) using modern models and technologies for 1.5 years. Using WRF-Chem/dust, CAMS and HYSPLIT mathematical models; MODIS satellite images; and PM10 field data, 38 cases of not strong ADD invasions to Georgia were found, and two typical cases are presented and analyzed in this paper. The results of the modeling studies from 15 March 2023 to 15 September 2024 showed that the WRF-Chem/dust (GOCART) v.4.5.1 model simulated the ADD transport to Georgia from the surrounding deserts quite well. Daily monitoring of ADD migration routes showed that in the easternmost region of Georgia (the most vinicultural and agricultural region), the number of ADD invasions was approximately three times higher than in other regions of Georgia, which is a novelty of this study due to the lack of ground dust measurement stations in the easternmost region of Georgia.
1. Introduction
Aerosols, tiny particles suspended in the atmosphere (dust, smoke, fumes, mist, fog, etc.) make up the bulk of air pollution, are hazardous to human health and are a major source of modern climate variability [1,2]. Dust (large particulate aerosols that mainly result from the deflation of erodible sediments and originate from desert storms) and smoke (fine particulate aerosols that mainly result from the combustion of biomass and petroleum products) are among the major components of atmospheric aerosols [3,4]. Among aerosols, mineral dust is a leader among natural aerosols, as 75% of the global aerosol mass is mineral dust [5]. It should be noted that the role of mineral dust in the Earth’s climate system is strengthened by its active participation in all scales of physical, chemical and biogeochemical processes [6,7,8]. For example, aeolian dust aerosol (ADA) absorbs and scatters shortwave and longwave radiation and, thereby, affects the radiation balance of the atmosphere, as well as the formation of clouds (precipitation), human health, and visibility [9,10]. Indeed, dust aerosols are effective ice nuclei, capable of increasing ice crystal concentrations; mass mixing coefficients of rain, graupel and snow up to 9.8%; and reducing droplet concentrations via the Wegener–Bergeron–Findeisen process in mixed-phase clouds [11]. In addition, ADA can rearrange the molecular and ionic structure of the atmosphere (clouds) through chemical reactions when passing through polluted areas and acting as giant cloud condensation nuclei (GCN), enhances droplet collisions (coalescence) and, therefore, increases the formation of warm precipitation [12,13]. At the same time, as satellite and airborne observations and laboratory studies have shown, a large amount of ADA in clouds can hinder precipitation by increasing the number of cloud condensation nuclei in warm clouds [14,15]. Thus, ADA affects the composition and processes in the atmosphere both through physical action and through participation in chemical reactions [11,12]. Indeed, in the case of deposition in clouds, ADA changes the albedo, as well as the optical properties, and thickens the cloud core (creating obstacles to cloud formation and precipitation) and, thus, indirectly affects climate change [12,16].
Arid and semi-arid regions of Georgia are the most sensitive to the ongoing climate change process, as they carry a higher risk of soil degradation and desertification [17,18]. Almost similar to global processes, over the past three decades, the surface warming process over arid and semi-arid lands has been 25–40% higher than over wetlands, the area of semi-arid regions has increased by 4.5% and Georgia has seen an acceleration of the global desertification process [19,20]. As a rule, arid and semi-arid areas adjacent to deserts suffer the most from dust storms; however, it should be noted that remote areas are also affected and not protected from severe dust storms [19]. Indeed, according to various studies, strong winds from the Sahara and Saudi Arabian deserts transport large amounts of dust to the atmosphere, from where about 30% settles in the deserts, 20% is transported regionally (territories adjacent to the deserts) and, interestingly, about 50% is transported across the Atlantic and Pacific Oceans beyond [21,22].
Aeolian desert dust (ADD) has a principal influence on drought and desertification processes and, as a rule, on global and regional climate change, especially in arid, semi-arid and mountainous regions [23,24,25,26]. For example, scientific studies have shown that the territory of the North Caucasus is one of the regions affected by ADD, which is carried from the deserts of Africa and the Middle East by strong air currents [27,28,29]. The origin and transport of ADD and its distribution routes are widely studied worldwide [2,3,4,5,6,7,8,9,10,11,12,13,14,15,16,17,19,20,21,22,23,24,25,26,27,28,29,30,31]. Theoretical studies, satellite imagery data, and the WRF-Chem model, combined with three types of dust modules, are widely used to study dust storms and simulate the transport of particulate matter from deserts to the Europe, Middle East, Asia and Caucasus regions [31,32,33,34,35,36,37,38,39,40,41,42,43]. According to the National Environmental Agency (NEA) of Georgia, dust is one of the main pollutants in Georgia, but the ADD transport from deserts to the territory of Georgia has not been properly studied yet [25,29,31,33]. The origin of long-range transported desert dust (LTDD) and its chemical composition has been investigated in many studies using analysis of LTDD samples deposited in the European Alps, Himalayas and Tibetan Plateau [32,34,39,40,43,44,45]. As for the Caucasus, the origin and chemical composition of LTDD reaching the Caucasus Mountains have been investigated in ice cores extracted from the summit of Mount Elbrus in Russia [27,28,46] and from the summit of Mount Kazbegi in Georgia [47]. Based on the materials obtained from ice cores extracted by scientific expeditions in 2009, 2012 and 2013 on Elbrus, it was shown that dust arrives between three and seven times a year, mainly from the deserts of the Middle East and, less frequently, from the northern Sahara [28]. The analysis of the first-ever extracted ice core (18 m) from the Kazbegi glacier located on the northern border of Georgia (at an altitude of ~4500 m above sea level) showed that along with the dust of local origin, it also contained dust brought only from the deserts of the Middle East and the Sahara [47]. It should be noted that it was further shown that LTDD was also repeatedly transported to the territory of Georgia from the Karakum and Kyzylkum deserts [29,31]. The study of the formation process of ADD and the transport routes of LTDD still remains an urgent task due to the direct and indirect influences of ADA on the climate but remains a difficult task due to many nonlinear influencing factors.
The main aim of this work is to study the frequency and routes of ADD transport to the territory of the Caucasus (Georgia) from the surrounding deserts for one and a half years under the conditions of the complex orography of the Caucasus and against the background of regional climate changes using modern scientific methods. Namely, to study the transport of ADD from the deserts to the territory of Georgia, the Weather Research and Forecasting WRF-Chem v.4.5.1 in combination with the GOCART dust module, Copernicus Atmosphere Monitoring Service (CAMS) (https://atmosphere.copernicus.eu/data (accessed on 20 September 2024)) and Hybrid Single-Particle Lagrangian Integrated Trajectory (HYSPLIT) (https://www.ready.noaa.gov/HYSPLIT.php (accessed on 30 September 2024)) models were used. The spatial and temporal capabilities of these models were assessed using an observational dataset (in situ particulate matter (PM10)) and Moderate Resolution Imaging Spectroradiometer (MODIS) (https://modis.gsfc.nasa.gov/about/ (accessed on 5 October 2024)) satellite products. The main significance and novelty of this work is that, for the first time, for 1.5 years, the possible transfer of the ADD to the territory of the Caucasus (Georgia) was studied daily (using modern numerical models, remote sensing and in situ data), in order to understand the role of the ADD in the overall dust pollution of the territory of Georgia. To illustrate the main features, routes and time of the long-distance dust transfer to the territory of Georgia, two typical cases (28–31 May 2024 and 24–30 April 2024) were selected and analyzed from daily numerical calculations carried out from 2 March 2023 to 20 September 2024.
2. Materials and Methods
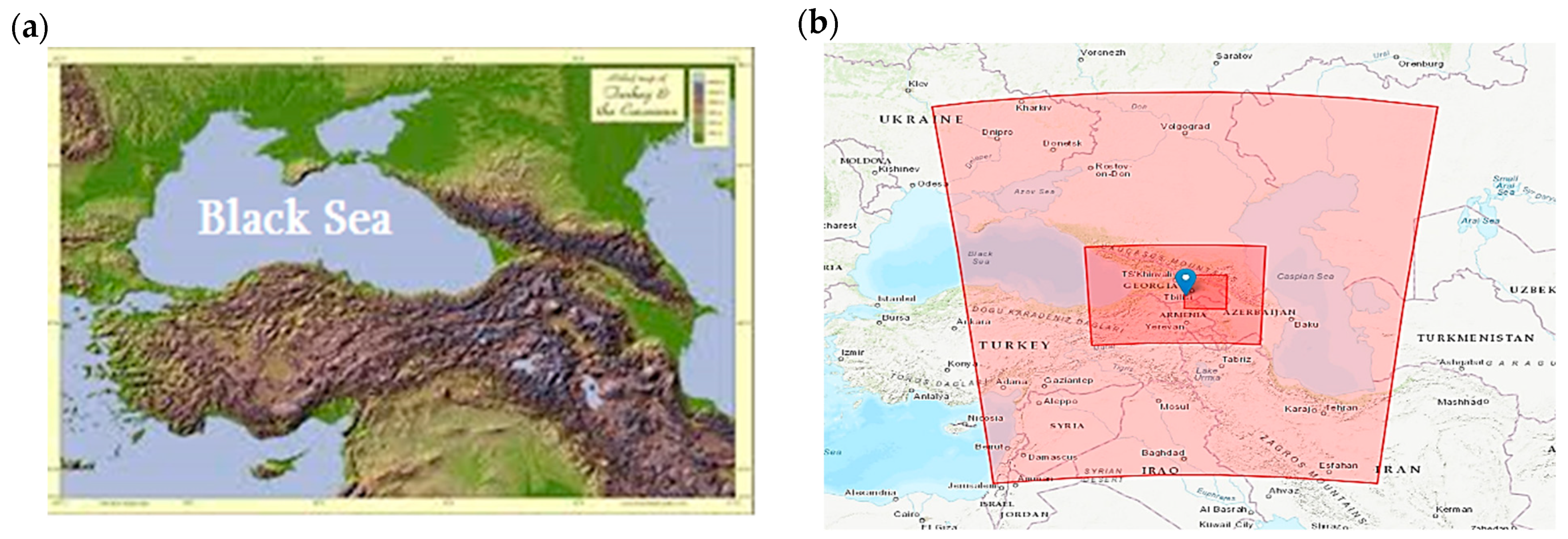
The transport, dispersion and deposition of mineral ADD to the Caucasus (Georgia) from nearby deserts by air flows in the lower and middle layers of the troposphere under the complex orography of the Caucasus (Figure 1a) have been discussed in various papers [24,26,27,28,30,32,45,46,47], but have never been studied over a long period of time (1.5 years) and using an ensemble of numerical models with remote sensing products and field data. The materials and methods used in this work to study the transport, dispersion and deposition of mineral ADD to the Caucasus (Georgia) from the deserts of Africa, the Middle East and the deserts of Western Asia are discussed in detail below.
Figure 1.
Physical map of the Caucasus region, showcasing the heterogeneous relief of Georgia and adjacent territories (a), and location of nested WRF-Chem model computational domains (b).
2.1. Method and Models
The methods and their order were identical for studying these two events. Namely, the analysis of the dust event started with the aerosol optical depth (AOD) of MODIS satellite images (showing the source and transport route of the dust plume) and then followed the analysis of the meteorological synoptic system of the event using the wind rose of the READY system. After that, PM10 data from 6 ground stations (Air Quality Portal of the NEA) were used to check the distribution of average daily PM10 concentrations over the territory of Georgia. Meanwhile, the back trajectories of the HYSPLIT model were used to track the routes of the long-range trail and determine the source location of the dust storm. Finally, the CAMS and WRF-Chem/dust forecasting systems were used for the final analysis of dust plume penetration and spread in Georgia.
2.1.1. WRF Model
This study used the latest generation’s WRF mesoscale model version 4.5.1, which can run with several nested grid variants to better reproduce mesoscale local features of atmospheric processes. The WRF model was developed primarily at the National Center for Atmospheric Research (NCAR) in collaboration with various agencies (such as the National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration (NOAA), National Centers for Environmental Prediction (NCEP), etc.) and has evolved to version 4.5.2 since 2000. WRF is an area-limited, non-hydrostatic, fluid-thermodynamic full systems equation model that, once initialized, uses all observational data from satellites, weather balloons, buoys, radars, etc., for several variants of different physical parameterization schemes that can be used as needed [48]. Nested grids can accurately account for orography, which makes the WRF model very useful for areas with complex relief, such as the Caucasus. In numerical calculations, WRF uses the Arakawa C horizontal grid together with the Runga Kutta third-order time integration schemes which with special filters guarantee stable calculations even under complex orography. For the Caucasus area, it is very important to run various physical modeling schemes to find the best combination for a specific local location.
2.1.2. WRF-Chem Model
In this study, the WRF v. 4.5.1 model [48] was coupled with the chemistry module [49] to simulate meteorology and dust transport in the complex orographic domain shown in Figure 1a. Specifically, the Eulerian, non-hydrostatic, compressible, mesoscale WRF-Chem v.4.5.1 model was used to both forecast and simulate regional weather and to study dust dispersion and the transport process of mineral dust from deserts to the Caucasus (Georgia) region using three nested grid domains shown in Figure 1b [49]. The outer grid, consisting of 128 × 128 cells with a resolution of 19.8 km, completely covered the Caucasus region. The middle-nested grid, consisting of 121 × 81 cells with a resolution of 6.6 km, completely covered the territory of Georgia (this nested grid was built with Tbilisi as its center), and the innermost nested grid, consisting of 81 × 81 cells with a resolution of 2.2 km, completely covered the easternmost region of Georgia (Figure 1b). The vertical structure of the model covered the whole troposphere with 32 horizontal layers vertically (for both nested domains). The boundary and initial conditions for the outer domain were extracted from the ECMWF ERA-Interim data (with a resolution of 0.75 degrees), available every 6 h. In the numerical simulations on the coarse grid, the time step was 60 s, and a time step of 10 s was used on the nested grid. All the WRF-Chem model simulations were performed on the GRENA (Georgian Research and Educational Networking Association) cluster (one computing node with 15 Intel Xeon CPU E5-2670 @2.60GHz cores). It should be noted that the WRF-Chem v.4.5.1 model includes 3 mineral dust emission modules (DUST-GOCART, DUSTGOCART/AFWA, and DUSTUOC), which are widely used in dust transport simulations. A comparison between the more recent DUST-GOCART/AFWA and DUSTUOC schemes showed that the GOCART/AFWA emission scheme overestimated the dust concentration, while the DUSTUOC scheme, on the contrary, slightly underestimated the dust concentration values [39,50]. That is why the DUST-GOCART scheme in the WRF-Chem v.4.5.1 model was chosen in our study, which provides the output of seven aerosol mass types, which is fully acceptable for our study [51].
2.1.3. Parameterizations
For the entire set of experiments performed using the WRF v.4.5.1 model with the Chemistry and Dust modules, the following physicochemical parameterization schemes were used (which are summarized in Table 1). The Thompson scheme [52], which includes ice, snow and graupel processes, is suitable for high-resolution simulations. The Cu_physics = 5 scheme (an improved version of the Grell and Deveneyi scheme) can be used at both high and coarser resolutions if subsidence propagation is enabled (option cugd_avedx) [53]. In this study, the “gray zone” (grid size ≥ 3 km to ≤10 km), where cumulus parameterization may or may not be necessary for use, was tested using the dx = 6.6 km nested domain. A newer version of the rapid radiative transfer model (RRTMG) was applied to the direct radiative forcing of dust [54]. The Mellor–Yamada–Janjic (MYJ) Eta operational scheme (a one-dimensional turbulent kinetic energy prediction scheme with local vertical mixing) was used to describe the planetary boundary layer [55]. The Janjic Eta Similarity Surface Layer scheme [55] and the NCEP/NCAR/AFWA unified scheme with soil temperature and moisture in a four-layer land surface model [56] were chosen to represent the surface layer physics and land surface interactions. In the dust experiments, only the dust tracer-1 dust collector scheme is activated and direct aerosol effects on radiative and atmospheric dynamics are considered.

Table 1.
Settings of the physical parameterizations used in the WRF-Chem setup.
