Elucidation of Flavor Profile Dynamics in Tea-Flavor Baijiu During Long-Term Storage Using Sensory Evaluation, Electronic Nose, HS-GC-IMS, and HS-SPME-GC-MS
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Samples and Reagents
2.2. Sensory Evaluation
2.3. E-Nose Analysis
2.4. HS-GC-IMS Analysis
2.5. HS-SPME-GC-MS Analysis
2.6. Relative Odor Activity Value (rOAV) Calculation
2.7. Statistical Analysis
3. Results and Discussion
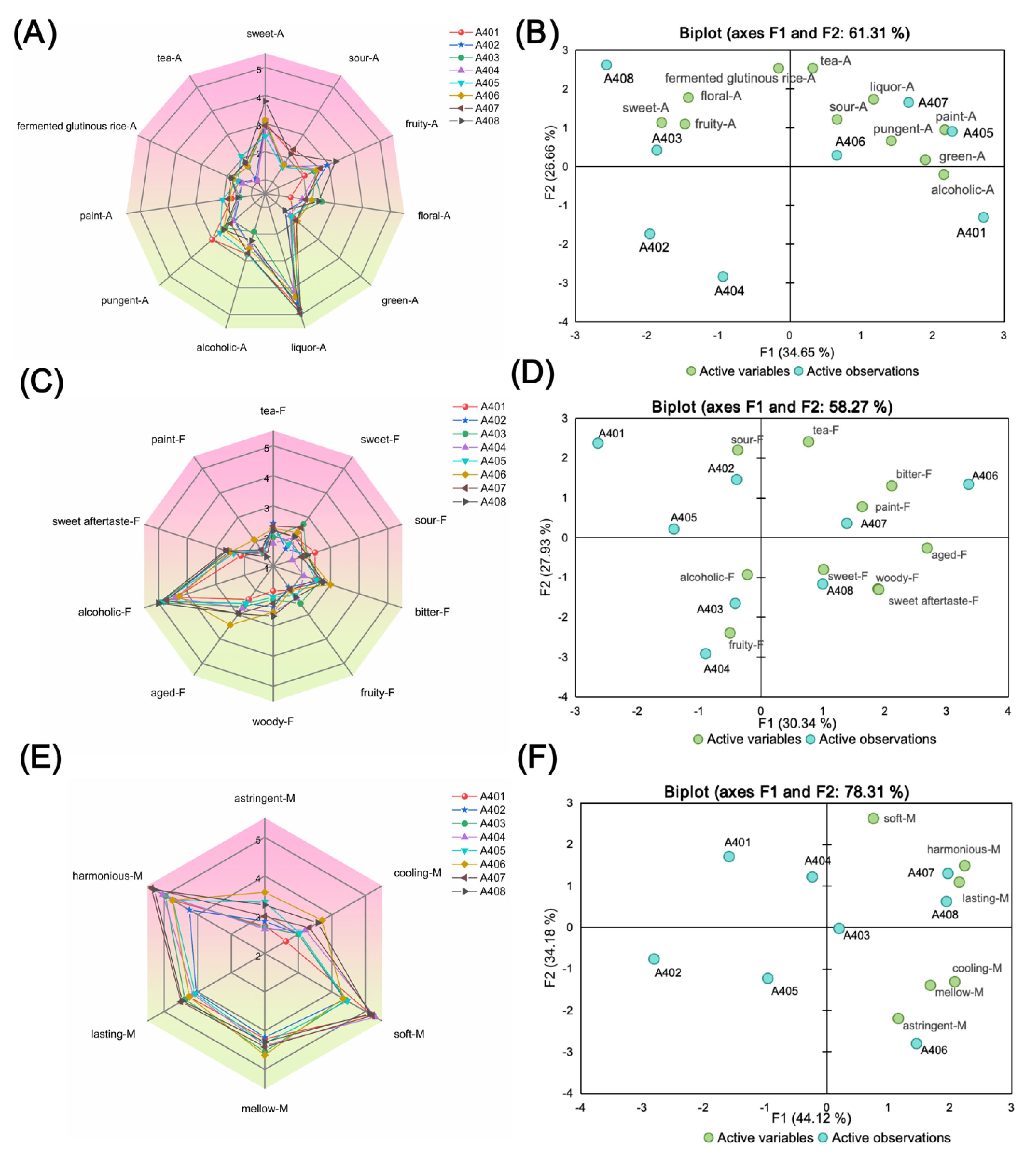
3.1. Characteristics of Aroma, Flavor and Mouthfeel in Samples
3.2. E-Nose Profiling of Volatile Compounds
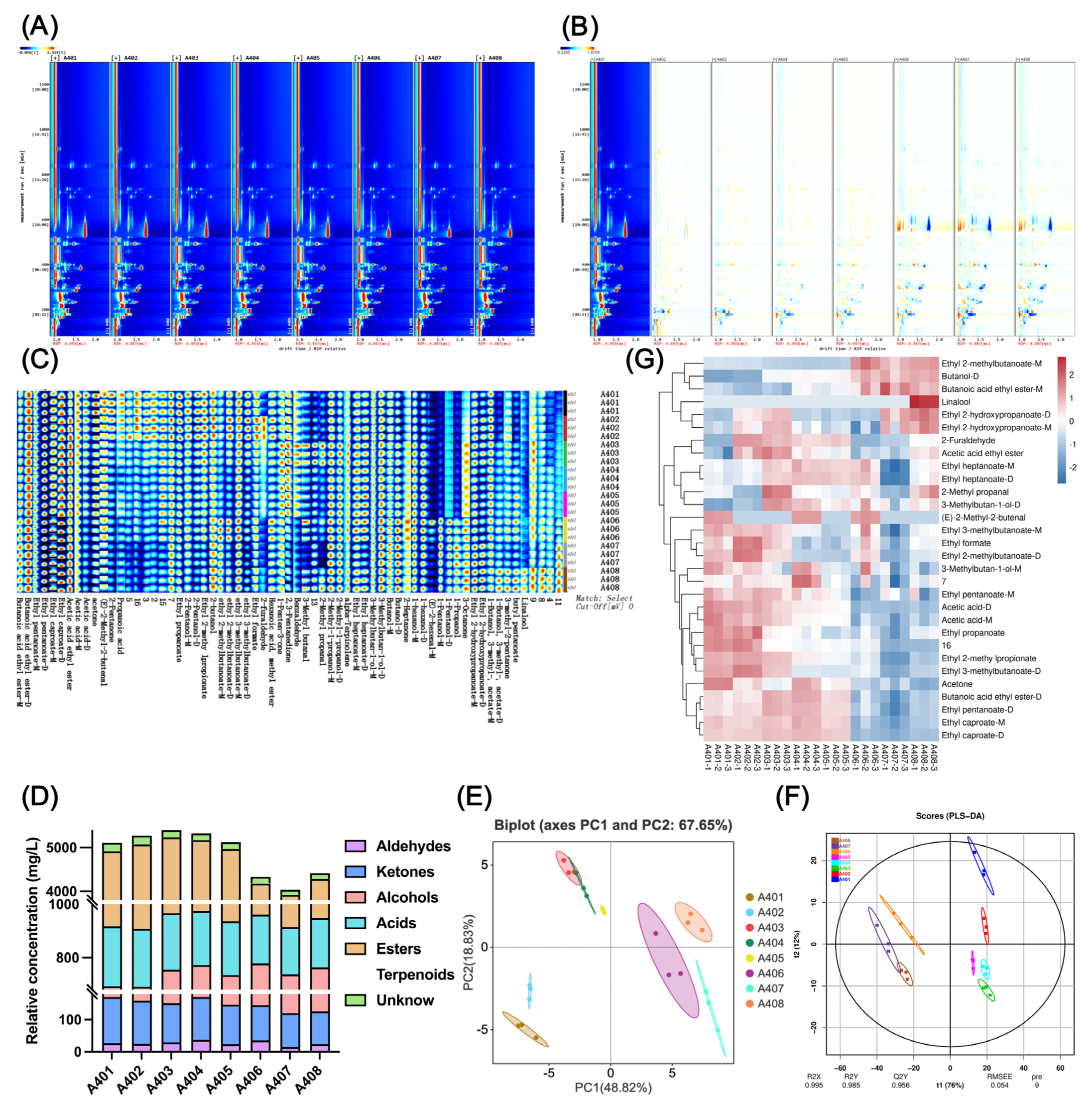
3.3. HS-GC-IMS Results
3.3.1. Variation in Volatile Compounds Across Storage Periods Identified by HS-GC-IMS
3.3.2. Multivariate Analyses (PCA, PLS-DA) Based on HS-GC-IMS Data
3.3.3. Calculation Results of rOAVs and ROAVs Based on HS-GC-IMS Data
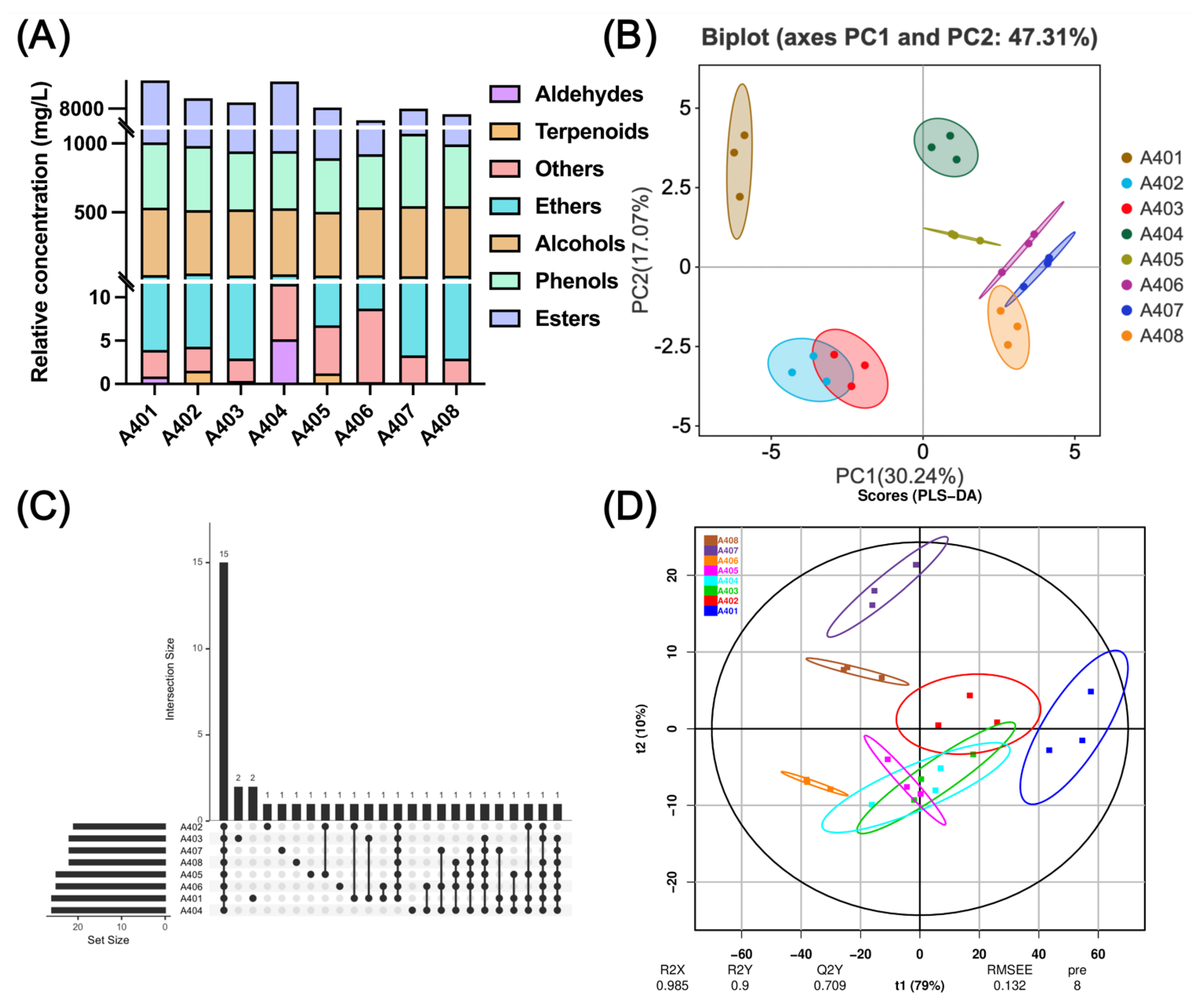
3.4. HS-SPME-GC-MS Results
3.4.1. Temporal Changes in Volatile Profiles Detected by HS-SPME-GC-MS
3.4.2. Integrated PCA, PLS-DA, and ROAV Analysis Based on Combined HS-SPME-GC-MS and HS-GC-IMS Data
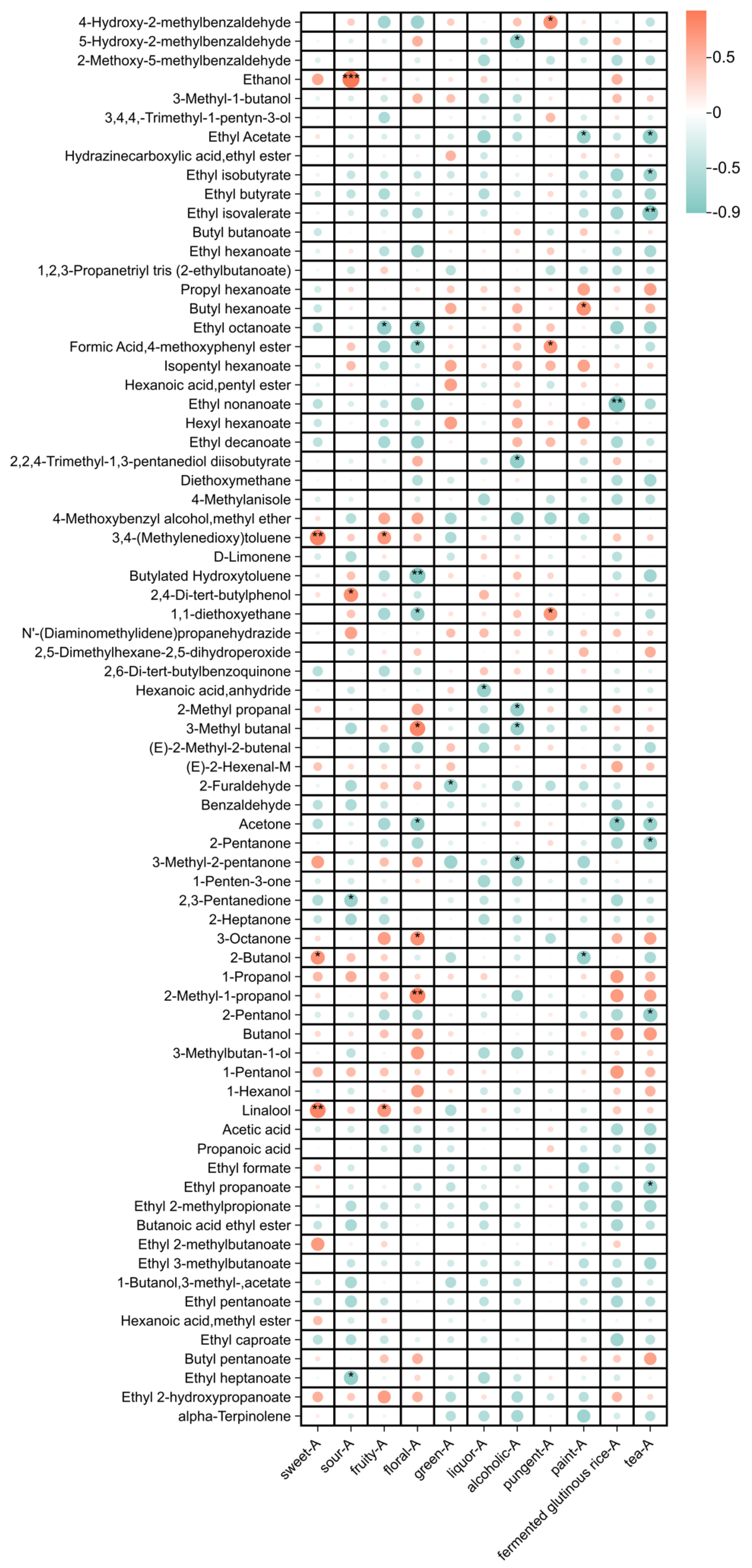
3.5. Correlation Between Sensory Attributes and Volatile Compounds
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Mou, Z.; Cai, X.M.; Liu, J.Y.; Deng, R.J.; Liu, Z.N.; Fan, R.Y.; Tang, J.; Luo, A.M. Elucidation of the key aroma compounds of floral and fruity aroma in sauce-flavored Baijiu by pervaporative membrane separation, GC-IMS, GC-MS, and Aroma Omission Studies. Food Biosci. 2025, 66, 106270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Q.R.; Lin, X.L.; Lu, Z.M.; Chai, L.J.; Wang, S.T.; Shi, J.S.; Zhang, S.Y.; Shen, C.H.; Zhang, X.J.; Xu, Z.H. Influence on the volatilization of ethyl esters: Nonnegligible role of long-chain fatty acids on Baijiu flavor via intermolecular interaction. Food Chem. 2024, 436, 137731. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ma, Y.; Wei, Z.Y.; Xiao, X.J.; Yu, K.J.; Huang, H.L.; Tan, J.X.; Wang, Y.; Du, Y.; Li, Y.J. Investigating the impact of various sorghum types on the key aroma compounds of Sichuan Xiaoqu Baijiu through application of the sensomics approach. Food Chem. X 2024, 22, 101367. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, Y.J.; Wang, L.; Li, Y.L.; Chen, Y.X.; Chen, G.J.; Jia, L.Y.; Ge, Y.H. Comparative analysis of key flavor compounds in various baijiu types using E-nose, HS-SPME-GC–MS/MS, and HS-GC-IMS technologies. Food Chem. X 2025, 29, 102689. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, C.; Yin, L.G.; Zhu, W.Y.; Luo, M.; Zou, M.X.; Song, Y.J.; Zhang, Y.L.; Qiu, S.Y.; Zeng, X.Y.; Yan, Y. Characterization of Xiaoqu Qingxiangxing Baijiu by gas chromatography-olfactometry, quantitative measurements, aroma recombination, and omission experiments. Food Chem. X 2025, 28, 102591. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, Y.; Ran, X.L.; Zhao, D.; Zheng, J.; Su, J.; Xu, Y. Aroma characterization and reconstitution of strong-aroma baijiu: Insights into sensory profiles and key odor-active compounds from Chinese core production areas. J. Food Compos. Anal. 2025, 147, 108076. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Xu, X.B.; Zhang, L.; Zhao, Q.Y.; Pan, J.F.; Fan, Y.F.; Wang, X.P. DMU-SPME variable temperature extraction: Revealing the flavor characteristics of strong-aroma baijiu by volatilomics. Food Chem. 2025, 493, 145681. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bai, B.Q.; Zhang, L.Q.; Zhang, Y.; Feng, B.; Bo, T.; Zhang, J.H.; Fan, S.H.; Yang, Y.K. Comparative analysis of flavor characteristics of two rounds of Qingxiangxing Baijiu by GC×GC-TOFMS, HS-GC-IMS, GC-E-nose and E-tongue. Food Biosci. 