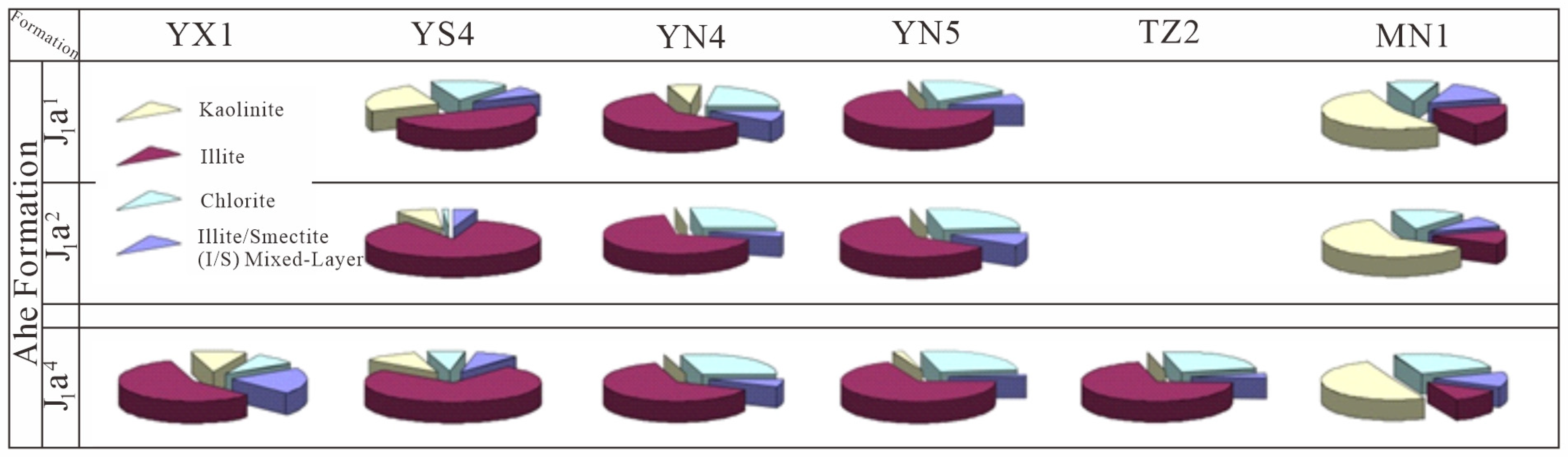
Figure 1.
Pie Chart of clay mineral distribution in the ZLX Ahe Formation reservoir, Eastern Kuqa Depression.
Figure 1.
Pie Chart of clay mineral distribution in the ZLX Ahe Formation reservoir, Eastern Kuqa Depression.
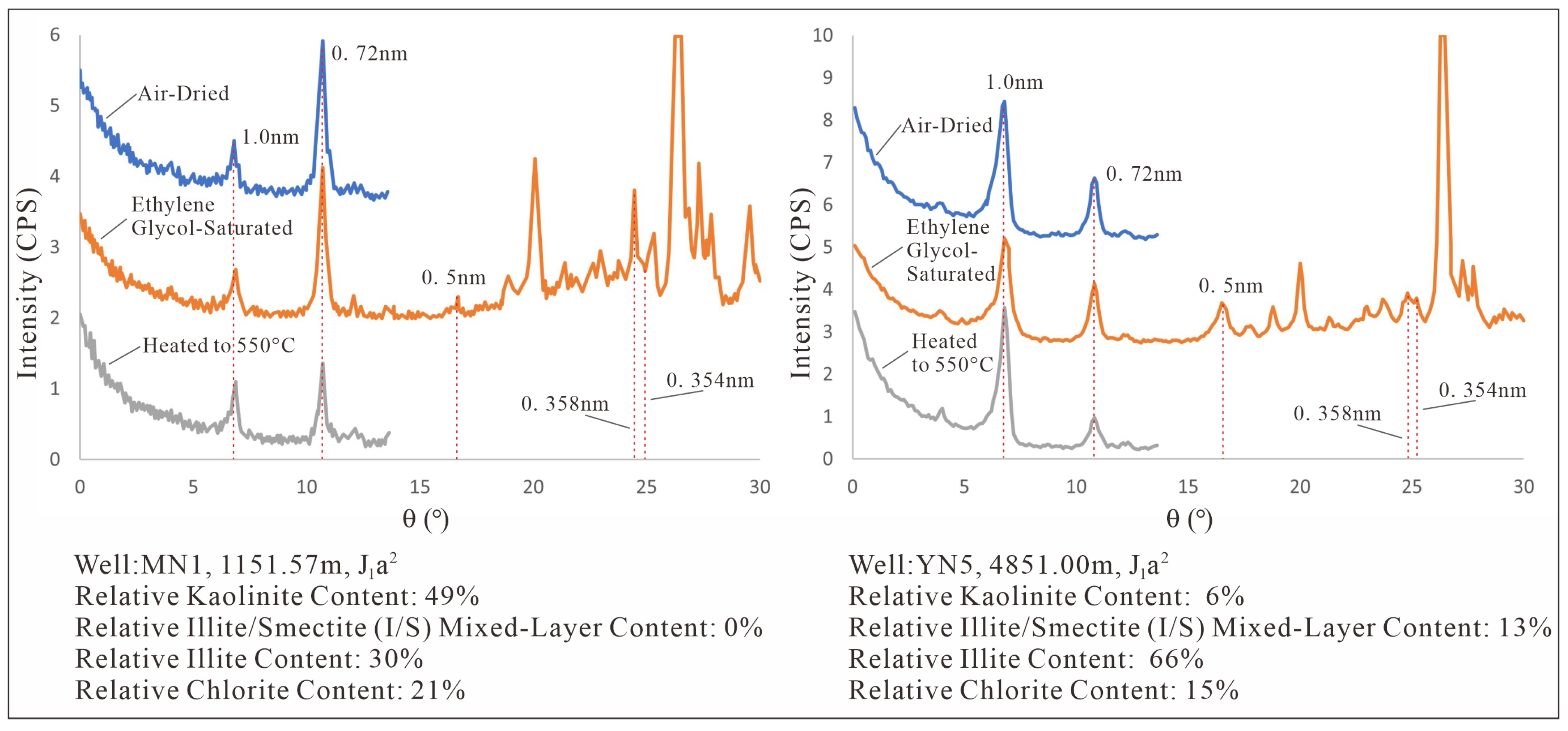
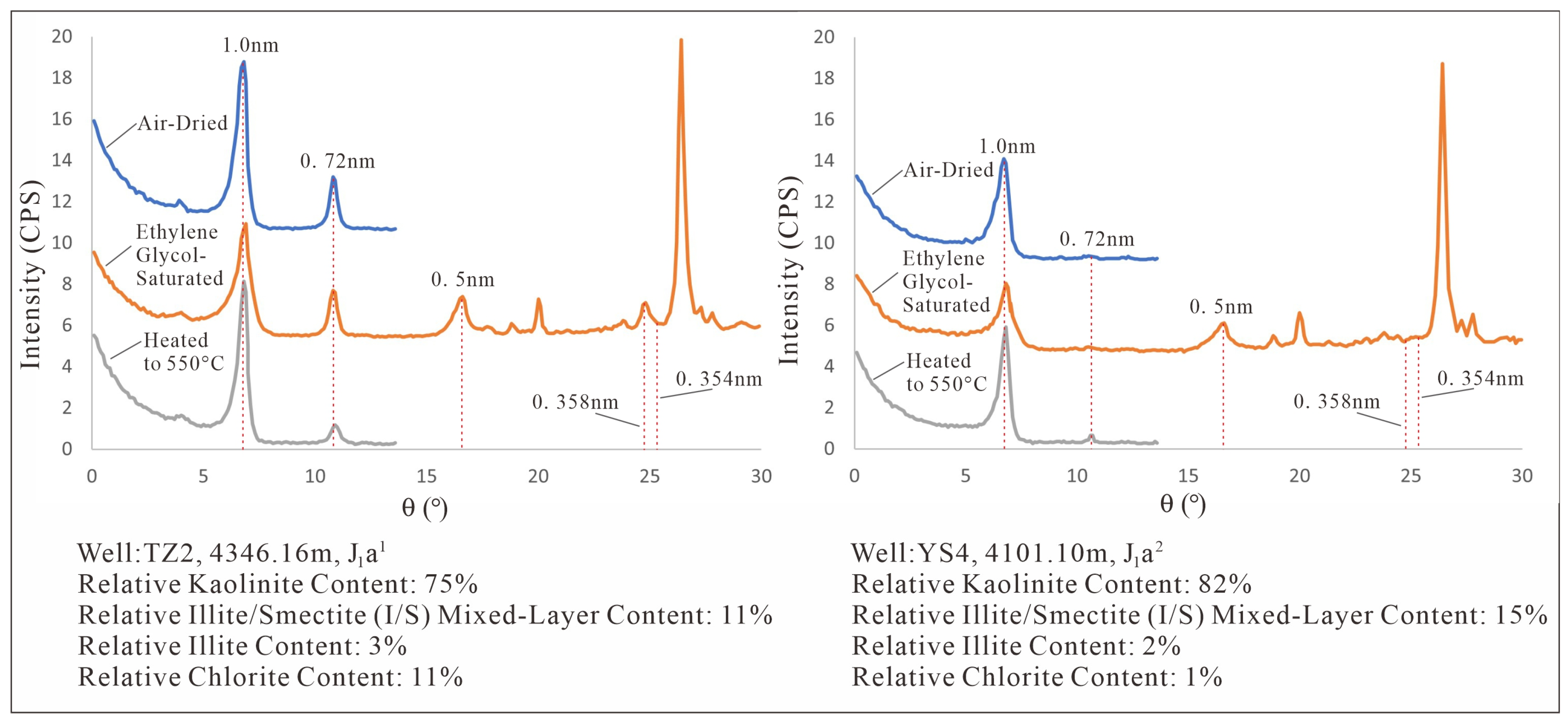
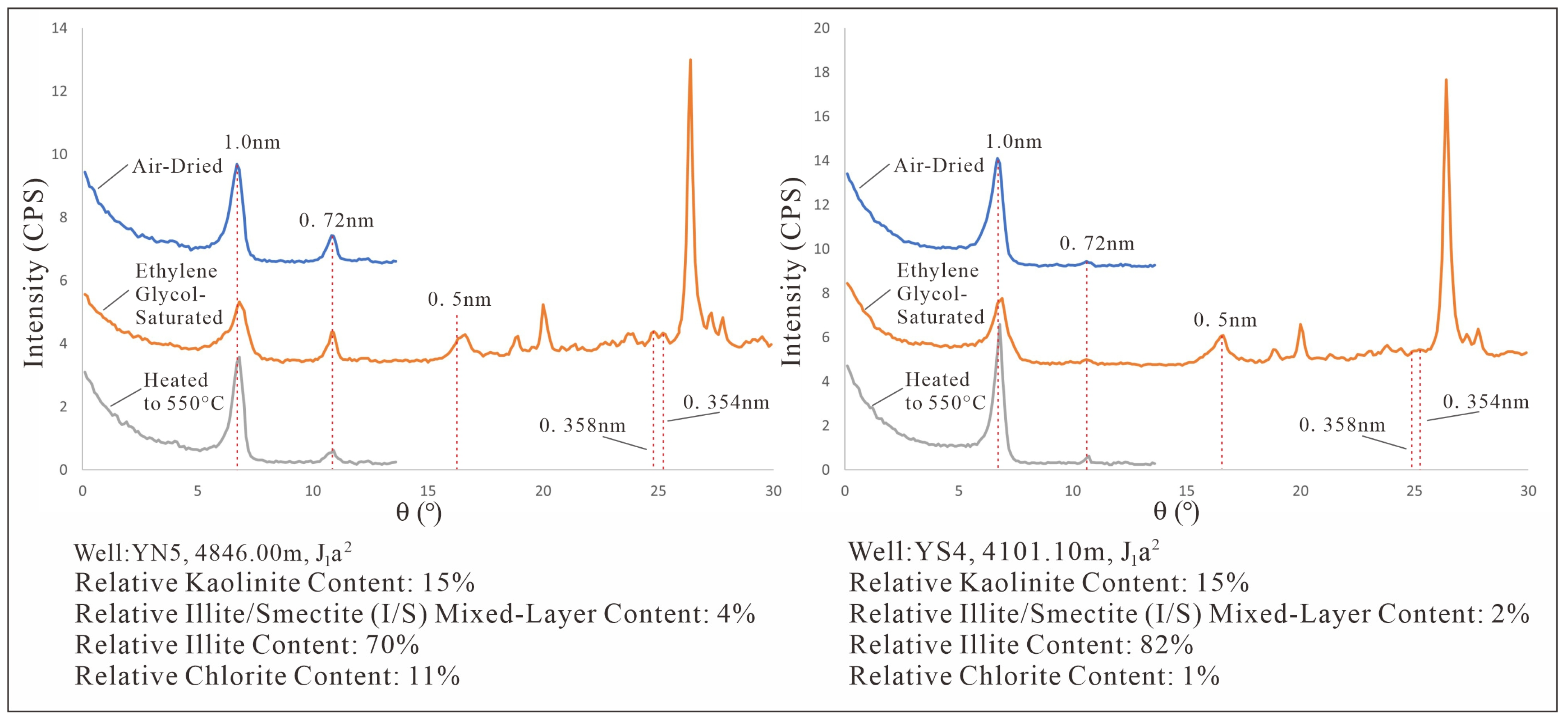
Figure 2.