2.1.4. Verification of the Results of Numerical Calculations of the WRF-Chem/Dust v.4.5.1 Model
To evaluate the obtained results of the WRF-Chem/Dust v.4.5.1 model, a comparative study was conducted of the calculation results of the WRF-Chem/Dust v.4.5.1 model with data obtained from MODIS, satellites and the results of in-kind measurements obtained from the National Environmental Agency of Georgia (NEA) (https://nea.gov.ge/ (accessed on 5 October 2024)). The HYSPLIT model and Copernicus Atmosphere Monitoring Service CAMS dust plume (https://atmosphere.copernicus.eu/charts/packages/cams_air_quality/products/plume_cams_eu_dust_web (accessed on 15 October 2024)) and CAMS particulate matter forecast (https://atmosphere.copernicus.eu/charts/packages/cams/products/particulate-matter-forecasts?base_time=202506200000&layer_name=composition_pm2p5&projection=classical_global&valid_time=202506200300 (accessed on 10 October 2024)) were also used to calculate the dispersion of trajectories and deposition of air pollutants from local to global scales and to validate the results of numerical simulations of the WRF-Chem/dust v.4.5.1 model.
2.1.5. Field Data
To assess the ability of the numerical models to accurately predict ADD paths and destinations, a ground-based dataset and NASA Ground-based observation data were used. Specifically, seven air quality monitoring stations that can measure PM2.5 and PM10 dust particles are distributed throughout Georgia; two of them are located in Western Georgia, in Batumi and Kutaisi; four of them are located in Eastern Georgia, in four different districts of the capital Tbilisi; and one station is in Rustavi, which is a neighboring city of Tbilisi.
2.1.6. MODIS Observation Data
MODIS is a key instrument onboard NASA’s Terra (since February 2000) and Aqua (since June 2002) satellites, which monitors the Earth daily over a wide spectral range. MODIS Terra and Aqua can accurately predict global environmental changes because they can cover a 2330 km wide swath at an altitude of 705 km and obtain data for 36 spectral wavelengths from 0.41 to 14 μm, which are used to derive aerosol spectral optical depth and aerosol size parameters over land every two days [43,57,58,59]. This paper used MODIS data (500 m RGB and 0.55 μm AOD obtained from MOD04 2) to evaluate predicted dust clouds and detect large dust cloud emission sources. Potential dust cells were identified based on the AOD values obtained by the MODIS sensor (according to [60], areas with AOD values greater than 0.75 were identified as potential dust cells).
2.1.7. HYSPLIT and CAMS Models
The NOAA HYbrid Single-Particle Lagrangian Integrated Trajectory (HYSPLIT) model provides aerosol trajectory information by tracking a parcel of air transported by a mean three-dimensional wind field (ignoring turbulence). HYSPLIT is based on both the Lagrangian approach to compute advection and diffusion trajectories of air parcel units from their initial location (using a moving reference frame) and a Eulerian methodology to compute airborne species concentrations [61,62]. The HYSPLIT model incorporates different aerosol trajectory types (normal, matrix and ensemble) and can be run to generate forward or backward trajectories using multiple available archived three-dimensional meteorological fields. This paper used matrix and ensemble types of forward and backward trajectories of HYSPLIT model products to identify potential dust sources and their transport routes, and compare and evaluate the results of WRF-Chem/dust model calculations.
The Copernicus Atmosphere Monitoring Service (CAMS) was launched as part of The Copernicus Programme in 2014 by the European Centre for Medium-Range Weather Forecasts (ECMWF). The CAMS describes the current situation, forecasts the situation several days in advance, analyzes historical data records and monitors air pollution, radiation, greenhouse gases and climate worldwide. For the European region, the CAMS produces daily air quality analyses and 4-day forecasts at a substantially finer spatial resolution (approximately 10 km) than is available in the global forecasts for ammonia, pollen, nitrogen oxides, ozone, dust, etc. Namely, for the analysis and forecasting of PM2.5 and PM10 using particulate matter forecasts, the CAMS provides the ability to analyze 4-day retrospective and observe 4-day forecasts both globally and in different 27 areas of the Earth. This work used both global and Western Asian PM10 maps, which provided good coverage of the Caucasus and adjacent desert areas.
3. Results
This section presents observational data and numerical model results for two dust events that affected Georgia in the spring. The following satellite products, reanalysis, ground measurements and model simulations were used to detect and analyze the dust events.
3.1. Modeling of ADD Transport in Georgia from 27 to 31 May 2024
3.1.1. Aerosol Optical Depth (AOD) Calculations Using MODIS
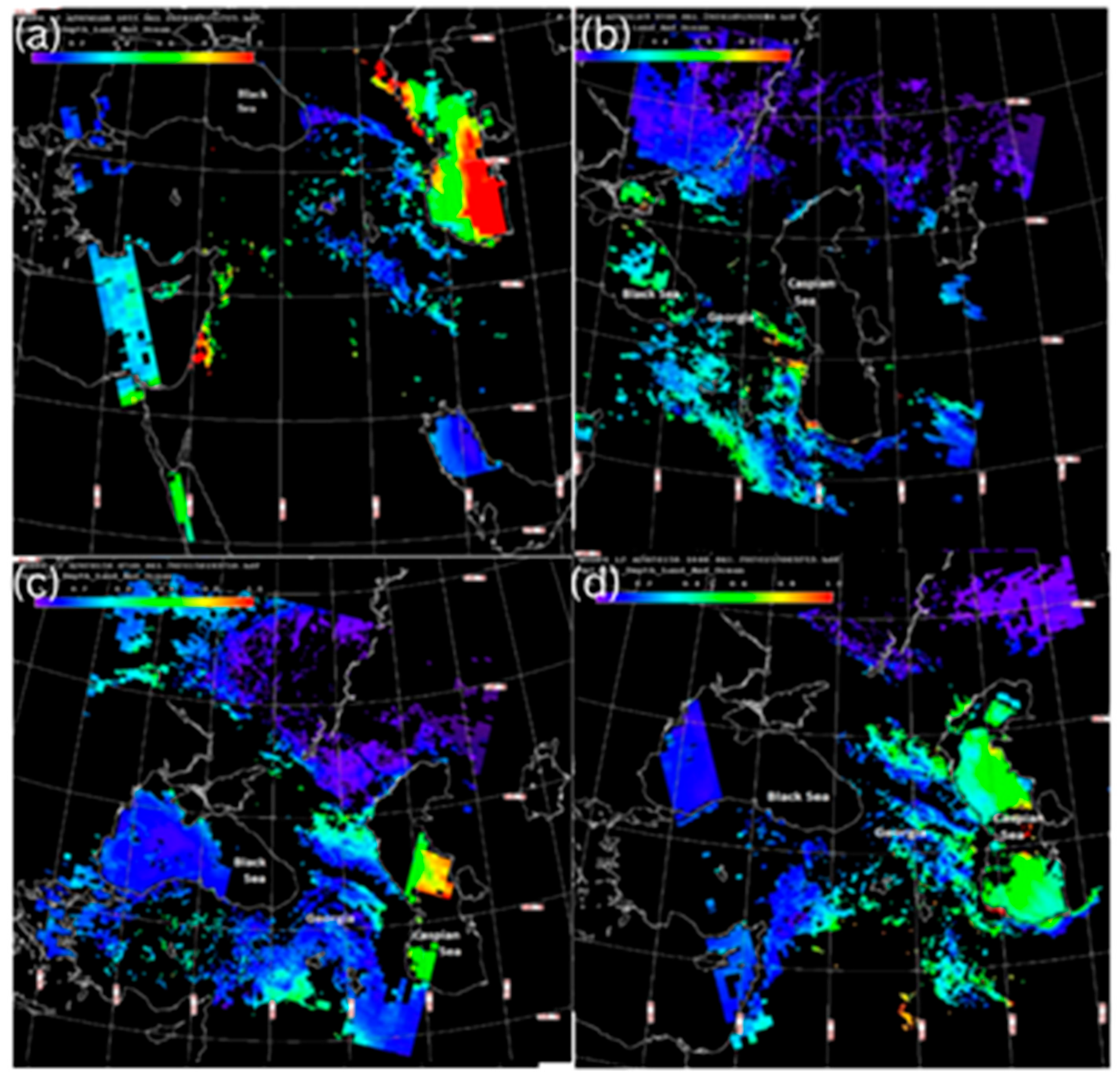
As mentioned above, to illustrate the main features (sources, routes and timing of long-range transport) of long-range airborne dust transport to the territory of Georgia in complex orographic conditions, two of the most typical cases (28–31 May 2024 and 24–30 April 2024) were selected from the 38 identified cases of long-range airborne dust penetration to the territory of Georgia. The maps of the altitude–orbit cross-section horizontal measurements of AOD obtained from MODIS version 3.40 at different times (UTC) show that the maximum AOD values were recorded over the Caspian Sea, on the eastern coast of the Mediterranean Sea, and weak AOD values were observed over the Main Caucasus Range at 10:55 a.m. on 27 May 2024 (Figure 2a). As can be seen from Figure 2b (presenting the AOD distribution pattern at 07:00 a.m. on 28 May 2024), the strong dust band left the Caspian Sea, was shifted from the Caspian Sea to the southwest and was distributed from the territory of Azerbaijan to the eastern part of Georgia. Figure 2c,d, presenting the AOD distribution pattern on 29 May 2024 at 07:40 and 10:40 a.m., respectively, show that the AOD values gradually increased and expanded throughout the Caspian Sea and almost reached the Black Sea in the westward direction (Figure 2d).
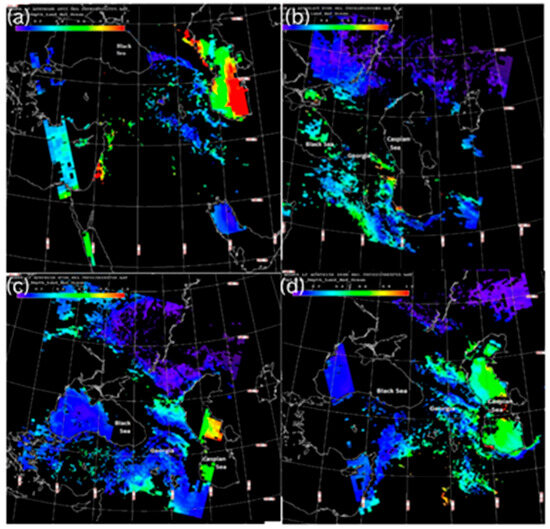
Figure 2.
The maps of the altitude–orbit cross-section horizontal measurements of aerosol optical depth (AOD) obtained using MODIS version 3.40 at different times (UTC): (a)—at 10:55 on 27 May 2024; (b)—at 07:00 on 28 May 2024; (c)—at 07:40 on 29 May 2024; (d)—at 10:40 on 29 May 2024.
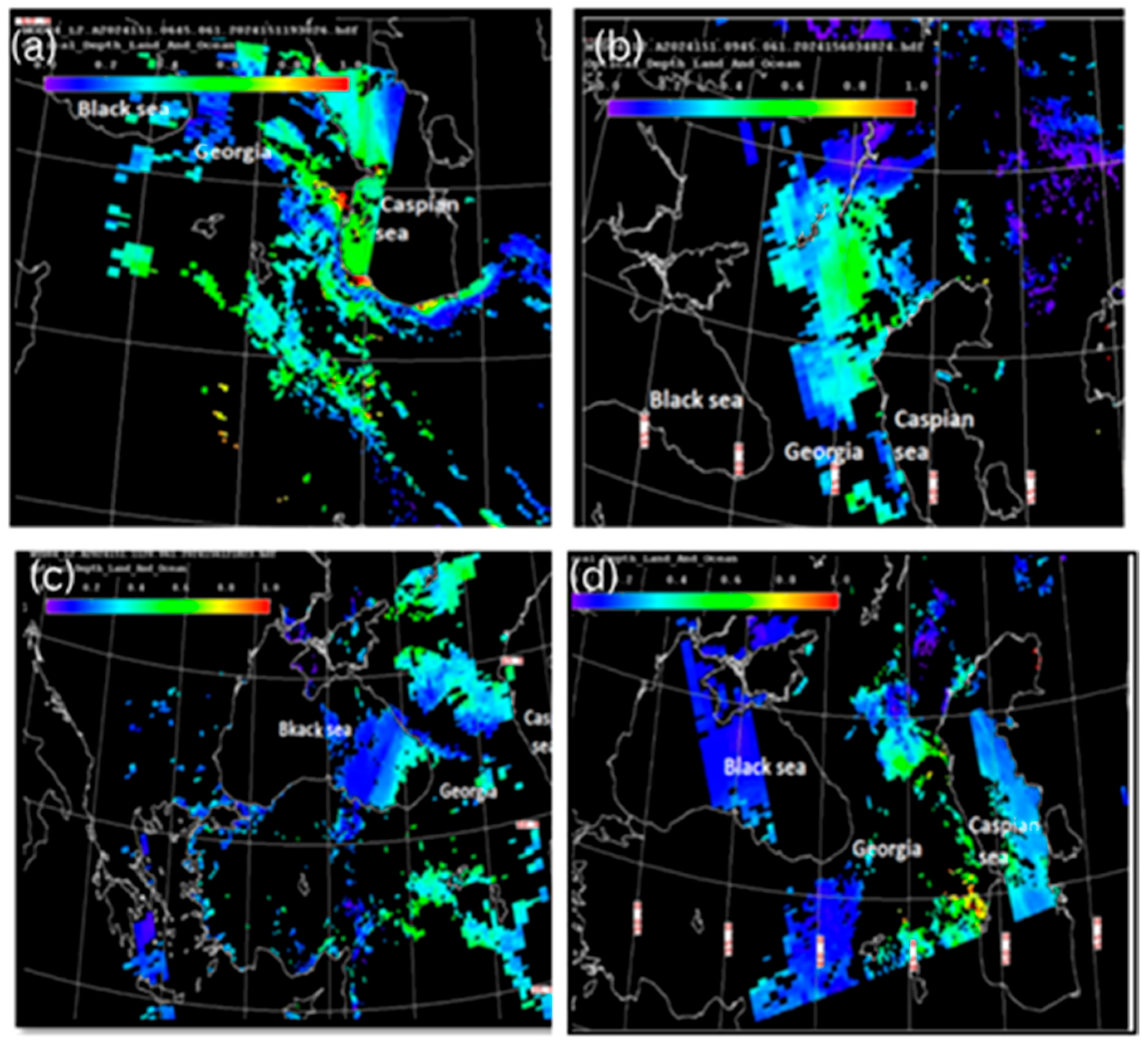
As can be seen from Figure 3a, the maximum AOD values were recorded in the western and southern parts of the Caspian Sea and adjacent land areas, which, in the western direction, reached the territory of eastern Georgia (where the AOD values varied from 0.4 to 0.6) at 06:45 on 30 May 2024. Figure 3b, which presents the AOD distribution 3 h later (at 09:45 on 30 May), shows that during this short period of time, the observed dust spots from the Caspian Sea mainly moved in the west–north direction over the territory of Russia but still covered the territories of Azerbaijan and eastern Georgia. Figure 3c shows that the area occupied by the dust cloud included the easternmost part of the Black Sea and the northern area bordering the territory of Georgia, but the territory of Georgia (except for the easternmost territory of Georgia) was free of dust spots. Figure 3d shows that the dust spot has again moved back into the Caspian Sea; however, in Georgia, residual concentrations of AOD were still only locally recorded in some regions at 10:25 on 31 May.
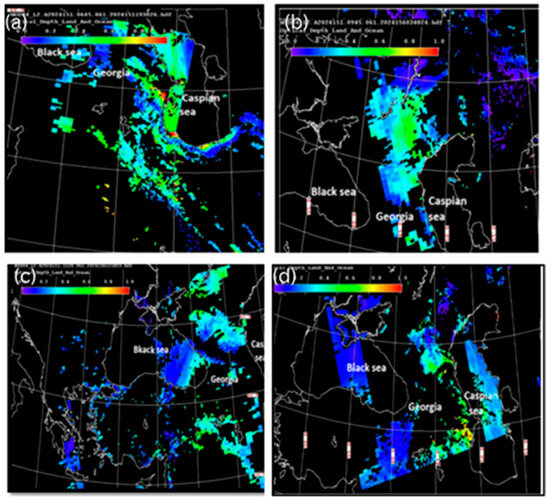
Figure 3.
The maps of the altitude–orbit cross-section horizontal measurements of aerosol optical depth (AOD) obtained using MODIS version 3.40 at different times (UTC): (a)—at 06:45 on 30 May 2024; (b)—at 09:45 on 30 May 2024; (c)—at 11:20 on 31 May 2024; (d)—at 10:25 on 31 May 2024.
