Abstract
Although oily sludge is an industrial waste and difficult to separate, its calorific value can still reach 6000 cal/g, thus possessing significant recycling value. This study compares various types of non-thermal plasma for refining oily sludge. The pre-treatment technology utilized filtration combined with solvent extraction to extract the oil portion from the oily sludge. Subsequently, two types of non-thermal plasma, DC streamer discharge and dielectric plasma discharge, were used to crack and activate the oily sludge under different operating conditions. The fuel compositions and properties of the refined fuel treated by two types of non-thermal plasma were compared. The elemental carbon and oxygen of the oily sludge after treatment in a direct DBD plasma reactor for 8 min were 1.96 wt.% less and 1.38 wt.% higher than those of commercial diesel. The research results indicate that the pre-treatment process can effectively improve the refined fuel properties. After pre-treatment, the calorific value of the primary product from the oily sludge can reach 10,598 cal/g. However, the carbon residue of the oily sludge after pre-treatment remained as high as 5.58 wt.%, which implied that further refining processes are required. The streamer discharge plasma reactor used a tungsten needle tip as a high-voltage electrode, leading to a rather small treated range. Corona discharge and arc formation are prone to being produced during the plasma action. Moreover, the addition of quartz glass beads can form a protruding area on the surface of the oily sludge, generating an increase in the reacting surface of the oily sludge, and hence an enhancement of treatment efficiency, in turn. The direct treatment of DBD plasma can thus have a wider and more uniform operating range of plasma generation and a superior efficiency of plasma reaction. Therefore, a direct DBD type of non-thermal equilibrium plasma reactor is preferable to treat oily sludge among those three types of plasma reactor designs. Additionally, when the plasma voltage is increased, it effectively enhances fuel properties.
1. Introduction
A large amount of oily sludge is generated during the refining, extraction, production, storage, and use of petroleum products, including the lubricating oil for transportation and industrial use. The global production of oily sludge is about 2.23 × 107 tons [1]. The petrochemical industry produces approximately 3 × 106 tons of oily sludge in China every year [2]. Oily sludge often accumulates at the bottom of storage tanks, typically in a solid or semi-solid form, and its composition includes petroleum hydrocarbons (PHCs) and other difficult-to-treat components, such as mud, sand, water, metal debris, inorganic compounds, rust, and ash. The sources of oily sludge include lubricating greases from various types of internal and external combustion engines used in transportation, waste lubricating oil replaced from vehicles, waste engine oil, and oily sludge generated from the greases used in steel mills or oil refineries [3,4]. Preliminary analysis indicates that the oily sludge produced at the end of the waste lubricating oil treatment process contains approximately 60 wt.% petroleum liquid, 25 wt.% water, and 15 wt.% sediments, with a calorific value of about 6000 cal/g [5]. Therefore, through appropriate treatment methods and refining technologies, this waste product from the industrial processes can be transformed via pyrolysis, microwave irradiation, plasma reaction, catalytic cracking, etc., into a valuable energy resource by producing fuel oil for boilers or diesel for vehicles. Conversely, oily sludge is regarded as industrial waste, and if not properly treated, its indiscriminate dumping into rivers or soil will cause irreversible environmental damage and harm to human or biological health [6,7,8].
If oily sludge enters the soil, it will disrupt the physical and chemical properties of the soil, leading to changes in its morphology [9]. Soil contaminated with oily sludge will result in a deficiency of nutrients, inhibiting seed germination and plant growth [10]. Due to the high viscosity of oily sludge, it easily forms a continuous cover layer on the surface of the soil, solidifies in the pores of the soil, or absorbs the mineral components into the soil. This reduces the soil’s ability to absorb and retain moisture, as well as its hygroscopic function, while also decreasing the exchange of moisture and outside air. The global pollution and hazards of oily sludge to agricultural land have been a long-term concern. Additionally, the petroleum hydrocarbons (PHCs) and heavy metal components in oily sludge can also cause toxic effects on the environment. Most heavy metals accumulate in the human body or in living organisms, making them particularly dangerous. Polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons (PAHs) in petroleum hydrocarbons (PHCs) are toxic to the genomes of humans and other biological organisms. The PHCs in oily sludge can enter the soil and subsequently contaminate groundwater [8].
Plasma is the fourth state of matter, which can be regarded as an ionized gas where positive and negative ions and electrons can move freely, exhibiting conductivity, unlike neutral gases, which do not conduct electricity. Plasma generation can occur by applying an external electric field; when the electric field strength is sufficiently high to cause an electron avalanche, plasma can be produced [11]. The process of dielectric plasma discharge is illustrated in Figure 1. The plasma contains positive and negative ions, electrons, and neutral gas molecules, and it also possesses various free radicals or excited particles [12]. The presence of these diverse and multi-characteristic particles is precisely why plasma can be widely applied in different fields. For example, high-energy electrons in plasma can excite numerous chemical reactions through collisions with other particles; ion bombardment is applied in semiconductor processes, free radicals can be used for material surface treatment, and excited molecules are utilized for illumination applications. If classified by temperature, plasma can be divided into low-temperature plasma (LTP) and high-temperature plasma (HTP) [13]. Among them, according to the energy balance state between particles, low-temperature plasma is further divided into thermal equilibrium plasma and non-thermal equilibrium plasma [14], with ion temperatures less than 2.0 × 104 K and greater than 1.0 × 107 K, respectively [15].
