Mitigation Effect of Low-Accumulation Rice Varieties and Soil Conditioners on Hg and Cd Pollution in Rice
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Experimental Site and Characterization
2.2. Plot Experiment
2.3. Sample Collection and Preservation
2.4. Analysis of Rice and Soil
2.4.1. Heavy Metal Content of Rice
2.4.2. Soil Physicochemical Characteristics
2.5. Assessment of Health Risk Reduction
2.5.1. Bio-Concentration Factor (BCF)
2.5.2. Health Risk Reduction
2.6. Data Analysis
3. Results
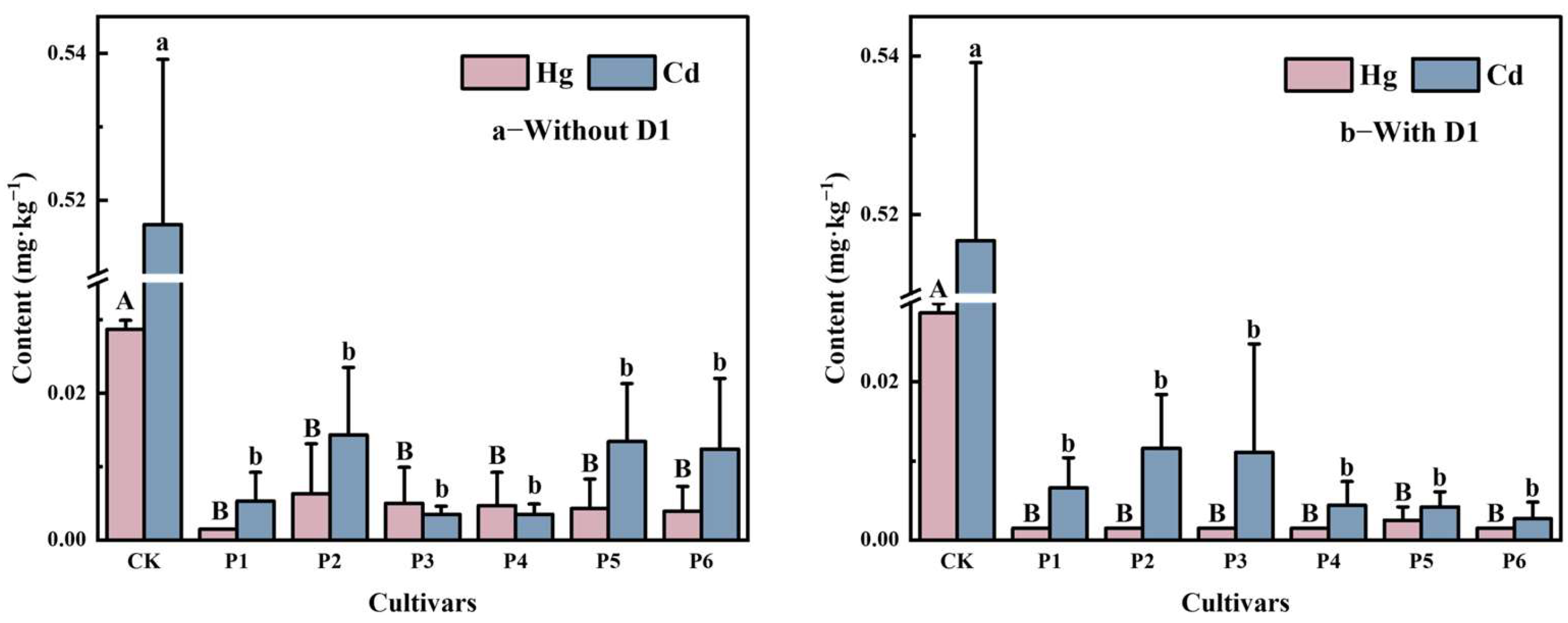
3.1. Effects of Different Varieties on the Accumulation of Heavy Metal in Rice
3.2. Effect of Application of Soil Conditioners on Heavy Metal Level and Soil Quality in Rice
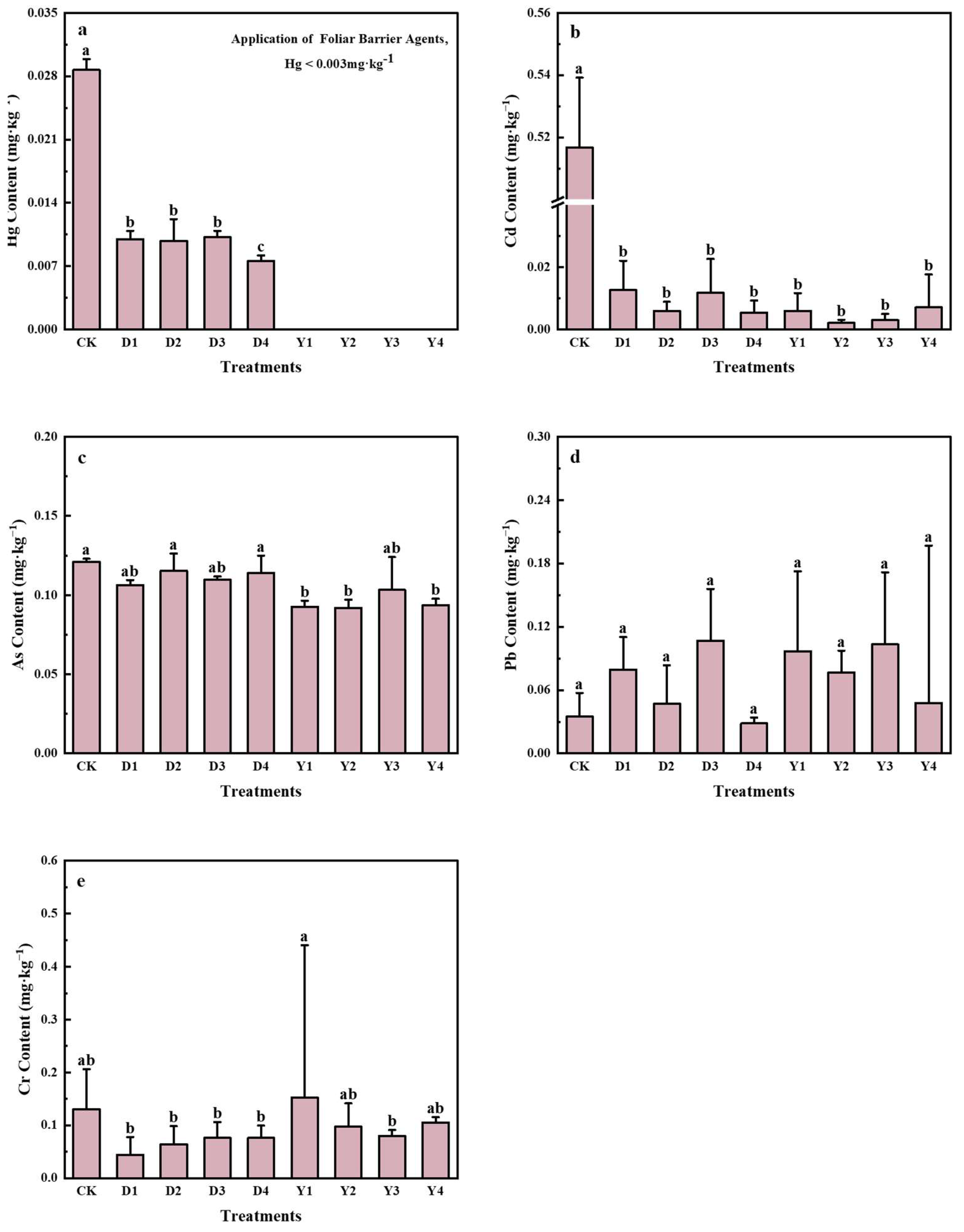
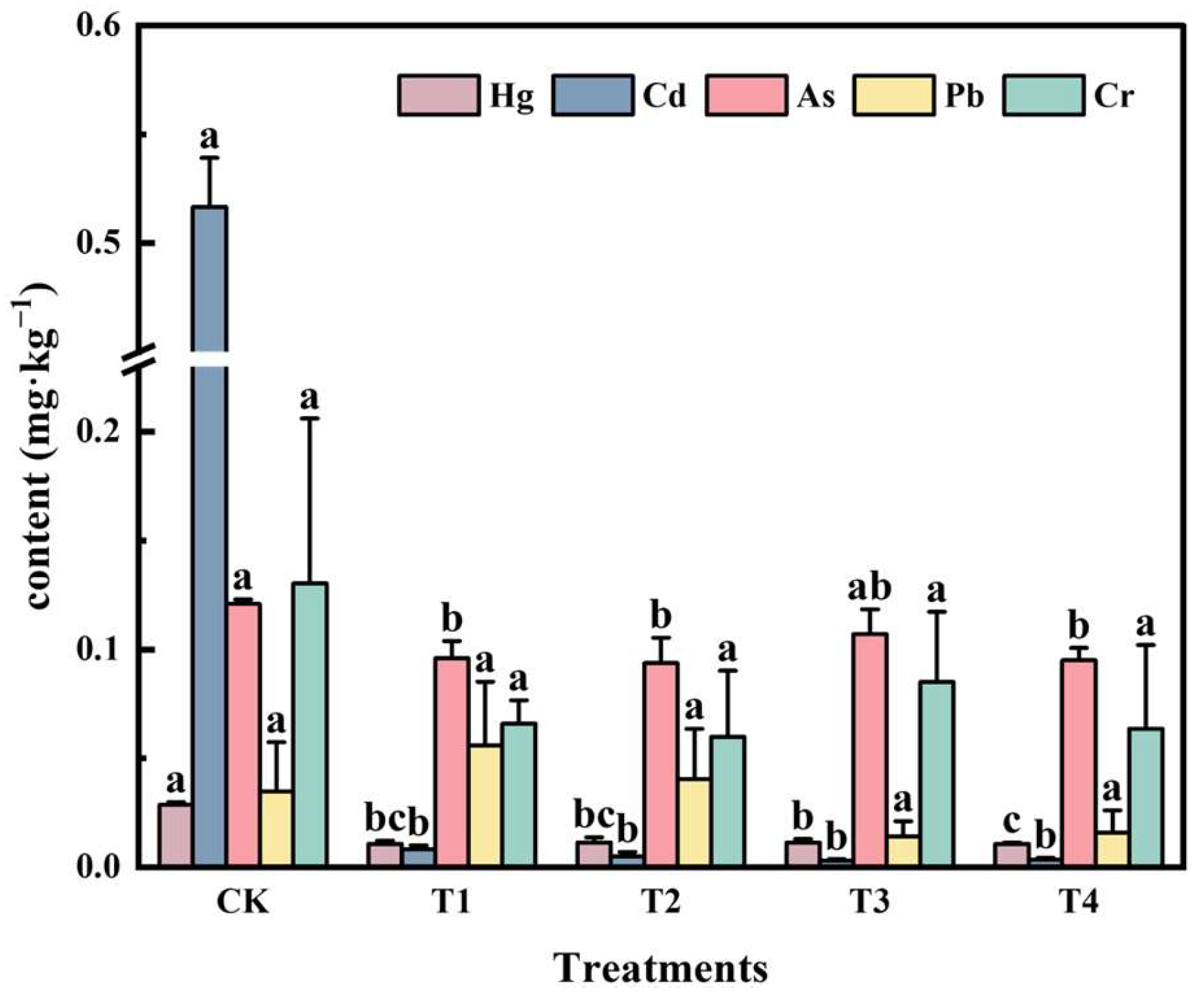
3.2.1. Impact of Conditioners on the Field Experiment’s Heavy Metal Level of Longliangyouhuanglizhan
3.2.2. Impact of Conditioners on Available Hg and Cd Content
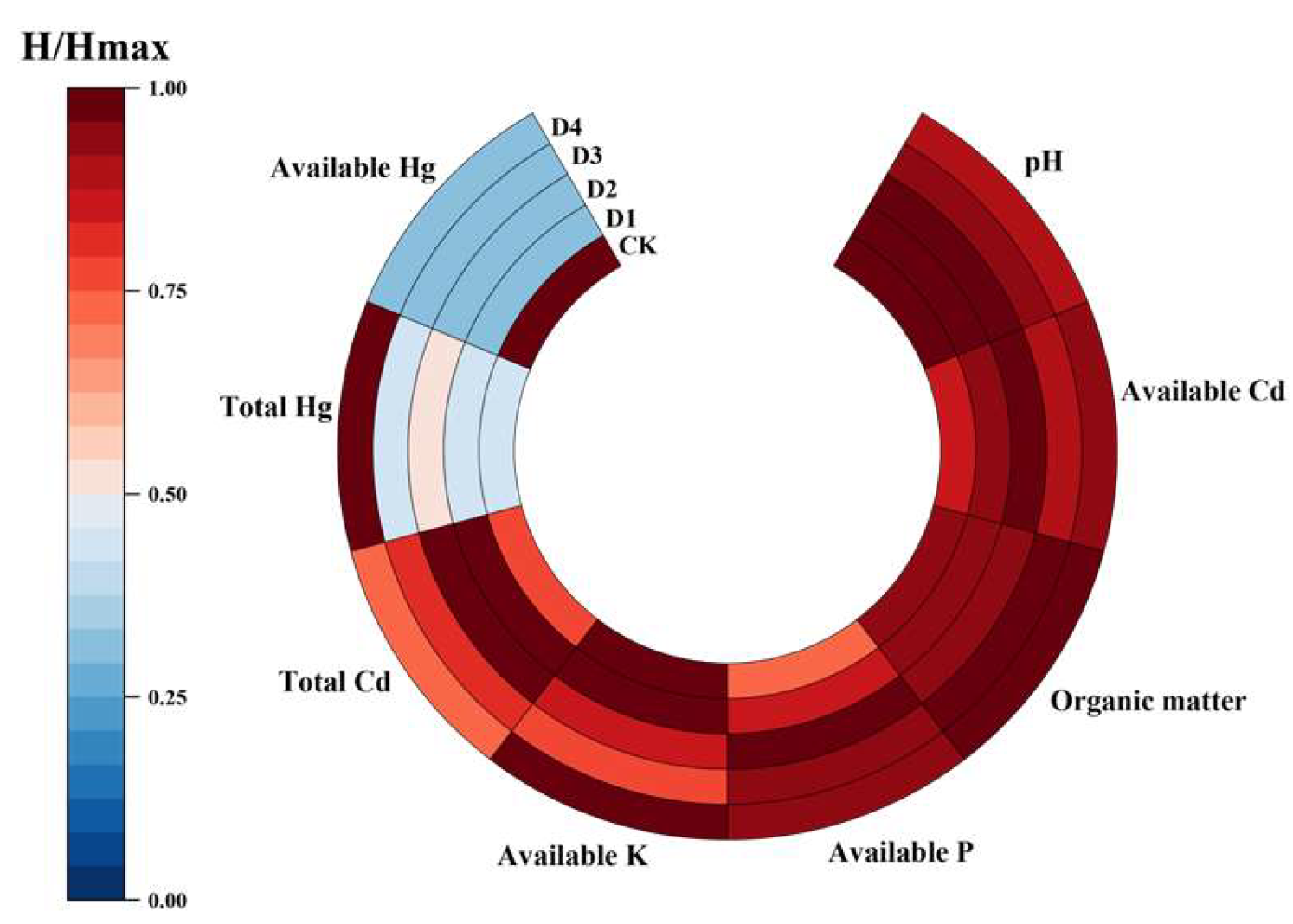
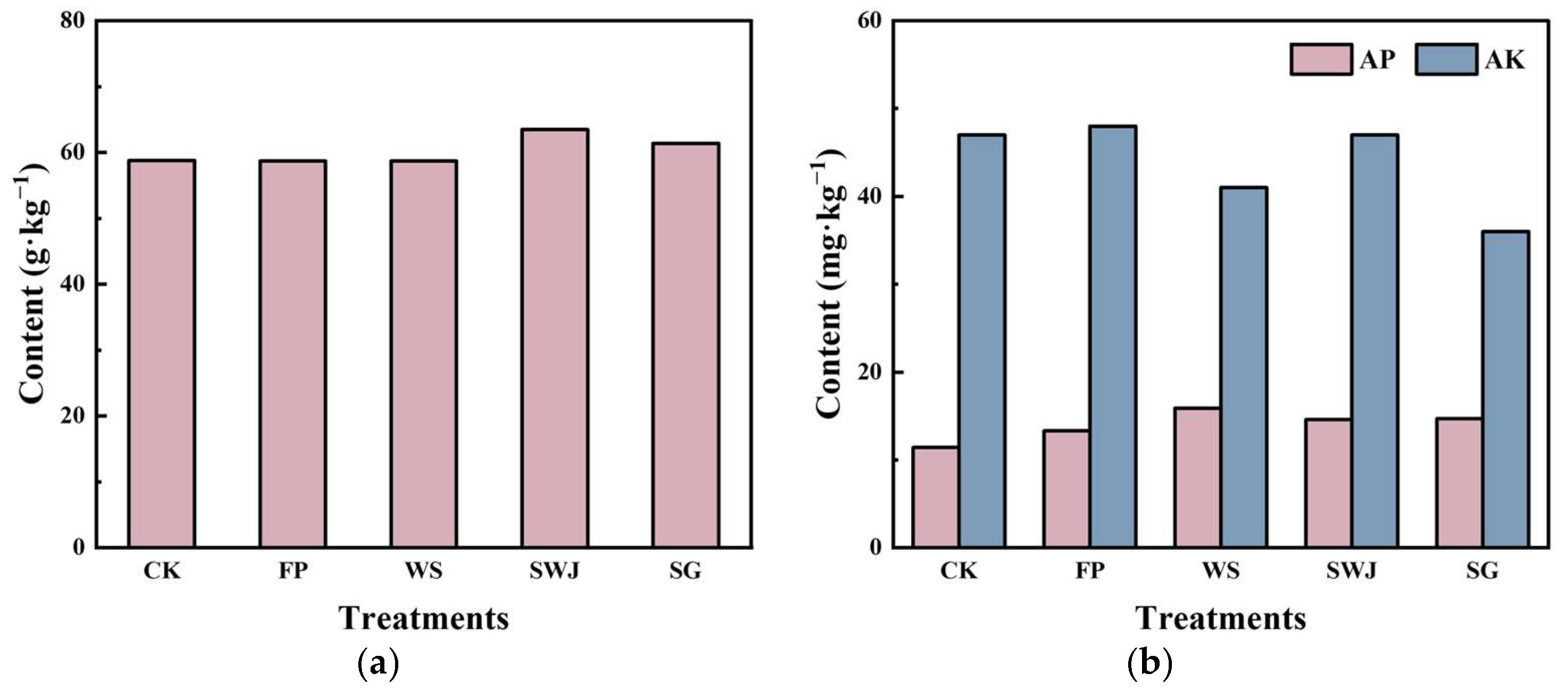
3.2.3. Impact of Conditioners on Soil Physicochemical Characteristics
3.2.4. Effect of Conditioner Content on Heavy Metal Content in Rice
3.3. Effects of Conditioners on Enrichment Differences in Heavy Metal Uptake and Health Risks in Rice
3.3.1. Effect of Application of Different Soil Conditioners on Bio-Concentration Factor
3.3.2. Impact of Soil Conditioners on Reducing Health Risks
3.3.3. Economic Analysis of Conditioner Applications
4. Discussion
4.1. Effect of Different Cultivars on the Accumulation of Hg and Cd in Rice
4.2. Adsorption Mechanism of Soil Heavy Metals Hg-Cd
4.3. Effect of Conditioners on Soil Quality
4.4. Effects of Conditioning Agents on Bio-Concentration Factor and Health Risks
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| Hg | Mercury |
| Cd | Cadmium |
| As | Arsenic |
| Pb | Lead |
| Cr | Chromium |
| Se | Selenium |
| OM | Organic Matter |
| AP | Available Phosphorus |
| AK | Available Potassium |
References
