Abstract
The selective catalytic reduction (SCR) of NOx emissions by hydrocarbons (HCs) using a silver (Ag)-based catalyst offers significant advantages over conventional SCR systems that rely on ammonia reductants and vanadium-based catalysts. However, the conversion rate of SCR is influenced by several factors, among which catalyst poisoning is a major concern. Toxic metals such as sodium (Na), potassium (K), magnesium (Mg), and calcium (Ca) can degrade catalyst activity and lead to deactivation. Poisoned catalysts suffer from reduced conversion rates and premature deactivation before reaching their intended operational lifespan. In particular, calcium poisoning results in the formation of CaO (calcium oxide), which reacts to produce a CaWO4 compound that severely impairs SCR performance. This study investigates the role of antimony (Sb) in mitigating Ca-induced deactivation in HC-SCR of NOx. Five catalysts with varying Sb loadings were prepared and tested to evaluate Sb’s effect on NOx conversion rate at a space velocity of 30,000 h−1. The results demonstrate that Sb effectively suppresses Ca deactivation, enhancing the conversion rate across all engine test conditions. The highest NOx conversion rate (95.88%) was achieved using a catalyst with 3% Sb.
1. Introduction
Air pollution is defined as the alteration of the natural composition of atmospheric air due to the introduction of foreign substances. One of the primary contributors to this change is combustion-based energy production, particularly from fossil fuels. Among various pollution sources, internal combustion engine vehicles play a significant role, emitting high levels of harmful pollutants such as CO, HC, NOx, and particulate matter (PM) [1].
NOx emissions are especially concerning due to their severe impact on human health and the environment. Diesel engines—widely used in transportation, power generation, agriculture, and industry—are a major source of NOx emissions. These emissions contribute to greenhouse gas effects, acid rain, respiratory diseases, tropospheric ozone formation, and reduced visibility [2].
NOx emissions primarily form under high-temperature combustion conditions (>1600 °C), where atmospheric nitrogen (N2) and oxygen (O2) react. The key factors driving NOx formation are peak combustion temperature and oxygen availability. The majority of NOx consists of nitric oxide (NO) and nitrogen dioxide (NO2), produced via the Zeldovich mechanism (Equations (1)–(3)) [3].
O + N2 ↔ NO + N
N + O2 ↔ NO + O
N + OH ↔ NO + H
The hydroperoxyl radical (HO2) forms at low temperatures and promotes NO2 formation. However, at elevated temperatures, NO2 undergoes decomposition through reactions with active hydrogen (H) and oxygen (O) species (Equations (4)–(6)) [4].
NO + HO2 → NO2 + OH
NO2 + H → NO + OH
NO2 + O → NO + O2
The significant adverse effects of NOx emissions on human health and the environment necessitate stringent control and reduction of these pollutants. Various techniques—including exhaust gas recirculation (EGR), fuel injection control, lean NOx traps (LNTs), and fuel property optimization—have been implemented to mitigate NOx emissions from diesel engines. However, these methods often fail to achieve the desired NOx reduction efficiency. In contrast, SCR has emerged as a highly effective solution for NOx abatement [5].
In SCR systems, NOx in the exhaust gas is converted into nitrogen (N2) and water vapor (H2O) through catalytic reactions. These reactions occur on the catalyst surface with the aid of an injected reducing agent, typically either aqueous urea solution or hydrocarbons (HCs). Compared to urea-based systems, hydrocarbon-selective catalytic reduction (HC-SCR) demonstrates a superior NOx conversion rate at low temperatures [6]. Notably, oxygenated HCs (e.g., methanol, ethanol, and propanol) significantly enhance NOx reduction performance.
While various metal catalysts (e.g., Pd, Co, Pt, Cu, Fe) have been explored for HC-SCR, silver (Ag)-based catalysts remain the most widely used due to their effectiveness [7]. Noble metals (Pt, Pd, Rh) offer high activity but are costly and sulfur-sensitive, while metal-exchanged zeolites (Cu-ZSM-5, Fe-ZSM-5) provide good hydrothermal stability and moderate-temperature performance but can suffer from coking and hydrothermal degradation. Transition metal oxides (MnOx, CoOx) and perovskite-type catalysts (LaCoO3, LaMnO3) are cost-effective alternatives with tunable redox properties but often exhibit narrow temperature windows or require high operating temperatures. Key challenges include oxygen competition, hydrocarbon selectivity, sulfur poisoning, and water tolerance, with recent advances focusing on bimetallic systems (Ag-Co/CeO2), core-shell structures (MnOx@CeO2), and doped zeolites (Fe-Cu-ZSM-5) to enhance activity, stability, and resistance to deactivation [3].
