Abstract
Selective alkaline leaching was evaluated to remove arsenic (As) and antimony (Sb) from a polymetallic copper concentrate from Zimapán, Mexico, where these metalloids cause environmental risk and smelter penalties. Batch tests used sodium sulfide (Na2S) in alkaline media, varying reagent concentrations and temperature; kinetic modeling identified the rate-controlling step, and X-ray diffraction (XRD) plus scanning electron microscopy/energy-dispersive spectroscopy (SEM–EDS) assessed phase changes. The kinetic analysis indicated chemical control with a higher reaction order for Na2S than for NaOH. A quadratic regression described the process and identified Na2S concentration and temperature as the dominant factors. Maximum extractions reached 91.9% for As and 72.1% for Sb while limiting dissolution of value-bearing sulfides, as supported by XRD and SEM–EDS. Environmental indices (Igeo, EF) classified As and Sb as highly contaminating and geochemically enriched in the feed, underscoring the need for selective removal. Overall, alkaline leaching with Na2S provides a technically feasible and environmentally favorable route to remediate metalloids and upgrade polymetallic concentrates.
1. Introduction
The Zimapán mining district (Hidalgo, Mexico) is known for producing polymetallic concentrates containing metals of interest such as copper and silver; however, they often contain arsenic (As) and antimony (Sb), elements that pose environmental, regulatory, and metallurgical challenges by increasing toxicological risk and leading to commercial penalties [1,2,3,4,5,6,7,8]. In parallel, the demand for Cu and Ag for electronics, transportation, and low-carbon energy technologies continues to rise [9,10], which is driving metal recovery from both primary materials—ores and their concentrates (process intermediates)—and secondary resources, including tailings, slags, smelter dusts, and waste electrical and electronic equipment (WEEE), in order to reduce pressure on natural resources and mitigate environmental impacts [11,12]. Both arsenic and antimony occur in these material types and can be mobilized under acidic to neutral conditions through redox processes, facilitating dispersion into surrounding soils and waters [13,14,15,16,17,18,19,20].
This high mobility promotes accumulation in terrestrial and aquatic ecosystems, complicating remediation and posing risks to public health [21,22,23,24,25,26,27,28,29,30,31,32,33,34]. In response, international regulations have established maximum permissible limits for these elements in waters, soils, and industrial emissions [35,36,37]. From a metallurgical standpoint, As and Sb hinder selective flotation, complicate leaching and smelting, and depress concentrate value via market penalties [1,2,38]. Consequently, multiple strategies have been developed for their selective removal from concentrates and mining by-products to reduce environmental impact, improve product quality, and avoid penalties [38]. Among the most used methods are differential flotation, removal from industrial effluents, and selective acidic leaching with H2SO4, HCl, and HNO3, which have shown high efficiency but can generate toxic gases [39,40,41,42,43].
In contrast, the Na2S–NaOH system has been investigated for its high selectivity in extracting As and Sb from copper concentrates rich in enargite and tetrahedrite, enabling preferential dissolution of these elements without affecting copper recovery and thereby enhancing metallurgical efficiency [44,45,46,47].
In this context, this study identifies the variables that significantly influence the removal of As and Sb from a copper concentrate from the Zimapán district. We analyze the kinetic behavior of alkaline dissolution via reaction orders and activation energy (Ea) to understand how operating variables affect the reaction rate, and we develop a quadratic regression model to determine the relative influence of each factor on extraction efficiency. The study is complemented by mineralogical and morphological characterization to validate concentrate composition and the selectivity of the Na2S–NaOH system and by estimating the geoaccumulation index (Igeo) and enrichment factor (EF) to contextualize the potential environmental impact.
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials
The copper concentrate from Zimapán, Hidalgo, Mexico, was homogenized and classified using ASTM sieves (150, 106, 75, 53, 45, 38, and <38 μm). Unless otherwise stated, the particle size used during experimentation was the −149/+105 μm fraction. The elemental composition was determined by Inductively Coupled Plasma–Optical Emission Spectrometry ICP-OES (PerkinElmer 8300) (PerkinElmer Inc., Waltham, MA, USA) after aqua regia digestion. Approximately 0.1000 ± 0.0001 g of dried sample was placed in Erlenmeyer flasks, 20 mL of freshly prepared aqua regia (HCl:HNO3, 3:1) was added, and the mixture was digested at 388–393 K for 2 h on a hot plate with a reflux cap to minimize As/Sb losses by volatilization. After cooling to room temperature, the digest was quantitatively transferred and diluted to 100 mL with deionized water and then filtered. The crystalline phases present in the sample were identified by XRD (INEL EQUINOX 2000, Co-Ka1 radiation, λ = 1.78901 Å., (INEL S.A., Artenay, France)). Morphology was examined by SEM-EDS (JEOL JSM-5900LV)., (JEOL Ltd., Tokyo, Japan), coupled with an energy-dispersive X-ray spectroscopy (EDS, Oxford) system. Thermodynamic modeling of the reactions was performed using HSC Chemistry software version 6 (Metso Outotec, Espoo, Finland). For the leaching tests of As and Sb, deionized water was used along with sodium sulfide (Na2S·9H2O, purity > 99%, molecular weight: 240.18 g/mol, supplied by Técnica Química S.A., Mexico City, Mexico) and sodium hydroxide (NaOH, purity > 97%, molecular weight: 40.0 g/mol, supplied by MEYER., Mexico City, Mexico). Based on the data obtained by ICP, the geoaccumulation index (Igeo) and enrichment factor (EF) were calculated for selected trace elements in order to assess the contaminant potential of the concentrate. The geoaccumulation index was calculated using the expression proposed by Müller (1979) (Equation (1)), with Fe considered as the normalizing element [48].
where Cₙ is the concentration of the element of interest in the sample and Bₙ is the geochemical background concentration of the element in the Earth’s crust. The Igeo index allows for the classification of contamination levels, ranging from unpolluted (Igeo ≤ 0) to extremely polluted (Igeo > 5).
In addition to Igeo, we computed the (x/Fe) index, defined as the concentration ratio of element x to Fe. Values with (x/Fe)sample ≈ (x/Fe)background indicate a lithogenic behavior (no enrichment); (x/Fe)sample > (x/Fe)background suggests a relative enrichment of x; and (x/Fe)sample < (x/Fe)background implies depletion. Fe is used as the denominator due to its abundance and relatively conservative behavior in sulfide-rich matrices, serving as a suitable internal normalizer to compare element-to-element variations, and was calculated using the following expression:
where (x/Fe)sample is the ratio between the concentration of the element of interest and the concentration of iron in the sample, and (x/Fe)Crust refers to the corresponding ratio in the Earth’s crust. Iron was used as the reference element, as it is the most abundant economically relevant base element in the parent rock [49,50]. The enrichment factor highlights relative enrichment or depletion with respect to the chosen background and can be used to support the identification of elements with potential for recovery [51].
2.2. Leaching Test
Leaching tests were carried out in batch mode in a thermostated glass reactor with agitation (ω = 600 min−1). Solutions of Na2S (0.25–1.75 mol·L−1) and NaOH (0.75–2.0 mol·L−1) were prepared in deionized water. The −149/+105 µm fraction of the concentrate was fed at a constant solid-to-liquid ratio of S/L = 10 g/L, and the pH was kept ≥ 12 throughout the reaction. The temperature was set between 343 and 373 K depending on the condition, and each test was run for 360 min. pH was monitored throughout each test and remained ≥ 12 in all cases. ORP was checked periodically to confirm operation within an alkaline-reducing window consistent with the Na2S–NaOH system. At the end, the liquor was filtered, the solid was washed and dried for XRD, and the filtrate was analyzed by ICP–OES for As and Sb. Each condition was executed as a single run; therefore, the curves are reported without error bars.
2.3. Kinetic Parameters: Reaction Orders (α, β) and Apparent Activation Energy (Ea)
The determination of reaction orders (α, β) and activation energy (Ea) enables the identification of the controlling mechanism governing the leaching of As and Sb in heterogeneous solid–liquid systems (Equation (3)), such as their removal from metal sulfides.
In this equation, a and b are the stoichiometric coefficients, while A and B represent the fluid and solid-phase reactants, respectively. If the surface reaction occurs rapidly and mass transfer is the limiting step, the process is diffusion-controlled. Conversely, if the chemical reaction at the solid–liquid interface is slow—such as the cleavage of metal–sulfur bonds and the formation of sulfur complexes—then the process is chemically controlled. Distinguishing between these mechanisms is essential for optimizing process efficiency and selecting appropriate operating conditions. Accordingly, both control mechanisms can be expressed as a function of fractional conversion (XAs and XSb) and fitted to kinetic models to evaluate the nature of the process [52,53], as summarized in Table 1.
The reaction rate in a heterogeneous system can be expressed as the change in the concentration of the solid reactant B (nB) over time (t), normalized with respect to the specific reaction surface area (S), as shown in Equation (4):
where k is the rate constant (min−1), and represents the product of the concentrations of the reactants in solution raised to their respective reaction orders, as shown below:
where α and β in Equation (5) represent the apparent reaction orders with respect to each reactant. Their experimental determination helps identify which reactant has the greatest influence on the reaction rate, thus enabling optimization of its concentration in future applications. Previous studies have shown that the leaching of As and Sb from complex sulfides such as tetrahedrite or enargite in alkaline media predominantly follows a chemically controlled mechanism [54,55,56].

Table 1.
Integrated equations for the different rate-controlling stages.
Table 1.
Integrated equations for the different rate-controlling stages.
| Rate Controlling Stage | Kinetic Equation (as a Function of the Conversion XAs,Sb) | Experimental Rate Constant, kexp | Symbol |
|---|---|---|---|
| Transport in the fluid film | kff = experimental rate constant in the fluid film in min−1 | ||
| b = stoichiometric a | |||
| D = molecular diffusion coefficient in m2 min−1 | |||
| [A] = fluid reagent concentration in mol m−3a | |||
| = molar density in mol m−3a | |||
| r0 = initial radius of the particle in m | |||
| Chemical reaction | kcr = experimental rate constant in the chemical reaction in min−1, | ||
| k0′ = chemical rate constant in (mol m−3)1−n min−1 n = reaction order |
a consider in Equation (3).
On the other hand, to identify the reacted fraction of As and Sb, Equation (10) is used:
2.4. Statistical Analysis and Predictive Modeling
Based on the experimentally obtained extraction percentages for As and Sb, predictive statistical models were constructed using quadratic regression. These models were developed with the Statgraphics Centurion software 16.1 (Statgraphics Technologies, Inc., The Plains, VA, USA), considering Na2S concentration, NaOH concentration, and temperature as independent variables. Quadratic terms were applied to generate predictive equations for both responses. Model validity was assessed through analysis of variance (ANOVA), taking into account F-values, p-values, and coefficients of determination (R2 and adjusted R2), all of which indicated excellent goodness of fit. Using these equations, extraction values were calculated for various experimental combinations, serving as the basis for the analysis of main effects and factor interactions.
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Characterization Details
The elemental composition of the copper concentrate (Table 2) revealed that copper (Cu), iron (Fe), and zinc (Zn) are the predominant elements in the sample. Silver (Ag), calcium (Ca), and lead (Pb) were also detected. Notably, the metalloids arsenic (As) and antimony (Sb) were identified at concentrations of 1.82 and 0.51 wt%, respectively. It is worth mentioning that the highest proportion of these elements was found in the particle size fraction between −149 and +105 µm.

Table 2.
Elemental analysis of the copper concentrate.
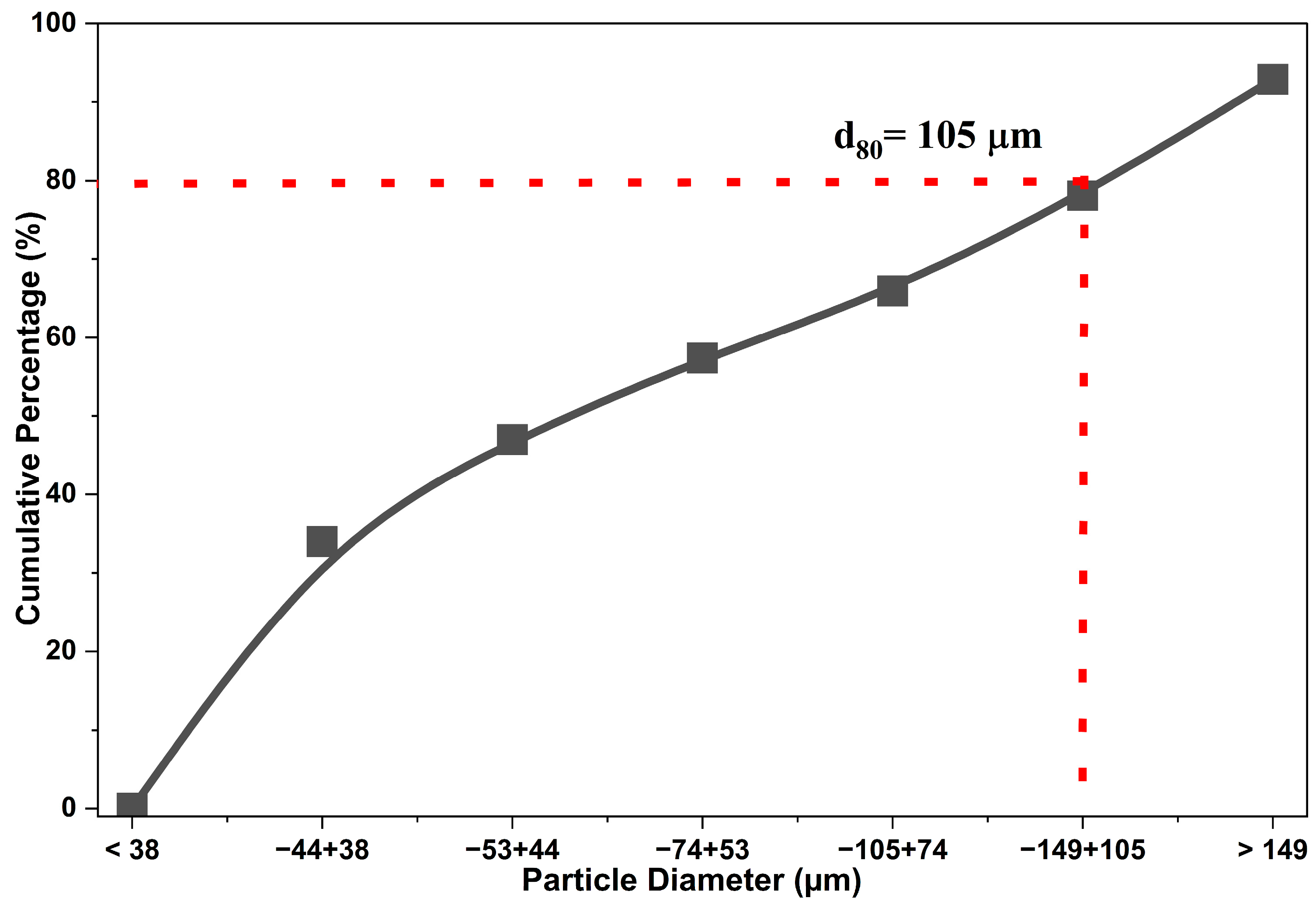
In the particle size distribution analysis (Figure 1), the d80 percentile corresponds to a particle diameter of 105 µm, indicating that 80% of the particles have a size equal to or greater than this value. It is important to note that, according to the elemental analysis, this particle size range exhibits the highest concentration (wt%) of As and Sb.
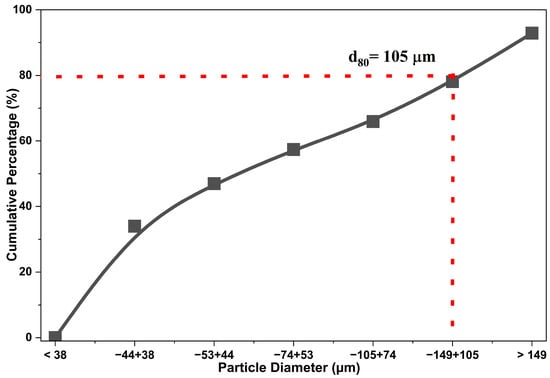
Figure 1.
Particle size distribution of the copper concentrate.
