Proteins from Kappaphycus alvarezii: Identification by Mass Spectrometry and Antifungal Potential
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Biological Materials and Chemicals
2.2. Protein Extraction
2.3. Antifungal Assays
2.4. Mechanism of Action
2.4.1. Membrane Integrity Assay
2.4.2. Detection of Reactive Oxygen Species (ROS) Assay
2.4.3. Morphological Assessments by Scanning Electron Microscopy (SEM)
2.5. Enzymatic Activities
2.5.1. Total Protease Activity
2.5.2. Guaiacol Peroxidase (GPOX) Activity
2.5.3. β-1,3-glucanase (β-1,3-GLU) Activity
2.5.4. Chitinase Activity (CHI)
2.5.5. Serine Protease Inhibitory Activity
2.5.6. Cysteine Protease Inhibitory Activity
2.6. Protein Identification by Mass Spectrometry (MS/MS)
2.7. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
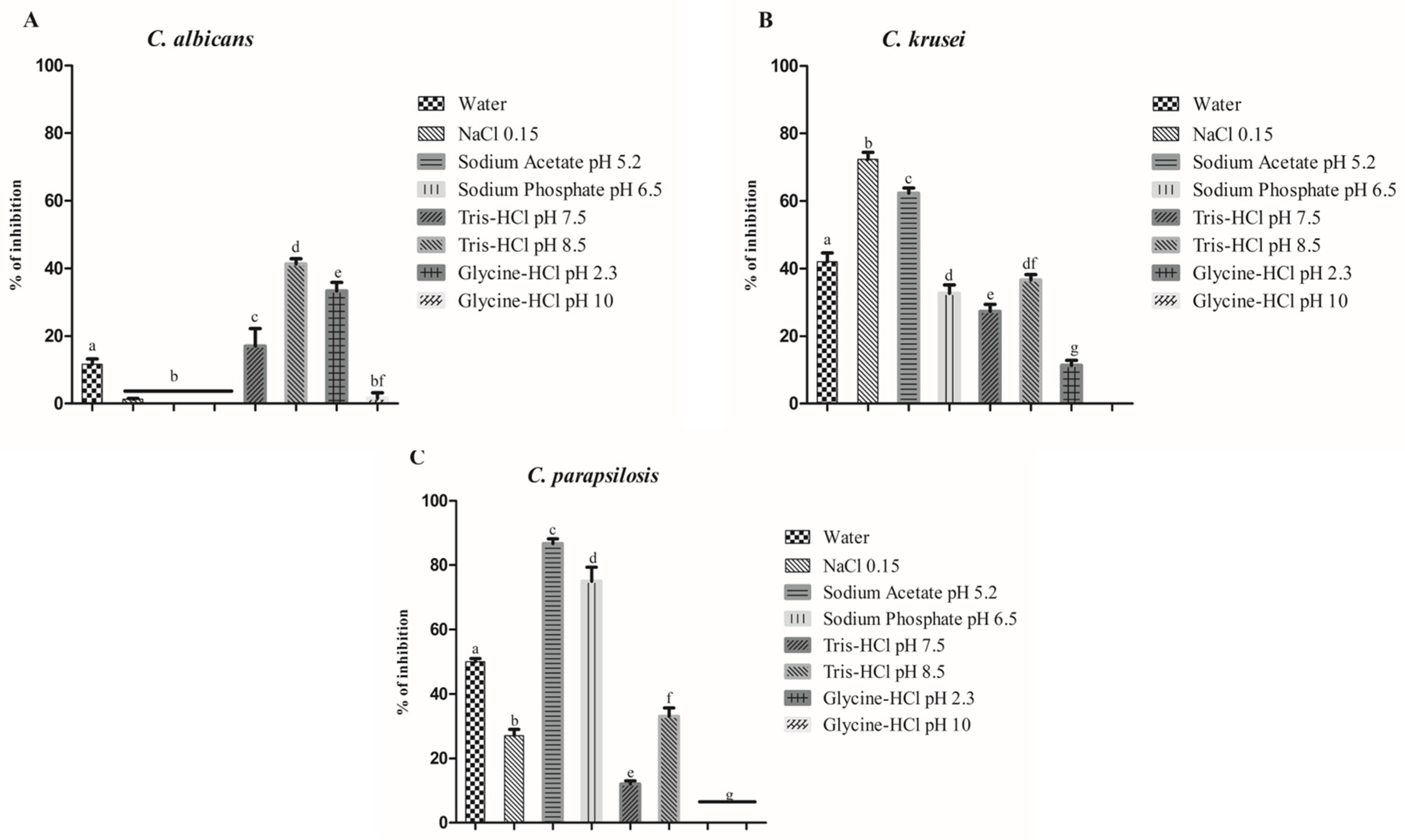
3.1. Protein Extraction and Antimicrobial Activity
3.2. Mechanisms of Action
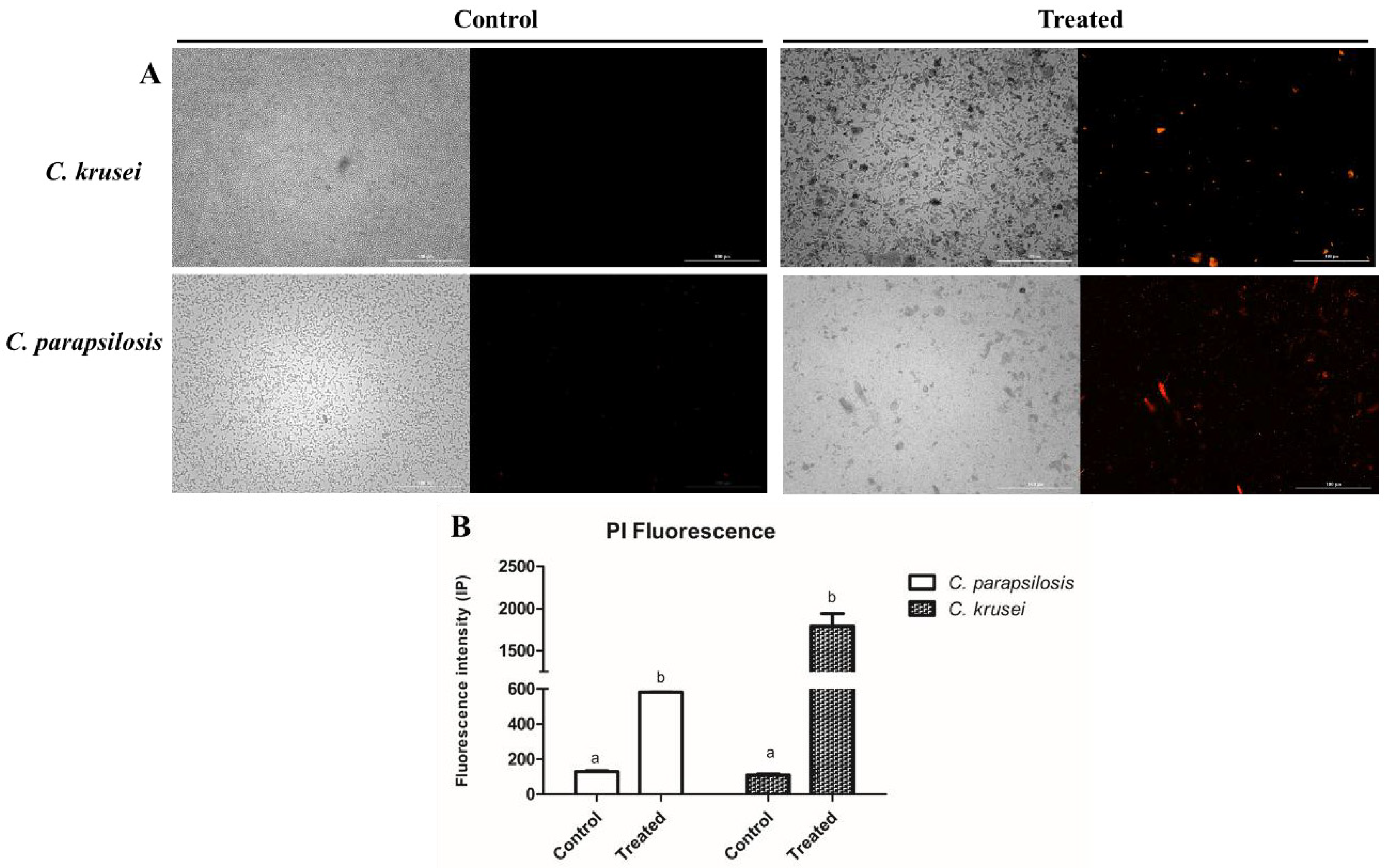
3.2.1. Membrane Permeability and Pore Formation
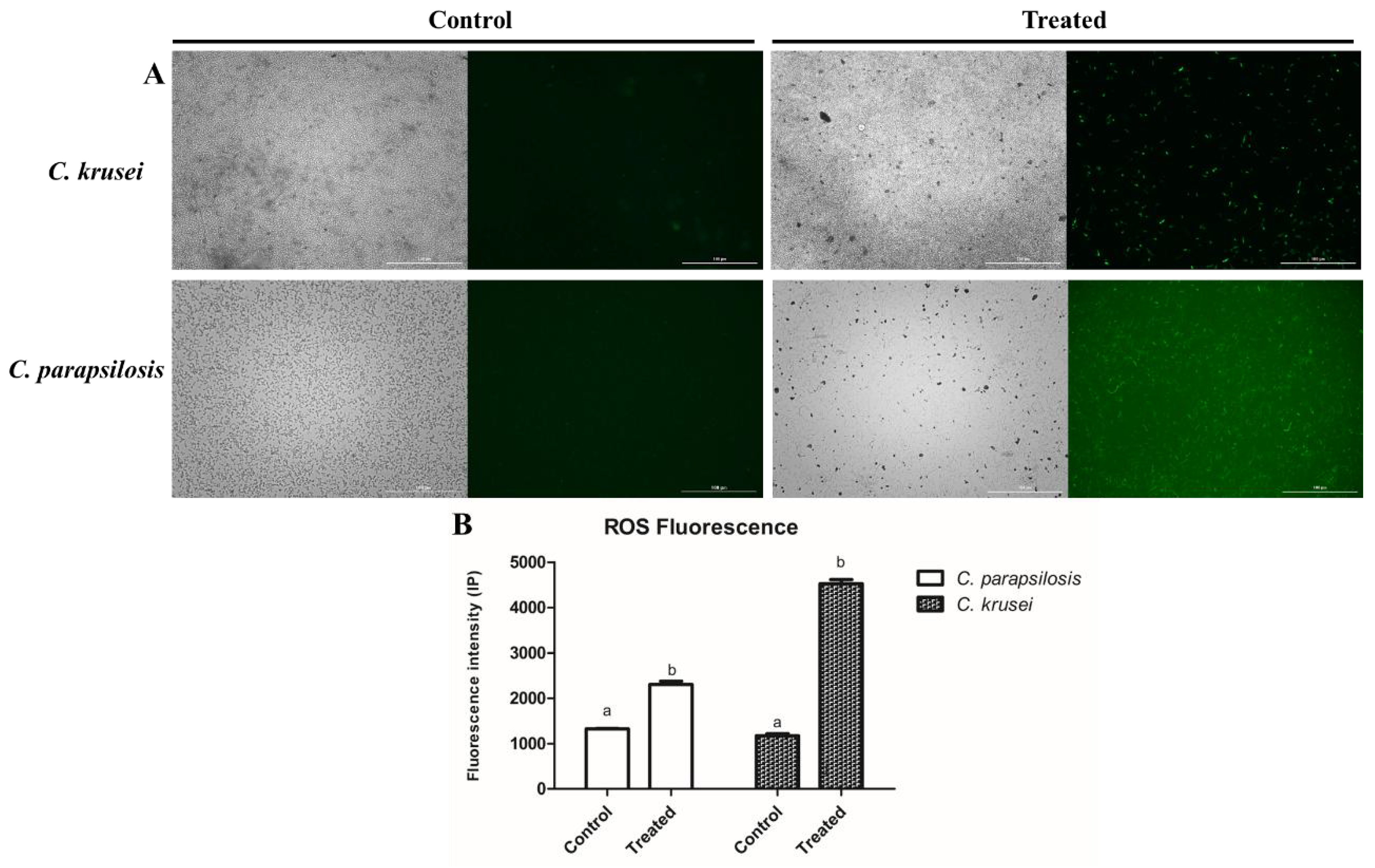
3.2.2. ROS Overaccumulation and Apoptosis
3.2.3. Evaluation of Change in Cell Morphology by Scanning Electron Microscopy (SEM)
3.3. Identification and Characterization of Proteins in the K. alvarezzi Extract
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Pickering, T.D.; Skelton, P.; Sulu, R.J. Intentional introductions of commercially harvested alien seaweeds. Bot. Mar. 2007, 50, 338–350. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hayashi, L.; Santos, A.A.; Faria, G.S.M.; Nunes, B.G.; Souza, M.S.; Fonseca, A.L.D.; Barreto, P.L.M.; Oliveira, E.C.; Bouzon, Z.L. Kappaphycus alvarezii (Rhodophyta, Areschougiaceae) cultivated in subtropical waters in Southern Brazil. J. Appl. Phycol. 2011, 23, 337–343. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Canuto, M.M.; Rodero, F.G. Antifungal drug resistance to azoles and polyenes. Lancet Infect. Dis. 2002, 2, 550–563. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fayaz, M.; Namitha, K.K.; Murthy, K.N.C.; Swamy, M.M.; Sarada, R.; Khanam, S.; Subbarao, P.V.; Ravishankar, G.A. Chemical composition, iron bioavailability, and antioxidant activity of Kappaphycus alvarezzi (Doty). J. Agric. Food Chem. 2005, 53, 792–797. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sanjivkumar, M.; Chandran, M.N.; Suganya, A.M.; Immanuel, G. Investigation on bio-properties and in-vivo antioxidant potential of carrageenans against alloxan induced oxidative stress in Wistar albino rats. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2020, 151, 650–662. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raman, M.; Doble, M. κ-Carrageenan from marine red algae, Kappaphycus alvarezii—A functional food to prevent colon carcinogenesis. J. Funct. Foods 2015, 15, 354–364. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morgan, J.; Meltzer, M.I.; Plikaytis, B.D.; Sofair, A.N.; Huie-White, S.; Wilcox, S.; Harrison, L.H.; Seaberg, E.C.; Hajjeh, R.A.; Teutsch, S.M. Excess Mortality, Hospital Stay, and Cost Due to Candidemia: A Case-Control Study Using Data From Population-Based Candidemia Surveillance. Infect. Control Hosp. Epidemiol. 2005, 26, 540–547. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brown, G.D.; Denning, D.W.; Gow, N.A.R.; Levitz, S.M.; Netea, M.G.; White, T.C. Hidden Killers: Human Fungal Infections. Sci. Transl. Med. 2012, 4, 165rv13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sanguinetti, M.; Posteraro, B.; Lass-Flörl, C. Antifungal drug resistance among Candida species: Mechanisms and clinical impact. Mycoses 2015, 58 (Suppl. 2), 2–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Antinori, S.; Milazzo, L.; Sollima, S.; Galli, M.; Corbellino, M. Candidemia and invasive candidiasis in adults: A narrative review. Eur. J. Intern. Med. 2016, 34, 21–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Quindós, G. Epidemiology of candidaemia and invasive candidiasis. A changing face. Rev. Iberoam. Micol. 2014, 31, 42–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schneider, J.; Mateo, E.; Marcos-Arias, C.; Eiró, N.; Vizoso, F.; Pérez-Fernández, R.; Eraso, E.; Quindós, G. Antifungal activity of the human uterine cervical stem cells conditioned Medium (hUCESC-CM) against Candida albicans and other medically relevant species of Candida. Front. Microbiol. 2018, 9, 2818. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chaves, G.M.; Cavalcanti, M.A.Q.; Porto, A.L.F. Pathogenicity characteristics of stocked and fresh yeasts strains. Braz. J. Microbiol. 2003, 34, 197–202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pinto, T.N.; Kohn, A.; Da Costa, G.L.; Oliveira, L.M.A.; Pinto, T.C.A.; Oliveira, M.M.E. Candida guilliermondii as an agent of postpartum subacute mastitis in Rio de Janeiro, Brazil: Case report. Front. Microbiol. 2022, 13, 964685. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Naglik, J.R.; Challacombe, S.J.; Hube, B. Candida albicans secreted aspartyl proteinases in virulence and pathogenesis. Microbiol. Mol. Biol. Rev. 2003, 67, 400–428. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Puig-Asensio, M.; Pemán, J.; Zaragoza, R.; Garnacho-Montero, J.; Martín-Mazuelos, E.; Cuenca-Estrella, M.; Almirante, B. Impact of therapeutic strategies on the prognosis of Candidemia in the ICU. Crit. Care Med. 2014, 42, 1423–1432. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Monge, R.A.; Roman, E.; Nombela, C.; Pla, J. The MAP kinase signal transduction network in Candida albicans. Microbiology 2006, 152, 905–912. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Colombo, A.L.; Guimarães, T. Epidemiology of hematogenous infections due to Candida spp. Rev. Soc. Bras. Med. Trop. 2003, 36, 599–607. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Berkow, E.L.; Lockhart, S.R. Fluconazole resistance in Candida species: A current perspective. Infect. Drug Resist. 2017, 10, 237–245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Silva, A.L.; Bezerra, L.P.; Freitas, C.D.T.; Silva, A.F.B.; Mesquita, F.P.; Neto, N.A.S.; Oliveira, J.P.B.; Aguiar, T.K.B.; Nagano, C.S.; Carneiro, R.F.; et al. Luffa operculata seed proteins: Identification by LC-ESI-MS/MS and biotechnological potential against Candida albicans and C. krusei. Anal. Biochem. 2022, 655, 114851. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bradford, M.M. A rapid and sensitive method for the quantitation of microgram quantities of protein utilizing the principle of protein-dye binding. Anal. Biochem. 1976, 72, 248–254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lopes, F.E.S.; da Costa, H.P.S.; Souza, P.F.N.; Oliveira, J.P.B.; Ramos, M.V.; Freire, J.E.C.; Jucá, T.L.; Freitas, C.D.T. Peptide from thaumatin plant protein exhibits selective anticandidal activity by inducing apoptosis via membrane receptor. Phytochemistry 2019, 159, 46–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Crowley, L.C.; Scott, A.P.; Marfell, B.J.; Boughaba, J.A.; Chojnowski, G.; Waterhouse, N.J. Measuring cell death by propidium iodide uptake and flow cytometry. Cold Spring Harb. Protoc. 2016, 2016, 647–651. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Maurya, I.K.; Pathak, S.; Sharma, M.; Sanwal, H.; Chaudhary, P.; Tupe, S.; Deshpande, M.; Chauhan, V.S.; Prasad, R. Antifungal activity of novel synthetic peptides by accumulation of reactive oxygen species (ROS) and disruption of cell wall against Candida albicans. Peptides 2011, 32, 1732–1740. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Staniszewska, M.; Bondaryk, M.; Swoboda-Kopec, E.; Siennicka, K.; Sygitowicz, G.; Kurzatkowski, W. Candida albicans morphologies revealed by scanning electron microscopy analysis. Braz. J. Microbiol. 2013, 44, 813–821. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xavier-Filho, J.; Campos, F.A.P.; Ary, M.B.; Silva, C.P.; Carvalho, M.M.M.; Macedo, M.L.R.; Lemos, F.J.A.; Grant, G. Poor Correlation between the Levels of Proteinase Inhibitors Found in Seeds of Different Cultivars of Cowpea (Vigna unguiculata) and the Resistance/Susceptibility to Predation by Callosobruchus maculatus. J. Agric. Food Chem. 1989, 37, 1139–1143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Urbanek, H.; Kuzniak-Gebarowska, E.; Herka, K. Elicitation of defence responses in bean leaves by Botrytis cinerea polygalacturonase. Acta Physiol. Plant. 1991, 13, 43–50. [Google Scholar]
- Song, Y.Y.; Zeng, R.S.; Xu, J.F.; Li, J.; Shen, X. Interplant Communication of Tomato Plants through Underground Common Mycorrhizal. PLoS ONE 2010, 5, e13324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karpievitch, Y.V.; Polpitiya, A.D.; Anderson, G.A.; Smith, R.D.; Dabney, A.R. Liquid Chromatography Mass Spectrometry-Based Proteomics: Biological and Technological Aspects. Ann. Appl. Stat. 2010, 4, 1797. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Illera-Vives, M.; Seoane Labandeira, S.; Fernández-Labrada, M.; López-Mosquera, M.E. Agricultural Uses of Seaweed. In Sustainable Seaweed Technologies; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2020; pp. 591–612. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khotijah, S.; Irfan, M.; Muchdar, F. Nutritional Composition of Seaweed Kappaphycus alvarezii. Agrikan J. Agribisnis Perikan. 2020, 13, 139–146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, T.; Wang, Y.C.; Ma, J.; Cui, Y.; Wang, L. In silico discovery and anti-tumor bioactivities validation of an algal lectin from Kappaphycus alvarezii genome. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2024, 275, 133311. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hirayama, M.; Shibata, H.; Imamura, K.; Sakaguchi, T.; Hori, K. High-Mannose Specific Lectin and Its Recombinants from a Carrageenophyta Kappaphycus alvarezii Represent a Potent Anti-HIV Activity Through High-Affinity Binding to the Viral Envelope Glycoprotein gp120. Mar. Biotechnol. 2016, 18, 215–231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Das, D.; Arulkumar, A.; Paramasivam, S.; Lopez-Santamarina, A.; del Carmen Mondragon, A.; Miranda Lopez, J.M. Phytochemical Constituents, Antimicrobial Properties and Bioactivity of Marine Red Seaweed (Kappaphycus alvarezii) and Seagrass (Cymodocea serrulata). Foods 2023, 12, 2811. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yulianti, E.; Sunarti; Wahyuningsih, M.S.H. The effect of Kappaphycus alvarezii fraction on plasma glucose, Advanced Glycation End-products formation, and renal RAGE gene expression. Heliyon 2021, 7, e05978. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sit, N.W.; Chan, Y.S.; Lai, S.C.; Lim, L.N.; Looi, G.T.; Tay, P.L.; Tee, Y.T.; Woon, Y.Y.; Khoo, K.S.; Ong, H.C. In vitro antidermatophytic activity and cytotoxicity of extracts derived from medicinal plants and marine algae. J. Mycol. Med. 2018, 28, 561–567. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sousa, A.J.S.; Souza, P.F.N.; Gifoni, J.M.; Dias, L.P.; Freitas, C.D.T.; Oliveira, J.T.A.; Sousa, D.O.B.; Vasconcelos, I.M. Scanning electron microscopy reveals deleterious effects of Moringa oleifera seed exuded proteins on root-knot nematode Meloidogyne incognita eggs. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2020, 154, 1237–1244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mota, T.R.; Linhares, H.V.S.; Araújo-Filho, J.H.; Veras, D.M.; Costa, H.P.S.; Souza, C.M.P.; Souza, P.F.N.; Martins, T.F. Protein extract from Cereus jamacaru (DC.) inhibits Colletotrichum gloeosporioides growth by stimulating ROS generation and promoting severe cell membrane damage. Microb. Pathog. 2019, 130, 71–80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Etxaniz, A.; González-Bullón, D.; Martín, C.; Ostolaza, H. Membrane Repair Mechanisms against Permeabilization by Pore-Forming Toxins. Toxins 2018, 10, 234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lima, A.M.; Azevedo, M.I.G.; Sousa, L.M.; Oliveira, N.S.; Andrade, C.R.; Freitas, C.D.T.; Souza, P.F.N. Plant antimicrobial peptides: An overview about classification, toxicity and clinical applications. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2022, 214, 10–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lima, P.G.; Oliveira, J.T.A.; Amaral, J.L.; Freitas, C.D.T.; Souza, P.F.N. Synthetic antimicrobial peptides: Characteristics, design, and potential as alternative molecules to overcome microbial resistance. Life Sci. 2021, 278, 119647. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Souza, P.F.N.; Marques, L.S.M.; Oliveira, J.T.A.; Lima, P.G.; Dias, L.P.; Neto, N.A.S.; Lopes, F.E.S.; Sousa, J.S.; Silva, A.F.B.; Caneiro, R.F.; et al. Synthetic antimicrobial peptides: From choice of the best sequences to action mechanisms. Biochimie 2020, 175, 132–145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lockhart, S.R.; Chowdhary, A.; Gold, J.A.W.; Aspergillus, A. The rapid emergence of antifungal-resistant human-pathogenic fungi. Nat. Rev. Microbiol. 2023, 21, 818–832. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Taei, M.; Chadeganipour, M.; Mohammadi, R. An alarming rise of non-albicans Candida species and uncommon yeasts in the clinical samples; a combination of various molecular techniques for identification of etiologic agents. BMC Res. Notes 2019, 12, 779. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Berman, J.; Krysan, D.J. Drug resistance and tolerance in fungi. Nat. Rev. Microbiol. 2020, 18, 319–331. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kumar, M.; Brar, A.; Yadav, M.; Chawade, A.; Vivekanand, V.; Pareek, N. Chitinases—Potential Candidates for Enhanced Plant Resistance towards Fungal Pathogens. Agriculture 2018, 8, 88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Žiarovská, J.; Zamiešková, L.; Bilčíková, J.; Fialková, V.; Sabo, J.; Kunová, S.; Kačániová, M. Expression of Specific Class I Chitinase mRNA Levels in Different Grape Varieties and Their Antimicrobial Activity. Agronomy 2020, 10, 1176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stewart, G.G. The Structure and Function of the Yeast Cell Wall, Plasma Membrane and Periplasm. In Brewing and Distilling Yeasts; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2017; pp. 55–75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Freitas, C.D.T.; Silva, R.O.; Ramos, M.V.; Porfírio, C.T.M.N.; Farias, D.F.; Sousa, J.S.; Oliveira, J.P.B.; Souza, P.F.N.; Dias, L.P.; Grangeiro, T.B. Identification, characterization, and antifungal activity of cysteine peptidases from Calotropis procera latex. Phytochemistry 2020, 169, 112163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Díaz, M.E.; Rocha, G.F.; Kise, F.; Rosso, A.M.; Guevara, M.G.; Parisi, M.G. Antimicrobial activity of an aspartic protease from Salpichroa origanifolia fruits. Lett. Appl. Microbiol. 