- Xiang, S.; Zheng, Y.; Zhou, Q.; Jin, M.; Fu, L.; Wu, W. nZVI/BC as a Soil Amendment and Its Effects on Potted Rice Growth and Soil Properties. Agronomy 2024, 14, 1710. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yoon, D.-H.; Choi, W.S.; Hong, Y.K.; Lee, Y.B.; Kim, S.C. Effect of chemical amendments on reduction of bioavailable heavy metals and ecotoxicity in soil. Appl. Biol. Chem. 2019, 62, 53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, T.; Gao, G.; Yang, W.; Sun, Y.; Huang, Q.; Wang, L.; Liang, X. High-efficiency remediation of Hg and Cd co-contaminated paddy soils by Fe–Mn oxide modified biochar and its microbial community responses. Biochar 2024, 6, 57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moutcine, A.; Laghlimi, C.; Ziat, Y.; Smaini, M.A.; Qouatli, S.E.E.; Hammi, M.; Chtaini, A. Preparation, characterization and simultaneous electrochemical detection toward Cd (II) and Hg(II) of a phosphate/zinc oxide modified carbon paste electrode. Inorg. Chem. Commun. 2020, 116, 107911. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peera Sheikh Kulsum, P.G.; Khanam, R.; Das, S.; Nayak, A.K.; Tack, F.M.G.; Meers, E.; Vithanage, M.; Shahid, M.; Kumar, A.; Chakraborty, S.; et al. A state-of-the-art review on cadmium uptake, toxicity, and tolerance in rice: From physiological response to remediation process. Environ. Res. 2023, 220, 115098. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Riyazuddin, R.; Nisha, N.; Ejaz, B.; Khan, M.I.R.; Kumar, M.; Ramteke, P.W.; Gupta, R. A Comprehensive Review on the Heavy Metal Toxicity and Sequestration in Plants. Biomolecules 2021, 12, 43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Genchi, G.; Sinicropi, M.S.; Lauria, G.; Carocci, A.; Catalano, A. The Effects of Cadmium Toxicity. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2020, 17, 3782. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Spiller, H.A.; Hays, H.L.; Casavant, M.J. Rethinking treatment of mercury poisoning: The roles of selenium, acetylcysteine, and thiol chelators in the treatment of mercury poisoning: A narrative review. Toxicol. Commun. 