Abstract
The enzymatic hydrolysis process is important in the field of textile waste reuse in the circular economy context. Currently, enzymatic cellulase treatment of waste textiles, such as bamboo mixture with spandex samples (BS), cotton jeans (CJ), linen (L), and cotton T-shirts (CT), has been tested, in which glucose production was measured at the presence of 6 and 8% NaOH solution. The characteristics of the textiles and hydrolysis capacity were evaluated by the amount of glucose (g) obtained from each textile. The following indicators were also measured during the experiment: temperature, pH, enzymatic cellulase solution composition, final glucose concentrations, turbidity, and color intensity. The temperature of the mixture was maintained at 50 °C, and a pH level of 5–7 along with a contact time of 48–94 min were controlled. The experiments demonstrated that when the enzymatic hydrolysis was active, turbidity increased from 86 nephelometric turbidity unit (NTU) to >1000 NTU; the color of the hydrolyzed samples was obtained from 86 NTU to >1000 NTU; and the final glucose concentration was approximately between 0.49 and 33.9 mmol/L for L, CT, and CJ samples measured to produce up to one gram of glucose from 3.330 g of textile, and a BS samples produced one gram of glucose from 3.164 g of textile. The findings show that recycled glucose obtained from textile waste materials is environmentally sustainable. Such textile waste can then be reused rather than being dumped in already overloaded landfills.
1. Introduction
The impact of the textile industry has a wide ecological footprint. In recent years, the negative effect of textile production on the environment has significantly increased. This ranges from environmental impacts, the use of certain raw materials, how garments are processed and ultimately produced, transportation and distribution, consumer use, and end-of-life [1]. However, it is difficult to estimate the environmental impacts of the consumption of textiles because due to the effect of globalization, the apparel industry manufactures more clothing at lower costs due to the outsourced production to low-cost countries as well as the anticipated trend [2]. Information provided by the Global Fashion Agenda (GFA) suggests that the environmental footprint of EU countries caused by the purchase of garments is anywhere from 4 to 6%. In addition to the impact caused by crops grown to produce textiles (as well as other raw materials), industrial textile processing contributes to environmental pollution. Cotton is just one of the raw materials used in garment production and provides about 40% of the fibers in production in the EU. Among all the textiles used in clothing manufacturing, cotton has the greatest environmental impact. This is due to the huge amounts of water used in processing, as well as the need to cultivate large areas of land, which requires toxic chemical fertilizers as well as water to irrigate the crop. Using ecological or bio-cotton is a good substitute due to its lower input requirements and minimized environmental impact. According to the investigation results of cotton textile [3], a maximum glucose concentration of 19.82 mg/mL was achieved after 5 days of enzymatic hydrolysis. A percentage of theoretical glucose yield of 99.1% was reached [3]. Following review on sustainable textile raw materials [2], cotton fibers are composed of approximately 96% cellulose. The textile industry is actively seeking alternative natural materials, such as hemp, linen, flax, and nettle, because these materials require a significantly smaller number of resources for processing.
In fact, independent of the garment or textile produced, a huge amount of energy is required due to the high energy needed for textile processing machinery. While it takes comparatively little time for production, synthetic fiber does not degrade under natural conditions and cannot be easily recycled through the recovery of secondary materials [4]. The immense amounts of energy used to produce garments also increases the soil acidification and leads to higher emissions of carbon dioxide. Cotton dyeing is the most environmentally harmful step in textile production [5]. The hydrolysis of PET, cotton, and wool fibers involves a heterogeneous reaction, taking place primarily at the fiber surface [6], then primary treatment uses many resources and severely harms the environment.
There have been few studies on the percentage of clothing collected that was used for recycling [7,8,9]. A European Union report of 2019 found that once clothes are collected, they can either be re-used as second-hand clothes or recycled. Recycling is not particularly efficient since less than one percent of all materials used in garments are currently recycled to produce new clothing.
Researchers [10] found out that the total amount of glucose in the waste textiles corresponds to 1.11 times the cellulose content, since water is added to the cellulose during hydrolysis. Using the enzymatic hydrolysis method could not only reduce the environmental impact [11] but also help the textile industry to reposition itself as a significant player in the circular economy. This would eventually take away the first step of growing a raw material and hence free up land to grow organic food. Prominent examples of enzymatic hydrolysis include degradation of wool fiber, recovery of nano-cellulose by hydrolysis [12], recovery of glucose and polyester through enzymatic hydrolysis, recovery of cotton and polyester from jeans waste, as well as other technologies [13,14,15]. It is important to use detailed insights into enzymatic activity, because this would help us to understand the main idea of possible technology, i.e., material recovery by enzymatic degradation of substrate (textile waste). Scientists have achieved the efficiency of hydrolysis at 85% to 98% in tests where they have used relatively higher substrate loading and relatively higher enzyme loading [11]. Anaerobic digestion of glucose can generate biogas (primarily methane), which can be used for heating, electricity generation, or as a vehicle fuel. Glucose can be used to cultivate microorganisms for producing single-cell proteins (SCPs) or other microbial biomass, useful in animal feed or food supplements. Glucose can be employed in microbial fermentations to produce enzymes, organic acids (e.g., citric acid, lactic acid), or amino acids.
Glucose can act as a raw material for synthesizing various pharmaceutical intermediates or nutraceuticals through biotransformation processes. The glucose itself can be used directly as a sweetener or further processed into high-fructose corn syrup. The novelty of this research is that the improved technology was created where solely the one-reagent NaOH freezing method was used for pre-treatment of the textile, whereas other studies have used a method where the freezing mixture consisted of NaOH and urea [11]. When setting the goal, the main hypotheses were related to achieving the simplicity and sustainability of the textile waste enzymatic recycling process.
The aim of this research was to develop a simple and easy method to recycle different common waste textiles into glucose. We aimed to see how different the usage is among 6 and 8% NaOH treatments in achievement of textile glucose formation efficiency.