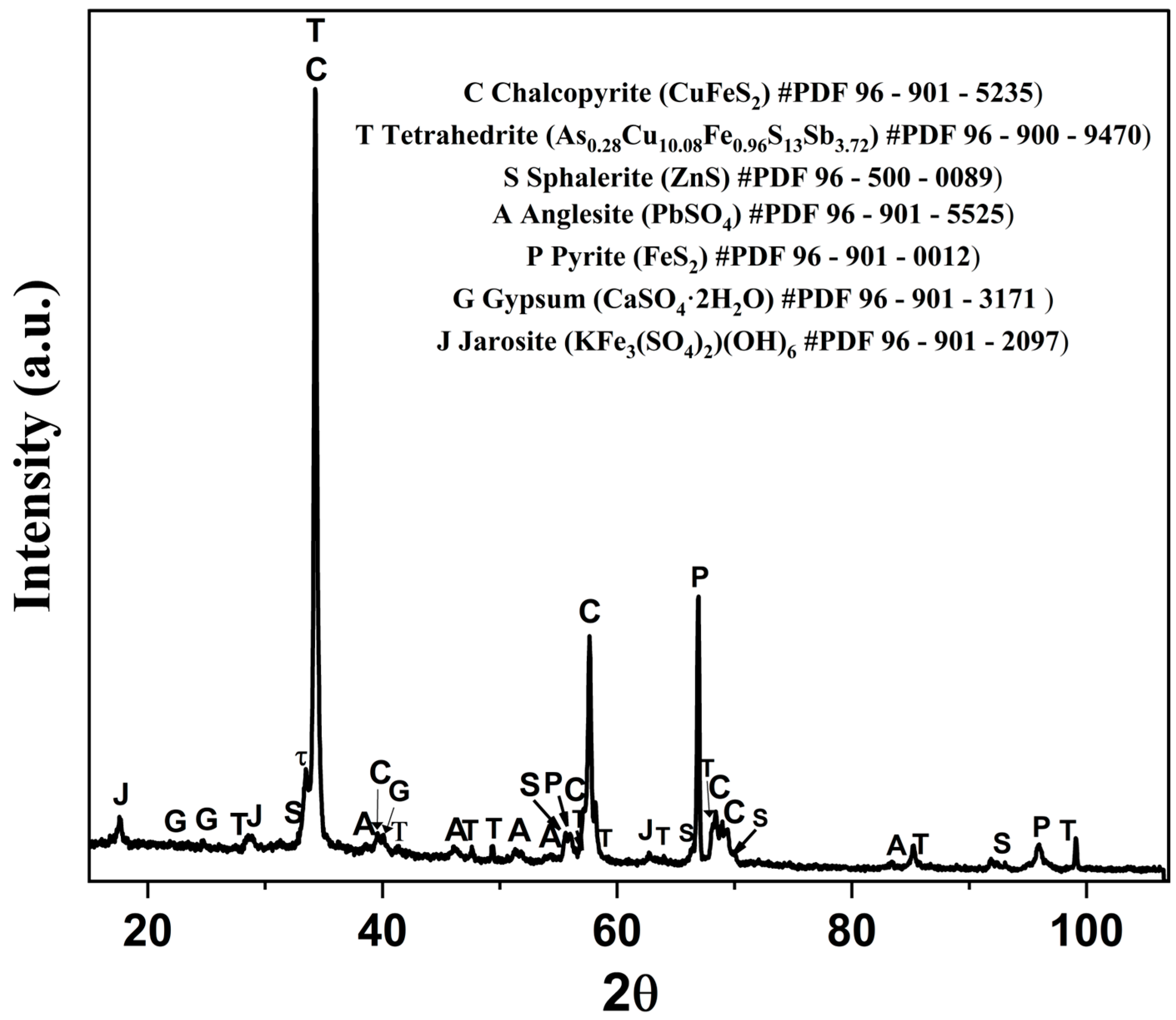
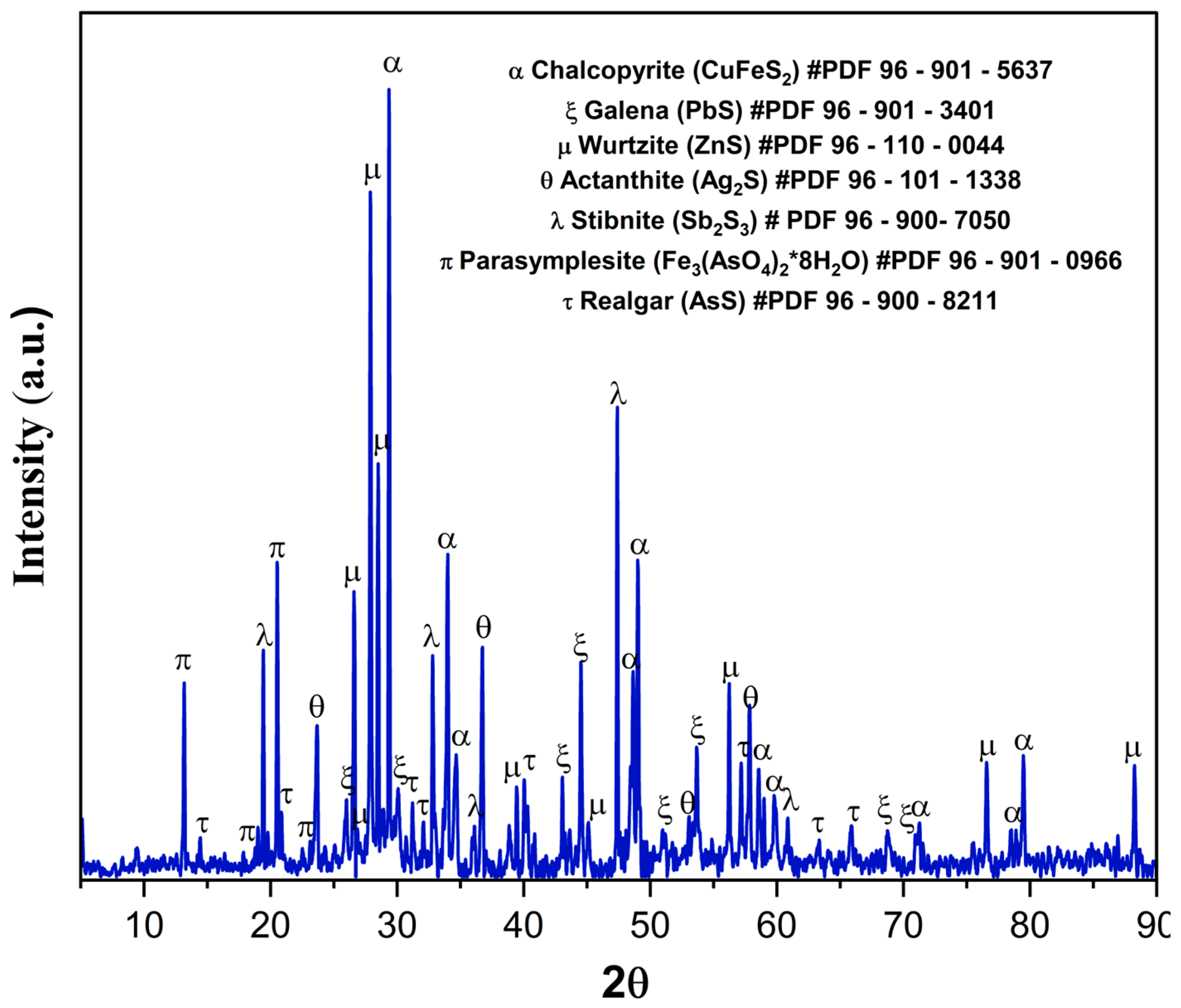
The XRD pattern in Figure 2 reveals the presence of phases such as chalcopyrite (CuFeS2), sphalerite (ZnS), anglesite (PbSO4), and pyrite (FeS2). Additionally, arsenic, antimony, and silver were identified as being predominantly present in the tetrahedrite phase (As0.28Cu10.08Fe0.96S13Sb3.72). Characteristic peaks of gypsum (CaSO4·2H2O) and jarosite (KFe3(SO4)2(OH)6) were also detected in minor amounts. These results are consistent with the mineralogy previously reported in the Zimapán mining district, Hidalgo, Mexico, where the presence of these minerals has been documented in studies on hydrometallurgical processes (7). Pyrite and chalcopyrite have been reported as the dominant sulfides in the mineral deposits of the region, while sphalerite and anglesite are associated with lead and zinc mineralization in the mineral concentrates [57,58]. Additionally, the presence of jarosite and gypsum is linked to metal neutralization and precipitation processes in leach residues [59,60].
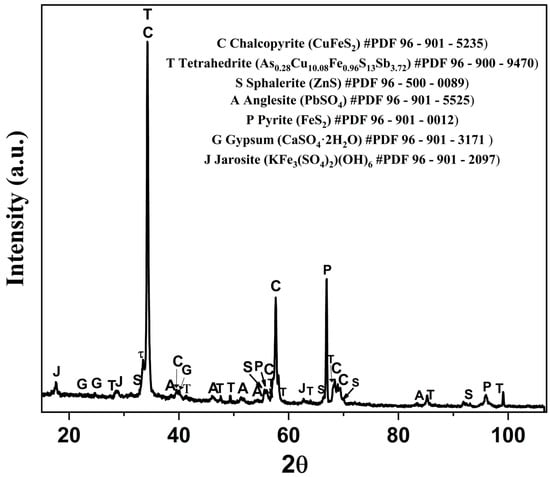
Figure 2.
XRD pattern corresponding to the copper concentrate. # indicates the ICDD PDF card number used for phase matching.
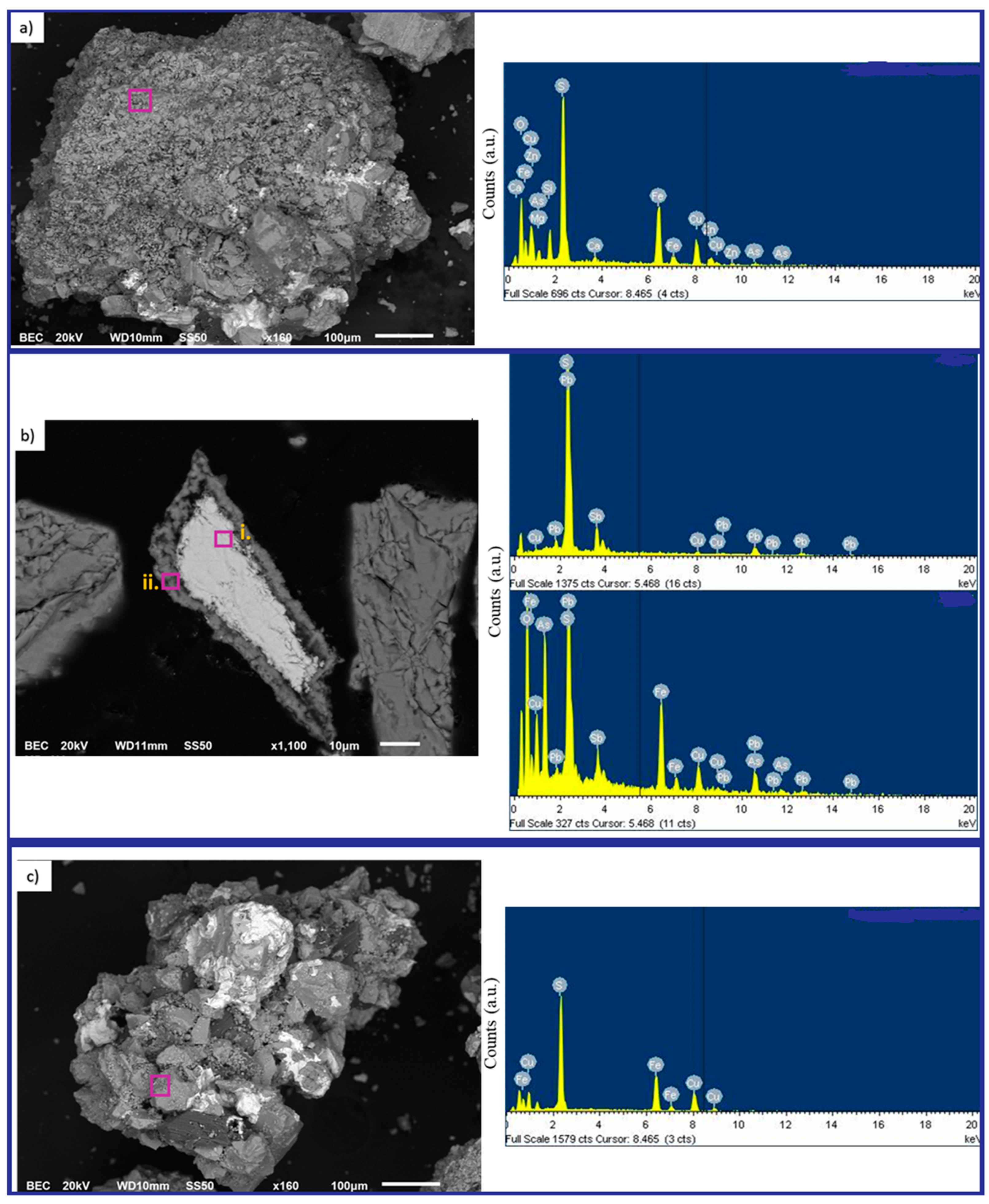
According to scanning electron microscopy coupled with energy-dispersive X-ray spectroscopy (SEM–EDS) (Figure 3), arsenic (As) occurs predominantly on particle surfaces in association with Cu, Fe, Zn, S, and, locally, Ca and Mg (Figure 3a). A magnified view (Figure 3b) shows an elongated aggregate where As and Sb coexist together with Cu–Fe–Zn–Pb–S, consistent with complex sulfosalt assemblages (e.g., tetrahedrite-type or Pb–Cu sulfosalts), in line with the XRD results. Point analyses marked i. and ii. correspond to Sb-rich and As-rich microdomains, respectively. For reference, panel (c) displays a chalcopyrite (CuFeS2) area that is essentially free of As/Sb, representative of the major sulfide matrix.
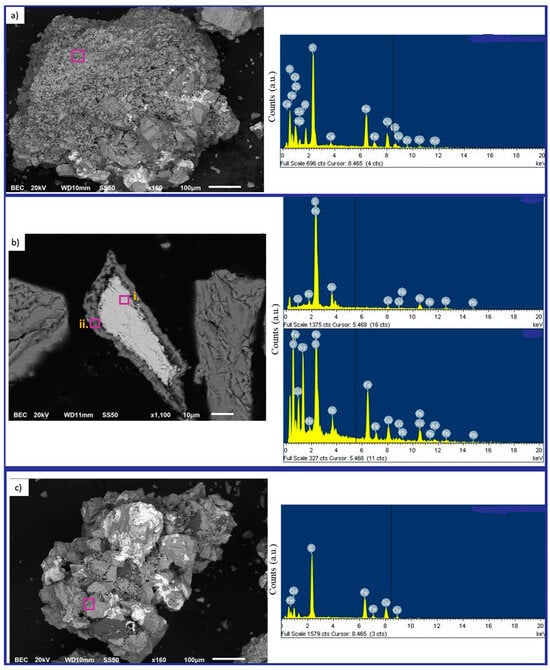
Figure 3.
(a) SEM overview of the feed concentrate (scale bar = 100 µm). (b) SEM detail of a sulfide aggregate; purple boxes indicate regions of interest (ROIs) selected for EDS interrogation. Markers i. and ii. denote point-analysis locations corresponding to Sb-rich and As-rich microdomains, respectively. (c) Reference chalcopyrite (CuFeS2) area showing the base sulfide matrix with negligible As/Sb signals.