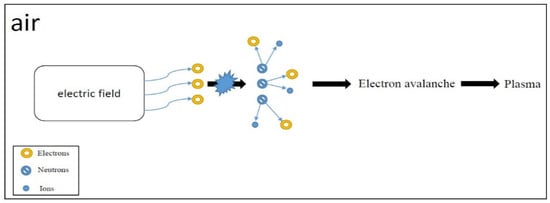
Figure 1.
Dielectric plasma discharge processes.
Traditionally, there are many methods for treating oily sludge, which can be broadly categorized into thermal treatment (such as direct incineration), physical treatment (such as filtration and separation), chemical treatment (such as extraction and solidification using chemical additives), or containment methods (such as landfill). Although these methods have industrial applications and can effectively treat oily sludge, each method has its drawbacks. For example, while direct incineration can significantly reduce the volume of oily sludge waste, the ash and exhaust gases produced may still contain dioxin components, necessitating additional exhaust treatment processes to mitigate environmental impacts. For example, treating oily sludge through landfill may allow certain components to decompose via biochemical reactions.
Therefore, before conducting further plasma treatment experiments, pre-treatment steps such as natural gravity sedimentation, centrifugal treatment, screening filtration, solvent extraction, vacuum filtration, and moisture removal must be performed to ensure that the samples do not contain moisture or other impurities, which might lead to errors in the experimental results.
A pre-treatment process which can be divided into physical methods and chemical methods was applied in this study. By utilizing physical methods such as filtration, centrifugation, and solvent extraction in conjunction with chemical methods like catalytic cracking, impurities in the oily sludge can be filtered out, moisture and metal debris can be removed, and the longer carbon chains in the pre-treated oily sludge can be broken down using cracking catalysts. The properties of the oil products can thus be enhanced.
Catalytic cracking requires alkaline or acidic catalysts; the latter can utilize solid zeolites or silica-alumina to break bonds and generate highly unstable hydride ions and carbon cations. During cracking, B-site chain breaks occur at C-C bonds [16] along with hydrogen atom transfers between molecules. The free radicals and ionic mediators in this process can regenerate, leading to serial chain reactions.
A few technologies have been developed successfully to treat oily sludge. Appleton et al. [17] applied microwave energy with a microwave frequency in the range between 900 and 2450 MHz to process oily sludge by use of its molecular interaction with the electromagnetic field. Ultrasonic vibration was used to treat petroleum hydrocarbons [18]. Emulsion instability of the water–oil emulsion and oil separation was caused by the cavitation phenomenon, leading to the separation of oil. High-speed rotating equipment with strong centrifugal force was used to centrifuge oily sludge via the direct centrifugation method. The separation of oily sludge might reach 92% [19]. Fenton oxidation has also been applied to treat oily sludge. During this oxidation process, multivalent metals play the role of a catalyst to activate H2O2 to generate reactive oxygen species (ROS). After 12 h of Fenton oxidation reaction, the oil removal rate can reach 90% [20].
In recent years, the use of plasma technology to treat oily sludge has gradually gained attention, with a few research teams actively developing plasma treatment techniques for oily sludge. However, research in this area is still quite limited, and the published literature is relatively scarce. Compared to the aforementioned traditional methods, the plasma treatment technology for oily sludge is not affected by the composition of the sludge, and it has a shorter processing time [21]. Compared to incinerating oily sludge, the gases produced from plasma treatment do not contain dioxin components, significantly reducing harmful residue substances and generating recyclable materials (such as slag) and energy. In addition, there are various types of non-thermal equilibrium plasma reactors, including streamer discharge and dielectric-barrier discharge (DBD), in direct and indirect types. Their operating effects that improve the properties of refined oily sludge have not been evaluated yet for the selection of an adequate plasma reactor.
Ali et al. [21] noted that after thermally treating oily sludge with plasma, if the flue gas contains methane, ethane, and acetylene, it has a higher calorific value. However, if the plasma power is too high, some of the oily sludge will convert into carbon monoxide and hydrogen [22], resulting in a decrease in the calorific value of the flue gas, accompanied by a significant increase in nitrogen oxides (NOx). Various modes of direct current discharges in argon at atmospheric pressure were investigated by Saifutdinov [23]. He found that two forms of arc discharge were obtained, with a contracted or diffuse current spot. In addition, during the transition from the Townsend to the normal glow discharge, voltage and current oscillations appeared. Timerkaev et al. [24] presented the results of plasma-chemical synthesis of nanodiamonds from carbon nanostructures in a microarc discharge on the surface of the copper electrode. They found that carbon nanotubes, graphene, and nanodiamonds were synthesized on the cathode surface, which were significantly influenced by the surrounding gaseous medium and the electrophysical parameters of the arc discharge (such as current and electric field intensity). NaKano and Nishida [25] investigated the effects of the voltage waveform on the performance of the DBD plasma actuator. They found that a waveform with a 70% negative-going voltage period achieved stronger thrust and a higher efficiency than those of the sinusoidal waveform.
Through a comprehensive review and analysis of the important relevant literature mentioned above, it was found that the oily sludge generated from oil refineries, steel mills, lubricating oils for vehicles, and industrial lubricating greases has a high calorific value and viscosity and contains various impurities, as well as components such as asphaltenes, moisture, and metal compounds, in addition to the petroleum hydrocarbons (PHCs). This sludge is a valuable resource that can be refined into boiler fuel oil or diesel for transportation. Extracting and recycling oily sludge is one of the effective ways to practice a circular economy [26]. Non-thermal equilibrium plasma has not been applied to refine oily sludge to produce fuel oil. Moreover, the fuel characteristics of the refined oily sludge after being treated by various types of non-thermal equilibrium plasma have not been comprehensively evaluated as a basis for selecting an adequate plasma design for refining oily sludge to produce a useful energy source [27]. Hence, the fuel properties of refined oily sludge after the plasma treatment processes and operating characteristics of the plasma reactors will be analyzed for a systematic evaluation of various types of non-thermal equilibrium plasma reactors, including streamer charge and DBD of the direct and indirect types, in this study.
