Abstract
To ensure the safety of supercritical CO2 pipelines and address the limitations of full-scale fracture tests, such as high risk and substantial investment, software for evaluating the crack arrest toughness of CO2 pipelines containing impurities was developed based on the Battelle Two-Curve Model (BTCM) in this study. The software is programmed in Python (v.3.12.4), with a graphical user interface (GUI) built using PyQt6 (v.6.10.0) and a three-tier architecture design. It integrates the resistance curve model and the decompression wave model. To determine the thermodynamic state of the fluid, a large property database covering pure components and various mixtures is embedded, incorporating state equations such as PR, HEOS, and GERG-2008. The software can generate pressure drop curves, decompression curves, and resistance curves. The pressure plateau can be quickly identified by examining the pressure drop curve. Whether the pipeline can achieve self-crack arrest can be rapidly judged by comparing the positional relationships between the decompression curve and the resistance curve. To verify the accuracy of the software’s calculation results, comparisons were conducted with previous decompression wave experimental data, full-scale burst test data of a CO2 pipeline, and the international HLP model. The calculation error of the software is within 10%. The development and application of this software provide a convenient, efficient, and accurate practical tool for the calculation of crack arrest toughness and crack arrest evaluation of supercritical CO2 pipelines.
1. Introduction
Since the signing of the Paris Agreement, unprecedented attention has been paid globally to climate change, and a fundamental consensus has been formed on the long-term goal of controlling carbon emissions and achieving carbon neutrality [1,2,3,4]. Carbon Capture, Utilization and Storage (CCUS) is recognized as a key pathway to achieve carbon neutrality, within which CO2 transportation serves as a critical intermediate link connecting various carbon handling processes. Among the methods for CO2 transport, pipeline transportation is widely acknowledged as the most economical and efficient option for long-distance, large-scale scenarios, with supercritical CO2 pipeline transportation being considered the most efficient method currently available [5,6,7,8].
Under supercritical CO2 transport conditions, the pipeline interior is maintained at high pressure. Compared to natural gas, CO2 exhibits a more pronounced Joule-Thomson effect. In the event of a pipeline leak caused by damage, defects, corrosion, or seismic events, the leakage leads to a rapid local temperature drop in the pipe material, a sharp decrease in toughness, and the initiation of cracks. The phase transition during supercritical CO2 decompression results in a saturation pressure, and the inability of the crack-tip pressure to release instantaneously can lead to long-running ductile fracture propagation [9,10]. Consequently, engineering requirements for the fracture arrest toughness of CO2 pipelines are significantly more stringent than those for natural gas pipelines.
Ductile fracture propagation in pipelines is highly hazardous, as it may cause damage to the pipeline system, harm the environment, and pose risks to personnel. Specialized research and analysis are required to determine the minimum fracture arrest toughness requirement, ensuring that the pipeline material can arrest fracture propagation autonomously upon crack initiation. The core of pipeline fracture control lies in specific design optimization and material selection to ensure the pipeline possesses sufficient fracture resistance to prevent crack propagation, thereby safeguarding structural integrity and operational safety. Among these, autonomous fracture arrest—achieved solely through the material’s inherent toughness without relying on external devices such as arrestors—represents a highly valuable approach to fracture control [11,12,13].
Currently, the Battelle Two-Curve Method (BTCM) is an effective criterion for verifying whether a pipeline can achieve autonomous crack arrest through its toughness. This method is a semi-empirical formula derived from full-scale fracture tests conducted on low-grade steel pipelines for natural gas transportation. It assesses the pipeline’s arrest toughness by comparing the crack propagation speed curve with the decompression wave speed curve. Clearly, materials with higher mechanical properties and toughness are more capable of resisting ductile fracture propagation than those with inferior properties. Research on CO2 decompression behavior and toughness-based arrest is a key and challenging focus in the safety design, risk assessment, and integrity management of CO2 pipelines.
Regarding decompression wave propagation characteristics, international experimental studies have been conducted to clarify the mechanisms and influencing factors of CO2 decompression waves. Europe and the United States have carried out early experimental work on CO2, with representative studies by Botros [14,15] and Cosham [16,17]. Full-scale fracture tests performed by Cosham et al. indicated that the decompression wave “pressure plateau” is caused by the formation of gas–liquid saturated phases due to pressure instability inside the pipe, preventing timely pressure reduction. The shock tube experimental setup established by Botros et al. was used to study the influence of temperature, pressure, and purity on the decompression wave speed in CO2 pipelines. It was found that the initial decompression wave speed is positively correlated with the initial pressure of CO2, while the initial temperature and concentration of CO2 affect the magnitude of the decompression wave “pressure plateau”.
Existing models for decompression waves in CO2 pipelines are primarily categorized into two types: the Homogeneous Equilibrium Model (HEM) and the Two-Fluid Model (TFM). Among the relatively well-established decompression wave calculation models are GASDECOM, GASMISC, and REFPORP, among others [18]. Based on a one-dimensional Homogeneous Equilibrium Model, the influences of pipeline diameter and wall thickness on decompression wave propagation were investigated by Picard et al. [19]. Aursand et al. [20] examined the relationship between decompression wave curves and the content/type of impurities in CO2 mixtures using different equations of state (EOS). An HEM was developed, the results of which showed good agreement with experimental data, and the decompression theory was optimized by considering factors such as friction and heat transfer. A decompression wave prediction model for CO2 containing impurities was established by Jie et al. [21]. By comparing with experimental data published by Cosham et al. [16,17], the effects of different EOS on the decompression wave speed in CO2 mixtures were analyzed, taking pipe wall roughness into account. The results indicated that the plateau pressure in the gaseous phase decompression wave was overestimated, and the assumptions of the homogeneous equilibrium model were no longer valid when wall friction was considered. Through studying the decompression process of CO2 mixtures with various impurities, Botros et al. [22] found that calculation results using the GERG-2008 EOS showed better agreement with experimental data compared to those obtained with the PR EOS. It was found by Guo et al. [23] that the variation trend of decompression wave propagation speed at different locations along the pipeline was almost identical. Furthermore, pipelines initially containing supercritical CO2 were more susceptible to long-running fracture propagation compared to those containing dense-phase CO2. Research by Li et al. [24,25] revealed that the introduction of non-polar impurities (impurity components with coinciding positive and negative charge centers, lacking a dipole moment, and exhibiting relatively stable chemical properties) led to an increase in the plateau pressure of the decompression wave curve for supercritical CO2 pipelines. This increased the likelihood of the curve intersecting with the pipeline crack propagation speed curve, thereby heightening the risk of pipeline fracture. Conversely, the presence of polar impurities was found to slightly reduce the plateau pressure of the decompression wave curve in supercritical CO2 pipelines, consequently reducing the risk of long-running fracture propagation.
Furthermore, full-scale fracture testing serves as a critical method for investigating pipeline crack propagation and arrest. For natural gas pipelines, extensive research and testing have been conducted on fracture control in both conventional and high-strength steel pipelines transporting lean and rich gases. Over the past 40 years, hundreds of full-scale burst tests have been performed to calibrate empirical and semi-empirical models for predicting the toughness values required for fracture arrest [12,26]. In contrast, only a limited number of full-scale burst tests have been conducted worldwide for CO2 transportation pipelines, as listed in Table 1. Key differences among several major full-scale test programs (e.g., COOLTRANS, SARCO2, CO2SAFE-ARREST) are reflected in their test parameters, crack arrest performance, and conclusions regarding modifications to the Battelle Two-Curve Method (BTCM). The COOLTRANS program involved three burst tests on X65 grade pipelines of different specifications (Φ 914 mm × 25.4 mm, Φ 609.6 mm × 19 mm). BTCM predictions were found to be non-conservative in all cases, requiring the application of a fixed correction factor ranging from 1.2 to 1.8. The SARCO2 program conducted two tests using X65 grade, Φ 609.6 mm pipelines with wall thicknesses of 12.5–13.7 mm. The crack arrest locations differed between the tests: in the first test, cracks arrested after short-distance propagation on both sides of the pipe body; in the second test, the crack on the north side arrested at a crack arrester, while the crack on the south side arrested in the second pipe segment following the initiation pipe. This program concluded that applying a fixed correction factor to the BTCM was difficult, suggesting instead a correction factor range between 1.6 and 2.2. The CO2SAFE-ARREST program utilized X65 grade, Φ 610 mm pipelines with wall thicknesses of 13.5–15.0 mm, performing two tests with different backfill conditions. The first test employed clay backfill at a burial depth of 1 m, resulting in crack arrest in the third pipe segment on either side of the initiation pipe. The second test used asymmetric backfill, leading to crack arrest in the fourth pipe segment. Even with a correction factor of 1.7, the BTCM prediction remained non-conservative.

Table 1.
Full-scale burst test data of CO2 pipelines.
Industrial-scale full-scale burst testing for CO2 pipelines is associated with high costs, significant challenges in data acquisition, lengthy preparation periods, and the need for high-precision data acquisition equipment [34]. Currently, full-scale pipeline fracture control testing facilities are only available in the UK, Italy, Russia, China, and Norway. The primary differences between CO2 and natural gas pipelines concerning ductile fracture propagation control are: (a) CO2 pipelines operate at higher pressures to maintain the CO2 in a dense-phase/liquid state. (b) The decompression behavior of CO2 mixtures differs due to the liquid-to-gas phase change. (c) Impurities have a more pronounced effect on the decompression behavior of CO2 mixtures compared to natural gas mixtures. Because the decompression process following a leak in supercritical CO2 maintains a high-pressure plateau due to phase transition, the BTCM tends to yield unsafe (non-conservative) predictions for fracture arrest in CO2 pipelines. Consequently, corrections based on full-scale burst tests are necessary, particularly for high-grade and high-toughness materials, requiring adjustments to the predicted toughness values. Standards such as ISO 27913 recommend that when considering carbon dioxide mixtures, the minimum correction factor is 1.2, but it shall be verified based on applicable test data [35].
In the context of the high costs and significant safety risks associated with current full-scale pipeline experiments, the development of specialized software dedicated to calculating the fracture arrest toughness of CO2 pipelines is considered to possess considerable practical significance and engineering value. Traditional physical testing methods not only require substantial investments of funding and time but are also accompanied by high operational risks and uncertainties in outcomes. Particularly in high-pressure application scenarios such as supercritical CO2 transport, the experimental challenges and safety risks are further exacerbated. By establishing a scientifically reliable numerical simulation tool, a portion of the high-cost physical tests can be effectively substituted, thereby providing a low-cost, high-efficiency, and repeatedly verifiable computational solution for material selection, structural design, and safety assessment of CO2 pipelines. The successful development of such software is expected to vigorously promote the safety development of key long-distance pipeline infrastructure within the Carbon Capture, Utilization and Storage (CCUS) technological framework. Consequently, it will provide crucial technical support for the implementation of green energy strategies and the achievement of carbon neutrality goals.