3.2. Geoaccumulation Index and Enrichment Factors
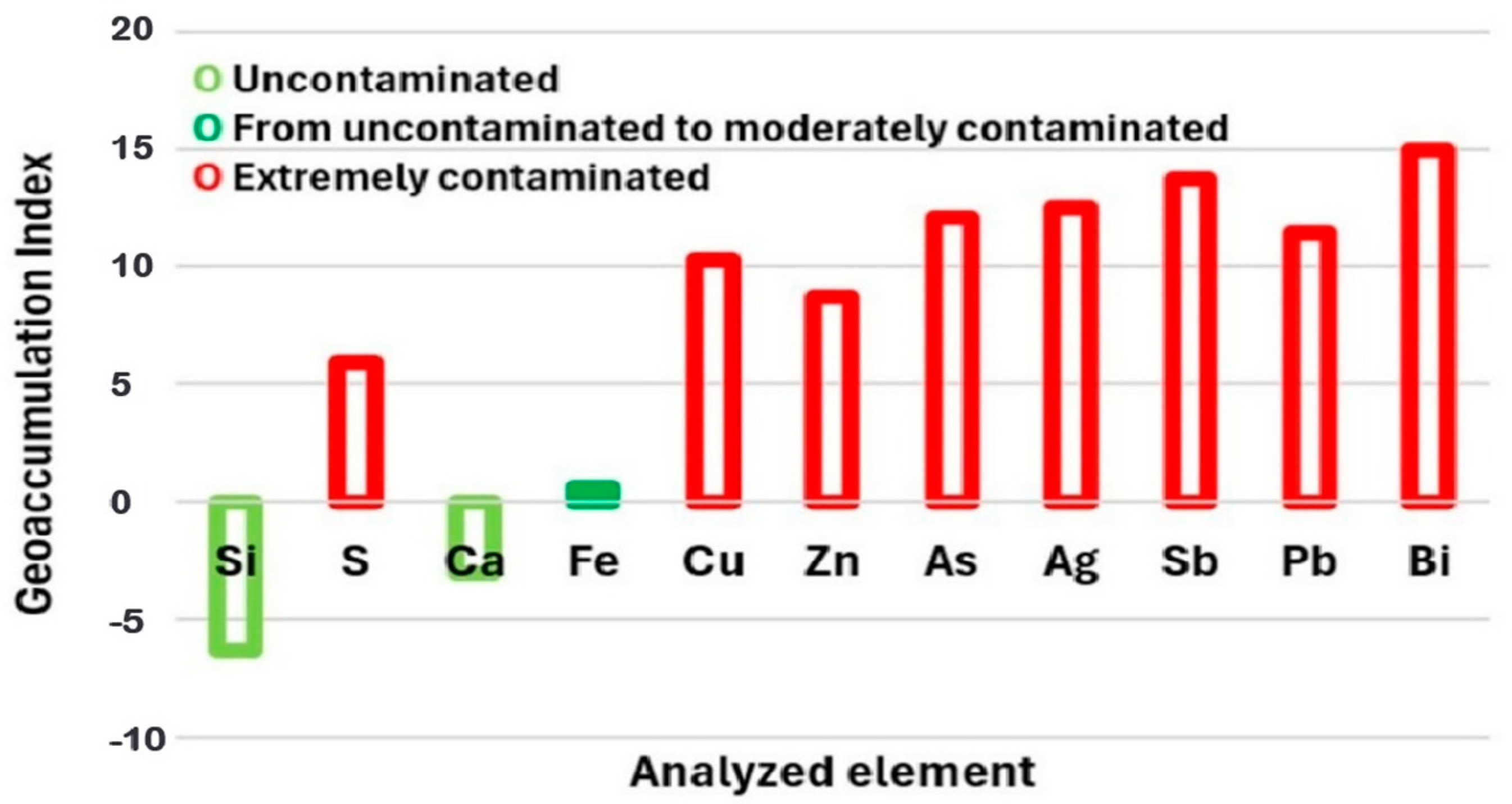
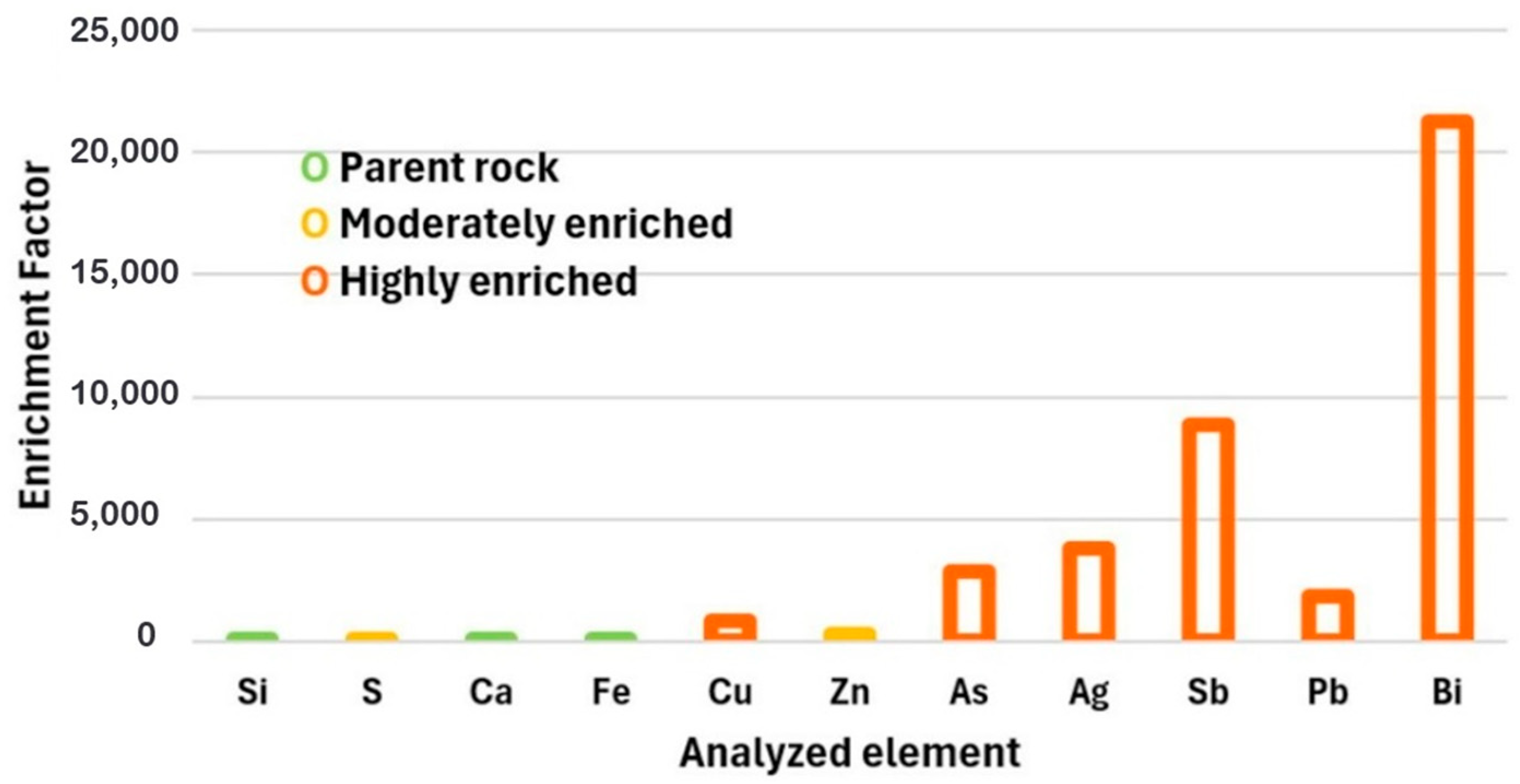
In the Zimapán mining district, Hidalgo, a medium-scale mining company produces approximately 500 tons of polymetallic concentrate per day, which is mostly stored outdoors in areas near urban settlements. This condition facilitates exposure to erosion and weathering processes, promoting the mobility of trace elements such as arsenic (As) and antimony (Sb), particularly under sulfide oxidation and surface geochemical alteration environments [61]. In these materials, the presence of As and Sb is commonly associated with complex sulfosalts such as pyrargyrite, proustite, xanthoconite, and tetrahedrite, which form part of the mineral matrix that also contains copper, iron, lead, and silver [27,62]. This type of mineralogical association favors the release of As and Sb during natural oxidation of the residues or their surface storage without encapsulation. To evaluate the contaminant potential of the studied concentrate, elemental compositions obtained by ICP were used to calculate the geoaccumulation index (Igeo) and the enrichment factor (EF), summarized in Figure 4 and Figure 5. Figure 4 shows that elements such as iron (Fe) and calcium (Ca) exhibited Igeo values < 0 and EF ≈ 1, classifying them as elements with no evidence of contamination or enrichment, and therefore not representing an immediate environmental threat. Iron (Fe), although present in high concentrations, showed intermediate values that place it within the moderately contaminated category, reflecting its primarily lithogenic origin [63,64]. In contrast, arsenic (As) and antimony (Sb) exhibited Igeo values greater than 5 and EF values above 10, placing them in the categories of extreme contamination and very high geochemical enrichment, respectively [65].
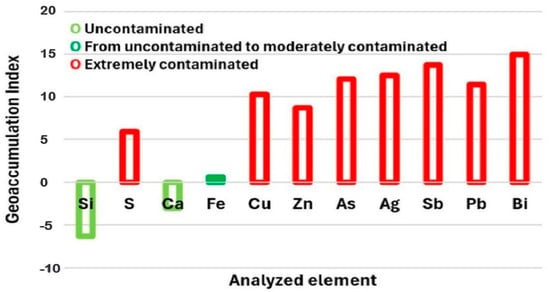
Figure 4.
Contamination potential of the polymetallic concentrate based on Igeo and FE.
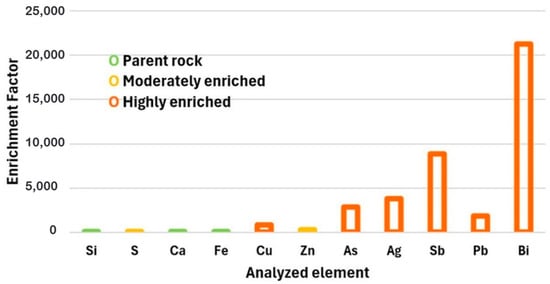
Figure 5.
Geo-enrichment profile of the polymetallic concentrate.
This classification indicates not only a high relative concentration compared to background values but also a strong anthropogenic influence and high potential mobility under environmental conditions. Given the toxic nature of both arsenic (As) and antimony (Sb)—and the carcinogenicity of As, particularly in its trivalent form—these results reinforce the need for targeted mitigation measures to prevent its dispersion into the environment [66,67].
Figure 5 analyzed the calculated enrichment factors (EF) for the elements present in the concentrate. Elements such as calcium (Ca) and iron (Fe), previously identified as environmentally non-prioritary, exhibit EF values close to 1, confirming their lithogenic origin and natural abundance in the parent rock. Zinc (Zn), with a moderate enrichment value (1 < EF < 5), suggests limited potential for primary recovery but may be considered a byproduct if specific beneficiation stages are integrated into the metallurgical process [8,68]. In contrast, silver (Ag), arsenic (As), and antimony (Sb) exhibit the highest enrichment levels, supporting the classification of the concentrate as a viable secondary source of these strategic elements. Particularly, As and Sb stand out not only for their economic value but also for their environmental impact, highlighting the need for targeted recovery and mitigation strategies [69,70].
3.3. Extraction Profiles of As and Sb
The extraction of As and Sb from mineral phases such as tetrahedrite in an alkaline medium using Na2S proceeds according to Equations (11)–(14), where both arsenic and antimony are dissolved as thioanions (AsS33−, AsS43−, SbS33−, and SbS43−):
Accordingly, it is important to examine the stability of the sulfide ion (S2−) during the leaching process. Equations (15) and (16) represent the acid–base equilibrium of the sulfide ion [71,72,73]. Initially, in an alkaline medium, the sulfide ion is present at a high concentration. However, as the pH decreases, protonation of the sulfide ion occurs, leading to the formation of the hydrosulfide ion (HS−) (Equation (15)):
If the pH decreases below 7, the predominant aqueous species (Equation (16)) becomes H2S, resulting from a second protonation step:
To ensure efficient dissolution of As and Sb and to avoid the formation of undesirable species, it is essential to maintain a controlled pH during the leaching process [74]. For this reason, an alkaline medium is critical to stabilize the thioanions formed during tetrahedrite leaching and to maintain an adequate concentration of S2− in solution (Equation (17)):
In an alkaline medium, the sulfide ion plays a role as a nucleophile in the bonds formed of the metal–sulfur characteristic of the tetrahedrite structure, inciting the rupture of said bonds and the formation of thioarsenate and thioantimonate species, according to Equations (11)–(14). The reaction proceeds with the parallel formation of Cu2S/CuS as sparingly soluble phases, which “protect” the valuable sulfides (Cu, Ag) from an extensive dissolution process.
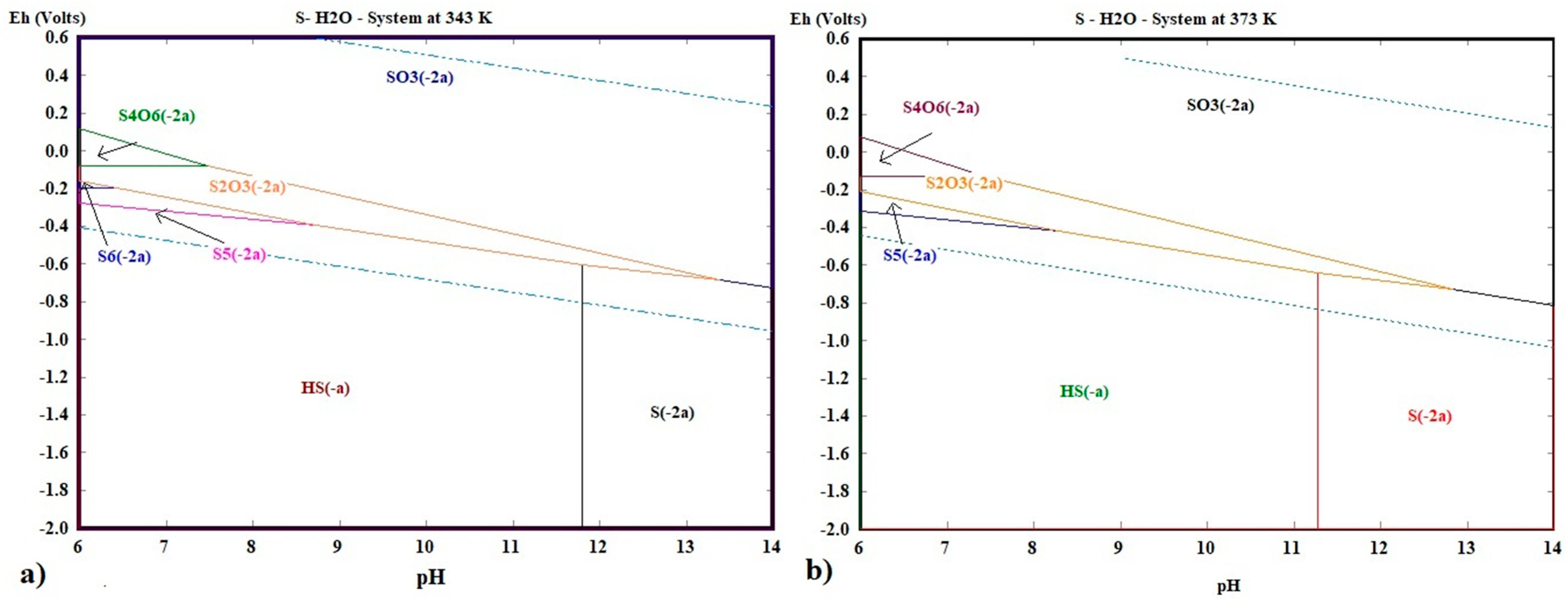
The speciation of the sulfide reagent is governed by the equilibria ; therefore, working at a high pH is essential to maximize the free fraction of and stabilize the complexes with As and Sb. Finally, to evaluate the influence of temperature on the stability of the leaching system, Eh–pH diagrams for the S–H2O system were constructed at 343 K and 373 K (Figure 6a,b). These figures show that increasing the temperature broadens the stability region of the S2− ion, favoring its participation in the process. Specifically, at 343 K, the sulfide ion remains stable within a pH range of 11.8 to 14 under reducing conditions, while at 373 K, this range extends from 11.27 to 14. Although the pH variation is minor, the results suggest that temperature not only enhances the reaction rate but also stabilizes the leaching ion within the reaction medium. Previous studies have shown that temperature is a critical factor in the leaching of sulfides, as it can improve the solubility of target species [75].
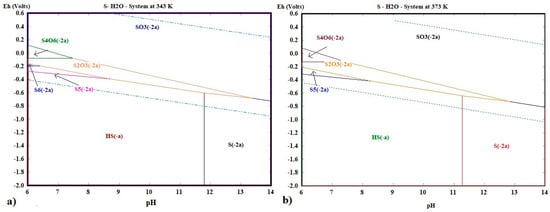
Figure 6.
Eh—pH diagram of the S—H2O system at: (a) 343.15 K and (b) 373.15 K.