2. Materials and Methods
The experiments tested a novel method for the recovery of materials from textile waste and their conversion to glucose. The procedure is the following: 1. Pretreatment of textile waste: mechanical and chemical treatment with freezing NaOH methods. 2. Enzymatic hydrolysis of textile waste: Enzyme solution was thoroughly blended (pretreated dry textile flakes submerged into solution of enzymes and mixed for the process of hydrolysis); hydrolysis in a bioreactor (closed glass cell with magnetic stirring mechanism in a thermostat) under mild conditions (50 °C and pH level of pH = 5–7) was completed within 2–4 days. Non-biodegradable material (for example, polyester) remained intact and was separated as a solid and liquid form by filtration. 3. Additional step: in this research, only the first two of the three steps were performed, i.e., pretreatment of textile waste and enzymatic hydrolysis of textile waste. The experimental scheme of this research is presented in Figure 1.
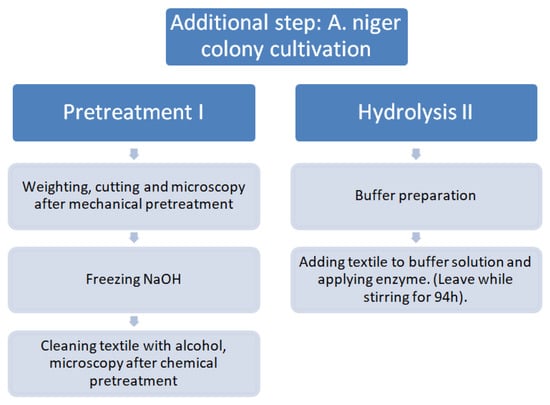
Figure 1.
Scheme of the experiment.
Raw material was obtained from common household textile waste to simulate conditions close to commercial textile supply for recycling [16]. Thus, 100% cotton jeans (hard cotton), 100% cotton T-shirt (light cotton), 100% handmade linen, and 95% bamboo and 5% spandex underwear were used (Figure 2). The cotton was made of cellulose, with possible interference received by the enzymatic hydrolysis. Textile samples were cut into random-shaped pieces of 1 cm width and 1 cm length. Sample pieces of each clothing unit were investigated under a microscope (Motic (Xiamen, China)), with magnifications of 40× and 100× to observe the raw material structure and to evaluate the characteristics of different investigated household textile waste materials.

Figure 2.
Textile samples prepared for the experiment.
Black-colored samples (Figure S1) were obtained from CJ materials and were considered with the highest quality of dyes gained by the hydrolysis processes. Samples obtained after hydrolysis were collected from the reacted liquid phase (Figure S1) and transported to the laboratory for analysis and measurement of glucose concentration. The instrument used for glucose concentration was YSI (Model 2300 STAT PLUS, YSI Incorporated 1725 Brannum Lane Yellow Springs, Ohio, USA), and this analyzer was controlled according to the Standards NIST.
Two types of textile pretreatment methods were carried out: freezing NaOH and mixing. For freezing using the NaOH method, textile waste was frozen in the alkaline mixture of 6% and 8% sodium hydroxide content at −20 °C for 24 h. The amount of textile for chemical pretreatment used was 3 g for each sample. The pretreated samples were sterilized using a solution of 70% ethanol to remove microorganisms and pre-washed with distilled water until reaching pH = 7 to remove alkaline residues and then dried at +28 °C to +32 °C in an oven equipped with a thermostat.
The current study used a commercial cellulase blend with a density of 1.0–1.3 g/mL and ≥1000 U/g containing cellulases, ß-glucosidases, and hemicellulose. At the beginning of this experiment, each piece of raw textile sample had a mass of 3 g. Also, a phosphate buffer was used to balance samples’ pH at ~5–6. Fresh buffer solution was made before every sample run. Samples were subsequently analyzed to determine the concentration of glucose. The information considered in the evaluations includes the material characteristics of the applied textile, initial solids loading, initial substrate to enzymes ratios, and glucose concentrations before and after hydrolysis.
Enzymatic hydrolysis was performed using 3 g of unprocessed cellulose, which was added to 250 mL of buffer solution, and 0.75 g of cellulase was supplemented to the mixture. The mixture was left in the flask under a magnetic stirrer for up to 5 days with regular sampling at +50 °C temperature. The same amount (4 mL) of sample of each hydrolysis run was taken after every day (24 h) during 5 days of experiment and kept in a cold and dry environment. This procedure was repeated with both 8% and 6% NaOH pretreated samples. Samples were taken at different time intervals (0 days, 1 day, 2 days, 3 days, 4 days, and 5 days) during the hydrolysis process (Table 1).

Table 1.
Glucose concentration recovered during hydrolysis. Standard deviations were gained using the YSI (2300 STAT PLUS model) analysis referential instrument.
The obtained results were statistically analyzed by IBM SPSS Statistics 23 software, and the hydrolysis results at different conditions were compared using one-way analysis of variance (ANOVA). The significant differences between researched criteria were determined from normally distributed data by a paired sample test and correlation analysis. The Duncan multiple range test and a significance level at a p-value < 0.05 were assessed using multiparametric statistical analysis, analysis of variance (ANOVA).
3. Results
3.1. Discussions of Technological Constraints
Mechanical and chemical pretreatment using NaOH had a noticeable effect on the textile, whose texture turned to a consistent product from a hard gel structure resembling glucose. The textile samples were observed after treatment with 6 and 8% of NaOH solution to determine changes in glucose formation.
Cotton T-shirt textile was transformed into hard textile rolls, and a yellow-colored discoloration was also observed at the ends of textile rolls [17]. This could be a sign of the 8% NaOH concentration being too high for the test, since with the 8% NaOH treatment, the sample showed more yellow signs of discoloration than the 6% NaOH-treated sample.
The samples collected from the cotton jeans influenced the characteristics of dyes released, which were more intensively released from fibers. Tiny fiber particles were also observed in the melted sample. The 8% of alkali NaOH treatment cotton sample released more dye, in which higher intensity was easily observed. The linen sample was significantly affected, with its textile fiber structure completely untangled, leaving the textile in slimy strains of yarn. No change in color was observed. Almost no effects were observed in the bamboo and spandex sample between 6 and 8% NaOH treatments. The only effect that could be noticed (mostly during microscopy) was the textile texture becoming somewhat relaxed or less taut at the 8% NaOH treatment compared with the 6% treatment. No coloration changes and no difference between the concentration of NaOH were observed of treated bamboo and spandex samples.