In the HC-SCR system, the catalytic reaction mechanism proceeds through two primary steps: oxidation of nitric oxide (NO) to nitrogen dioxide (NO2) on the catalyst surface (Equation (7)), followed by reaction (Equation (8)) of the formed NO2 with hydrocarbons (HCs) to produce nitrogen (N2), carbon dioxide (CO2), and water (H2O).
NO + O2 → NO2
CxHyOz + NO2 → N2 + CO2 + H2O
The efficiency of HC-SCR systems is fundamentally dependent on several key parameters, including the catalytic material composition, reducing agent type, HC/NOx ratio, and operating temperature range [8]. A critical challenge in these systems is catalyst poisoning, which refers to the chemical deactivation of active sites through interactions with specific contaminants, distinct from physical degradation mechanisms such as thermal decomposition. Particularly detrimental are alkali and alkaline earth metals, including sodium (Na), potassium (K), magnesium (Mg), and calcium (Ca), which adsorb onto catalytic surfaces, reduce active site availability, and ultimately lead to premature deactivation and decreased NOx conversion rate [9]. Research by Chang et al. [10] demonstrated that both Na and K significantly reduce activity in CeO2-based catalysts within the 150–500 °C operating range, with potassium exhibiting more severe poisoning effects due to its stronger interaction with active sites. However, innovative approaches such as the Fe3+ and Zr4+ co-doping strategy developed by Kang et al. [11] have shown promise in mitigating these effects, maintaining NOx conversion rates up to 84% in CeTiOx catalysts by enhancing potassium resistance through structural and electronic modifications of the catalytic material.
In vanadium (V) and tungsten (W)-based catalysts, excessive calcium oxide (CaO) leads to the formation of calcium tungstate (CaWO4), which effectively deactivates the tungsten component and consequently reduces the overall acidity of the catalyst system. This chemical deactivation mechanism significantly impairs the reduction efficiency of the SCR system. Li et al. [12] systematically investigated various calcium compounds and established a poisoning severity trend: calcium carbonate (CaCO3) > calcium oxide (CaO) > calcium sulfate (CaSO4). The deactivating effects of calcium salts present in ash deposits have been particularly observed in cerium (Ce)-based catalyst systems, where the poisoning effect exhibits strong temperature dependence. Below 200 °C, calcium’s impact on NH3-SCR systems remains relatively minor; however, above this critical temperature threshold, the poisoning effect becomes markedly more severe due to the progressive inhibition of both ammonia (NH3) adsorption and subsequent activation processes [13].
Compared to the deactivating effect of potassium and magnesium, potassium has been shown to have a stronger poisoning effect. In a study on manganese-based catalysts, potassium exhibited greater poisoning than magnesium. The addition of K and Mg reduced the specific surface area and promoted TiO2 crystallization. Furthermore, the presence of K and Mg increased the reduction tendency of the catalyst and NH3 while also decreasing adsorption capacity. Notably, the poisoning effect on Mn/TiO2-Mg was weaker at 200 °C, whereas Mn/TiO2-K showed significantly stronger poisoning at the same temperature [14].
Like potassium, magnesium, and calcium, sodium is an alkali metal that exhibits a poisoning effect on catalysts. A study comparing the poisoning effects of Na+ and Ca2+ ions in a vanadium-based (V2O5/TiO2) catalyst revealed significant differences. The analysis considered not only the increase in catalyst acidity but also the decrease in reduction tendency. Due to sodium’s high reactivity with vanadium, the formation of Na-V species (measured as Na-V molarity) was significantly higher than that of Ca-V species. Consequently, the Na-V2O5/TiO2 catalyst exhibited both increased acidity and a reduced reduction tendency. In contrast, the Ca-V2O5/TiO2 catalyst demonstrated a stronger reducing tendency compared to its sodium-doped counterpart [15].
Alkali and alkaline earth metals (e.g., Na, K, Mg, Ca) are indeed components of particulate matter (PM) emitted from combustion engines. These metals originate from engine lubricants, fuel additives, and wear debris. Calcium, in particular, is prevalent in diesel exhaust due to its presence in lubricating oils (e.g., calcium sulfonates as detergents) and ash particles from biodiesel combustion. The adsorption of Ca onto catalytic surfaces reduces active site availability, thereby decreasing the NOx conversion rate.
To simulate this realistic poisoning scenario, calcium was deliberately incorporated into the Ag/TiO2 catalyst system, enabling systematic evaluation of its deactivation mechanisms. The effect of antimony (Sb) on calcium (Ca) deactivation in a HC-SCR catalyst was investigated experimentally. Antimony was selected for this study due to its unique properties as a semi-metal and the lack of prior research on its application in SCR or other emission control catalysts. To evaluate the influence of Sb on Ca-induced deactivation, Sb was incorporated into the Ca-poisoned catalyst at three different concentrations (1%, 2%, and 3%). Catalytic activity tests were then conducted to compare the performance of catalysts containing varying Sb loadings.