- Influence of Na2S Concentration on the Extraction of As and Sb
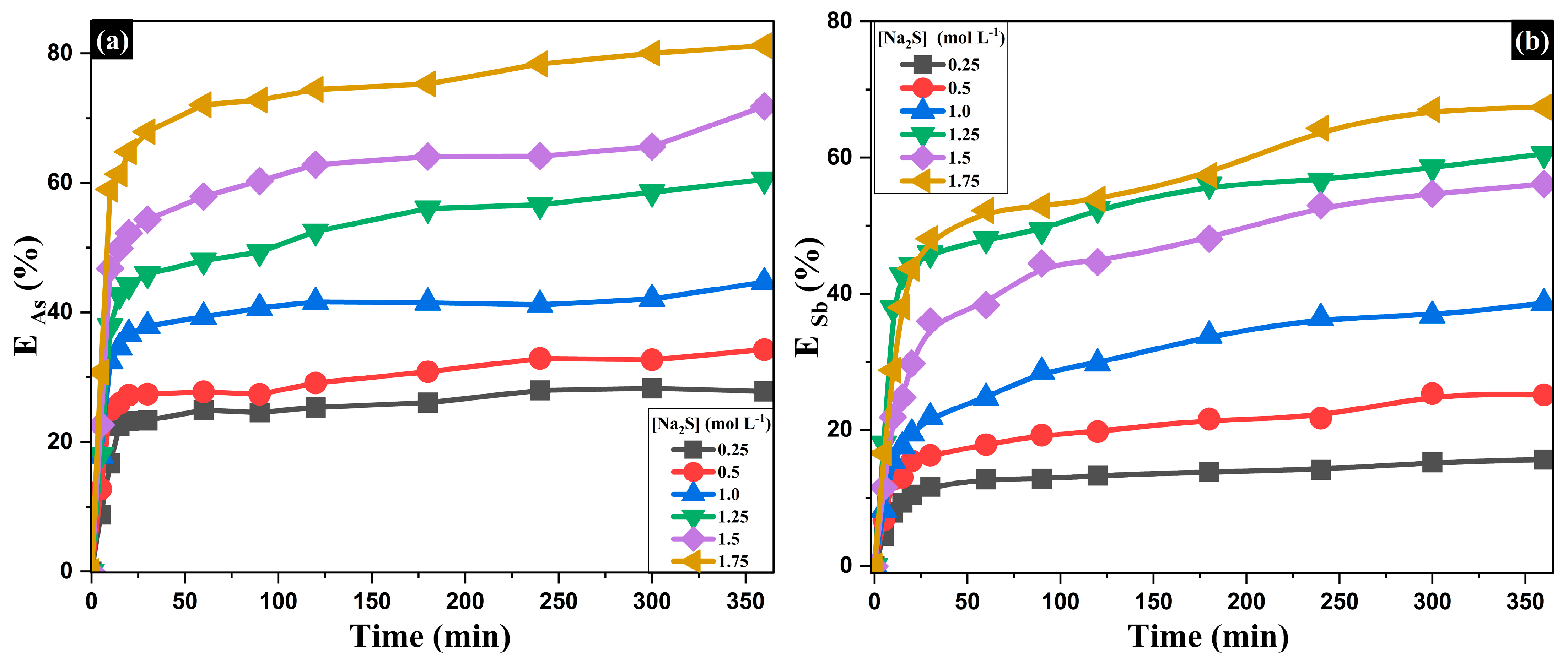
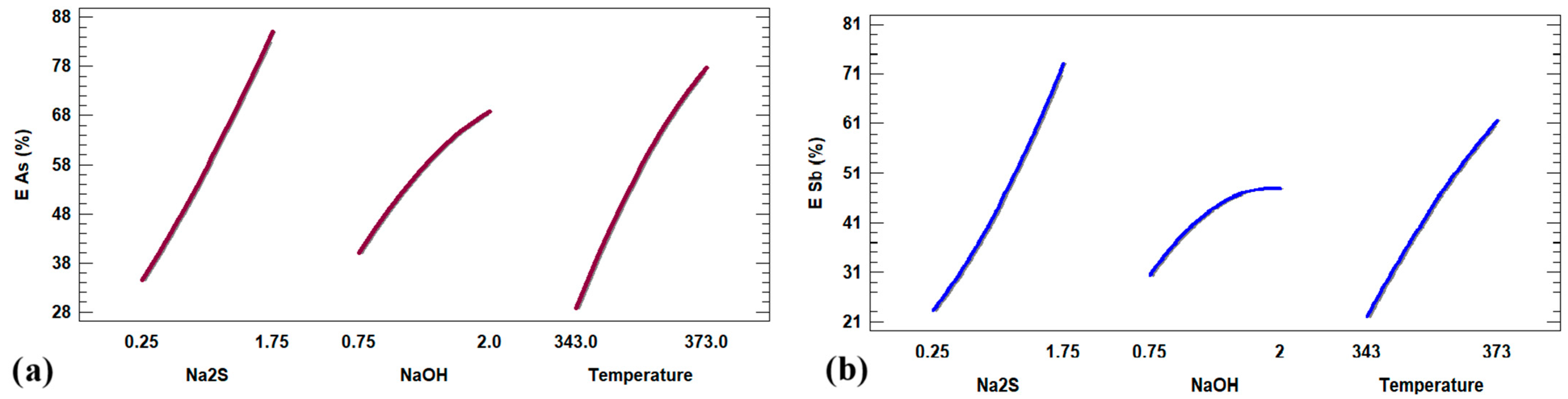
The effect of Na2S concentration on the extraction of As and Sb was evaluated over a range of 0.25 to 1.75 mol·L−1, while keeping temperature (353.15 K) and NaOH concentration (1.5 mol·L−1) constant (Figure 7). After 360 min of reaction, a low Na2S concentration (0.25 mol·L−1) resulted in limited extraction of As (28.3%) and Sb (15.7%). Increasing the concentration to 1.0 mol·L−1 improved recovery to 44.7% and 38.6%, respectively, indicating that higher Na2S levels enhance the leaching of both elements. However, the most significant increase was observed between 1.0 and 1.5 mol·L−1, where As and Sb dissolution reached 71.8% and 56.1%, respectively, highlighting the critical role of sulfur-based ligands in the process. At higher concentrations (1.75 mol·L−1), As and Sb extraction reached 81.2% and 67.4%, respectively. In the absence of Na2S (pH ≥ 12), no appreciable As/Sb leaching is anticipated because the thiocomplexation pathway is not available [46,76,77,78].
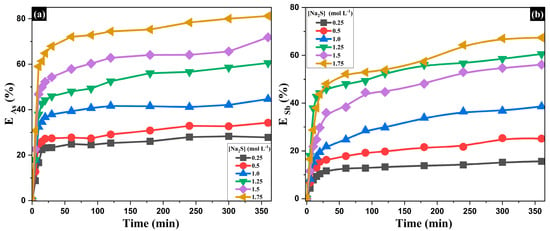
Figure 7.
Influence of Na2S concentration on the extraction of (a) arsenic and (b) antimony at 353.15 K and [NaOH] = 1.5 mol·L−1.
- 2.
- Influence of NaOH concentration on the extraction of As and Sb
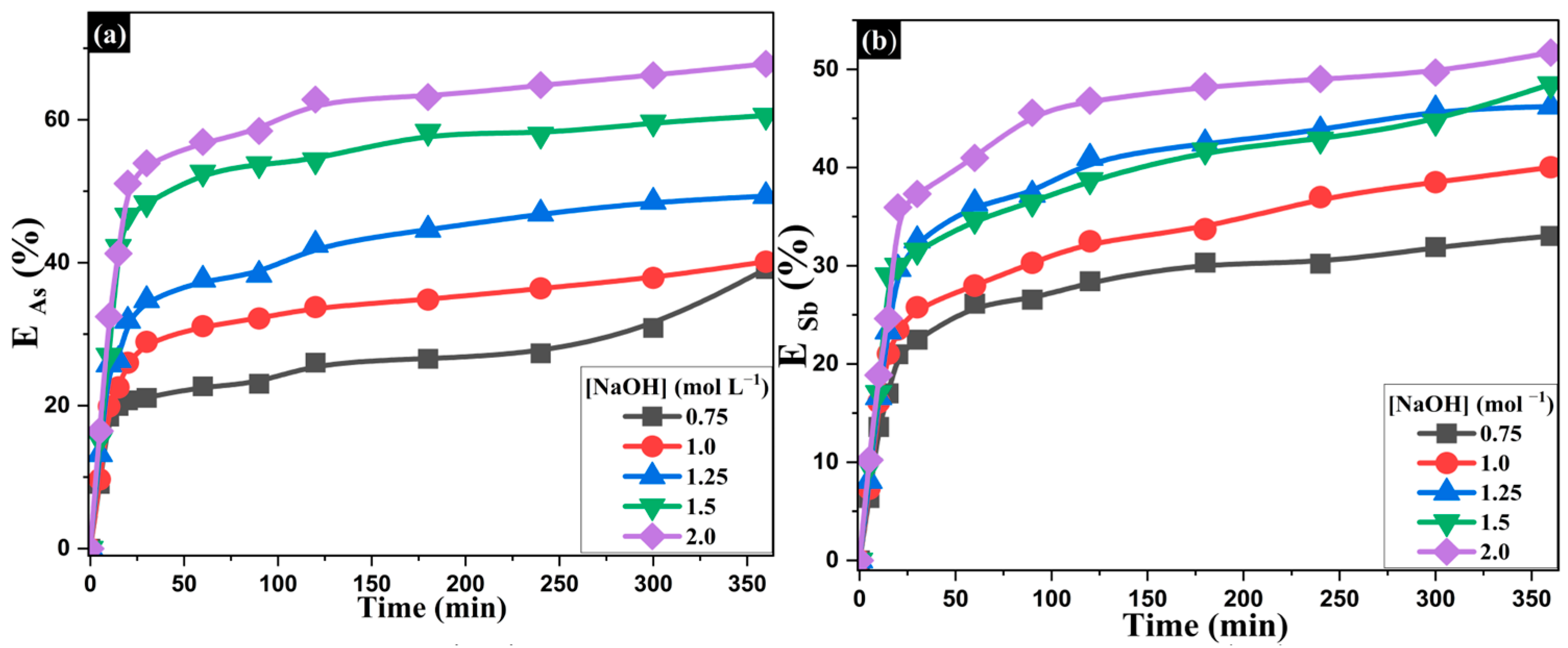
Figure 8 shows the effect of NaOH concentration (0.75–2.0 mol·L−1) on the extraction of As and Sb while keeping the temperature (353 K) and Na2S concentration (1.25 mol·L−1) constant. The results revealed that increasing NaOH concentration progressively enhances the dissolution of both elements. At 0.75 mol·L−1, the extraction efficiencies for As and Sb were 39.1% and 33.0%, respectively, whereas at 2.0 mol·L−1, the values reached 67.8% and 51.7%. Although this effect is positive, it is not as pronounced as the effect observed when varying Na2S concentration, where the increases were more substantial. These findings suggest that while an alkaline medium is essential for the stability of soluble species, the availability of sulfide ions plays a more decisive role in the overall efficiency of the leaching process.
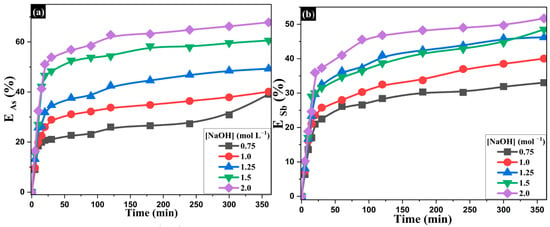
Figure 8.
Influence of NaOH concentration on the extraction of (a) arsenic and (b) antimony at 353 K and [Na2S] = 1.25 mol·L−1.
- 3.
- Influence of Temperature on the Extraction of As and Sb
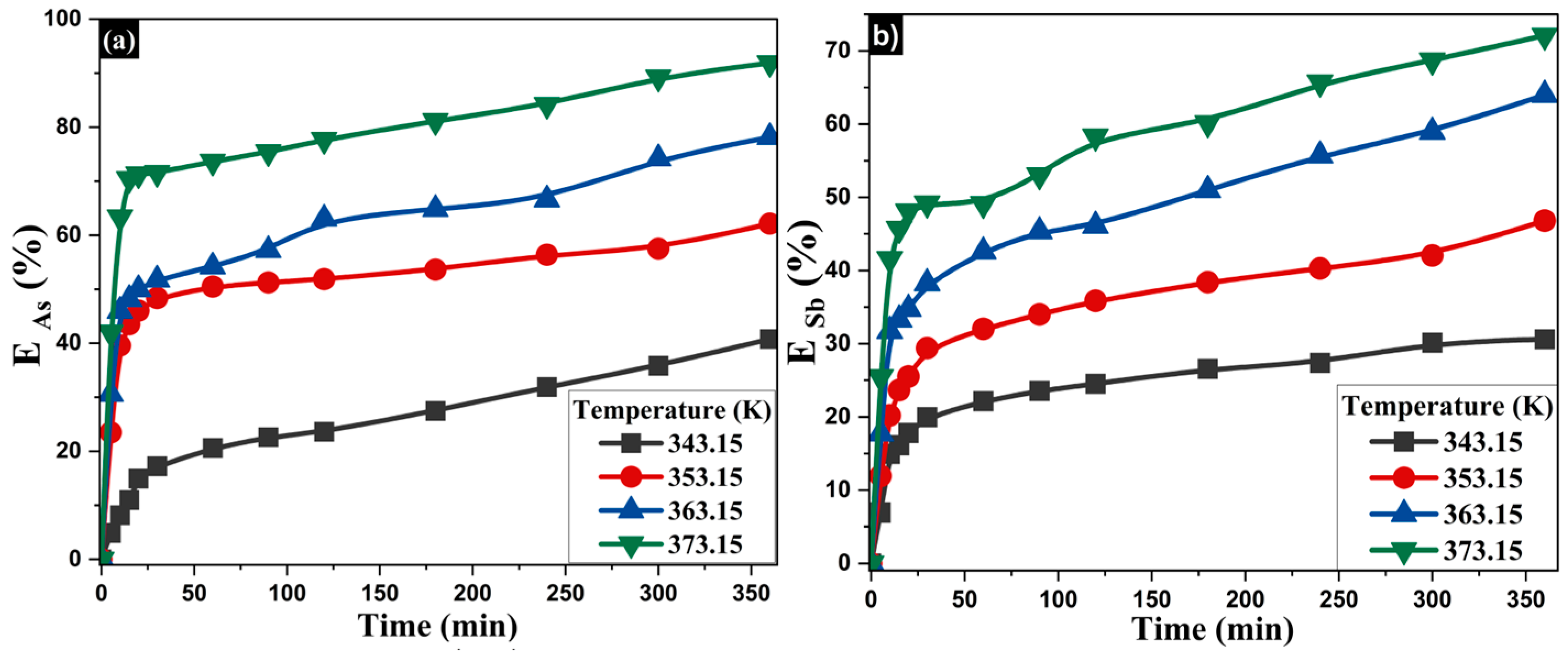
Based on the results shown in Figure 9, the influence of temperature (343–373 K) on the extraction of As and Sb was evaluated while keeping the concentrations of Na2S (1.25 mol·L−1) and NaOH (1.5 mol·L−1) constant. A direct correlation was observed between increased temperature and enhanced extraction of both elements. At 343 K, extraction rates reached 47.2% for As and 36.9% for Sb, while at 373 K, they increased to 87.5% and 66.4%, respectively. This behavior is attributed to the acceleration of dissolution kinetics at higher temperatures, as well as to the enhanced stability of sulfurous species (S2−) in alkaline media, which promotes the formation of soluble complexes with As (Figure 9a) and Sb (Figure 9b). When comparing the three evaluated parameters (Na2S concentration, NaOH concentration, and temperature), it is confirmed that although all positively influence the leaching process, Na2S concentration and temperature exert a significantly greater effect than alkalinity alone. This underscores the importance of a comprehensive design of leaching conditions to optimize metalloid recovery. The results from all three variables are summarized in Table 3.
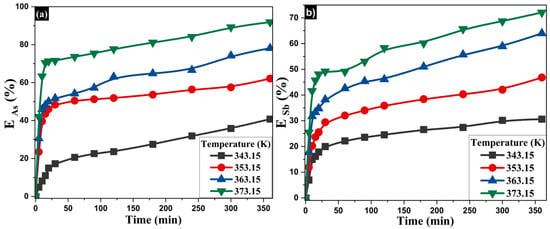
Figure 9.
Influence of temperature on the extraction of (a) arsenic and (b) antimony.

Table 3.
Conditions and results of As and Sb extraction experiments in alkaline medium with S2−.
3.4. Reaction Orders (α, β) and Activation Energy (Ea)
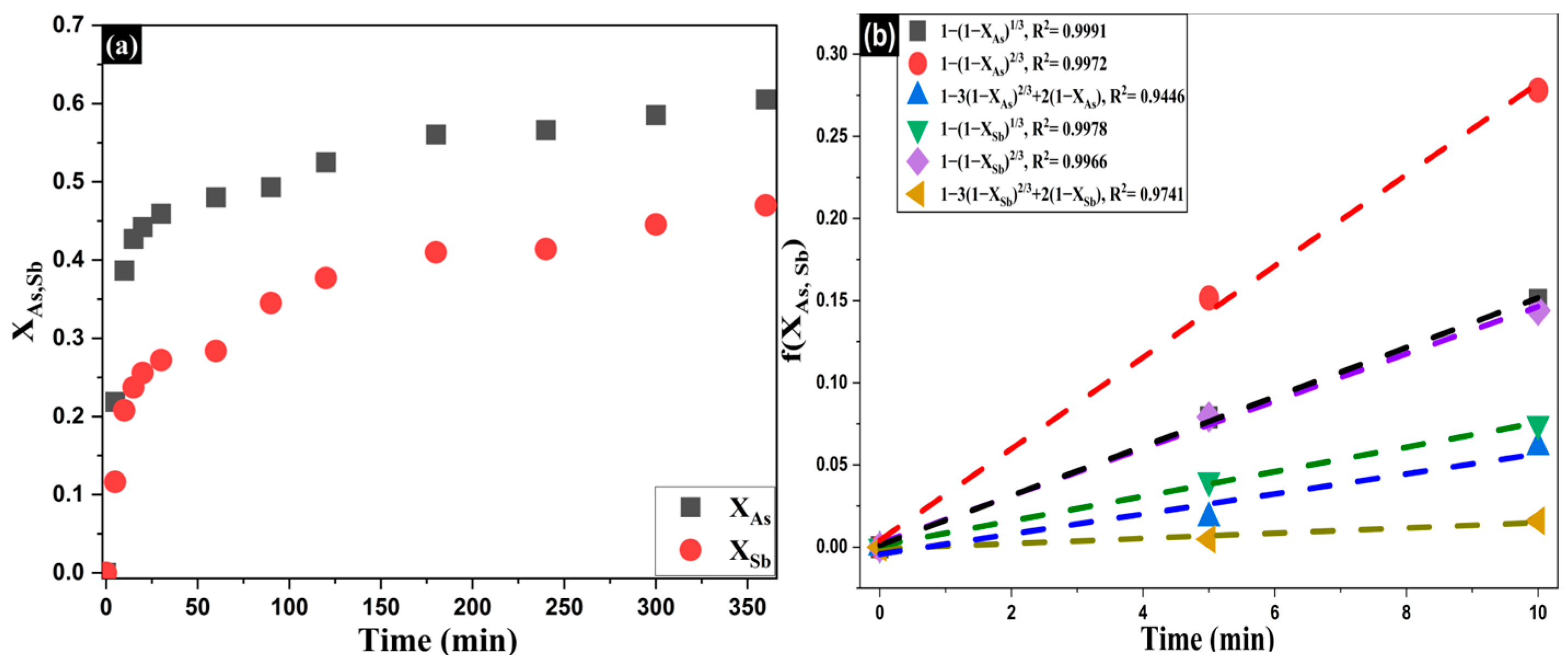
Considering Equation (10), which enables a quantitative assessment of the leaching progress as a function of time, Figure 10a shows the evolution of As and Sb conversion at [Na2S] = 1.25 mol·L−1, [NaOH] = 1.5 mol·L−1, and 353 K. Figure 10b presents linearized fits to the three classical shrinking-core limits: external film diffusion (1 − (1 − X)2/3 = kft), diffusion through the product layer [ 1 − 3(1 − X)2/3+2(1 − X) = k dt ], and surface chemical-reaction control [ 1 − (1 − X)1/3 = kct ]. The chemical-reaction model provides the best description of the data for both As and Sb (e.g., R2 = 0.9991 and 0.9978, respectively), whereas the diffusion-controlled models (film and product layer) yield lower determination coefficients and more structured residuals. Thus, under these conditions the rate-limiting step is dominantly the surface chemical reaction, while a diffusional contribution cannot be completely ruled out.