As seen in the above investigation, chemical pretreatment was successful. As expected, organic, natural fiber degradation to glucose was the most affected by a higher concentration of NaOH treatment. Researchers have mentioned [18] that the cotton residues taken from the textile industry waste shredded into fibers, can be directly immersed in NaOH solution to recycle glucose. Bamboo with spandex was the least affected because it had already been highly processed during textile fiber treatment [18] and the mechanical knitting processes. The importance of pretreatment mentioned in the short state-of-the-art review [19] explained that the fiber feedstock recycling means breaking down the polymeric structure of the molecules in the textile into smaller pieces. This pretreatment step enlarged the surface area even more [19], which should increase final glucose yield [20] and ensure an adequate conversion of cellulose to glucose by considering the lignocellulosic biomass nature. In contrast to starch, cellulose creates insoluble fibers that are cross-linked with protein, restricting the access of digestive enzymes on cellulose breakdown. Further reasons why biological degradation by cellulases are not efficient for cellulose breakdown are outlined followingly: cellulose is a highly crystalline polymer, which makes it resistant to enzymatic breakdown. The enzyme mixture might lack the necessary components for complete cellulose degradation, causing lack of degradation. Efficient cellulose hydrolysis typically requires a combination of endoglucanases, exoglucanases (cellobiohydrolases), and β-glucosidases. Even with a high enzyme load, if there is an imbalance in the ratios of these enzymes, the overall conversion efficiency can suffer. As cellulose is broken down, cellobiose and glucose accumulate. These products can inhibit the activity of cellulolytic enzymes, slowing down the reaction rate. Specifically, cellobiose inhibits exoglucanases, while glucose can inhibit β-glucosidases, creating a feedback loop that reduces enzyme efficiency.
At very high substrate concentrations, cellulose itself can inhibit enzyme activity by causing steric hindrance or blocking active sites on the enzymes.
Enzyme activity is highly sensitive to environmental factors such as pH, temperature, and ionic strength. If these conditions are not optimized, the enzymes may not function at their full potential.
Enzymatic hydrolysis was performed successfully. Special samples with no additive (Control, blank) are presented in Table 2 for the purpose of comparison; in case of “*” marked samples, there were no improvements seen in glucose yield from the experiment. The glucose yield was estimated by dividing the amount of glucose released by the initial amount of cellulose and was approximately equal to 30–47.6%.

Table 2.
Samples’ glucose concentration trend overview without NaOH additives. CT—cotton T-shirt, L—linen.
3.2. Environmental and Safety Considerations
Environmental degradability and resistance are two basic criteria in determining the behavior of natural substances in the ecological area and during the reliable treatment of waste materials. Using these two requirements of treatment, textile substances can be divided into the following background groups: enzymatically degradable and non-resistant substances; enzymatically degradable and resistant substances; enzymatically nondegradable and nonresistant substances; enzymatically nondegradable and resistant substances. Compounds of the first group are not of concern, while substances of the second group are, after sufficient treatment, decomposed by enzymatic processes. Discharge of the third group, and thereafter the fourth group, in nature should be limited or recirculated in an appropriate way. Colored organic compounds basically impact only a small part of the total organic content in textile; however, their high level of color is easily detectable and detracts from the ecologic value of residual and produced garments. Residual sources from the textile industry emanate from cotton, linen, and synthetic textiles and may contain toxic or other hazardous substances. Therefore, small quantities may have significant impact.
Large quantities of waste liquid effluent are discharged by the textile sector, including production, packaging, and laundry lines. Discharged pollutants include colorants, suspended solids, salts, heavy metals, line turbidity, and alkaline and organic compounds. Other pollutant examples are shown in dry weight and pH for the cotton, linen, and synthetic fibers.
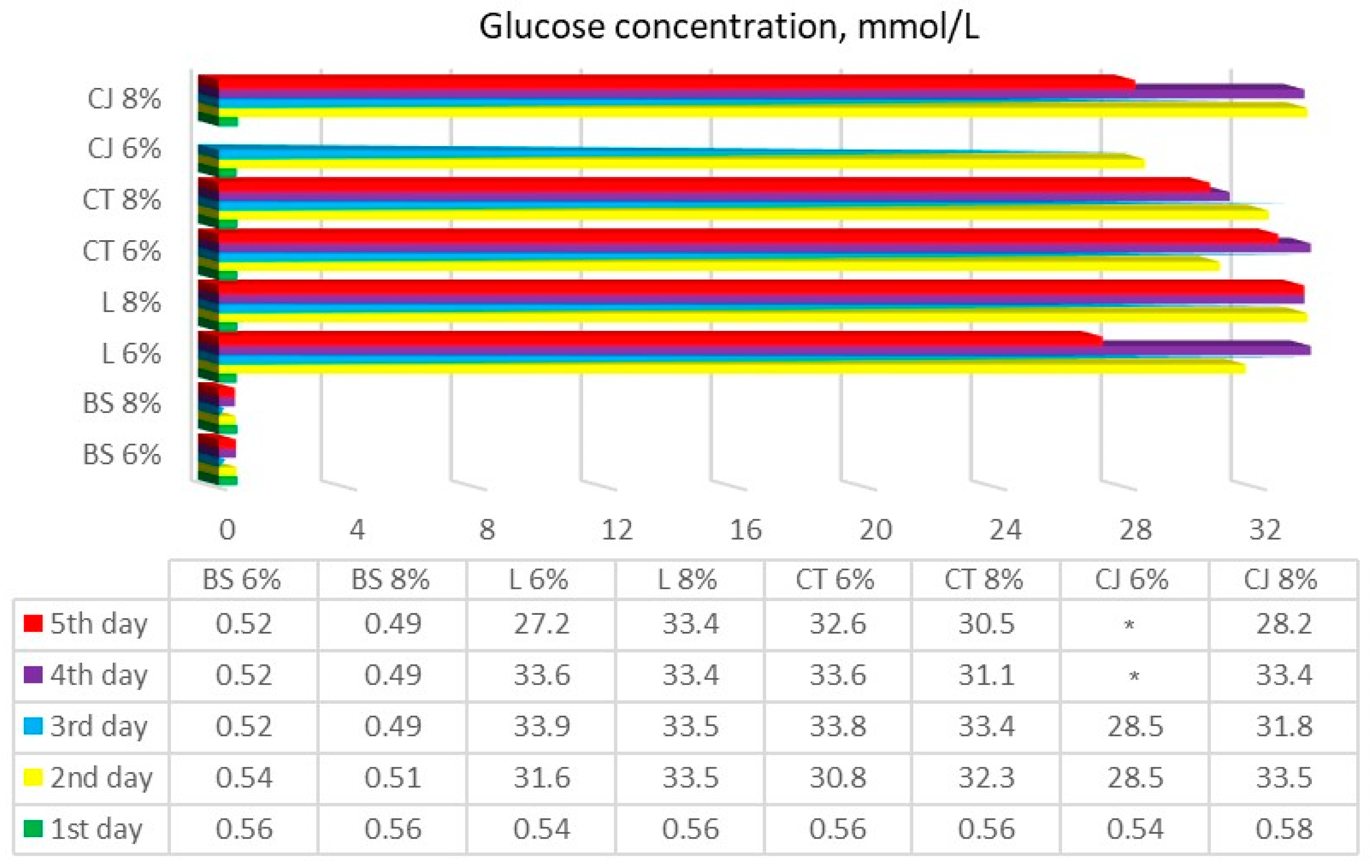
Results of textile-released glucose concentration after experimental runs can be observed in Figure 3.