XRD pattern of Kaolinite in the ZLX Ahe Formation reservoir, Eastern Kuqa Depression.
Figure 2.
XRD pattern of Kaolinite in the ZLX Ahe Formation reservoir, Eastern Kuqa Depression.
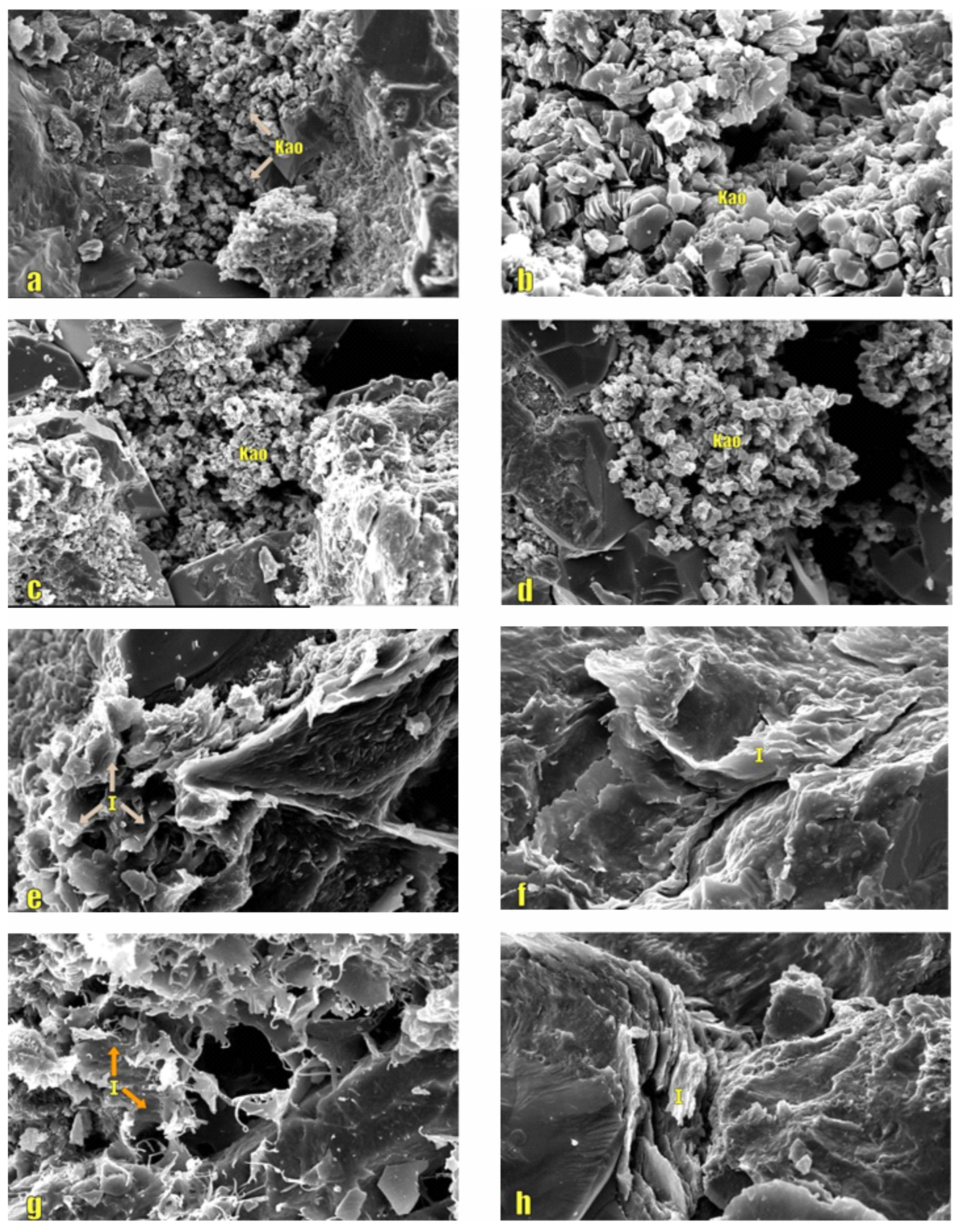
Figure 3.
Photomicrographs of Kaolinite and Illite in the ZLX Ahe Formation reservoir, Eastern Kuqa Depression. (a–d) SEM image of kaolinite; (e–h) SEM image of illite. Kao: Kaolinite; I: Illite.
Figure 3.
Photomicrographs of Kaolinite and Illite in the ZLX Ahe Formation reservoir, Eastern Kuqa Depression. (a–d) SEM image of kaolinite; (e–h) SEM image of illite. Kao: Kaolinite; I: Illite.
Figure 4.
XRD pattern of Illite in the ZLX Ahe Formation reservoir, Eastern Kuqa Depression.
Figure 4.
XRD pattern of Illite in the ZLX Ahe Formation reservoir, Eastern Kuqa Depression.
Figure 5.
XRD pattern of Chlorite in the ZLX Ahe Formation reservoir, Eastern Kuqa Depression.
Figure 5.
XRD pattern of Chlorite in the ZLX Ahe Formation reservoir, Eastern Kuqa Depression.
Figure 6.
Photomicrograph of Chlorite in the ZLX Ahe Formation reservoir, Eastern Kuqa Depression. (a) SEM image of chlorite; (b) SEM image of chlorite. c: Chlorite.
Figure 6.
Photomicrograph of Chlorite in the ZLX Ahe Formation reservoir, Eastern Kuqa Depression. (a) SEM image of chlorite; (b) SEM image of chlorite. c: Chlorite.
Figure 7.
XRD pattern of Illite/Smectite mixed layer in the ZLX Ahe Formation reservoir, Eastern Kuqa Depression.
Figure 7.
XRD pattern of Illite/Smectite mixed layer in the ZLX Ahe Formation reservoir, Eastern Kuqa Depression.
Figure 8.
Photomicrograph of Illite/Smectite mixed layer in the ZLX Ahe Formation reservoir, Eastern Kuqa Depression. (a–d) SEM image of illite/smectite mixed layer. I/S: Illite/Smectite mixed layer.
Figure 8.
Photomicrograph of Illite/Smectite mixed layer in the ZLX Ahe Formation reservoir, Eastern Kuqa Depression. (a–d) SEM image of illite/smectite mixed layer. I/S: Illite/Smectite mixed layer.
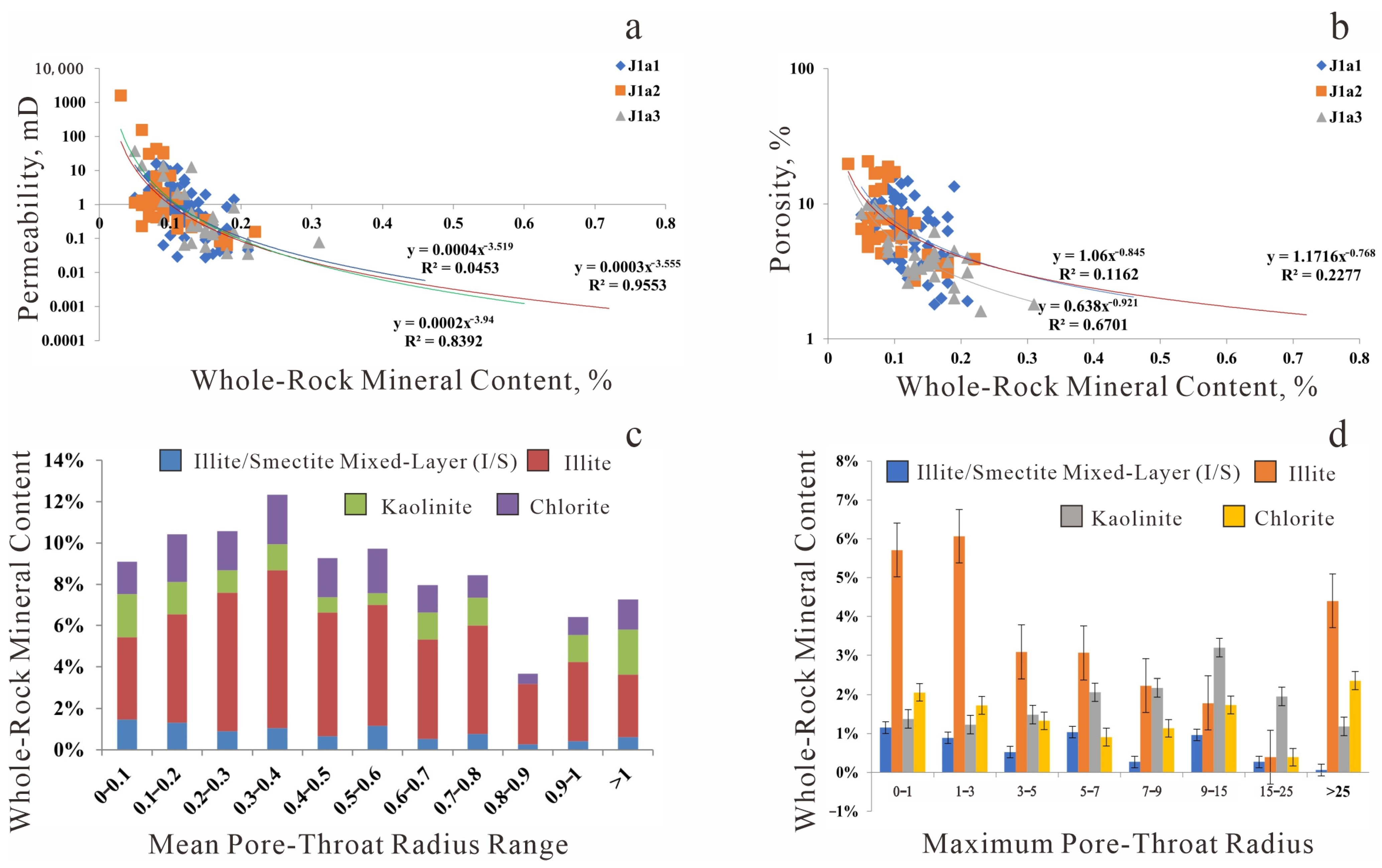
Figure 9.
Relationship between clay minerals and reservoir properties. (a) Total clay content vs. Permeability; (b) Total clay content vs. Porosity; (c) Average pore-throat radius range vs. Total clay content; (d) Maximum pore-throat radius range vs. total clay content.
Figure 9.
Relationship between clay minerals and reservoir properties. (a) Total clay content vs. Permeability; (b) Total clay content vs. Porosity; (c) Average pore-throat radius range vs. Total clay content; (d) Maximum pore-throat radius range vs. total clay content.
Figure 10.
Relationship between mineral content and Permeability (the blue square in the graph represent permeability values at different contents, while the orange area indicates the trend of the data). (a) Illite vs. Permeability; (b) Illite/Smectite mixed layer vs. Permeability; (c) Kaolinite vs. Permeability; (d) Chlorite vs. Permeability.
Figure 10.
Relationship between mineral content and Permeability (the blue square in the graph represent permeability values at different contents, while the orange area indicates the trend of the data). (a) Illite vs. Permeability; (b) Illite/Smectite mixed layer vs. Permeability; (c) Kaolinite vs. Permeability; (d) Chlorite vs. Permeability.