2. Pipeline Fracture Arrest Assessment Model
Since the concept of fracture mechanics was introduced by Griffith, the theoretical framework in this field has been continuously supplemented and refined by scholars for over a century. Among these contributions, Irwin’s extension of Griffith’s theoretical system laid the foundation for the establishment of ductile fracture theory. In 1972, the Battelle Two-Curve Method (BTCM) was proposed by Maxey [36], which remains a fundamental approach widely applied in the field of pipeline ductile fracture control. Over the following decades, extensive research has been conducted by scholars on pipeline decompression wave propagation behavior and crack propagation mechanisms, leading to significant progress both theoretically and practically.
It was proposed by Maxey that a correspondence exists between the driving force for ductile fracture propagation and the gas pressure within the crack tip plane. Under steady-state conditions, the pressure value at the crack tip is related to the corresponding propagation speed of the crack itself. Based on this hypothesis, the BTCM assesses whether the pipeline’s arrest toughness can prevent fracture propagation by comparing the crack propagation speed curve with the decompression wave speed curve [37]. When a pipeline undergoes rapid decompression due to leakage or rupture, a decompression wave is generated at the leak point and propagates towards both ends of the pipeline. If the decompression wave speed exceeds the crack propagation speed, arrest will occur; conversely, if the decompression wave speed is lower, the crack will continue to propagate indefinitely until an obstruction is encountered.
Whether a crack continues to propagate is determined by the relative positions of the crack propagation velocity curve and the gas decompression curve. Ductile crack arrest is achieved when the two curves do not intersect, as the decompression wave speed exceeds the crack speed at any pressure. If the curves intersect, indefinite propagation occurs at the pressure where the speeds are equal, until an obstruction is met. The minimum required arrest toughness value for the pipeline can be determined when the two curves are tangent, as illustrated in Figure 1.

Figure 1.
Schematic of the fracture arrest assessment using BTCM.
The decompression curve is expressed as a functional relationship between the pipeline internal pressure or hoop pressure and the decompression wave velocity, and it is a key factor promoting crack propagation. Driving factors for decompression wave velocity include the temperature of the transported medium, the local speed of sound, and the outflow velocity of the fluid in the pipeline. The crack propagation velocity curve is defined as a functional relationship between the pipeline internal pressure or hoop pressure and the crack propagation velocity, characterizing the fracture velocity at different toughness levels. Driving factors for crack propagation velocity include the stress in the pipeline, the pipeline geometry, the crack arrest toughness of the pipe material, and the pipeline backfill constraints (e.g., soil, water, air). Obviously, materials with higher mechanical properties and toughness are more resistant to ductile fracture propagation than those with inferior properties.
The BTCM was initially developed based on specific assumptions, including pure methane flow within the pipeline (with only minimal impurities) and the gas being in a state of adiabatic isentropic flow. Under this premise, the relationship between the decompression wave speed and pressure can be derived, as shown in Equation (1).
In the formula, Pd is the gas decompression pressure in the pipeline, MPa; P0 is the initial pressure of the pipeline before fracture, MPa; V is the decompression wave velocity at the pressure Pd, m/s, Va is the speed of sound in the gas under initial pressure and temperature, m/s; γ is the initial specific heat ratio of the gas, J/(mol·K).
2.1. Resistance Curve Model
Currently, the BTCM based on Charpy impact toughness remains the most standardized and widely applied method for fracture arrest design in industry. The specific approach is based on the premise that crack velocity depends on flow stress and fracture resistance. By analyzing existing full-scale experimental data, the relationship between crack velocity and pressure is determined, as shown in Equation (2). The expressions for the arrest hoop stress and arrest pressure are provided in Equations (3) and (4), respectively. Equation (4) gives the intercept of the crack propagation velocity curve on the pressure axis [26].
In the equation, Vf is the crack propagation speed, m/s; C is the backfill constraint coefficient, taken as 3.79 for air backfill, 2.75 for soil backfill, and 2.34 for water backfill; CVN is the Charpy impact energy (full-size Charpy V-notch specimen), J; A is the cross-sectional area of the Charpy V-notch specimen, mm2; is the flow stress (=specified minimum yield strength of the pipe material + 68.95 MPa), MPa; is the arrest stress, MPa; is the arrest hoop stress, MPa.
In the equation, E denotes the elastic modulus, MPa; R represents the average radius of the pipeline, mm; t indicates the wall thickness of the pipeline, mm; Pa is the crack tip arrest pressure, MPa.
The Battelle Two-Curve Model (BTCM) method has been validated on low-to-medium grade pipeline steels with a Charpy impact energy of 100 J. However, the toughness value of standard pipe materials currently produced can be guaranteed to exceed 250 J, indicating significant differences between the materials used for model validation in the 1970s and modern steel materials. In recent years, the results of several full-scale burst tests conducted on high-grade and high-toughness natural gas pipelines have been inconsistent with the predictions of BTCM to a certain extent. For the application of the BTCM method in modern steel materials, especially high-grade and high-toughness materials, modifications to the predicted toughness values are required, which are generally referred to as BTCM correction factors.
The latest versions of standards issued by the International Organization for Standardization (ISO) and Det Norske Veritas (DNV) have proposed a new method for evaluating the resistance of pipeline ductile fracture propagation events during the transportation of carbon dioxide mixtures. For carbon dioxide mixtures, the plateau period in their decompression curves is extremely long, and the tangent point of the resistance curve often occurs within this plateau region. The crack arrest pressure can be easily calculated using the BTCM equation, where the saturation pressure is the starting point of the plateau on the right side of the decompression curve. The calculation methods recommended in ISO 27913 are shown in Equations (5) and (6).
In the equations, CVN denotes the Charpy V-notch impact energy (full-size specimen), J; E represents the elastic modulus, MPa; AC is the shear area of the impact specimen (80 mm2 for full-size specimens), mm2; refers to the flow stress ( = yield stress + 68.95 MPa), MPa; R is the average radius of the steel pipe, mm; T denotes the wall thickness of the steel pipe, mm; OD is the outer diameter of the steel pipe, mm; Ccf is the correction factor (Ccf ≥ 1.2); and ps represents the maximum saturation pressure, MPa.
As mentioned earlier, standards such as ISO 27913 recommend that when considering carbon dioxide mixtures, the minimum correction factor is 1.2, but it shall be verified based on applicable test data [35]. By applying the BTCM prediction to 5 selected tests from the published full-scale tests of carbon dioxide mixture pipelines (see Table 2), it is found that there is a 60% error in the BTCM prediction, and all errors are related to the predicted crack propagation. Through trial calculations of different correction factors, it is determined that the correction factor ranges between 1.6 and 2.2, which is much higher than the minimum value of 1.2 recommended by ISO standards. The evaluation results of the correction factor are shown in Figure 2. This range is bounded by an upper limit and a lower limit, where the upper limit is a conservative threshold above which all crack propagation can be avoided. It should be noted that due to the limited number of existing tests on CO2 pipelines and the large dispersion of existing test results, more research and tests are required to determine a reliable correction factor.

Table 2.
Five full-scale burst tests of CO2 gas mixtures listed in published literature and correction factors.
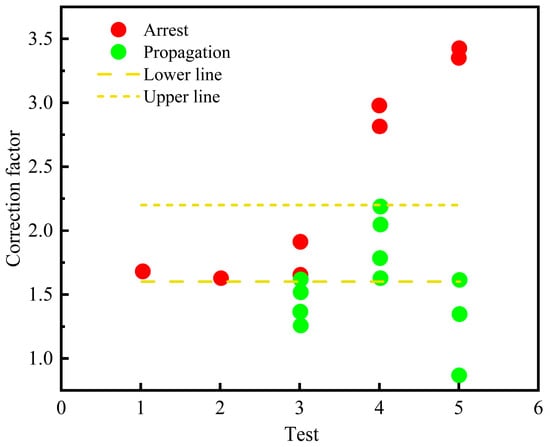
Figure 2.
Evaluation of the BTCM correction coefficient in the transportation of CO2 mixtures.
2.2. Decompression Wave Model
A decompression wave refers to a pressure wave generated by a sudden pressure drop in a pipeline due to reasons such as pipeline leakage, pipeline fracture, or blockage inside the pipeline. The propagation speed and attenuation characteristics of the pressure wave are crucial for the safe operation of the pipeline.
The characteristics of decompression waves, including their propagation speed and pressure variation, are influenced by multiple factors, such as the composition, phase state, pressure, and temperature of the fluid, as well as the pipe material and pipeline dimensions [38,39]. The composition of the fluid directly affects the fluid’s physical property parameters, leading to changes in the characteristics of decompression waves [20,40]. The higher the initial pressure or flow velocity of the fluid, the greater the energy stored in the fluid; thus, the larger the energy released when the pipeline ruptures, resulting in a higher propagation speed of the decompression wave [18]. When the temperature of the fluid changes, it affects the density and viscosity of the fluid, altering the propagation characteristics of the decompression wave. In gas–liquid two-phase flow, the interaction between the two phases makes the propagation of decompression waves more complex, and the propagation characteristics of decompression waves in supercritical fluids also have their uniqueness [41,42]. In small-diameter pipelines, due to the significant non-isentropic effect, isentropic and non-isentropic models need to be established to calculate the speed of decompression waves [43].
Since full-scale pipeline experiments require higher costs than numerical simulations and are difficult to repeat, scholars have mostly adopted numerical simulation methods to study the propagation characteristics of decompression waves. Existing CO2 pipeline decompression wave models are mainly divided into two categories: one is the Homogeneous Equilibrium Model (HEM), and the other is the Two-Fluid Model (TFM). These models simulate the influence of different physical conditions on the propagation of decompression waves, such as pipeline diameter, wall thickness, impurity content and types, providing important references for theory and practical operations.