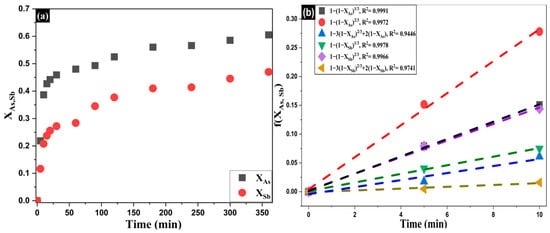
Figure 10.
(a) XAs,Sb vs. time using Equation (10); (b) Linearized fits to external film diffusion, product-layer diffusion, and surface reaction control.
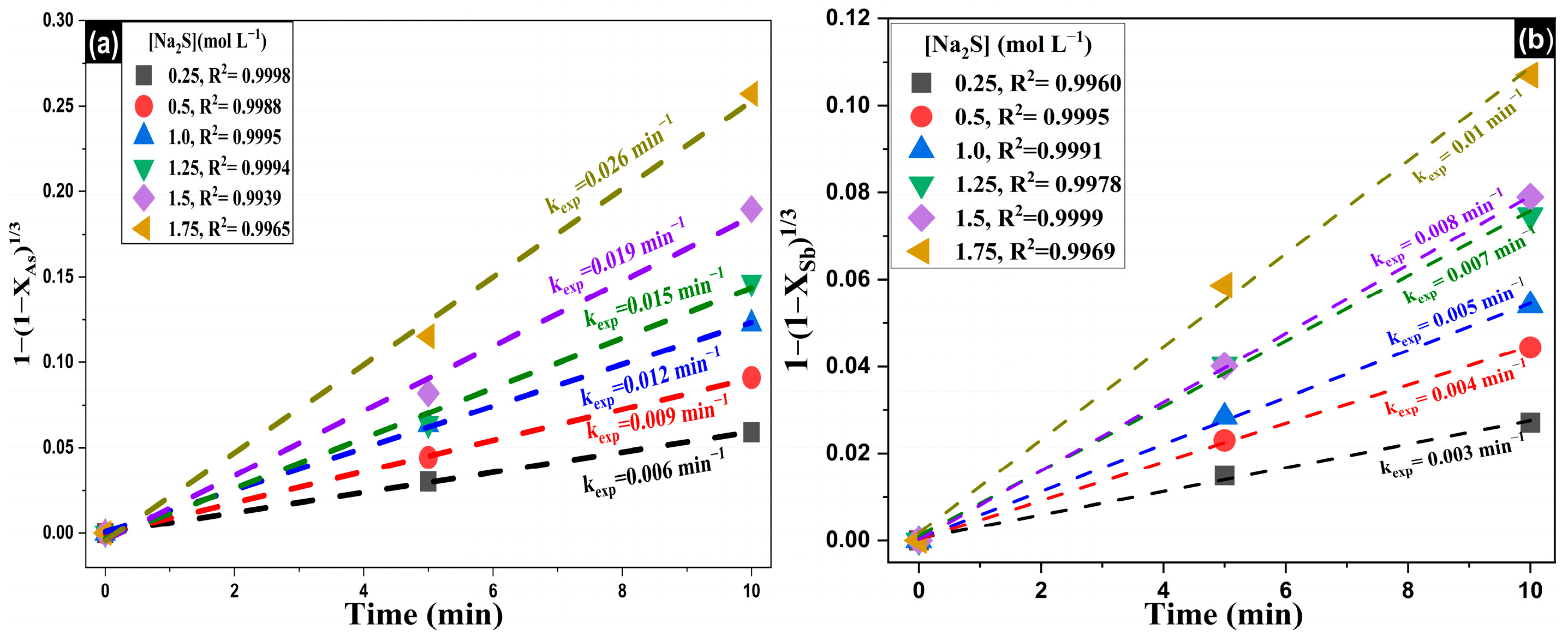
Once it was confirmed that the kinetic model governing the removal of As and Sb corresponds to a chemically controlled reaction (Equation (8)), the influence of reactant concentration on the reaction rate was evaluated. Experimental rate constants (kexp) were determined from linear fits of the integrated chemical control model equation, using various Na2S concentrations (0.25–1.75 mol·L−1) while keeping [NaOH] and temperature constant. The results obtained for As and Sb are shown in Figure 11a and Figure 11b, respectively.
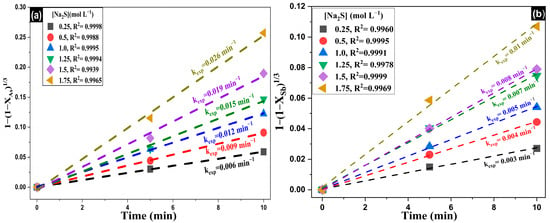
Figure 11.
Experimental data fitted to the integrated shrinking core model under chemical reaction control for the leaching of (a) arsenic and (b) antimony, using varying concentrations of Na2S.
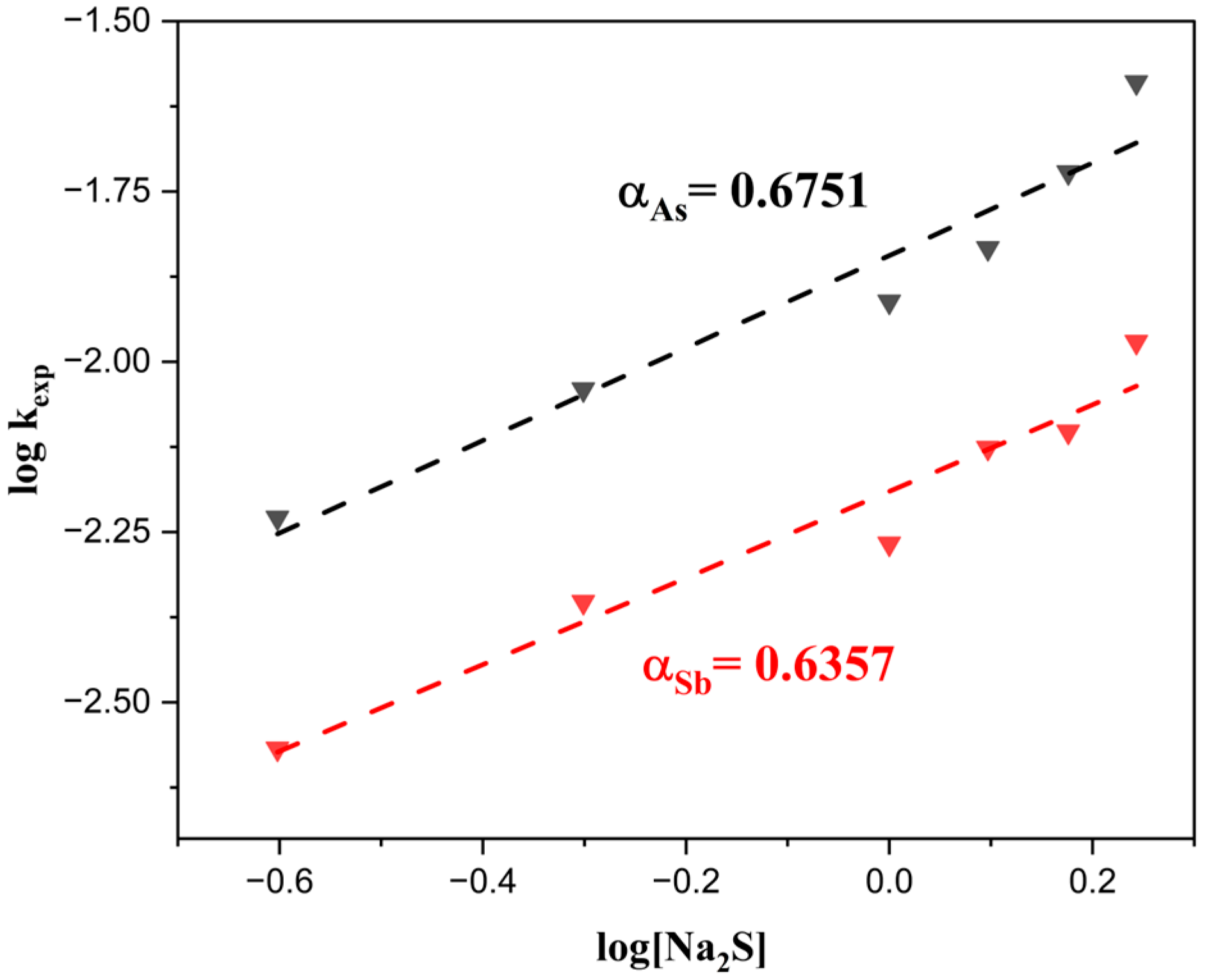
As shown in Figure 11, the rate constants (kexp) for both As and Sb increase progressively with rising Na2S concentration. However, the increase is more pronounced for As, indicating a higher sensitivity of its removal rate to sulfide ion concentration compared to Sb. Finally, by plotting log [Na2S] vs. log(kexp) (Figure 12), the reaction orders (α) for As and Sb were determined to be 0.6751 and 0.6357, respectively, confirming that the removal rates of both elements are influenced by sodium sulfide concentration. Nevertheless, the magnitude of the reaction orders suggests that the rate does not depend exclusively on the reactant concentration but is also affected by complementary phenomena [79,80].
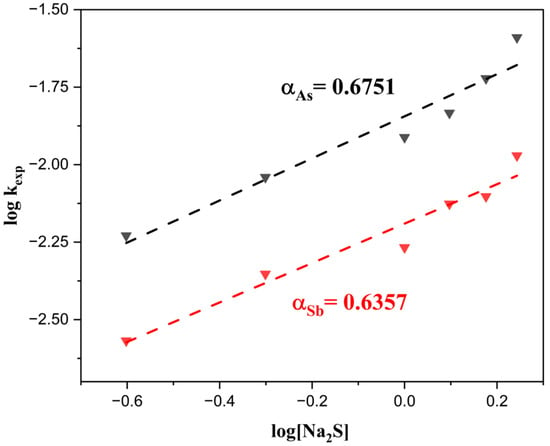
Figure 12.
Reaction orders (α) with respect to Na2S concentration in the extraction of As and Sb.
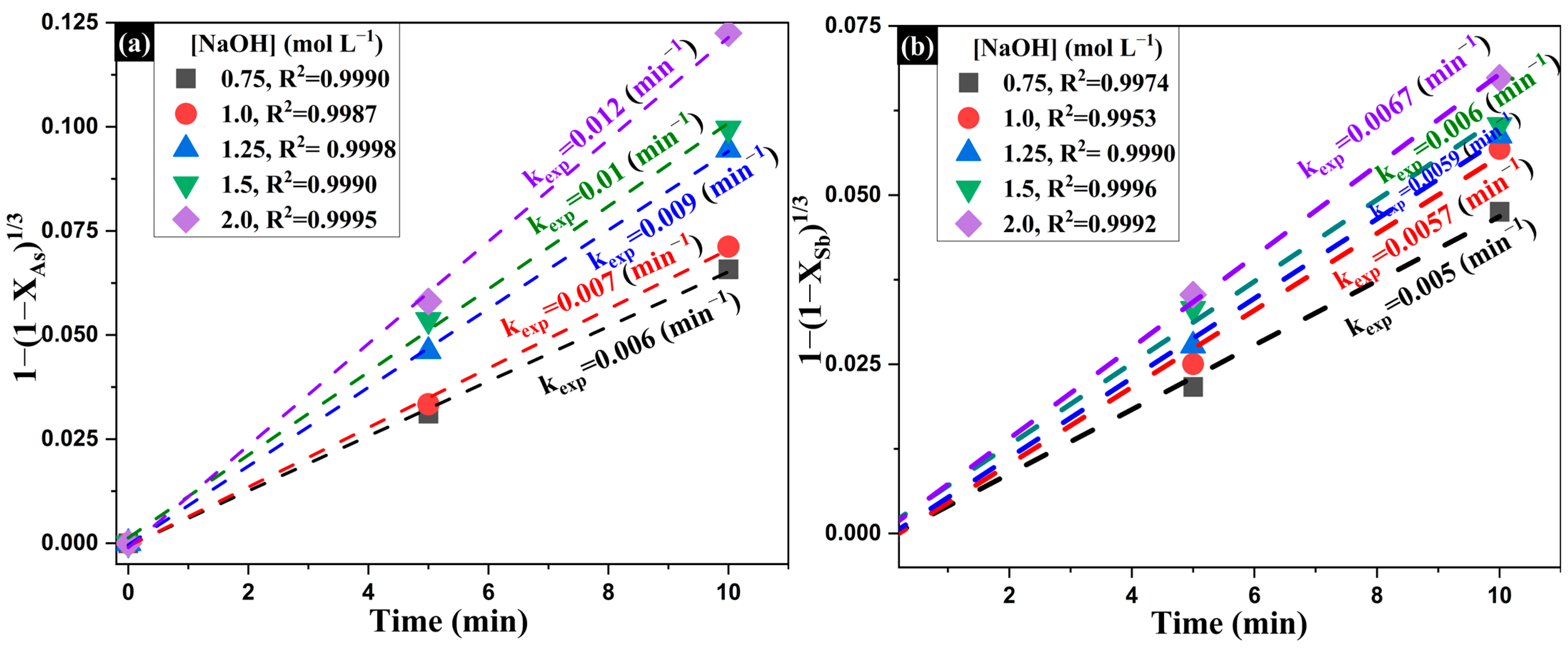
Once the reaction order with respect to Na2S was determined, the influence of NaOH concentration on the removal rate of As and Sb was evaluated. Figure 13a,b show the fitting of the experimental XAs and XSb data to Equation (8) for different NaOH concentrations. Although the rate constants (kexp) increase with NaOH concentration, the variation is more moderate compared to that observed for sodium sulfide. For As, kₑₓₚ increases from 0.006 to 0.012 min−1, while for Sb it rises from 0.005 to 0.0067 min−1. Additionally, a linear fit with correlation coefficients above 0.995 was observed in all cases, further confirming the validity of the chemical reaction control model in describing the system.
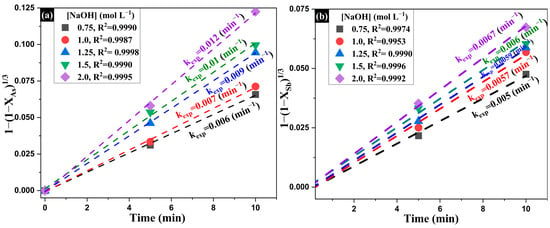
Figure 13.
Experimental data fitted to the integrated shrinking core model under chemical reaction control for the leaching of (a) arsenic and (b) antimony, using varying concentrations of NaOH.