2021, 5, 19–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, L.; Wu, W.; Han, F.; Li, J.; Ye, W.; Fu, H.; Yan, Y.; Ma, Y.; Wang, Q. Agronomic Management and Rice Varieties Controlling Cd Bioaccumulation in Rice. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2019, 16, 2376. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiao, A.; Chi, Y.; Huang, L.; Li, W.C.; Ye, Z. Effects of cultivar, water condition and their interactions on Cd accumulation in rice grains. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2023, 262, 115168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ding, Y.; Di, X.; Norton, G.J.; Beesley, L.; Yin, X.; Zhang, Z.; Zhi, S. Selenite Foliar Application Alleviates Arsenic Uptake, Accumulation, Migration and Increases Photosynthesis of Different Upland Rice Varieties. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2020, 17, 3621. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Senila, M.; Cadar, O.; Senila, L.; Angyus, B.S. Simulated Bioavailability of Heavy Metals (Cd, Cr, Cu, Pb, Zn) in Contaminated Soil Amended with Natural Zeolite Using Diffusive Gradients in Thin-Films (DGT) Technique. Agriculture 2022, 12, 321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, Q.; Ji, J.; Tang, X.; Wang, C.; Sun, H. Bioavailability Assessment of Heavy Metals and Organic Pollutants in Water and Soil Using DGT: A Review. Appl. Sci. 2023, 13, 9760. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hseu, Z.-Y.; Su, S.-W.; Lai, H.-Y.; Guo, H.-Y.; Chen, T.-C.; Chen, Z.-S. Remediation techniques and heavy metal uptake by different rice varieties in metal-contaminated soils of Taiwan: New aspects for food safety regulation and sustainable agriculture. Soil Sci. Plant Nutr. 2010, 56, 31–52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiao, R.; Huang, Z.; Li, X.; Chen, W.; Deng, Y.; Han, C. Lime and Phosphate Amendment Can Significantly Reduce Uptake of Cd and Pb by Field-Grown Rice. Sustainability 2017, 9, 430. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmad, M.; Lee, S.S.; Lee, S.E.; Al-Wabel, M.I.; Tsang, D.C.W.; Ok, Y.S. Biochar-induced changes in soil properties affected immobilization/mobilization of metals/metalloids in contaminated soils. J. Soils Sediments 2017, 17, 717–730. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, L.-L.; Huang, D.-Y.; Zhang, Q.; Zhu, H.-H.; Xu, C.; Li, B.; Zhu, Q.-H. Meta-analysis of the effects of liming on soil pH and cadmium accumulation in crops. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2021, 223, 112621. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jin, Y. Dynamic response of cadmium immobilization to a Ca-Mg-Si soil conditioner in the contaminated paddy soil. Sci. Total Environ. 2024, 908, 168394. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, T.; Duan, L.; Cheng, S.; Jiang, S.; Yan, B. The preparation of paddy soil amendment using granite and marble waste: Performance and mechanisms. J. Environ. Sci. 2023, 127, 564–576. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, J.; Wang, C.; Wang, Z.; Yang, S.; Li, P. Mercury concentration and speciation in mine wastes in Tongren mercury mining area, southwest China and environmental effects. Appl. Geochem. 2019, 106, 112–119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- GB15618-2018; National Standard Soil Environmental Quality Risk Control Standard for Soil Contamination of Agricultural Land. Ministry of Ecology and Environment (MEE): Beijing, China, 2018.
- Kong, X.; Liu, T.; Yu, Z.; Chen, Z.; Lei, D.; Wang, Z.; Zhang, H.; Li, Q.; Zhang, S. Heavy Metal Bioaccumulation in Rice from a High Geological Background Area in Guizhou Province, China. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2018, 15, 2281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.-Y.; You, L.-C.; Lyu, H.-H.; Liu, Y.-X.; He, L.-L.; Hu, Y.-D.; Luo, F.-C.; Yang, S.-M. Role of biochar–mineral composite amendment on the immobilization of heavy metals for Brassica chinensis from naturally contaminated soil. Environ. Technol. Innov. 2022, 28, 102622. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, S.; Wang, L.; Gao, J.; Zhou, B.; Hao, W.; Feng, D.; Sun, X. Effect of biochar on biochemical properties of saline soil and growth of rice. Heliyon 2024, 10, e23859. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, T.; Wang, G.; Yin, Q.; Zhou, Z.; Deng, N. Sulfur/zinc co-doped biochar for stabilization remediation of mercury-contaminated soil: Performance, mechanism and ecological risk. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2024, 281, 116601. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lyu, H.-H.; Cheng, K.; He, L.-L.; Yang, S.-M.; Liu, Y.-X.; You, L.-C.; Wang, Y.-Y. Efficiency of talcum-biochars in immobilization of heavy metals and promotion of the growth of Brassica chinensis in contaminated agricultural soil. Plant Stress 2025, 16, 100836. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wan, X.; Lei, M.; Yang, J.; Chen, T. Three-year field experiment on the risk reduction, environmental merit, and cost assessment of four in situ remediation technologies for metal(loid)-contaminated agricultural soil. Environ. Pollut. 2020, 266, 115193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, Y.; Li, D.; Xiao, D.; Xiang, Z.; Yang, X.; Xiao, Y.; Xiao, X.; Cheng, J.; Lu, Q.; Zhang, Q. Co-exposure of heavy metals in rice and corn reveals a probabilistic health risk in Guizhou Province, China. Food Chem. X 2023, 20, 101043. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, G.; Chen, F.; Zhang, H.; Wang, Z. Pollution and health risk assessment of heavy metals in soils of Guizhou, China. Ecosyst. Health Sustain. 2021, 7, 1859948. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- United States Environmental Protection Agency (USEPA). Exposure Factors Handbook; United States Environmental Protection Agency: Washington, DC, USA, 2011. [Google Scholar]
- Jiang, Y.; Chao, S.; Liu, J.; Yang, Y.; Chen, Y.; Zhang, A.; Cao, H. Source apportionment and health risk assessment of heavy metals in soil for a township in Jiangsu Province, China. Chemosphere 2017, 168, 1658–1668. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- GB 2762-2022; National Food Safety Standard for Maximum Levels of Contaminants in Foods. NHC/SAMR: Beijing, China, 2022.