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Chemical Materials Used in the Production of Catalysts
The brands and specifications of the chemical materials used in catalyst production are listed in Table 1. Prior to coating the cordierite substrates with the catalyst material, the cordierite was pretreated with oxalic acid (C2H2O4). Additionally, ethanol (C2H5OH) was employed as a reducing agent in this study.

Table 1.
The chemical materials used in catalyst production.
2.2. The Production of Catalysts
Cordierite (2Al2O3 · 5SiO2 · 2MgO) was used as the substrate for catalyst production. This material features a fine pore structure (average pore diameter: ~18 µm), high thermal stability, and a low surface area (~0.5 m2/g) [16]. To enhance its surface area, the cordierite was pretreated with oxalic acid.
For the pretreatment, 750 mL of a 33% (w/w) aqueous oxalic acid solution was prepared. Each cordierite sample was immersed in the oxalic acid solution for 3 h, followed by oven drying for 3 h. The dried samples were then calcined at 550 °C to prepare them for catalyst coating.
The weight percentages of elements used in catalyst production and the corresponding production flowchart are presented in Table 2 and Figure 1, respectively. The first catalyst (AT) was prepared as a 50 g mixture containing 2 wt% silver (1 g Ag) and 98 wt% titanium dioxide (49 g TiO2). To achieve the desired silver content, 1.575 g of silver nitrate (AgNO3) was precisely weighed along with 49 g TiO2. The mixture was dissolved in 200 mL of deionized water and stirred magnetically for approximately one hour while being heated to evaporate excess water. As the water evaporated, the solution gradually transformed into a thick, viscous slurry. This slurry was then transferred to a drying oven and maintained at 130 °C for three hours to ensure complete water removal. Following drying, the solid material was scraped from the beaker, placed in a porcelain crucible, and calcined at 550 °C for three hours in a muffle furnace to convert it into a fine powder.

Table 2.
Percentage distribution by weight of elements used in catalyst production.
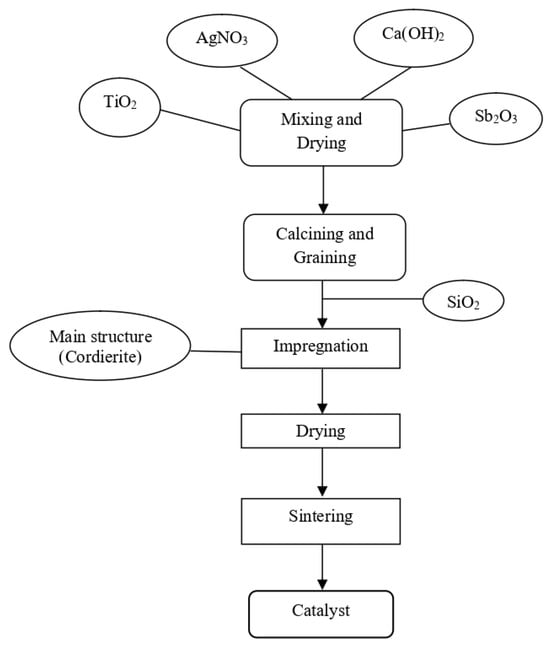
Figure 1.
Flowchart of catalyst production.
After calcination, the catalyst powder was milled and mixed with silicon oxide (1 wt% of the powder weight) to enhance its adhesion to the cordierite substrate. The mixture was combined with 400 mL of deionized water and stirred for one hour without heating. Meanwhile, the acid-pretreated cordierite substrates were weighed before being immersed in the catalyst slurry. The dip-coating process was repeated twice, with intermediate drying at 130 °C for one hour between coatings. Following the final coating, the catalyst-loaded cordierite was calcined again at 550 °C for three hours to complete the preparation of the AT catalyst.
The same methodology was employed for preparing four additional catalysts with modified compositions. The second catalyst (ACT) contained 2 wt% Ag, 1.5 wt% Ca, and 96.5 wt% TiO2, using 1.39 g calcium hydroxide (Ca(OH)2) as the calcium source. The third catalyst (ACS1T) incorporated 1 wt% antimony (0.6 g Sb2O3) in addition to the silver and calcium components. Two more antimony-containing variants were prepared: ACS2T with 2 wt% Sb (1.2 g Sb2O3) and ACS3T with 3 wt% Sb (1.8 g Sb2O3). In all cases, the same sequential process of mixing, drying, calcining, milling, and dip-coating was carefully followed to ensure consistency in catalyst preparation.