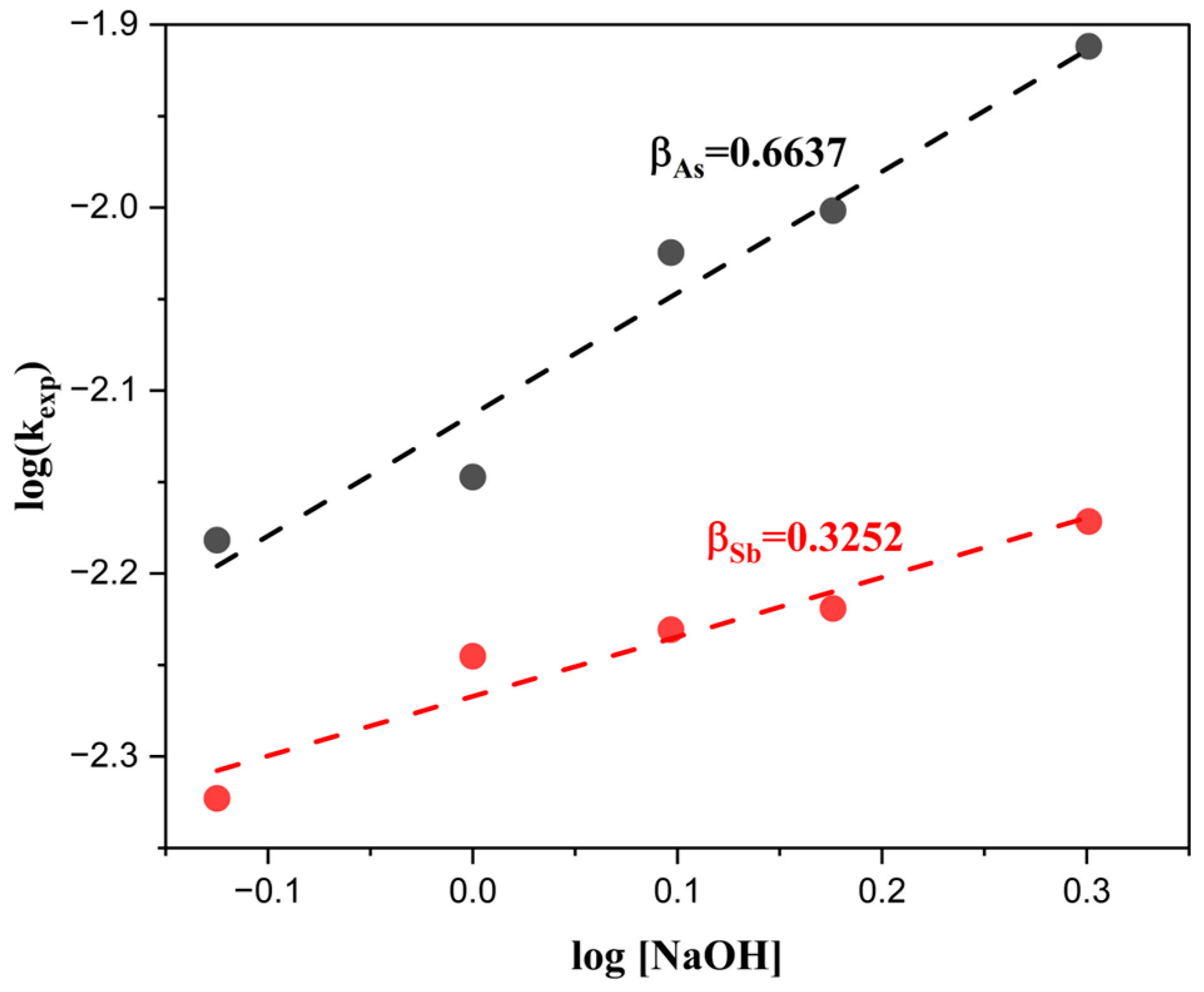
Finally, the obtained kexp values were plotted against log [NaOH] for both As and Sb, allowing the determination of the reaction orders β, which were 0.6637 for As and 0.3252 for Sb (Figure 14). These results confirm that although the hydroxide ion participates in the surface dissolution mechanism, its influence is less significant compared to that of the sulfide ion.
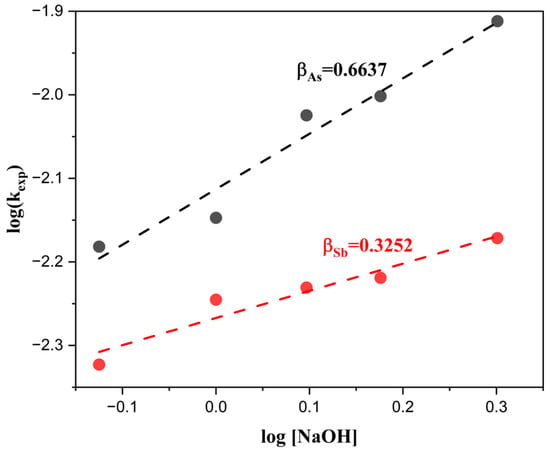
Figure 14.
Reaction orders (β) with respect to NaOH concentration in the extraction of As and Sb.
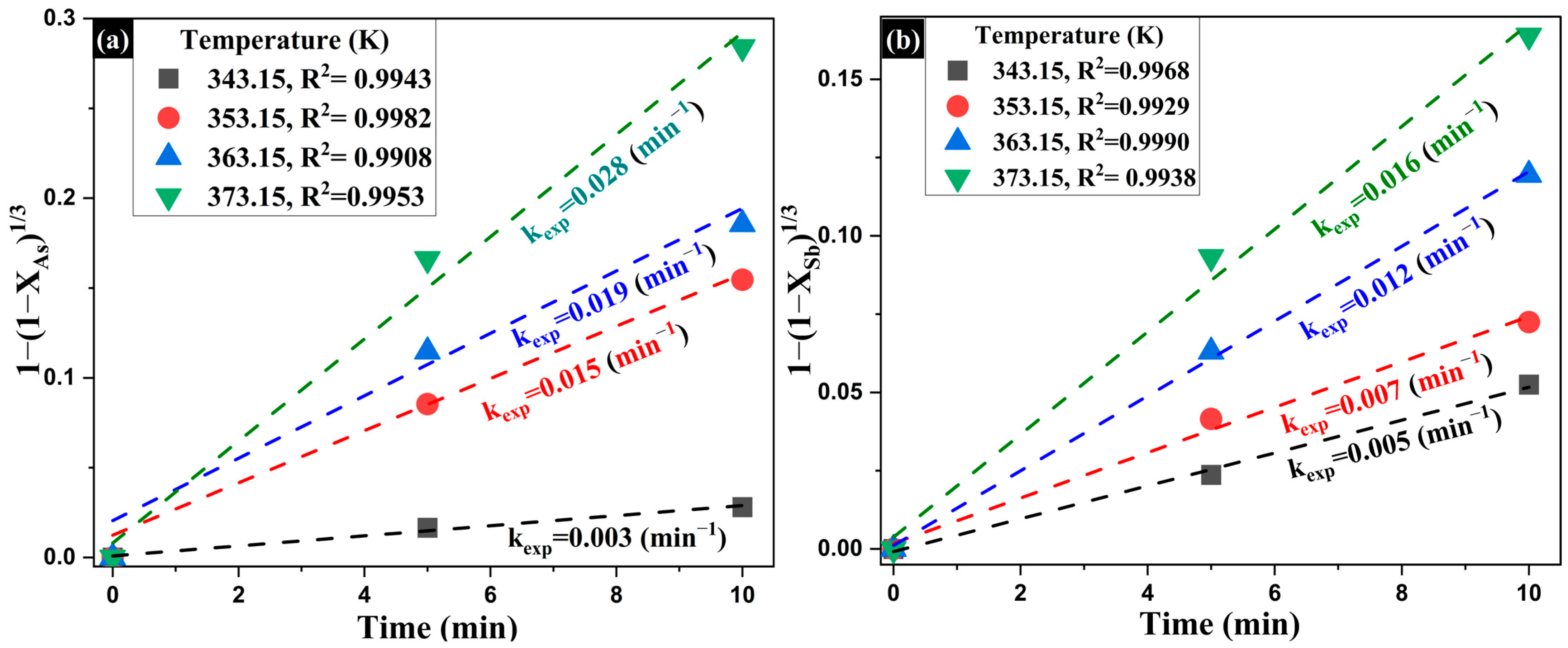
Once the reaction orders (α and β) were determined, the influence of temperature on the removal rate of As and Sb was evaluated. For this purpose, the experimental rate constants (kexp) were calculated at different temperatures under constant reagent concentrations (Figure 15). To determine the activation energy (Ea), the effect of temperature on the removal process was assessed by calculating the values of kexp at four different temperatures (343.15 to 373.15 K), while keeping Na2S and NaOH concentrations constant. Figure 15a,b show the linear fittings obtained for As and Sb, respectively, consistent with the chemically controlled model previously validated. In both cases, a significant increase in kexp was observed with temperature: from 0.003 to 0.028 min−1 for As, and from 0.005 to 0.016 min−1 for Sb. This progressive increase in the kinetic constant is characteristic of a process limited by chemical reaction at the solid–liquid interface, as this type of mechanism is highly temperature-dependent, a behavior widely reported in kinetic studies on the leaching of complex minerals [81,82,83].
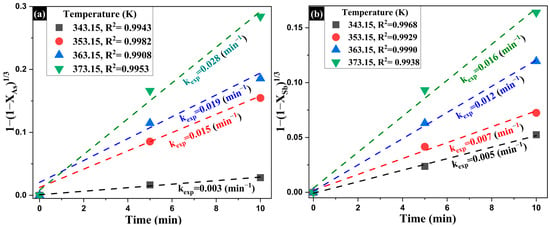
Figure 15.
Experimental data fitted to the integrated shrinking core model under chemical reaction control for the leaching of (a) arsenic and (b) antimony, using varying temperature.
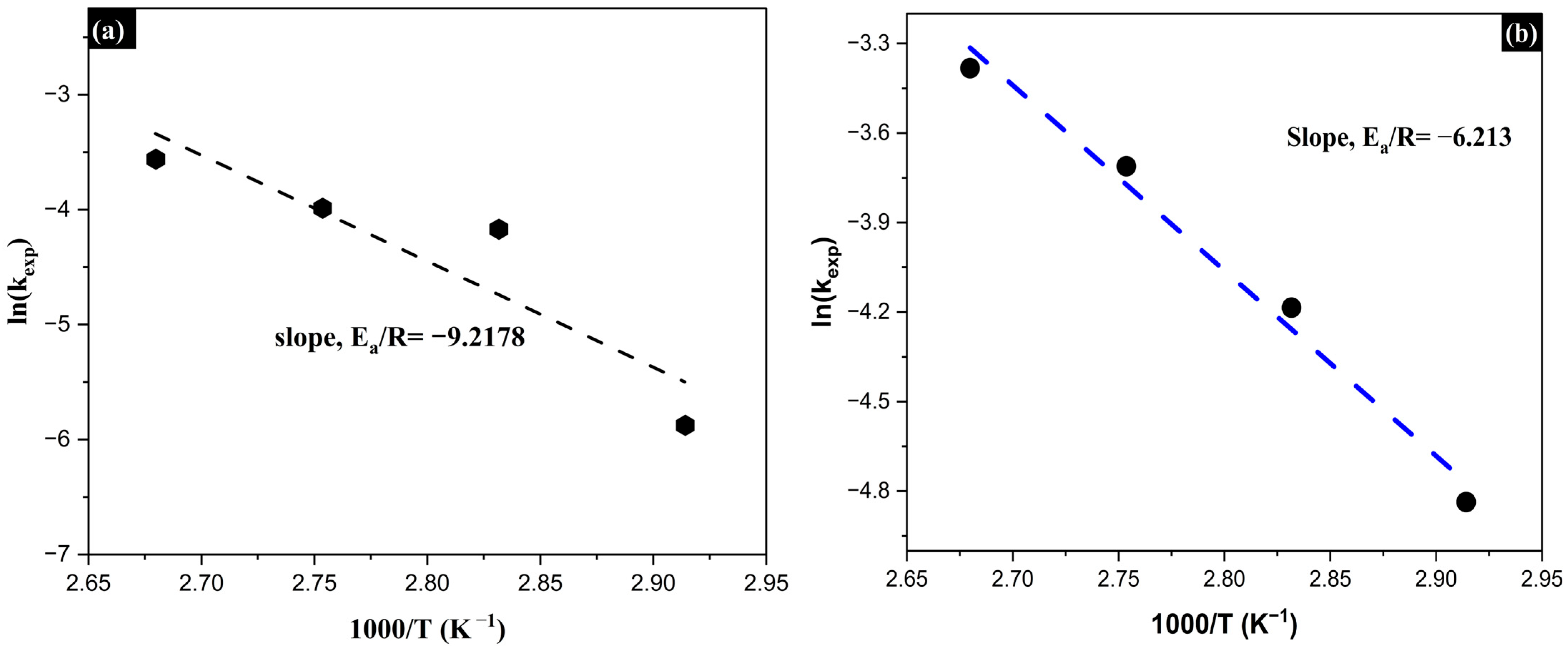
Based on the obtained kexp values, Arrhenius plots were constructed by representing ln(kexp) as a function of 1000/T. The slopes of the linear regressions allowed for the calculation of the activation energy (Ea) using the Arrhenius equation:
where R is the universal gas constant (8.314 J·mol−1 K−1). The activation energy (Ea) values obtained were 76.6 kJ·mol−1 for As and 41.6 kJ·mol−1 for Sb, confirming that the rate-limiting step in both cases corresponds to a chemically controlled mechanism. The higher activation energy associated with arsenic leaching suggests a greater sensitivity of the process to temperature, which may be attributed to a higher energy barrier required for bond cleavage and the formation of soluble species (Figure 16).
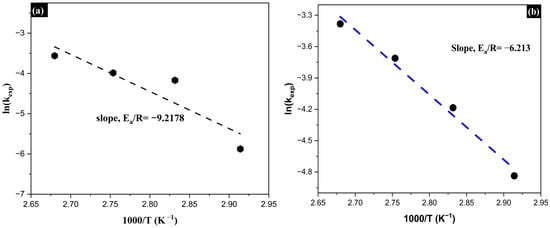
Figure 16.
Calculation of the activation energy (Ea) for the removal of As (a) and Sb (b) using the Arrhenius model.
The global kinetic expression describing the removal rate of As and Sb was formulated by integrating the experimentally determined kinetic parameters (α, β, Ea, and k0) into the shrinking core model under chemical reaction control. The pre-exponential factor k0 was calculated from the intercept of the linear Arrhenius plots obtained using the rate constants at different temperatures. This integration enabled the development of a general equation that quantitatively models the system behavior under the evaluated conditions. The resulting expression is shown below:
Using the kinetic parameters determined experimentally (α, β, Ea) and the pre-exponential factor k0 from Equation (18), Equations (20) and (21) were derived. These expressions can be used to calculate kcalc based on different values of X and t:
3.5. Exploratory Quadratic Modeling of As and Sb Extraction
Based on the data obtained during the experimental campaign (Table 3), we conducted an exploratory statistical analysis to model the extraction of arsenic (As) and antimony (Sb) as a function of sodium sulfide concentration [Na2S], sodium hydroxide concentration [NaOH], and temperature (T). Quadratic regression (Statgraphics) was applied to derive compact response equations (Equations (22) and (23)). The resulting fits show high coefficients of determination (R2 = 99.99% for As and R2 = 99.93% for Sb) within the tested data set. We emphasize that this analysis is non-confirmatory: experiments were single-run per condition, no independent validation was performed, and the data set does not originate from a full factorial DoE; therefore, the models are intended to check mechanistic consistency and guide operating ranges, rather than to provide general predictive capability or to resolve potential cooperative/competitive effects among variables outside the explored space.
The statistical significance of the terms included in the models was evaluated using analysis of variance (ANOVA) (Table 4).

Table 4.
Analysis of variance (ANOVA) for the quadratic regression models of arsenic (As) and antimony (Sb) extraction as a function of Na2S, NaOH, and temperature.
For arsenic (As), all main factors—[Na2S], [NaOH], and temperature—were statistically significant (p < 0.05), together with their quadratic terms, as supported by high F-values within the tested data set. For antimony (Sb), both [Na2S] and [NaOH] were also significant (p = 0.0197 and 0.0203, respectively), whereas temperature yielded a p-value of 0.0604, indicating a less pronounced yet near-significant effect. In this case, the quadratic interaction of [NaOH] was statistically significant (p = 0.0442), while other quadratic terms showed trends but did not reach statistical significance. The mean absolute error (MAE) of the models was low, particularly for As (MAE = 0.0934), indicating minimal deviation between observed and predicted values. To assess the influence of the variables on the extraction of As and Sb, a single-block data set design was carried out, considering different combinations of sodium sulfide concentration, sodium hydroxide concentration, and temperature. Based on the quadratic regression models (Equations (22) and (23)), the extraction percentages were estimated for each experimental point. These predicted values, presented in Table 5, served as the basis for generating main effects plots and response surface diagrams, which were used to analyze the behavior of the system.

Table 5.
Experimental design combinations and estimated extraction percentages of As and Sb based on the regression equations.