2025, 63, 105789. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, X.Y.; Wang, H.W.; Wang, Z.R.; Huang, P.M.; Kan, J.Q. Discrimination and characterization of the volatile organic compounds in eight kinds of huajiao with geographical indication of China using electronic nose, HS-GC-IMS and HS-SPME-GC-MS. Food Chem. 2022, 375, 131671. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, Y.; He, Y.C.; Zhu, Z.R. Understanding of formation and change of chiral aroma compounds from tea leaf to tea cup provides essential information for tea quality improvement. Food Res. Int. 2023, 167, 112703. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meremäe, K.; Raudsepp, P.; Rusalepp, L.; Laun, T.; Roasto, M. Polyphenolic profiles, antioxidant capacity, and antibacterial activity of green tea, matcha tea, black tea, and yerba mate extracts. Appl. Food Res. 2025, 5, 101080. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, C.; Liao, Y.H.; Wu, A.M.; He, C.L.; Du, X.; Chen, S.X.; Tan, L.Q.; Zou, Y.; Baimawangzha; Tang, Q.; et al. Tibetan dark tea Theabrownin alleviates LPS-induced inflammation by modulating the Nrf2/NF-κB signaling pathway and host microbial metabolites. Food Chem. 2025, 483, 144264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rahman, S.M.A.; Ruhi, R.A.; Maruf, M.M.H.; Shariar, M.R.; Shehab, M.N.; Sujon, K.M.; Islam, M.S.; Aziz, M.A.; Ahmed, F.; Saha, A.K.; et al. Green synthesis of silver nanoparticles using the BT5 tea cultivar of Bangladesh: Unveiling molecular mechanisms of anti-cancer activity in mice model. Nanoscale Adv. 2025, 7, 3375–3386. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cheng, J.; Huang, S.Y.; Xiong, R.G.; Wu, S.X.; Yang, Z.J.; Zhou, D.D.; Saimaiti, A.; Zhao, C.N.; Zhu, H.L.; Li, H.B. Vine tea kombucha ameliorates non-alcoholic fatty liver disease in high-fat diet fed mice via antioxidation, anti-inflammation and regulation of gut microbiota. Food Biosci. 2024, 62, 105400. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, J.S.; Fu, Y.Q.; Chen, Q.; Huang, T.; Yang, J.; Li, D. Consumption of Chinese tea-flavor liquor improves circulating insulin levels without affecting hepatic lipid metabolism-related gene expression in Sprague-Dawley rats. Sci. World J. 2013, 2013, 842343. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, Z.J.; Yu, J.J.; Chen, Y.L.; Wang, W.; Du, S.F.; Wang, D.L.; Xue, J.; Tao, Y.S. Characterization of key aroma compounds contributing to tea-aroma in green tea-flavor liquor. J. Food Compos. Anal. 2025, 148, 108235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.H.; Zheng, J.; Zhang, D.N.; Pan, S.Y.; Xu, X.Y.; Yuan, F. Flavoromic exploration of regional variations, consumer preferences, and the role of volatile and nonvolatile compounds in strong-aroma baijiu. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2025, 73, 17888–17900. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Melios, S.; Grasso, S.; Bolton, D.; Crofton, E. Sensory characterisation of meatless and nitrite-free cooked ham alternatives in comparison to conventional counterparts: Temporal dominance of sensations and partial napping with ultra-flash profiling. Food Res. Int. 2024, 190, 114625. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, J.; Chen, R.; Li, X.; Fu, Z.; Xian, C.; Zhao, W.; Zhao, C.; Wu, X. Comprehensive identification of key compounds in different quality grades of soy sauce-aroma type baijiu by HS-SPME-GC-MS coupled with electronic nose. Front. Nutr. 2023, 10, 1132527. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, J.; Rao, W.; Hu, S.; Li, X.; Ouyang, L.; Zhu, S. Unveiling aroma evolution in Chinese Te-flavor baijiu with ageing times using GC-IMS, GC-O-QTOF and electronic sensory techniques. Food Chem. 2025, 491, 145250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, X.; Fan, W.L.; Xu, Y.; Cheng, P.Y.; Sun, Y.L.; Zhu, X.C.; Hu, J.F. Characterization of volatile bitter off-taste compounds in Maotai-flavor baijiu (Chinese liquor). LWT-Food Sci. Technol. 2025, 217, 117363. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, J.Q.; Wang, Y.J.; Li, J.Y.; Zhang, J.X.; Wei, Y.M.; Yan, Y.X.; Wang, H.P.; Pan, Y.; Xiong, Z.C.; Wang, R.J.; et al. Aroma formation mechanism by the drying step during Congou black tea processing: Analyses by HP-SPME and SAFE with GC-MS. Lwt-Food Sci. Technol. 2024, 198, 116019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bi, J.C.; Zhang, J.Y.; Chen, Z.; Li, L.Y.; Li, Y.B.; Liu, W.H.; Qin, R.B.; Zhang, L.W.; He, H.J. Dynamic patterns of quality deterioration, oxidative stability, and flavor evolution in yuba during long-term storage. Food Chem. X 2025, 29, 102760. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hong, J.X.; Huang, H.; Zhao, D.R.; Sun, J.Y.; Huang, M.Q.; Sun, X.T.; Sun, B.G. Investigation on the key factors associated with flavor quality in northern strong aroma type of Baijiu by flavor matrix. Food Chem. 2023, 426, 136576. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Qi, Z.H.; Huang, W.J.; Liu, Q.Y.; Ning, J.M. Variation in the aroma composition of Jasmine tea with storage duration. Foods 2024, 13, 2524. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sun, X.Z.; Qian, Q.Q.; Xiong, Y.Q.; Xie, Q.Q.; Yue, X.X.; Liu, J.H.; Wei, S.X.; Yang, Q. Characterization of the key aroma compounds in aged Chinese Xiaoqu Baijiu by means of the sensomics approach. Food Chem. 2022, 384, 132452. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, W.; Xiao, Y.; Deng, R.J.; Wang, Y.; Qiu, Y.; Sun, Q.Y.; Luo, A.M. An electric-field instrument for accelerated aging to improve flavor of Chinese Baijiu. LWT-Food Sci. Technol. 2023, 174, 114446. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, A.J.; Feng, X.Y.; Yang, G.; Peng, X.W.; Du, M.Y.; Song, J.; Kan, J.Q. Impact of aroma-enhancing microorganisms on aroma attributes of industrial Douchi: An integrated analysis using E-nose, GC-IMS, GC-MS, and descriptive sensory evaluation. Food Res. Int. 2024, 182, 114181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, W.L.; Qian, M.C. Characterization of aroma compounds of Chinese “Wuliangye” and “Jiannanchun” liquors by aroma extract dilution analysis. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2006, 54, 2695–2704. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, W.L.; Shen, H.Y.; Xu, Y. Quantification of volatile compounds in Chinese soy sauce aroma type liquor by stir bar sorptive extraction and gas chromatography-mass spectrometry. J. Sci. Food Agric. 2011, 91, 1187–1198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tan, Y.B.; Cao, J.J.; Ma, Z.C.; Sun, Y.; Wan, X.C.; Liu, L.L. Post-harvest UV-B radiation enhances flavor quality of white and green teas. Sci. Hortic. 2025, 345, 114164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, F.; Luo, L.Y.; Sun, F.W.; Zhang, B.W.; Yang, J.; Liu, Y.; Zeng, L. Flavor characteristic and characterization of key sweet aroma compounds in Camellia nanchuanica black tea. Food Res. Int. 2025, 209, 116179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cha, J.Y.; Han, J.; Heo, J.; Yu, H.H.; Kim, Y.J.; Jang, H.W.; Kim, M.R.; Choi, Y.S. Variation of volatile compounds and sensory profile for Protaetia brevitarsis larvae fermented with lactic acid bacteria and yeast. Food Chem. 2024, 452, 139480. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ranau, R.; Steinhart, H. Identification and evaluation of volatile odor-active pollutants from different odor emission sources in the food industry. Eur. Food Res. Technol. 2005, 220, 226–231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, J.C.; Xiao, Z.B. Characterization of the key aroma compounds in peach by gas chromatography-olfactometry, quantitative measurements and sensory analysis. Eur. Food Res. Technol. 2019, 245, 129–141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.S.; Chen, H.; Wu, Y.S.; Zhao, D.R. Uncover the flavor code of strong-aroma baijiu: Research progress on the revelation of aroma compounds in strong-aroma baijiu by means of modern separation technology and molecular sensory evaluation. J. Food Compos. Anal. 2022, 109, 104499. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tandon, K.S.; Baldwin, E.A.; Shewfelt, R.L. Aroma perception of individual volatile compounds in fresh tomatoes (Lycopersicon esculentum, Mill.) as affected by the medium of evaluation. Postharvest Biol. Tec. 2000, 20, 261–268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blazy, V.; de Guardi, A.; Benoist, J.C.; Daumoin, M.; Lemasle, M.; Wolbert, D.; Barrington, S. Odorous gaseous emissions as influence by process condition for the forced aeration composting of pig slaughterhouse sludge. Waste Manag. 2014, 34, 1125–1138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sellami, I.; Mall, V.; Schieberle, P. Changes in the key odorants and aroma profiles of Hamlin and Valencia orange juices not from concentrate (NFC) during chilled storage. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2018, 66, 7428–7440. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, H.Y.; Zhang, Z.T.; Yang, Z.J.; Blank, I.; Zhong, F.; Wang, B.; Wang, Y.B.; Zeng, H. A comparative study to determine the key aroma components of yogurt aroma types based on Sensomics and Flavoromics. Food Chem. 2024, 460, 140618. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kun, J.; Luo, Z.F.; Gong, M.H.; Meng, Q.; Chen, Y.J.; Yuan, L.Y.; Weng, Y.W.; Sun, J.; Dai, H.W.; Tong, H.R. Characterization of the key aroma compounds in the floral honey-like cup aroma of Fenghuang Dancong oolong tea by application of the sensomics approach. Food Chem. X 2025, 28, 102538. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pino, J.A.; Tolle, S.; Gök, R.; Winterhalter, P. Characterisation of odour-active compounds in aged rum. Food Chem. 2012, 132, 1436–1441. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, Y.; Zhang, R.G.; He, W.Y.; Geng, J.Z.; Wang, P.; Tian, H.L.; Zhan, P. Characterization of aroma release and perception during ginger-infused stewed beef oral processing. Food Chem. 2025, 475, 143155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pang, X.L.; Guo, X.F.; Qin, Z.H.; Yao, Y.B.; Hu, X.S.; Wu, J.H. Identification of aroma-active compounds in Jiashi muskmelon juice by GC-O-MS and OAV calculation. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2012, 60, 4179–4185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhu, J.C.; Xiao, Z.B. Characterization of odor-active volatiles in hawthorn puree using thermal desorption system coupled to gas chromatography-mass spectrometry-olfactometry and GC-flame photometric detector. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2018, 66, 12296–12305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wen, S.; Jiang, R.G.; An, R.; Ouyang, J.; Liu, C.W.; Wang, Z.; Chen, H.Y.; Ou, X.C.; Zeng, H.Z.; Chen, J.H.; et al. Effects of pile-fermentation on the aroma quality of dark tea from a single large-leaf tea variety by GC×GC-QTOFMS and electronic nose. Food Res. Int. 2023, 174, 113643. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, Q.; Liu, Y.; Tian, L.; Xiong, F.Q.; He, Z.J.; Zhao, Y.H.; Xiang, S.Q.; Qiu, X.P.; Yu, J.S.; Guan, T.W. Effects of storage time on flavor characteristics of bran-free fermented Baijiu by using electronic sensory, descriptive sensory analysis, GC×GC-MS, and ICP-MS. Food Chem. X 2024, 23, 101667. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, Q.F.; Wu, F.R.; Wu, W.; Yu, W.J.; Zhang, G.W.; Huang, X.Y.; Hao, Y.B.; Luo, L.P. Identification and quality evaluation of Lushan Yunwu tea from different geographical origins based on metabolomics. Food Res. Int. 2024, 186, 114379. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anaya, J.A.; Alvarez, I.; García, M.J.; Lizama, V. Application of green tea extract and catechin on the polyphenolic and volatile composition of Monastrell red wines. Int. J. Food Sci. Tech. 2022, 57, 6097–6111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Q.C.; Yu, P.H.; Li, Z.Y.; Wang, Y.H.; Liu, Y.F.; Zhu, Y.; Fu, H.H. Re-rolling treatment in the fermentation process improves the aroma quality of black tea. Foods 2023, 12, 3702. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alves, R.O.; de Oliveira, R.L.; de Moraes, M.M.; Santos, W.W.V.; da Camara, C.A.G.; da Silva, S.P.; Porto, C.S.; Porto, T.S. Evaluation of the impact of fermentation conditions, scale up and stirring on physicochemical parameters, antioxidant capacity and volatile compounds of green tea Kombucha. Fermentation 2025, 11, 201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, G.H.; Zhu, G.M.; Xie, H.; Zhang, J.; Huang, J.N.; Liu, Z.H.; Wang, C. Characterization of the key differential aroma compounds in five dark teas from different geographical regions integrating GC-MS, ROAV and chemometrics approaches. Food Res. Int. 2024, 194, 114928. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, C.; Li, J.; Wang, M.; Jian, G.; Zhu, C.; Li, H.; Jia, Y.; Tang, J.; Zeng, L. (R)-Linalool is a key indicator of aroma quality levels of a distinctive black tea (Camellia sinensis var. Yinghong No. 9). Ind. Crops Prod. 2025, 225, 120506. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marcq, P.; Schieberle, P. Characterization of the key aroma compounds in a commercial amontillado sherry wine by means of the sensomics approach. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2015, 63, 4761–4770. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, X.X.; Fan, W.L.; Xu, Y. Comparison on aroma compounds in Chinese soy sauce and strong aroma type liquors by gas chromatography—Olfactometry, chemical quantitative and odor activity values analysis. Eur. Food Res. Technol. 2014, 239, 813–825. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.; Li, H.Y.; Nie, J.G.; Wu, D.; Huang, Q.L. Unveiling flavor formation and variation in fermented vinasse grass carp based on the dynamic correlation of microbiota with metabolites by multi-omics and bioinformatics approaches. Food Chem. 2025, 487, 144730. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rodriguez, A.; Peris, J.E.; Redondo, A.; Shimada, T.; Costell, E.; Carbonell, I.; Rojas, C.; Peña, L. Impact of D-limonene synthase up- or down-regulation on sweet orange fruit and juice odor perception. Food Chem. 2017, 217, 139–150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, H.; Yu, C.W.; Sun, Y.N.; Cui, N.; Zhong, B.Z.; Peng, B.; Hu, M.M.; Li, J.L.; Tu, Z.C. Characterization of key off-odor compounds in grass carp cube formed during room temperature storage by molecular sensory science approach. Food Chem. X 2024, 24, 102011. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| No. | Compound | Odor a | OT b (μg/L) | rOAV | ROAV | ||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| A401 | A402 | A403 | A404 | A405 | A406 | A407 | A408 | A401 | A402 | A403 | A404 | A405 | A406 | A407 | A408 | ||||