The propagation speed of a decompression wave depends on the outflow velocity at the leak orifice and the local sound speed of the fluid. The local sound speed of the fluid depends on the thermodynamic state of the fluid. Due to the extremely strong Joule-Thomson effect of CO2, once a CO2 pipeline ruptures, the sudden drop in pressure and temperature causes the CO2 inside the pipe to undergo a phase transition into the gas–liquid two-phase region. The mixing of gas and liquid phases greatly changes the flow structure of the medium, resulting in its compressibility being much greater than that of single-phase gas or liquid, causing a sudden drop in the decompression wave. In this case, the establishment of a decompression wave model for CO2 pipelines containing impurities needs to be based on the homogeneous equilibrium model framework, combined with the gas state equation and sound speed equation. The model makes the following assumptions: (a) The CO2 inside the pipe is one-dimensional isentropic flow, ignoring the effects of heat conduction and convection; (b) The pipeline is a horizontal pipe, without considering the effects of height difference and pipe diameter; (c) The initial state of CO2 inside the pipe is a thermodynamic equilibrium state; (d) There is no slip between the gas and liquid phases.
The decompression wave reflects the relationship between the medium pressure inside the pipe and the decompression wave speed. The calculation method for the decompression wave speed (W, m/s) is shown in Equation (7). After pipeline leakage, CO2 inside the pipeline flows from the leak orifice to the atmosphere. At the moment of pipeline leakage, the outflow velocity of the fluid at the leak orifice is 0. As the leakage process proceeds, according to the method of characteristics in computational fluid dynamics, the outflow velocity (U, m/s) of the fluid inside the pipe is given in the form of Riemann invariants, and the calculation method is shown in Equation (8). For large-diameter pipelines, the decompression process can be regarded as one-dimensional isentropic and adiabatic, and the final simplified form is shown in Equation (9). The calculation method for the local sound speed (a, m/s) is shown in Equation (10). The local sound speed of the fluid depends on the thermodynamic state of the fluid. During calculation, the initial temperature at the time of leakage is taken as the reference, and the pressure is trial-calculated with ΔT as the temperature reduction step. According to the assumed isentropic process conditions, when the entropy values corresponding to the two temperatures in the calculation are equal, the pressure value is output, and then the sound speed, medium outflow velocity, and decompression wave speed are calculated. When the calculated decompression wave speed or pressure is zero, the program terminates. The program block diagram is shown in Figure 3.
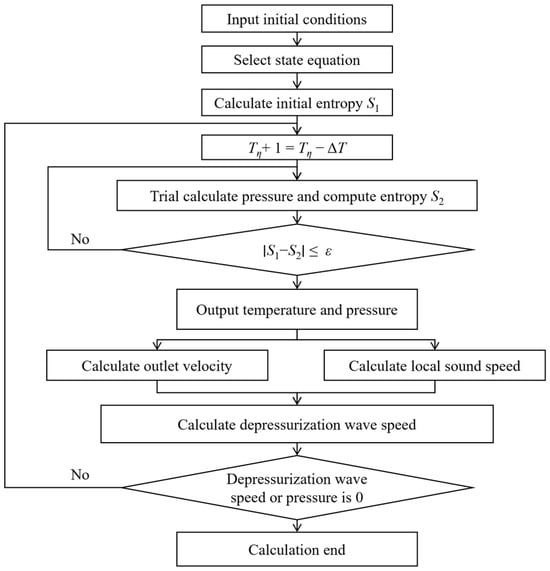
Figure 3.
Model calculation flowchart.
In the equation, W denotes the propagation speed of the decompression wave, m/s; a represents the local sound speed of the medium inside the pipe, m/s; U is the outflow velocity of the fluid inside the pipe, m/s. p is the fluid pressure, kPa; ρl is the average density of the fluid, kg/m3. The subscript η indicates physical parameters under different calculation steps; the subscript s denotes the isentropic process.
2.2.1. Calculation of Local Sound Speed Based on Isochoric Thermodynamics
For the calculation of decompression wave speed, scholars have focused on the calculation of local sound speed. The influence of discontinuous sound speed on the propagation speed of decompression waves was discussed by Lund et al. [44]. A calculation model for local sound speed was proposed by Flatten et al. [45] to calculate the decompression wave speed. However, when calculating supercritical CO2, especially for CO2 fluid near the critical point (Pc = 7.38 MPa, Tc = 31.1 °C), the model often fails to converge.
The sound speed calculation in this model is based on the parameter tracking method of isochoric thermodynamics, which can avoid non-convergence problems. From the perspective of isochoric thermodynamics, Bell et al. [46] calculated the thermodynamic parameters of mixtures. By taking the Helmholtz energy density as the basic thermodynamic potential and converting the mole fraction into molar density (or concentration), the problem of difficult differential calculation was effectively avoided. This method takes molar density as an independent variable, which does not affect other variables, and treats the concentration difference in each component as an independent variable, simplifying the mathematical expression and calculation process, and it is no longer necessary to consider whether a phase transition occurs during the flow process.
The calculation process of local sound speed is shown in Figure 4. Different algorithms are used to solve the nonlinear equations and differential equations in the Helmholtz energy density expression. It is found that far from the critical region, the solution of the differential equations converges rapidly; near the critical region, the solution of the differential equations is numerically unstable, and at this time, the solution effect of the nonlinear equations is better. By substituting the calculation results into the explicit form of the GERG-2008 equation of state, the physical parameters such as medium temperature, pressure, density, adiabatic coefficient, and compression factor can be solved, and thus the local sound speed can be obtained.
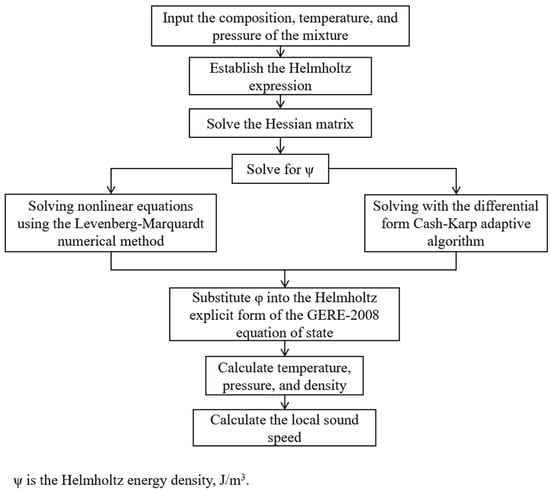
Figure 4.
Flowchart for local sound speed calculation based on isochoric thermodynamics.
2.2.2. Equation of State
To determine the thermodynamic state of the fluid, three equations of state, namely the PR equation, HEOS equation, and GERG-2008 equation, are selected as thermodynamic models for calculation when studying the characteristics of decompression waves.
- (1)
- PR Equation
The PR equation of state was proposed by Peng and Robinson in 1976 [47] and is used to describe the behavior of common gases or liquids, and can be applied to simulate a variety of complex fluid systems. Its equations are shown in Equations (11)–(14).
In the equations, p is the system pressure, MPa; R is the gas constant with a value of 8.314 J/(mol·K); T is the thermodynamic temperature, K; V is the gas volume, m3/mol (note: corrected from m2/mol for physical consistency); b is the characteristic parameter of the substance; α(T) is a function of temperature; Tr is the reduced temperature, K; ac is the acentric factor; and k is the coefficient of α(T).
Since the isentropic partial derivative has the relationship shown in Equation (15) with the isothermal partial derivative and temperature derivative, substituting Equation (15) into Equation (10) yields Equation (16).
- (2)
- HEOS Equation
The Helmholtz Energy Equation of State (HEOS) is used to describe the thermodynamic properties of substances under different states. Based on the concept of Helmholtz free energy, it can effectively characterize the phase behavior of gases, liquids, and solids. In the initial stage of supercritical CO2 pipeline leakage, the rapid drop in pressure at the leak orifice leads to a significant temperature change, and the sharp pressure reduction causes a phase transition of supercritical CO2. According to the principle of isochoric thermodynamics, the initial stage of pipeline segment leakage is approximated as an isochoric process. The change in internal energy is mainly caused by temperature variation, so the temperature change under specific heat exchange and internal energy change can be calculated, thereby determining the phase transition behavior during the leakage process. The central thermodynamic potential of isochoric thermodynamics is the Helmholtz energy density, and its expression is shown in Equation (18) [48].
In the equation, Ψ denotes the energy density, J/m3; A represents the total Helmholtz free energy, J; V is the total volume of the mixture, m3. Among these parameters, A can be expressed as a function of two independent variables, namely density ρ and temperature T, and its expression is shown in Equation (19).
In the equation, ρ denotes the molar density of the mixture, mol/m3; the superscript o indicates the ideal state; and r represents the part related to the compressibility of the fluid.
The Helmholtz free energy equation is a fundamental thermodynamic equation, from which other thermodynamic parameters can be derived. Among these, the expression for pressure is shown in Equation (20). By dividing Ψ into an ideal part and a real part (see Equation (21), the pressure can be further expressed as Equation (22) [49].
In the equation, p denotes the medium pressure, kPa; Ψr represents the real Helmholtz energy density, which itself is a function of T and ρ, with the unit of J/m3. The subscript i denotes different components.
A numerical method must be adopted to solve for Ψ. Taking two components as an example, to ensure numerical stability in the numerical calculation and solution process, a Hessian matrix is introduced. The expression of the Hessian matrix for the local curvature of Ψ(T,ρ) is shown in Equation (23) [46].
Combined with the isochoric phase equilibrium characteristics, different algorithms can be adopted to solve the nonlinear equations and differential equations. Equations (24)–(26) form a system of nonlinear equations, which can be solved using the Levenberg–Marquardt numerical method.
In the equations, ρ denotes the liquid-phase molar density, mol/m3; ρ″ represents the vapor-phase molar density, mol/m3; p′ is the liquid-phase pressure, kPa; p″ is the vapor-phase pressure, kPa. The subscript 1 indicates component 1, and 2 indicates component 2.
In addition, the differential expression for the isochoric phase equilibrium process is shown in Equation (27).
In the equation, denotes the i-th row of the Hessian matrix; σ represents the derivative taken along the phase envelope. The first-order derivative of the concentration in the vapor phase can be obtained through the linear system of equations (Equation (28).
In the equation, has been obtained through Equation System (27), and the remaining parts can be solved by combining the differential equation system (Equation (27) using the adaptive Cash-Karp algorithm.
Both of the above solution methods can be used to calculate the Helmholtz energy density. For the solution of nonlinear equation systems, high requirements are imposed on the initial conditions, and convergence cannot generally be guaranteed. If convergence is achieved, the accuracy of the solution is independent of the initial solution. For the solution of differential equation systems, accurate initial values are required, and the accuracy of the solution depends on the quality of the solution from the previous state. During the simulation and calculation process in this study, the above different calculation methods were selected according to the magnitude of the calculation result error. It was found that far from the critical region, the solution using the differential form converges rapidly; near the critical region, the solution of the differential equation system is numerically unstable, and at this time, the solution effect using the nonlinear equation system is better.