- Zhang, H.; Feng, X.; Larssen, T.; Shang, L.; Li, P. Bioaccumulation of Methylmercury versus Inorganic Mercury in Rice (Oryza sativa L.) Grain. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2010, 44, 4499–4504. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, W.; Xu, B.; Song, Q.; Liu, X.; Xu, J.; Brookes, P.C. The identification of ‘hotspots’ of heavy metal pollution in soil–rice systems at a regional scale in eastern China. Sci. Total Environ. 2014, 472, 407–420. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, H.; Zeng, M.; Zhou, X.; Liao, B.-H.; Peng, P.-Q.; Hu, M.; Zhu, W.; Wu, Y.-J.; Zou, Z.-J. Heavy metal translocation and accumulation in iron plaques and plant tissues for 32 hybrid rice (Oryza sativa L.) cultivars. Plant Soil 2015, 386, 317–329. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, M.; Zhu, W.; Hong, L.; Wang, W.; Yao, Y.; Zhu, F.; Hong, C.; He, S. Assessing Pb-Cr Pollution Thresholds for Ecological Risk and Potential Health Risk in Selected Several Kinds of Rice. Toxics 2022, 10, 645. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Powell, K.J.; Brown, P.L.; Byrne, R.H.; Gajda, T.; Hefter, G.; Sjöberg, S.; Wanner, H. Chemical Speciation of Hg(II) with Environmental Inorganic Ligands. Aust. J. Chem. 2004, 57, 993. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tran, T.A.T.; Dinh, Q.T.; Zhou, F.; Zhai, H.; Xue, M.; Du, Z.; Bañuelos, G.S.; Liang, D. Mechanisms underlying mercury detoxification in soil–plant systems after selenium application: A review. Env. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2021, 28, 46852–46876. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Björnberg, A.; Håkanson, L.; Lundbergh, K. A theory on the mechanisms regulating the bioavailability of mercury in natural waters. Environ. Pollut. 1988, 49, 53–61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Syversen, T.; Kaur, P. The toxicology of mercury and its compounds. J. Trace Elem. Med. Biol. 2012, 26, 215–226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, Y.; Wong, J.W.C.; Wei, L. Silicon-mediated enhancement of cadmium tolerance in maize (Zea mays L.) grown in cadmium contaminated soil. Chemosphere 2005, 58, 475–483. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiao, Z.; Peng, M.; Mei, Y.; Tan, L.; Liang, Y. Effect of organosilicone and mineral silicon fertilizers on chemical forms of cadmium and lead in soil and their accumulation in rice. Environ. Pollut. 2021, 283, 117107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, J.; Lu, H.; Qin, S.; Pan, P.; Tang, S.; Chen, L.; Wang, X.; Tang, F.; Tan, Z.; Wen, R.; et al. Soil conditioners improve Cd-contaminated farmland soil microbial communities to inhibit Cd accumulation in rice. J. Integr. Agric. 2023, 22, 2521–2535. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yin, K.; Wang, Q.; Lv, M.; Chen, L. Microorganism remediation strategies towards heavy metals. Chem. Eng. J. 2019, 360, 1553–1563. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, K.; Fang, L.; Li, F.; Hou, D.; Liu, C.; Song, Y.; Ran, Q.; Pang, Y.; Du, Y.; Yuan, Y.; et al. Sustainability assessment and carbon budget of chemical stabilization based multi-objective remediation of Cd contaminated paddy field. Sci. Total Environ. 2022, 819, 152022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raza, T.; Qadir, M.F.; Khan, K.S.; Eash, N.S.; Yousuf, M.; Chatterjee, S.; Manzoor, R.; Rehman, S.U.; Oetting, J.N. Unraveling the potential of microbes in decomposition of organic matter and release of carbon in the ecosystem. J. Environ. Manag. 2023, 344, 118529. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Su, J.; Weng, X.; Luo, Z.; Huang, H.; Wang, W. Impact of Biochar on Soil Properties, Pore Water Properties, and Available Cadmium. Bull. Env. Contam. Toxicol. 2021, 107, 544–552. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, J.; Jin, X.; Wang, X.C.; Jin, P. Preferential binding properties of carboxyl and hydroxyl groups with aluminium salts for humic acid removal. Chemosphere 2019, 234, 478–487. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schaller, J.; Faucherre, S.; Joss, H.; Obst, M.; Goeckede, M.; Planer-Friedrich, B.; Peiffer, S.; Gilfedder, B.; Elberling, B. Silicon increases the phosphorus availability of Arctic soils. Sci. Rep. 2019, 9, 449. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.; Mu, G.; Zhang, Z.; Huang, X.; Fang, H. Speciation Variation and Bio-Activation of Soil Heavy Metals (Cd and Cr) in Rice-Rape Rotation Lands in Karst Regions. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2021, 18, 1364. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mu, Y.; Cui, J.; Liu, A.; Wang, S.; Shi, Q.; Wang, J.; Wei, S.; Zhang, J. Interactions and quantification of multiple influencing factors on cadmium accumulation in soil-rice systems at a large region. Sci. Total Environ. 2023, 881, 163392. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]



