Application of Ultrasound in Proteins: Physicochemical, Structural Changes, and Functional Properties with Emphasis on Foaming Properties
Abstract
:1. Introduction
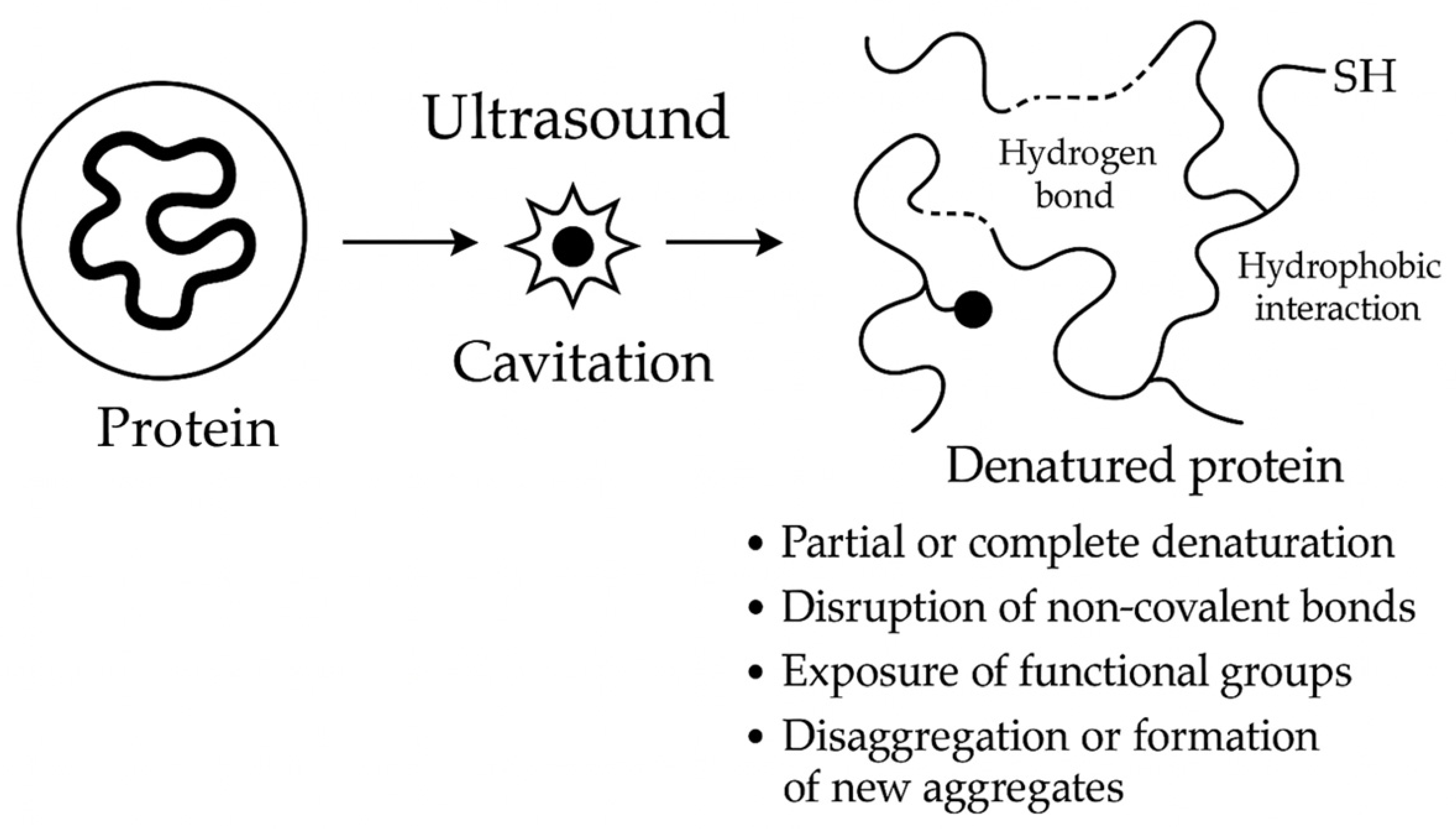
2. Mechanism of Ultrasound
3. Effects of Ultrasound on Physicochemical Properties of Proteins
3.1. Protein Solubility
3.2. Viscosity of Protein Solutions
3.3. Particle Size
3.4. Thermal Denaturation
4. Structural Changes Induced by Ultrasound
4.1. Effects on Secondary Structure of Proteins
4.2. Effects on Tertiary Structure of Proteins
5. Foaming Properties of Proteins
6. Challenges and Limitations of Ultrasound Application in Food Industry
7. Future Perspectives and Research Directions
8. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Małecki, J.; Muszyński, S.; Sołowiej, B.G. Proteins in food systems—Bionanomaterials, conventional and unconventional sources, functional properties, and development opportunities. Polymers 2021, 13, 2506. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yousefi, N.; Abbasi, S. Food proteins: Solubility & Thermal stability improvement techniques. Food Chem. Adv. 2022, 1, 100090. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kang, S.; Zhang, J.; Guo, X.; Lei, Y.; Yan, M. Effects of Ultrasonic Treatment on the Structure, Functional Properties of Chickpea Protein Isolate and Its Digestibility In Vitro. Foods 2022, 11, 880. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Arredondo-Parada, I.; Torres-Arreola, W.; Suárez-Jiménez, G.M.; Ramírez-Suárez, J.C.; Juárez-Onofre, J.E.; Rodríguez-Félix, F.; Marquez-Rios, E. Effect of ultrasound on physicochemical and foaming properties of a protein concentrate from giant squid (Dosidicus gigas) mantle. LWT-Food Sci. Technol. 2020, 121, 108954. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kavimughil, M.; Dutta, S.; Moses, J.A.; Anandharamakrishnan, C. Sonication of egg and its effect on foaming behavior. Sustain. Food Technol. 2023, 1, 511–527. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Higuera-Barraza, O.A.; Toro-Sánchez, C.L.; Ruiz-Cruz, S.; Márquez-Ríos, E. Effects of High-energy ultrasound on the functional properties of proteins. Ultrason. Sonochem. 2016, 31, 558–562. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Darsana, K.; Sivakumar, P. Potential of ultrasound in food processing: An overview. Curr. J. Appl. Sci. Technol. 2023, 42, 14–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cruz-López, S.O.; Escalona-Buendía, H.B.; Martinez-Arellano, I.; Domínguez-Soberanes, J.; Alvarez-Cisneros, Y.M. Physicochemical and techno-functional characterization of soluble proteins extracted by ultrasound from the cricket Acheta domesticus. Heliyon 2024, 10, e40718. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, X.; Das, R.S.; Bhavya, M.L.; Garcia-Vaquero, M.; Tiwari, B.K. Acoustic cavitation for agri-food applications: Mechanism of action, design of new systems, challenges and strategies for scale-up. Ultrason. Sonochem. 2024, 105, 106850. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, H.; Carrascal, C.A.; Xie, H.; Shamdasani, V.; Anthony, B.W. 2-D ultrasound shear wave elastography with multi-sphere-source external mechanical vibration: Preliminary phantom results. Ultrasound Med. Biol. 2020, 46, 2505–2519. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tan, W.K.; Cheah, S.C.; Parthasarathy, S.; Rajesh, R.P.; Pang, C.H.; Manickam, S. Fish pond water treatment using ultrasonic cavitation and advanced oxidation processes. Chemosphere 2021, 274, 129702. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bucur, M.; Radulescu, M.; Radu, G.L.; Bucur, B. Cavitation-effect-based treatments and extractions for superior fruit and milk valorisation. Molecules 2023, 28, 4677. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiong, Y.; Li, Q.; Miao, S.; Zhang, Y.; Zheng, B.; Zhang, L. Effect of ultrasound on physicochemical properties of emulsion stabilized by fish myofibrillar protein and xanthan gum. Innov. Food Sci. Emerg. Technol. 2019, 54, 225–234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rajasekaran, B.; Singh, A.; Ponnusamy, A.; Patil, U.; Zhang, B.; Hong, H.; Benjakul, S. Ultrasound treated fish myofibrillar protein: Physicochemical properties and its stabilizing effect on shrimp oil-in-water emulsion. Ultrason. Sonochem. 2023, 98, 106513. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Li, B.; Guo, Y.; Liu, C.; Liu, J.; Tan, B.; Guo, Z.; Wang, Z.; Jiang, L. Effects of ultrasound on the structural and emulsifying properties and interfacial properties of oxidized soybean protein aggregates. Ultrason. Sonochem. 2022, 87, 106046. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Malik, M.A.; Sharma, H.K.; Saini, C.S. High intensity ultrasound treatment of protein isolate extracted from dephenolized sunflower meal: Effect on physicochemical and functional properties. Ultrason. Sonochem. 2017, 39, 511–519. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Resendiz-Vazquez, J.; Ulloa, J.; Urías-Silvas, J.; Bautista-Rosales, P.; Ramírez-Ramírez, J.; Rosas-Ulloa, P.; González-Torres, L. Effect of high-intensity ultrasound on the technofunctional properties and structure of jackfruit (Artocarpus heterophyllus) seed protein isolate. Ultrason. Sonochem. 2017, 37, 436–444. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, H.; Wang, P.; Shen, Q.; Yang, H.; Xie, H.; Huang, M.; Zhang, J.; Zhao, Q.; Luo, Q.; Jin, D.; et al. Insight into the effect of ultrasound treatment on the rheological properties of myofibrillar proteins based on the changes in their tertiary structure. Food Res. Int. 2022, 157, 111136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, D.; Xu, Y.; Zhang, W.; Liu, Y.; Zhang, T.; Liu, H.; Jiang, Y.; Li, D. Enhancement of foaming property of ormosia protein: Insights into the effect of high-intensity ultrasound on physicochemical properties and structure analysis. Food Hydrocoll. 2024, 152, 109902. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Higuera-Barraza, O.A.; Torres-Arreola, W.; Juárez-Onofre, E.J.; Carrillo-Torres, R.C.; Suárez-Jiménez, G.M.; Ruíz-Cruz, S.; Márquez-Ríos, E. Ultrasound treatment improved the emulsifying property of a protein concentrate obtained from giant squid. Fisheries Sci. 2024, 90, 1035–1042. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yolandani; Ma, H.; Li, Y.; Liu, D.; Zhou, H.; Liu, X.; Wan, Y.; Zhao, X. Ultrasound-assisted limited enzymatic hydrolysis of high concentrated soy protein isolate: Alterations on the functional properties and its relation with hydrophobicity and molecular weight. Ultrason. Sonochem. 2023, 95, 106414. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mao, R.; Xiong, G.; Zheng, H.; Qi, J.; Zhang, C. Effect of ultrasound on the functional properties and structural changes of chicken liver insoluble proteins isolated by isoelectric solubilization/precipitation. Ultrason. Sonochem. 2025, 112, 107165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kang, Z.; Zhang, S.; Kong, Y.; Wu, Z.; Li, Y.; Liu, T.; Xie, F. Modification of soybean protein isolate by pH-shifting combined with ultrasonic treatment: Structural, viscosity, and functional properties. Food Struct. 