- (3)
- GERG-2008 Equation
For the calculation of the thermodynamic properties of mixtures, the GERG-2008 equation of state is adopted in the model. Developed by the Groupe Européen de Recherches Gazières (GERG), the GERG-2008 equation of state is a multi-parameter Helmholtz equation. It was designed for various natural gas types, including those with high contents of nitrogen, carbon dioxide, ethane, and other components, and exhibits high accuracy. Covering a wide range of temperature and pressure conditions, it is applicable to gaseous, liquid, supercritical, and gas–liquid two-phase states, and has been recognized by the International Organization for Standardization (ISO) as a standard equation for calculating the physical properties of natural gas. All thermodynamic parameters can be derived by substituting the calculation results of the HEOS equation into the explicit Helmholtz form of the GERG-2008 equation of state.
Based on the HEOS equation, the GERG-2008 equation of state incorporates the interactions between multi-component substances, and its expression is shown in Equation (29). The specific expression for the Helmholtz free energy of the ideal mixture gas is presented in Equation (30), while the expression for the residual Helmholtz free energy of the mixture gas is given in Equation (31) [49].
In the equation, φo denotes the Helmholtz free energy of the ideal fluid in the mixture; φr represents the Helmholtz free energy of the residual fluid in the mixture; ρ and T are the density and temperature of the mixture, respectively; is the molar ratio of each substance.
In the equation, is the dimensionless form of the Helmholtz free energy of the ideal gas for component i; N is the number of components in the mixture; is the mole fraction of component i.
In Equation (31), the first term on the right-hand side is the linear summation of the product of the residual properties of pure gases and their mole fractions; the second term represents the influence of interactions between all binary mixtures on the Helmholtz free energy.
3. Development of Pipeline Fracture Arrest Assessment Software
To address the lack of effective quantitative calculation and analysis methods in the field of pipeline resistance to ductile fracture propagation, this study established a computational analysis technique for assessing the resistance of CO2 pipelines to ductile fracture extension. This was achieved by comparing gas decompression models with experimental data and defining the applicable range of correction factors. The developed technique is not only applicable to CO2 pipelines but can also be extended to long-distance natural gas pipelines, demonstrating its cross-media practicality.
Based on this methodology, a computational software for determining the fracture arrest toughness of CO2 pipelines containing impurities was developed using computer programming, grounded in the Battelle two-curve model. This software provides theoretical support for CO2 pipeline design by enabling: (1) rapid calculation of the minimum impact toughness required to resist ductile fracture propagation, verifying whether the pipeline possesses sufficient toughness to arrest fractures autonomously, and (2) delivering precise data for the design phase, thereby enhancing the safety of pipeline construction.
3.1. Development Environment and Technology
The software uses Python (v.3.12.4) as the primary development language. Known for its concise and readable syntax, Python offers robust scientific computing and data processing libraries such as NumPy (v.1.26.4), SciPy (v.1.13.0), and Pandas (v.2.2.2), which can efficiently support numerical simulations and data analysis tasks in this study. Thus, it is well-suited as the foundational language for the software development. The graphical user interface (GUI) was developed using the PyQt6 (v.6.10.0) framework and designed based on a modular approach and a three-tier architecture (data layer, logic layer, and presentation layer). The overall framework structure of the software is detailed in Figure 5.
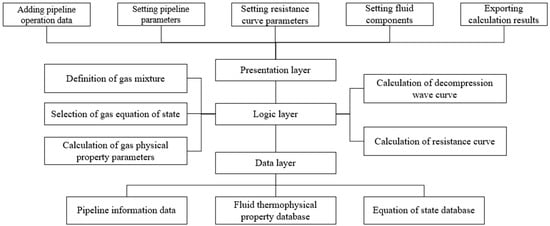
Figure 5.
Overall software framework structure.
Within the three-tier architecture, the bottom layer is the Data Layer, which is primarily responsible for reading various critical data from external sources, including pipeline information data, thermophysical property databases for fluids, and equations of state databases. The middle layer is the Logic Layer; it handles the core tasks of data analysis and computation. This layer can first perform macro-definitions for gas mixtures and select appropriate equations of state, then proceed to calculate gas physical properties, decompression wave curves, and resistance curves. The top layer is the Presentation Layer, encompassing the interactive interface and built-in functions directly accessible to users. At this level, users can set pipeline-related parameters and obtain the final calculation results. The pseudocode for each layer within the three-tier structure, along with the pseudocode for their interaction workflow, is shown in Figure 6.


Figure 6.
Pseudocode for individual layers and their interaction workflow in the three-tier architecture.
The GUI is divided into three main functional areas. The upper-left section is the input parameter area, containing thermodynamic parameters (e.g., temperature, pressure, pressure step size), EOS equation of state selection, a fluid composition table supporting custom input or quick selection of “pre-/post-combustion components” (the table automatically validates that the mole fractions sum to 100%), and input fields for structural parameters like wall thickness and elastic modulus. All parameters are directly editable. The lower-left section is the results display area, featuring a text box for calculation status, a results data table showing six key parameters (including pressure, temperature, speed of sound, and density), along with “Save Results” (export to CSV) and “Save Image” (export chart) buttons. The right section is the chart display area, with the BTCM curve (including the crack propagation velocity comparison line) displayed above and the pressure drop curve below. The charts support real-time refreshing and high-resolution export. The key operational workflow is as follows: First, select the fluid composition (either custom or by quick-selecting preset components). Next, input the thermodynamic and structural parameters. Then, choose the equation of state (HEOS/REFPROP; REFPROP offers GERG/PR sub-options). Click “Run Calculation” to initiate the computation. The results table and charts will then be displayed, and users can click the export buttons to save data or images as needed. The software GUI is shown in Figure 7.
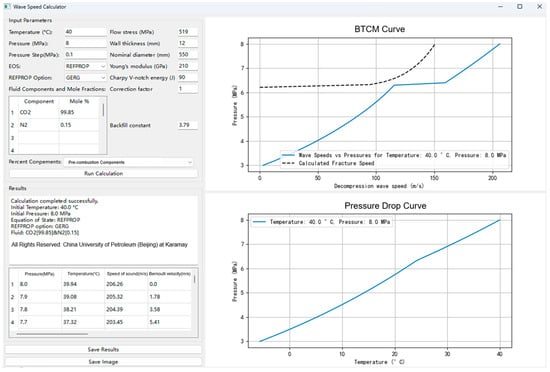
Figure 7.
Layout of the software GUI.
3.2. Software Usage
3.2.1. Input Parameter Settings
The parameter input interface is shown in Figure 8. Users only need to set the initial pressure and temperature of the pipeline transport medium, the calculation step size, select an appropriate equation of state, and define the gas components and their mole fractions. The software will then output the decompression wave curve and the pressure drop curve.
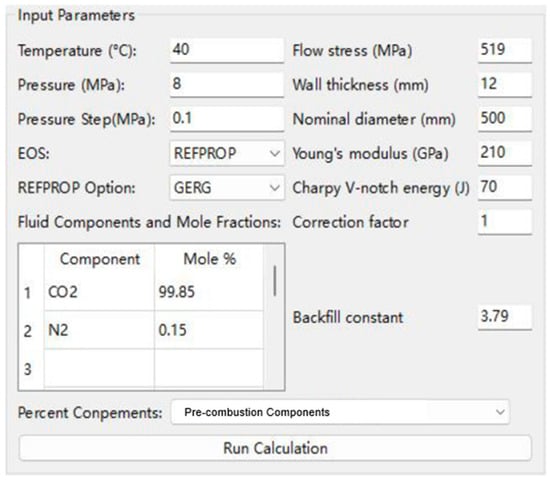
Figure 8.
Input parameter panel of the software.
For supercritical CO2 pipelines, the operating temperature is typically maintained between 40 °C and 50 °C, and the operating pressure between 9 MPa and 15 MPa. A smaller step size can improve calculation accuracy; a value between 0.1 MPa and 0.5 MPa is recommended. When simulating non-hydrocarbon pure components, the HEOS equation of state is recommended. When simulating mixtures or hydrocarbon components, the REFPROP database is recommended, allowing selection of either the GERG-2008 or Peng-Robinson (PR) equation of state based on specific requirements. The gas composition and mole fractions can be adjusted according to the actual gas components. For convenience, the software includes typical gas compositions for three common capture scenarios: pre-combustion capture, post-combustion capture, and oxy-fuel combustion capture.
To calculate the pipeline fracture arrest toughness, users need to input parameters such as flow stress, pipe diameter, wall thickness, elastic modulus, Charpy impact energy, correction factors, and backfill coefficients (accounting for environments such as soil, water, or air).
3.2.2. Output Results Visualization
Upon completion of the simulation, the software outputs parameters such as the decompression wave propagation velocity and local speed of sound as pressure and temperature decrease. The results output interface is shown in Figure 9. Additionally, both the BTCM curve and the pressure drop curve are simultaneously generated, as illustrated in Figure 10.
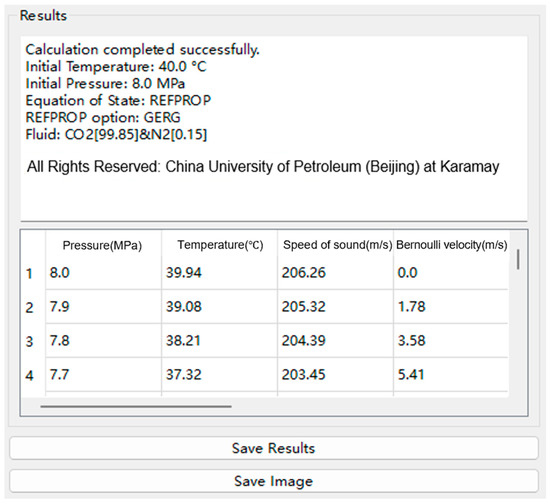
Figure 9.
Results display panel of the software.