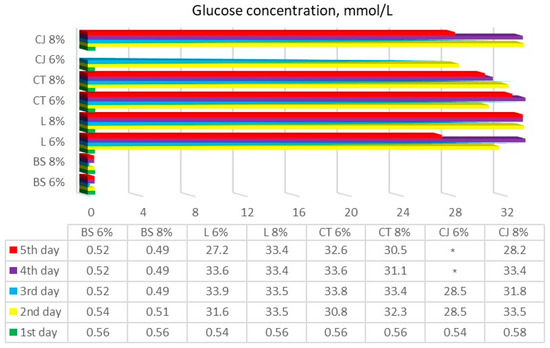
Figure 3.
Textile-released glucose concentration after performing enzymatic hydrolysis during 5 days of testing. BS—bamboo and spandex samples, L—linen, CT—cotton T-shirts, CJ—cotton jeans (* samples that were not determined) at treatment with 6% and 8% NaOH, indicated after each textile class.
Our results showed that linen, cotton T-shirt, and cotton jeans samples were affected by enzymatic hydrolysis in a similar way. After two days of the hydrolysis process, all these samples produced 30–35 mmol/L of glucose, whose yield remained the same until the last day of hydrolysis. However, and as we anticipated, samples of the bamboo and spandex blend textiles produced no change in glucose yield whatsoever. A samples-applied ANOVA multiparametric statistical t-test confirmed that there was no statistically significant glucose concentration change observed throughout all the enzymatic hydrolysis processes in bamboo and spandex textile samples (p > 0.05). The blank sample with no NaOH pretreatment of linen only showed glucose yield on the last days of hydrolysis, while a blank sample of cotton T-shirt reacted the same way, except that glucose yield was even less than for the linen blank sample. According to the formulas obtained from the researchers [10], the glucose yield in the experiments can be calculated by multiplying the glucose concentration in the liquid product by the volume of the liquid product and then dividing by the total amount of glucose in the raw material.
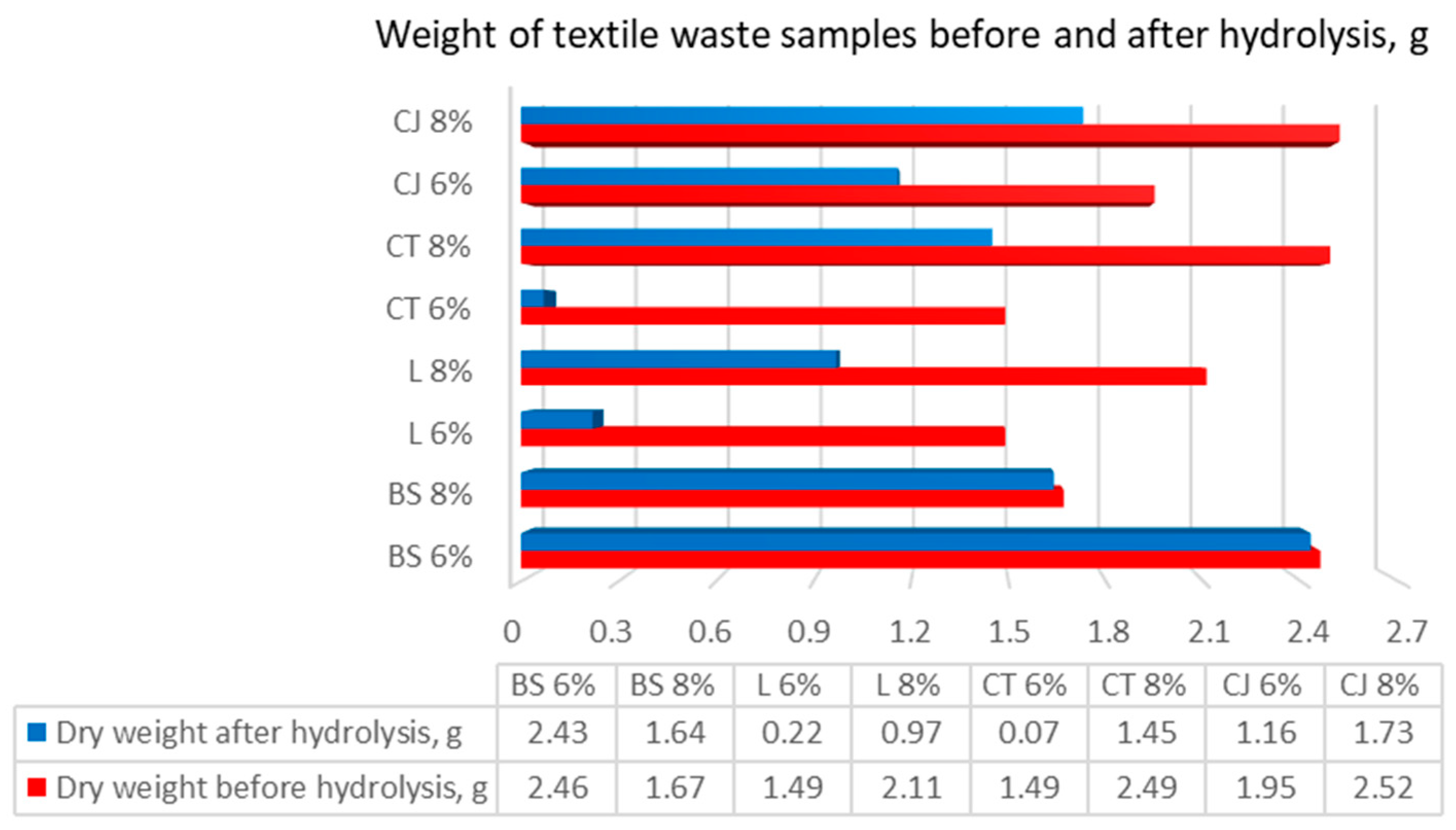
After every hydrolysis run, the textile left was filtered, dried, and weighed. The results of this procedure can be observed in Figure 4.