2024, 42, 100383. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amiri, A.; Sharifian, P.; Soltanizadeh, N. Application of ultrasound treatment for improving the physicochemical, functional and rheological properties of myo fi brillar proteins. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2018, 111, 139–147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yanjun, S.; Jianhang, C.; Shuwen, Z.; Hongjuan, L.; Jing, L.; Lu, L.; Uluko, H.; Yanling, S.; Wenming, C.; Wupeng, G.; et al. Effect of power ultrasound pre-treatment on the physical and functional properties of reconstituted milk protein concéntrate. J. Food Eng. 2014, 124, 11–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mao, J.; Gao, Y.; Ye, W.; Meng, Z. Impact of high-intensity ultrasound on interfacial protein adsorption of non-dairy whipping cream: Whipping properties and foam stabilization model. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2025, 286, 138466. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jambrak, A.R.; Mason, T.J.; Lelas, V.; Paniwnyk, L.; Herceg, Z. Effect of ultrasound treatment on particle size and molecular weight of whey proteins. J. Food Eng. 2014, 121, 15–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hong, Z.; Kong, Y.; Guo, R.; Huang, Q. Stabilizing effect of silver carp myofibrillar protein modified by high intensity ultrasound on high internal phase emulsions: Protein denaturation, interfacial adsorption and reconfiguration. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2024, 265, 130896. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, R.; Fu, W.; Li, D.; Dong, C.; Bao, Z.; Wang, C. Structure and functionality of whey protein, pea protein, and mixed whey and pea proteins treated by pH shift or high-intensity ultrasound. J. Dairy Sci. 2023, 107, 726–741. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, H.; Huang, C.; Liu, S.; Chen, X.; Wang, X.; Hu, P. Effect of ultrasound treatment on the oxidation and conformational structure of myofibrillar protein of beef marinated in red sour soup. Meat Sci. 2025, 224, 109779. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duan, Y.; Yang, X.; Deng, D.; Zhang, L.; Ma, X.; He, L.; Zhu, X.; Zhang, X. Effects of ultrasonic waves of different powers on the physicochemical properties, functional characteristics, and ultrastructure of bovine liver peptides. Ultrason. Sonochem. 2024, 110, 107031. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Frydenberg, R.P.; Hammershøj, M.; Andersen, U.; Greve, M.T.; Wiking, L. Protein denaturation of whey protein isolates (WPIs) induced by high intensity ultrasound during heat gelation. Food Chem. 2016, 192, 415–423. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Farahnak, R.; Nourani, M.; Riahi, E. Ultrasound thawing of mushroom (Agaricus bisporus): Effects on thawing rate, protein denaturation and some physical properties. LWT-Food Sci. Technol. 2021, 151, 112150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lai, Y.; Zhu, Y.; Li, X.; Zhang, G.; Lian, J.; Wang, S. Ultrasound-induced structural changes in partial nitrification sludge: Unravelling the mechanism for improved nitrogen removal. Environ. Res. 2024, 261, 119637. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vanga, S.K.; Wang, J.; Orsat, V.; Raghavan, V. Effect of pulsed ultrasound, a green food processing technique, on the secondary structure and in-vitro digestibility of almond milk protein. Food Res. Int. 2020, 137, 109523. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, K.; Kang, Z.L.; Zhao, Y.Y.; Xu, X.L.; Zhou, G.H. Use of high-intensity ultrasound to improve functional properties of batter suspensions prepared from pse-like chicken breast meat. Food Bioprocess Technol. 2014, 7, 3466–3477. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, H.; Wu, J.; Li-Chan, E.C.; Zhu, L.; Zhang, F.; Xu, X.; Fan, G.; Wang, L.; Huang, X.; Pan, S. Food Hydrocolloids Effects of ultrasound on structural and physical properties of soy protein isolate (SPI) dispersions. Food Hydrocoll. 2013, 30, 647–655. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, X.; Wei, L.; Mao, Y.; Zhao, A.; Pu, M.; Liu, Y.; Wang, B. A Comparative study of ultrasound and thermal processing: Effects on stability and protein structure in goat milk. J. Dairy Sci. 2025, in press. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xue, S.; Xu, X.; Shan, H.; Wang, H.; Yang, J.; Zhou, G. Effects of high-intensity ultrasound, high-pressure processing, and highpressure homogenization on the physicochemical and functional properties of myofibrillar proteins. Innov. Food Sci. Emerg. Technol. 2018, 45, 354–360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.; Zhao, H.; Tao, H.; Yu, B.; Cui, B.; Wang, Y. Ultrasound improves the physicochemical and foam properties of whey protein microgel. Front. Nutr. 2023, 10, 1140737. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, W.; Ma, H.; Wang, Y.Y. Recent advances in modified food proteins by high intensity ultrasound for enhancing functionality: Potential mechanisms, combination with other methods, equipment innovations and future directions. Ultrason. Sonochem. 2022, 85, 105993. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ampofo, J.; Ngadi, M. Ultrasound-assisted processing: Science, technology and challenges for the plant-based protein industry. Ultrason. Sonochem. 2022, 84, 105955. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mir, N.A.; Riar, C.S.; Singh, S. Physicochemical, molecular and thermal properties of high-intensity ultrasound (HIUS) treated protein isolates from album (Chenopodium album) seed. Food Hydrocoll. 2019, 96, 433–441. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, W.; Boateng, I.D.; Xu, J. How does ultrasound-assisted ionic liquid treatment affect protein? A comprehensive review of their potential mechanisms, safety evaluation, and physicochemical and functional properties. Compr. Rev. Food Sci. Food Saf. 2024, 23, e13261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chavan, P.; Sharma, P.; Sharma, S.R.; Mittal, T.C.; Jaiswal, A.K. Application of High-Intensity Ultrasound to Improve Food Processing Efficiency: A Review. Foods 2022, 11, 122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tan, M.C.; Chin, L.N.; Yusof, Y.A.; Taip, F.S.; Abdullah, J. Characterisation of improved foam aeration and rheological properties of ultrasonically treated whey protein suspensión. Int. Dairy J. 2015, 43, e7–e14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, A.; Benjakul, S.; Kijroongrojana, K. Effect of ultrasonication on physicochemical and foaming properties of squid ovary powder. Food Hydrocoll. 2018, 77, e286–e296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stefanović, A.B.; Jovanović, J.R.; Dojčinović, M.B.; Lević, S.M.; Nedović, V.A.; Bugarski, B.M.; Knežević-Jugović, Z.D. Effect of the controlled high-intensity ultrasound on improving functionality and structural changes of egg white proteins. Food Bioprocess Technol. 