| Aldehydes | |||||||||||||||||||
| Ald1 | 2-Methyl propanal | banana, melon, slightly nutty | 1 c | 2757.0 | 1095.5 | 5619.2 | 3143.4 | 2645.5 | 3174.7 | 1020.6 | 4646.5 | 0.56 | 0.22 | 1.15 | 0.64 | 0.54 | 0.65 | 0.21 | 0.95 |
| Ald2 | 3-Methyl butanal | chocolate, fat | 0.005 c | / | 264,477.8 | 489,700.0 | 377,924.7 | 318,975.7 | 408,865.3 | 163,990.7 | 363,408.5 | / | 54.01 | 100.00 | 77.17 | 65.14 | 83.49 | 33.49 | 74.21 |
| Ald3 | (E)-2-Methyl-2-butenal | null | N | / | / | / | / | / | / | / | / | / | / | / | / | / | / | / | / |
| Ald4 | (E)-2-Hexenal-M | green, banana, fat | 82 d | / | / | / | / | / | 117.7 | 64.3 | 60.4 | / | / | / | / | / | <0.1 | <0.1 | <0.1 |
| Ald5 | 2-Furaldehyde | sweet, woody, almond, bready | 44029 e | / | <1 | <1 | <1 | <1 | / | <1 | <1 | / | <0.1 | <0.1 | <0.1 | <0.1 | / | <0.1 | <0.1 |
| Ald6 | Benzaldehyde | bitter almond, cherry, nutty | 2000 e | 4.8 | 5.2 | 5.6 | 4.8 | 5.3 | 3.1 | 2.9 | 3.2 | <0.1 | <0.1 | <0.1 | <0.1 | <0.1 | <0.1 | <0.1 | <0.1 |
| Ketones | |||||||||||||||||||
| K1 | Acetone | fresh, apple, pear | 832 f | 121.5 | 108.1 | 100.5 | 115.9 | 105.2 | 92.5 | 92.9 | 85.4 | <0.1 | <0.1 | <0.1 | <0.1 | <0.1 | <0.1 | <0.1 | <0.1 |
| K2 | 2-Pentanone | acetone, fresh, sweet fruity, wine | 0.098 g | 286,461.8 | 268,470.6 | 180,665.0 | 166,637.1 | 162,625.8 | 151,879.3 | 121,177.1 | 130,672.4 | 58.50 | 54.82 | 36.89 | 34.03 | 33.21 | 31.01 | 24.75 | 26.68 |
| K3 | 3-Methyl-2-pentanone | mint, honey | N | / | / | / | / | / | / | / | / | / | / | / | / | / | / | / | / |
| K4 | 1-Penten-3-one | strong pungent odors | 0.94 h | 5220.7 | 5029.6 | 5893.1 | 6125.8 | 5382.6 | 5169.2 | 5091.0 | 5329.4 | 1.07 | 1.03 | 1.20 | 1.25 | 1.10 | 1.06 | 1.04 | 1.09 |
| K5 | 2,3-Pentanedione | sweet, cream, caramel, nuts, cheese | 20 i | 349.7 | 373.9 | 413.6 | 422.7 | 408.3 | 289.2 | 234.0 | 265.1 | <0.1 | <0.1 | <0.1 | <0.1 | <0.1 | <0.1 | <0.1 | <0.1 |
| K6 | 2-Heptanone | pear, banana, fruity, slight medicinal fragrance | 1 j | 1629.3 | 1586.8 | 1813.9 | 1627.7 | 1585.8 | 1519.6 | 1344.9 | 1392.3 | 0.33 | 0.32 | 0.37 | 0.33 | 0.32 | 0.31 | 0.27 | 0.28 |
| K7 | 3-Octanone | moldy, green, vegetable, mushroom, cheese, fruity | 21 k | / | 152.0 | 180.1 | 165.1 | 171.5 | 225.6 | 224.1 | 237.9 | / | <0.1 | <0.1 | <0.1 | <0.1 | <0.1 | <0.1 | <0.1 |
| Alcohols | |||||||||||||||||||
| Alc1 | 2-Butanol | fruity | 0.66 g | 29,069.9 | 28,715.9 | 27,655.3 | 28,106.3 | 25,502.2 | 26,927.2 | 27,425.8 | 29,464.4 | 5.94 | 5.86 | 5.65 | 5.74 | 5.21 | 5.50 | 5.60 | 6.02 |
| Alc2 | 1-Propanol | alcohol, pungent | 54,000 e | <1 | <1 | <1 | <1 | <1 | <1 | <1 | <1 | <0.1 | <0.1 | <0.1 | <0.1 | <0.1 | <0.1 | <0.1 | <0.1 |
| Alc3 | 2-Methyl-1-propanol-M | fresh, alcoholic, leather | 40 e | 1271.2 | 1275.7 | 1393.7 | 1310.8 | 1299.1 | 1371.5 | 1354.2 | 1409.2 | 0.26 | 0.26 | 0.28 | 0.27 | 0.27 | 0.28 | 0.28 | 0.29 |
| Alc4 | 2-Methyl-1-propanol-D | fresh, alcoholic, leather | 40 e | 367.4 | 402.0 | 512.6 | 498.7 | 494.7 | 475.5 | 464.7 | 489.0 | 0.08 | 0.08 | 0.10 | 0.10 | 0.10 | 0.10 | 0.09 | 0.10 |
| Alc5 | 2-Pentanol-D | fusel oil, green | 1 g | 6357.2 | 6348.1 | 5369.2 | 5031.5 | 4959.7 | 4557.0 | 3916.1 | 3658.1 | 1.30 | 1.30 | 1.10 | 1.03 | 1.01 | 0.93 | 0.80 | 0.75 |
| Alc6 | 2-Pentanol-M | fusel oil, green | 1 g | 19,990.2 | 18,881.8 | 18,821.1 | 18,056.3 | 16,442.2 | 16,002.2 | 15,750.2 | 15440.2 | 4.08 | 3.86 | 3.84 | 3.69 | 3.36 | 3.27 | 3.22 | 3.15 |
| Alc7 | Butanol-D | wine | 2733.35 e | 28.9 | 30.0 | 39.6 | 41.2 | 41.5 | 46.2 | 46.3 | 47.7 | <0.1 | <0.1 | <0.1 | <0.1 | <0.1 | <0.1 | <0.1 | <0.1 |
