A Study on Combined Effect of Monoterpenoid Essential Oils and Polyphenols from Grape Pomace on Selected Pathogenic and Probiotic Bacteria Strains
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results
2.1. Minimum Inhibition Concentration of Pathogenic Bacteria
2.2. Effect on Growth of Lactiplantibacillus Plantarum
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Essential Oils and Polyphenols Stock Solution
4.2. Bacteria Culture
4.3. Antibacterial Activity
4.4. Statistical Analysis
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| EO | Essential Oil |
| MIC | Minimal Inhibition Concentration |
| PP | Polyphenol |
References
- Bartkiene, E.; Ruzauskas, M.; Bartkevics, V.; Pugajeva, I.; Zavistanaviciute, P.; Starkute, V.; Zokaityte, E.; Lele, V.; Dauksiene, A.; Grashorn, M.; et al. Study of the Antibiotic Residues in Poultry Meat in Some of the EU Countries and Selection of the Best Compositions of Lactic Acid Bacteria and Essential Oils against Salmonella enterica. Poult. Sci. 2020, 99, 4065–4076. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kaur, K.; Singh, S.; Kaur, R. Impact of Antibiotic Usage in Food-Producing Animals on Food Safety and Possible Antibiotic Alternatives. Microbe 2024, 4, 100097. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Center for Disease Control and Prevention. Antibiotic Resistance Threats in the United States; CDC: Atlanta, GA, USA, 2020.
- Adhikari, P.; Kiess, A.; Adhikari, R.; Jha, R. An Approach to Alternative Strategies to Control Avian Coccidiosis and Necrotic Enteritis. J. Appl. Poult. Res. 2020, 29, 515–534. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Projahn, M.; Pacholewicz, E.; Becker, E.; Correia-Carreira, G.; Bandick, N.; Kaesbohrer, A. Reviewing Interventions against Enterobacteriaceae in Broiler Processing: Using Old Techniques for Meeting the New Challenges of ESBL E. coli? BioMed Res. Int. 2018, 2018, 7309346. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vinueza-Burgos, C.; Baquero, M.; Medina, J.; De Zutter, L. Occurrence, Genotypes and Antimicrobial Susceptibility of Salmonella Collected from the Broiler Production Chain within an Integrated Poultry Company. Int. J. Food Microbiol. 2019, 299, 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xue, F.; Shi, L.; Li, Y.; Ni, A.; Ma, H.; Sun, Y.; Chen, J. Effects of Replacing Dietary Aureomycin with a Combination of Plant Essential Oils on Production Performance and Gastrointestinal Health of Broilers. Poult. Sci. 2020, 99, 4521–4529. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Balta, I.; Linton, M.; Pinkerton, L.; Kelly, C.; Stef, L.; Pet, I.; Stef, D.; Criste, A.; Gundogdu, O.; Corcionivoschi, N. The Effect of Natural Antimicrobials against Campylobacter spp. and Its Similarities to Salmonella spp., Listeria spp., Escherichia coli, Vibrio spp., Clostridium spp. and Staphylococcus spp. Food Control 2021, 121, 107745. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marchese, A.; Orhan, I.E.; Daglia, M.; Barbieri, R.; Di Lorenzo, A.; Nabavi, S.F.; Gortzi, O.; Izadi, M.; Nabavi, S.M. Antibacterial and Antifungal Activities of Thymol: A Brief Review of the Literature. Food Chem. 2016, 210, 402–414. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Radünz, M.; dos Santos Hackbart, H.C.; Camargo, T.M.; Nunes, C.F.P.; de Barros, F.A.P.; Dal Magro, J.; Filho, P.J.S.; Gandra, E.A.; Radünz, A.L.; da Rosa Zavareze, E. Antimicrobial Potential of Spray Drying Encapsulated Thyme (Thymus vulgaris) Essential Oil on the Conservation of Hamburger-like Meat Products. Int. J. Food Microbiol. 2020, 330, 108696. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- El Asbahani, A.; Miladi, K.; Badri, W.; Sala, M.; Addi, E.H.A.; Casabianca, H.; El Mousadik, A.; Hartmann, D.; Jilale, A.; Renaud, F.N.R.; et al. Essential Oils: From Extraction to Encapsulation. Int. J. Pharm. 