The physicochemical properties of the prepared catalysts were thoroughly characterized using advanced analytical techniques. Field emission scanning electron microscopy (FE-SEM) was performed using an FEI Quanta 650 instrument to examine surface morphology. Crystalline phases were identified by X-ray diffraction analysis (Panalytical Empyrean XRD), while specific surface areas were determined through nitrogen physisorption measurements using a Micromeritics TriStar II BET analyzer. This comprehensive characterization approach provided detailed insights into the structural and surface properties of each catalyst formulation.
2.3. Experimental Setup
The experimental setup for catalyst testing is illustrated in Figure 2. The system employed an AKSA A2CRX08 diesel engine (2-cylinder, water-cooled, 3000 rpm, 50 Hz) coupled with a 10 kW loading unit. The loading unit comprised ten resistance heaters, each rated at 1 kW, allowing precise power adjustment in 1 kW increments. Engine load was controlled by selectively activating the resistance heaters to achieve the desired power output. During testing, the engine was progressively loaded by systematically engaging the resistance units while maintaining constant monitoring of operational parameters. This configuration permitted controlled evaluation of catalyst performance across varying engine load conditions while ensuring stable operating temperatures through the integrated water-cooling system.
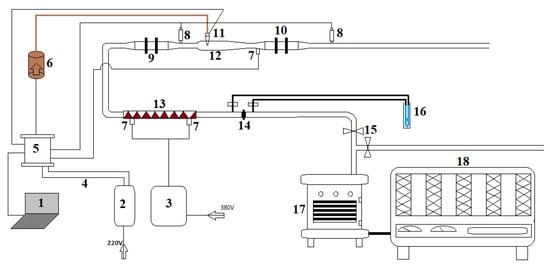
Figure 2.
Performance test system (1—Computer, 2—Electricity supply control unit, 3—Exhaust gas heater control unit, 4—12/24 V supply circuit, 5—Microprocessor, 6—Reductant pump and tank, 7—Temperature sensor (thermocouple), 8—NOxsensor, 9—Diesel oxidation catalyst (DOC), 10—SCR catalyst, 11—Reductant injector, 12—Mixing chamber, 13—Exhaust gas heater, 14—Orifice plate, 15—Valves, 16—U manometer, 17—Diesel engine, 18—Engine loading unit).
The experimental system incorporated two Continental UniNOx sensors for critical emissions monitoring—one positioned upstream of the SCR catalyst and one downstream. These sensors transmitted real-time NOx concentration data through a CANBUS Shield interface connected to an Arduino Due microcontroller, enabling continuous computer recording throughout testing. For reductant delivery, an SRD-05VDC-SL-C controlled pump maintained precise 3–3.5 bar pressure to a 6-hole injector, ensuring optimal pulverization of the reducing agent into the exhaust stream.
Temperature regulation was achieved using K-type thermocouples (−200 to 1370 °C range) monitoring an electric heater that maintained exhaust gases within the 170–270 °C test range. The exhaust flow path included control valves, an orifice plate calibrated for 30,000 h−1 space velocity, and a diesel oxidation catalyst before reaching the mixing chamber where the reductant was introduced. This configuration enhanced contact between the exhaust gases and reducing agents prior to entering the SCR catalyst.
Testing followed a standardized protocol beginning with a 15-min engine warm-up period. Measurements were then taken at 10 °C intervals across the temperature range, with each condition tested in triplicate to ensure data reliability. The system automatically calculated NOx conversion rates by comparing upstream and downstream sensor readings, generating real-time performance graphs while recording all operational parameters. Complete uncertainty analysis for all measured parameters is presented in Table 3, validating the experimental results.

Table 3.
Uncertainties of the measurements.
The catalytic performance was systematically evaluated across three distinct engine load conditions (1 kW, 3 kW, and 5 kW) for each developed catalyst. Load adjustment was precisely controlled through the engine control unit, which activated specific combinations of the 1 kW heating coils to achieve the target power output. This loading mechanism enabled accurate power regulation in 1 kW increments, ensuring consistent test conditions. During evaluation, the engine load was progressively increased by sequentially engaging additional heating coils while maintaining stable operating parameters. This approach allowed for a comprehensive assessment of catalyst conversion rate across a representative range of engine operating conditions, from light (1 kW) to moderate (5 kW) loading states.