2018, 67, 168–174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guevara, M.G.; Oliva, C.R.; Huarte, M.; Daleo, G.R. An aspartic protease with antimicrobial activity is induced after infection and wounding in intercellular fluids of potato tubers. Eur. J. Plant Pathol. 2002, 108, 131–137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Torres-Ossandón, M.J.; Vega-Gálvez, A.; Salas, C.E.; Rubio, J.; Silva-Moreno, E.; Castillo, L. Antifungal activity of proteolytic fraction (P1G10) from (Vasconcellea cundinamarcensis) latex inhibit cell growth and cell wall integrity in Botrytis cinerea. Int. J. Food Microbiol. 2019, 289, 7–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rashed, N.A.; MacDonald, M.H.; Matthews, B.F. Protease Inhibitor Expression in Soybean Roots Exhibiting Susceptible and Resistant Interactions with Soybean Cyst Nematode. J. Nematol. 2008, 40, 138. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Zhang, H.; Mao, J.; Liu, F.; Zeng, F. Expression of a nematode symbiotic bacterium-derived protease inhibitor protein in tobacco enhanced tolerance against Myzus persicae. Plant Cell Rep. 2012, 31, 1981–1989. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Araújo, N.M.S.; Dias, L.P.; Costa, H.P.S.; Sousa, D.O.B.; Vasconcelos, I.M.; de Morais, G.A.; Oliveira, J.T.A. ClTI, a Kunitz trypsin inhibitor purified from Cassia leiandra Benth. seeds, exerts a candidicidal effect on Candida albicans by inducing oxidative stress and necrosis. Biochim. Biophys. Acta Biomembr. 2019, 1861, 183032. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Melo, I.R.S.; Dias, L.P.; Araújo, N.M.S.; Vasconcelos, I.M.; Martins, T.F.; de Morais, G.A.; Gonçalves, J.F.C.; Nagano, C.S.; Carneiro, R.F.; Oliveira, J.T.A. ClCPI, a cysteine protease inhibitor purified from Cassia leiandra seeds has antifungal activity against Candida tropicalis by inducing disruption of the cell surface. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2019, 133, 1115–1124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]




| Protein Extracts | mgP |
|---|---|
| Water | 1.35 ± 0.070 |
| 0.15 M NaCl | 1.87 ± 0.009 |
| Sodium acetate pH 5.2 | 1.21 ± 0.002 |