Figure 11.
Relationship between mineral content and Porosity (the blue square in the graph represent porosity values at different contents, while the orange area indicates the trend of the data). (a) Illite vs. Porosity; (b) Illite/Smectite mixed layer vs. Porosity; (c) Kaolinite vs. Porosity; (d) Chlorite vs. Porosity.
Figure 11.
Relationship between mineral content and Porosity (the blue square in the graph represent porosity values at different contents, while the orange area indicates the trend of the data). (a) Illite vs. Porosity; (b) Illite/Smectite mixed layer vs. Porosity; (c) Kaolinite vs. Porosity; (d) Chlorite vs. Porosity.
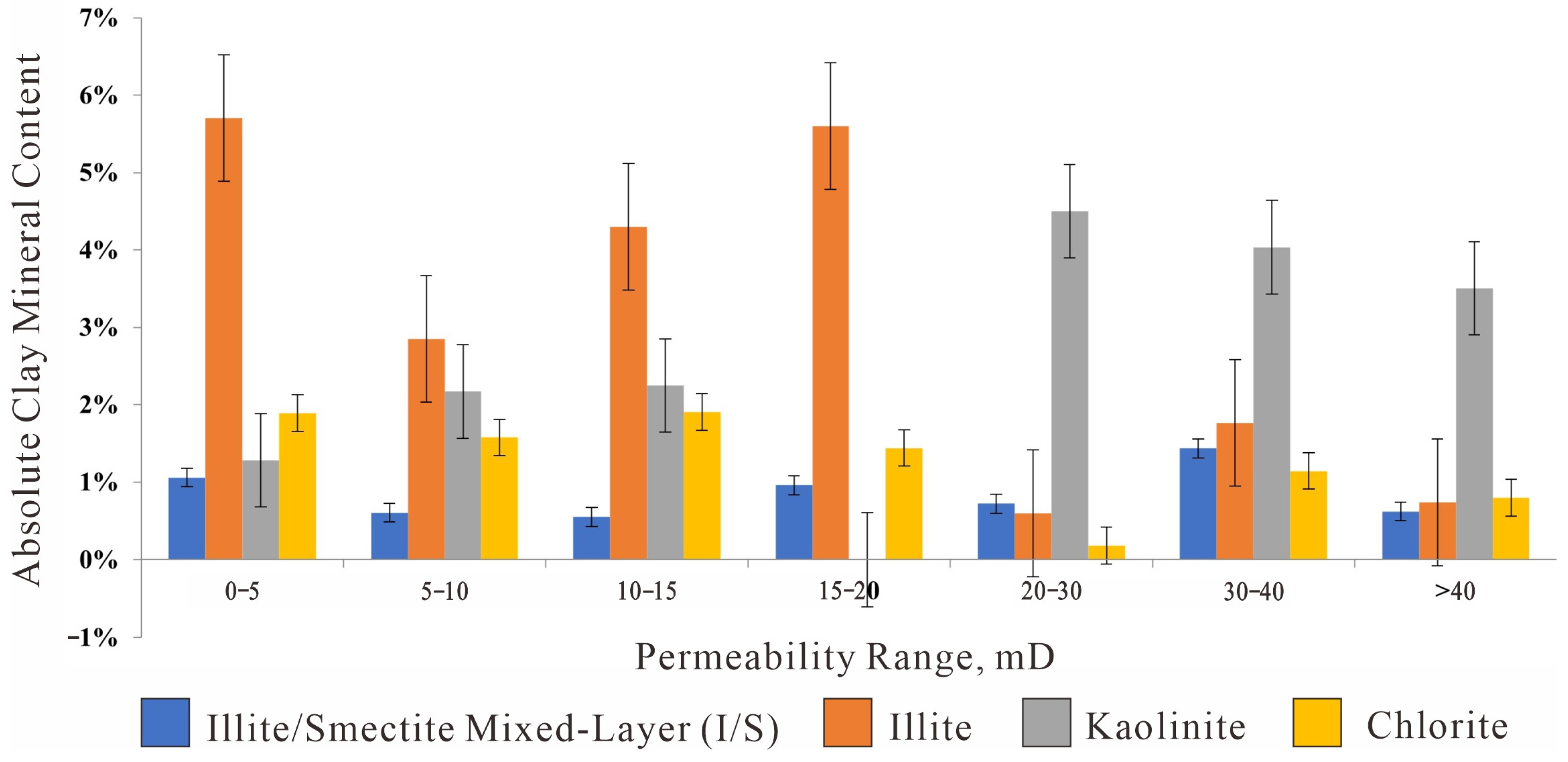
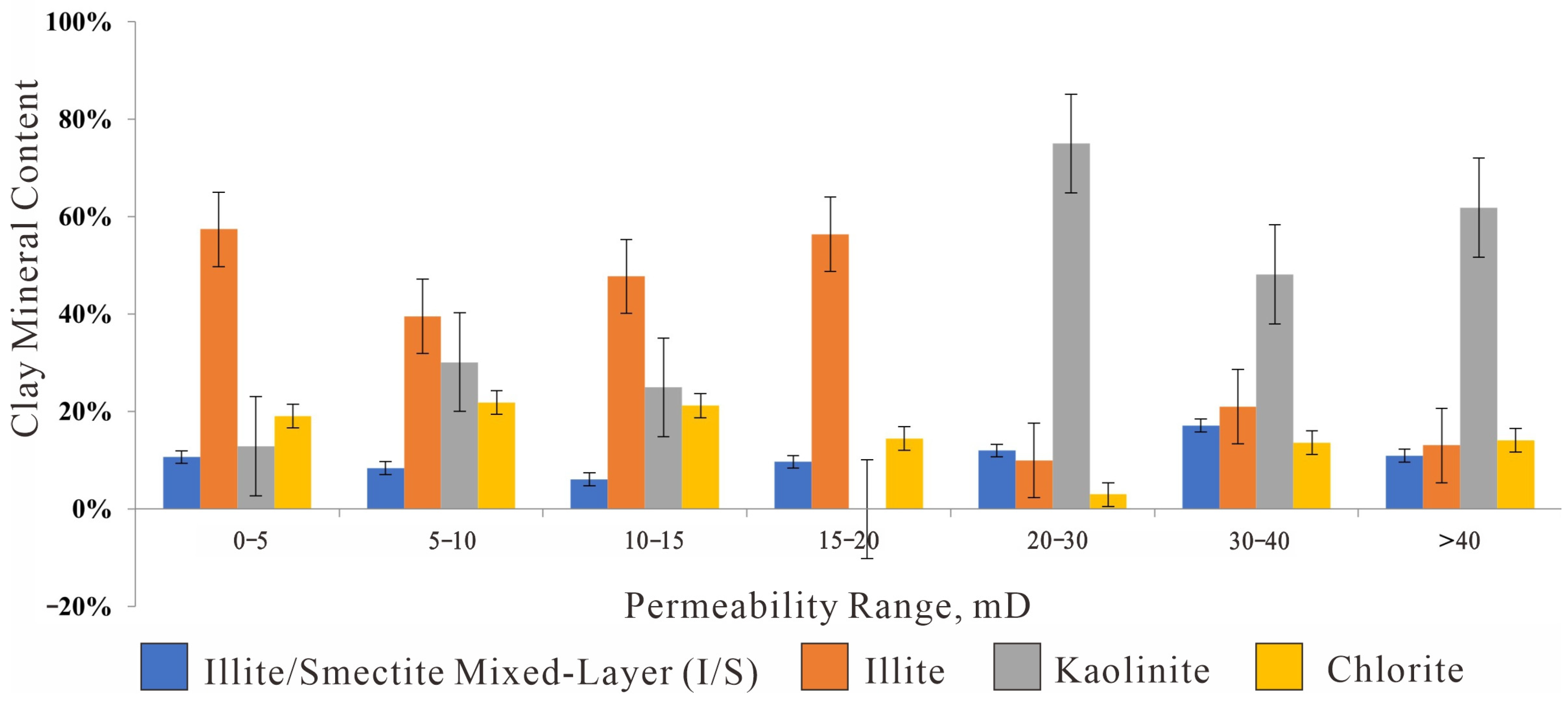
Figure 12.
Absolute content of clay minerals in different Permeability ranges (Bar Chart).
Figure 12.
Absolute content of clay minerals in different Permeability ranges (Bar Chart).
Figure 13.
Relative proportion of clay Minerals in different Permeability ranges (Bar Chart).
Figure 13.
Relative proportion of clay Minerals in different Permeability ranges (Bar Chart).
Figure 14.
Absolute content of clay minerals in different Porosity ranges (Bar Chart).
Figure 14.
Absolute content of clay minerals in different Porosity ranges (Bar Chart).
Figure 15.
Relative proportion of clay minerals in different Porosity ranges (Bar Chart).
Figure 15.
Relative proportion of clay minerals in different Porosity ranges (Bar Chart).
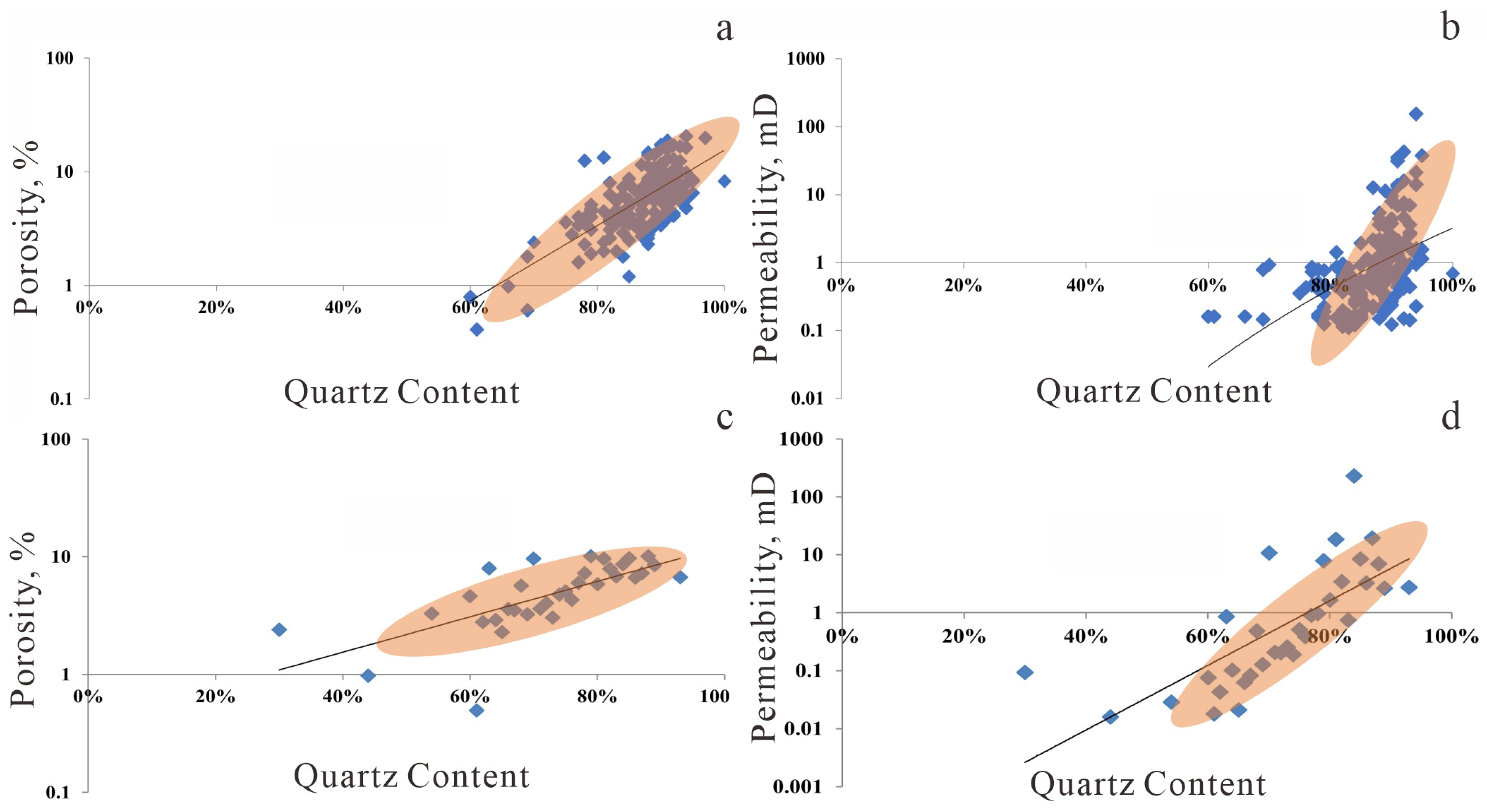
Figure 16.