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. The Properties of Catalysts
The FE-SEM analysis results in Figure 3 compare the surface morphology of uncoated cordierite substrates with the synthesized catalysts at various magnifications. The micrographs reveal that all samples possess a well-defined nanostructured surface with preserved porosity. The catalyst particles demonstrate homogeneous distribution across the cordierite support, though minor clustering of additives is observed on the coated surfaces. Importantly, the coating process maintains the fundamental porous architecture of the substrate, which is essential for ensuring sufficient surface area for catalytic reactions, effective gas diffusion pathways, and accessibility to active sites. The observed nanostructuring and retained porosity indicate successful uniform deposition of the catalytic materials without compromising the structural integrity of the cordierite support. These morphological characteristics suggest the prepared catalysts possess favorable physical properties for SCR applications.
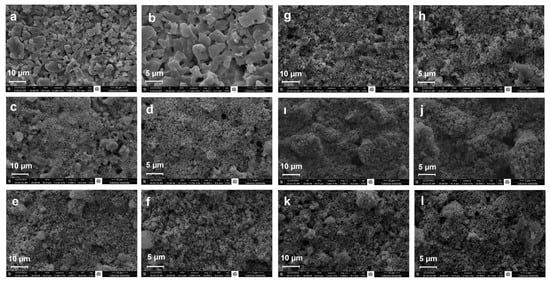
Figure 3.
FE-SEM images of catalysts (a) Cordierite (10 µm), (b) Cordierite (5 µm), (c) AT (10 µm), (d) AT (5 µm), (e) ACT (10 µm), (f) ACT (5 µm), (g) ACS1T (10 µm), (h) ACS1T (5 µm), (i) ACS2T (10 µm), (j) ACS2T (5 µm), (k) ACS3T (10 µm), (l) ACS3T (5 µm).
The BET-specific surface areas of both uncoated cordierite and the five synthesized catalysts were determined through nitrogen (N2) physisorption measurements at liquid nitrogen temperature (77 K). As shown in Table 4, the bare cordierite substrate exhibited a relatively low surface area of approximately 0.5 m2/g, which was significantly enhanced following treatment with oleic acid [16]. However, subsequent catalyst preparation steps—including additive incorporation, coating, and sintering processes—resulted in substantial surface area reduction. Notably, the Sb-modified catalysts demonstrated a pronounced decrease in BET surface area, showing more than 58% reduction compared to the acid-treated cordierite reference material. This significant reduction can be attributed to partial pore blocking and structural modifications induced by the deposition of catalytic components and thermal treatment processes.

Table 4.
BET analysis results of acidic cordierite materials and catalysts.
X-ray diffraction (XRD) analysis was performed to characterize the crystallographic properties of the catalyst materials. As a non-destructive technique, XRD provided detailed information about the atomic arrangements and phase composition of the samples. The diffraction patterns (Figure 4) revealed distinct peak profiles for each crystalline component: silver (Ag) exhibited characteristic cubic structure peaks at 2θ = 24.3°, 38.3°, 44.6°, 62.4° and 77.9°; titanium dioxide (TiO2) showed tetragonal phase reflections at 2θ = 25.2°, 36.8°, 47.9°, 54.9° and 68.5°; calcium (Ca) displayed hexagonal structure peaks at 2θ = 27.3°, 28.1°, 39.6°, 47.9° and 64.2°; while antimony (Sb) presented primarily hexagonal (with occasional cubic) phase peaks at 2θ = 17.9°, 24.2°, 28.2°, 35.1°, 58.1°, 62.1° and 68.9°. These well-defined diffraction patterns confirm the successful incorporation and crystalline nature of each component in the catalyst system, with peak positions matching expected values for their respective crystal structures. The XRD results provide fundamental structural verification that supports subsequent catalytic performance evaluations.
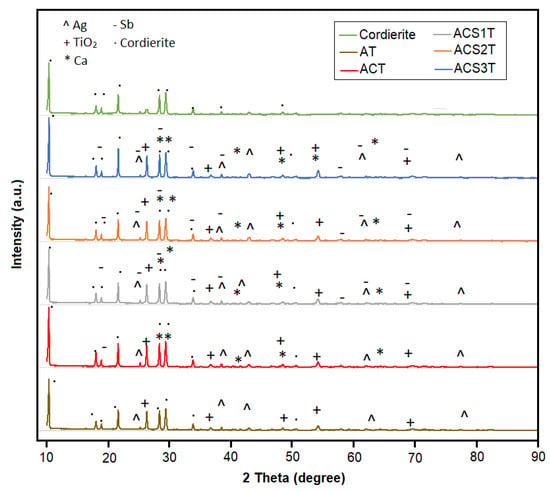
Figure 4.
XRD analysis results.
3.2. Reaction Mechanism Analysis
The mechanism of Sb Suppressing Ca Poisoning in Ag/TiO2/Cordierite Catalyst is schematically illustrated in Figure 5.