2015, 483, 220–243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bao, H.; Ding, H.H.; Charles, A.P.R.; Hui, D.; Rakshit, S.; Nahashon, S.; Wu, Y. Application of Yellow Mustard Mucilage in Encapsulation of Essential Oils and Polyphenols Using Spray Drying. Food Hydrocoll. 2023, 143, 108815. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de Souza Rodrigues, H.L.; Kolososki, I.M.M.; Benevides, V.P.; Saraiva, M.M.S.; Berchieri Junior, A. Essential Oils Used in the Poultry Industry: Would It Be an Effective Green Alternative against Salmonella spp. Dissemination and Antimicrobial Resistance? Microbe 2025, 6, 100248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Valcourt, C.; Saulnier, P.; Umerska, A.; Zanelli, M.P.; Montagu, A.; Rossines, E.; Joly-Guillou, M.L. Synergistic Interactions between Doxycycline and Terpenic Components of Essential Oils Encapsulated within Lipid Nanocapsules against Gram Negative Bacteria. Int. J. Pharm. 2016, 498, 23–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kaschubek, T.; Mayer, E.; Rzesnik, S.; Grenier, B.; Bachinger, D.; Schieder, C.; König, J.; Teichmann, K. Effects of Phytogenic Feed Additives on Cellular Oxidative Stress and Inflammatory Reactions in Intestinal Porcine Epithelial Cells1. J. Anim. Sci. 2018, 96, 3657–3669. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zumbaugh, C.A.; Murugesan, G.R.; Wong, E.A.; Syed, B.; Persia, M.E. Evaluation of a Phytogenic Feed Additive on Performance, Nutrient Digestion, and Absorption in Turkey Poults. Anim. Feed Sci. Technol. 2020, 267, 114575. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gadde, U.; Kim, W.H.; Oh, S.T.; Lillehoj, H.S. Alternatives to Antibiotics for Maximizing Growth Performance and Feed Efficiency in Poultry: A Review. Anim. Health Res. Rev. 2017, 18, 26–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pei, R.; Zhou, F.; Ji, B.; Xu, J. Evaluation of Combined Antibacterial Effects of Eugenol, Cinnamaldehyde, Thymol, and Carvacrol against E. Coli with an Improved Method. J. Food Sci. 2009, 74, M379–M383. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rai, M.; Paralikar, P.; Jogee, P.; Agarkar, G.; Ingle, A.P.; Derita, M.; Zacchino, S. Synergistic Antimicrobial Potential of Essential Oils in Combination with Nanoparticles: Emerging Trends and Future Perspectives. Int. J. Pharm. 2017, 519, 67–78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bassanetti, I.; Carcelli, M.; Buschini, A.; Montalbano, S.; Leonardi, G.; Pelagatti, P.; Tosi, G.; Massi, P.; Fiorentini, L.; Rogolino, D. Investigation of Antibacterial Activity of New Classes of Essential Oils Derivatives. Food Control. 2017, 73, 606–612. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duarte, I.F.; Barros, A.; Almeida, C.; Spraul, M.; Gil, A.M. Multivariate Analysis of NMR and FTIR Data as a Potential Tool for the Quality Control of Beer. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2004, 52, 1031–1038. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Olszewska, M.A.; Gędas, A.; Simões, M. Antimicrobial Polyphenol-Rich Extracts: Applications and Limitations in the Food Industry. Food Res. Int. 2020, 134, 109214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Severino, R.; Ferrari, G.; Vu, K.D.; Donsì, F.; Salmieri, S.; Lacroix, M. Antimicrobial Effects of Modified Chitosan Based Coating Containing Nanoemulsion of Essential Oils, Modified Atmosphere Packaging and Gamma Irradiation against Escherichia coli O157:H7 and Salmonella typhimurium on Green Beans. Food Control. 