3.1.2. Wind Rose of the READY System for 28–29 May 2024
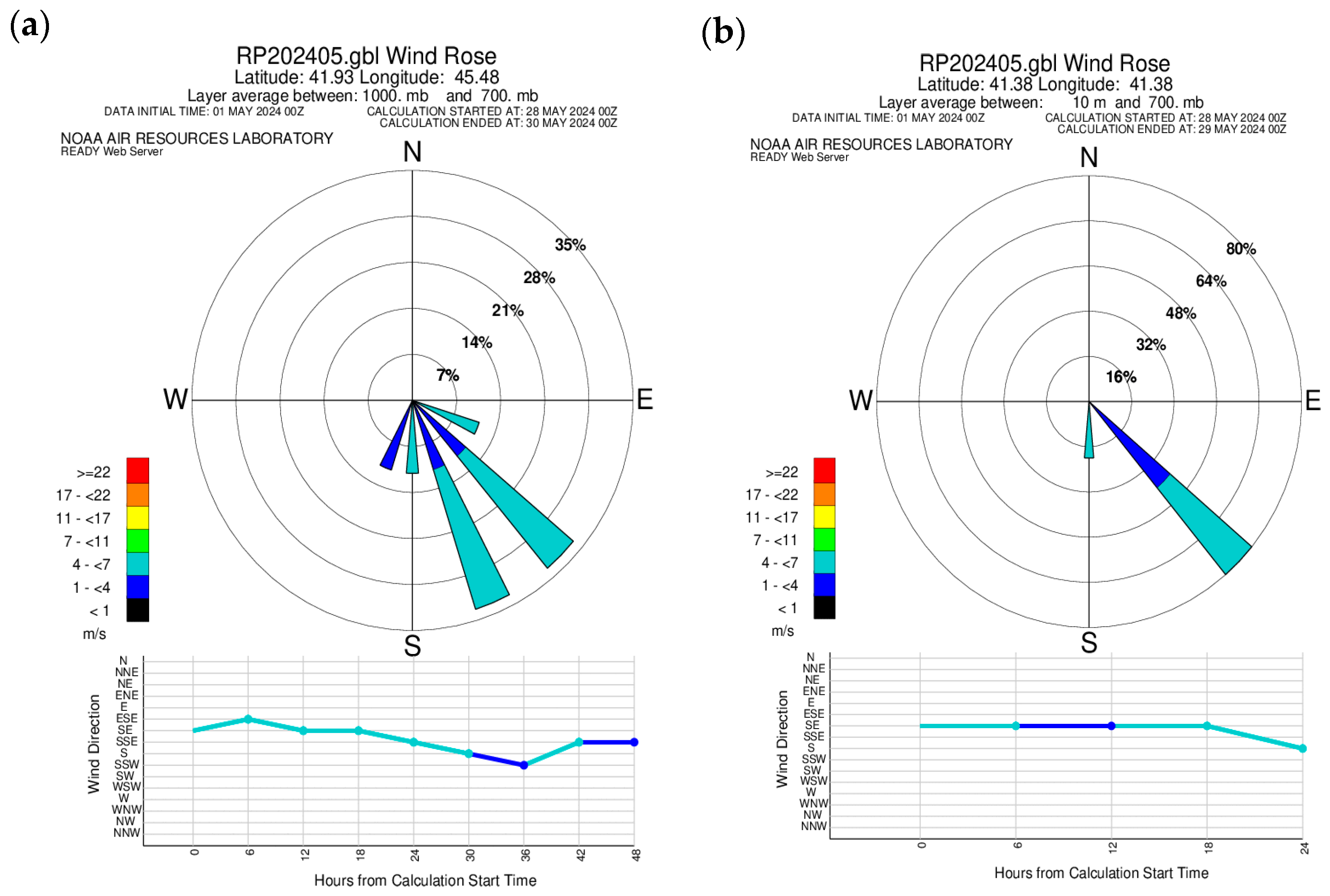
To understand the strength and direction of the air flow in the study of ADD incursion into Georgia, the wind rose of the READY system was used. Figure 4a,b show the wind roses constructed from the earth’s surface to the 700 mb level, for Telavi (eastern Georgia, 41°55′11.21″ N 45°28′23.34″ E) and Batumi (western Georgia, 41°38′32.21″ N 41°38′2.11″ E), respectively, on 28–29 May 2024 (the legend indicates the numerical values of the wind, and the circles indicate the numerical value and frequency of wind direction in percent). As can be seen from Figure 4a,b, the main wind direction for both regions was southeast (which is consistent with MODIS images), and it should be noted that the numerical value of the wind in neither region exceeded 4–7 m/s.
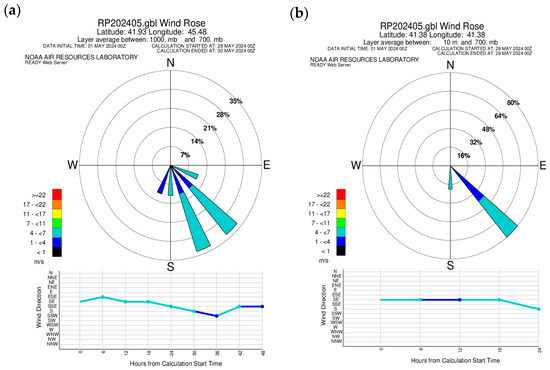
Figure 4.
Wind roses constructed for Telavi—(a) and Batumi—(b) on 28–29 May 2024.
3.1.3. In Situ PM10 Observations from 28 to 31 May 2024
Table 2 presents the average daily PM10 concentration measurements using data from seven NEA air quality monitoring stations, of which two stations are located in Western Georgia. One station is in Batumi (located on the Black Sea coast, 41°38′32.21″ N 41°38′2.11″ E), another one is in Kutaisi (located in the central part of Western Georgia, 42°20′39″ N 42°59′24″ E) and six stations are in Eastern Georgia, of which five are located in different districts of the capital of Georgia, Tbilisi (41°41′38.80″ N, 44°50′1.25″ E), and one is in Rustavi (41°31′59.99″ N, 45°00′0.00″ E), which is a city located 20 km southeast of the capital Tbilisi. It is obvious that the monitoring stations are unevenly distributed in eastern Georgia. Unfortunately, six monitoring stations are located only in a small central part of eastern Georgia, and none are in the south, southeast and easternmost agricultural areas of eastern Georgia. Analysis of the data in Table 2 shows significant differences in the spatial and temporal distribution of PM10 from 28 to 31 May 2024.

Table 2.
Distribution of daily average PM10 concentrations in western Georgia (Batumi and Kutaisi) and eastern Georgia (Rustavi and four districts of Tbilisi) from 28 to 31 May 2024.
Namely Table 2 shows that high PM10 concentration values (colored red) were observed in the eastern part of Georgia (Tbilisi and Rustavi), while in the western part of Georgia, the PM10 concentration values were well below the maximum permissible concentration (50 μg/m3).
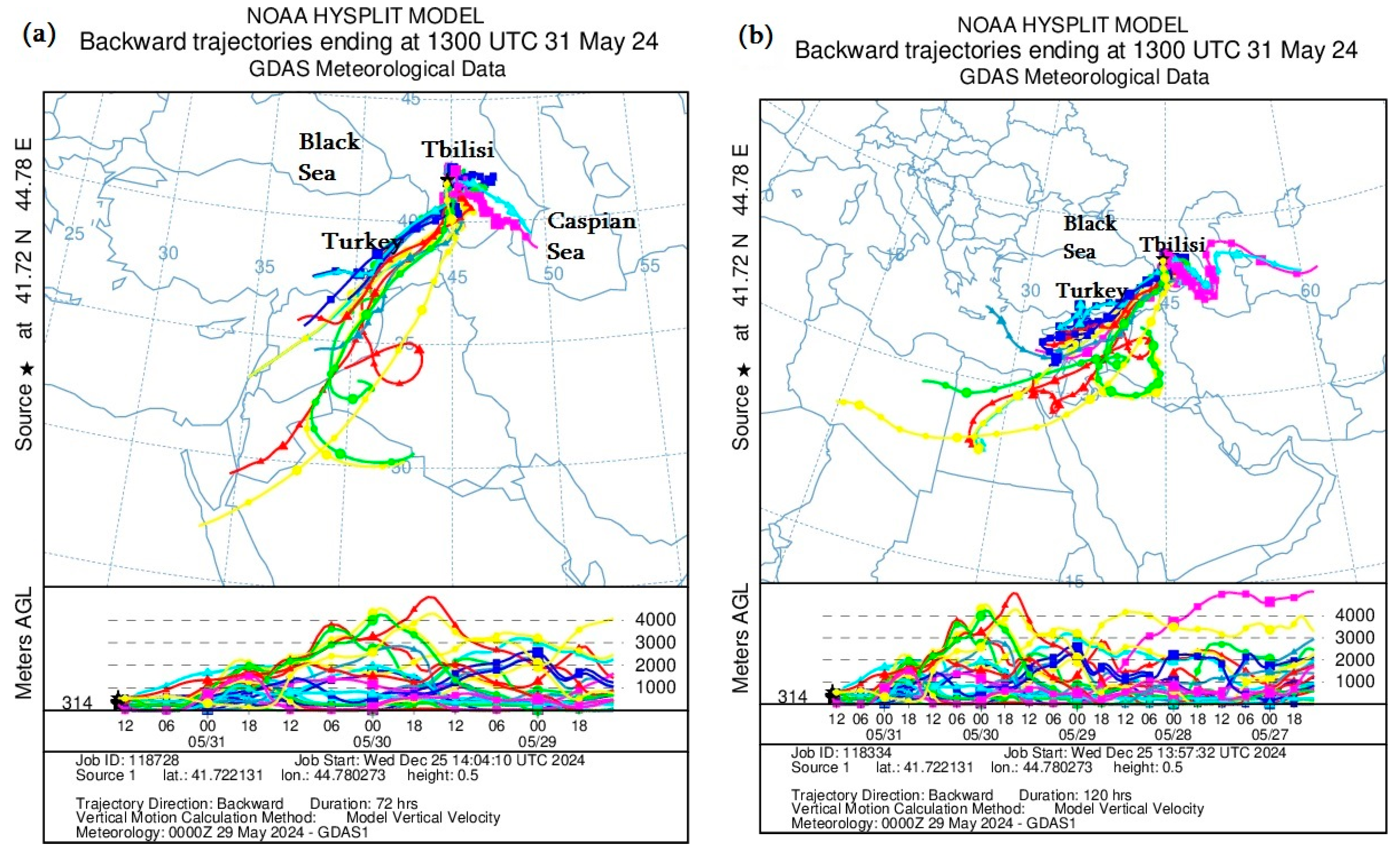
3.1.4. HYSPLIT Model Calculations
To better understand dust storm traces and the exact location of dust storm sources, this paper constructs and analyzes backward trajectories of the HYSPLIT model for Tbilisi and Rustavi. As can be seen from Figure 5, mineral dust was mainly transported to the territory of Tbilisi and Rustavi by the tropospheric layers of the atmosphere from the southwest and southeast. In particular, Figure 5a,c, which present the ADD transport from 29 to 31 May 2024, show that mineral dust in relatively high atmospheric layers (approximately 1–4 km) was transported from the territories of Syria and Iraq through the territory of Turkey, while below 1 km, it was transported from the Caspian Sea through the territory of Azerbaijan. Figure 5b,d, which present the transport of ADD from 27 to 31 May 2024, show that mineral dust was transported from Libya, Egypt and Jordan across Syria and Iraq in relatively high atmospheric layers (1–4 km) from 27 to 29 May 2024, and ADD was transported from the territory of Turkmenistan across the southwestern Caspian Sea by both relatively high atmospheric layers (above 4 km) and atmospheric boundary layers (below 2 km) from 27 to 29 May 2024. The above HYSPLIT model calculation results are in good agreement with both the actual NEA measurements and the MODIS images (see Table 2, Figure 2 and Figure 3).
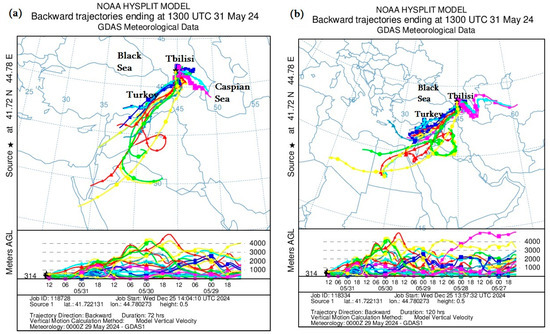
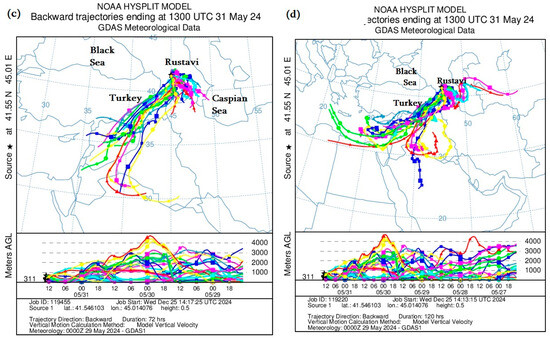
Figure 5.
Distribution of mineral dust calculated by the Backward Ensemble trajectory of the HYSPLIT model at different atmospheric heights over the territory of Georgia ((a,c)—from 31 to 29 May 2024; (b,d)—from 31 to 27 May 2024).
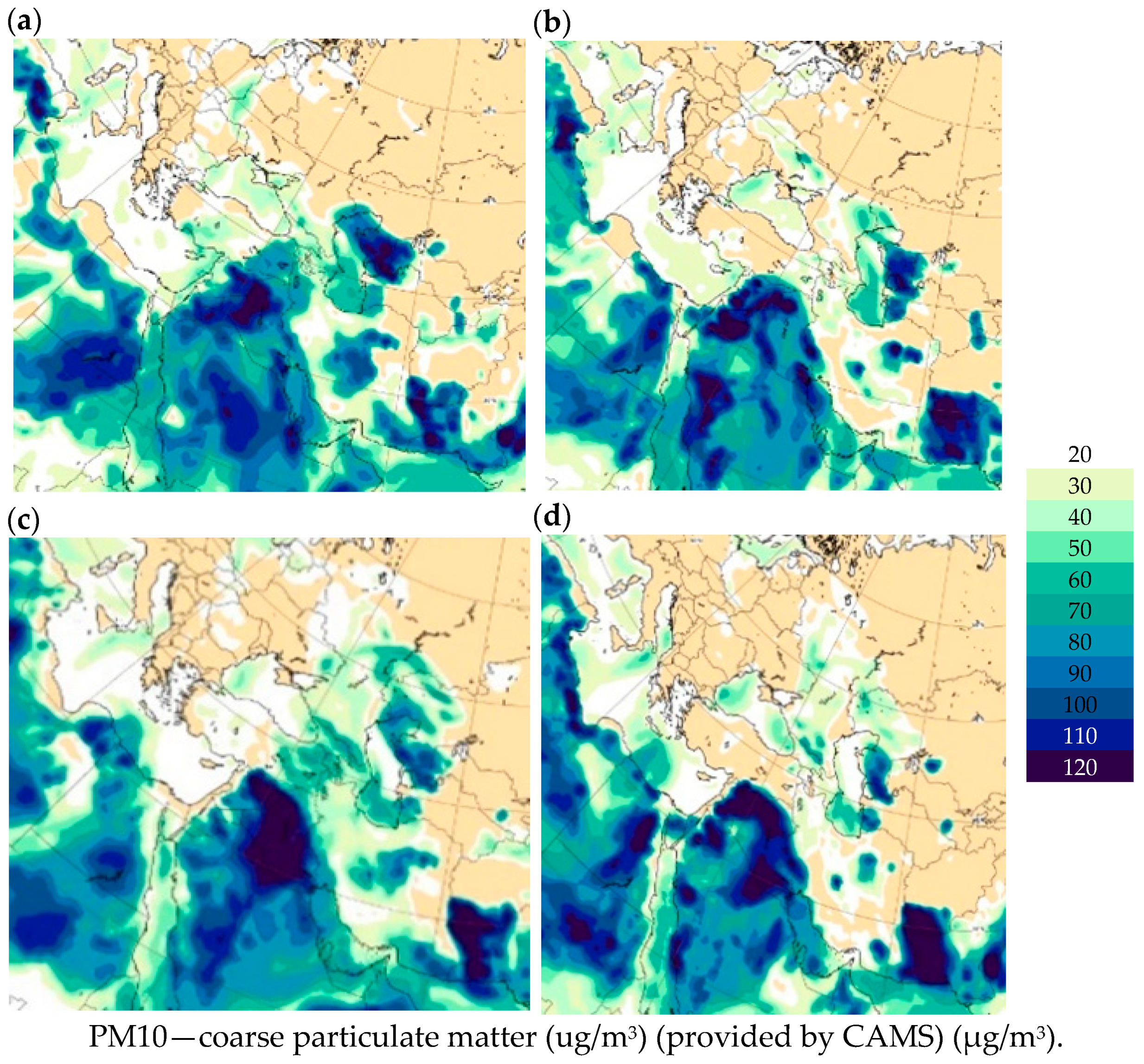
3.1.5. CAMS Calculations
Figure 6a, which presents the CAMS forecast of PM10 aerosol at 06:00 UTC on 29 May 2024, shows that a strong dust storm was observed over Turkmenistan (Karakum and Kyzylkum deserts), as well as over Syria, Iraq, Egypt and Libya. Relatively weak dust clouds were observed over Turkey and Azerbaijan, and a light dust spot was observed in the easternmost part of Georgia. Figure 6b, which presents the PM10 forecast in 12 h, shows that a strong dust cloud has formed around the Caucasus region, but there was not even a dust spot in Georgia. However, it should be noted that according to field observations (Table 2), the maximum PM10 concentrations were observed in Tbilisi and Rustavi on 29 May 2024, which is not visible in Figure 6a,b. Visual analysis of Figure 6c shows that strong dust cloud bands were observed over the Main Caucasus Range and over the southern border of Georgia, but only isolated dust plumes were observed over the territory of Georgia at 06:00 UTC on 31 May 2024. Figure 6d shows that over the next 12 h, the dust clouds gradually lost their positions over the territory of Georgia but generally maintained their position over the Main Caucasus Range at 18 UTC on 31 May 2024.