2017, 1224–1239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morales, R.; Martínez, K.D.; Ruiz-Henestrosa, V.M.P.; Pilosof, A.M.R. Modification of foaming properties of soy protein isolate by high ultrasound intensity: Particle size effect. Ultrason. Sonochem. 2015, 26, 48–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xiong, T.; Xiong, W.; Ge, M.; Xia, J.; Li, B.; Chen, Y. Effect of high intensity ultrasound on structure and foaming properties of pea protein isolate. Food Res. Int. 2018, 109, 260–267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Flores-Jiménez, N.T.; Ulloa, J.A.; Urías Silvas, J.E.; Ramírez Ramírez, J.C.; Rosas Ulloa, P.; Bautista Rosales, P.U.; Silva Carrillo, Y.; Gutiérrez Leyva, R. Effect of high-intensity ultrasound on the compositional, physicochemical, biochemical, functional and structural properties of canola (Brassica napus L.) protein isolate. Food Res. Int. 2019, 121, 947–956. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Arruda, T.R.; Vieira, P.; Silva, B.M.; Freitas, T.D.; Amaral, A.J.B.D.; Vieira, E.N.R.; Leite Júnior, B.R.C. What are the prospects for ultrasound technology in food processing? An update on the main effects on different food matrices, drawbacks, and applications. J. Food Process Eng. 2021, 4, e13872. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saran, V.; Pavithra, R.; Koli, V.; Dattatrya, P.A.; Nikashini, T.; Ashika, R.; Gowda, N.A.N.; Sunil, C.K. Ultrasound modification of techno-functional, structural, and physico-chemical properties of legume proteins: A review. Food Biosci. 2024, 60, 104456. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jadhav, H.B.; Das, M.; Das, A.; Geetha, V.; Choudhart, P.; Annapure, U.; Alaskar, K. Enhancing the functionality of plant-based proteins with the application of ultrasound-A review. Meas. Food 2024, 13, 100139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lei, Y.; Hou, J.; Fang, C.; Tian, Y.; Naidu, R.; Zhang, J.; Zhang, X.; Zeng, Z.; Cheng, Z.; He, J.; et al. Ultrasound-based advanced oxidation processes for landfill leachate treatment: Energy consumption, influences, mechanisms and perspectives. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2023, 263, 115366. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Knorr, D.; Zenker, M.; Heinz, V.; Lee, D.U. Applications and potential of ultrasonics in food processing. Trends Food Sci. Technol. 2004, 15, 261–266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gallo, M.; Ferrara, L.; Naviglio, D. Application of ultrasound in food science and technology: A perspective. Foods 2018, 7, 164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Awad, T.S.; Moharram, H.A.; Shaltout, O.E.; Asker, D.; Youssef, M.M. Applications of ultrasound in analysis, processing and quality control of food: A review. Food Res. Int. 2012, 48, 410–427. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhargava, N.; Mor, R.S.; Kumar, K.; Sharanagat, V.S. Advances in application of ultrasound in food processing: A review. Ultrason. Sonochem. 2021, 70, 105293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nazari, B.; Mohammadifar, M.A.; Shojaee-Aliabadi, S.; Feizollahi, E.; Mirmoghtadaie, L. Effect of ultrasound treatments on functional properties and structure of millet protein concentrate. Ultrason. Sonochem. 2018, 41, 382–388. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| Protein Source | Frequency (kHz) | Treatment | Results | Reference |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Egg white | 20 | 2, 5, 10, 15, and 20 min; 40% amplitude | At 15 min the capacity (60.6%) and foaming stability (193.3%) increased. | Stefanović et al. [48] |