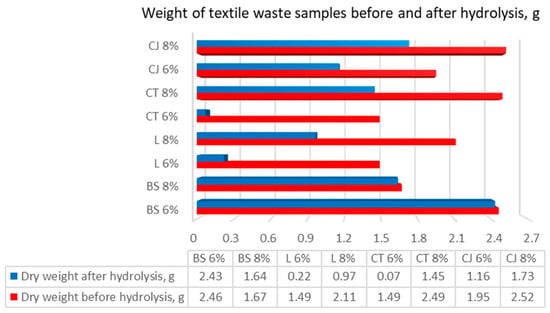
Figure 4.
Weight of textile waste samples before and after hydrolysis. BS—bamboo and spandex samples, L—linen, CT—cotton T-shirts, CJ—cotton jeans at treatment with 6 and 8% NaOH, indicated after each textile class.
As presented in Figure 4, dry weight before hydrolysis varied, which is due to differences in the efficiency of chemical and mechanical pretreatment. Some samples were changed significantly, but not all of them showed a similar trend (dry weight before chemical pretreatment was 3 g).
The results showed that the highest weight loss was observed for cotton T-shirt (95%) and linen (85%) samples introduced to 6% of NaOH. Thus, chemical pretreatment had no significant effect on weight loss in bamboo and spandex (8% NaOH), cotton jeans (6% NaOH), and blank cotton T-shirt (No NaOH) samples. Minimal values range from 1% to 5% of loss in weight.
Figure 4 and Figure 5 are referring to the minimum experimental concentrations of sodium hydroxide of 6 and 8% and showed some possibilities to the hydrolysis enhancement, however, as hydrolysis efficiency did not reach 100%, and further testing will be under investigation in future research.
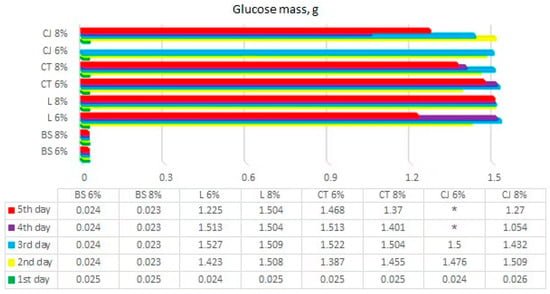
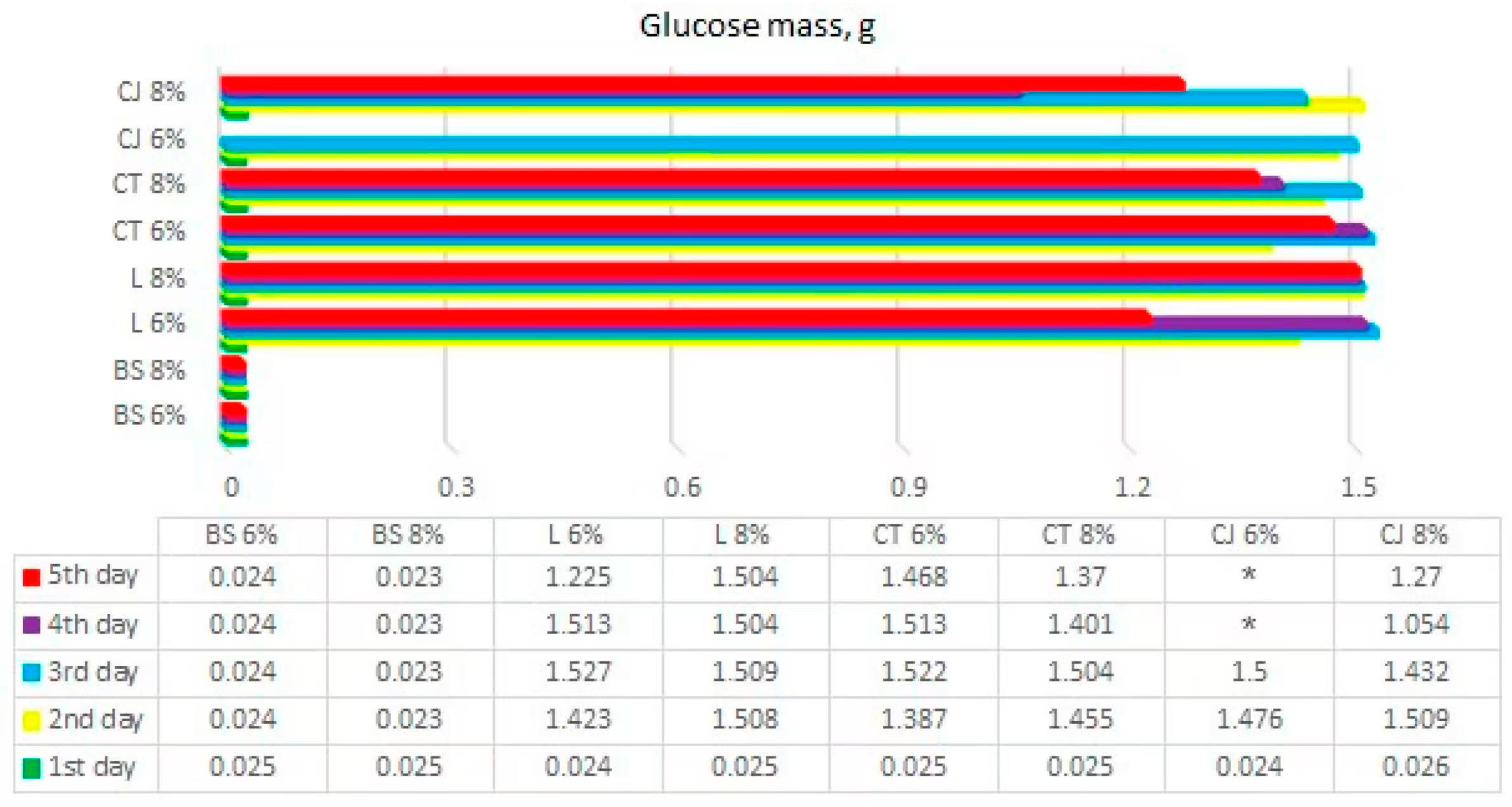
Figure 5.