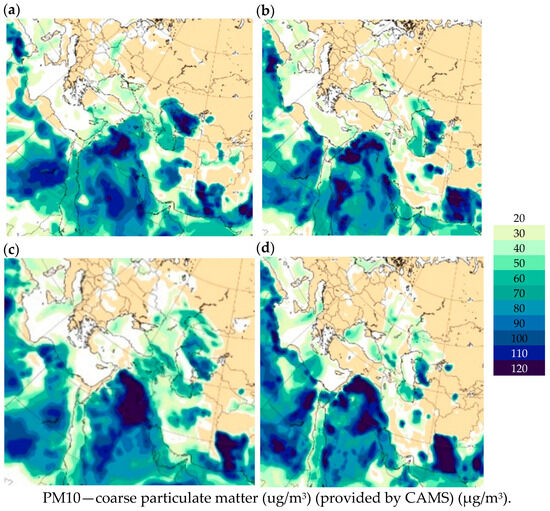
Figure 6.
CAMS forecasts of PM10 using the Western Asia option at 06:00 UTC on 29 May 2024—(a); at 18:00 UTC on 29 May 2024—(b); at 06:00 UTC on 31 May 2024—(c); and at 18:00 UTC on 31 May 2024—(d).
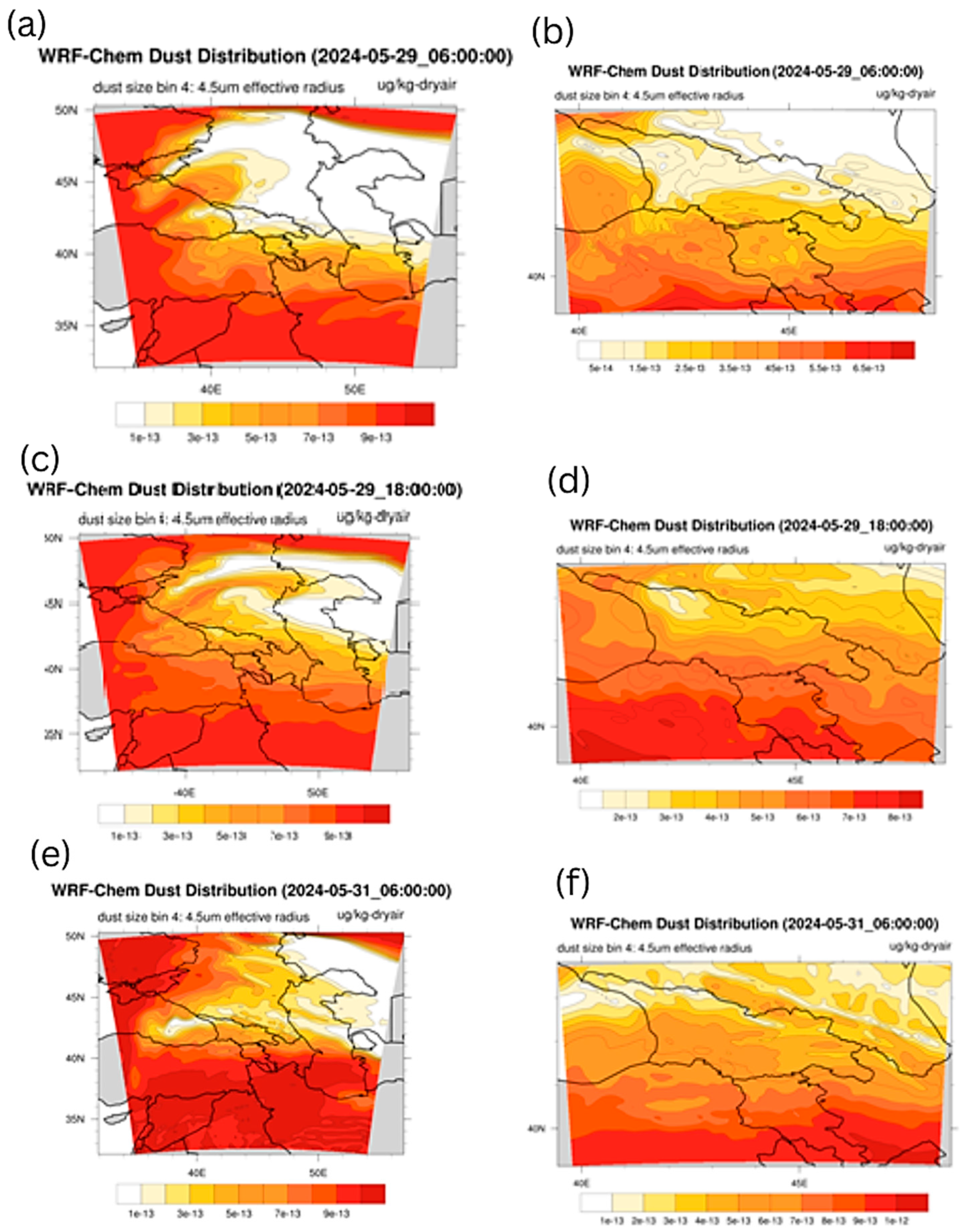
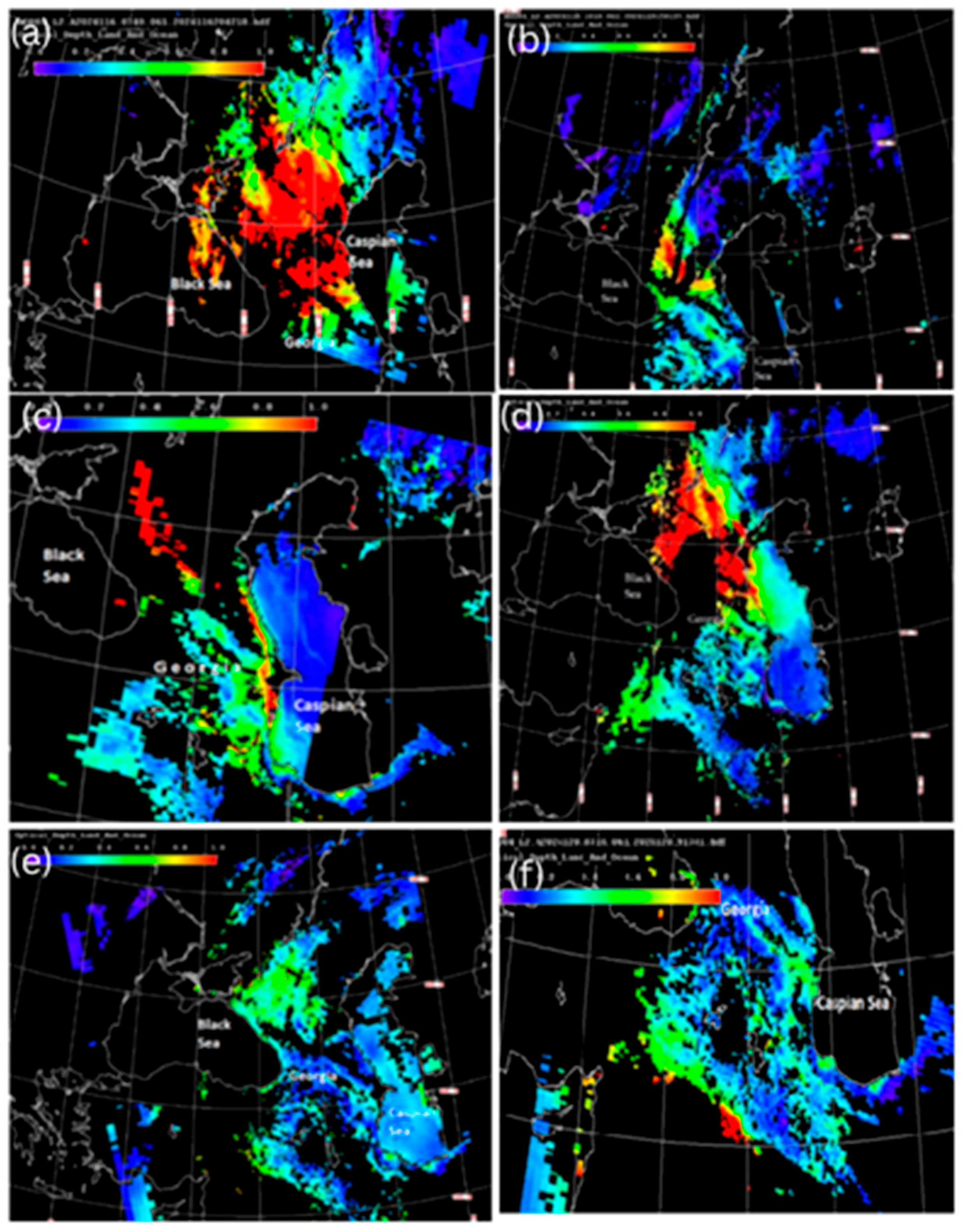
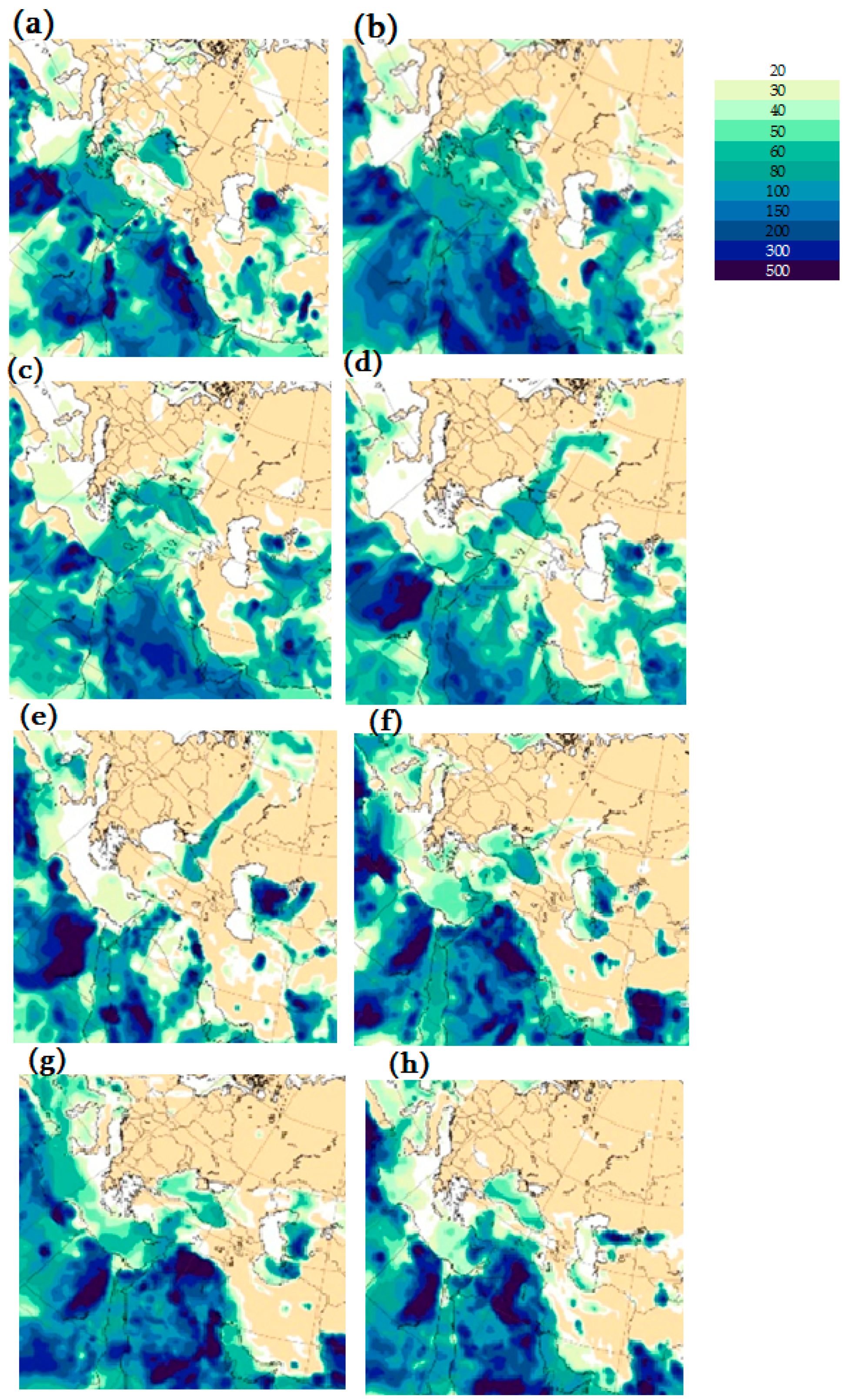
3.1.6. Results of Calculations Performed Using the WRF-Chem Model
In this study, WRF-Chem used a fourth dust particle size category (dust bin size 4) with a mean radius of 4.5 μm, allowing the WRF-Chem model to model dust transport and deposition processes in more detail. The results of the WRF-Chem v.4.5.1 model (in combination with the GOCART dust module), performed on a coarse grid at 06:00 UTC on 29 May 2024, show that strong dust clouds were observed around the territory of Georgia (see Figure 7a). Namely, strong dust clouds were observed over the territories of Turkey, Syria, Iraq and Iran. Also, a dust strip stretched over the Black Sea from the territory of Turkey to the territory of Russia, but only weak emissions of dust strips were observed over the territory of Georgia (in the southern and easternmost regions) at 06:00 UTC on 29 May 2024. Figure 7b, which presents the results of the fine grid calculations performed at 06 UTC on 29 May 2024, shows that weak dust emissions were observed in Tbilisi and Rustavi, which was not observed in the coarse grid calculations presented in Figure 7a. Figure 7c, which presents the results of the coarse grid calculations performed at 18:00 UTC on 29 May 2024, shows that within 12 h, the dust band stretching over the Black Sea from Turkey to Russia shifted and reached the northwestern coast of the Caspian Sea. It is also evident that during this period of time, dust clouds penetrated the territory of southern Georgia and increased dust pollution in this area. Figure 7d, which is the result of the fine grid calculation at 18:00 UTC on 29 May 2024, shows that the ADD penetrated into the southern parts of Georgia from Turkey and even reached the Main Caucasus Mountain Range (which was not detected by the WRF-Chem calculations on the coarse grid). Figure 7e, which is the result of the coarse grid calculation at 06:00 UTC on 31 May 2024, shows that the dust aerosol pollution around the Caucasus region increased over 48 h, and at the same time, the dust pollution was more pronounced in the easternmost, southernmost and westernmost regions of Georgia. Figure 7f, which presents the fine grid results for 06:00 UTC on 31 May 2024, shows more clearly than Figure 7e that the areas around Tbilisi and Rustavi were covered by only weak dust flux, which was confirmed by both CAMS forecasts and MODIS images and NEA ground-based data.
