Application of Hybrid SMA (Slime Mould Algorithm)-Fuzzy PID Control in Hip Joint Trajectory Tracking of Lower-Limb Exoskeletons in Multi-Terrain Environments
Abstract
1. Introduction
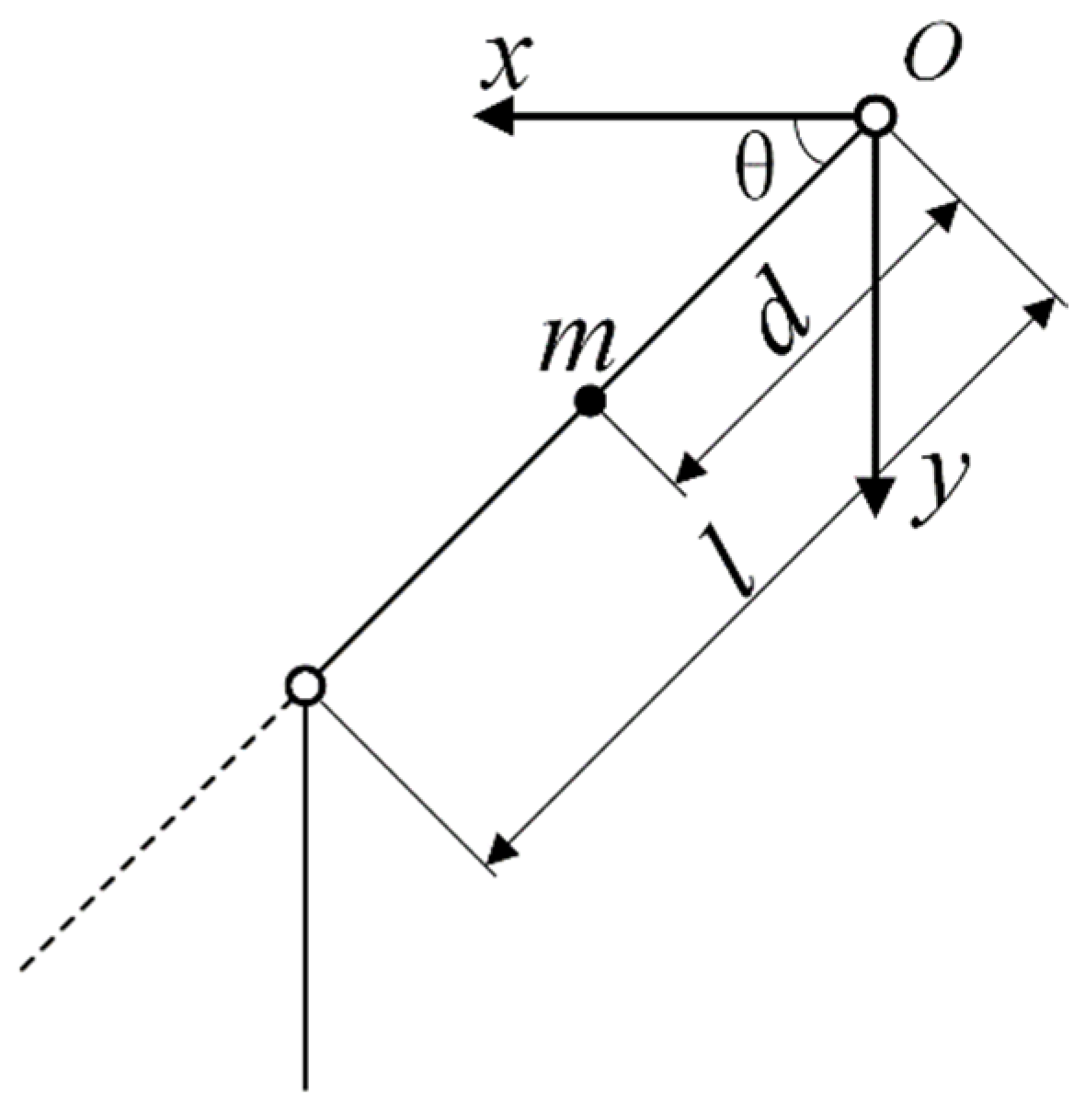