Calculated results of glucose mass from BS—bamboo and spandex samples, L—linen, CT—cotton T-shirts, CJ—cotton jeans (* samples that were not determined) at treatment with 6 and 8% NaOH.
The mass of glucose in samples was calculated, and obtained results of glucose mass in each sample are presented in Figure 5.
The results showed that the maximum amount of glucose recovered from 3 g of textile waste was 1.527 g/g. Linen, cotton T-shirt, and jeans samples were calculated to produce glucose of 3.33 g/g in a best-case scenario. Bamboo and spandex samples were calculated to produce 3.164 g/g of glucose. It means that experimental recovery of glucose from linen, cotton T-shirt, and jeans samples had around 50% completion in comparison to the theoretical yield. However, earlier research [11] showed that a maximum glucose recovery yield of 98.3% from organic textile samples could be achieved after 96 h of the hydrolysis process. The main methodological difference in the previous and current research was the addition of urea in the NaOH pretreatment, as well as a higher cellulase to cellulose ratio present in the current research. The bamboo and spandex blended sample had even less glucose recovery yield, at <1%. This could be explained by bamboo textile containing viscose/rayon—a fiber made from cellulose present in the bamboo, which is then extruded to create fibers. This is also in agreement with other studies [21], where it was stated that synthetic material is not effectively treated by hydrolysis.
According to the results of multi-criteria analysis (displayed in Figure 5), the average concentration of dye substances and microfiber volume had no effect on the glucose concentration throughout the hydrolysis process. Microfiber volume and average concentration of dye substances in cotton jeans samples showed a drastic increase during hydrolysis. The microfiber volume of the cotton jeans samples steadily increased throughout the daily hydrolysis, resulting in a turbidity increase from 94 nephelometric turbidity units (NTU) to >3000 NTU value, which was above the observable limit. The average concentration of dye substances in cotton jeans samples showed a drastic increase from 86 NTU to >1000 NTU during the 4th day of hydrolysis. Theoretically, an increased average concentration of dye substances and microfiber volume [11] should lower the glucose concentration recovery.
After performing multi-parametric analysis, two pairs of samples were selected: a linen and cotton T-shirt sample [22]. Comparative analysis between those two samples revealed that pre-treatment had varying effects on the average concentration of dye substances conversion and on the microfiber volume, as well as on the concentration and mass of glucose formed.
4. Discussion
Results showed that pretreatment with lower 6% concentration of NaOH resulted in a lower concentration of dye substances and microfiber volume; and pretreatment with 8% NaOH presented a higher concentration of dye substances and microfiber volume (Figure 5).
4.1. Technological Constraints
The mass of the glucose was not affected either by pretreatment differences or by concentration of initial dye substances and microfiber volume. Further investigation will be concentrated on more reliable sorting [23,24], sustainable materials [25], consumer textile purchase behavior [26], and the newest obtained valuable knowledge in the field [27,28].
Linen, light cotton T-shirts, and cotton jeans exhibited identical enzymatic hydrolysis behavior during glucose production, yielding 30–35 mmol/L of glucose by the 2nd day of the hydrolysis process. The glucose concentration remained constant until the fifth day of hydrolysis. As anticipated, bamboo and spandex blends showed minimal change, producing only 0.49–0.56 mmol/L of glucose. No statistically significant differences were observed in glucose production between pretreatment methods. This supports the hypothesis that pretreatment methods do not significantly impact glucose yield from refractory textiles like bamboo and spandex. One of the important aims of an advanced glucose production is the recycling of garments’ waste products in a safe and ecologically responsible way. The controlled treatment of textile in many countries had its conceptions in the “afterlife” value of the textile wastes and other materials. The clothes previously have been made of organic materials, whose content is very small compared to the synthetic textile nowadays. Materials from synthetic textile processes are being produced in increasing quantities and may contain harmful and hardly degradable fibers. They are often comparably stronger than organic threads, thus many reuse systems are not designed to handle them. In addition, the consumption of “fast fashion” on a global scale has increased to such a degree that now it is not unusual to find that the consumers receiving treated textile cannot give them reuseable value.
The technological process for treating wasted textile has not kept pace with the changes in the complexity of available enzymes, though there have been considerable advances in chemistry and biotechnology, and the simplicity of the reliable methods has increased, which still forms the major routes for textile reuse.
4.2. Environmental and Safety and Storing Considerations
Although the concept of applying enzymatic processes to treat contaminated residuals and textiles has been realized for many years, fermentation remains one of the more innovative bio-engineering processes. Such information in turn leads to the development of sustainable and higher quality enzymes and insight on how such qualities of enzymes will be improved by the processes and conditions. This relation between the producing processes and the eventual quality of the enzymatic products will lead to further development and application of enzymatic processes in waste textile treatment.
4.3. Energy and Other Requirements
It is possible to develop and produce energetically cost-saving treatment enzymes for specific treatment and residual reuse purposes. This is perhaps reflected by the current world-wide interest in the energy savings, smart production, and reuse of enzymatic products made from ecological ingredients and a range of other raw materials such as green, bioorganic, and sustainable materials. According to the “Green Deal” of European Union countries, advanced technologies are not the cheapest and energy efficient the moment when performing this research, but they are worth the use in the future because of the ecological advances they bring. The following relevant published study is the future way of how this can be integrated in the collection of clean recyclable materials [29].
Optimization of pretreatment for enhancing enzymatic hydrolysis of cotton textile waste has been previously conducted [30,31]. The concept of circular economy in the context of the textile industry and glucose production can be addressed through key attributes such as resource efficiency, waste reduction, and value recovery according to the following principles:
Resource efficiency: in a circular economy, the textile industry aims to minimize raw material inputs by reusing and recycling fibers. Similarly, glucose production from textile waste involves breaking down cellulose-rich materials (e.g., cotton) into fermentable sugars, optimizing the use of existing resources.