Relationship between rock grain content and reservoir properties (the blue square in the graph represent porosity values at different Quartz contents, while the orange area indicates the trend of the data). (a) Effect of Quartz and feldspar content on Porosity; (b) Effect of Quartz and feldspar content on Permeability; (c) Effect of Quartz content on Porosity; (d) Effect of Quartz content on Permeability.
Figure 16.
Relationship between rock grain content and reservoir properties (the blue square in the graph represent porosity values at different Quartz contents, while the orange area indicates the trend of the data). (a) Effect of Quartz and feldspar content on Porosity; (b) Effect of Quartz and feldspar content on Permeability; (c) Effect of Quartz content on Porosity; (d) Effect of Quartz content on Permeability.
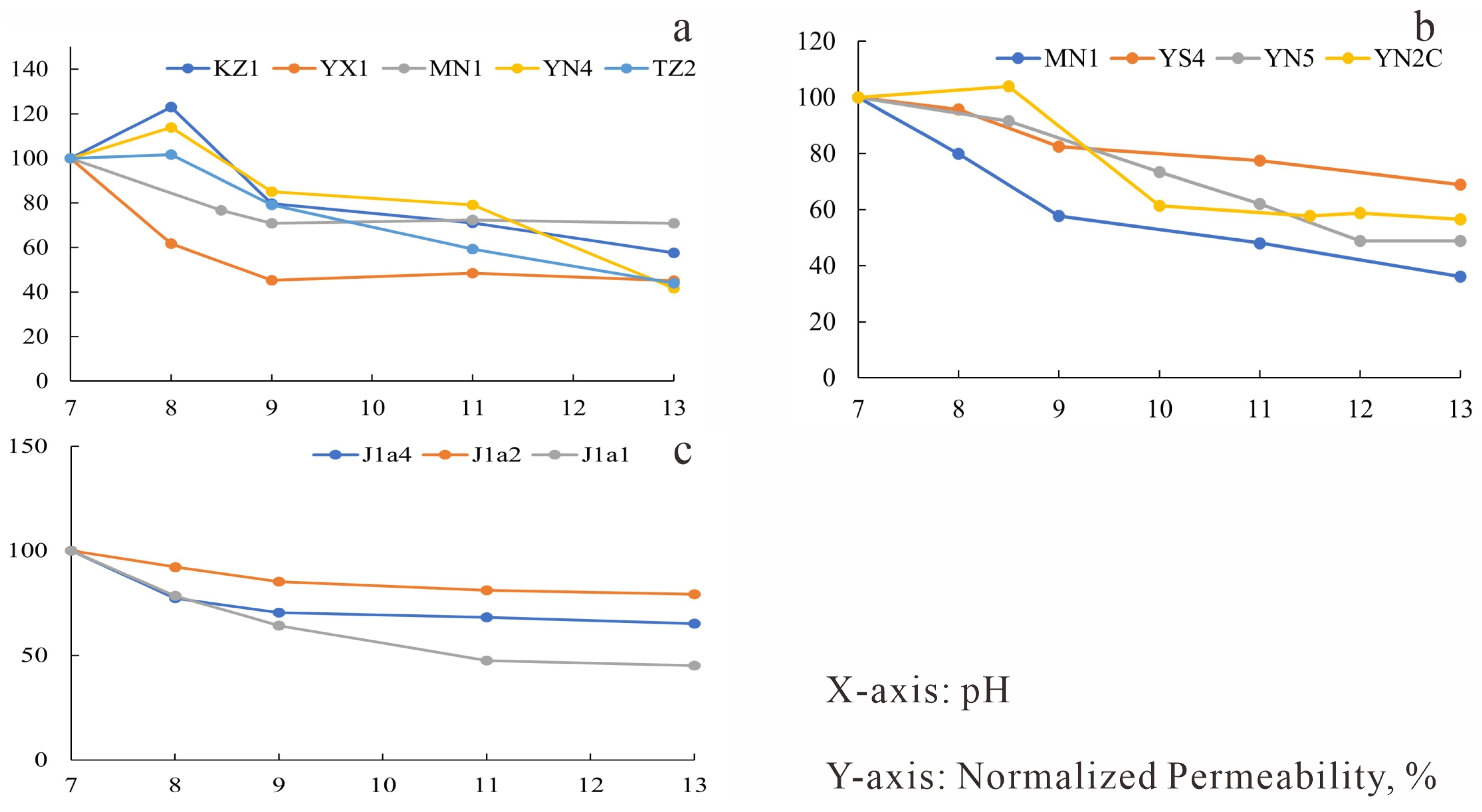
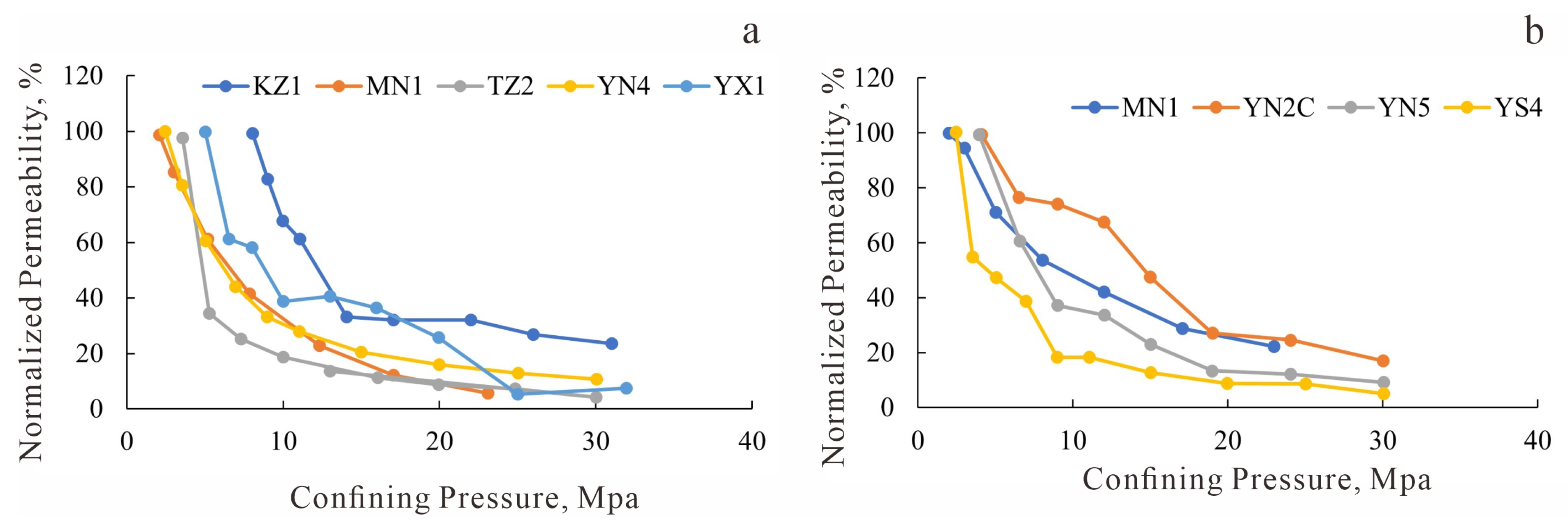
Figure 17.
Water sensitivity experimental curves. (a) J1a4 layer, Eastern Kuqa Depression; (b) J1a4 layer, Eastern Kuqa Depression; (c) J1a2 layer, Eastern Kuqa Depression; (d) J1a1 layer, Eastern Kuqa Depression; (e) Well Yishen-4, Northeastern Kuqa Depression; (f) Well Yinan-5, Eastern Kuqa Depression; (g) Well Mingnan-1, Eastern Kuqa Depression.
Figure 17.
Water sensitivity experimental curves. (a) J1a4 layer, Eastern Kuqa Depression; (b) J1a4 layer, Eastern Kuqa Depression; (c) J1a2 layer, Eastern Kuqa Depression; (d) J1a1 layer, Eastern Kuqa Depression; (e) Well Yishen-4, Northeastern Kuqa Depression; (f) Well Yinan-5, Eastern Kuqa Depression; (g) Well Mingnan-1, Eastern Kuqa Depression.
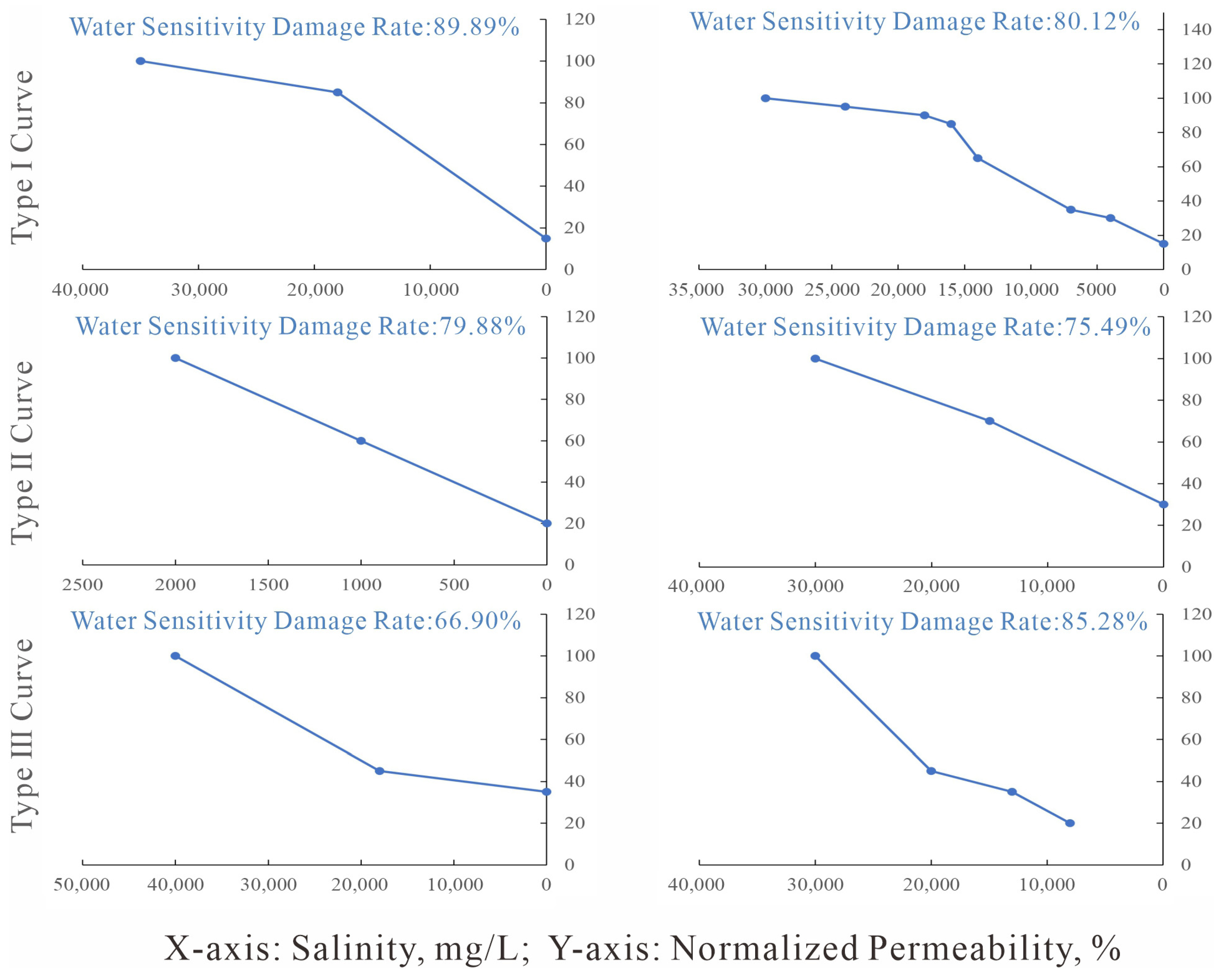
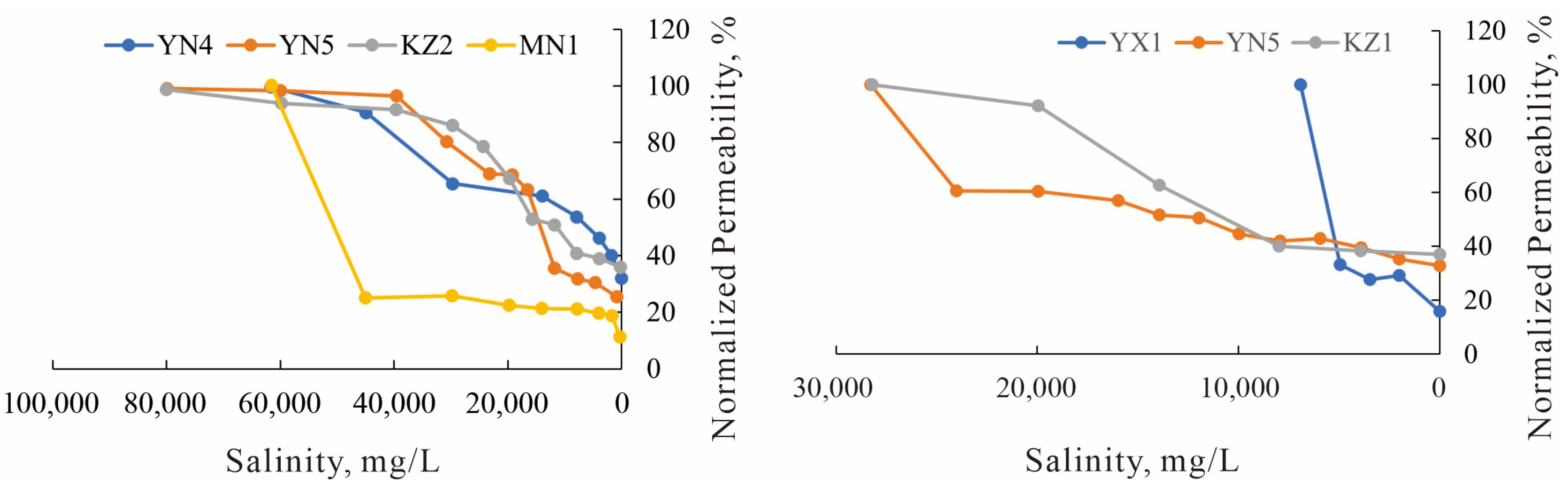
Figure 18.