2. Experimental Details
This study explored the effective treatment technologies and non-thermal plasma reactors, including streamer discharge and dielectric-barrier discharge (DBD) of the direct and indirect types, used to convert oily sludge into diesel or fuel oil, and conducted tests on various fuel characteristics, including the calorific value and carbon residue content, as well as elemental compositions.
The experimental equipment, analyzing instruments, research methods, experimental configuration, process design, and testing procedures of related fuel properties are described below.
2.1. Pre-Treatment Process Design for Oily Sludge
In addition to fats, oily sludge contains moisture, metal debris, sand, and other solid materials. The pre-treatment process includes the following steps: (1) Natural gravity sedimentation: Place the oily sludge in a container and leave it stationary for several hours. The impurities with higher density in the oily sludge will settle at the bottom of the container due to natural gravity, and the lighter oily sludge will float on the upper layer of the container. (2) Centrifugal treatment: A pipette was used to extract the lighter oily sludge floating on the upper layer of the container and place it in a centrifuge tube. A centrifuge was run at a speed of 3000 rpm for at least 3 min to separate the components of the oily sludge with different specific gravities. The impurities with a higher density settled at the bottom of the tube, the heavier oil products were in the middle layer, and the lighter oil products floated on the upper layer of the tube. (3) Screen filtration: Screens of different mesh sizes ranging from 100 to 500 mesh were used to sequentially pass the oily sludge through them, to filter out impurities of various particle sizes in the oil.
2.2. Construction of Non-Thermal Plasma Treatments Refining Oily Sludge into Fuel Oil
This study aimed to design various types of non-thermal plasma treatments for cracking and refining reactions of the oil composition of oily sludge after the aforementioned pre-treatment process, producing fuel oil for diesel engines. The non-thermal plasma treatments designed in this study included two forms: DC streamer discharge and dielectric barrier discharge (DBD), as shown in Figure 2 and Figure 3. The latter uses an alternating-current power supply to generate silk-like discharge, and the former uses a direct current to produce a plasma arc or streamer discharge acting on the oily sludge. This study therefore used one high-voltage direct-current power supply and one high-voltage alternating-current power supply.
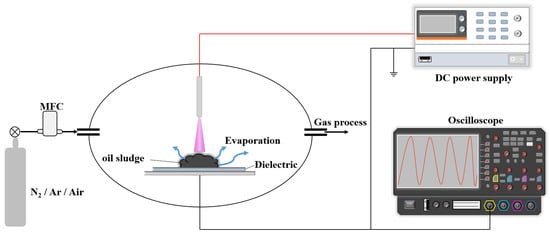
Figure 2.
Schematic diagram of the experimental setup for streamer discharge plasma treatment of oily sludge.
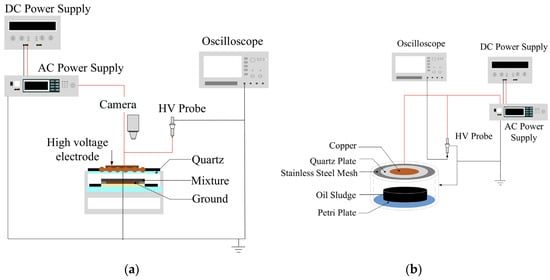
Figure 3.
Experimental setup of DBD plasma reactor for treating oily sludge: (a) indirect treatment, and (b) direct treatment.
The non-thermal plasma reactor was designed to operate in an atmospheric environment to treat oily sludge. It also controlled the electric field voltage and operating frequency, to test and compare the fuel characteristics of solid residues, liquid, or gaseous products obtained from refining oily sludge under different operating conditions, including various types of non-thermal plasma. The experiments were carried out under voltages ranging from 0 kV to 20 kV, frequencies from 15 kHz to 25 kHz, and operating times from 0.5 min to 8 min during the experiment.
2.3. Utilizing Non-Thermal Equilibrium Plasma to Refine Oily Sludge into Fuel Oil
This study designed two types of non-thermal plasma, including DC streamer discharge and dielectric barrier discharge (i.e., DBD); the former generates streamer discharge or a plasma arc based on the voltage level, while the latter produces silk-like discharge. The liquid oil is primarily composed of hydrocarbons generated from the non-thermal plasma treatment produced in both liquid and gaseous states through plasma pyrolysis. The gaseous components were condensed and collected into liquid products using a vacuum rotary concentrator (model R-2000V1-B1/B2, Panchum Scientific Corp., New Taipei City, Taiwan). The collected gases were cooled and condensed in a glass bowl circulated with iced water at 0 °C to cool the collected gases. The collected gases were condensed to become liquid fuel. The fuel composition and the fuel properties of the condensed liquid fuel were then analyzed.
The high-voltage AC power supply, the programmable DC power supply, and the oscilloscope were first turned on, and the wires and alligator clips were connected between the devices to ensure that all equipment operated normally. An appropriate amount of the prepared sample was taken and evenly spread over the active area of the DBD plasma reactor, ensuring that the sample did not touch the upper glass or overflow the plasma active area. Next, the current output switch was turned on, we slowly increased the current to 80 mA, and we observed whether the plasma generation area covered most of the active area. The blue–purple light area indicates the plasma action range. Then, according to the experimental design, the plasma action time was changed from 0.5 min to 8 min based on a series of pre-experiments to select the optimum experimental conditions. After the plasma action was completed, the sample was removed and placed in a centrifuge tube.