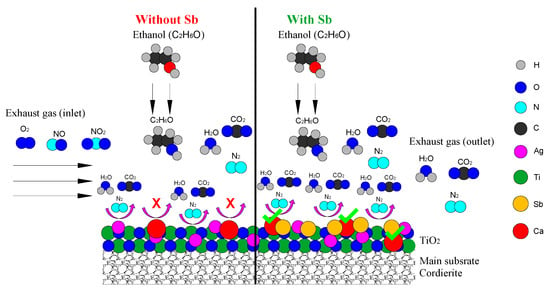
Figure 5.
Graphical representation of Sb Suppressing Ca Poisoning over Ag/TiO2/Cordierite Catalyst using ethanol as reductant.
Sb plays a crucial role in suppressing Ca poisoning in the SCR of NOx using ethanol over Ag/TiO2/cordierite catalysts by preserving active sites and maintaining key reaction pathways. The primary active sites include Ag nanoparticles (Ag0/Ag+) for NO activation, TiO2 Brønsted/Lewis acid sites for ethanol adsorption, and oxygen vacancies (OVs) for NO adsorption. Ca poisons the catalyst by blocking Ag sites, neutralizing TiO2 acid sites, and filling OVs, thereby hindering NO activation and ethanol-derived intermediate formation. Sb mitigates these effects through multiple mechanisms. First, it competitively adsorbs on TiO2, forming stable Sb-O-Ti linkages that prevent Ca from occupying critical sites, thus preserving OVs for NO activation (Equation (9)).
NO + Ovacancy → NO− (activated)
Second, Sb3+/Sb5+ redox cycling enhances electron transfer to Ag, compensating for Ca-induced electron deficiency and promoting NO oxidation to NO2, a key SCR step. Third, Sb reacts with Ca to form inert Ca-Sb-O complexes (e.g., Equation (10)), sequestering Ca away from active sites. Additionally, Sb maintains Brønsted acidity on TiO2, enabling ethanol to form reactive enolic intermediates (Equation (11)), which are crucial for NOx reduction (Equation (12)).
Ca2+ + Sb2O3 → CaSb2O4
C2H5OH → CH3CHO → CH2 = CH-O−
NO + CH2 = CH-O− → N2 + CO2 + H2O
By protecting Ag dispersion, sustaining redox activity, and preserving ethanol activation pathways, Sb effectively counteracts Ca poisoning, ensuring efficient NOx reduction over Ag/TiO2/cordierite catalysts.
3.3. Activity of Catalysts
Ethanol was used as a reducing agent and was sprayed upstream of the AT, ACT, ACS1T, ACS2T, and ACS3T catalysts. The emission test results and their effects on NOx conversion rate were analyzed based on temperature and engine load rates. Emission measurements were conducted between 170 and 270 °C, at a space velocity of 30,000 h−1, and at engine loads of 1 kW, 3 kW, and 5 kW.
Figure 6 shows the NOx conversion rates for the catalysts at 1 kW, 3 kW, and 5 kW. Analysis of the test results revealed that NOx conversion rates increased slightly with higher engine loads due to increased HC radicals. In HC-SCR, hydrocarbons reduce NO2 to form N2, CO2, and H2O. The highest conversion rates were achieved at 5 kW, with an average of 93.23%, compared to 91.92% at 1 kW. The improved catalytic activity at higher engine loads can be attributed to enriched mixture conditions, which enhance HC radical formation and modify exhaust gas composition [17,18].
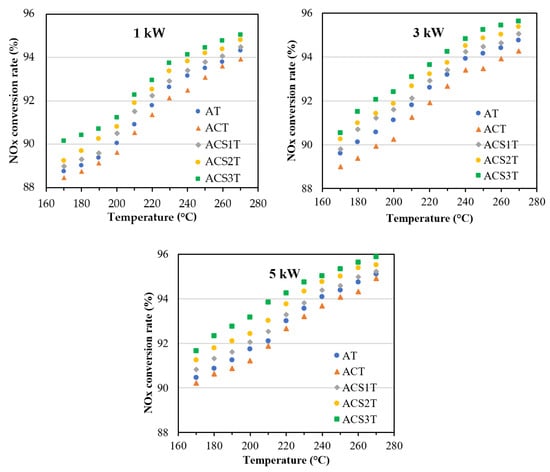
Figure 6.
NOx conversion rates for catalysts at 1 kW, 3 kW and 5 kW, respectively.
The experimental results indicate a positive correlation between temperature and NOx conversion rates—as temperature increases, so do NOx conversion rates. When analyzing the data at 1 kW, 3 kW, and 5 kW engine loads, the highest conversion rates consistently occurred at 270 °C. Temperature clearly plays a critical role in catalytic activity, with higher temperatures significantly enhancing the catalyst’s NOx conversion rate [19,20].