Salinity sensitivity experimental curves for the J1a4 layer in the study area.
Figure 18.
Salinity sensitivity experimental curves for the J1a4 layer in the study area.
Figure 20.
Microstructural comparison of Illite/Smectite mixed-llayer before and after swelling.
Figure 20.
Microstructural comparison of Illite/Smectite mixed-llayer before and after swelling.
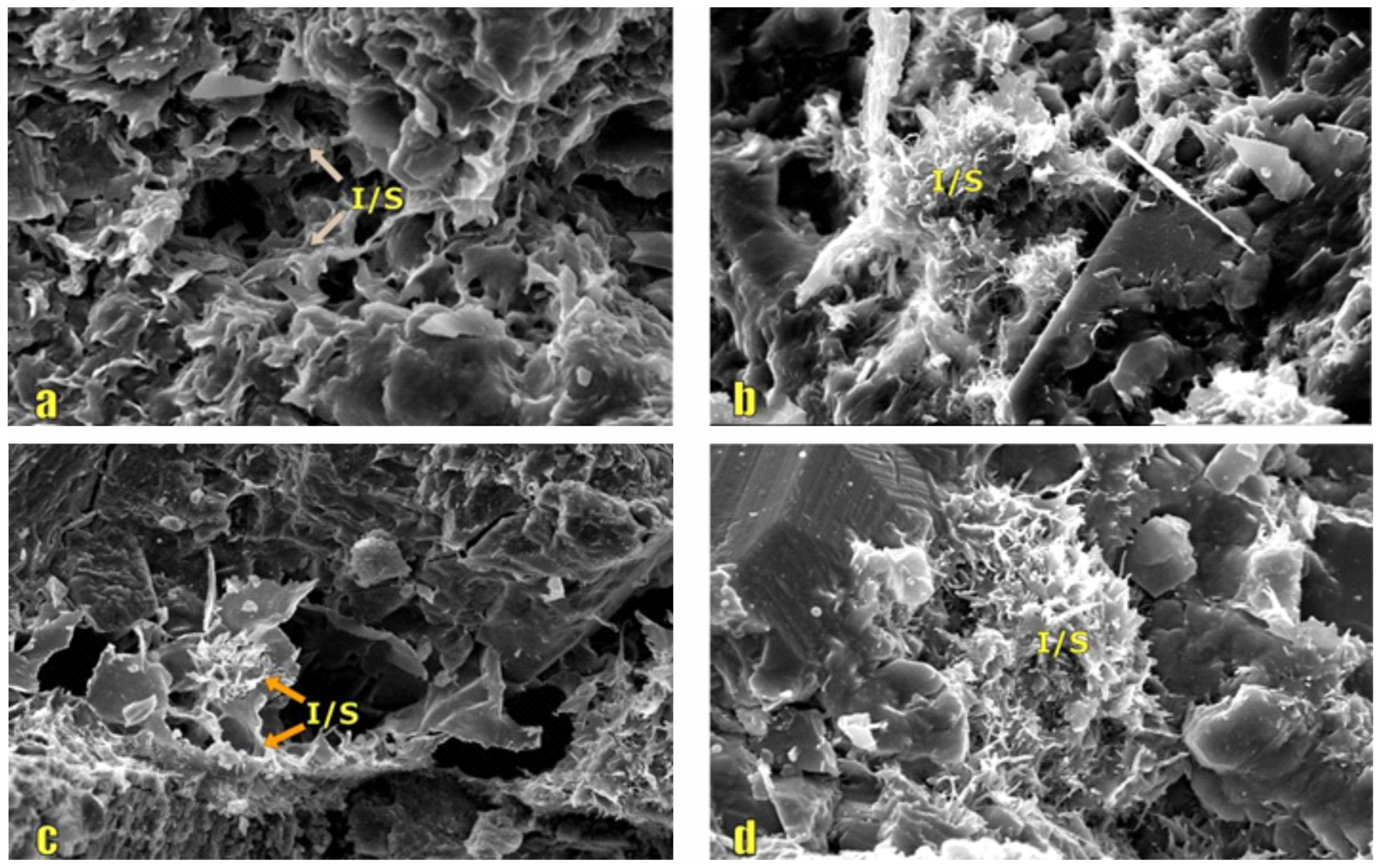
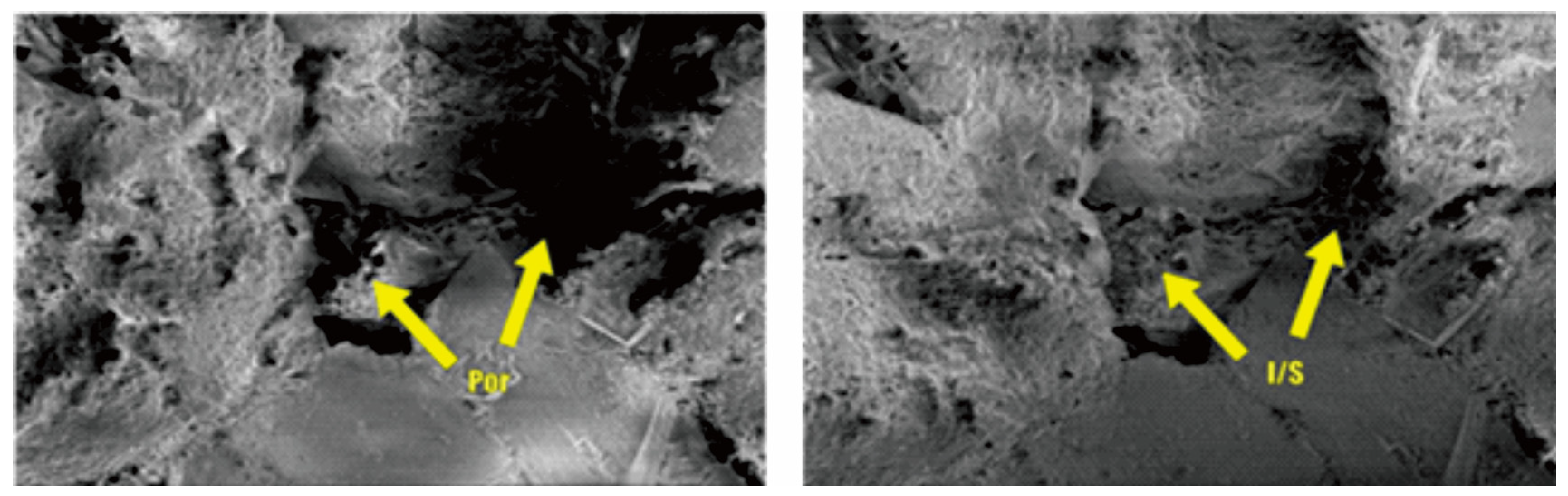
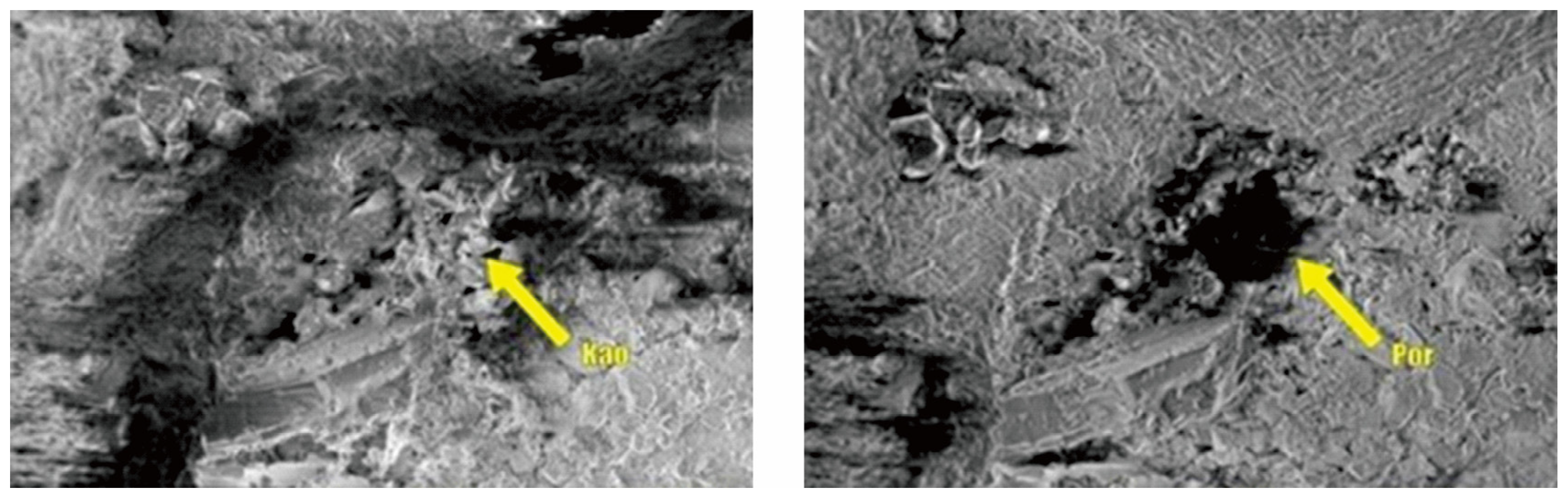
Figure 21.
Microstructural comparison before and after migration of Kaolinite and other particles.
Figure 21.
Microstructural comparison before and after migration of Kaolinite and other particles.