2.4. Fuel Analysis of the Fuel Oil Refined by a Non-Thermal Equilibrium Plasma Reactor
This study used two types of non-thermal plasma: DC streamer discharge and dielectric barrier discharge (referred to as DBD). The former generates streamer discharge or a plasma arc based on the voltage level, while the latter produces silk-like discharge. Plasma will be generated in the gap between the quartz plate and the surface of the oily sludge to treat the sludge. The appearance changes before and after treatment were recorded using a camera. The methods for analyzing the compositions and properties of the fuel oil are described as follows: An elemental analyzer (CHN-OS Rapid Element Analyzer, Heraeus Ltd., Hanau, Germany) was used to analyze the elemental C/H/O/N contents of the refined fuel oil produced from the oily sludge through the plasma action. The weight ratio of the carbon particle left after the burning process to the original weight of the fuel oil in a crucible was calculated and recorded as the carbon residue of the fuel. The heating value of the refined fuel oil was measured by an automatic insulated oxygen-bomb calorimeter (model 1261, Parr Instrument Corp., Moline, IL, USA) according to the temperature rise of tank water after the fuel was burned in the calorimeter and released heat to the tank water. A higher heating value associated with a lower carbon residue is preferrable as it indicates a superior fuel combustion efficiency and a higher amount of heat release [28].
2.5. Limitations of This Study and Opportunities for Future Study
This experiment was carried out in the laboratory. The experimental equipment used for this study was limited to the lab’s scale. The results may be extended to the industrial scale for a further and more detailed inspection. The sources and compositions of the collected oily sludge samples may vary from case to case. Hence, the results presented in this study may not be applied to other fuel samples. In addition, the treating capability of this study is limited to the lab’s quantity and equipment, particularly the plasma reactor.
For future studies, the experimental scale could be enlarged to the industrial scale, and more representative oily sludge could be collected in more comprehensive tests to obtain more referenceable results. We also encourage tests of various gases surrounding the plasma reactors and which might affect the test results, for example, inert gases like CO2, argon, and N2. Engine tests using a dynamometer are helpful to verify the applicability of the fuel oil refined via the plasma reactor as an engine fuel. We suggest comparing the engine performance and emission characteristics with super-low-sulfur diesel.
3. Results and Discussion
The mean values were obtained by repeating each experiment at least three times. The uncertainties of the heating value and carbon residue were ±1.52 and ±2.03, respectively.
3.1. Pre-Treatment Process of Oily Sludge and Properties of Oil Products After Pre-Treatment
The oily sludge was sequentially poured into filters with various mesh sizes, of 10 mesh, 50 mesh, 100 mesh, and 200 mesh, to initially filter out larger solid impurities, as shown in Figure 4a. Figure 4b shows the impurities remaining on the filter mesh after filtration, clearly indicating that the particle sizes of the impurities were large and could not be reused, necessitating further treatment. A centrifuge was used to separate oil products by gravity difference, with impurities settling at the bottom, heavy oil in the middle, and light oil at the top.
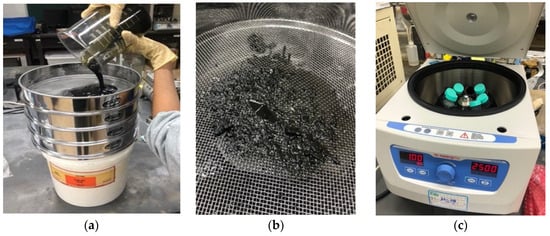
Figure 4.
(a) Oily sludge filtered through a series of filter meshes; (b) impurities remaining on the filter mesh after filtration; (c) centrifugal treatment using a centrifuge.
Next, the solvent extraction method was used, where the purer oil products were mixed with a solution of n-hexane and isopropanol in a 2/1 ratio. This type of solution is easily miscible with oil products, has a lower boiling point, and can be used for solvent extraction. The mixed solution was poured into an ultrasonic vibrator for uniform mixing, then taken out and placed in a beaker. An electromagnetic heating stirrer was used to stir at a speed of 50 rpm, starting from 50 °C in a fume hood, increasing the temperature by 10 °C each time, and maintaining the temperature for 10 min until reaching 150 °C, to facilitate the removal of solvents and moisture contained in the oil products. Hence, the oily content in the oily sludge after removing the solvent and water was extracted by the solvent. Finally, a catalytic cracking method was used, where 1 g of zeolite and SiO2 catalyst was added to 10 g of extracted oil products, with those placed in a high-temperature furnace to calcine at 560 °C for 4 h, to carry out the catalytic reaction to produce short-carbon-chain molecules of high calorific value. Wang et al. [29] prepared a heterogeneous catalyst supported by zeolite and SiO2 to catalyze syngas. They found that the catalyst presented a high olefin conversion rate (>90%) and selectivity (>40%) to C6+ aldehydes. It is inferred that the zeolite and SiO2 catalyst might improve the conversion efficiency of oily sludge to fuel oil, as shown in this study.