| Sodium phosphate pH 6.5 | 1.67 ± 0.018 |
| Tris-HCl pH 7.5 | 1.76 ± 0.057 |
| Tris-HCl pH 8.5 | 2.15 ± 0.005 |
| Glycine-HCl pH 2.3 | 0.53 ± 0.007 |
| Glycine-HCl pH 10.0 | 2.55 ± 0.025 |
| Protein Activity | Units a |
|---|---|
| Proteolytic (UA mg−1 of protein min−1) | 581.70 ± 2.405 |
| β-1,3-glucanase (ƞkatal mg−1 of protein) | 0.35 ± 0.007 |
| Chitinase (ƞkatal mg−1 of protein) | 0.52 ± 0.012 |
| Serine protease inhibitor activity (UI mg−1 of protein) | 250.30 ± 2.314 |
| Cysteine protease inhibitor activity (UI mg−1 of protein) | 171.70 ± 0.723 |
| Superoxide Dismutase (UI mg−1 of protein) | 50.12 ± 0.101 |
| Catalase (UI mg−1 of protein) | 25.45 ± 0.001 |
| Ascorbate Peroxidase (UI mg−1 of protein) | 38.15 ± 0.005 |
| Guaiacol Peroxidase (UA mg−1 of protein) | 10.14 ± 0.002 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Souza, P.F.N.; Lima, P.G.; Filho, N.S.d.S.; Mororó, J.L.T.; Gomes, F.I.R.; de Oliveira, A.V.C.; Malagueta, G.B.; Soares, B.M.; da Silva, E.L.; Castelo-Branco, D.d.S.C.M.; et al. Proteins from Kappaphycus alvarezii: Identification by Mass Spectrometry and Antifungal Potential. Processes 2025, 13, 1569. https://doi.org/10.3390/pr13051569
Souza PFN, Lima PG, Filho NSdS, Mororó JLT, Gomes FIR, de Oliveira AVC, Malagueta GB, Soares BM, da Silva EL, Castelo-Branco DdSCM, et al. Proteins from Kappaphycus alvarezii: Identification by Mass Spectrometry and Antifungal Potential. Processes. 2025; 13(5):1569. https://doi.org/10.3390/pr13051569
Chicago/Turabian StyleSouza, Pedro Filho Noronha, Patrícia Gomes Lima, Nicholas Silva dos Santos Filho, João Lucas Timbó Mororó, Francisco Italo Rodrigues Gomes, Amanda Vitória Carmo de Oliveira, Guilherme Barbosa Malagueta, Bruno Moreira Soares, Emerson Lucena da Silva, Débora de Souza Collares Maia Castelo-Branco, and et al. 2025. "Proteins from Kappaphycus alvarezii: Identification by Mass Spectrometry and Antifungal Potential" Processes 13, no. 5: 1569. https://doi.org/10.3390/pr13051569
APA StyleSouza, P. F. N., Lima, P. G., Filho, N. S. d. S., Mororó, J. L. T., Gomes, F. I. R., de Oliveira, A. V. C., Malagueta, G. B., Soares, B. M., da Silva, E. L., Castelo-Branco, D. d. S. C. M., Filho, J. H. d. A., Nunes, J. V. S., Montenegro, R. C., & Mesquita, F. P. (2025). Proteins from Kappaphycus alvarezii: Identification by Mass Spectrometry and Antifungal Potential. Processes, 13(5), 1569. https://doi.org/10.3390/pr13051569