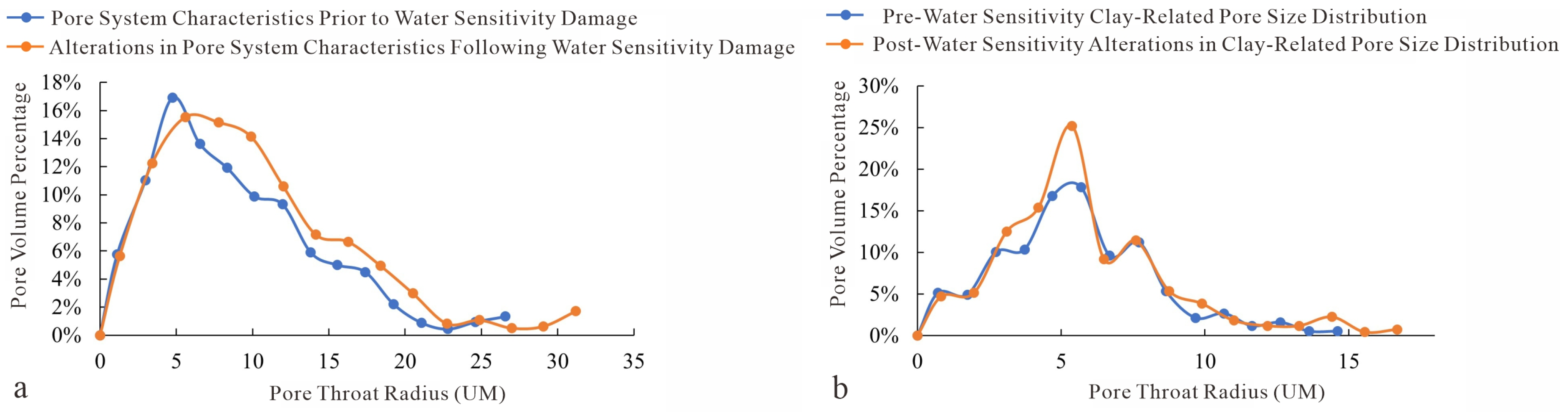
Figure 22.
Relationship between pore radius and pore volume before and after water sensitivity damage. (a) Dissolution intergranular pores; (b) Micropores.
Figure 22.
Relationship between pore radius and pore volume before and after water sensitivity damage. (a) Dissolution intergranular pores; (b) Micropores.
Figure 23.
Velocity sensitivity experimental curves (Partial core samples exhibited increased flow velocity due to fluid-induced damage to sandstone grains). (a) J1a4 layer, Eastern Kuqa Depression; (b) J1a4 layer, Eastern Kuqa Depression; (c) Well YS4, Eastern Kuqa Depression; (d) Well YN5, Eastern Kuqa Depression; (e) Well MN1, Eastern Kuqa Depression.
Figure 23.
Velocity sensitivity experimental curves (Partial core samples exhibited increased flow velocity due to fluid-induced damage to sandstone grains). (a) J1a4 layer, Eastern Kuqa Depression; (b) J1a4 layer, Eastern Kuqa Depression; (c) Well YS4, Eastern Kuqa Depression; (d) Well YN5, Eastern Kuqa Depression; (e) Well MN1, Eastern Kuqa Depression.
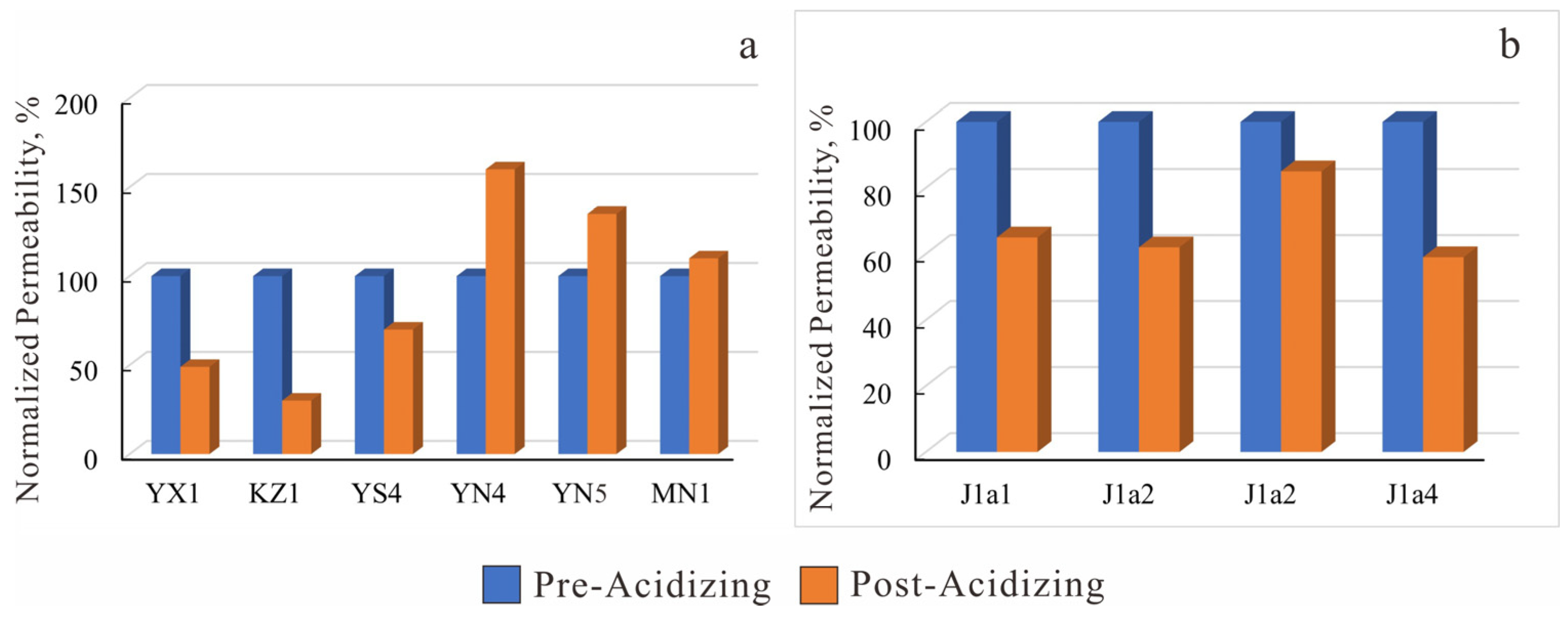
Figure 24.
Acid sensitivity experimental histogram. (a) J1a4 layer in the study area; (b) Well YN5 in the study area.
Figure 24.
Acid sensitivity experimental histogram. (a) J1a4 layer in the study area; (b) Well YN5 in the study area.
Figure 25.
Alkali sensitivity experimental curves. (a) J1a4 layer in the study area; (b) J1a1 layer in the study area; (c) Well MN1 in the study area.
Figure 25.
Alkali sensitivity experimental curves. (a) J1a4 layer in the study area; (b) J1a1 layer in the study area; (c) Well MN1 in the study area.
Figure 26.
Experimental curves of maximum damage rate for stress sensitivity. (a) J1a4 layer in the study area; (b) J1a1 layer in the study area.
Figure 26.
Experimental curves of maximum damage rate for stress sensitivity. (a) J1a4 layer in the study area; (b) J1a1 layer in the study area.
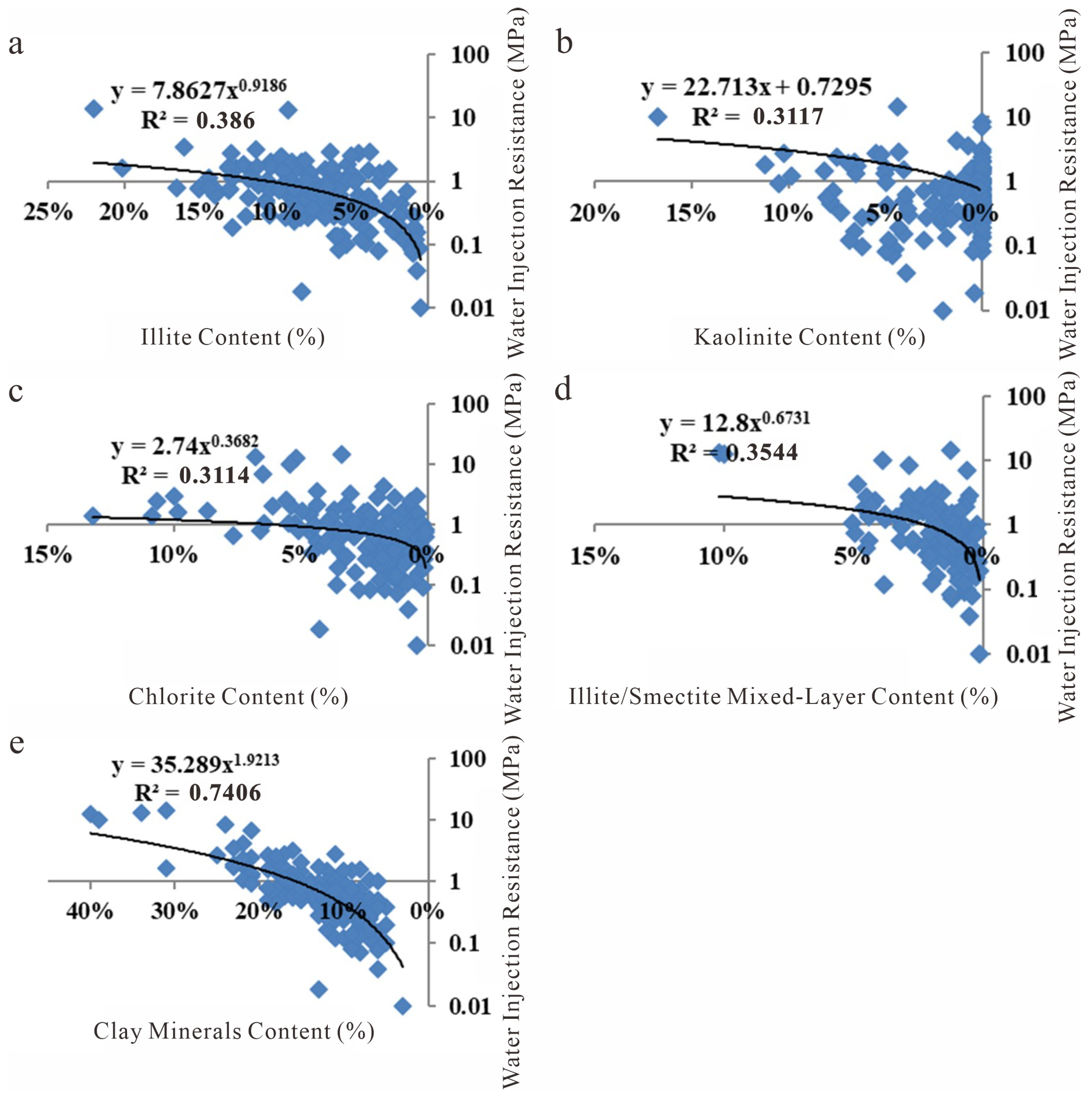
Figure 27.
Relationship between total clay content and water injection resistance (the blue square represent water injection resistance values at different mineral contents, and the black line indicates the trend line.). (a) Relationship between Illite content and water injection resistance; (b) Relationship between Kaolinite content and water injection resistance; (c) Relationship between Chlorite content and water injection resistance; (d) Relationship between Illite/Smectite mixed-layer content and water injection resistance; (e) Relationship between Clay Mineral content and water injection resistance.
Figure 27.
Relationship between total clay content and water injection resistance (the blue square represent water injection resistance values at different mineral contents, and the black line indicates the trend line.). (a) Relationship between Illite content and water injection resistance; (b) Relationship between Kaolinite content and water injection resistance; (c) Relationship between Chlorite content and water injection resistance; (d) Relationship between Illite/Smectite mixed-layer content and water injection resistance; (e) Relationship between Clay Mineral content and water injection resistance.