Waste valorization: textile waste, often considered landfill material, can be converted into valuable products like glucose through processes such as hydrolysis. This aligns with circular principles by transforming waste into a renewable feedstock for bio-based industries.
Closed-loop systems: a circular approach in textiles ensures that end-of-life products are reintegrated into production cycles. For glucose production, this involves using recycled cellulose from textiles to produce biofuels, bioplastics, or other biochemicals, reducing dependency on virgin resources.
Sustainability: by integrating glucose production from textile waste, the industry reduces its carbon footprint and environmental impact, promoting sustainable practices that support long-term ecological balance.
In summary, the circular economy attributes in this context emphasize the transformation of textile waste into glucose, fostering resource conservation, waste minimization, and sustainable value creation.
5. Conclusions
The results showed that the highest mass decrease of textile was obtained in samples of the cotton T-shirt (95%) and linen (85%) treated with 6% of NaOH. The results also showed that chemical pretreatment had no significant effect on the achievement of mass decrease among bamboo and spandex (8% NaOH), cotton jeans (6% NaOH), and blank cotton T-shirt (No NaOH) samples. The highest mass decrease was in the minimal percentage range from 1% to 5% for the latter textiles.
Spectrometry analysis showed a rapid increase in microfiber volume on the second day of hydrolysis (resulting in turbidity of 7–930 NTU). The sample most affected was cotton from the jeans (up to 3000+ NTU), with no increase in microfiber volume observed in blank samples with no pretreatment. This proved the hypothesis that pretreatment of textile waste before hydrolysis to increase the surface area by separating fibers is crucial, with the result that glucose production is increased.
The results obtained through multi-criteria analysis showed that color intensity and turbidity had no effect on glucose concentration throughout the hydrolysis process. Neither microfiber volume of the sample from the cotton jeans (resulted in a turbidity of 94 NTU to >3000 NTU) nor color intensity (86 NTU to >1000 NTU) affected the glucose concentration of samples. This was unexpected since our research anticipated that turbidity and color intensity would reduce the recovery of glucose. Dyes used in garment production and microfibers released after pretreatment did not significantly affect released glucose concentration (p > 0.05).
A positive answer to the main requirement of the “Green Deal” in EU countries was gained—using a simple method to obtain glucose production instead of overloading landfills with textile.
A perspective on future research directions in this important field can be directed to simple, affordable methods of textile recycling processes. Also, a relation to benefits from applying circular economy rules in the waste processing should be used in any recycling facilities of textile processing. The future research will perform more successful glucose productions from textile waste while relying on current experiments, i.e., using a polyester + cotton blend and/or using different ratios of polyester and cotton in the blends and testing different types of enzymes to enhance glucose production.
Supplementary Materials
The following supporting information can be downloaded at: https://www.mdpi.com/article/10.3390/pr13041165/s1, Figure S1: Textile samples after NaOH and cellulase solutions treatments prepared for glucose measurements.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, M.V.; methodology, M.V. and G.J.; validation, M.V.; data curation, M.V. and G.J.; writing—original draft preparation, M.V.; writing—review and editing, M.V. and I.Z. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research was funded by projects SARASWATI 2 “Identifying best available technologies for decentralized wastewater treatment and resource recovery for India” and SLTKT20427 “Sewage sludge treatment from heavy metals, emerging pollutants and recovery of metals by fungi” and by University of Tartu Development fund PLTKT ARENG53. Financial support of these studies from Gdańsk University of Technology by the DEC-6/2021/IDUB/II.2/Sc/035336 grant under the SCANDIUM—‘Excellence Initiative—Research University’ program and Interreg BSR—Improving quality of BSR waters by advanced treatment processes (AdvIQwater), “In-situ catalytic bioconversion of pharmaceutically active compounds in wastewater“, Enlight “PLANTED” project and by COST actions: CA20101, CA20127, CA20138, CA22102, CA22110, CA22123, CA22162, CA22146 is gratefully acknowledged.
Data Availability Statement
The original contributions presented in this study are included in the article/Supplementary Materials. Further inquiries can be directed to the corresponding author.
Acknowledgments
Authors express gratitude to Tomas Zemaitis the Head of Laboratory from Vilnius Gediminas Technical University (Lithuania) for his valuable administrative and technical support.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
References
- Amaral, M.C.D.; Zonatti, W.F.; Silva, K.L.D.; Karam Junior, D.; Amato Neto, J.; Baruque-Ramos, J. Industrial textile recycling and reuse in Brazil: Case study and considerations concerning the circular economy. Gestão Produção 2018, 25, 431–443. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suen, D.W.-S.; Chan, E.M.-H.; Lau, Y.-Y.; Lee, R.H.-P.; Tsang, P.W.-K.; Ouyang, S.; Tsang, C.-W. Sustainable Textile Raw Materials: Review on Bioprocessing of Textile Waste via Electrospinning. Sustainability 2023, 15, 11638. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cho, E.J.; Lee, Y.G.; Song, Y.; Kim, H.Y.; Nguyen, D.-T.; Bae, H.-J. Converting textile waste into value-added chemicals: An integrated bio-refinery process. Environ. Sci. Ecotechnol. 2023, 15, 100238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haslinger, S.; Hummel, M.; Anghelescu-hakala, A.; Määttänen, M.; Sixta, H. Upcycling of cotton polyester blended textile waste to new man-made cellulose fibers. Waste Manag. 