At 270 °C under a 5 kW load, the catalysts achieved their maximum NOx conversion rates, with AT reaching 95.47%, ACT 94.91%, ACS1T 95.1%, ACS2T 95.52%, and ACS3T demonstrating the highest conversion rate at 95.88%. In contrast, the minimum conversion rates were observed at 170 °C under a 1 kW load, where AT showed 88.74%, ACT 88.45%, ACS1T 89.24%, ACS2T 88.98%, and ACS3T performed slightly better at 90.13%. These results clearly demonstrate the significant impact of temperature and load conditions on catalytic performance, with higher temperatures consistently yielding improved NOx conversion rates across all catalyst formulations.
The incorporation of calcium (Ca) into the silver-based catalyst (ACT) induced a poisoning effect, leading to reduced NOx conversion rates across all engine loads. Specifically, Ca addition decreased average conversion rates by 0.4% at 1 kW, 0.67% at 3 kW, and 0.36% at 5 kW. In contrast, the introduction of antimony (Sb) to the ACT catalyst significantly enhanced catalytic performance. The ACS3T formulation demonstrated the greatest improvement, showing average NOx conversion rate increases of 1.68%, 1.88%, and 1.67% at 1 kW, 3 kW, and 5 kW, respectively, compared to the baseline ACT catalyst. The maximum performance enhancement (2.38%) was observed with ACS3T at 180 °C and 3 kW. Notably, Sb addition not only mitigated Ca-induced deactivation but also substantially improved overall catalytic activity.
4. Conclusions
This study demonstrates the significant potential of antimony (Sb) to mitigate calcium (Ca)-induced deactivation in silver-based HC-SCR catalysts, achieving a peak NOx conversion rate of 95.88% under optimal conditions (3% Sb, 270 °C, 5 kW). Mechanistic insights reveal that Sb preserves catalytic activity by forming stable Sb-O-Ti linkages and inert Ca-Sb-O complexes, preventing Ca from blocking active sites and maintaining redox functionality. The Sb-doped catalysts consistently outperformed their Ca-poisoned counterparts across a range of temperatures (170–270 °C) and engine loads (1–5 kW), with improvements of up to 2.38%, highlighting Sb’s robustness in real-world exhaust conditions. These findings address a critical challenge in SCR systems—catalyst deactivation—and position Sb as a scalable solution for enhancing catalyst longevity and efficiency. By elucidating Sb’s dual role as a poisoning inhibitor and performance promoter, this work advances the design of durable emission control systems, supporting stricter environmental regulations and sustainable combustion technologies. Future research should explore Sb’s long-term stability and compatibility with alternative fuels to further optimize its industrial applicability.
Author Contributions
Data curation, B.K. and H.O.; formal analysis, A.K. and H.O.; investigation, I.A.R., A.K. and B.K.; project administration, I.A.R.; supervision, A.K.; writing–original draft, I.A.R.; writing—review and edit, H.O. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research received no external funding.
Data Availability Statement
The original contributions presented in this study are included in the article. Further inquiries can be directed to the corresponding author.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Abbreviations
The following abbreviations are used in this manuscript:
| AgNO3 | Silver nitrate | NO | Nitrogen Oxide |
| Al2O3 | Aluminium Oxide | NO2 | Nitrogen Dioxide |
| BET | Brunauer-Emmett-Teller | NOx | Nitrogen Oxides |
| Ca | Calcium | PM | Particulate Matter |
| CaO | Calcium oxide | Pt | Platinum |
| CO | Carbon monoxide | Sb | Antimony |
| C2H2O4 | Oxalic acid | SCR | Selective Catalytic Reduction |
| DOC | Diesel Oxidation Catalyst | SO2 | Sulfur Dioxide |
| HC | Hydrocarbon | TiO2 | Titanium Dioxide |
| NH3 | Ammonia | V2O5 | Vanadium Pentoxide |
References
- Bej, D.; Chattaraj, N. Air pollution from vehicle-tailpipe emissions and diagnostic approaches through cyber–physical platform—A review. Microprocess. Microsyst. 2023, 98, 104805. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Islam, A.; Teo, S.H.; Ng, C.H.; Taufig-Yap, Y.H.; Choong, S.Y.T.; Awual, M.R. Progress in recent sustainable materials for greenhouse gas (NOx and SOx) emission mitigation. Prog. Mater. Sci. 2023, 132, 101033. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Resitoglu, I.A. NOx pollutants from diesel vehicles and trends in the control technologies. In Diesel and Gasoline Engines; Viskup, R., Ed.; Intechopen: London, UK, 2020; pp. 161–176. [Google Scholar]