2015, 50, 215–222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, C.; Chowdhury, M.A.; Huo, Y.; Gong, J. Phytogenic Compounds as Alternatives to In-Feed Antibiotics: Potentials and Challenges in Application. Pathogens 2015, 4, 137–156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Horn, S.J.; Aspmo, S.I.; Eijsink, V.G.H. Growth of Lactobacillus Plantarum in Media Containing Hydrolysates of Fish Viscera. J. Appl. Microbiol. 2005, 99, 1082–1089. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xia, E.-Q.; Deng, G.-F.; Guo, Y.-J.; Li, H.-B. Biological Activities of Polyphenols from Grapes. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2010, 11, 622–646. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aditya, S.; Ohh, S.-J.; Ahammed, M.; Lohakare, J. Supplementation of Grape Pomace (Vitis vinifera) in Broiler Diets and Its Effect on Growth Performance, Apparent Total Tract Digestibility of Nutrients, Blood Profile, and Meat Quality. Anim. Nutr. 2018, 4, 210–214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, H.; Venancio, V.P.; Fang, C.; Dupont, A.W.; Talcott, S.T.; Mertens-Talcott, S.U. Mango (Mangifera indica L.) Polyphenols Reduce IL-8, GRO, and GM-SCF Plasma Levels and Increase Lactobacillus Species in a Pilot Study in Patients with Inflammatory Bowel Disease. Nutr. Res. 2020, 75, 85–94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Axling, U.; Olsson, C.; Xu, J.; Fernandez, C.; Larsson, S.; Ström, K.; Ahrné, S.; Holm, C.; Molin, G.; Berger, K. Green Tea Powder and Lactobacillus Plantarum Affect Gut Microbiota, Lipid Metabolism and Inflammation in High-Fat Fed C57BL/6J Mice. Nutr. Metab. 2012, 9, 105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Llano, D.; Gil-Sánchez, I.; Esteban-Fernández, A.; Ramos, A.; Cueva, C.; Moreno-Arribas, M.; Bartolomé, B. Some Contributions to the Study of Oenological Lactic Acid Bacteria through Their Interaction with Polyphenols. Beverages 2016, 2, 27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Burt, S. Essential Oils: Their Antibacterial Properties and Potential Applications in Foods—A Review. Int. J. Food Microbiol. 2004, 94, 223–253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohamed, H.G.; Gaafar, A.M.; Soliman, A.S. Antimicrobial Activities of Essential Oil of Eight Plant Species from Different Families Against Some Pathogenic Microorganisms. Res. J. Microbiol. 2016, 11, 28–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moon, S.H.; Waite-Cusic, J.; Huang, E. Control of Salmonella in Chicken Meat Using a Combination of a Commercial Bacteriophage and Plant-Based Essential Oils. Food Control 2020, 110, 106984. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yap, P.S.X.; Yiap, B.C.; Ping, H.C.; Lim, S.H.E. Essential Oils, A New Horizon in Combating Bacterial Antibiotic Resistance. Open Microbiol. J. 2014, 8, 6–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Arumugam, G.; Swamy, M.; Sinniah, U. Plectranthus amboinicus (Lour.) Spreng: Botanical, Phytochemical, Pharmacological and Nutritional Significance. Molecules 2016, 21, 369. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cheng, F.; Chen, M.; Duan, Z.; Zou, Y.; He, Y.; Zeng, F.; Yuan, Y.; Fu, T.; Tu, H.; Li, R.; et al. Fabrication, Characterization, and Bioactivity of Self-Assembled Carrier-Free Colloidal Dispersions from Citrus × Limon ‘Rosso’ Essential Oil and Tea Polyphenols. Food Chem. 2024, 457, 140058. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, X.; Lan, W.; Xie, J. Natural Phenolic Compounds: Antimicrobial Properties, Antimicrobial Mechanisms, and Potential Utilization in the Preservation of Aquatic Products. Food Chem. 2024, 440, 138198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- UL Prospector, ExGrapeTM Total Product Detail. Available online: https://www.ulprospector.com/en/na/Food/Detail/5677/202864/exGrape-Total (accessed on 18 May 2025).