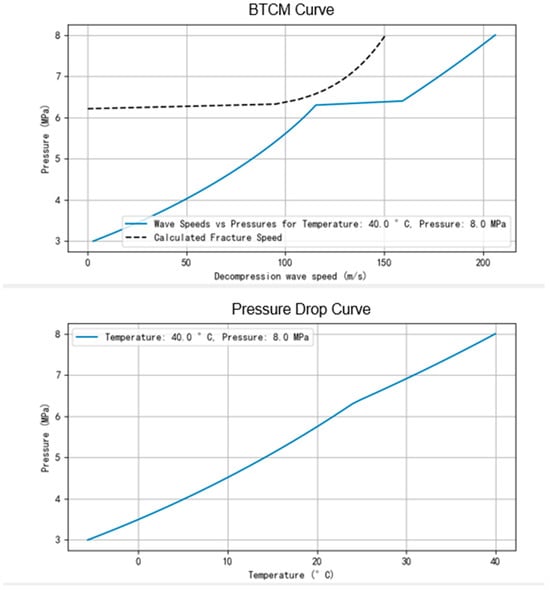
Figure 10.
BTCM curve and pressure drop curve.
When the fracture arrest curve lies above the decompression wave curve, the pipeline can arrest a crack relying on its inherent fracture arrest toughness. Conversely, if the fracture arrest curve falls below the decompression wave curve, the pipeline will be unable to arrest the crack, leading to crack propagation. The presence of an inflection point on the pressure drop curve indicates that the internal gas has entered the gas–liquid two-phase region.
3.3. Software Advantages and Potential Applications
The core advantage of this software lies in its two precise models: an accurate thermodynamic model and an accurate fracture arrest toughness evaluation model. Together, these form the foundation supporting the software’s core functionality and application value.
The accurate thermodynamic model provides the essential basis for physical property calculations required for decompression wave analysis and pipeline fracture arrest assessment. The software incorporates an extensive built-in database of physical properties covering pure components and various mixtures, integrated with mainstream equations of state such as HEOS (Helmholtz Energy Equation of State). Utilizing these resources, the software can accurately calculate a range of key physical parameters—including fluid density, speed of sound, enthalpy, entropy, and phase equilibrium boundaries—across a broad range of temperatures and pressures. This ensures the scientific reliability and engineering value of the subsequent fracture arrest toughness predictions.
The accurate fracture arrest toughness evaluation model operates on the core principle of comparing the relative positions of the decompression wave curve and the pipeline’s fracture arrest toughness curve to determine the crack propagation tendency. Based on this model, the software delivers core functionalities such as decompression wave velocity calculation and toughness assessment, providing direct support for pipeline fracture arrest analysis.
Leveraging these advantages, the software is primarily applicable to the safety design and assessment of ductile fracture control in high-pressure gas pipelines within the energy, chemical engineering, and CCUS sectors. It can precisely characterize decompression wave propagation behavior and evaluate whether a pipeline meets safe operating conditions. Specific application scenarios include the safety design of new pipelines, integrity assessment of existing pipelines, and evaluation of pipeline repurposing for different transport media.
4. Verification of Software Calculation Accuracy
4.1. Experimental Validation of the Decompression Wave Prediction Model
To verify the accuracy and reliability of the built-in decompression wave model, the software’s calculation results were compared and analyzed against experimental data. This study selected relevant experimental data from sources such as Botros for reference. Comparative analyses were conducted on the predicted decompression wave curves for two typical scenarios: pure CO2 and impurity-containing CO2 (with a CO2 volume fraction of 96.67% and an O2 volume fraction of 3.33%) pipeline leaks. The initial conditions were 36.5 °C and 34.0 MPa, and 35.1 °C and 14.6 MPa, respectively. The specific comparison results are shown in Figure 11.
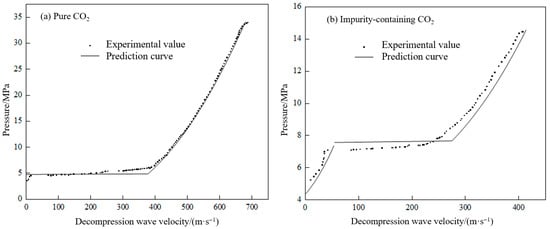
Figure 11.
Comparison of predicted decompression wave curves with experimental data.
The decompression wave curves calculated by the model show a consistent trend with the experimental values. A pressure plateau appears in both cases upon entering the gas–liquid two-phase region. For the prediction of the decompression wave curve in pure CO2 pipeline leaks, the model’s predictions fit the experimental values well across various pressure zones. For the impurity-containing CO2 pipeline leak scenario, the model’s predicted pressure plateau is slightly higher than the experimental value. A higher predicted plateau pressure corresponds to a higher saturation pressure, which in turn leads to a greater required fracture arrest toughness for the pipeline. From a pipeline design perspective, this result is more conservative.
4.2. Engineering Verification of the Pipeline Fracture Arrest Assessment Model
4.2.1. Project Overview
On 15 May 2023, China conducted its first full-scale burst test of a CO2 pipeline [33]. The test section consisted of pipe segments made of X65 grade steel with an outer diameter of 323.9 mm (1 initiation pipe and 6 test pipes). The wall thickness of the initiation pipe was 7.0 mm. Symmetrically arranged on both sides of the initiation pipe were pipes with increasing toughness, having wall thicknesses of 7.0 mm, 7.2 mm, and 7.6 mm, respectively. The specific arrangement and parameters are shown in Figure 12 and Table 3. The test gas composition was 95% CO2 + 4% N2 + 1% H2. The initial pressure of the gas inside the steel pipe was 11.85 MPa, and the initial temperature was 12.6 °C.
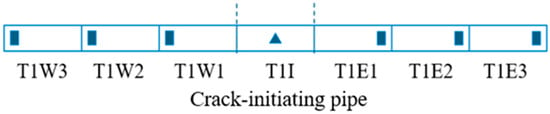
Figure 12.
Schematic diagram of the distribution of steel pipes in the burst test.

Table 3.
Material properties of the burst test pipeline.
The test involved the installation of 8 high-frequency pressure sensors and 6 temperature sensors. Pressure sensors were installed on the east and west sides of T1W3, and on the west sides of T1W2, T1W1, T1E1, T1E2, and T1E3. One insertion temperature sensor (at the midpoint of T1I) was inserted into the pipe interior, and five patch-type temperature sensors (installed at T1W1, T1W2, T1E1, T1E2, and T1E3) were attached to the external surface of the pipe to measure temperature changes inside and on the surface of the pipeline.
After initiation, the crack propagated from the center of the initiation pipe towards both sides, as shown in Figure 13. On the west side of the initiation point, after penetrating the initiation pipe, the crack continued to extend along test pipe T1W1. The average crack propagation speed in this section was 124.7 m/s, and arrest was ultimately achieved at the girth weld between test pipe T1W1 and the second test pipe, T1W2. On the east side of the initiation point, the crack first propagated continuously within test pipe T1E1 at an average speed of 132.5 m/s, then entered test pipe T1E2 and extended a further 0.75 m before finally being arrested by the inherent toughness of the base pipe material.
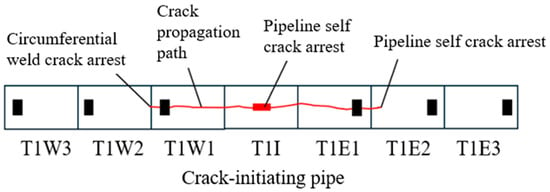
Figure 13.
Schematic diagram of pipeline fracture.
4.2.2. Comparison of Software Calculation Results
The decompression wave curve from the on-site burst test was plotted based on pressure change data captured by dynamic pressure sensors. The software calculated the predicted decompression wave curve using the composition, initial pressure, and temperature of the test gas. As shown in Figure 14, the predicted decompression wave curve shows a high degree of overlap with the experimental curve. The calculated saturation pressure plateau value is close to the experimental value, both around 6.9 MPa, with an error within 5%, demonstrating good predictive accuracy. A detailed error analysis between the calculated and experimental values of the decompression wave curve during the pressure plateau period is listed in Table 4. A noticeable discrepancy exists between the experimental data and the software’s predictions when the decompression wave velocity exceeds 300 m/s. This discrepancy is primarily attributed to the limited number of pressure monitoring points in the field test. The sparse data points in this high-velocity range struggle to adequately capture the continuous relationship between pressure and wave velocity, consequently amplifying experimental errors.
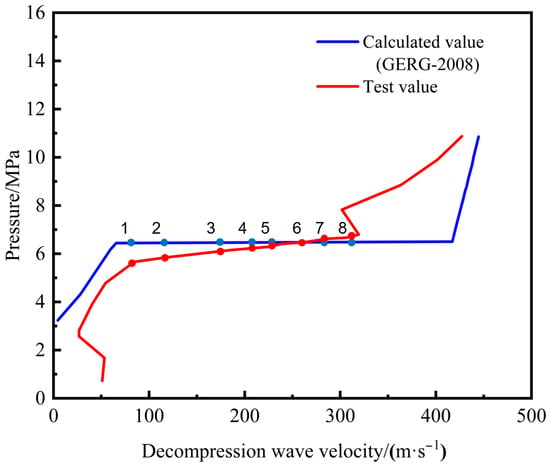
Figure 14.
Comparison of decompression wave curves: software prediction vs. experimental results.

Table 4.
Error analysis between calculated and experimental values during the pressure plateau period.
Furthermore, by inputting the specific parameters of pipe segments T1I, T1W1, and T1E1 into the software, it generated their respective resistance curves, as shown in Figure 15. In the figure, the resistance curves of segments T1I, T1W1, and T1E1 are arranged from right to left, demonstrating sequentially increasing toughness, which is consistent with field observations. Additionally, all three curves intersect the decompression curve, confirming that crack propagation occurred in the pipe segments, thereby validating the accuracy of the software’s predictions.
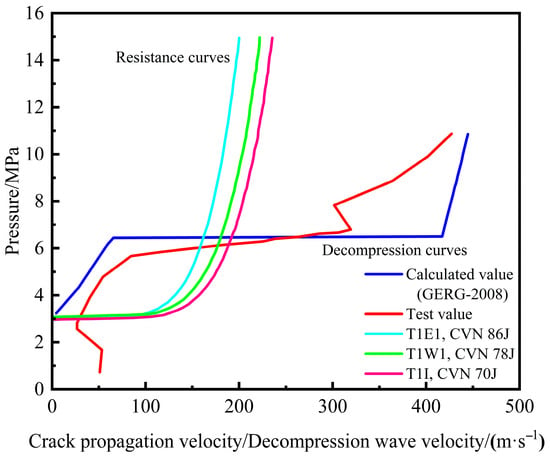
Figure 15.
Comparison of BTCM curves predicted by software and obtained from experiments.