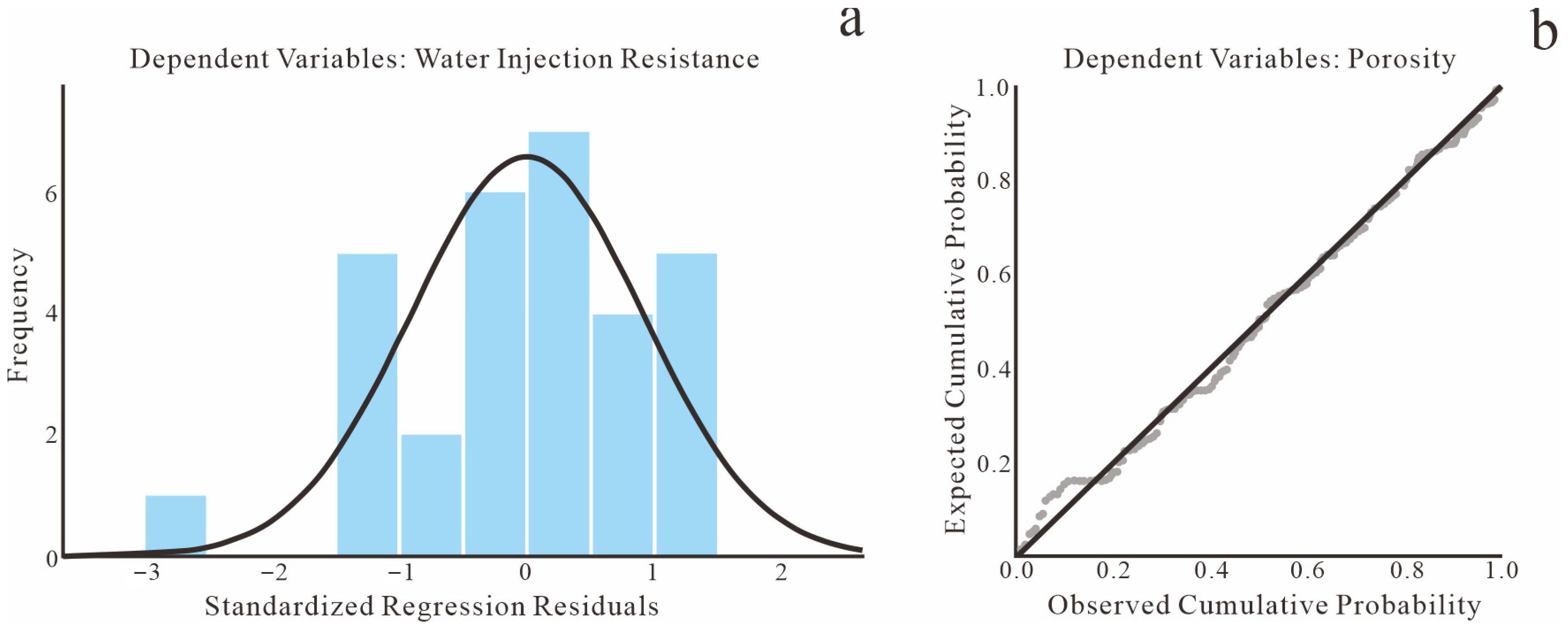
Figure 28.
Distribution characteristics of standardized regression residuals. (a) Histogram; (b) Normal P-P plot.
Figure 28.
Distribution characteristics of standardized regression residuals. (a) Histogram; (b) Normal P-P plot.
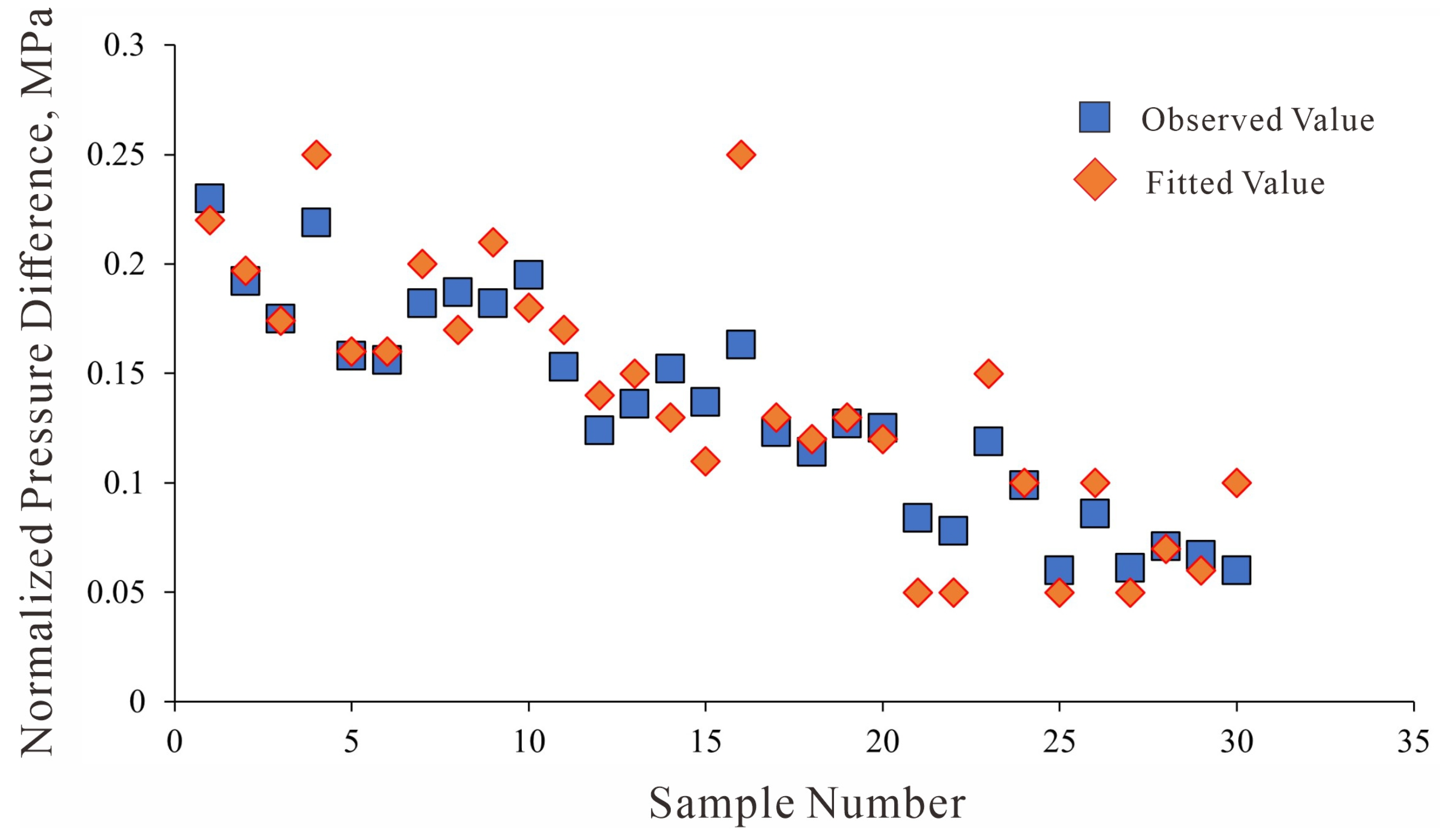
Figure 29.
Comparison between normalized observed data and model predictions.
Figure 29.
Comparison between normalized observed data and model predictions.
Table 1.
Experimental results of water sensitivity damage for reservoirs in the Eastern Kuqa Depression.
Table 1.
Experimental results of water sensitivity damage for reservoirs in the Eastern Kuqa Depression.
| No. | Well | Depth (m) | Formation | Permeability (mD) | Porosity (%) | Damage Rate (%) | Damage Degree |
|---|
| 1 | YX1 | 412.10 | J1a4 | 0.020 | 3.333 | 63.4 | Moderate to Strong |
| 3683.00 | J1a4 | 0.015 | 0.912 | 65.6 | Moderate to Strong |
| 2 | KZ1 | 4359.00 | J1a4 | 0.038 | 1.876 | 42.6 | Moderate to Strong |
| 3 | YS4 | 4007.80 | J1a1 | 0.606 | 7.611 | 68.4 | Moderate to Strong |
| 4068.50 | J1a2 | 0.704 | 9.320 | 83.7 | Strong |
| 4101.70 | J1a4 | 0.027 | 4.491 | 46.6 | Moderate to Weak |
| 4 | YN4 | 4376.34 | J1a1 | 0.495 | 9.391 | 68.2 | Moderate to Strong |
| 4478.30 | J1a2 | 0.191 | 7.648 | 67.7 | Moderate to Strong |
| 4537.00 | J1a3 | 0.119 | 6.718 | 37.0 | Moderate to Weak |
| 4594.80 | J1a4 | 0.066 | 5.626 | 78.1 | Strong |
| 4649.00 | J1a4 | 0.042 | 6.407 | 52.1 | Moderate to Strong |
| 5 | YN5 | 4896.00 | J1a2 | 0.580 | 6.650 | 35.7 | Moderate to Weak |
| 4896.80 | J1a2 | 3.950 | 8.930 | 66.4 | Moderate to Strong |
| 4936.60 | J1a4 | 0.427 | 4.990 | 51.0 | Moderate to Strong |
| 5012.60 | J1a1 | 0.897 | 7.862 | 64.9 | Moderate to Strong |
| 6 | YN2C | 4752.55 | J1a1 | 9.900 | 7.310 | 66.4 | Moderate to Strong |
| 7 | TZ2 | 4405.72 | J1a4 | 1.046 | 7.069 | 58.2 | Moderate to Strong |
| 8 | MN1 | 952.44 | J1a1 | 19.788 | 18.007 | 49.2 | Moderate to Weak |
| 968.85 | J1a2 | 41.764 | 18.815 | 97.2 | Strong |
| 1028.82 | J1a2 | 42.885 | 5.947 | 48.6 | Moderate to Weak |
| 1151.87 | J1a4 | 19.778 | 18.007 | 32.1 | Moderate to Weak |
| 1154.67 | J1a4 | 4.445 | 11.236 | 86.4 | Strong |
Table 2.
Experimental results of salinity sensitivity damage for reservoirs in the Eastern Kuqa Depression (Critical Salinity: The critical salinity at which permeability changes abruptly).
Table 2.
Experimental results of salinity sensitivity damage for reservoirs in the Eastern Kuqa Depression (Critical Salinity: The critical salinity at which permeability changes abruptly).
| No. | Well | Depth (m) | Formation | Permeability (mD) | Porosity (%) | Critical Salinity (mg/L) | Damage Rate (%) | Damage Degree |
|---|
| 1 | YX1 | 412.70 | J1a4 | 0.016 | 3.478 | 28,300 | 66.8 | Moderate to Strong |
| 2 | KZ1 | 4357.50 | J1a4 | 0.086 | 2.050 | 20,000 | 62.2 | Moderate to Strong |
| 3 | YS4 | 4002.70 | J1a1 | 0.297 | 9.880 | 20,000 | 69.9 | Moderate to Strong |
| 4101.70 | J1a4 | 0.297 | 4.491 | 14,150 | 49.1 | Moderate to Weak |
| 4 | YN4 | 4376.04 | J1a1 | 0.203 | 7.032 | 60,000 | 52.6 | Moderate to Strong |
| 4603.47 | J1a4 | 2.082 | 9.430 | 45,000 | 67.9 | Moderate to Strong |
| 5 | YN5 | 4894.60 | J1a2 | 0.098 | 4.382 | 20,000 | 42.2 | Moderate to Weak |
| 4936.30 | J1a4 | 2.096 | 9.169 | 7000 | 83.7 | Strong |
| 4936.30 | J1a4 | 19.890 | 29.14 | 40,000 | 75.5 | Strong |
| 5012.90 | J1a1 | 1.518 | 8.522 | 50,000 | 57.7 | Moderate to Strong |
| 6 | YN2C | 4752.50 | J1a1 | 2.252 | 8.290 | 7000 | 92.9 | Strong |
| 4752.86 | J1a1 | 0.136 | 7.960 | 24,000 | 31.2 | Moderate to Weak |
| 7 | TZ2 | 4403.42 | J1a4 | 0.277 | 7.016 | 30,000 | 62.7 | Moderate to Strong |
| 8 | MN1 | 968.85 | J1a1 | 74.611 | 16.599 | 60,000 | 60.5 | Moderate to Strong |
| 968.85 | J1a2 | 71.245 | 19.171 | 2000 | 51.8 | Moderate to Strong |
| 1154.67 | J1a4 | 4.054 | 11.113 | 61,600 | 89.6 | Strong |
Table 3.
Classification of water sensitivity curve types.
Table 3.