The primary oily sludge product treated using the aforementioned pre-treatment process was tested for its calorific value and carbon residue content. The test results are revealed in Table 1. The goal of this study was to refine waste oily sludge into ultra-low-sulfur diesel for road diesel vehicles, with a sulfur content of less than 10 ppm. Table 1 shows that the calorific value of the treated primary oily sludge product ranged from 10,433.6 cal/g to 10,598.0 cal/g, while the carbon residue content ranged from 1.49 wt.% to 5.58 wt.%. That indicates that the calorific value of this primary product is approaching the standard for ultra-low-sulfur diesel (ULSD); however, the carbon residue content is significantly higher. Further improvements in subsequent processing are needed to reduce the carbon residue content, or adjustments to the operating conditions of the plasma process should be made to enhance the combustion efficiency of the oily sludge product and decrease the generation of carbon residue [30].

Table 1.
Heating value and carbon residue content of oil products after pre-treatment.
3.2. Comparison Among Different Types of Plasma Reactors for Treating Oily Sludge
In the experiment, when treating oily sludge using the streamer discharge plasma reactor, the working voltage and frequency of the plasma were fixed at 10.006 kV and 20 kHz, respectively. The mass of the oily sludge before treatment was 2 g, and the mass reduction of the oily sludge was recorded every 10 min of treatment. When analyzing the appearance of the treated samples (as shown in Figure 5), it can be observed that the areas treated by the plasma are more viscous than other areas of the oily sludge, which is considered to be caused by the evaporation of moisture in the treated areas. The analysis of the mass reduction of the treated samples shows that the first group only decreased by 0.035 g, while the second group also only decreased by 0.099 g. From the experimental results in Figure 5, it is found that due to the very small area of the needle tip, the range of oily sludge that can be treated after plasma generation is also very limited [31]. Moreover, because of the small area of the needle tip, it is easy to produce corona discharge and form an arc during the experimental process. When the arc is formed, its high temperature ignites the oily sludge sample, causing a large amount of oily sludge to evaporate instantly, which results in excessive weight loss of the treated oily sludge [32]. Therefore, it is not recommended to use the needle tip as a high-voltage electrode, nor to use the streamer discharge plasma reactor to treat oily sludge.

Figure 5.
(a) Reaction range of streamer discharge plasma; (b) appearance of oily sludge after treatment.
In the experiment, when treating oily sludge using an indirect DBD plasma reactor, the voltage and frequency of the plasma operation were fixed at 11.2 kV and 20 kHz, respectively. The mass of the oily sludge before treatment was 10 g, and the mass reduction of the oily sludge was recorded every 10 min of treatment. When analyzing the appearance of the treated samples, as shown in Figure 6, it can be observed that the surface of the oily sludge became uniformly viscous and produced slight bubbles. This is considered to be due to the broader and more uniform plasma generation range of the DBD compared to a needle tip, resulting in the uniform evaporation of moisture from the overall surface of the oily sludge during the plasma treatment. However, this viscous phenomenon only occurred on the surface layer of the oily sludge [33], indicating that the plasma was unable to treat the internal sludge. The analysis of the mass reduction of the treated samples showed that the first to fourth groups only reduced by 1.9 g, 1.5 g, 1.2 g, and 0.9 g, respectively. The corresponding oil recovery rates of the treated samples were 81%, 85%, 88%, and 91%. The overall mass reduction of the oily sludge was lower than that of the streamer discharge plasma reactor. It is considered that this is due to the plasma being generated only between the quartz plate and the stainless-steel mesh, which cannot make contact with the surface of the oily sludge. Therefore, the thermal energy and high-energy free radicals produced by the plasma cannot effectively treat the oily sludge, resulting in a lower mass reduction. When the electron density in the plasma is high, high-energy electrons frequently collide with neutral gas molecules, allowing energy to be transferred to the neutral gas molecules through collisions. According to the Arrhenius Law [13], the chemical reaction rate and the oxidation rate of fuel molecules are thus enhanced. Not only can plasma provide the free radicals necessary for chemical reactions but also high-energy electrons and ions can generate numerous reactive free radicals through collisions with fuel molecules and oxidizers.

Figure 6.
(a) Reaction range of the indirectly treated DBD plasma; (b) appearance of the treated oily sludge.
Compared to the streamer discharge plasma reactor, the DBD plasma reactor has a wider treatment range and generates more stable plasma without forming arc discharge. Therefore, it is recommended to adopt the design of the DBD plasma reactor, allowing the plasma to directly treat oily sludge. Under the action of non-thermal equilibrium plasma reaction, the nitrogen contained in the oily sludge resulted in the formation of N-O bonds, which were transformed into nitrogen oxides and escaped to the atmosphere. The reaction mechanism is expressed in Equations (1)–(4) [34].
where O* and N* denote an excited oxygen radical and excited nitrogen radical. The non-thermal plasma effect may also lead some of the oxygen radicals to continue to be oxidized and thereafter form ozone (O3) released into the atmosphere, or lead them continue to react with NO in Equations (2) and (3) to form nitrogen dioxide (NO2) in Equation (4).