- Man, A.; Santacroce, L.; Iacob, R.; Mare, A.; Man, L. Antimicrobial Activity of Six Essential Oils Against a Group of Human Pathogens: A Comparative Study. Pathogens 2019, 8, 15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
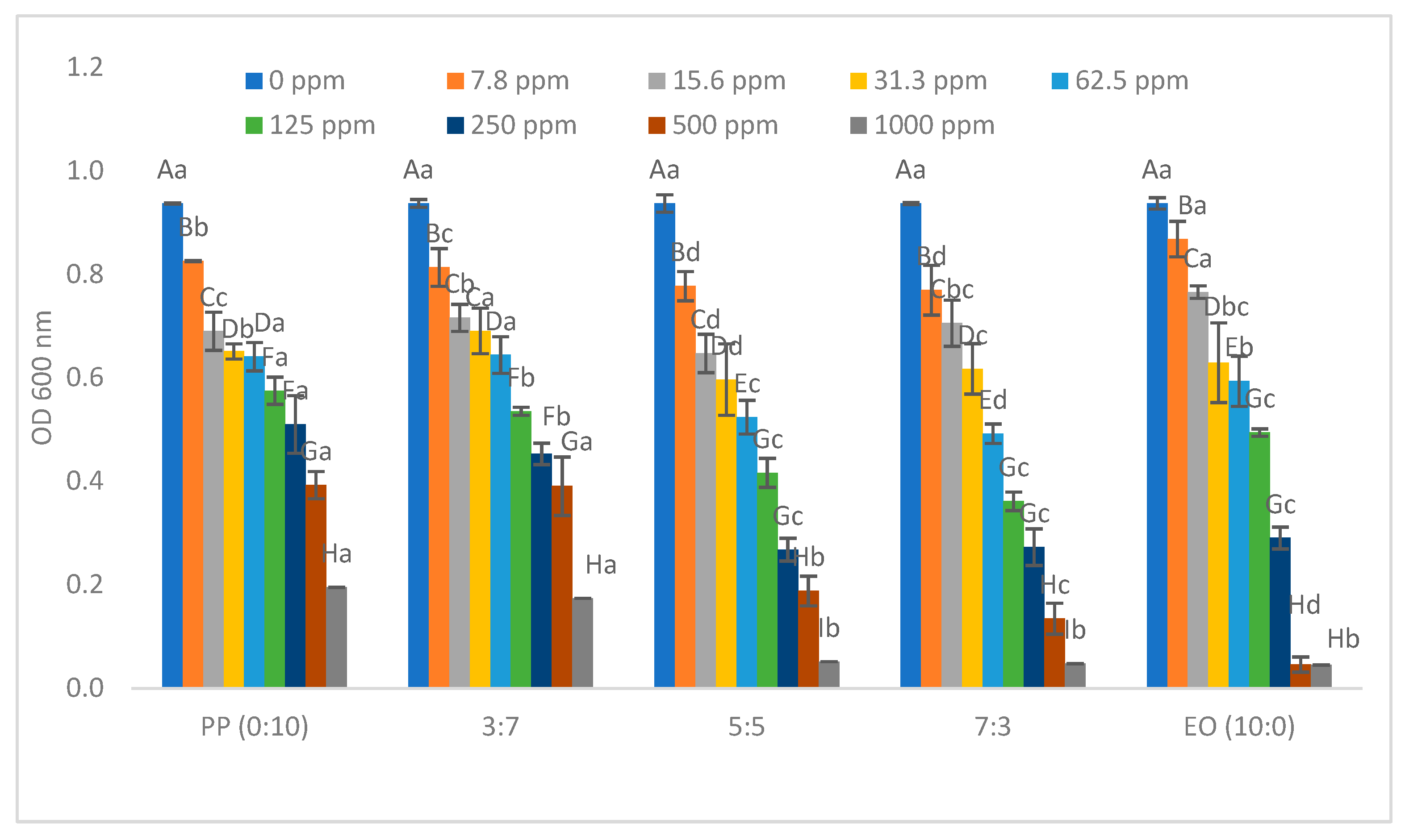
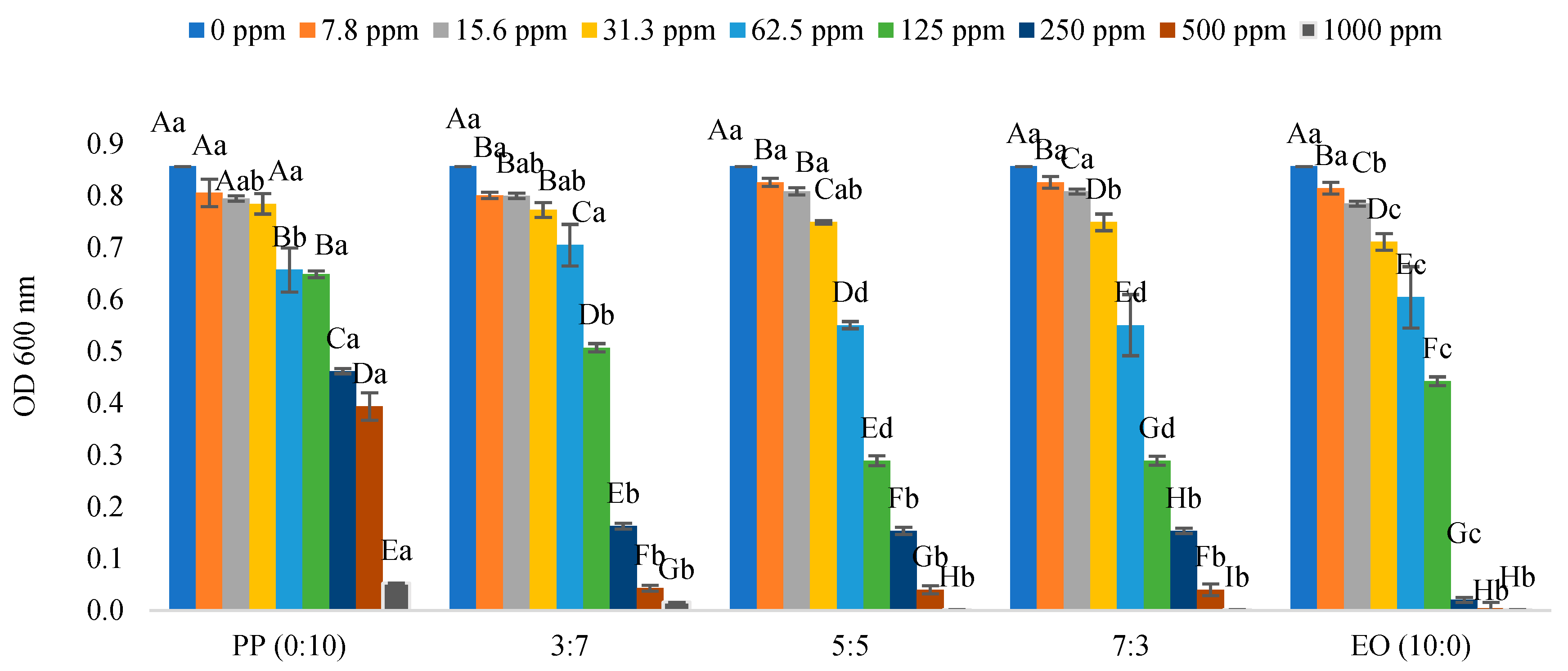
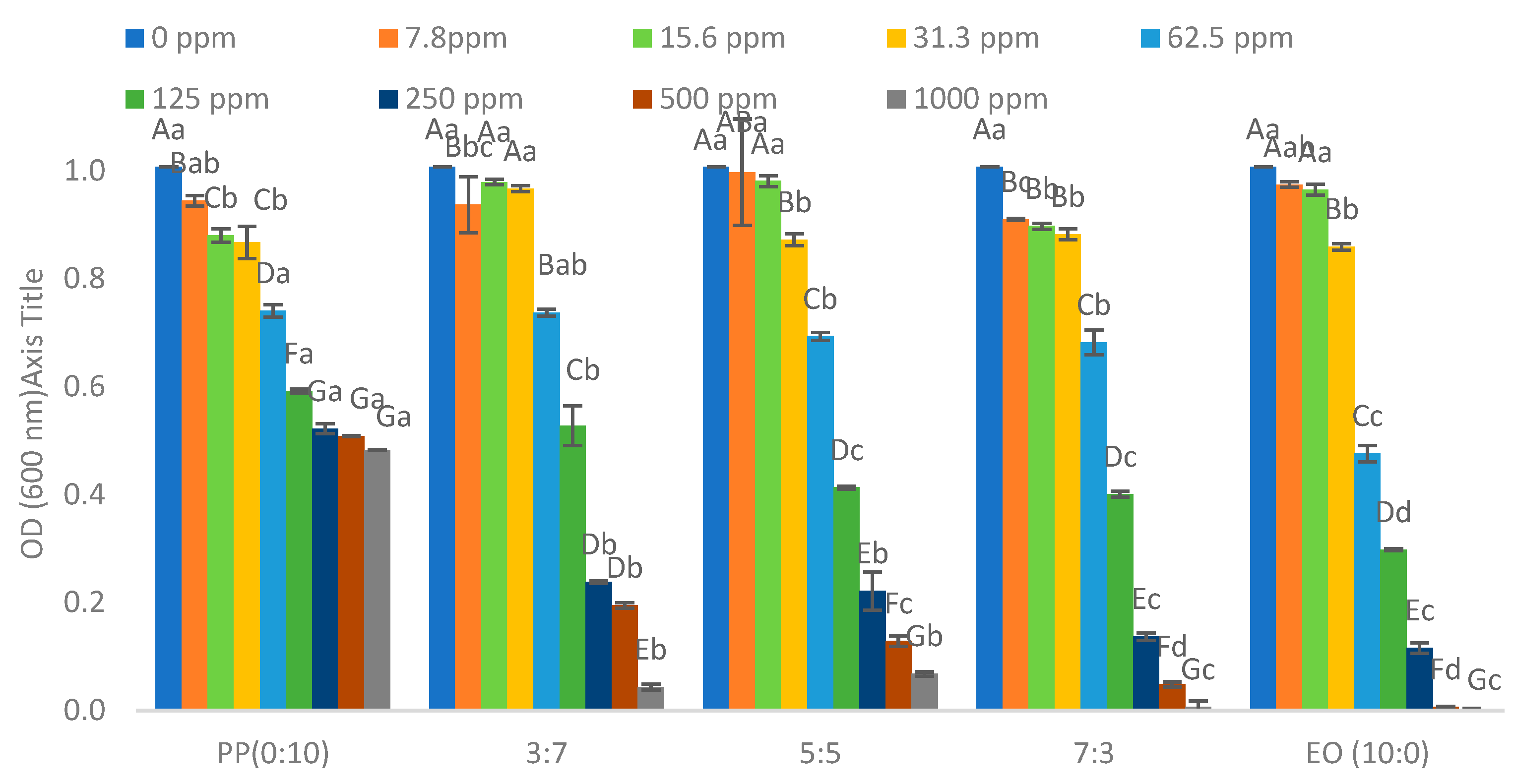
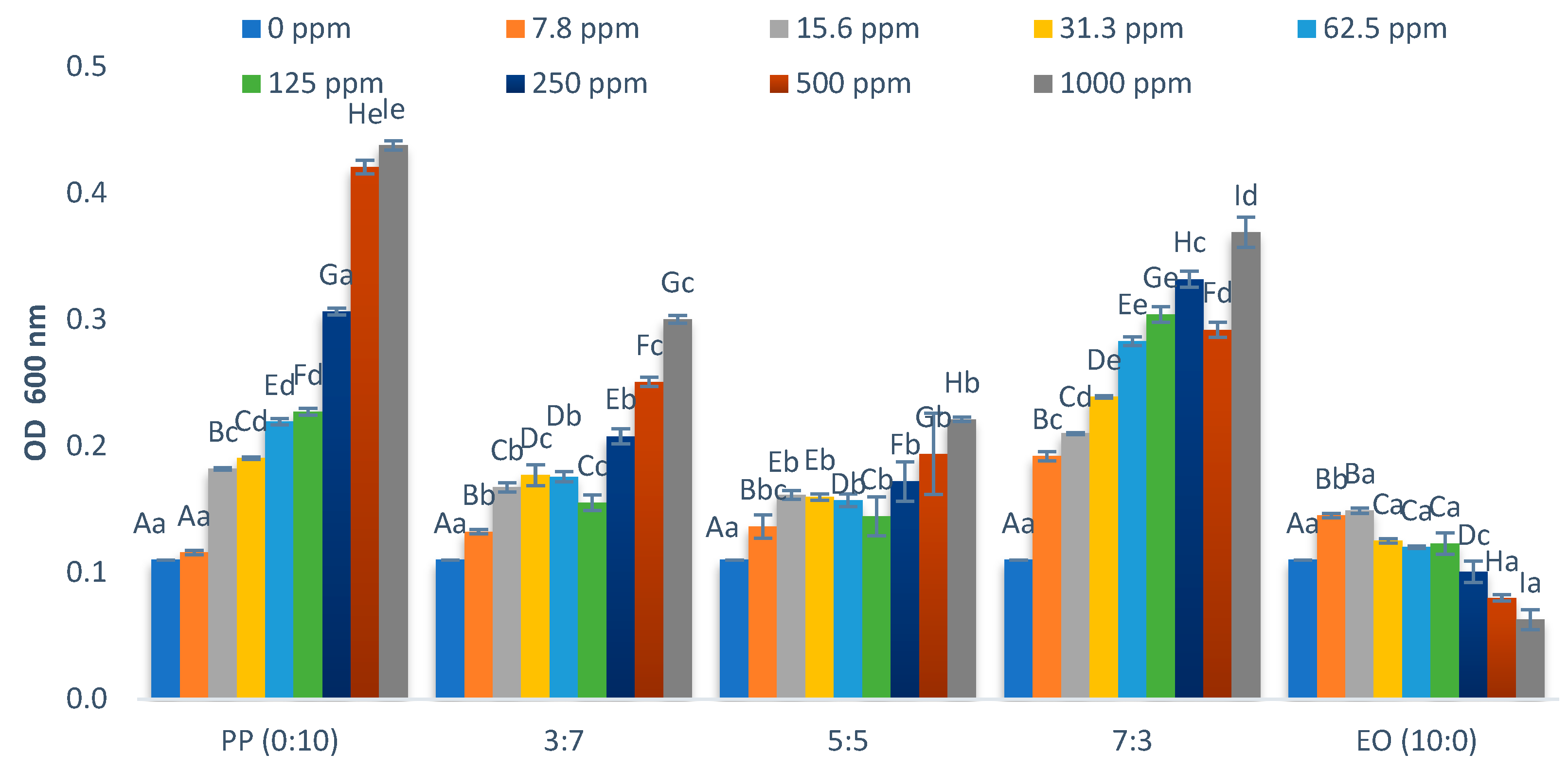
| * EO/PP Ratio | Escherichia coli O157:H7 | Salmonella typhimurium | Enterococcus cloacae | Lactiplantibacillus plantarum |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0/10 (polyphenols only) | >1000 ppm | 1000 ppm | >1000 ppm | >1000 ppm |