Classification of water sensitivity curve types.
| No. | Well | Depth (m) | Illite/Smectite Mixed Layer | Illite and Kaolinite | Chlorite | Clay Minerals | Curve Type |
|---|
| Relative Content (%) |
|---|
| 1 | YS4 | 4069.1 | 3.3 | 80.0 | 16.7 | 100 | Type I |
| YS4 | 4044.0 | 10.0 | 87.2 | 1.4 | 100 |
| YN5 | 4781.5 | 12.8 | 72.5 | 15.3 | 100 |
| MN1 | 1028.0 | 18.2 | 77.3 | 5.5 | 100 |
| YN4 | 4533.4 | 5.0 | 83.3 | 11.7 | 100 |
| 2 | TD2 | 4138.7 | 32.3 | 57.5 | 11.0 | 100 | Type II |
| TD2 | 4136.3 | 27.3 | 64.5 | 8.2 | 100 |
| DT1 | 2257.5 | 35.2 | 64.8 | 0.0 | 100 |
| 3 | DT4 | 4204.4 | 48.0 | 24.2 | 27.8 | 100 | Type III |
| TZ4 | 4212.5 | 56.8 | 27.9 | 15.3 | 100 |
| DB102 | 5094.5 | 54.7 | 31.3 | 14.1 | 100 |
Table 4.
Experimental results of velocity sensitivity damage for reservoirs in the Eastern Kuqa Depression (Critical Flow Velocity: Flow rate at the critical point of rapid permeability alteration).
Table 4.
Experimental results of velocity sensitivity damage for reservoirs in the Eastern Kuqa Depression (Critical Flow Velocity: Flow rate at the critical point of rapid permeability alteration).
| No. | Well | Depth (m) | Formation | Permeability (mD) | Porosity (%) | Critical Flow Velocity (m/d) | Damage Rate (%) | Damage Degree |
|---|
| 1 | KZ1 | 4357.10 | J1a4 | 0.033 | 3.131 | 1.817 | 31.5 | Moderate to Weak |
| 2 | YX1 | 413.10 | J1a4 | 0.017 | 3.213 | 1.772 | 26.3 | Weak |
| 3683.00 | J1a1 | 0.045 | 1.091 | 10.425 | 42.7 | Moderate to Weak |
| 3 | YS4 | 3998.90 | J1a1 | 0.907 | 9.912 | 5.737 | 29.9 | Weak |
| 4006.00 | J1a1 | 0.874 | 8.760 | 3.246 | 66.9 | Moderate to Strong |
| 4101.10 | J1a4 | 0.017 | 6.504 | 2.186 | 42.9 | Moderate to Weak |
| 4042.00 | J1a2 | 3.067 | 8.499 | 6.691 | 29.0 | Weak |
| 4 | YN4 | 4375.44 | J1a1 | 0.119 | 7.627 | 1.863 | 24.0 | Moderate to Weak |
| 4497.35 | J1a2 | 0.506 | 9.078 | 3.132 | 84.7 | Strong |
| 4573.29 | J1a4 | 0.499 | 8.018 | 2.867 | 68.7 | Moderate to Strong |
| 5 | YN2C | 4734.20 | J1a1 | 0.155 | 7.181 | 2.772 | 20.6 | Weak |
| 4740.17 | J1a1 | 0.386 | 5.320 | 5.345 | 72.5 | Strong |
| 6 | TZ2 | 4347.06 | J1a4 | 0.485 | 8.768 | 2.594 | 62.6 | Moderate to Strong |
| 4406.57 | J1a4 | 0.031 | 5.315 | 4.284 | 34.1 | Moderate to Weak |
| 7 | YN5 | 4851.20 | J1a2 | 0.254 | 4.370 | 1.952 | 83.1 | Strong |
| 4894.90 | J1a2 | 0.205 | 4.424 | 6.433 | 31.5 | Moderate to Weak |
| 4936.60 | J1a1 | 6.460 | 7.728 | 3.680 | 69.4 | Moderate to Strong |
| 4941.50 | J1a4 | 0.205 | 7.540 | 1.131 | 41.7 | Moderate to Weak |
| 5012.60 | J1a1 | 1.580 | 8.610 | 1.020 | 79.7 | Strong |
| 8 | MN1 | 951.14 | J1a1 | 27.715 | 17.532 | 1.622 | 57.6 | Moderate to Strong |
| 1028.32 | J1a2 | 21.671 | 14.162 | 1.405 | 50.7 | Moderate to Strong |
| 1154.37 | J1a4 | 2.728 | 11.219 | 1.774 | 41.2 | Moderate to Weak |
Table 5.
Experimental results of acid sensitivity damage for reservoirs in the Eastern Kuqa Depression.
Table 5.
Experimental results of acid sensitivity damage for reservoirs in the Eastern Kuqa Depression.
| No. | Well | Depth (m) | Formation | Permeability (mD) | Porosity (%) | Damage Rate (%) | Damage Degree |
|---|
| 1 | YX1 | 412.70 | J1a4 | 0.015 | 3.296 | 48.5 | Moderate to Weak |
| 2 | KZ1 | 4359.20 | J1a4 | 0.021 | 2.623 | 65.9 | Moderate to Strong |
| 3 | YS4 | 3995.00 | J1a1 | 0.012 | 4.710 | 56.5 | Moderate to Strong |
| 3995.00 | J1a2 | 0.084 | 5.465 | 46.0 | Moderate to Weak |
| 4104.00 | J1a4 | 0.144 | 3.535 | 32.5 | Moderate to Weak |
| 4 | YN4 | 4375.04 | J1a1 | 2.834 | 6.871 | 45.0 | Moderate to Weak |
| 4465.66 | J1a2 | 0.092 | 6.998 | 33.2 | Moderate to Weak |
| 4538.60 | J1a3 | 0.044 | 6.264 | 34.0 | Moderate to Weak |
| 4604.97 | J1a4 | 2.379 | 9.376 | 69.1 | Moderate to Strong |
| 4639.66 | J1a4 | 0.013 | 7.684 | 33.2 | Moderate to Weak |
| 5 | YN5 | 4846.90 | J1a2 | 0.947 | 5.749 | 12.1 | Weak |
| 4894.00 | J1a2 | 0.403 | 4.120 | 34.3 | Moderate to Weak |
| 4936.20 | J1a4 | 5.230 | 7.990 | 37.9 | Moderate to Weak |
| 5013.00 | J1a1 | 1.711 | 6.802 | 32.5 | Moderate to Weak |
| 6 | YN2C | 4746.40 | J1a1 | 0.076 | 6.930 | 26.9 | Weak |
| 7 | TZ2 | 4403.92 | J1a4 | 0.405 | 6.968 | 21.9 | Weak |
| 8 | MN1 | 952.74 | J1a1 | 7.847 | 16.183 | 26.7 | Weak |
| 969.75 | J1a2 | 40.626 | 18.686 | 56.8 | Moderate to Strong |
| 1154.37 | J1a4 | 2.529 | 11.655 | 9.8 | Weak |
Table 6.
Experimental results of alkali sensitivity damage for reservoirs in the Eastern Kuqa Depression.
Table 6.
Experimental results of alkali sensitivity damage for reservoirs in the Eastern Kuqa Depression.
| No. | Well | Depth (m) | Formation | Permeability (mD) | Porosity (%) | pH | Damage Rate (%) | Damage Degree |
|---|
| 1 | YX1 | 412.70 | J1a4 | 0.020 | 3.393 | 7 | 54.7 | Moderate to Strong |
| 2 | KZ1 | 4359.60 | J1a4 | 0.014 | 2.115 | 11 | 43.2 | Moderate to Weak |
| 3 | YS4 | 4003.50 | J1a1 | 0.063 | 9.408 | 9 | 32.5 | Moderate to Weak |
| 4043.20 | J1a2 | 2.992 | 10.140 | 7 | 45.4 | Moderate to Weak |
| 4088.90 | J1a2 | 2.450 | 9.880 | 7 | 41.2 | Moderate to Weak |
| 4 | YN4 | 4460.75 | J1a2 | 2.733 | 11.205 | 9 | 51.3 | Moderate to Strong |
| 4525.40 | J1a4 | 0.280 | 4.120 | 9 | 58.1 | Moderate to Strong |
| 4606.60 | J1a4 | 0.317 | 3.347 | 8 | 36.8 | Moderate to Weak |
| 5 | YN5 | 4896.60 | J1a1 | 1.028 | 7.654 | 9 | 59.4 | Moderate to Strong |
| 4936.60 | J1a4 | 0.710 | 6.274 | 11 | 23.1 | Weak |
| 5012.60 | J1a1 | 0.547 | 8.950 | 9 | 50.8 | Moderate to Strong |
| 6 | YN2C | 4739.73 | J1a1 | 0.155 | 4.959 | 9 | 44.3 | Moderate to Strong |
| 4750.08 | J1a1 | 0.411 | 10.530 | 9 | 51.1 | Moderate to Strong |
| 4765.20 | J1a1 | 0.288 | 8.120 | 9 | 53.9 | Moderate to Strong |
| 7 | TZ2 | 4405.82 | J1a4 | 0.478 | 6.445 | 8 | 55.9 | Moderate to Strong |
| 4450.15 | J1a4 | 0.620 | 7.350 | 8 | 47.6 | Moderate to Weak |
| 8 | MN1 | 956.94 | J1a1 | 62.827 | 18.725 | 7 | 63.9 | Moderate to Strong |
| 1026.92 | J1a2 | 50.761 | 16.066 | 7 | 73.0 | Strong |
| 1085.60 | J1a2 | 45.200 | 17.850 | 7 | 68.5 | Strong |
| 1154.37 | J1a4 | 3.056 | 11.549 | 7 | 29.1 | Weak |
Table 7.
Experimental results of stress sensitivity damage for reservoirs in the Eastern Kuqa Depression.
Table 7.
Experimental results of stress sensitivity damage for reservoirs in the Eastern Kuqa Depression.
| No. | Well | Depth (m) | Formation | Permeability (mD) | Porosity (%) | Maximum Damage Rate (%) | Damage Degree |
|---|
| 1 | YX1 | 409.80 | J1a4 | 0.021 | 2.684 | 94.2 | Strong |
| 2 | KZ1 | 4359.00 | J1a4 | 0.027 | 2.010 | 76.1 | Strong |
| 3 | YS4 | 4001.60 | J1a1 | 0.139 | 8.970 | 94.5 | Strong |
| 4 | YN4 | 4607.50 | J1a4 | 0.323 | 3.856 | 88.9 | Strong |
| 5 | YN5 | 4773.63 | J1a1 | 1.289 | 6.150 | 89.7 | Strong |
| 4941.50 | J1a2 | 0.279 | 6.431 | 97.4 | Strong |
| 6 | TZ2 | 4406.62 | J1a4 | 0.174 | 5.685 | 94.7 | Strong |
| 7 | YN2C | 4758.72 | J1a1 | 0.023 | 6.150 | 81.9 | Strong |
| 8 | MN1 | 968.85 | J1a1 | 41.764 | 18.815 | 77.4 | Strong |
| 1026.92 | J1a2 | 85.718 | 15.448 | 52.9 | Moderate to Strong |
| 1154.37 | J1a4 | 2.456 | 11.542 | 93.1 | Strong |
Table 8.
Overview of model fitting results.
Table 8.
Overview of model fitting results.
| | Modified Statistics | |
|---|
| R | R2 | Adjusted R2 | ΔR2 | ΔF | Significance | Durbin–Watson |
|---|
| 0.702 | 0.838 | 0.824 | 0.838 | 47.208 | 0 | 2.038 |
Table 9.
ANOVA (F-test).
| | Sum of Squares | Degrees of Freedom | Mean Square | F | Significance |
|---|
| Regression | 0.05 | 5 | 0.01 | 11.736 | 000 |
| Residual | 0.02 | 24 | 0.001 | | |
| Total | 0.07 | 29 | | | |
Table 10.
Coefficients output (t-test).
Table 10.
Coefficients output (t-test).
| | Unstandardized Coefficients | Standardized Coefficients | T | Significance | Collinearity Statistics |
|---|
| | B | Standard Error | Beta | | | Tolerance | VIF |
|---|
| (Constant) | −0.494 | 0.704 | | −0.701 | 0.49 | | |
| Total Clay Content | 0.015 | 0.002 | 0.746 | 6.513 | 0 | 0.922 | 1.085 |
| Chlorite | 0.003 | 0.008 | 0.153 | 0.408 | 0.687 | 0.086 | 1.594 |
| Illite | 0.006 | 0.007 | 0.593 | 0.897 | 0.379 | 0.028 | 0.116 |
| Kaolinite | 0.004 | 0.007 | 0.402 | 0.578 | 0.569 | 0.025 | 0.91 |
| Illite-Smectite Mixed Layer | 0.001 | 0.008 | 0.073 | 0.197 | 0.846 | 0.089 | 1.256 |