| Chicken meat | 20 | 6 min, 450 W; 60% amplitude | Decrease in particle size and conformational changes | Xue et al. [39] |
| Beef | 20 | 10, 20, and 30 min; 100 and 300 W | Amiri et al. [26] | |
| Wheat | 20 y 40 | 15 and 30 min; 43–48 W/cm2 | Jambrak et al. [27] | |
| Soy | 20 | 5, 10, 15, and 20 min; 20% amplitude | Foaming capacity: Without ultrasound (153.3%) After 5 min with ultrasound (248.3%) After 20 min with ultrasound (268.2%) | Morales et al. [49] |
| Squid ovary (Loligo formosana) | 20 | 30 min; 70% amplitude | Foaming capacity: Without ultrasound (244%) With ultrasound (320%) | Singh et al. [47] |
| Pea | 20 | 30 min; 30, 60, and 90% amplitude | HIU at 90% amplitude for 30 min showed an increase in foaming capacity (from 145.6% to 200%) and foaming stability (from 58% to 73.3%). | Xiong et al. [50] |
| Chickpea | - | 10, 15, and 30 min; 200, 400 and 600 W | The foaming properties increased significantly with the treatment of 200 W power and 15 min | Kang et al. [3] |
| Ormosia | - | 20 min; 0, 125, 250, 375, and 500 W | Increasing ultrasound power (0, 125, 250, 375, and 500 W) improved different properties and characteristics such as solubility, particle size, FC, and FS. | Huang et al. [19] |
| Squid mantle | 20 | 0–5 min; 20–40% amplitude | The application of 40% amplitude for 1 min showed the best foaming capacity, while the best stability was achieved using 40% amplitude for 5 min. | Arredondo-Parada et al. [4] |
| Whey protein | 20 | 160, 320, 480, and 640 W | The 480 W application showed better foaming ability, while the low energy use (160 and 320 W) presented better stability. | Wang et al. [40] |
| Cricket protein | 20 | 20 min; 90% amplitude | The effect of the protein extraction method on its main functional properties was studied. Ultrasonic extraction was found to have the best foaming capacity and stability. | Cruz-López et al. [8] |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Antunez-Medina, J.R.; Suárez-Jiménez, G.M.; Ocano-Higuera, V.M.; Tolano-Villaverde, I.d.J.; Ornelas-Paz, J.d.J.; Torres-Arreola, W.; Márquez-Ríos, E. Application of Ultrasound in Proteins: Physicochemical, Structural Changes, and Functional Properties with Emphasis on Foaming Properties. Processes 2025, 13, 1646. https://doi.org/10.3390/pr13061646
Antunez-Medina JR, Suárez-Jiménez GM, Ocano-Higuera VM, Tolano-Villaverde IdJ, Ornelas-Paz JdJ, Torres-Arreola W, Márquez-Ríos E. Application of Ultrasound in Proteins: Physicochemical, Structural Changes, and Functional Properties with Emphasis on Foaming Properties. Processes. 2025; 13(6):1646. https://doi.org/10.3390/pr13061646
Chicago/Turabian StyleAntunez-Medina, José Ramón, Guadalupe Miroslava Suárez-Jiménez, Víctor Manuel Ocano-Higuera, Iván de Jesús Tolano-Villaverde, José de Jesús Ornelas-Paz, Wilfrido Torres-Arreola, and Enrique Márquez-Ríos. 2025. "Application of Ultrasound in Proteins: Physicochemical, Structural Changes, and Functional Properties with Emphasis on Foaming Properties" Processes 13, no. 6: 1646. https://doi.org/10.3390/pr13061646
APA StyleAntunez-Medina, J. R., Suárez-Jiménez, G. M., Ocano-Higuera, V. M., Tolano-Villaverde, I. d. J., Ornelas-Paz, J. d. J., Torres-Arreola, W., & Márquez-Ríos, E. (2025). Application of Ultrasound in Proteins: Physicochemical, Structural Changes, and Functional Properties with Emphasis on Foaming Properties. Processes, 13(6), 1646. https://doi.org/10.3390/pr13061646