2019, 97, 88–96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karthik, T.; Gopalakrishnan, D. Environmental analysis of textile value chain: An overview. In Roadmap to Sustainable Textiles and Clothing: Environmental and Social Aspects of Textiles and Clothing Supply Chain; Muthu, S.S., Ed.; Springer: Singapore, 2014; pp. 153–188. ISBN 978-981-287-109-1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aneja, A.; Kupka, K.; Militký, J.; Venkataraman, M. Kinetics of Hydrolytic Depolymerization of Textile Waste Containing Polyester. Fibers 2024, 12, 82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- To, M.H.; Uisan, K.; Ok, Y.S.; Pleissner, D.; Lin, C.S.K. Recent trends in green and sustainable chemistry: Rethinking textile waste in a circular economy. Curr. Opin. Green Sustain. Chem. 2019, 20, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zamani, B.; Svanstrom, M.; Peters, G.; Rydberg, T. A Carbon Footprint of Textile Recycling: A Case Study in Sweden. J. Ind. Ecol. 2015, 19, 676–687. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bianchi, S.; Bartoli, F.; Bruni, C.; Fernandez-Avila, C.; Rodriguez-Turienzo, L.; Mellado-Carretero, J.; Spinelli, D.; Coltelli, M.-B. Opportunities and Limitations in Recycling Fossil Polymers from Textiles. Macromol 2023, 3, 120–148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ruuth, E.; Sanchis-Sebastiá, M.; Larsson, P.T.; Teleman, A.; Jiménez-Quero, A.; Delestig, S.; Sahlberg, V.; Salén, P.; Sanchez Ortiz, M.; Vadher, S.; et al. Reclaiming the Value of Cotton Waste Textiles: A New Improved Method to Recycle Cotton Waste Textiles via Acid Hydrolysis. Recycling 2022, 7, 57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Hu, Y.; Du, C.; Ki Lin, C.S. Recovery of Glucose and Polyester from Textile Waste by Enzymatic Hydrolysis. Waste Biomass Valorization 2019, 10, 3763–3772. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prado, K.; Gonzales, D.; Spinacé, M.A.S. Recycling of viscose yarn waste through one-step extraction of nanocellulose. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2019, 136, 729–737. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Navone, L.; Moffitt, K.; Hansen, K.-A.; Blinco, J.; Payne, A.; Speight, R. Closing the textile loop: Enzymatic fibre spearation and recycling of wool/polyester fabric blends. Waste Manag. 2020, 102, 149–160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thapa, S.; Mishra, J.; Arora, N.; Mishra, P.; Li, H.; O’Hair, J.; Bhatti, S.; Zhou, S. Microbial cellulolytic enzymes: Diversity and biotechnology with reference to lignocellulosic biomass degradation. Rev. Environ. Sci. Bio/Technol. 2020, 19, 621–648. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yousef, S.; Tatariants, M.; Tichonovas, M.; Kliucininkas, L.; Lukošiūtė, S.I.; Yan, L. Sustainable green technology for recovery of cotton fibers and polyester from textile waste. J. Clean. Prod. 2020, 254, 120078. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karell, E.; Niinimaki, K. Addressing the Dialogue between Design, Sorting and Recycling in a Circular Economy. Des. J. 2019, 22, 997–1013. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De la Motte, H.; Hasani, M.; Brelid, H.; Westman, G. Molecular characterization of hydrolyzed cationized nanocrystalline cellulose, cotton cellulose and softwood kraft pulp using high resolution 1D and 2D NMR. Carbohydr. Polym. 2011, 85, 738–746. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Patti, A.; Cicala, G.; Acierno, D. Eco-Sustainability of the Textile Production: Waste Recovery and Current Recycling in the Composites World. Polymers 2021, 13, 134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Piribauer, B.; Bartl, A. Textile recycling processes, state of the art and current developments: A mini review. Waste Manag. Res. 2019, 37, 112–119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pino, M.S.; Rodríguez-Jasso, R.M.; Michelin, M.; Flores-Gallegos, A.C.; Morales-Rodriguez, R.; Teixeira, J.A.; Ruiz, H.A. Bioreactor design for enzymatic hydrolysis of biomass under the biorefinery concept. Chem. Eng. J. 2018, 347, 119–136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Esteve-Turrillas, F.A.; De la Guardia, M. Environmental impact of Recover cotton in textile industry. Resour. Conserv. Recycl. 2017, 116, 107–115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sandin, G.; Peters, G.M. Environmental impact of textile reuse and recycling—A review. J. Clean. Prod. 2018, 184, 353–365. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cura, K.; Rintala, N.; Kamppuri, T.; Saarimäki, E.; Heikkilä, P. Textile Recognition and Sorting for Recycling at an Automated Line Using Near Infrared Spectroscopy. Recycling 2021, 6, 11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Riba, J.R.; Cantero, R.; Canals, T.; Puig, R. Circular economy of post-consumer textile waste: Classification through infrared spectroscopy. J. Clean. Prod. 2020, 272, 123011. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roos, S.; Sandin, G.; Zamani, B.; Peters, G.; Svanström, M. Will Clothing Be Sustainable? Clarifying Sustainable Fashion. In Textiles and Clothing Sustainability. Textile Science and Clothing Technology; Muthu, S., Ed.; Springer: Singapore, 2017; pp. 1–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jalil, M.H.; Shaharuddin, S.S. Consumer purchase behavior of eco-fashion clothes as a trend to reduce clothing waste. Int. J. Innov. Technol. Explor. Eng. 2019, 8, 4224–4233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Umar, A.; Khan, M.S.; Alam, S.; Zekker, I.; Burlakovs, J.; dC Rubin, S.S.; Bhowmick, G.D.; Kallistova, A.; Pimenov, N.; Zahoor, M. Synthesis and Characterization of Pd-Ni Bimetallic Nanoparticles as Efficient Adsorbent for the Removal of Acid Orange 8 Present in Wastewater. Water 2021, 13, 1095. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jabeen, S.; Sufaid Khan, M.; Khattak, R.; Zekker, I.; Burlakovs, J.; Rubin, S.S.d.; Ghangrekar, M.M.; Kallistova, A.; Pimenov, N.; Zahoor, M.; et al. Palladium-Supported Zirconia-Based Catalytic Degradation of Rhodamine-B Dye from Wastewater. Water 2021, 13, 1522. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsimnadis, K.; Kyriakopoulos, G.L.; Arabatzis, G.; Zervas, E. Waste collection and treatment networks with source separation from Mobile Green Points (MGP): Citizens awareness and spatial planning for the collection of clean recyclable materials. IOP Conf. Ser. Earth Environ. Sci. 2022, 1123, 012069. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, A.; Singh, S.; Gupta, R.K. Optimization of Alkaline Pretreatment for Enhancing Enzymatic Hydrolysis of Cotton Textile Waste. J. Clean. Prod. 2020, 264, 121738. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martinez, E.; Rodriguez, P.; Garcia, A. Mechano-Biological Pretreatment of Textiles for Enhanced Glucose Production via Enzymatic Hydrolysis. Bioresour. Technol. 2022, 335, 125268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).