| Experimental Field | Test Setup | pH | Organic Matter (g·kg−1) | AP (mg·kg−1) | AK (mg·kg−1) | Total Hg (mg·kg−1) | Total Cd (mg·kg−1) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | Conditioner Type Screening | 7.74 | 69.7 | 11.4 | 47 | 12.6 | 3.01 |
| 2 | Screening of application concentrations | 8.29 | 53.4 | 20.8 | 53 | 11.6 | 5.41 |
| 3 | Combination process, soil conditioner + foliar retardant | 7.97 | 71.6 | 11.4 | 47 | 12.1 | 4.94 |
| Treatments | Soil Conditioner Ingredients | Application Rate | Cost | Note |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CK | / | / | / | / |
| D1 | CaO ≥ 20.0% MgO ≥ 12.0% SiO2 ≥ 12.0% Se: 40~60 mg·kg−1 S: 150~200 mg·kg−1 pH = 10–12 | 150 kg/mu | 1350 yuan·t−1 | The precursor of the composite conditioning agent was synthesized using gabbro slag and silicate materials as raw materials, and sodium selenite and zinc sulfate monohydrate were subsequently blended and added to this base. |
| D2 | CaO ≥ 20.0% MgO ≥ 12.0% SiO2 ≥ 12.0% pH = 10.0–12.0 | 150 kg/mu | 1380 yuan·t−1 | / |
| D3 | Microbial agent | 1 kg/mu D3 + 15 kg/mu Nitrogen-phosphate-potassium fertilizers | 50,000 yuan·t−1 | / |
| D4 | CaO ≥ 30% SiO2 ≥ 20% MgO ≥ 5% pH = 9–11 Se = 10–30 mg·kg−1 | 15 kg/mu | 2200 yuan·t−1 | The raw materials used were quicklime, wollastonite, perlite, and zeolite. |
| Foliar Barrier Agents | Silicon powder + Microorganisms | 750 g/mu | 50,000 yuan·t−1 | Silica micro-powder is primarily composed of silicon elements and is typically derived from silicon-containing minerals such as wollastonite and quartz. The main component of its composition is silicon dioxide (SiO2). |
| Serial Number | Rice Variety | Variety Type | Number | Whole Growth Period (Day) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CK | Yuxiang203 | Indica Three-line Hybrid Rice | Nationally Approved Rice Variety 2,010,006 | 156.8 |
| P1 | Longliangyouhuanglizhan | Indica Two-line Hybrid Rice | Nationally Approved Rice Variety 20,176,002 | 155.3 |
| P2 | Jingliangyouhuazhan | Indica Two-line Hybrid Rice | Jiangxi Approved Rice Variety 2,016,007 | 129.3 |
| P3 | Jingliangyou7818 | Indica Two-line Hybrid Rice | Nationally Approved Rice Variety 20,196,054 | 136.3 |
| P4 | Longliangyou1988 | Indica Two-line Hybrid Rice | Nationally Approved Rice Variety 2,016,609 | 138.6 |
| P5 | Yixiangyou62 | Indica Two-line Hybrid Rice | Guizhou Approved Rice Variety 20,180,022 | 152.4 |
| P6 | Yixiangyou800 | Indica Two-line Hybrid Rice | Guizhou Approved Rice Variety 2,014,007 | 156 |
| Rice Cultivars | Standard Limit mg·kg−1 | Rice Seed mg·kg−1 | Soil Samples mg·kg−1 |
|---|---|---|---|
| Longliangyouhuanglizhan (P1) | GB2762-2017 (National food safety standard Contamination Limit in Food) polished rice 0.02 mg·kg−1 | ≤0.02 | 17.9 |
| Jingliangyouhuazhan (P2) | ≤0.02 | 21.4 |
| Number | Treatment | Application | Replicates | Description |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CK | None | / | 3 | Control group, no amendment applied |
| D1 | Fupei conditioner | 150 kg/mu | 3 | Soil conditioner type applied |
| D2 | Wansan conditioner | 150 kg/mu | 3 | Soil conditioner type applied |
| D3 | Shengwujun conditioner | 1 kg/mu+15 kg/mu Nitrogen-phosphate-potassium fertilizers | 3 | Soil conditioner type applied |
| D4 | Shigou conditioner | 150 kg/mu | 3 | Soil conditioner type applied |
| Y1 | Fupei conditioner + Foliar Barrier Agents | 150 kg/mu (Fupei conditioner) + 750 g/mu Foliar Barrier Agents | 3 | Soil conditioner and Foliar Barrier Agents applied |
| Y2 | Wansan conditioner + Foliar Barrier Agents | 150 kg/mu (Wansan conditioner) + 750 g/mu Foliar Barrier Agents | 3 | Soil conditioner and Foliar Barrier Agents applied |
| Y3 | Shengwujun conditioner + Foliar Barrier Agents | 1 kg/mu + 15 kg/mu Nitrogen-phosphate-potassium fertilizers + 750 g/mu Foliar Barrier Agents | 3 | Soil conditioner and Foliar Barrier Agents applied |
| Y4 | Shigou conditioner + Foliar Barrier Agents | 150 kg/mu (Shigou conditioner) + 750 g/mu Foliar Barrier Agents | 3 | Soil conditioner and Foliar Barrier Agents applied |
| P1 | Longliangyouhuanglizhan | / | 3 | Screening of rice varieties |
| P2 | Jingliangyouhuazhan | / | 3 | Screening of rice varieties |