4.3. Comparison with International HLP Model Calculation Results
The self-developed software was used to analyze and calculate the fracture arrest toughness for two CO2 pipeline projects (Project A and Project B). The results were compared with those obtained from the High-strength Line Pipe (HLP) model developed by the JFE Holdings, Inc. (Tokyo, Japan).
For project A, the pipeline material is X52 grade steel with an outer diameter of 406.4 mm, a wall thickness of 7.1 mm, a design pressure of 4.5 MPa, and a design temperature range of 5–50 °C. The gas composition is listed in Table 5. A comparison of the fracture arrest toughness calculation results between this software and the HLP model is shown in Figure 16. The HLP model calculated a value of 14 J, while this software calculated 14.6 J, resulting in a relative error of 4.29%. Both the graphical representation and the numerical results show good agreement between the two methods.

Table 5.
Gas composition of project A.
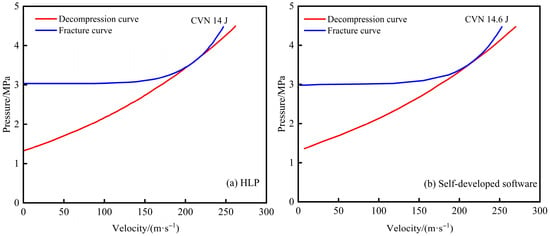
Figure 16.
Comparison of fracture arrest toughness calculation results for project A.
For project B, the pipeline utilizes X52 grade steel with an outer diameter of 273.1 mm, a wall thickness of 11.1 mm, a design pressure of 12.0 MPa, and a design temperature range of 13.1–50 °C. The source gas composition is detailed in Table 6. A comparison of the fracture arrest toughness results calculated by this software and the HLP model is presented in Figure 17. The HLP model yields a result of 18 J, whereas this software calculates 16.3 J, resulting in a relative error of 9.44%. The graphical representations from both methods show good agreement.

Table 6.
Gas composition of project B.
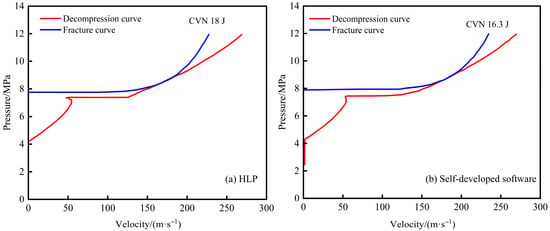
Figure 17.
Comparison of fracture arrest toughness calculation results for project B.
5. Parameter Sensitivity Analysis
5.1. Decompression Wave Propagation Characteristics
5.1.1. Gas Composition
Gas composition varies depending on the carbon capture technology employed. Post-combustion capture typically yields the highest concentration of carbon dioxide, while pre-combustion capture introduces the highest level of impurities. The composition and content of gases from three different carbon capture processes are detailed in Table 7.

Table 7.
Gas composition and concentrations under different carbon capture methods.
The decompression characteristics of CO2 released from pipelines vary significantly depending on the carbon capture method. Using an initial temperature of 40 °C and a medium pressure of 12 MPa as the starting conditions, the decompression wave propagation characteristics for different capture methods are shown in Figure 18.
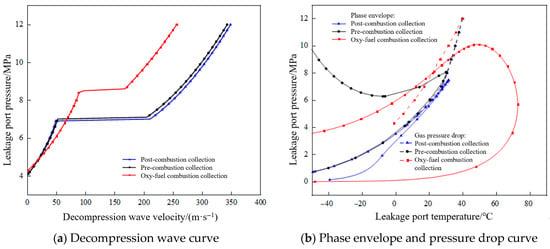
Figure 18.
Propagation characteristics of pipeline decompression waves under different carbon capture methods.
For post-combustion captured CO2, the decompression curve follows the bubble point line during depressurization. In contrast, for pre-combustion captured CO2, the decompression curve follows the dew point line. For oxy-fuel combustion captured CO2, the initial decompression wave velocity decreases from approximately 345 m/s (as in pre- or post-combustion capture) to 256 m/s, representing a reduction of about 26%. Meanwhile, the plateau pressure of the decompression wave significantly increases from around 7.00 MPa (pre- or post- combustion capture) to 8.53 MPa, a rise of 22%, and the plateau range is narrowed. During the depressurization process, the pipeline medium no longer follows the gas–liquid equilibrium line but enters the two-phase region.
5.1.2. Initial Phase State
Using the gas composition from post-combustion capture as the simulation subject, the decompression wave propagation characteristics following a pipeline fracture were calculated for both supercritical phase and dense-phase CO2. The initial conditions for supercritical CO2 were set at 40 °C and 12 MPa, and for dense-phase CO2 at 20 °C and 9 MPa. The calculation results are presented in Figure 19.
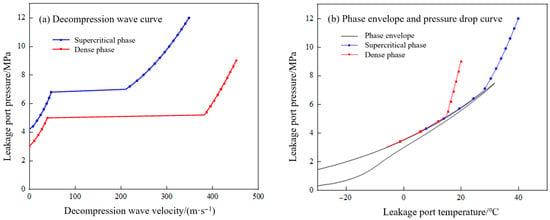
Figure 19.
Propagation characteristics of pipeline decompression waves under different initial phases.
As shown in Figure 19a, the initial decompression wave velocity for a dense-phase CO2 pipeline leak (approximately 452 m/s) is higher than that for a supercritical CO2 pipeline leak (approximately 350 m/s). This is because dense-phase CO2 possesses a higher density and initial speed of sound, allowing the decompression wave to maintain a higher velocity even when it enters the gas–liquid two-phase region. Furthermore, the pressure plateau for the dense-phase CO2 pipeline leak is longer than that for the supercritical CO2 leak and occurs at a lower pressure.
From Figure 19b, it can be observed that the saturation pressure corresponding to the intersection point of the supercritical CO2 pipeline pressure drop curve and the CO2 bubble point curve is higher (6.89 MPa), approximately 26% higher than that of the dense-phase CO2 pipeline. A higher saturation pressure at this intersection point leads to a higher pressure plateau in the decompression wave curve. This indicates that during the operation of a supercritical CO2 pipeline, compared to dense-phase transport, a leak event would require a higher fracture arrest toughness value from the pipeline, result in a lower likelihood of autonomous crack arrest, and pose a greater risk of ductile crack propagation.
5.1.3. Pipeline Initial Pressure
The decompression wave propagation characteristics were calculated and analyzed for a supercritical CO2 pipeline at different initial pressures of 9 MPa, 12 MPa, and 15 MPa. The results are shown in Figure 20.
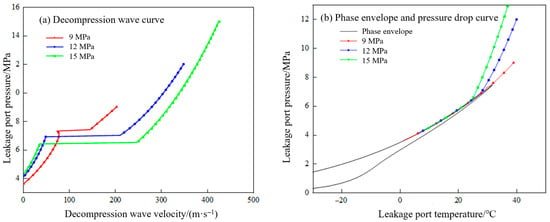
Figure 20.
Propagation characteristics of pipeline decompression waves under different initial leakage pressures.
The corresponding initial decompression wave velocities were approximately 203 m/s, 349 m/s, and 424 m/s, respectively, while the pressure plateau levels were 7.4 MPa, 7.0 MPa, and 6.4 MPa, respectively. This indicates that a higher initial leak pressure results in a greater initial decompression wave velocity, a lower pressure plateau, a reduced required fracture arrest toughness for the pipeline, and consequently, a lower risk of fracture. Appropriately increasing the transportation pressure within the allowable range of operational conditions can effectively lower the pressure plateau and enhance the safety factor of pipeline operation.
5.1.4. Pipeline Initial Temperature
The decompression wave propagation characteristics of a supercritical CO2 pipeline were calculated and analyzed at different initial temperatures of 35 °C, 40 °C, and 45 °C. The results are shown in Figure 21.

Figure 21.
Propagation characteristics of pipeline decompression waves under different initial leakage temperatures.
The corresponding initial decompression wave velocities were approximately 391 m/s, 349 m/s, and 308 m/s, respectively, while the plateau pressures were approximately 6.5 MPa, 6.9 MPa, and 6.9 MPa, respectively. Therefore, for a supercritical CO2 pipeline, a lower operating temperature corresponds to a smaller required fracture arrest toughness in the event of a pipeline leak. Under actual pipeline operating conditions, moderately reducing the operating temperature can effectively lower the pressure plateau and reduce the required fracture arrest toughness of the pipeline. This helps prevent ductile crack propagation and enhances operational safety.
5.2. Pipe Material Toughness Analysis
A fracture arrest analysis was conducted for pipelines of three different steel grades: X65, X60, and X56. The outer diameter of the pipelines was set at 355.6 mm, and the design pressure was set at 13 MPa. Calculations were performed to determine the arrest pressure corresponding to different Charpy impact energies for each given steel grade and various wall thicknesses. The Charpy impact energy was generally within the range of 80 J to 200 J, and the arrest pressure values were determined based on the Charpy impact energies within this range.
The critical pressure of the carbon dioxide pipeline medium is 7.38 MPa. Considering the minor effects caused by fluctuations in the medium composition, an arrest pressure of no less than 8.0 MPa is adopted for fracture arrest control.
The calculated results for the arrest pressure of the 355.6 mm outer diameter pipeline with different steel grades and wall thicknesses are listed in Table 8. The relationship between CVN and arrest pressure for the three wall thicknesses under the X65, X60, and X56 steel grades is shown in Figure 22. Therefore, by increasing the wall thickness, the minimum wall thicknesses required for the straight pipe with a 355.6 mm outer diameter to meet the fracture arrest control criteria for the X65, X60, and X56 steel grades are 12.5 mm, 12.5 mm, and 14.2 mm, respectively.

Table 8.
Table of arrest pressure calculations for 355.6 mm outer diameter pipelines with different steel grades and wall thicknesses.