- Gill, S.S. Controlling Diesel NOx and PM Emissions Using Fuel Components and Enhanced Aftertreatment Techniques. Ph.D. Thesis, The University of Birmingham, Birmingham, UK, 2012. [Google Scholar]
- Zhao, M.; Xue, P.; Liu, J.; Liao, J.; Guo, J. A review of removing SO2 and NOx by wet scrubbing. Sustain. Energy Technol. Assess. 2021, 47, 101451. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sawatmongkhon, B. Modelling of Catalytic Aftertreatment of NOx Emissions Using Hydrocarbon as a Reductant. Ph.D. Thesis, School of Mechanical Engineering, The University of Birmingham, Birmingham, UK, 2011. [Google Scholar]
- Elkaee, S.; Phule, A.D.; Yang, J.H. Advancements in (SCR) technologies for NOx reduction: A comprehensive review of reducing agents. Process Saf. Environ. 2024, 184, 854–880. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Piumetti, M.; Bensaid, S.; Fino, D.; Russo, N. Catalysis in Diesel Engine NOx Aftertreatment: A review. Catal. Struct. React. 2015, 1, 155–173. [Google Scholar]
- Zhao, H.; Meng, P.; Gao, S.; Wang, Y.; Sun, P.; Wu, Z. Recent advances in simultaneous removal of NOx and VOCs over bifunctional catalysts via SCR and oxidation reaction. Sci. Total Environ. 2024, 906, 167553. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chang, H.; Ma, L.; Yang, S.; Li, J.; Chen, L.; Wang, W.; Hao, J. Comparison of preparation methods for ceria catalyst and the effect of surface and bulk sulfates on its activity toward NH3-SCR. J. Hazard. Mater. 2013, 262, 782–788. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kang, K.; Yao, X.; Huang, Y.; Cao, J.; Rong, J.; Zhao, W.; Luo, W.; Chen, Y. Insights into the co-doping effect of Fe3+ and Zr4+ on the anti-K performance of CeTiOx catalyst for NH3-SCR reaction. J. Hazard. Mater. 2021, 416, 125821. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, X.; Li, X.; Yang, R.T.; Mo, J.; Li, J.; Hao, J. The poisoning effects of calcium on V2O5-WO3/TiO2 catalyst for the SCR reaction: Comparison of different forms of calcium. Mol. Catal. 2017, 434, 16–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, S.M.; Guo, R.T.; Wang, S.X.; Pan, W.G.; Sun, P.; Li, M.Y.; Liu, S. Deactivation mechanism of Ca on Ce/TiO2 catalyst for selective catalytic reduction of NOx with NH3. J. Taiwan. Ins. Chem. Eng. 2017, 78, 290–298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, R.T.; Wang, S.X.; Pan, W.G.; Li, M.Y.; Sun, P.; Liu, S.M.; Sun, X.; Liu, S.; Liu, J. Different poisoning effect of K and Mg on the Mn/TiO2 catalyst for selective catalytic reduction of NOx with NH3: A mechanistic Study. J. Phys. Chem. C 2017, 121, 7881–7891. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, F.; Xu, B.; Shi, H.; Qiu, J.; Fan, Y. The poisoning effect of Na+ and Ca+ ions doped on the V2O5/TiO2 catalysts for selective catalytic reduction of NO by NH3. Appl. Catal. B-Environ. 2010, 94, 71–76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Berdys, M.; Koreniuk, A.; Maresz, K.; Pudlo, W.; Jarzebski, A.B.; Mrowiec-Bialon, J. Fabrication and performance of monolithic continuous-flow silica microreactors. Chem. Eng. J. 2015, 282, 137–141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bai, S.; Han, J.; Liu, M.; Qin, S.; Wang, G.; Li, G. Experimental investigation of exhaust thermal management on NOx emissions of heavy-duty diesel engine under the world Harmonized transient cycle (WHTC). Appl. Therm. Eng. 2018, 142, 421–432. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boriboonsomsin, K.; Durbin, T.; Scora, G.; Johnson, K.; Sandez, D.; Vu, A.; Jiang, Y.; Burnette, A.; Yoon, S.; Collins, J.; et al. Real-world exhaust temperature profiles of on-road heavy-duty diesel vehicles equipped with selective catalytic reduction. Sci. Total Environ. 2018, 634, 909–921. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, K.; Choi, B.; Kim, C.; Lee, C.; Oh, K. De-NOx characteristics of HC-SCR system employing combined Ag/Al2O3 and CuSn/ZSM-5 catalyst. J. Ind. Eng. Chem. 2021, 93, 461–475. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khatri, P.; Bhatia, D. Influence of catalyst composition on NOx storage and reduction characteristics of Ag catalyst supported on MgO-doped alumina. Chem. Eng. Res. Des. 2023, 197, 476–495. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).