O* + N2 → NO + N*
O* + N2 → NO + N*
N* + O2 → NO + O*
O* + NO → NO2
In the experiment, when directly treating oily sludge with the DBD plasma reactor, the working voltage and frequency of the plasma were fixed at 12.75 kV and 20 kHz, respectively, with the mass of the oily sludge before the treatment being 1 g. When analyzing the uniformity of the plasma on a sieve from overhead, it can be observed that the range of plasma generation is broader and more uniform (as shown in Figure 7). This is considered to be due to the addition of quartz glass beads, which create numerous raised areas on the surface of the oily sludge [35]. Compared to the high-voltage electrode, these raised areas are more likely to facilitate corona discharge, thus generating plasma. Furthermore, these raised areas on the surface increase the surface area of the oily sludge. The plasma treatment area was thereafter expanded, resulting in a broader and more uniform plasma generation range. The black area below is considered to be caused by the sample not being completely flattened. When analyzing the appearance of the treated samples (as shown in Figure 7), it can be observed that most of the liquid has evaporated, leaving only glass beads and residual oily sludge, where the black products are tar and other carbon-containing compounds. When analyzing the effect of the presence of glass beads on the applied voltage, it can be found that when no glass beads are added, the oily sludge primarily consists of hydrocarbons with few dielectric materials, and there are no obvious protruding areas on the surface of the oily sludge. This results in the inability to generate plasma even when the applied voltage is adjusted to 14.0 kV. However, after adding glass beads, plasma can be uniformly generated at just 12.75 kV, saving more than 2 kV in overall applied voltage. Therefore, it is concluded that the added quartz glass beads can enhance the treatment efficiency [36]. As a consequence, the fuel properties of the oily sludge treated by the DBD plasma were improved accordingly.
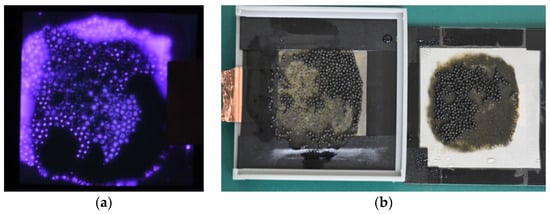
Figure 7.
Direct treatment type of DBD plasma reactor: (a) treating oily sludge (top view); (b) appearance of treated oily sludge.
3.3. Elemental Analysis
Table 2 presents the results of elemental analysis for the oil products after pre-treatment, with a dielectric particle size of 1000 μm and a weight ratio of oily sludge to oil product of 4/1, and those when subjected to plasma treatment for different durations, along with commercial diesel, resulting in eight different oil samples. Firstly, starting with the carbon content analysis, the oil products after plasma treatment exhibited nearly a 2 wt.% lower carbon content compared to commercial diesel, which is likely one of the reasons why the calorific value of oily sludge was slightly lower than that of diesel. That is not to mention the plasma-treated products; it can be observed that the increase in carbon content in the oil products after plasma treatment is not significant. The increase in elemental carbon in a fuel oil increases the heat release after its burning process and improves fuel characteristics.

Table 2.
Elemental analysis (wt.%) results.
Since oil products are composed of hydrocarbons, both hydrogen and carbon contents are major components, and the results confirm this. The analysis of sulfur content shows that commercial diesel has a lower sulfur content than the oil products after pre-treatment. However, the results indicate a trend of decreasing sulfur content in the oil products after plasma treatment [37], while the sulfur content of the oil product treated with plasma for 0.5 min increased, suggesting that sulfur components may have been introduced during the plasma treatment process. The increase in plasma operating time to 8 min caused the elemental sulfur content to decrease to 0.19 wt.%, which was the same as that of petrol-derived diesel when the elemental oxygen increased to 2.61 wt.%, which was about two times that of ultra-low-sulfur diesel. Sulfur oxide compounds were formed via the oxidation of sulfur content in the oily sludge under the high-temperature reaction of the DBD plasma reactor. The sulfur oxides were then vaporized away into the atmospheric air. Therefore, the sulfur content decreased with the elapse of plasma operating time, as shown in Table 2. In contrast, the elemental C and H compositions were lower than those of the commercial diesel by about 2 wt.%, respectively. This is primarily proposed to have occurred because the pre-treated oil product underwent settling and centrifugation, resulting in the removal of some oil product components and thus a reduction of C and H compositions. In addition to the plasma reaction method, pyrolysis is also considered a cost-effective technology to treat oily sludge. Chang et al. [38] pyrolyzed oily sludge to obtain fuel oil at a temperature of 713 K. They found that the elemental carbon, oxygen, nitrogen, and hydrogen were represented at 46.89, 0.63, 0.54, and 9.5 wt.%, respectively. The heating value of the fuel oil after the pyrolysis process was 40.6 MJ/kg, which was lower than that from the present study, or it was 44 MJ/kg when the C/H weight ratio reached 8.41, significantly higher than that of the present study, which was 6.06. This implies that the fuel oil produced in the present study has a superior burning efficiency, meaning a higher heating value is released from the combustion process.
According to the specifications of ISO 8217:2024, the kinetic viscosity, sulfur content, heating value, and density of diesel fuel are 2–4.5 mm2/s, 50 ppm, >42.7 MJ/kg, and 820–900, respectively [39,40]. The elemental contents and heating value of the fuel oil produced via plasma reaction can reach the specifications of ISO 8217:2024. However, the sulfur content of the present sample is still too high, and further treatment methods for desulfurization are required to meet the sulfur specification of the ISO 8217 standard.
4. Conclusions
The pre-treatment process can effectively improve the recovery of lubricating oil from the originally discarded oily sludge, prior to the subsequent non-thermal plasma refining process. This study was intended to develop advanced technologies for refining oily sludge into high-quality ultra-low-sulfur diesel for commercial applications.
The calorific value of the primary product from the oily sludge after pre-treatment can reach 10,598 cal/g, meeting the calorific value standard of general ultra-low-sulfur diesel; however, its carbon residue content remains relatively high at 5.58 wt.%. Further efforts using various types of non-thermal plasma were made to continue refining the oily sludge after pre-treatment.