| P3 | Jingliangyou 7818 | / | 3 | Screening of rice varieties |
| P4 | Longliangyou 1988 | / | 3 | Screening of rice varieties |
| P5 | Yixiangyou 62 | / | 3 | Screening of rice varieties |
| P6 | Yixiangyou 800 | / | 3 | Screening of rice varieties |
| T1 | 50 kg/mu | 50 kg/mu | 3 | Screening of soil conditioner concentrations |
| T2 | 100 kg/mu | 100 kg/mu | 3 | Screening of soil conditioner concentrations |
| T3 | 150 kg/mu | 150 kg/mu | 3 | Screening of soil conditioner concentrations |
| T4 | 300 kg/mu | 300 kg/mu | 3 | Screening of soil conditioner concentrations |
| Parameter | Symbol | Units | Value | References |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Body weight | BW | kg | 60.6 | [29] |
| Exposure duration | ED | a | 24 | [30] |
| Exposure frequency | EF | d·a−1 | 350 | [30] |
| Life expectancy | LE | d | 74.8 × 365 | [29] |
| Reference dose | RfD (Hg) | mg·(kg·d)−1 | 3.00 × 10−4 | [30,31] |
| RfD (Cd) | 1.00 × 10−3 | |||
| RfD (As) | 3.00 × 10−4 | |||
| RfD (Pb) | 3.50 × 10−3 | |||
| RfD (Cr) | 3.00 × 10−3 |
| Rice Varieties | No D1 Applied | Application of Conditioner D1 | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| As mg·kg−1 | Cr mg·kg−1 | Pb mg·kg−1 | As mg·kg−1 | Cr mg·kg−1 | Pb mg·kg−1 | |
| CK | 0.1210 ± 0.002 a | 0.1304 ± 0.0758 a | 0.0349 ± 0.0225 a | 0.1210 ± 0.002 a | 0.1304 ± 0.0758 a | 0.0349 ± 0.0225 a |
| P1 | 0.0948 ± 0.0141 b | 0.1470 ± 0.0086 a | 0.1028 ± 0.0677 a | 0.1030 ± 0.0075 a | 0.1071 ± 0.0180 a | 0.1174 ± 0.0971 a |
| P2 | 0.0979 ± 0.0082 b | 0.0910 ± 0.0474 a | 0.1306 ± 0.0556 a | 0.1233 ± 0.0087 a | 0.0706 ± 0.0220 a | 0.1261 ± 0.0948 a |
| P3 | 0.0895 ± 0.0073 b | 0.0877 ± 0.0444 a | 0.0347 ± 0.0078 a | 0.1227 ± 0.0214 a | 0.1443 ± 0.0354 a | 0.1069 ± 0.1528 a |
| P4 | 0.1049 ± 0.0098 ab | 0.1015 ± 0.0196 a | 0.0529 ± 0.0268 a | 0.1110 ± 0.0203 a | 0.1133 ± 0.0591 a | 0.0667 ± 0.0366 a |
| P5 | 0.1000 ± 0.0101 ab | 0.2740 ± 0.2044 a | 0.1336 ± 0.0593 a | 0.0983 ± 0.0110 a | 0.0975 ± 0.0320 a | 0.0780 ± 0.0351 a |
| P6 | 0.0968 ± 0.0049 b | 0.2853 ± 0.2087 a | 0.0934 ± 0.0520 a | 0.1003 ± 0.0172 a | 0.0807 ± 0.0367 a | 0.0594 ± 0.0172 a |
| Treatments | Hg | Cd | As | Pb | Cr | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| EDI | RI | EDI | RI | EDI | RI | EDI | RI | EDI | RI | |
| CK | 5.67 × 10−5 | 0.1889 | 1.02 × 10−3 | 1.0205 | 2.39 × 10−4 | 0.7966 | 6.89 × 10−5 | 0.0197 | 2.58 × 10−4 | 0.0858 |
| D1 | 1.97 × 10−5 | 0.0658 | 2.51 × 10−5 | 0.0251 | 2.10 × 10−4 | 0.6998 | 1.57 × 10−4 | 0.0448 | 8.75 × 10−5 | 0.0292 |
| D2 | 1.94 × 10−5 | 0.0645 | 1.18 × 10−5 | 0.0118 | 2.28 × 10−4 | 0.7590 | 9.28 × 10−5 | 0.0265 | 1.27 × 10−4 | 0.0422 |
| D3 | 2.01 × 10−5 | 0.0671 | 2.33 × 10−5 | 0.0233 | 2.17 × 10−4 | 0.7222 | 2.11 × 10−4 | 0.0603 | 1.50 × 10−4 | 0.0500 |
| D4 | 1.50 × 10−5 | 0.0500 | 1.07 × 10−5 | 0.0107 | 2.25 × 10−4 | 0.7505 | 5.61 × 10−5 | 0.0160 | 1.50 × 10−4 | 0.0501 |
| Y1 | 2.96 × 10−6 | 0.0099 | 1.18 × 10−5 | 0.0118 | 1.83 × 10−4 | 0.6103 | 1.91 × 10−4 | 0.0546 | 3.01 × 10−4 | 0.1004 |
| Y2 | 2.96 × 10−6 | 0.0099 | 4.15 × 10−6 | 0.0041 | 1.82 × 10−4 | 0.6057 | 1.51 × 10−4 | 0.0433 | 1.92 × 10−4 | 0.0641 |
| Y3 | 2.96 × 10−6 | 0.0099 | 5.92 × 10−6 | 0.0059 | 2.04 × 10−4 | 0.6800 | 2.04 × 10−4 | 0.0583 | 1.58 × 10−4 | 0.0527 |
| Y4 | 2.96 × 10−6 | 0.0099 | 1.40 × 10−5 | 0.0140 | 1.85 × 10−4 | 0.6162 | 9.46 × 10−5 | 0.0270 | 2.08 × 10−4 | 0.0693 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Fu, X.; Liang, Y.; Hu, H.; Wang, S.; Li, K.; Zhang, K.; Lu, R.; Hou, G.; Sun, Z.; Wang, W.; et al. Mitigation Effect of Low-Accumulation Rice Varieties and Soil Conditioners on Hg and Cd Pollution in Rice. Processes 2025, 13, 1542. https://doi.org/10.3390/pr13051542
Fu X, Liang Y, Hu H, Wang S, Li K, Zhang K, Lu R, Hou G, Sun Z, Wang W, et al. Mitigation Effect of Low-Accumulation Rice Varieties and Soil Conditioners on Hg and Cd Pollution in Rice. Processes. 2025; 13(5):1542. https://doi.org/10.3390/pr13051542
Chicago/Turabian StyleFu, Xiaohua, Yingqi Liang, Huimin Hu, Shuo Wang, Kun Li, Kuifu Zhang, Rui Lu, Guiqiong Hou, Zhihua Sun, Wei Wang, and et al. 2025. "Mitigation Effect of Low-Accumulation Rice Varieties and Soil Conditioners on Hg and Cd Pollution in Rice" Processes 13, no. 5: 1542. https://doi.org/10.3390/pr13051542
APA StyleFu, X., Liang, Y., Hu, H., Wang, S., Li, K., Zhang, K., Lu, R., Hou, G., Sun, Z., Wang, W., Deng, J., & Wang, Z. (2025). Mitigation Effect of Low-Accumulation Rice Varieties and Soil Conditioners on Hg and Cd Pollution in Rice. Processes, 13(5), 1542. https://doi.org/10.3390/pr13051542