The analysis of main effects reveals that, for both metalloids, the concentration of [Na2S] exerts a clear positive influence on extraction efficiency—consistent with the monotonic trends observed in Figure 7, Figure 8 and Figure 9. In the case of arsenic (As), increases in both [Na2S] and temperature significantly enhance recovery, consistent with kinetic parameters such as reaction order and activation energy (Figure 17a) and the time–conversion profiles in Figure 7 and Figure 9. For antimony (Sb) (Figure 17b), increasing [Na2S] from 0.25 M to 1.75 M leads to a notable rise in extraction, which is attributed to the formation of soluble complexes. Regarding [NaOH], its effect exhibits a curvilinear behavior, with an optimal concentration at which the extraction efficiency is maximized before stabilizing or slightly decreasing at higher concentrations. As for temperature, a positive correlation was observed between rising temperatures and Sb leaching efficiency, aligning with the known acceleration of dissolution reactions at elevated temperatures.
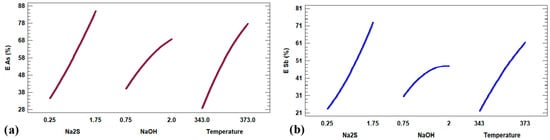
Figure 17.
Effect of independent variables on the extraction efficiency of As (a) and Sb (b).
3.6. Solid Residue Characterization by XRD
To assess the mineralogical changes induced by the selective leaching of As and Sb, the solid residues were characterized by X-ray diffraction (XRD) (Figure 18). The diffractogram exhibits intense peaks corresponding to chalcopyrite, galena, wurtzite, and acanthite, confirming that the valuable metallic phases of the concentrate remained virtually unaltered after treatment. This observation supports the high selectivity of the Na2S–NaOH system, as it demonstrates minimal interaction with Cu, Pb, and Ag sulfides. Additionally, signals corresponding to stibnite, parasymplesite, and realgar were identified, indicating that a residual fraction of Sb and As remained in the solid post-leaching [84]. These phases may be associated with less accessible or partially encapsulated structures, suggesting opportunities for process optimization or the need for an additional pretreatment stage.
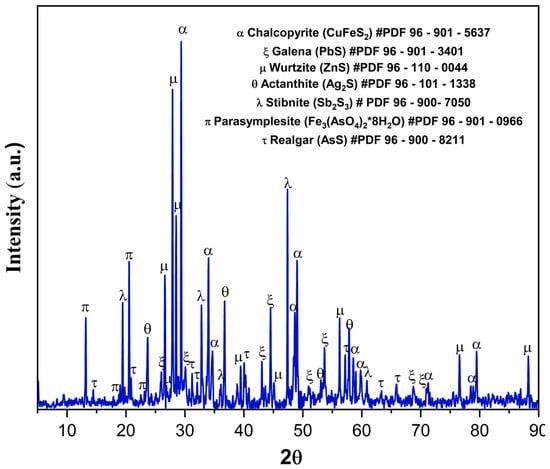
Figure 18.
X-ray diffraction (XRD) pattern of solid residues. # indicates the ICDD PDF card number used for phase matching.
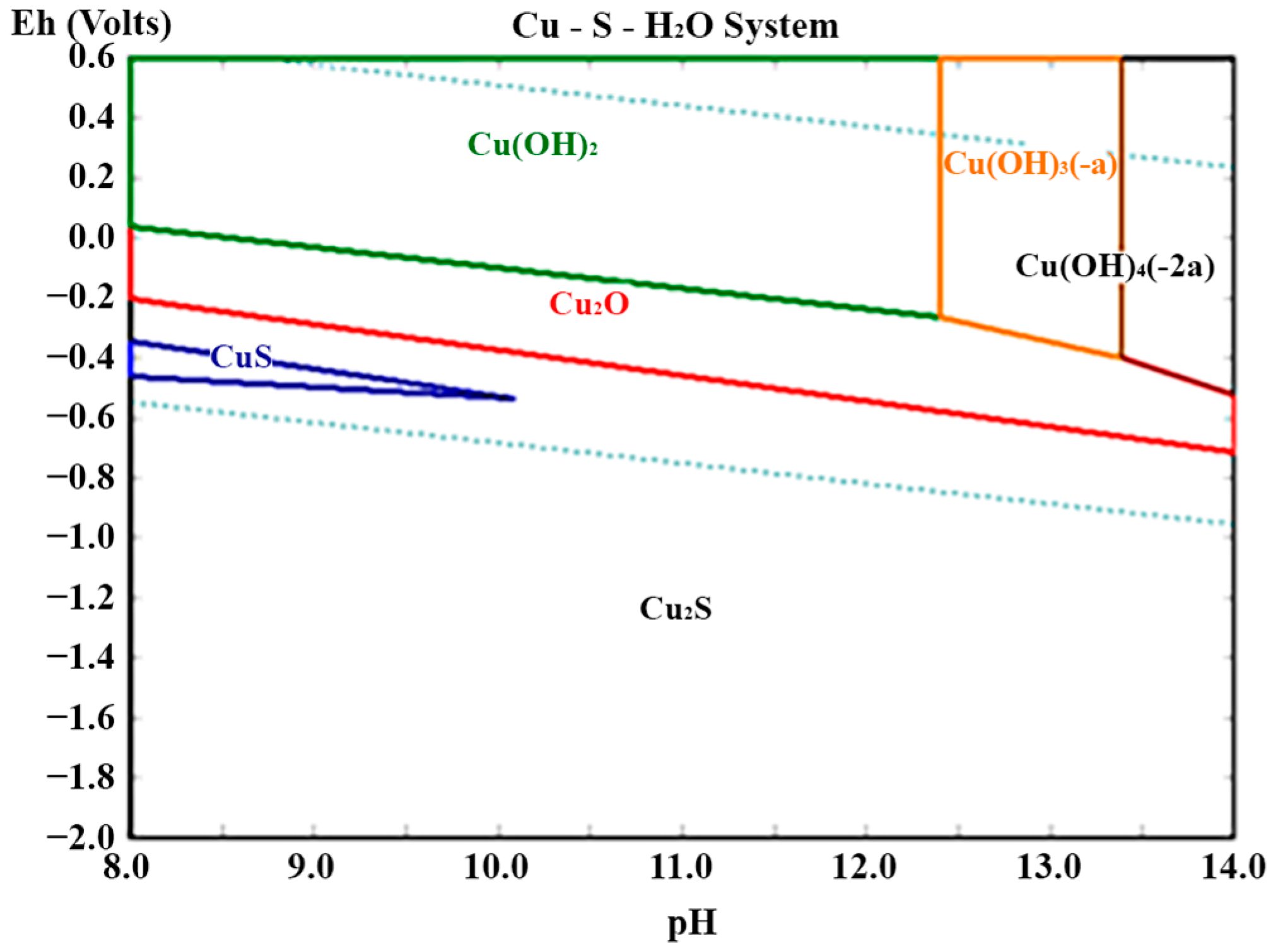
Accordingly, the Eh–pH diagram in Figure 19 indicates that, within the alkaline–reducing interval of the leaching system employed, the stable Cu phases are sparingly soluble solids (Cu2S/CuS y Cu2O/Cu(OH)2, under oxidizing environments) and, therefore, the process shows high selectivity toward As and Sb with null or minimal co-dissolution of copper.
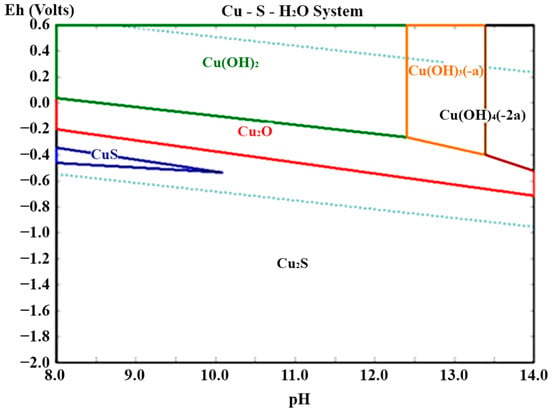
Figure 19.
Eh–pH Diagram for the Cu–S–H2O System at 353 K.
The absence of well-defined copper sulfide peaks in the XRD pattern (Figure 18) is consistent with amounts below the detection limit or with peak overlap.
3.7. Feasibility and Scale-Up Conditions
The sulfide required for the leaching process can be supplied as commercial Na2S (e.g., Na2S·9H2O) or generated in situ in an alkaline medium; this flexibility facilitates plant supply. Based on the dissolution reactions toward thiosalts (Equations (11)–(14)), the removal of As and Sb requires approximately 1.5 mol of Na2S per mol of As + Sb. Using the head grades of 1.82 wt% As and 0.51 wt% Sb as reference, this corresponds to ≈ 0.427 kmol or 55.5 kg of 60% Na2S (flakes) per metric ton of concentrate. Considering a typical cost range of the reagent (630–720 US$/t) and the stoichiometric ratio above, the direct sulfide expense is 35–40 US$ per ton of concentrate [85]. It is worth noting that NaOH does not have a fixed stoichiometric consumption (it depends on pulp density and make-up strategy), because it is mainly used to maintain pH ≥ 12. Likewise, liquor recirculation with a minimal purge (oxidized to sulfate before disposal) reduces the net sulfide consumption and the effluent load, reinforcing the circularity of the process [76].
4. Conclusions
This study demonstrated the effectiveness of a selective alkaline leaching system based on Na2S–NaOH for the controlled removal of arsenic (As) and antimony (Sb) from a polymetallic concentrate originating from the Zimapán mining district in Hidalgo, Mexico. From an environmental perspective, the geoaccumulation index (Igeo) and enrichment factors (EF) classified As and Sb as extremely contaminating and highly enriched elements, underscoring the need for their removal in materials derived from mining activities. High extraction efficiencies were achieved for both metalloids while preserving valuable metal phases such as chalcopyrite, galena, and acanthite, as confirmed by XRD analysis. These results support the use of this leaching system as an effective treatment strategy to reduce and control the adverse effects associated with the presence of contaminant metalloids in mineral concentrates.
The kinetic analysis of the process revealed that the dissolution of As and Sb follows a chemically controlled mechanism, with notable sensitivity to temperature changes, suggesting the presence of significant energy barriers related to the cleavage of metal–sulfur bonds. This insight contributes valuable information for the potential industrial scalability of the system, as it relies on adjustable operational parameters such as temperature and reagent concentration.
Statistical modeling through quadratic regression enabled the identification of the relative influence of operational variables on extraction efficiency. For both As and Sb, the Na2S concentration and temperature were found to be the most impactful factors, followed by NaOH concentration. The generated models exhibited excellent predictive capability and statistical significance (p < 0.05), validating their application for optimizing the proposed leaching process.
Finally, the system’s high selectivity was confirmed through the characterization of the leaching residues, which showed the presence of secondary phases such as stibnite and realgar, while the main metal-bearing phases of the concentrate remained unaltered. These findings confirm the potential of the process as a technically and environmentally viable alternative for the treatment of polymetallic concentrates.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, J.C.J., G.C. and A.M.T.; methodology, G.C. and A.M.T.; software, M.R. and M.U.F.; validation, I.A.R. and G.U.; formal analysis, G.U.; investigation, J.I.M.; resources, G.C.; data curation, M.R.; writing—original draft preparation, G.C.; writing—review and editing, J.C.J. and I.A.R.; visualization, M.U.F.; supervision, J.C.J. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research received no external funding.
Data Availability Statement
The original contributions presented in this study are included in the article. Further inquiries can be directed to the corresponding authors.
Acknowledgments
The authors gratefully acknowledge support from the Secretariat of Science, Humanities, Technology and Innovation (SECIHTI) through a federal scholarship and from the Council for Science, Technology, and Innovation of the State of Hidalgo (CITNOVA). We also thank the Autonomous University of the State of Hidalgo (UAEH) for providing access to the equipment and infrastructure used during the experimental phase of this study.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
References
- Pérez, K.; Toro, N.; Gálvez, E.; Robles, P.; Wilson, R.; Navarra, A. Environmental, economic and technological factors affecting Chilean copper smelters—A critical review. J. Mater. Res. Technol. 2021, 15, 213–225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moats, M.; Alagha, L.; Awuah-Offei, K. Towards resilient and sustainable supply of critical elements from the copper supply chain: A review. J. Clean. Prod. 2021, 307, 127207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ruiz, A.T.; Juárez-Tapia, J.C.; Cisneros-Flores, G.; Martínez-Soto, J.I.; Reyes-Pérez, M.; Reyes-Domínguez, I.A.; Ortiz, H.G.; Flores Guerrero, U.M. Characterization of Solid Mining Waste in the Urbanized Area of Zimapan, Hidalgo, for the Identification of Economically Valuable Elements and Trace Elements. In Proceedings of the TMS 153rd Annual Meeting & Exhibition, Orlando, FL, USA, 3–7 May 2024; pp. 1876–1885. [Google Scholar]
- Prieto García, F.; Acevedo Sandoval, O.A.; Pérez Moreno, F.; Prieto Méndez, J.; Canales Flores, R.A. Arsenic contamination in groundwater in Zimapan, Hidalgo, Mexico. Desalination Water Treat. 2016, 57, 13038–13047. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Espinosa, E.; Armienta, M.A.; Cruz, O.; Aguayo, A.; Ceniceros, N. Geochemical distribution of arsenic, cadmium, lead and zinc in river sediments affected by tailings in Zimapán, a historical polymetalic mining zone of México. Environ. Geol. 2009, 58, 1467. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chango-Cañola, A.P.; González-Sandoval Mdel, R.; Alarcón-Herrera, M.T.; García-Villanueva, L.A.; Fernández-Villagómez, G. Health and environmental risk due to acid mine drainage generating tailings in Zimapán, Mexico. Environ. Res. Commun. 2025, 7, 25015. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Angeles, L.; Reyes, M.; Perez, M.; Palacios, E.; Patiño, F.; Reyes, I.; Flores, M. Chemical and Mineralogical Characterization of a Mixed Sulphide Ore at Zimapan, Hidalgo, Mexico. In Characterization of Minerals, Metals, and Materials; Springer: Cham, Switzerland, 2017; pp. 607–615. [Google Scholar]
- Teja Ruiz, A.M.; Juárez Tapia, J.C.; Reyes Domínguez, I.A.; Hernández Cruz, L.E.; Reyes Pérez, M.; Patiño Cardona, F.; Flores Guerrero, M.U. Kinetic Study of Ag Leaching from Arsenic Sulfosalts in the S2O32−-O2-NaOH System. Metals 2017, 7, 411. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grandell, L.; Lehtilä, A.; Kivinen, M.; Koljonen, T.; Kihlman, S.; Lauri, L.S. Role of critical metals in the future markets of clean energy technologies. Renew. Energy 2016, 95, 53–62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de Koning, A.; Kleijn, R.; Huppes, G.; Sprecher, B.; van Engelen, G.; Tukker, A. Metal supply constraints for a low-carbon economy? Resour. Conserv. Recycl. 2018, 129, 202–208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kinnunen, P.; Karhu, M.; Yli-Rantala, E.; Kivikytö-Reponen, P.; Mäkinen, J. A review of circular economy strategies for mine tailings. Clean. Eng. Technol. 2022, 8, 100499. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Faris, N.; Pownceby, M.I.; Bruckard, W.J.; Chen, M. The Direct Leaching of Nickel Sulfide Flotation Concentrates—A Historic and State-of-the-Art Review Part I: Piloted Processes and Commercial Operations. Miner. Process. Extr. Metall. Rev. 2023, 44, 407–435. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, Y.; Wang, H.; Wang, H.; Dong, K.; Zhu, R.; Jiang, Z.; Wei, G. Mechanism of arsenic distribution and migration during iron extraction by copper slag-steel slag combined reforming: A potential solution to refractory wastes. J. Clean. Prod. 2023, 420, 138399. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, H.; Wang, Y.; He, Y.; Xu, S.; Hu, B.; Cao, H.; Zhou, J.; Zheng, G. Efficient and safe disposition of arsenic by incorporation in smelting slag through copper flash smelting process. Min. Eng. 2021, 160, 106661. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, Z.; Wang, L.; Zheng, Q.; Che, X.; Cui, X.; Wei, S.; Li, H.; Shi, X. Present Situation and Research Progress of Comprehensive Utilization of Antimony Tailings and Smelting Slag. Sustainability 2023, 15, 13947. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, W.; Wang, Q.; Wang, Y.; Long, T.; Deng, S. Effects of pyrite, quartz and sodium sulfite on roasting of a refractory sulfide concentrate and gold, silver, copper leaching during cyanidation. Hydrometallurgy 2024, 226, 106306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Multani, R.S.; Feldmann, T.; Demopoulos, G.P. Antimony in the metallurgical industry: A review of its chemistry and environmental stabilization options. Hydrometallurgy 2016, 164, 141–153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dupont, D.; Arnout, S.; Jones, P.T.; Binnemans, K. Antimony Recovery from End-of-Life Products and Industrial Process Residues: A Critical Review. J. Sustain. Metall. 2016, 2, 79–103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Armienta, M.A.; Mugica, V.; Reséndiz, I.; Arzaluz, M.G. Arsenic and metals mobility in soils impacted by tailings at Zimapán, México. J. Soils Sediments 2016, 16, 1267–1278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Armienta, M.A.; Villaseñor, G.; Cruz, O.; Ceniceros, N.; Aguayo, A.; Morton, O. Geochemical processes and mobilization of toxic metals and metalloids in an As-rich base metal waste pile in Zimapán, Central Mexico. Appl. Geochem. 2012, 27, 2225–2237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zou, H.; Ren, B. Analyzing topsoil heavy metal pollution sources and ecological risks around antimony mine waste sites by a joint methodology. Ecol. Indic. 2023, 154, 110761. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Palma-Lara, I.; Martínez-Castillo, M.; Quintana-Pérez, J.; Arellano-Mendoza, M.; Tamay-Cach, F.; Valenzuela-Limón, O.; García-Montalvo, E.; Hernández-Zavala, A. Arsenic exposure: A public health problem leading to several cancers. Regul. Toxicol. Pharmacol. 2020, 110, 104539. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Corona Sánchez, J.E.; González Chávez Mdel, C.A.; Carrillo González, R.; Scheckel, K.; Tapia Maruri, D.; García Cue, J.L. Metal(loid) bioaccessibility of atmospheric particulate matter from mine tailings at Zimapan, Mexico. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2021, 28, 19458–19472. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhuang, F.; Huang, J.; Li, H.; Peng, X.; Xia, L.; Zhou, L.; Zhang, T.; Liu, Z.; He, Q.; Luo, F.; et al. Biogeochemical behavior and pollution control of arsenic in mining areas: A review. Front. Microbiol. 2023, 14, 1043024. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, C.; Liu, T.; Yang, Z.; Wu, P.; Zhang, K.; Chen, S. Study on antimony and arsenic cycling, transformation and contrasting mobility in river-type reservoir. Appl. Geochem. 2022, 136, 105132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raju, N.J. Arsenic in the geo-environment: A review of sources, geochemical processes, toxicity and removal technologies. Environ. Res. 2022, 203, 111782. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Radková, A.B.; Jamieson, H.E.; Campbell, K.M.; Hudson-Edwards, K.A. Antimony in Mine Wastes: Geochemistry, Mineralogy, and Microbiology. Econ. Geol. 2023, 118, 621–637. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Patel, K.S.; Pandey, P.K.; Martín-Ramos, P.; Corns, W.T.; Varol, S.; Bhattacharya, P.; Zhu, Y. A review on arsenic in the environment: Contamination, mobility, sources, and exposure. RSC Adv. 2023, 13, 8803–8821. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Monteiro De Oliveira, E.C.; Caixeta, E.S.; Santos, V.S.V.; Pereira, B.B. Arsenic exposure from groundwater: Environmental contamination, human health effects, and sustainable solutions. J. Toxicol. Environ. Health Part B 2021, 24, 119–135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Johnston, S.G.; Bennett, W.W.; Doriean, N.; Hockmann, K.; Karimian, N.; Burton, E.D. Antimony and arsenic speciation, redox-cycling and contrasting mobility in a mining-impacted river system. Sci. Total Environ. 2020, 710, 136354. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Escot-Espinoza, V.M.; Rodríguez-Márquez, S.; Briseño-Bugarín, J.; López-Luna, M.A.; Flores de la Torre, J.A. Presence of Potentially Toxic Elements in Historical Mining Areas in the North-Center of Mexico and Possible Bioremediation Strategies. Toxics 2024, 12, 813. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Drahota, P.; Venhauerova, P.; Strnad, L. Speciation and mobility of arsenic and antimony in soils and mining wastes from an abandoned Sb–Au mining area. Appl. Geochem. 2023, 152, 105665. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bundschuh, J.; Armienta, M.A.; Morales-Simfors, N.; Alam, M.A.; López, D.L.; Delgado Quezada, V.; Dietrich, S.; Schneider, J.; Tapia, J.; Sracek, O.; et al. Arsenic in Latin America: New findings on source, mobilization and mobility in human environments in 20 countries based on decadal research 2010–2020. Crit. Rev. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2021, 51, 1727–1865. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Briseño-Bugarín, J.; Araujo-Padilla, X.; Escot-Espinoza, V.M.; Cardoso-Ortiz, J.; Flores de la Torre, J.A.; López-Luna, A. Lead (Pb) Pollution in Soil: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis of Contamination Grade and Health Risk in Mexico. Environments 2024, 11, 43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, H.; He, M.; Wang, X. Concentration and speciation of antimony and arsenic in soil profiles around the world’s largest antimony metallurgical area in China. Environ. Geochem. Health 2015, 37, 21–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sundar, S.; Chakravarty, J. Antimony Toxicity. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2010, 7, 4267–4277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Long, J.; Tan, D.; Deng, S.; Lei, M. Pollution and ecological risk assessment of antimony and other heavy metals in soils from the world’s largest antimony mine area, China. Hum. Ecol. Risk Assess. Int. J. 2018, 24, 679–690. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lane, D.J.; Cook, N.J.; Grano, S.R.; Ehrig, K. Selective leaching of penalty elements from copper concentrates: A review. Min. Eng. 2016, 98, 110–121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ye, L.; Ouyang, Z.; Chen, Y.; Chen, Y. Ferric chloride leaching of antimony from stibnite. Hydrometallurgy 2019, 186, 210–217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ling, H.; Malfliet, A.; Blanpain, B.; Guo, M. Selective removal of arsenic from crude antimony trioxide by leaching with nitric acid. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2022, 281, 119976. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hernández, M.C.; Benavente, O.; Roca, A.; Melo, E.; Quezada, V. Selective Leaching of Arsenic from Copper Concentrates in Hypochlorite Medium. Minerals 2023, 13, 1372. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dembele, S.; Akcil, A.; Panda, S. Technological trends, emerging applications and metallurgical strategies in antimony recovery from stibnite. Min. Eng. 2022, 175, 107304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Awe, S.A.; Sundkvist, J.E.; Bolin, N.J.; Sandström, Å. Process flowsheet development for recovering antimony from Sb-bearing copper concentrates. Min. Eng. 2013, 49, 45–53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, K.; Ma, B.; An, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Chen, Y.; Wang, C. A Summary of Smelting and Secondary Recovery Process of Antimony. JOM 2025, 77, 2666–2683. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baláž, P.; Achimovičová, M. Selective leaching of antimony and arsenic from mechanically activated tetrahedrite, jamesonite and enargite. Int. J. Min. Process 2006, 81, 44–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Awe, S.A.; Sandström, Å. Selective leaching of arsenic and antimony from a tetrahedrite rich complex sulphide concentrate using alkaline sulphide solution. Min. Eng. 2010, 23, 1227–1236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aghazadeh, S.; Abdollahi, H.; Gharabaghi, M.; Mirmohammadi, M. The Novel Lixiviants for Maximizing Antimony Extraction from Tetrahedrite-Rich Concentrate: Mechanism and Kinetic Studies. Miner. Process. Extr. Metall. Rev. 2022, 43, 798–812. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ji, Y.; Feng, Y.; Wu, J.; Zhu, T.; Bai, Z.; Duan, C. Using geoaccumulation index to study source profiles of soil dust in China. J. Environ. Sci. 2008, 20, 571–578. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Q.; Liao, Y.; Zheng, Y.; Jin, H.; Huang, W.; Liu, Q.; Shou, L.; Zeng, J.; Chen, Q.; Chen, J. Elemental geochemical evidence for the river-derived sources of trace metals in surface sediments from Hangzhou Bay, East China Sea. Environ. Res. 2024, 250, 118588. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Q.; Cao, Y.; Meng, T.; He, L.; Zhang, S. Biogeochemical behavior, health risk assessment and source identification of antimony and arsenic in soil from a legacy antimony smelter in Gansu, Northwest China. Environ. Sci. Eur. 2023, 35, 114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, B.S.M.; Angeli, J.L.F.; Ferreira, P.A.L.; de Mahiques, M.M.; Figueira, R.C.L. Critical evaluation of different methods to calculate the Geoaccumulation Index for environmental studies: A new approach for Baixada Santista—Southeastern Brazil. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2018, 127, 548–552. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ballester, A.; Verdeja, L.F.; Sancho, J. Metalurgia Extractiva Fundamentos; Síntesis S.A.: Madrid, Spain, 2000; Volume 1. [Google Scholar]
- Levenspiel, O. Ingeniería de las Reacciones Químicas; Reverté: Barcelona, Spain, 2010. [Google Scholar]
- Ruiz, M.C.; Daroch, F.; Padilla, R. Digestion kinetics of arsenic removal from enargite–tennantite concentrates. Min. Eng. 2015, 79, 47–53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parada, F.; Jeffrey, M.I.; Asselin, E. Leaching kinetics of enargite in alkaline sodium sulphide solutions. Hydrometallurgy 2014, 146, 48–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blanco-Vino, W.; Zamora, G.; Ordóñez, J.I. Selective Removal of Arsenic and Antimony from Pb-Ag Sulfide Concentrates by Alkaline Leaching: Thermodynamic and Kinetic Studies. Mining 2024, 4, 284–301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Labastida, I.; Armienta, M.A.; Lara, R.H.; Briones, R.; González, I.; Romero, F. Kinetic approach for the appropriate selection of indigenous limestones for acid mine drainage treatment with passive systems. Sci. Total Environ. 2019, 677, 404–417. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duarte Zaragoza, V.M.; Gutiérrez Castorena, E.V.; del Carmen Gutiérrez Castorena, M.; Carrillo González, R.; Ortiz Solorio, C.A.; Trinidad Santos, A. Heavy metals contamination in soils around tailing heaps with various degrees of weathering in Zimapán, Mexico. Int. J. Environ. Stud. 2015, 72, 24–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Calla-Choque, D.; Nava-Alonso, F.; Fuentes-Aceituno, J.C. Acid decomposition and thiourea leaching of silver from hazardous jarosite residues: Effect of some cations on the stability of the thiourea system. J. Hazard. Mater. 2016, 317, 440–448. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Navarro Flores, A.; Martínez Sola, F. Evaluation of Metal Attenuation from Mine Tailings in SE Spain (Sierra Almagrera): A Soil-Leaching Column Study. Mine Water Environ. 2010, 29, 53–67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qiao, W.; Wang, Y.; He, P.; Yin, X.; Zhang, D.; Bai, G.; Sun, W.; Luo, Z.; Wei, X.; Lan, J.; et al. Groundwater arsenic and antimony mobility from an antimony mining area: Controls of sulfide oxidation, carbonate and silicate weathering, and secondary mineral precipitation. Water Res. 2025, 273, 123086. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barago, N.; Mastroianni, C.; Pavoni, E.; Floreani, F.; Parisi, F.; Lenaz, D.; Covelli, S. Environmental impact of potentially toxic elements on soils, sediments, waters, and air nearby an abandoned Hg-rich fahlore mine (Mt. Avanza, Carnic Alps, NE Italy). Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2023, 30, 63754–63775. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tongggiroh, A.; Imran, A.M.; Haerany, S. Environmental Geochemistry of Heavy Metals and Plagioclase Background Enrichment Factor in Coastal Sediments at Lumpue-Parepare, South Sulawesi, Indonesia. IOP Conf. Ser. Earth Environ. Sci. 2019, 370, 12002. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Looi, L.J.; Aris, A.Z.; Yusoff FMd Isa, N.M.; Haris, H. Application of enrichment factor, geoaccumulation index, and ecological risk index in assessing the elemental pollution status of surface sediments. Environ. Geochem. Health 2019, 41, 27–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Seifi, M.; Mahvi, A.H.; Hashemi, S.Y.; Arfaeinia, H.; Pasalari, H.; Zarei, A.; Changani, F. Spatial distribution, enrichment and geo-accumulation of heavy metals in surface sediments near urban and industrial areas in the Persian Gulf. Desalination Water Treat. 2019, 158, 130–139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barbieri, M. The Importance of Enrichment Factor (EF) and Geoaccumulation Index (Igeo) to Evaluate the Soil Contamination. J. Geol. Geophys. 2016, 5, 1–4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Castro, L.N.; Rendina, A.E.; Orgeira, M.J. Assessment of toxic metal contamination using a regional lithogenic geochemical background, Pampean area river basin, Argentina. Sci. Total Environ. 2018, 627, 125–133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Teja-Ruiz, A.M.; Juárez-Tapia, J.C.; Hernández-Cruz, L.E.; Reyes-Pérez, M.; Patiño-Cardona, F.; Reyes-Dominguez, I.A.; Flores-Guerrero, M.U.; Palacios-Beas, E.G. Influence of Temperature on the Formation of Ag Complexed in a S2O32−–O2 System. Minerals 2017, 7, 16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Teja-Ruiz, A.; Juárez-Tapia, J.; Hernández-Ortiz, O.; Reyes-Domínguez, I.; Cisneros-Flores, G.; Martínez-Soto, J.; Flores-Guerrero, U.; Beas, E.P. Alkaline-reductive pretreatment proposal for the removal of economically burdened semimetals from silver sulfosalts. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2025, 361, 131243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, L.; Guo, X.; Tian, Q.; Qin, H. Selective removal of arsenic from high arsenic dust in the NaOH-S system and leaching behavior of lead, antimony, zinc and tin. Hydrometallurgy 2021, 202, 105607. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cuevas, J.; Bruckard, W.J.; Pownceby, M.I.; Sparrow, G.J.; Torpy, A. Alkaline sulphide leaching of tennantite in copper flotation concentrates to selectively dissolve arsenic. Miner. Process. Extr. Metall. 2022, 131, 229–238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Delfini, M.; Ferrini, M.; Manni, A.; Massacci, P.; Piga, L. Arsenic leaching by Na2S to decontaminate tailings coming from colemanite processing. Min. Eng. 2003, 16, 45–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, H.; Wang, J.; Li, Y.; Song, Z.; Sivaprasada, M. Thermodynamic analysis of hot water leaching of sulphur from desulphurisation slag by Eh–pH diagrams of the Ca-S-H2O system. Miner. Process. Extr. Metall. 2019, 128, 161–167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sparrow, G.J.; Woodcock, J.T. Cyanide and Other Lixiviant Leaching Systems for Gold with Some Practical Applications. Miner. Process. Extr. Metall. Rev. 1995, 14, 193–247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, C.; Wang, W.; Xie, F.; Zhang, T. Mechanism and kinetics of mercuric sulfide leaching with cuprous-thiosulfate solutions. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2017, 177, 223–232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anderson, C.G.; Twidwell, L.G. The Alkaline Sulfide Hydrometallurgical Separation, Recovery and Fixation of Tin, Arsenic, Antimony, Mercury and Gold. In Proceedings of Lead & Zinc 2008; SAIMM: Johannesburg, South Africa, 2008; pp. 121–132. Available online: https://scholar.google.com/citations?user=zS4bYV8AAAAJ&hl=en&oi=ao (accessed on 10 October 2025).
- Suess, E.; Planer-Friedrich, B. Thioarsenate formation upon dissolution of orpiment and arsenopyrite. Chemosphere 2012, 89, 1390–1398. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Anderson, C.G. The Application and Economics of Industrial Alkaline Leaching of Copper Enargite Concentrates. In Proceedings of the Copper Cobalt Africa Conference, Livingstone, Zambia, 6–8 July 2015. [Google Scholar]
- Faraji, F.; Alizadeh, A.; Rashchi, F.; Mostoufi, N. Kinetics of leaching: A review. Rev. Chem. Eng. 2022, 38, 113–148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nolasco, M.C.; Rodríguez, I.; Vilasó, J.E.; Flores, M.U.; Pandiyan, T.; Gutiérrez, E.J.; Aguilar, J.; Reyes, M.; Reyes, I.A. Selective extraction of silver from jarosite residues produced in the zinc hydrometallurgical process using thiourea under acidic conditions: Kinetic analysis and leaching optimization. Hydrometallurgy 2025, 231, 106396. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ibrahim, A.S.; Baba, A.A. Dissolution kinetics studies of kaolin ore as raw material for mesoporous silica by acid leaching. Can. Metall. Q. 2024, 63, 203–212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tunç Parlak, T.; Yildiz, K. Investigation of the effect of mechanical activation on nickel and cobalt extraction from laterite at atmospheric pressure by kinetics and leach residue analysis. Can. Metall. Q. 2025, 64, 680–697. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, Y.; Liu, Y.; Niu, L.; Jing, T.; Zhang, T. Effect of mechanical activation on leaching of zinc and indium from indium-bearing zinc ferrite with sulphur dioxide as leachant and reductant. Can. Metall. Q. 2021, 60, 150–159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Đorđević, T.; Kolitsch, U.; Serafimovski, T.; Tasev, G.; Tepe, N.; Stöger-Pollach, M.; Hofmann, T.; Boev, B. Mineralogy and Weathering of Realgar-Rich Tailings At a Former As-Sb-Cr Mine At Lojane, North Macedonia. Can. Mineral. 2019, 57, 403–423. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Intratec. Sodium Sulfides Price; Intratec Chemical Data: Houston, TX, USA; Available online: https://www.intratec.us/ (accessed on 14 October 2025).
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).