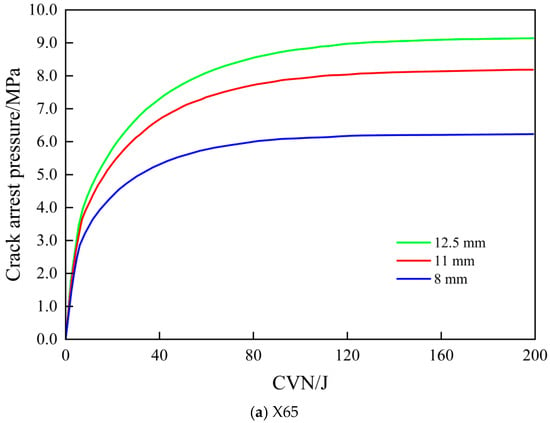
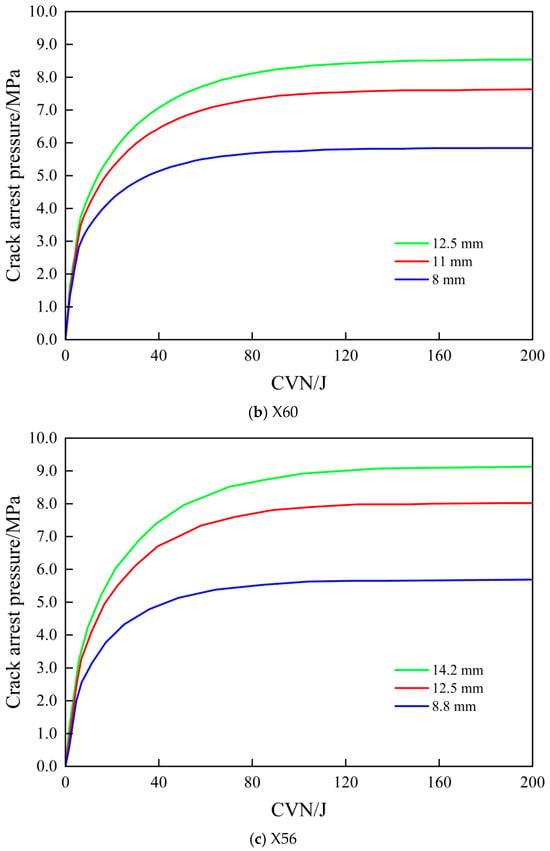
Figure 22.
Relationship between charpy impact energy and arrest pressure for D355.6 pipe with different steel grades.
6. Conclusions and Prospects
- (1)
- Computational software for determining the fracture arrest toughness of CO2 pipelines containing impurities has been developed. Centered on the Battelle Two-Curve Method (BTCM) and incorporating various thermodynamic models such as the Peng-Robinson (PR) and Helmholtz Energy Equation of State (HEOS) equations, this software successfully couples the effects of impurities on both the fluid decompression behavior of CO2 and the material toughness of the pipe. It can accurately determine the fracture arrest toughness boundary for a specific pipe material under given operating conditions. The calculated pressure plateau shows an error within 5% compared to decompression wave test data and full-scale burst test data. The calculated minimum toughness value exhibits an error within 10% compared to results from the international HLP model.
- (2)
- For post-combustion captured CO2 and pre-combustion captured CO2, the pressure drop curves follow the bubble point line and dew point line, respectively, during decompression. In contrast, oxy-fuel combustion captured CO2 shows approximately 26% lower initial decompression wave velocity and about 22% higher pressure plateau. As decompression progresses, the fluid inside the pipe no longer follows the vapor-liquid equilibrium line but directly enters the two-phase region. Compared to the dense phase, supercritical CO2 exhibits a saturation pressure at the intersection of the pressure drop curve and the CO2 bubble point line that is about 26% higher, resulting in a higher pressure plateau. Under different initial pressures of 9 MPa, 12 MPa, and 15 MPa, the pressure plateaus are 7.4 MPa, 7.0 MPa, and 6.4 MPa, respectively. Under different initial temperatures of 35 °C, 40 °C, and 45 °C, the pressure plateaus are approximately 6.5 MPa, 6.9 MPa, and 6.9 MPa, respectively. Lower operating temperatures and higher operating pressures can effectively reduce the pressure plateau.
- (3)
- This software can be used as an auxiliary tool for calculating and evaluating the crack arrest toughness of supercritical CO2 pipelines, providing data support for pipe material selection and operating condition optimization. During application, the recommended value range for the minimum correction factor is 1.6–2.2. Since the core model of the developed software is built based on existing test data and theoretical derivations, it cannot fully replicate the complex operating environment of pipelines in actual engineering. Without verification by professional engineers in combination with specific scenarios, it shall not replace full-scale burst tests as the basis for final decision-making.
- (4)
- Future work plans include introducing more advanced dynamic fracture mechanics models to describe the microscopic mechanisms of crack tip propagation more precisely. We intend to integrate more complex Equations of State (EOS) and a broader impurity database into the software to enhance its predictive capability under extreme compositions or operating conditions. Concurrently, we will study the feasibility of deploying the software at pipeline control centers and develop interfaces with SCADA systems. This upgrade would shift the software from offline manual input to real-time data interaction. By utilizing sensors to monitor gas composition, operational pressure, and temperature at different pipeline sections in real-time, and employing intelligent pigs for periodic wall thickness inspection, the software could enable real-time, continuous fracture arrest assessment for pipelines. Setting alarm thresholds and triggering warnings would provide a means for predicting pipeline safety risks.
- (5)
- In the next step, the software will be developed to include a solver for calculating the minimum toughness required to arrest pipeline crack propagation. The tangent point between the fracture velocity curve and the decompression curve of supercritical CO2 pipelines occurs in the pressure plateau region. Therefore, it is not necessary to determine the complete decompression wave velocity curve when measuring the crack arrest toughness of supercritical CO2 pipelines; it only needs to be ensured that the crack arrest pressure (the intercept of the crack propagation velocity curve on the pressure axis) is higher than the saturation pressure (consistent with the pressure plateau region on the gas decompression curve). Generally, the pipeline’s operating pressure, temperature, medium composition, and other parameters are design input conditions that cannot be easily modified, yet they are key factors for determining the decompression curve. To meet the pipeline crack arrest toughness requirements under the established decompression curve and determine the minimum toughness required to prevent pipeline crack propagation, optimization can be achieved by adjusting pipeline material properties (especially fracture toughness and minimum yield strength) and wall thickness. Of course, in engineering practice, the optimal pipe specification should also be ultimately determined by considering factors such as the price of different steel grades and the quality assurance of welding processes.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, X.L. and D.W.; methodology, D.W. and X.X.; software, X.L., D.W. and X.J.; validation, D.W., X.J. and Y.Y.; formal analysis, D.W.; investigation, X.J. and Y.Y.; resources, X.L., D.W. and X.X.; data curation, X.L., D.W. and X.J.; writing—original draft preparation, X.L., D.W. and Y.Y.; writing—review and editing, X.L., D.W. and Y.Y.; visualization, X.L., D.W. and Y.Y.; supervision, D.W.; project administration, X.L.; funding acquisition, X.L. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
Supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China for Regional Fund (52562047); Natural Science Foundation of Xinjiang Uygur Autonomous Region (2023D01A19); Xinjiang Uygur Autonomous Region “Tianchi talents” Introduction Plan Project (TCYC12); Xinjiang Tianshan Innovation Team for Research and Application of High-Efficiency Oil and Gas Pipeline Transportation Technology (2022TSYCTD0002); Xinjiang Uygur Autonomous Region “One Case, One Policy” Strategic Talent Introduction Project (XQZX20240054).
Data Availability Statement
The original contributions presented in this study are included in the article. Further inquiries can be directed to the corresponding author.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
References
- Van Vuuren, D.P.; Stehfest, E.; Gernaat, D.E.; Van Den Berg, M.; Bijl, D.L.; De Boer, H.S.; Daioglou, V.; Doelman, J.C.; Edelenbosch, O.Y.; Harmsen, M.; et al. Alternative pathways to the 1.5 C target reduce the need for negative emission technologies. Nat. Clim. Change 2018, 8, 391–397. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peters, G.P.; Andrew, R.M.; Canadell, J.G.; Friedlingstein, P.; Jackson, R.B.; Korsbakken, J.I.; Le Quéré, C.; Peregon, A. Carbon dioxide emissions continue to grow amidst slowly emerging climate policies. Nat. Clim. Change 2019, 10, 3–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Höhne, N.; Gidden, M.J.; Elzen, M.D.; Hans, F.; Fyson, C.; Geiges, A.; Jeffery, M.L.; Gonzales-Zuñiga, S.; Mooldijk, S.; Hare, W.; et al. Wave of net zero emission targets opens window to meeting the Paris Agreement. Nat. Clim. Change 2021, 11, 820–822. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grubler, A.; Wilson, C.; Bento, N.; Boza-Kiss, B.; Krey, V.; McCollum, D.L.; Rao, N.D.; Riahi, K.; Rogelj, J.; De Stercke, S.; et al. A low energy demand scenario for meeting the 1.5 °C target and sustainable development goals without negative emission technologies. Nat. Energy 2018, 3, 515–527. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chaudhry, A.U.; Abdullah, F.T.; Khan, M.S.; Rabbani, H.S.; Lal, B. Feasibility of Long-Distance Transportation of Captured CO2 using Transmission Pipelines: An Overview of Techno-economic Models. In Gas Hydrate in Carbon Capture, Transportation and Storage; CRC Press: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 2024; pp. 33–43. [Google Scholar]
- Joarder, M.S.A.; Islam, M.S.; Hasan, M.H.; Kutub, A.; Kabir, M.F.; Rashid, F.; Joarder, T.A. A comprehensive review of carbon dioxide capture, transportation, utilization, and storage: A source of future energy. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2025, 32, 9299–9332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Akinmoladun, A.; Tomomewo, O.S. Advances and future perspectives in post-combustion carbon capture technology using chemical absorption process: A review. Carbon Capture Sci. Technol. 2025, 16, 100461. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ighomuaye, E.; Asimatey, P.D.; Annankra, J.A. Strategies for Industrial Integration of Carbon Capture, Utilization, and Storage Technologies: A Critical Review. J. Eng. Comput. Sci. 2025, 4, 284–293. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, L.; Hu, Y.; Liu, Z.; Yan, X.; Yu, S.; Ding, J.; Liu, P.; Yu, J.; Chen, S. Experimental research on the fracture and arrest process of supercritical CO2 pipelines. Int. J. Press. Vessel. Pip. 2024, 212, 105314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, S.; Yan, X.; He, Y.; Yu, J.; Chen, S. Study on the leakage morphology and temperature variations in the soil zone during large-scale buried CO2 pipeline leakage. Energy 2023, 288, 129674. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xi, D.; Lu, H.; Xu, Z.-D.; Jiang, X.; Peng, H.; Fang, H. Prevention of natural gas pipeline cracking. In Advances in Natural Gas: Formation, Processing, and Applications; Volume 6: Natural Gas Transportation and Storage; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2024; pp. 293–313. [Google Scholar]