| Alc8 | Butanol-M | wine | 2733.35 e | 11.4 | 11.2 | 11.0 | 10.7 | 10.2 | 12.6 | 12.2 | 12.2 | <0.1 | <0.1 | <0.1 | <0.1 | <0.1 | <0.1 | <0.1 | <0.1 |
| Alc9 | 3-Methylbutan-1-ol-D | whiskey, banana, fruity | 179,000 e | <1 | 1.0 | 1.1 | 1.1 | 1.1 | 1.1 | 1.1 | 1.1 | <0.1 | <0.1 | <0.1 | <0.1 | <0.1 | <0.1 | <0.1 | <0.1 |
| Alc10 | 3-Methylbutan-1-ol-M | whiskey, banana, fruity | 179,000 e | <1 | <1 | <1 | <1 | <1 | <1 | <1 | <1 | <0.1 | <0.1 | <0.1 | <0.1 | <0.1 | <0.1 | <0.1 | <0.1 |
| Alc11 | 1-Pentanol-M | balsamic | 0.26 g | 14,981.4 | 14,604.6 | 18,563.7 | 18,185.4 | 18,511.5 | 58,509.3 | 56,677.3 | 53,587.5 | 3.06 | 2.98 | 3.79 | 3.71 | 3.78 | 11.95 | 11.57 | 10.94 |
| Alc12 | 1-Pentanol-D | balsamic | 0.26 g | / | / | / | / | / | 18,099.8 | 17,308.4 | 16525.6 | / | / | / | / | / | 3.70 | 3.53 | 3.37 |
| Alc13 | 1-Hexanol-D | fresh, fruity, wine, sweet, green | 5370 e | 3.2 | 3.4 | 5.0 | 4.9 | 4.9 | 4.9 | 4.4 | 4.6 | <0.1 | <0.1 | <0.1 | <0.1 | <0.1 | <0.1 | <0.1 | <0.1 |
| Alc14 | 1-Hexanol-M | fresh, fruity, wine, sweet, green | 5370 e | 8.3 | 8.6 | 10.3 | 10.5 | 10.2 | 10.3 | 9.6 | 9.8 | <0.1 | <0.1 | <0.1 | <0.1 | <0.1 | <0.1 | <0.1 | <0.1 |
| Alc15 | Linalool | citrus, rose, woody, blueberry | 4.4 m | / | / | / | / | / | / | / | 1226.1 | / | / | / | / | / | / | / | 0.25 |
| Acids | |||||||||||||||||||
| Aci1 | Acetic acid-D | spicy | 160,000 n | <1 | <1 | <1 | <1 | <1 | <1 | <1 | <1 | <0.1 | <0.1 | <0.1 | <0.1 | <0.1 | <0.1 | <0.1 | <0.1 |
| Aci2 | Acetic acid-M | spicy | 160,000 n | 1.2 | 1.2 | 1.2 | 1.1 | 1.1 | 1.0 | 1.0 | 1.0 | <0.1 | <0.1 | <0.1 | <0.1 | <0.1 | <0.1 | <0.1 | <0.1 |
| Aci3 | Propanoic acid | yogurt, vinegar | 18,100 e | <1 | <1 | <1 | <1 | <1 | <1 | <1 | <1 | <0.1 | <0.1 | <0.1 | <0.1 | <0.1 | <0.1 | <0.1 | <0.1 |
| Esters | |||||||||||||||||||
| E1 | Ethyl formate | spicy, stimulating taste, pineapple, rum | N | / | / | / | / | / | / | / | / | / | / | / | / | / | / | / | / |
| E2 | Acetic acid ethyl ester | fresh, fruity, sweet, grassy | 32,551.6 e | 16.7 | 20.9 | 21.6 | 19.7 | 19.1 | 17.6 | 17.9 | 19.9 | <0.1 | <0.1 | <0.1 | <0.1 | <0.1 | <0.1 | <0.1 | <0.1 |
| E3 | Ethyl propanoate | grape, pineapple, fruity, rum | 19,019.33 e | 3.1 | 3.2 | 2.8 | 2.8 | 2.6 | 2.7 | 2.4 | 2.7 | <0.1 | <0.1 | <0.1 | <0.1 | <0.1 | <0.1 | <0.1 | <0.1 |
| E4 | Ethyl 2-methylpropionate | sweet, fruity, alcoholic, rummy | 57.47 e | 1272.7 | 1312.1 | 1236.0 | 1105.5 | 1017.2 | 952.1 | 626.2 | 829.9 | 0.26 | 0.27 | 0.25 | 0.23 | 0.21 | 0.19 | 0.13 | 0.17 |
| E5 | Butanoic acid ethyl ester-M | pineapple, fruity, ester, whiskey | 81.5 e | 209.5 | 198.2 | 200.4 | 220.5 | 217.4 | 237.3 | 252.5 | 240.7 | <0.1 | <0.1 | <0.1 | <0.1 | <0.1 | <0.1 | <0.1 | <0.1 |
| E6 | Butanoic acid ethyl ester-D | pineapple, fruity, ester, whiskey | 81.5 e | 5746.8 | 5722.3 | 5976.6 | 6019.5 | 5794.1 | 5189.1 | 4861.4 | 5217.9 | 1.17 | 1.17 | 1.22 | 1.23 | 1.18 | 1.06 | 0.99 | 1.07 |
| E7 | Ethyl 2-methylbutanoate-D | apple | 0.1 o | 196,725.0 | 233,229.2 | 181,965.1 | 126,622.1 | 119,544.9 | 180,230.5 | 99,246.1 | 143,955.4 | 40.17 | 47.63 | 37.16 | 25.86 | 24.41 | 36.80 | 20.27 | 29.40 |
| E8 | Ethyl 2-methylbutanoate-M | apple | 0.1 o | 179,083.6 | 176,825.6 | 163,212.1 | 155,824.4 | 158,842.7 | 291,663.8 | 252,109.6 | 274,496.2 | 36.57 | 36.11 | 33.33 | 31.82 | 32.44 | 59.56 | 51.48 | 56.05 |
| E9 | Ethyl 3-methylbutanoate-D | apple, banana, sour, sweet | 6.89 e | 8092.0 | 8955.5 | 7396.0 | 5306.4 | 5103.4 | 5444.0 | 3142.3 | 4559.1 | 1.65 | 1.83 | 1.51 | 1.08 | 1.04 | 1.11 | 0.64 | 0.93 |
| E10 | Ethyl 3-methylbutanoate-M | apple, banana, sour, sweet | 6.89 e | 7645.8 | 7556.0 | 7471.8 | 7091.5 | 6776.8 | 7440.0 | 6264.3 | 7108.7 | 1.56 | 1.54 | 1.53 | 1.45 | 1.38 | 1.52 | 1.28 | 1.45 |