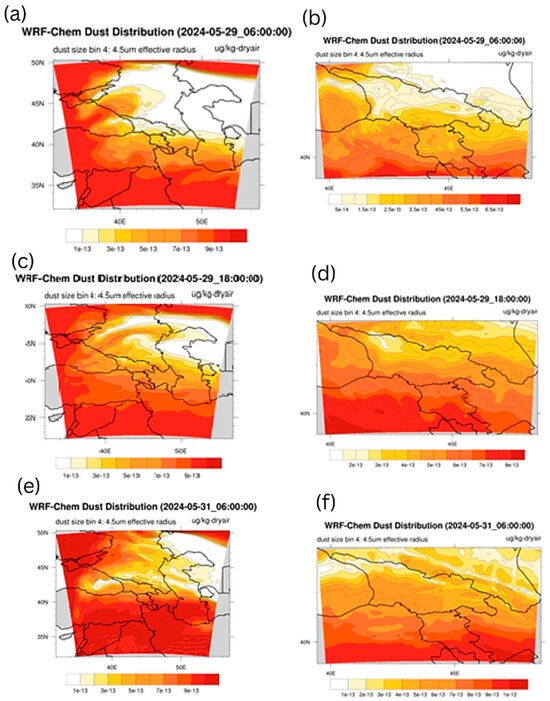
Figure 7.
Results of numerical calculations of the WRF-Chem v.4.5.1 model, performed in a coarse domain with a resolution of 19.8 km, at 06:00 UTC on 29 May 2024—(a); at 18:00 UTC on 29 May 2024—(c); at 06:00 UTC on 31 May 2024—(e); and in a fine mesh grid with a resolution of 6.6 km, at 06:00 UTC on 29 May 2024—(b); at 18:00 UTC on 29 May 2024—(d); at 06:00 UTC on 31 May 2024—(f).
3.2. Modeling the Transfer of ADD to the Territory of Georgia from 24 to 30 April 2024
The second case of mineral dust transport to the eastern territories of Georgia, considered here, mainly originated from the eastern deserts of Turkmenistan, Kazakhstan or the southeastern deserts located in Syria, Iraq, Iran and Saudi Arabia. It should be noted that the daily analysis of annual ADA incursions into the territory of Georgia showed that the incursions from the east and southeast were approximately three times larger in number than the western and southwestern incursions. Therefore, the case of ADA transport to the territory of Georgia from 24 to 30 April 2024 is considered an example that was similar to many others that often originate from the eastern and southeastern territories.
3.2.1. Aerosol Optical Depth Calculations Using MODIS
Figure 8a shows that a wide aerosol band extended from the eastern coast of the Caspian Sea towards the Black Sea, which intensified in the western direction (over the territory of Georgia), and the maximum AOD values were observed in the northeastern part of the Black Sea at 07:40 on 25 April 2024. Figure 8a also shows that strong dust clouds were observed in the northern and northwestern directions of the Main Caucasus Range over the territory of Russia. Figure 8b shows that after 2 h and 35 min, strong dust clouds stretched between the Black and Caspian Seas, and a weak dust band completely covered the territory of Georgia. Figure 8c, which corresponds to 06:45 on 26 April 2024, shows that the above aerosol band has shifted slightly to the north, but the AOD distribution over the territory of Georgia has remained almost the same. Figure 8d, which presents the AOD distribution at 07:25 on 27 April 2024, shows that the aerosol intensity has increased at the easternmost coast of the Black Sea, namely in Batumi, while it has remained almost unchanged over the rest of Georgia. Figure 8e, obtained at 10:50 on 28 April 2024, shows that the aerosol intensity has increased at the easternmost coast of the Black Sea, namely in Batumi, but the overall aerosol distribution over the territory of Georgia has remained almost unchanged. Figure 8f, collected at 07:10 on 29 April 2024, shows that a new large aerosol cloud has appeared in southern Georgia, increasing the aerosol impact on the easternmost part of Georgia.
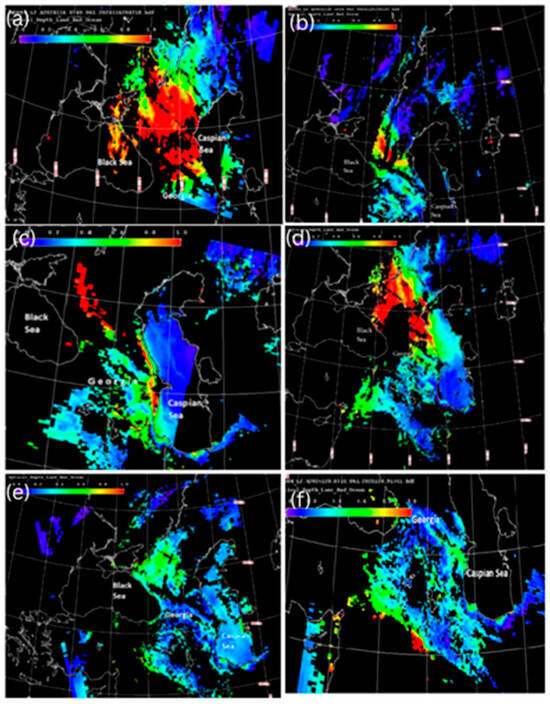
Figure 8.
The maps of the altitude–orbit cross-section horizontal measurements of aerosol optical depth (AOD) obtained using MODIS version 3.40 at different points in time (UTC): (a)—at 07:40 on 25 April 2024; (b)—at 10:25 on 25 April 2024; (c)—at 06:45 on 26 April 2024; (d)—at 07:25 on 27 April 2024; (e)—at 10:50 on 28 April 2024; (f)—at 07:10 on 29 April 2024.
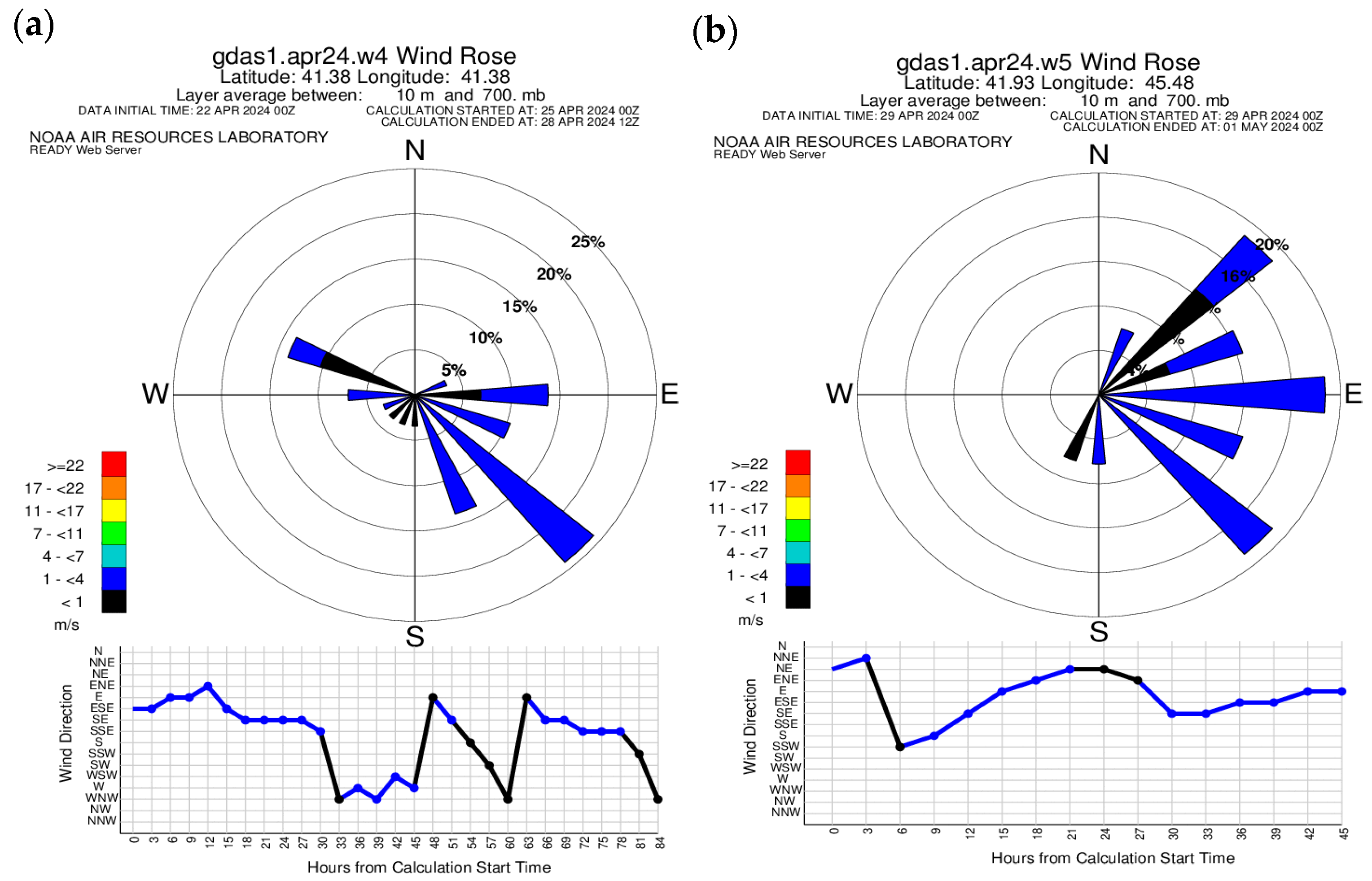
3.2.2. Wind Rose of the READY System for 24–28 April 2024
According to MODIS, on 25–28 April 2024, the maximum concentration of AOP was recorded in Western Georgia, and on 29–30 April, the maximum concentration was recorded in Eastern Georgia. Therefore, to study the main atmospheric flows for this period, Batumi in Western Georgia and Telavi in Eastern Georgia were selected and a wind rose of the READY system was constructed for these two regions (Figure 9). As can be seen from Figure 9a, the main wind direction for the Batumi region was southeast, although at the same time, a weak westerly and northwesterly wind was recorded on 25–28 April 2024. From Figure 9b, it is clear that on 29–30 April 2024, the main wind directions for Telavi were east, southeast and northeast.
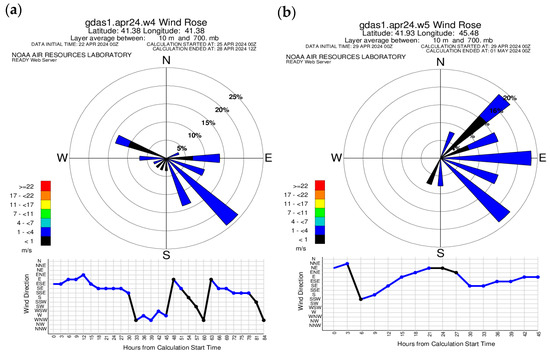
Figure 9.
Wind roses, constructed for Batumi—(a) and Telavi—(b) on 25–28 April 2024.
3.2.3. On-Site Observations from 24 to 30 April 2024
The analysis of Table 3 shows that relatively high values of the average daily PM10 concentrations (colored red) were observed in western Georgia (Batumi, Kutaisi) on 26 April 2024. More detailed hourly analysis of PM10 concentrations of NEA air quality monitoring stations data showed that high PM10 concentrations were observed throughout the day in Batumi and Kutaisi on 26 April 2024 and 27 April 2024, although their value slightly decreased on 27 April 2024.

Table 3.
Distribution of daily average PM10 concentrations in western Georgia (Batumi and Kutaisi) and eastern Georgia (Rustavi and four districts of Tbilisi) from 24 to 30 April 2024, obtained by NEA air quality monitoring stations.
Average PM10 concentrations dropped below the permissible PM10 concentration limits on 29 April 2024, simultaneously in Batumi and Kutaisi, indicating the cessation of dust cloud invasion from the Black Sea region. Also, the hourly analysis of PM10 concentrations in Rustavi and different districts of Tbilisi from 28 to 30 April 2024 shows that relatively high PM10 values were observed from 14:00 to 24:00, which was apparently caused by the outbreak of a dust clouds coming from the east or southeast (see Figure 9b).