- Gu, X.T.; Guo, Y. Crack Arrest Toughness of High Grade Gas Pipeline. Mater. Sci. Forum 2017, 898, 758–765. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhen, Y.; Jiao, Z.; Cao, Y.; Niu, R. Unified correlation of constraints with crack arrest toughness for high-grade pipeline steel. Int. J. Press. Vessel. Pip. 2021, 193, 104454. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Botros, K.K.; Geerligs, J.; Rothwell, B.; Robinson, T. Measurements of decompression wave speed in pure carbon dioxide and comparison with predictions by equation of state. J. Press. Vessel. Technol. 2015, 138, 031302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Botros, K.K.; Igi, S.; Kondo, J. Measurements of decompression wave speed in natural gas containing 2–8%(mole) hydrogen by a specialized shock tube. In Proceedings of the 2016 11th International Pipeline Conference, Calgary, AB, Canada, 26–30 September 2016; American Society of Mechanical Engineers: New York, NY, USA, 2016; Volume 50275, p. V003T05A001. [Google Scholar]
- Cosham, A.; Jones, D.G.; Armstrong, K.; Allason, D.; Barnett, J. The decompression behaviour of carbon dioxide in the dense phase. In Proceedings of the 2012 9th International Pipeline Conference, Calgary, AB, Canada, 24–28 September 2012; American Society of Mechanical Engineers: New York, NY, USA, 2012; Volume 45141, pp. 447–464. [Google Scholar]
- Cosham, A.; Jones, D.G.; Armstrong, K.; Allason, D.; Barnett, J. Analysis of a dense phase carbon dioxide full-scale fracture propagation test in 24 inch diameter pipe. In Proceedings of the 2016 11th International Pipeline Conference, Calgary, AB, Canada, 26–30 September 2016; American Society of Mechanical Engineers: New York, NY, USA, 2016; Volume 50275, p. V003T05A012. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, Z.; Lu, Z.; Wang, J.; Liu, D.; Xiao, C.; Fan, D. Effects of initial flow velocity on decompression behaviours of GLE CO2 upstream and downstream the pipeline. Int. J. Greenh. Gas Control 2022, 118, 103690. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Picard, D.J.; Bishnoi, P.R. The importance of real-fluid behavior in predicting release rates resulting from high-pressure sour-gas pipeline ruptures. Can. J. Chem. Eng. 1989, 67, 3–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aursand, E.; Aursand, P.; Hammer, M.; Lund, H. The influence of CO2 mixture composition and equations of state on simulations of transient pipeline decompression. Int. J. Greenh. Gas Control 2016, 54, 599–609. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jie, H.E.; Xu, B.P.; Wen, J.X.; Cooper, R.; Barnett, J. Predicting the decompression characteristics of carbon dioxide using computational fluid dynamics. In Proceedings of the 2012 9th International Pipeline Conference, Calgary, AB, Canada, 24–28 September 2012; American Society of Mechanical Engineers: New York, NY, USA, 2012; Volume 45141, pp. 585–595. [Google Scholar]
- Botros, K.K.; Geerligs, J.; Rothwell, B.; Robinson, T. Effects of Argon as the primary impurity in anthropogenic carbon dioxide mixtures on the decompression wave speed. Can. J. Chem. Eng. 2016, 95, 440–448. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, X.; Xu, S.; Chen, G.; Yan, X.; Cao, Q. Fracture criterion and control plan on CO2 pipelines: Theory analysis and full-bore rupture (FBR) experimental study. J. Loss Prev. Process. Ind. 2021, 69, 104394. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gu, S.; Li, Y.; Teng, L.; Wang, C.; Hu, Q.; Zhang, D.; Ye, X.; Wang, J.; Iglauer, S. An experimental study on the flow characteristics during the leakage of high pressure CO2 pipelines. Process. Saf. Environ. Prot. 2019, 125, 92–101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Teng, L.; Zhang, D.; Li, Y.; Wang, W.; Wang, L.; Hu, Q.; Ye, X.; Bian, J.; Teng, W. Multiphase mixture model to predict temperature drop in highly choked conditions in CO2 enhanced oil recovery. Appl. Therm. Eng. 2016, 108, 670–679. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dakhel, A.Y.; Lukács, J. Full-scale tests of transporting pipeline sections—A review and consequences to our investigations. Des. Mach. Struct. 2023, 13, 24–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maxey, W.A. Long shear fractures in CO2 lines controlled by regulating saturation, arrest pressures. Oil Gas J. 1986, 84, 31. [Google Scholar]
- Cosham, A.; Jones, D.G.; Armstrong, K.; Allason, D.; Barnett, J. Ruptures in gas pipelines, liquid pipelines and dense phase carbon dioxide pipelines. In Proceedings of the 2012 9th International Pipeline Conference, Calgary, AB, Canada, 24–28 September 2012; American Society of Mechanical Engineers: New York, NY, USA, 2012; Volume 45141, pp. 465–482. [Google Scholar]
- Cosham, A.; Jones, D.G.; Armstrong, K.; Allason, D.; Barnett, J. Analysis of two dense phase carbon dioxide full-scale fracture propagation tests. In Proceedings of the 2014 10th International Pipeline Conference, Calgary, AB, Canada, 29 September–3 October 2014; American Society of Mechanical Engineers: New York, NY, USA, 2014; Volume 46124, p. V003T07A003. [Google Scholar]
- Biagio, M.D.; Lucci, A.; Mecozzi, E.; Spinelli, C.M. Fracture propagation prevention on CO2 pipelines: Full scale experimental testing and verification approach. In Proceedings of the Pipeline Technology Conference, Berlin, Germany, 1–5 May 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Linton, V.; Leinum, B.H.; Newton, R.; Fyrileiv, O. CO2SAFE-ARREST: A full-scale burst test research program for carbon dioxide pipelines—Part 1: Project overview and outcomes of test 1. In Proceedings of the 2018 12th International Pipeline Conference, Calgary, AB, Canada, 24–28 September 2018; American Society of Mechanical Engineers: New York, NY, USA, 2018; Volume 51883, p. V003T05A008. [Google Scholar]
- Michal, G.; Davis, B.; Østby, E.; Lu, C.; Røneid, S. CO2SAFE-ARREST: A Full-Scale Burst Test Research Program for Carbon Dioxide Pipelines—Part 2: Is the BTCM Out of Touch with Dense-Phase CO2. In Proceedings of the 2018 12th International Pipeline Conference, Calgary, AB, Canada, 24–28 September 2018; American Society of Mechanical Engineers: New York, NY, USA, 2018; Volume 51883, p. V003T05A009. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, D.; Wang, R.; Ouyang, X.; Fu, Y.; Wang, H.; Yan, F.; Liu, X. Experimental study of the full-scale burst failure behavior of carbon dioxide steel pipeline. J. Pipeline Sci. Eng. 2025, 5, 100221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, L.; Hu, Y.; Yang, K.; Yan, X.; Yu, S.; Yu, J.; Chen, S. Fracture process characteristic study during fracture propagation of a CO2 transport network distribution pipeline. Energy 2023, 283, 129060. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- ISO 27913:2024; Carbon Dioxide Capture, Transportation And geological Storage—Pipeline Transportation Systems. International Organization for Standardization (ISO): Geneva, Switzerland, 2024.
- Maxey, W.; Kiefner, J.; Eiber, R.; Duffy, A. Ductile fracture initiation, propagation, and arrest in cylindrical vessels. In Fracture Toughness: Part II; ASTM International: West Conshohocken, PA, USA, 1972; pp. 70–81. [Google Scholar]
- Rothwell, A.B. The application of the Battelle “Short Formula” to the determination of ductile fracture arrest toughness in gas pipelines. In Proceedings of the 2000 3rd International Pipeline Conference, Calgary, AB, Canada, 1–5 October 2000; American Society of Mechanical Engineers: New York, NY, USA, 2000; Volume 40245, p. V001T02A019. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, L.; Hu, Y.; Yang, K.; Yan, X.; Yu, S.; Yu, J.; Chen, S. Experimental study of decompression wave characteristics and steel pipe applicability of supercritical CO2 pipeline. Gas Sci. Eng. 2023, 121, 205203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gu, S.; Li, Y.; Teng, L.; Hu, Q.; Zhang, D.; Ye, X.; Wang, C.; Wang, J.; Iglauer, S. A new model for predicting the decompression behavior of CO2 mixtures in various phases. Process. Saf. Environ. Prot. 2018, 120, 237–247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mahgerefteh, H.; Brown, S.; Martynov, S. A study of the effects of friction, heat transfer, and stream impurities on the decompression behavior in CO2 pipelines. Greenh. Gases Sci. Technol. 2012, 2, 369–379. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Terenzi, A. Influence of real-fluid properties in modeling decompression wave interacting with ductile fracture propagation. Oil Gas Sci. Technol. 2005, 60, 711–719. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Teng, L.; Li, Y.; Zhao, Q.; Wang, W.; Hu, Q.; Ye, X.; Zhang, D. Decompression characteristics of CO2 pipelines following rupture. J. Nat. Gas Sci. Eng. 2016, 36, 213–223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Botros, K.K.; Geerligs, J.; Fletcher, L.; Rothwell, B.; Venton, P.; Carlson, L. Effects of pipe internal surface roughness on decompression wave speed in natural gas mixtures. In Proceedings of the 8th International Pipeline Conference, Calgary, AB, Canada, 27 September–1 October 2010; Volume 44212, pp. 907–922. [Google Scholar]
- Lund, H. Relaxation Models for Two-Phase Flow with Applications to CO2 Transport. Ph.D. Thesis, NTNU—Institutt for Energi- og Prosessteknikk (EPT), Trondheim, Norway, 2013. [Google Scholar]
- Flåtten, T.; Lund, H. Relaxation two-phase flow models and the subcharacteristic condition. Math. Model. Methods Appl. Sci. 2011, 21, 2379–2407. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bell, I.H.; Deiters, U.K. On the construction of binary mixture p-x and T-x diagrams from isochoric thermodynamics. AIChE J. 2018, 64, 2745–2757. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peng, D.Y.; Robinson, D.B. A new two-constant equation of state. Ind. Eng. Chem. Fundam. 1976, 15, 59–64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Simão, J.S.D.; Emmanuel, L.; João, A.A.; Manuel, E.J.L.; Nzinga, E.J.; Cangue, F.R.; Barros, A.A.C. Analysis of the thermodynamic behavior of gaseous mixtures using equations of state. S. Afr. J. Chem. Eng. 2024, 49, 339–347. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kunz, O.; Wagner, W. The GERG-2008 wide-range equation of state for natural gases and other mixtures: An expansion of GERG-2004. J. Chem. Eng. Data 2012, 57, 3032–3091. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).