2. Kinematic Analysis of the Lower-Limb Exoskeleton Hip Joint Mechanism
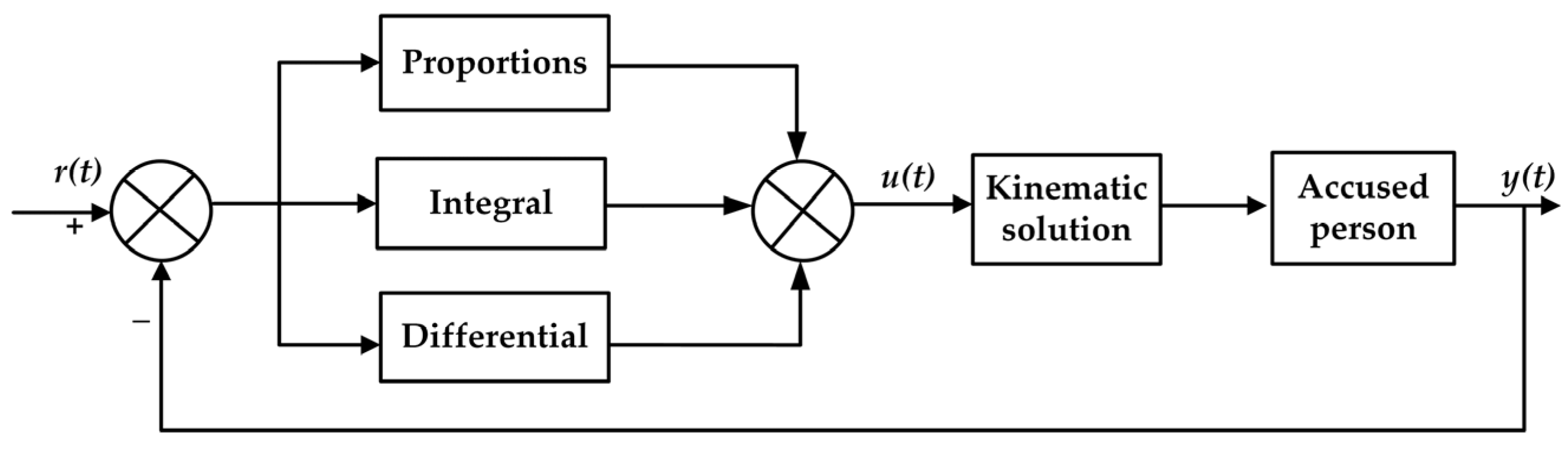
3. Design of the Control System
3.1. Proportional-Integral-Derivative (PID) Controller