When the streamer discharge plasma reactor was used, the needle-shaped electrode showed the capacity to easily produce corona discharge and generate arc discharge that ignites the oily sludge, so the design of the streamer discharge plasma reactor is not recommended for treating oily sludge. The plasma cannot make contact with the oily sludge, resulting in a lower mass reduction of oily sludge. The design of the direct-treatment DBD plasma reactor allows the plasma to come into contact with the oily sludge, and the benefit of adding quartz glass beads to the oily sludge is that it creates numerous protruding areas on the surface of the sludge, making it easier to form corona discharge and thus generate plasma. For this study, the design of the direct-treatment DBD plasma reactor is selected to treat oily sludge. The total applied voltage for the plasma reactor with added glass beads can be 2 kV less than that of indirect DBD plasma. The oil recovery rate can reach 91%. The increase in plasma operating time increased the elemental O composition and decreased the S composition. The S and O compositions reached 0.19 wt.% and 2.61 wt.%, respectively, after 8 min of plasma operation.
Funding
This research was funded by the National Science and Technology Council, Taiwan under the contract number NSTC 110-2221-E-019-055-MY2.
Data Availability Statement
The original contributions presented in this study are included in the article. Further inquiries can be directed to the corresponding author.
Acknowledgments
The experimental assistance from Y.H. Liao, C. Fu, and Tzu-Hsuan Hsu is appreciated.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
References
- Teng, Q.; Zhang, D.; Yang, C. A review of the application of different treatment processes for oily sludge. Evironment. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2021, 28, 121–132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xiao, N.; Zhu, L.; Wang, C.Y.; Yang, Z.Y.; Zhang, Y.N.; Qi, M.R. Experimental study and process parameters optimzation for oily sludge treatment by chemical cleaning. Chin. J. Environ. Eng. 2019, 13, 1202–1208. [Google Scholar]
- Hu, G.; Feng, H.; He, P.; Li, J.; Hewage, K.; Sadiq, R. Comparative life-cycle assessment of traditional and emerging oily sludge treatment approaches. J. Clean. Prod. 2020, 251, 119594. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.; Gong, Z.; Wang, Z.; Li, X.; Chu, Z. Application and development of pyrolysis technology in petroleum oily sludge treatment. Environ. Eng. Res. 2020, 26, 190460. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hamidi, Y.; Ataei, S.A.; Sarrafi, A. A simple, fast and low-cost method for the efficient separation of hydrocarbons from oily sludge. J. Hazard. Mater. 2021, 413, 125328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Zhang, F.; Guan, B.; Sun, J.; Liao, G. Review on oily sludge treatment technology. Energy Environ. Sci. 2020, 467, 012173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Borgheipour, H.; Moghaddas, Z.; Abbassi, M.; Abbaszadeh Tehrani, N. Application of DEA technique in SWOT analysis of oily sludge management using fuzzy data. Glob. J. Environ. Sci. Manag. 2018, 4, 183–194. [Google Scholar]
- Gao, N.; Jia, X.; Gao, G.; Ma, Z.; Quan, C.; Naqvi, S.R. Modeling and simulation of coupled pyrolysis and gasification of oily sludge in a rotary kiln. Fuel 2020, 279, 118152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jasmine, J.; Mukherji, S. Impact of bioremediation strategies on slurry phase treatment of aged oily sludge from a refinery. J. Environ. Manag. 2019, 246, 625–635. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shahzad, A.; Bano, A.; Siddiqui, S. Effect of bacterial consortium on alfalfa (Medicago sativa L.) plant nutrient uptake and antioxidant enzymes at different levels of oily sludge. Isr. J. Plant Sci. 2020, 67, 158–170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Environmental Protection Administration; Executive Yuan. Establishment of a Management Mechanism and Strategy for the Recycling and Treatment of Waste Lubricating Oil, First Progress Report; Taiwan Industrial Service Foundation: Taipei, Taiwan, 2020. [Google Scholar]
- Wu, X.F.; Qin, H.B.; Zheng, Y.X.; Zhang, Y.; Chen, W.; Zuo, J.Y.; Chen, G.J. A novel method for recovering oil from oily sludge via water-enhanced CO2 extraction. J. CO2 Util. 2019, 33, 513–520. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hippler, R.; Kersten, H.; Schmidt, M.; Schoenbach, K.H. Low Temperature Plasmas: Fundamentals, Technologies and Techniques, 2nd ed.; Wiley-VCH: Weinheim, Germany, 2008. [Google Scholar]
- Osorio-Tejada, J.; van’t Veer, K.; Long, N.V.D.; Tran, N.N.; Fulcheri, L.; Patil, B.S.; Hessel, V. Sustainability analysis of methane-to-hydrogen-to-ammonia conversion by integration of high-temperature plasma and non-thermal plasma processes. Energy Convers. Manag. 2022, 269, 116095. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cocean, A.; Cocean, G.; Postolachi, C.; Garofalide, S.; Pricop, D.A.; Munteanu, B.S.; Gurlui, S. High Energy Pulsed Laser Beam to Produce a Thin Layer of Crystalline Silver without Heating the Deposition Substrate and Its Catalytic Effects. Quantum Beam Sci. 2024, 8, 16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Acciarri, M.D.; Moore, C.; Baalrud, S.D. Strong Coulomb coupling influences ion and neutral temperatures in atmospheric pressure plasmas. Plasma Sources Sci. Technol. 2022, 31, 125005. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- von Woedtke, T.; Laroussi, M.; Gherardi, M. Foundations of plasmas for medical applications. Plasma Sources Sci. Technol. 2022, 31, 054002. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Du, J.S. Complex Nanoparticle Systems: Structures, Structure–Property Relationships, and Dynamics. Ph.D. Dissertation, Northwestern University, Evanston, IL, USA, 2021. [Google Scholar]