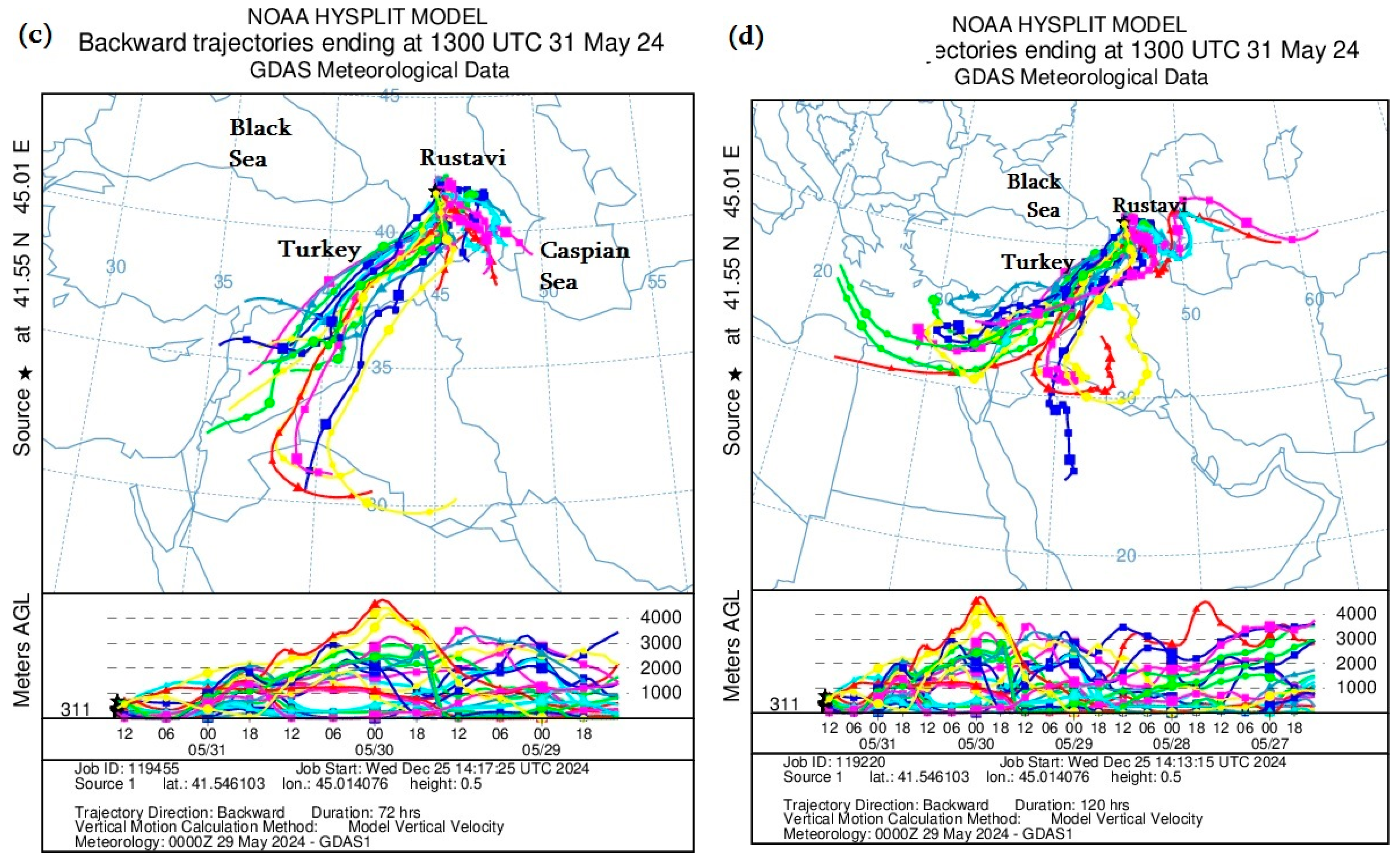
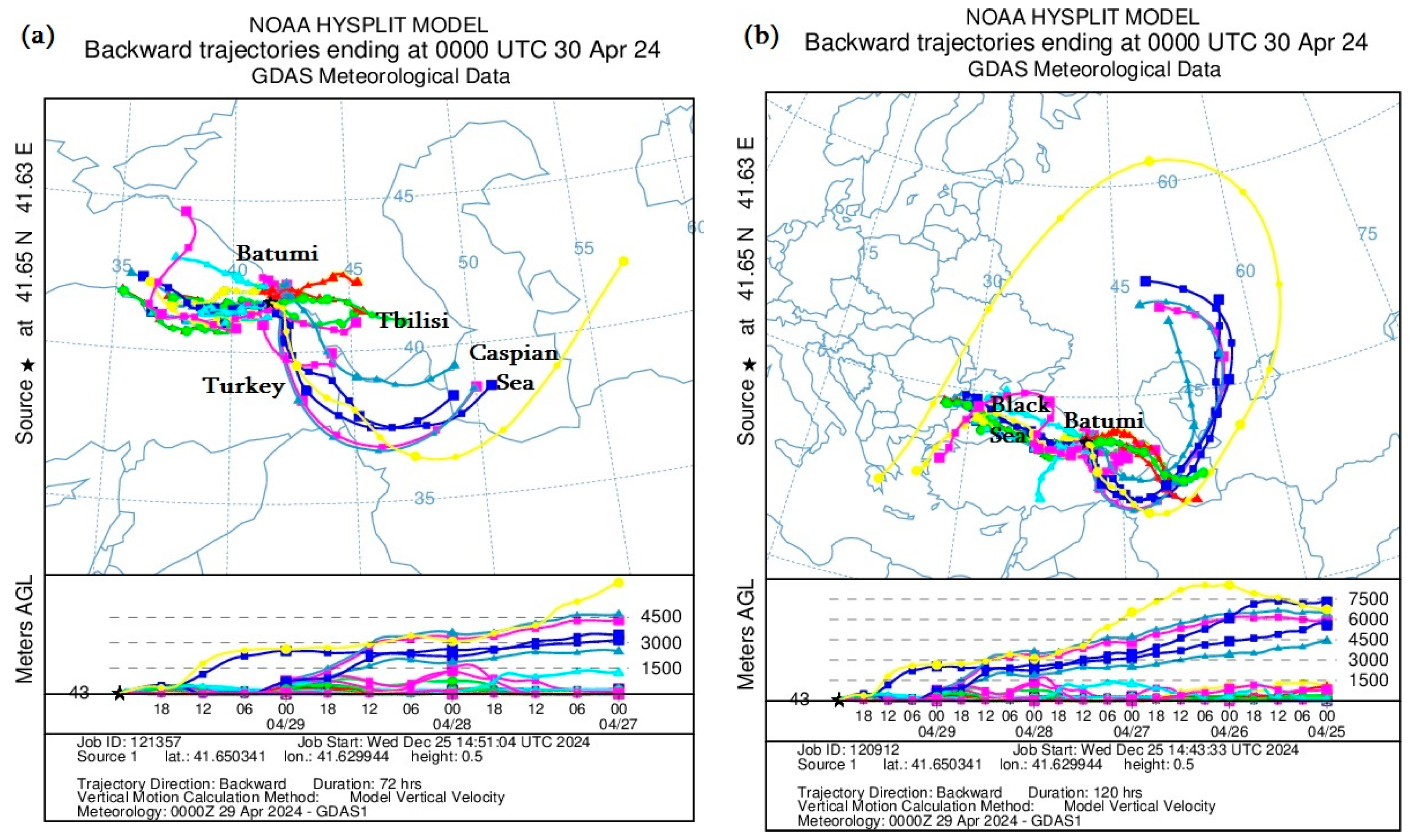
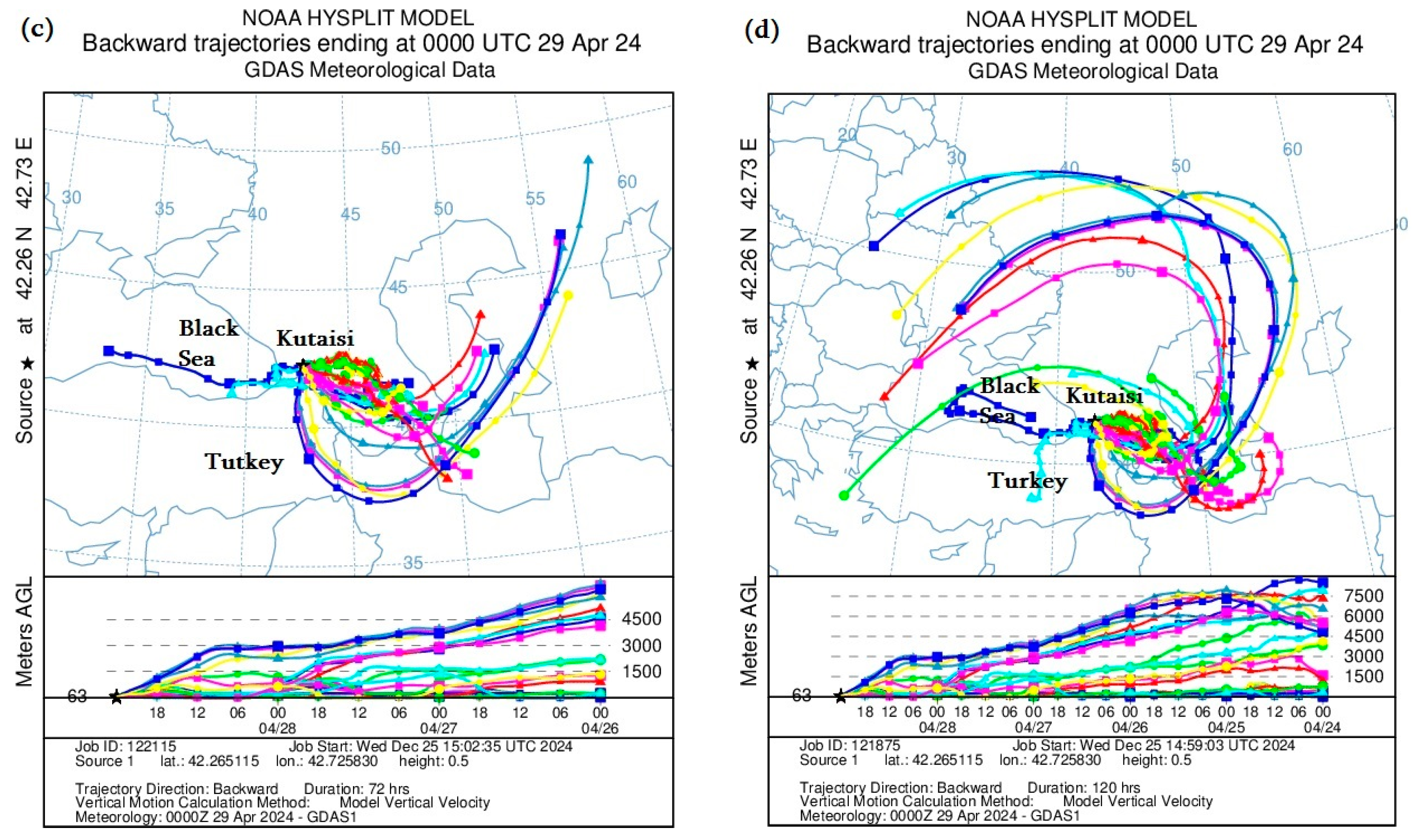
3.2.4. HYSPLIT Model Calculations
Figure 10 presents the mineral dust distribution trajectories calculated using the Backward Ensemble trajectory of the HYSPLIT model at different altitudes in the atmosphere, showing from which country and in what period the dust entered the territory of Georgia.
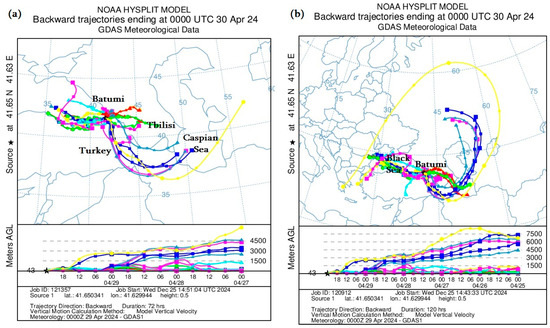
Figure 10.
Distribution of mineral dust calculated by the Backward Ensemble trajectory of the HYSPLIT model at different atmospheric heights over the territory of Georgia ((a,c)—from 29 to 26 April 2024; (b,d)—from 29 to 24 April 2024).
Namely, Figure 10a,c shows the distribution of atmospheric dust from 26 to 30 April 2024, and Figure 10b,d shows the trajectories of mineral dust from 24 to 30 April 2024. In addition, Figure 10a,b shows the trajectories of dust entering the territory of Batumi, and Figure 10c,d shows the trajectories of dust entering the territory of Kutaisi. As can be seen from Figure 10, mineral dust mainly entered the territory of western Georgia (Batumi and Kutaisi) from the south and west. However, it is worth noting that dust plume movement trajectories had a rather strange cyclonic nature. In particular, as shown in Figure 10a,c, atmospheric dust entered the territory of western Georgia from both the Black Sea and the Aral Sea Desert, where the path first went towards the southern Caspian Sea, then from the territory of Iran through the territory of Turkey to Georgia. However, over a longer period (see Figure 10b,c), the dust movement trajectory originated from the territories of Eastern Europe and Russia, went around the Caspian Sea from the north and then moved in a circle from the Aral Sea Desert towards Batumi and Kutaisi. The results obtained using the HYSPLIT model coincide with the images obtained using MODIS, which showed that the maximum dust concentration was concentrated both in the northwestern and southeastern parts of Georgia.
3.2.5. CAMS PM10 Forecast Results for 24–29 April 2024
Figure 11 shows the CAMS (West Asia Maps) PM10 forecasts obtained at different times from 24 to 30 April 2024. In particular, Figure 11a shows that a strong PM10 dust plume was observed over the Sahara (Libya), Saudi Arabia and West Asia (Karakum Desert) deserts, and a dust plume band extending from the Sahara (Libya) across the eastern Mediterranean Sea to Ukraine almost completely covered the Black Sea at 03 UTC on 24 April. Figure 11b, obtained 9 h later, shows that the dust plume penetrated into western Georgia and especially affected its northern and southern regions, which is consistent with the ground-based measurements. Over the next 18 h, the dust plume moved slightly northward in Georgia and almost covered the Main Caucasus Range (Figure 11c). Figure 11d shows that at 06 UTC on 26 April 2024, the dust plume left the territory of Georgia, but strong dust plumes were observed in Turkmenistan, Iran, Saudi Arabia, Egypt, Turkey, the eastern Black Sea and Russia up to the North Sea, which is inconsistent with the in situ data presented in Table 3.
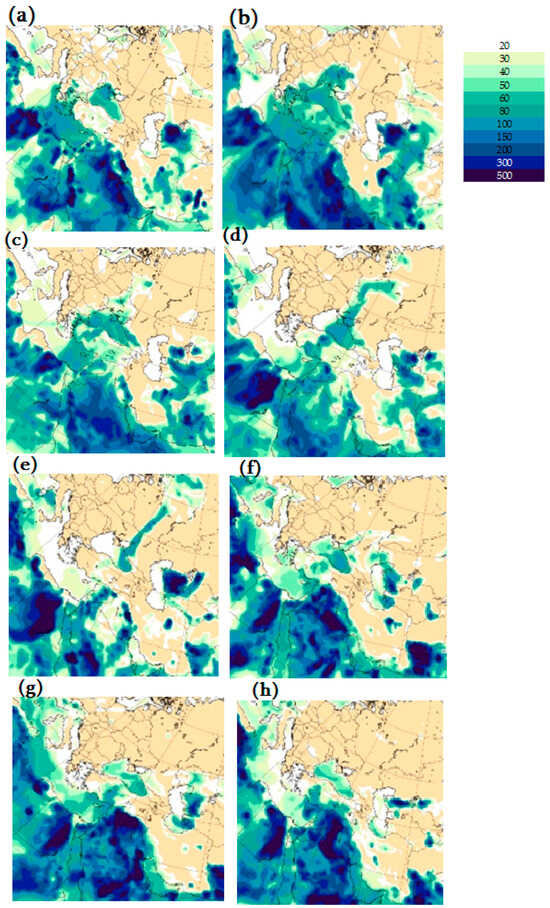
Figure 11.
CAMS PM10 forecasts over Western Asia and Eastern Europe made on 24–30 April 2024 at different points in time. Namely, at 03:00 UTC on 24 April 2024—(a); at 12:00 UTC on 24 April 2024—(b); at 06:00 UTC on 25 April 2024—(c); at 06:00 UTC on 26 April 2024—(d); at 00:00 UTC on 27 April 2024—(e); at 12:00 UTC on 29 April 2024—(f); at 00:00 UTC on 30 April 2024—(g); at 12:00 UTC on 31 April 2024—(h).
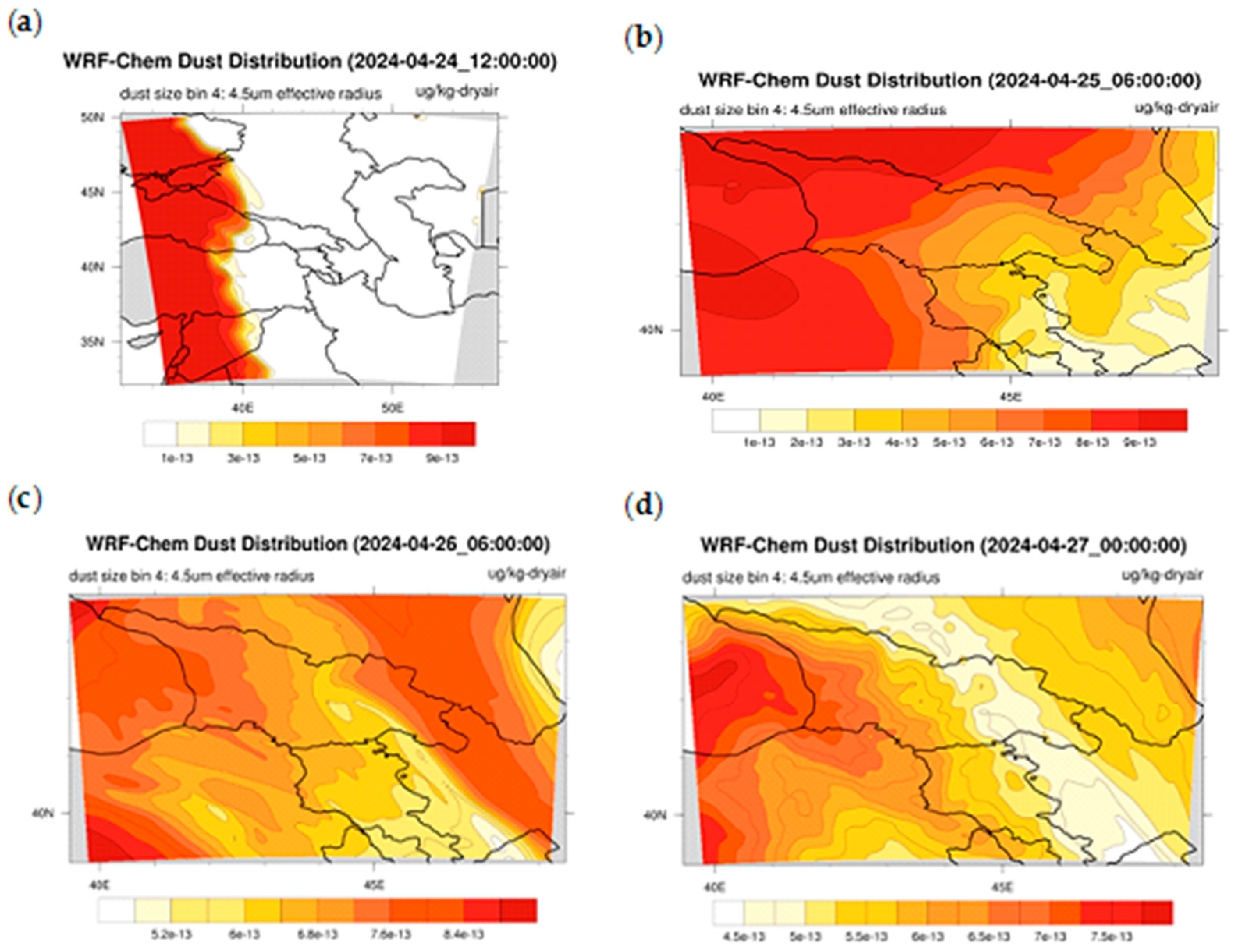
3.2.6. WRF v.4.5.1 Model Calculation
Figure 12 shows some results of the numerical simulations of the WRF-Chem v.4.5.1 model performed on coarse and nested grids from 24 to 27 April 2024. The result of the simulation performed on the coarse grid (see Figure 12a) shows that, as in the CAMS simulation, the dust plume band extended from the Sahara (Libya) across the Mediterranean Sea to Ukraine and almost completely covered the Black Sea, but no dust plume was observed in Georgia at 12:00 UTC on 24 April 2024. Figure 12b, obtained using fine-grid calculations at 06:00 UTC on 25 April 2024, shows that the dust band has moved both eastward to the eastern coast of the Black Sea (dust plumes are observed in western Georgia) and northward to the Main Caucasus Range. It should be noted that, contrary to the CAMS calculations, a weak dust plume has reached eastern Georgia (Tbilisi and Rustavi), which was confirmed by the ground-based observations presented in Table 1.