| 3/7 | >1000 ppm | 500 ppm | 1000 ppm | >1000 ppm |
| 5/5 | 1000 ppm | 500 ppm | 1000 ppm | >1000 ppm |
| 7/3 | 1000 ppm | 500 ppm | 500 ppm | >1000 ppm |
| 10/0 (essential oils only) | 500 ppm | 250 ppm | 500 ppm | 500 ppm |
| Family | Genus | Species | ATCC | Growth Conditions | Media 1 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Enterobacteriaceae | Salmonella | typhimurium | 23564 | Aerobic, 18–24 h, 37 °C | TSA, MHB |
| Enterobacteriaceae | Enterococcus | cloacae | 23355 | Aerobic, 18–24 h, 37 °C | TSA, MHB |
| Enterobacteriaceae | Escherichia | coli | 25922 | Aerobic, 18–24 h, 37 °C | TSA, MHB |
| Lactobacillaceae | Lactiplantibacillus | plantarum | 8014 | Anaerobic, 48–72 h, 37 °C | TSA, MHB |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Bao, H.; Muasya, C.M.; Chen, F.-C.; Kilonzo-Nthenge, A.; Wu, Y. A Study on Combined Effect of Monoterpenoid Essential Oils and Polyphenols from Grape Pomace on Selected Pathogenic and Probiotic Bacteria Strains. Processes 2025, 13, 1995. https://doi.org/10.3390/pr13071995
Bao H, Muasya CM, Chen F-C, Kilonzo-Nthenge A, Wu Y. A Study on Combined Effect of Monoterpenoid Essential Oils and Polyphenols from Grape Pomace on Selected Pathogenic and Probiotic Bacteria Strains. Processes. 2025; 13(7):1995. https://doi.org/10.3390/pr13071995
Chicago/Turabian StyleBao, Haona, Cosmas Mwendwa Muasya, Fur-Chi Chen, Agnes Kilonzo-Nthenge, and Ying Wu. 2025. "A Study on Combined Effect of Monoterpenoid Essential Oils and Polyphenols from Grape Pomace on Selected Pathogenic and Probiotic Bacteria Strains" Processes 13, no. 7: 1995. https://doi.org/10.3390/pr13071995
APA StyleBao, H., Muasya, C. M., Chen, F.-C., Kilonzo-Nthenge, A., & Wu, Y. (2025). A Study on Combined Effect of Monoterpenoid Essential Oils and Polyphenols from Grape Pomace on Selected Pathogenic and Probiotic Bacteria Strains. Processes, 13(7), 1995. https://doi.org/10.3390/pr13071995