| E11 | 1-Butanol, 3-methyl-, acetate-D | sweet, banana, fruity | 93.93 e | 7.0 | 7.8 | 12.1 | 12.6 | 13.0 | 15.2 | 14.0 | 21.4 | <0.1 | <0.1 | <0.1 | <0.1 | <0.1 | <0.1 | <0.1 | <0.1 |
| E12 | 1-Butanol, 3-methyl-, acetate-M | sweet, banana, fruity | 245 l | 101.9 | 104.2 | 105.7 | 107.2 | 104.5 | 92.6 | 89.6 | 95.8 | <0.1 | <0.1 | <0.1 | <0.1 | <0.1 | <0.1 | <0.1 | <0.1 |
| E13 | Ethyl pentanoate-M | apple, pineapple, green | 26.7 k | 2516.3 | 2519.4 | 2484.2 | 2426.1 | 2340.0 | 2057.1 | 2308.5 | 2187.2 | 0.51 | 0.51 | 0.51 | 0.50 | 0.48 | 0.42 | 0.47 | 0.45 |
| E14 | Ethyl pentanoate-D | apple, pineapple, green | 26.7 k | 14,120.5 | 14,208.4 | 14,945.5 | 14,860.6 | 14,235.7 | 12,525.0 | 10,884.8 | 12,301.5 | 2.88 | 2.90 | 3.05 | 3.03 | 2.91 | 2.56 | 2.22 | 2.51 |
| E15 | Hexanoic acid, methyl ester | pineapple, apricot, fruity | 10 p | 679.7 | 769.9 | 633.0 | 616.8 | 646.8 | 765.6 | 616.1 | 699.7 | 0.14 | 0.16 | 0.13 | 0.13 | 0.13 | 0.16 | 0.13 | 0.14 |
| E16 | Ethyl caproate-M | pineapple, fruity, wine | 55.3 e | 4637.3 | 4583.1 | 4659.6 | 4783.9 | 4573.3 | 3762.4 | 3531.3 | 3868.0 | 0.95 | 0.94 | 0.95 | 0.98 | 0.93 | 0.77 | 0.72 | 0.79 |
| E17 | Ethyl caproate-D | pineapple, fruity, wine | 55.3 e | 31,960.1 | 32,161.3 | 33,260.4 | 33,730.1 | 32,303.8 | 20,591.9 | 19,435.8 | 21,437.3 | 6.53 | 6.57 | 6.79 | 6.89 | 6.60 | 4.21 | 3.97 | 4.38 |
| E18 | Butyl pentanoate | fruity | N | / | / | / | / | / | / | / | / | / | / | / | / | / | / | / | / |
| E19 | Ethyl heptanoate-M | pineapple, fruity | 13,200 e | 3.1 | 3.1 | 3.3 | 3.3 | 3.3 | 3.3 | 2.5 | 3.1 | <0.1 | <0.1 | <0.1 | <0.1 | <0.1 | <0.1 | <0.1 | <0.1 |
| E20 | Ethyl heptanoate-D | pineapple, fruity | 13,200 e | 1.4 | 1.4 | 1.6 | 1.7 | 1.7 | 1.6 | <1 | 1.5 | <0.1 | <0.1 | <0.1 | <0.1 | <0.1 | <0.1 | <0.1 | <0.1 |
| E21 | Ethyl 2-hydroxypropanoate-D | fruity | 128,000 e | <1 | <1 | <1 | <1 | <1 | <1 | <1 | <1 | <0.1 | <0.1 | <0.1 | <0.1 | <0.1 | <0.1 | <0.1 | <0.1 |
| E22 | Ethyl 2-hydroxypropanoate-M | fruity | 128,000 e | <1 | <1 | <1 | <1 | <1 | <1 | <1 | <1 | <0.1 | <0.1 | <0.1 | <0.1 | <0.1 | <0.1 | <0.1 | <0.1 |
| Terpenoids | |||||||||||||||||||
| T1 | alpha-Terpinolene | fresh. woody, sweet, pine, citrus | 41 q | 103.9 | 99.6 | 108.0 | 106.6 | 95.7 | 93.4 | 88.6 | 101.9 | <0.1 | <0.1 | <0.1 | <0.1 | <0.1 | <0.1 | <0.1 | <0.1 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Liu, Q.; Lv, Y.; Zhou, Y.; Liu, M.; Feng, H.; Shen, C.; Wang, H.; Cao, X.; Kan, J. Elucidation of Flavor Profile Dynamics in Tea-Flavor Baijiu During Long-Term Storage Using Sensory Evaluation, Electronic Nose, HS-GC-IMS, and HS-SPME-GC-MS. Processes 2025, 13, 3359. https://doi.org/10.3390/pr13103359
Liu Q, Lv Y, Zhou Y, Liu M, Feng H, Shen C, Wang H, Cao X, Kan J. Elucidation of Flavor Profile Dynamics in Tea-Flavor Baijiu During Long-Term Storage Using Sensory Evaluation, Electronic Nose, HS-GC-IMS, and HS-SPME-GC-MS. Processes. 2025; 13(10):3359. https://doi.org/10.3390/pr13103359
Chicago/Turabian StyleLiu, Qingqing, Yan Lv, Yu Zhou, Min Liu, Huafang Feng, Caihong Shen, Hongwei Wang, Xiaonian Cao, and Jianquan Kan. 2025. "Elucidation of Flavor Profile Dynamics in Tea-Flavor Baijiu During Long-Term Storage Using Sensory Evaluation, Electronic Nose, HS-GC-IMS, and HS-SPME-GC-MS" Processes 13, no. 10: 3359. https://doi.org/10.3390/pr13103359
APA StyleLiu, Q., Lv, Y., Zhou, Y., Liu, M., Feng, H., Shen, C., Wang, H., Cao, X., & Kan, J. (2025). Elucidation of Flavor Profile Dynamics in Tea-Flavor Baijiu During Long-Term Storage Using Sensory Evaluation, Electronic Nose, HS-GC-IMS, and HS-SPME-GC-MS. Processes, 13(10), 3359. https://doi.org/10.3390/pr13103359