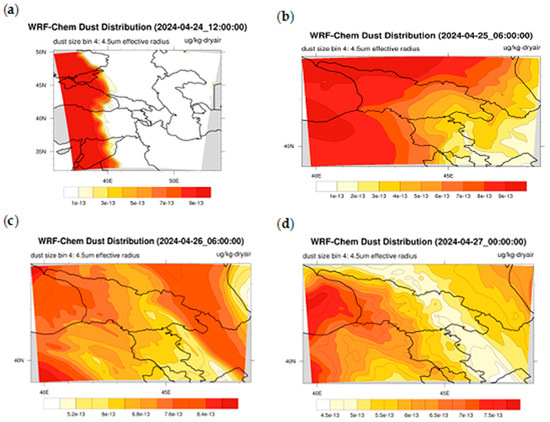
Figure 12.
Results of the numerical calculations of the WRF-Chem v.4.5.1 model, performed in a coarse domain with a resolution of 19.8 km, at 12:00 UTC on 24 April 2024—(a); and in a fine-resolution grid with a resolution of 6.6 km, at 06:00 UTC on 25 April 2024—(b); at 06:00 UTC on 26 April 2024—(c); and at 00:00 on 27 April 2024—(d).
Figure 12c, which presents the fine grid calculation results obtained at 06:00 on 26 April 2024, shows that the vicinity of Batumi (located on the Black Sea coast) was slightly more polluted than Kutaisi (located in the central part of western Georgia), while Tbilisi and Rustavi (located in the central part of eastern Georgia) were only very weakly polluted with PM10, and these results are consistent with the in situ data (see Table 3). Figure 12c also shows that a relatively strong dust plume reached the easternmost region of Georgia, which was confirmed by MODIS imagery (see Figure 8d) but is not reflected in Table 3 (due to the lack of air quality monitoring stations in the easternmost regions of Georgia). Figure 12d, which again presents the fine-grid simulation results at 00:00 on 27 April 2024, shows that although the PM10 value in the eastern Black Sea has increased slightly, the dust pollution over the whole of Georgia has weakened slightly. Namely, Batumi’s PM10 pollution has increased over 24 h, Kutaisi has become significantly less polluted than Batumi and Tbilisi and Rustavi in eastern Georgia had virtually no PM10 dust pollution at 00:00 on 27 April 2024. These results are in good agreement with the CAMS predictions (Figure 11e) and with the in situ data shown in Table 3.
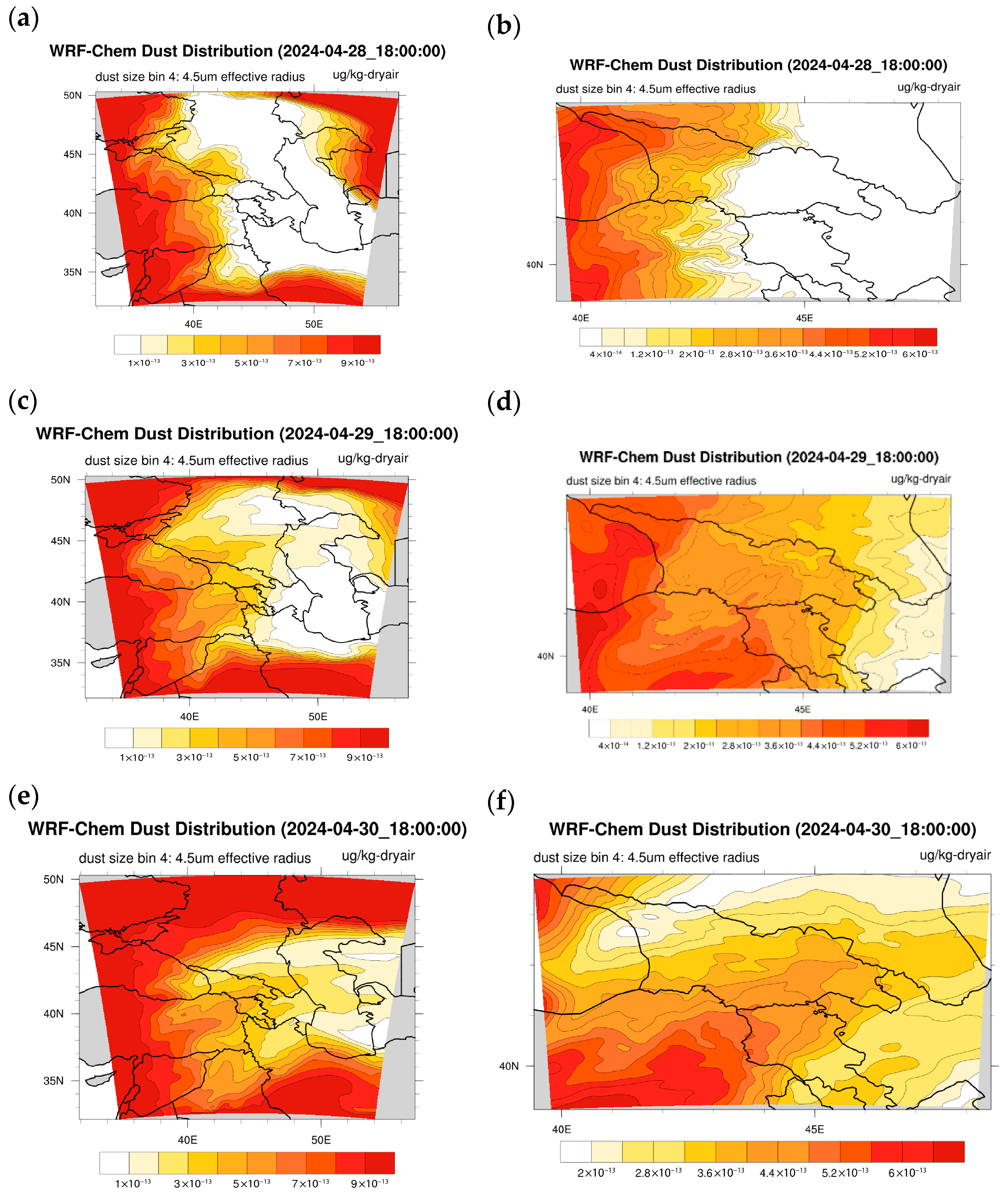
Figure 13 shows the results of numerical calculations of the WRF-Chem v.4.5.1 model performed from 28 to 30 April 2024. Namely, analysis of Figure 13a,c,e obtained from coarse grid simulations shows that there were strong dust plumes around the Caucasus region, extending over the Black Sea, Russia, the Aral Sea deserts, Iran, Iraq, Syria and Turkey. The position of the dust plumes over the eastern Black Sea and Turkey remained almost unchanged during 72 h, while the dust plumes located over Iran, Iraq and Syria moved towards Georgia and penetrated into eastern Georgia during 28–30 April 2024. It is worth noting that these WRF-Chem/GOCART simulation results are in good agreement with the corresponding MODIS images and HYSPLIT model simulation results. As for the results obtained by the nested grid calculations (Figure 13b,d,f), their analysis shows that PM10 pollution has increased in Georgia compared to the coarse grid calculations. For example, Figure 13d,f show a significant increase in dust concentrations in Tbilisi and Rustavi at 18:00 on 29 and 30 April, which was not present in the coarse grid calculation results but is consistent with the ground-based observations presented in Table 3.
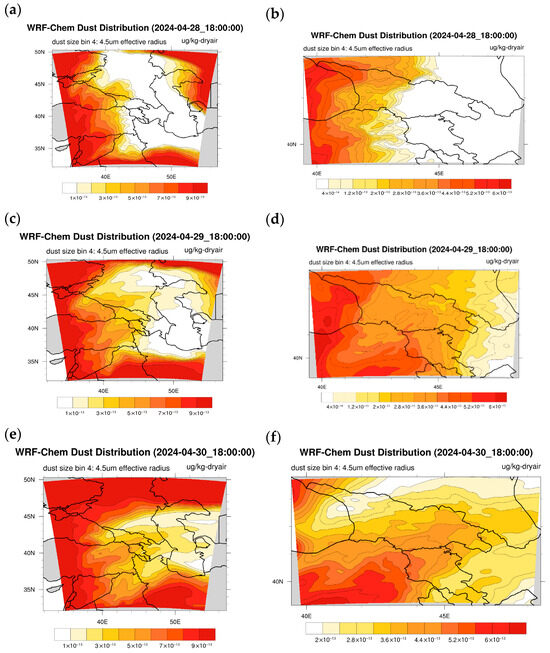
Figure 13.
Results of the numerical calculations of the WRF-Chem v.4.5.1 model, performed in a coarse domain with a resolution of 19.8 km, at 18:00 on 28 April 2024—(a); at 18:00 on 29 April 2024—(c); at 18:00 on 30 April 2024—(e); and in a fine-resolution grid with a resolution of 6.6 km, at 18:00 on 28 April 2024—(b); at 18:00 on 29 April 2024—(d); at 18:00 on 30 April 2024—(f).
4. Discussion
Current climate change, expressed as changes in weather patterns, vegetation cover and soil degradation, significantly affects the emissions, transport and deposition of aeolian dust [1,3]. A climate modeling study has shown that current climate change is well correlated with increased aeolian dust transport due to the reduced average precipitation and more frequent strong winds over land in warmer climates [31,38]. Studies have shown that the period from late February to early June is usually the beginning of the season of increased ADD transport from the Sahara and the Arabian Peninsula deserts to adjacent areas (as well as to the Caucasus) [3,5,21,22,29,31,35]. Indeed, analysis of synoptic weather maps (at the surface and in the upper air layers) and satellite data for this period showed that the areas of dust storm generation in the Sahara, northeastern Syria, various parts of Iraq, eastern Jordan and northern Saudi Arabia generally correspond to the merger of two baric systems, when wind speeds during these storms ranged from 4 to 12 m/s [37]. The period from February to May 2023 and 2024 was no exception for the Caucasus, as the WRF-Chem, CAMS and HYSPLIT models detected 38 mineral dust events transported from these deserts to Georgia from March 2023 to September 2024. But this time, the ADD intrusions were not as strong as those observed on 23–24 March (from the Sahara) and 27 July 2018 (from the Karakum Desert), which completely covered the entire territory of Georgia [29,42].
In order to identify possible routes of ADD penetration into the territory of Georgia, the strength and direction of prevailing air flows were studied using the READY system wind roses (in both eastern and western regions of Georgia) up to the heights of 3–5 km (the height of 3–5 km was determined using the HYSPLIT model forecast information on the distribution of the main aerosol concentrations by height). For example, Figure 4a,b, which show the wind roses on 28–29 May 2024, show that the main wind direction was southeast (which was confirmed by the MODIS images), and the wind speed of 4–7 m/s was a favorable condition for the deposition of PM10 dust particles (which is well reflected in the PM10 data presented in Table 2).
To study the sources and transport routes of dust storms, MODIS satellite imagery AOD data were used, which, among many methods, is one of the most suitable since it uses six predefined aerosol types that have great potential for detecting dust events. For example, analysis of Figure 8 shows that the maximum aerosol concentration shifted from the coastal zone of the Black Sea to the easternmost territory of Georgia during the period from 25 to 29 April 2024. And this unusual fact is well confirmed by the PM10 data presented in Table 3 and the wind rose data presented in Figure 9.
To better understand the dust storm tracks and their origins, both forward and backward HYSPLIT model trajectories were studied for Tbilisi, Rustavi, Batumi, Kutaisi, Telavi and the easternmost point of Georgia, Dedoplistskaro (41°27′ N, 46°6′ E), but in this paper, for simplicity, only the backward HYSPLIT model trajectories for Tbilisi, Rustavi and Telavi are plotted and analyzed. The HYSPLIT model calculations showed that the transfer of ADD had a rather different nature in different tropospheric layers of the atmosphere. For example, mineral dust was transferred to the territory of Tbilisi and Rustavi from the territories of Syria and Iraq (through the territory of Turkey) in relatively high layers of the atmosphere (1–4 km), and below 1 km, it was transferred from the Caspian Sea (through the territory of Azerbaijan) on 29–31 May 2024 (Figure 5). Also, atmospheric dust entered the territory of Western Georgia from both the Black Sea and the Aral Sea desert on 26–29 April 2024 (Figure 10a,c), and over a longer period of time, the trajectory of dust particles could have also had a strange cyclonic character on 24–29 April 2024 (Figure 10b,d), which indicates a rather complex nature of the ADD transfer paths in the conditions of the complex orography of the Caucasus (Figure 1a).
Thus, when studying the transfer of ADD to Georgia using WRF modeling, among a number of factors determining the transfer process, it is very important to more accurately take into account the complex orographic features of the Caucasus region. Indeed, the use of a high-resolution grid (6.6 km) in the WRF-Chem v.4.5.1 model (with similar physical parameterization schemes) allowed us to improve the quality of numerical results. For example, Figure 7b, which presents the fine grid results at 06:00 on 29 May 2024, shows that weak dust emissions were observed in Tbilisi and Rustavi, which was not observed in the coarse grid results presented in Figure 7a. Again, Figure 7d, which presents the fine grid results at 18:00 on 29 May 2024, shows the penetration of ADD from Turkey into Georgia, even reaching the Main Caucasus Range (confirmed by MODIS images), which was not observed in the coarse grid results presented in Figure 7c.
The results of numerical experiments showed that both the WRF-Chem/dust (GOCART) v.4.5.1 and CAMS models were able to simulate the ADD transport into Georgia under the complex orography of the Caucasus, but the WRF-Chem/dust (GOCART) v.4.5.1 calculation results were more reliable in several cases, estimated from MODIS and in situ data. For example, CAMS PM10 (West Asia map) forecasts obtained at different times on 24–30 April 2024 showed (see Figure 11) that the dust plume failed to penetrate into the territory of Eastern Georgia, while WRF-Chem/dust (GOCART) model calculations predicted this event satisfactorily, and nested grid calculations improved the calculation results (Figure 12 and Figure 13).
As it was mentioned above, the results of the WRF-Chem/GOCSRT v.4.5.1 model calculation performed from 2 March 2023 to 20 September 2024 (vitrificated by CAMS and HYSPLIT models, MODIS images and in situ PM10 data) showed 38 cases of ADD transfer to the territory of Georgia. It should be noted that these 38 ADD were invaded from the west, east, south, southwest and southeast and occurred in all seasons of the year. Namely, out of the 38 invasions, 2 were observed from the west, 7 times from the southwest, 9 times from the south, 6 times from the east and 14 times from the southeast, and these ADD events occurred in the spring (22 times), summer (7 times), autumn (8 times) and even winter (1 times) during the study period. It is noteworthy that of the 38 ADD intrusions studied in this work, only relatively strong ADD intrusions from the south and southeast reached the Main Caucasus Range. As for the relatively strong ADDs transferred from the deserts of Western Asia to the territory of Georgia and directed to the northwest, they often went around the Main Caucasus Range and even reached Mount Elbrus, whereas ADD intrusions from Western Asia had not previously been recorded in cores extracted from the glaciers of the Caucasus [46]. In addition, for the first time, the results of WRF and CAMS calculations showed that weak invasions of ADD to the territory of Georgia were frequent not only in spring but also in other seasons. For example, the calculation results showed that only in the period from 1 September to 20 September 2024, in the southeastern and especially in the easternmost regions of Georgia, seven weak ADD incursions were observed (from the deserts located in the east, southeast and south), of which only one ADD reached and was recorded by the automatic dust stations of Tbilisi and Rustavi.
The analysis of NEA air quality monitoring stations data presented in Table 2 shows that high PM10 concentration values (colored red) were observed in the eastern part of Georgia (Tbilisi and Rustavi), while in the western part of Georgia, PM10 values were well below the maximum permissible concentration (50 μg/m3) from 28 to 31 May 2024. It should also be noted that the analysis of PM10 concentrations in Table 2 shows that even in Rustavi (which is located approximately 20 km southeast of Tbilisi), the average PM10 concentration values were noticeably higher than at Varketili station, which is the easternmost air quality monitoring station in Tbilisi. Thus, it can be assumed that PM10 concentration values in the easternmost regions of Georgia should be higher than in Rustavi if ADD penetrates from the south, southeast and east. It should be noted that the analysis of 38 cases of ADA incursions into the territory of Georgia showed that the number of ADA incursions from the southern, southeastern and eastern sides into the territory of Georgia was three times greater than from the western and southwestern sides. Since the lack of a PM10 monitoring station in the easternmost regions of Georgia does not allow for a sufficient accurate assessment of the ADA invasion and the actual PM10 values, numerical modeling with satellite observations should be used to clarify this issue.