- Appleton, T.J.; Colder, R.I.; Kingman, S.; Lowndes, I.S.; Read, A.G. Microwave technology for energy-efficient processing of waste. Appl. Energ. 2005, 81, 85–113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Song, X.; Hu, G.; Thring, R.W. Ultrasonic desorption of petroleum hydrocarbons from crude oil contaminated soils. J. Environ. Sci. Health Part A 2013, 8, 1378–1389. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ali, A.M.; Abu Hassan, M.A.; Ibrahim, R.R.K.; Jalil, A.A.; Mat Nayan, N.H.; Abdulkarim, B.I.; Sabeen, A.H. Analysis of solid residue and flue gas from thermal plasma treatment of petroleum sludge. J. Environ. Chem. Eng. 2019, 7, 103207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mazzoni, L.; Janajreh, I.; Elagroudy, S.; Ghenai, C. Modeling of plasma and entrained flow co-gasification of MSW and petroleum sludge. Energy 2020, 196, 117001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saifutdinov, A.I. Numerical study of various scenarios for the formation of atmospheric pressure DC discharge char acteristics in argon: From glow to arc discharge. Plasma Sources Sci. Technol. 2022, 31, 094008. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Timerkaev, B.A.; Gevorgyan, R.K.; Zalyalieva, A.A. Plasma-Chemical Synthesis of Nanodiamonds on the Surface of a Microarc Discharge Cathode. J. Eng. Phys. Thermophy 2022, 95, 1201–1206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nakano, A.; Nishida, H. The effect of the voltage waveform on performance of dielectric barrier discharge plasma actuator. J. Appl. Phys. 2019, 126, 173303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cai, X.; Wei, X.; Du, C. Thermal plasma treatment and co-processing of sludge for utilization of energy and material. Energy Fuels 2020, 34, 7775–7805. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Giwa, A.S.; Maurice, N.J.; Luoyan, A.; Liu, X.; Yunlong, Y.; Hong, Z. Advances in sewage sludge application and treatment: Process integration of plasma pyrolysis and anaerobic digestion with the resource recovery. Heliyon 2023, 9, e19765. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Yu, H.; Jiang, Z.; Song, Y.; Zhang, T.; Siyal, A.A.; Fang, J. Microwave pyrolysis of oily sludge under different control modes. J. Hazard. Mater. 2021, 416, 125887. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, Y.; Cao, X.; Dai, Y.; Yan, T.; Zhang, X.; He, H.; He, P. Effect of Metal Dispersion in Rh-Based Zeolite and SiO2 Catalysts on the Hydroformylation of Olefin Mixtures from Fischer–Tropsch Synthesis. Catalysts 2025, 15, 212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.; Li, X.; Zheng, J.; Du, M.; Wu, X.; Song, J.; Yang, W. Non-thermal plasma-assisted ammonia production: A review. Energy Convers. Manag. 2023, 293, 117482. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, Y.; Xu, S.; Jiang, Y.; Fan, S.; Wen, T.; Wang, S.I.; Ding, L. Effect of biomass adsorbent on non-thermal plasma activated treatment of oil-based drilling cutting: Residual toxicity assessment. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2024, 332, 125784. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Starikovskaia, S.; Lacoste, D.A.; Colonna, G. Non-equilibrium plasma for ignition and combustion enhancement. Eur. Phys. J. D 2021, 75, 231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, Z.; Sun, H.; Dou, L.; Zhang, S.; Han, W.; Zhang, C.; Shao, T. One-step high-value conversion of heavy oil into H2, C2H2 and carbon nanomaterials by non-thermal plasma. Chem. Eng. J. 2023, 461, 141860. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miao, Y.; Yokochi, A.; Jovanovic, G.; Zhang, S.; von Jouanne, A. Application- oriented non-thermal plasma in chemical reaction engineering: A review. Green Energy Resour. 2023, 1, 100004. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhatsada, A.; Patumsawad, S.; Towprayoon, S.; Chiemchaisri, C.; Wangyao, K. Development of multivariable model for pre dicting heating value of bio-dried refuse-derived fuel from municipal solid waste. Biomass Bioenergy 2025, 197, 107795. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gan, Z.; Zhao, C.; Li, Y.; Chen, G.; Song, Z.; Zhang, Z.; Ran, W. Experimental investigation on smoldering combustion for oil sludge treatment: Influence of key parameters and product analysis. Fuel 2022, 316, 123354. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, T.; Fan, Y.; Li, H.; Ren, Z.; Kou, L.; Guo, X.; Zhu, L. Excess sludge disintegration by discharge plasma oxidation: Efficiency and underlying mechanisms. Sci. Total Environ. 2021, 774, 145127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chang, C.Y.; Shie, J.L.; Lin, J.P.; Wu, C.H.; Lee, D.J.; Chang, C.F. Major products obtained from the pyrolysis of oil sludge. Energy Fuels 2000, 14, 1176–1183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kwao-Boateng, E.; Ankudey, E.G.; Darkwah, L.; Danquah, K.O. Assessment of diesel fuel quality. Heliyon 2024, 10, e24733. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- ISO 8217:2024; Products from Petroleum, Synthetic and Renewable Sources—Fuels (Class F)—Specifications of Marine Fuels. ISO: Geneva, Switzerland, 2024.
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the author. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).