The fact is that in the easternmost region of Georgia, Kakheti, which is the most famous wine and agricultural region of Georgia, there is no automatic station for measuring PM2.5 and PM10 dust particles. Since the calculations showed that the non-strong invasion of ADD in the easternmost and southernmost regions of Georgia was frequent and seriously polluted the environment, in order to monitor the dust invasion in the territory of Georgia, it is desirable that this proposed ensemble modeling method be tested in practice by the National Environmental Protection Agency of Georgia.
5. Conclusions
In brief, the numerical simulation results showed that: (i) the WRF-Chem/dust (GOCART) v.4.5.1 model was able to simulate dust aerosol transport to the Caucasus under complex relief conditions; (ii) dust aerosols were transported almost equally from the deserts of Africa, the Middle East and Central (West) Asia during the study period; (iii) the use of high-resolution grid (6.6 km) in the WRF-Chem v.4.5.1 model improved the quality of the numerical simulations; (iv) dust aerosol is an important factor influencing the climate system of Georgia, since 38 cases of aeolian dust transport to the territory of Georgia were recorded during the one and a half-year period; (v) the calculations showed that the number of ADD penetration into the easternmost regions of Georgia (the most viticultural and agricultural region) was three times higher than in other regions of Georgia, which was not known due to the absence of a dust measuring station in the easternmost region of Georgia; (vi) the WRF-Chem/dust (GOCART) model (with the CAMS and HYSPLIT models) can be successfully used for forecasting dust aerosols in regions with complex relief conditions (in particular, by the National Environmental Protection Agency of Georgia in the daily air quality service).
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, T.D.; data curation, T.D. and I.S.; formal analysis, T.D. and I.S.; investigation, T.D. and I.S.; methodology, T.D.; writing—original draft, T.D.; writing—review and editing, T.D.; visualization, T.D. and I.S.; project administration, T.D. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
The funding for this article is provided by the Shota Rustaveli National Science Foundation of Georgia, Grant No. FR22_18445, in the amount of 2400.00 CHF.
Data Availability Statement
The data presented in this study are available on request from the corresponding author.
Acknowledgments
The authors would like to thank all those who contributed to this research. Namely, we appreciate the time and effort that all reviewers devoted to providing feedback on our manuscript; we are grateful for the insightful comments and valuable improvements to our paper and for giving us the opportunity to submit a revised draft of the manuscript. We would also like to thank the Georgian National Research and Education Association GE-01-GRENA led by Ramaz Kvatadze for providing computer time for WRF model calculations, Nino Chikhradze for reviewing the manuscript and for her valuable comments and Giorgi Banetishvili for his assistance in providing some of the WRF-Chem model calculations and visualization of its results. And, once again, our gratitude to the Shota Rustaveli National Science Foundation of Georgia, which provided us with the opportunity to conduct this research under Grant No. FR22_18445.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
References
- IPCC Sixth Assessment Report, Climate Change 2022: Impacts, Adaptation and Vulnerability. 2022. Available online: https://www.ipcc.ch/report/ar6/wg2/ (accessed on 28 February 2022).
- Al-Hemoud, A.; Al-Dousari, A.; Al-Shatti, A.; Al-Khayat, A.; Behbehani, W.; Malak, M. Health Impact Assessment Associated with Exposure to PM10 and Dust Storms in Kuwait. Atmosphere 2018, 9, 6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choobari, O.A.; Zawar-Reza, P.; Sturman, A. The global distribution of mineral dust and its impacts on the climate system. Atmosph. Res. 2014, 138, 152–165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.; Zhao, L.; Tong, D.Q.; Wu, G.; Dan, M.; Teng, B. A Systematic Review of Global Desert Dust and Associated Human Health Effects. Atmosphere 2016, 7, 158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ginoux, P.; Prospero, J.M. Global-scale attribution of anthropogenic and natural dust sources and their emission rates based on MODIS Deep Blue aerosol products. Rev. Geophys. 2012, 50, 1–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shao, Y.; Ishizuka, M.; Mikami, M.; Leys, J.F. Parameterization of size-resolved dust emission and validation with measurements. J. Geoph. Res. 2011, 116, 1–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rizza, U.; Anabor, V.; Mangia, C.; Miglietta, M.M.; Degrazia, G.A.; Passerini, G. WRF-Chem Simulation of a saharan dust outbreak over the mediterranean regions. Ciência e Nat. 2016, 38, 330–336. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Middleton, N.J. Desert dust hazards: A global review. Aeolian Res. 2017, 24, 53–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, K.W.; Kim, Y.J.; Oh, S.J. Visibility impairment during Yellow Sand periods in the urban atmosphere of Kwangju, Korea. Atmosp. Environ. 2001, 35, 5157–5167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Labban, A.; Farahat, A. Effect of Major Dust Events on Ambient Temperature and Solar Irradiance Components over Saudi Arabia. Atmosphere 2023, 14, 408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, R.; Liu, Y.; Luo, M.; Li, D.; Tan, Z.; Shao, T.; Alam, K. Dust effects on mixed-phase clouds and precipitation during a super dust storm over northern China. Atmos. Environ. 2023, 313, 120081. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Andreae, M.O.; Rosenfeld, D. Aerosol-cloud precipitation interactions. Part 1. The nature and sources of cloud-active aerosols. Earth-Sci. Rev. 2008, 89, 13–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Charlson, R.J.; Schwartz, S.E.; Hales, J.M. Climate forcing by anthropogenic aerosols. Science 1992, 255, 423–430. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rosenfeld, D.; Rudich, Y.; Lahav, R. Desert dust suppressing precipitation: A possible desertification feedback loop. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2001, 98, 5975–5980. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hui, W.J.; Cook, B.I.; Ravi, S.; Fuentes, J.D.; D’Odorico, P. Dust-rainfall feedbacks in the West African Sahel. Water Res. Res. 2008, 44, 1–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Twomey, S. Pollution and the planetary albedo. Atm. Environ. 1974, 8, 1251–1256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Urushadze, T.F.; Blum, W.E.H. Soils of Georgia; Nova: New York, NY, USA, 2014; 242p. [Google Scholar]
- Javakhishvili, S. Georgian Climate Description by the Months; Publishing House “Ganatleba”: Tbilisi, Kura, 1988; p. 198. (In Georgian) [Google Scholar]
- Huang, J.; Ji, M.; Xie, Y.; Wang, S.; He, Y.; Ran, J. Global semi-arid climate change over last 60 years. Clim. Dyn. 2016, 46, 1131–1150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kordzakhia, G.; Shavliashvili, L.; Kuchava, G.; Buachidze, N. Research of Soil Resources Degradation Processes in Georgia. Am. J. Environ. Prot. 2015, 4, 251–259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Al-Mutairi, M.; Labban, A.; Abdeldym, A.; Alkhouly, A.; Abdel Basset, H.; Morsy, M. Diagnostic Study of a Severe Dust Storm over North Africa and the Arabian Peninsula. Atmosphere 2023, 14, 196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Engelstaedter, S.; Tegen, I.; Washington, R. North African dust emissions and transport. Earth-Sci. Rev. 2006, 79, 73–100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, Y.; Dai, X.; Fang, X. Dust aerosols: A possible accelerant for an increasingly arid climate in North China. J. Arid. Environ. 2008, 72, 1476–1489. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Huang, J.; Ji, M.; Higuchi, K. Variability of East Asia dust events and their long-term trend. Atmos. Environ. 2008, 4, 3156–3165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Davitashvili, T.; Kutaladze, N.; Kvatadze, R.; Mikuchadze, G. Effect of dust aerosols in forming the regional climate of Georgia. Scalable Comp. Pract. Exp. 2018, 19, 199–208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jin, Z.; Yu, J.; Dai, K. Topographic Elevation’s Impact on Local Climate and Extreme Rainfall: A Case Study of Zhengzhou, Henan. Atmosphere 2024, 15, 234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shahgedanova, M.; Kutuzov, S.; White, K.H. Using the significant dust deposition event on the glaciers of Mt. Elbrus, Caucasus Mountains, Russia on 5 May 2009 to develop a method for dating and “provenancing” of desert dust events recorded in snow pack. Atm. Chem. Phys. 2013, 13, 1797–1808. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kutuzov, S.S.; Mikhalenko, V.N.; Shahgedanova, M.V. Ways of far-distance dust transport onto Caucasian glaciers and chemical composition of snow on the Western plateau of Elbrus. Lëd i Sneg. 2014, 54, 5–15. (In Russian) [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Davitashvili, T. Modelling transportation of desert dust to the South Caucasus using WRF Chem model. E3S Web Conf. 2019, 99, 03011. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, H.; Zhu, X.; Fang, Z.; Qiu, D.; Hu, Y.; Tian, C.; Ming, F. Study on the Vertical Distribution and Transport of Aerosols in the Joint Observation of Satellite and Ground-Based LiDAR. Atmosphere 2024, 15, 240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Davitashvili, T.; Samkharadze, I. Study of Aeolian transfer of mineral dust from deserts to the territory of Georgia. Arab. J. Geosci. 2021, 14, 67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eghbali, A.; Mirrokni, S.M.; Memarian, M.H. Dust storm simulation using WRF−Chem. Int. J. Rec. Res. Appl. Stud. 2016, 28, 1–12. [Google Scholar]
- Davitashvili, T. On Some Aspects of Climate Change in Georgia. Int. J. Energy Environ. 2018, 12, 80–86. [Google Scholar]
- Grousset, F.E.; Ginoux, P.; Bory, A. Case study of a Chinese dust plume reaching the French Alps. Geoph. Res. Lett. 2003, 30, 1277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hamzeh, N.H.; Kaskaoutis, D.G.; Rashki, A.; Mohammadpour, K. Long-Term Variability of Dust Events in Southwestern Iran and Its Relationship with the Drought. Atmosphere 2021, 12, 1350. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiao, X.; Dong, Z.; Brahney, J.; Parteli, E.J.; Li, F.; Augusto, M.; Wei, T. Uranium isotopes of aeolian dust deposited in northern Tibetan Plateau glaciers: Implications for tracing aeolian dust provenance. Fundam. Res. 2022, 2, 716–726. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Khidher, S.A. Dust Storms in Iraq: Past and Present. Theor. Appl. Clim. 2024, 155, 4721–4735. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Darvishi Boloorani, A.; Soleimani, M.; Neysani Samany, N.; Bakhtiari, M.; Qareqani, M.; Papi, R.; Mirzaei, S. Assessment of Rural Vulnerability to Sand and Dust Storms in Iran. Atmosphere 2023, 14, 281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rizza, U.; Barnaba, F.; Miglietta, M.M. WRF-Chem model simulations of a dust outbreak over the central Mediterranean and comparison with multi-sensor desert dust observations. Atm. Chem. Phys. 2017, 17, 93–115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Q.; Huang, Z.; Hu, Z.; Dong, Q.; Li, S. Long-range transportand evolution of Saharan dust over EastAsia from 2007 to 2020. J. Geophys. Res. Atmos. 2022, 127, 1–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lai, H.-C.; Dai, Y.-T.; Mkasimongwa, S.W.; Hsiao, M.-C.; Lai, L.-W. The Impact of Atmospheric Synoptic Weather Condition and Long-Range Transportation of Air Mass on Extreme PM10 Concentration Events. Atmosphere 2023, 14, 406. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Solomos, S.; Kalivitis, N.; Mihalopoulos, N. From Tropospheric Folding to Khamsin and Foehn Winds: How Atmospheric Dynamics Advanced a Record-Breaking Dust Episode in Crete. Atmosphere 2018, 9, 240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, L.; Sokolik, I.N. Analysis of Dust Aerosol Retrievals Using Satellite Data in Central Asia. Atmosphere 2018, 9, 288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schwikowski, M.; Brütsch, S.; Gäggeler, H.W. A high-resolution air chemistry record from an Alpine ice core: Fiescherhorn glacier, Swiss Alps. J. Geophys. Res. 1999, 104, 13709–13719. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kang, S.; Zhang, Y.; Zhang, Y. Variability of atmospheric dust loading over the central Tibetan Plateau based on ice core glacio-chemistry. Atm. Environ. 2010, 44, 2980–2989. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mikhalenko, V.; Sokratov, S.; Kutuzov, S. Investigation of a deep ice core from the Elbrus western plateau, the Caucasus, Russia. Cryosphere 2015, 9, 2253–2270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kutuzov, S.S.; Mikhalenko, V.N.; Grachev, A.M. First geophysical and shallow ice core investigation of the Kazbek plateau glacier, Caucasus Mountains. Environ. Earth Sci. 2016, 75, 1488. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Skamarock, W.C.; Klemp, J.B.; Dudhia, J.; Gill, D.O.; Barker, M.G.; Duda, X.; Huang, Y.; Wang, W.; Powers, J.G. A Description of the Advanced Research WRF Version 3; NCAR Tech. Note, NCAR/TN-475+STR; National Center for Atmospheric Research: Boulder, CO, USA, 2008; 113p. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grell, G.A.; Peckham, S.E.; Schmitz, R. Fully coupled “online” chemistry within the WRF model. Atm. Environ. 2005, 39, 6957–6976. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fountoukis, C.; Ackermann, L.; Ayoub, M.A.; Gladich, I.; Hoehn, R.D.; Skillern, A. Impact of atmospheric dust emission schemes on dust production and concentration over the Arabian Peninsula. Model. Earth Syst. Environ. 2016, 2, 115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chin, M.; Rood, R.B.; Lin, S.-J.; Muller, J.F.; Thomspon, A.M. Atmospheric sulfur cycle in the global model GOCART: Model description and global properties. J. Geophys. Res.-Atmos. 2000, 105, 24671–24687. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thompson, G.; Field, P.R.; Rasmussen, R.M.; Hall, W.D. Explicit Forecasts of Winter Precipitation Using an Improved Bulk Microphysics Scheme. Part II: Implementation of a New Snow Parameterization. Mon. Weather Rev. 2008, 136, 5095–5115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grell, G.A.; Devenyi, D. A generalized approach to parameterizing convection combining ensemble and data assimilation techniques. Geoph. Res. Lett. 2002, 29, 1693–1712. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iacono, M.J.; Delamere, J.S.; Mlawer, E.J.; Shephard, M.W.; Clough, S.A.; Collins, W.D. Radiative forcing by long-lived greenhouse gases: Calculations with the AER radiative transfer models. J. Geophys. Res. 2008, 113, D13103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Janić, Z.I. The Step-Mountain Eta Coordinate Model: Further Developments of the Convection, Viscous Sublayer, and Turbulence Closure Schemes. Mon. Weather Rev. 1994, 122, 927–945. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Janić, Z.I. Nonsingular implementation of the Mellor-Yamada level 2.5 scheme in the NCEP Meso model. Nation. Cent. Environ. Pred. 2001, 437, 38–40. Available online: https://repository.library.noaa.gov/view/noaa/11409 (accessed on 29 February 2016).
- Winker, D.; Hunt, W.; McGill, M. Initial Performance Assessment of CALIOP. Geoph. Res. Lett. 2007, 34, L19803. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Omar, A.H.; Winker, D.M.; Kittaka, C. The calipso automated aerosol classification and lidar ratio selection algorithm. J. Atmosph. Ocean. Technol. 2009, 26, 1994–2014. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Remer, L.A.; Kaufman, Y.J.; Tanr’e, D. The MODIS algorithm, products and validation. J. Atm. Sci. 2005, 62, 947–973. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Draxler, R.R.; Ginoux, P.; Stein, A.F. An empirically derived emission algorithm for wind-blown dust. J. Geoph. Res. 2010, 115, D16212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Draxler, R.R.; Hess, G.D. An overview of the HYSPLIT_4 modeling system for trajectories, dispersion, and deposition. Aust. Met. Mag. 1998, 47, 295–308. [Google Scholar]
- Stein, A.F.; Draxler, R.R.; Rolph, G.D.; Stunder, B.J.B.; Cohen, M.D.; Ngan, F. NOAA’s HYSPLIT atmospheric transport and dispersion modeling system. Bull. Amer. Meteor. Soc. 2015, 96, 2059–2077. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).