3.2. Design of the Fuzzy PID Controller
3.3. Hybrid SMA-Fuzzy PID Control System
3.3.1. Slime Mould Algorithm
3.3.2. Process of Establishing a Hybrid SMA-Fuzzy PID Control System
- (1.)
- Parameter Initialization and Algorithm Configuration
- (2.)
- Fitness Function Construction
- (3.)
- Joint Simulation Implementation
- (4.)
- Dynamic Optimization Process
4. Simulation Analysis
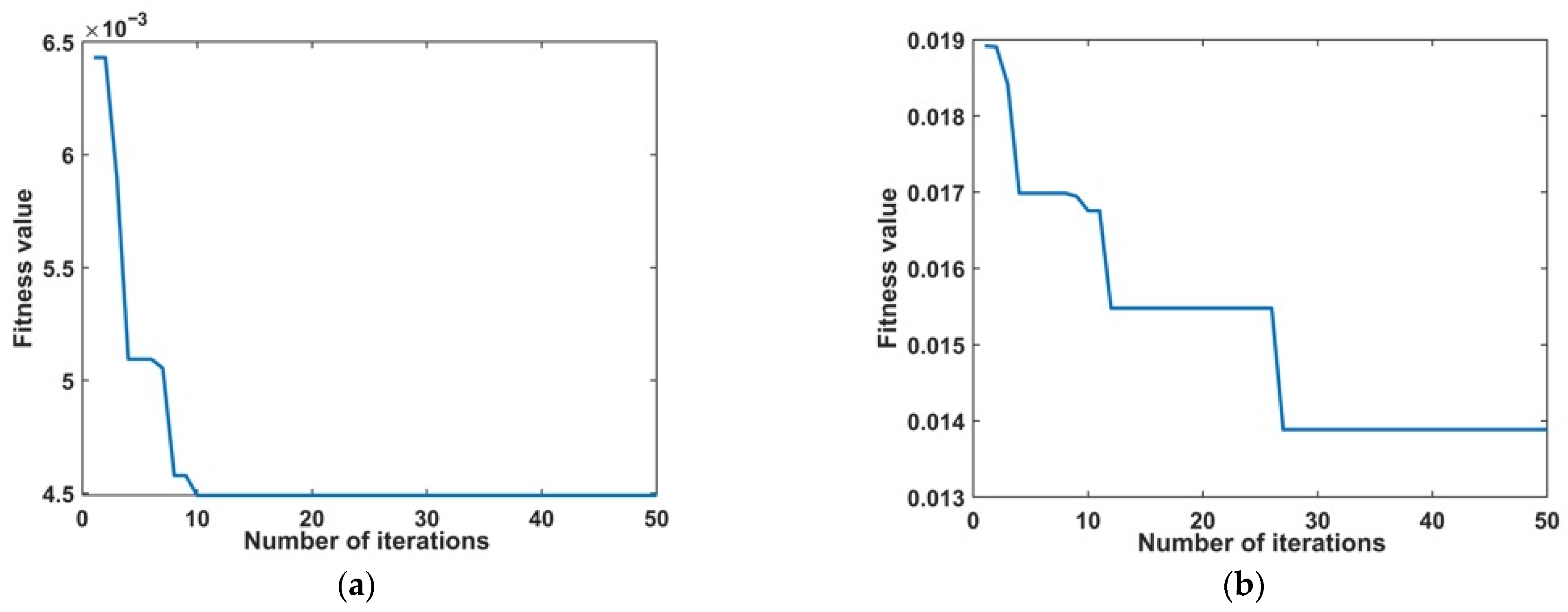
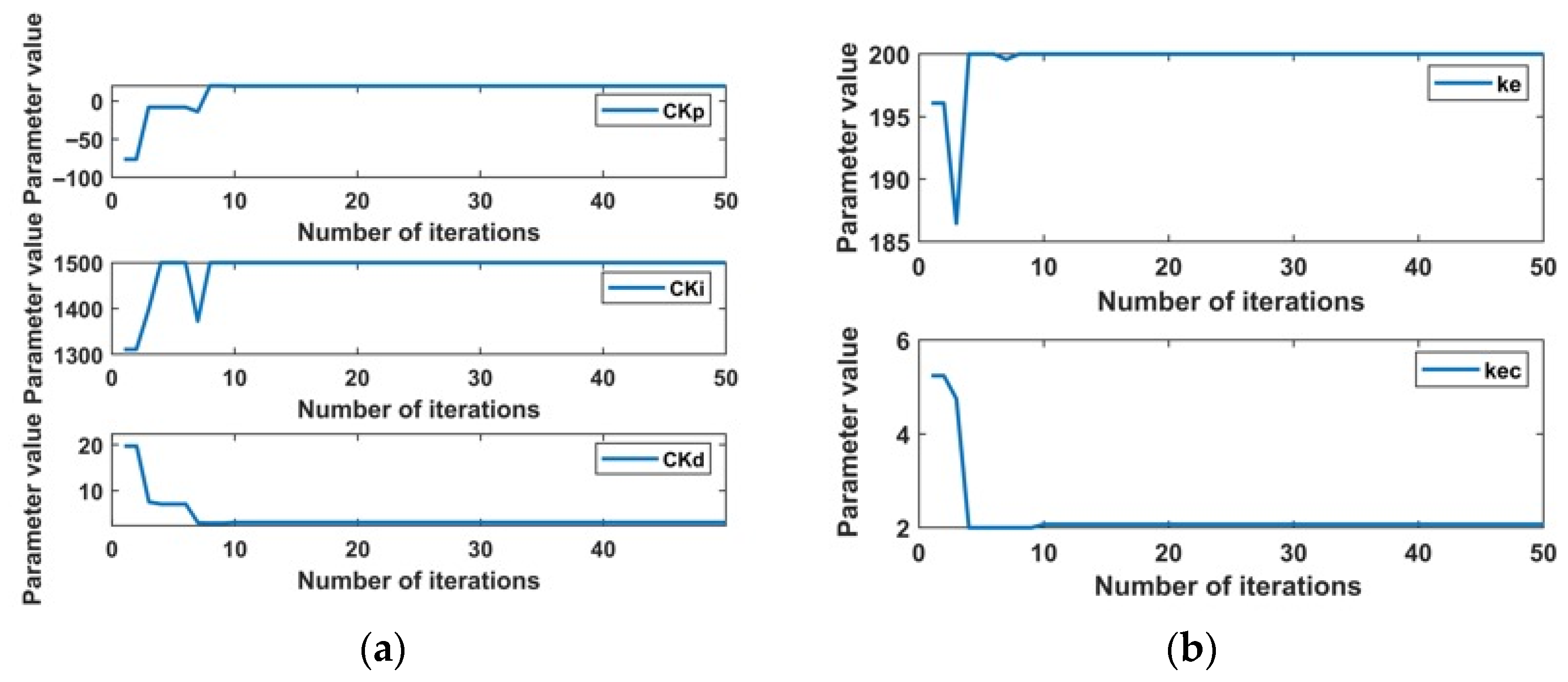
4.1. Parameter Tuning of Hybrid SMA-Fuzzy PID Control System
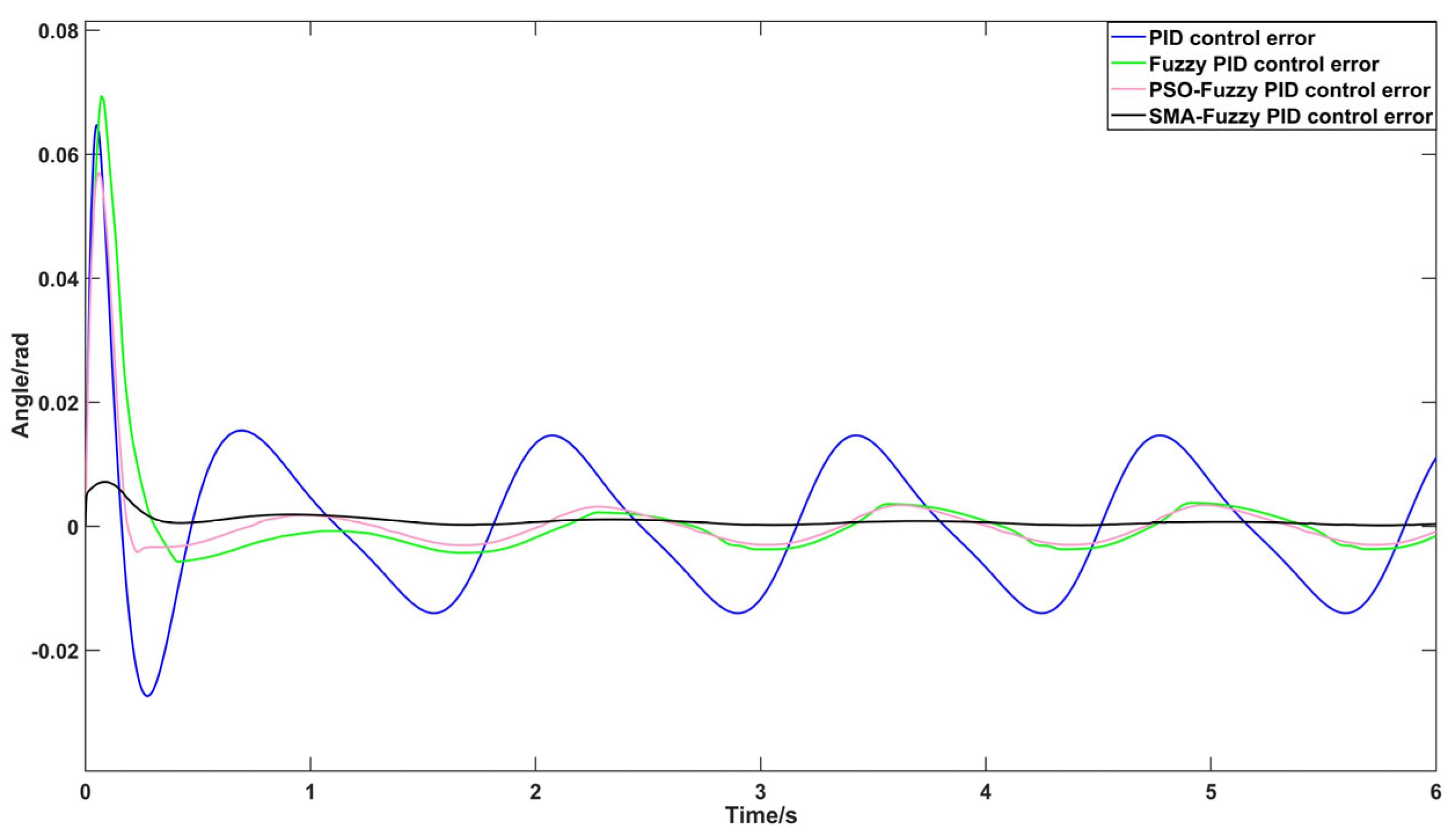
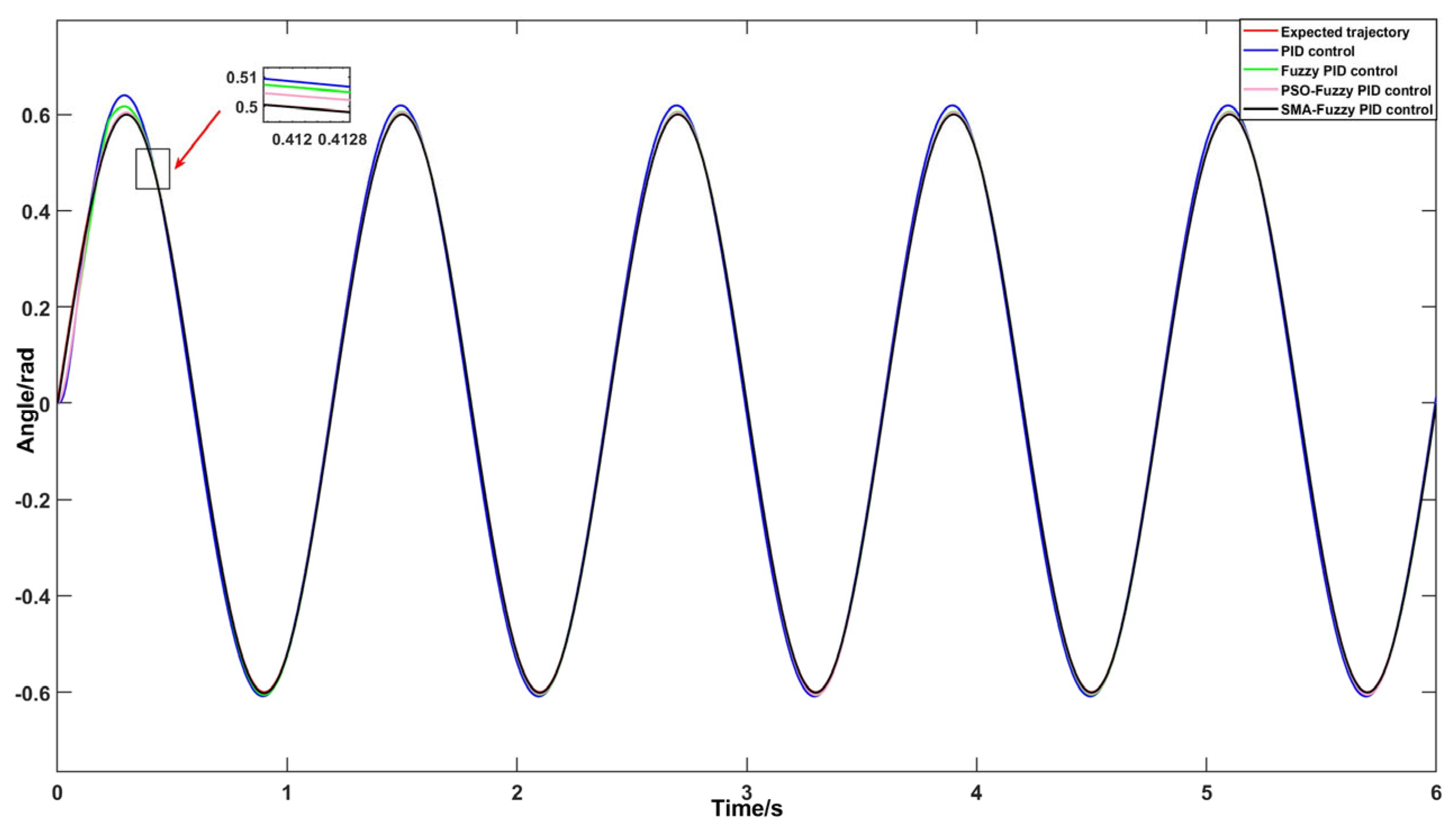
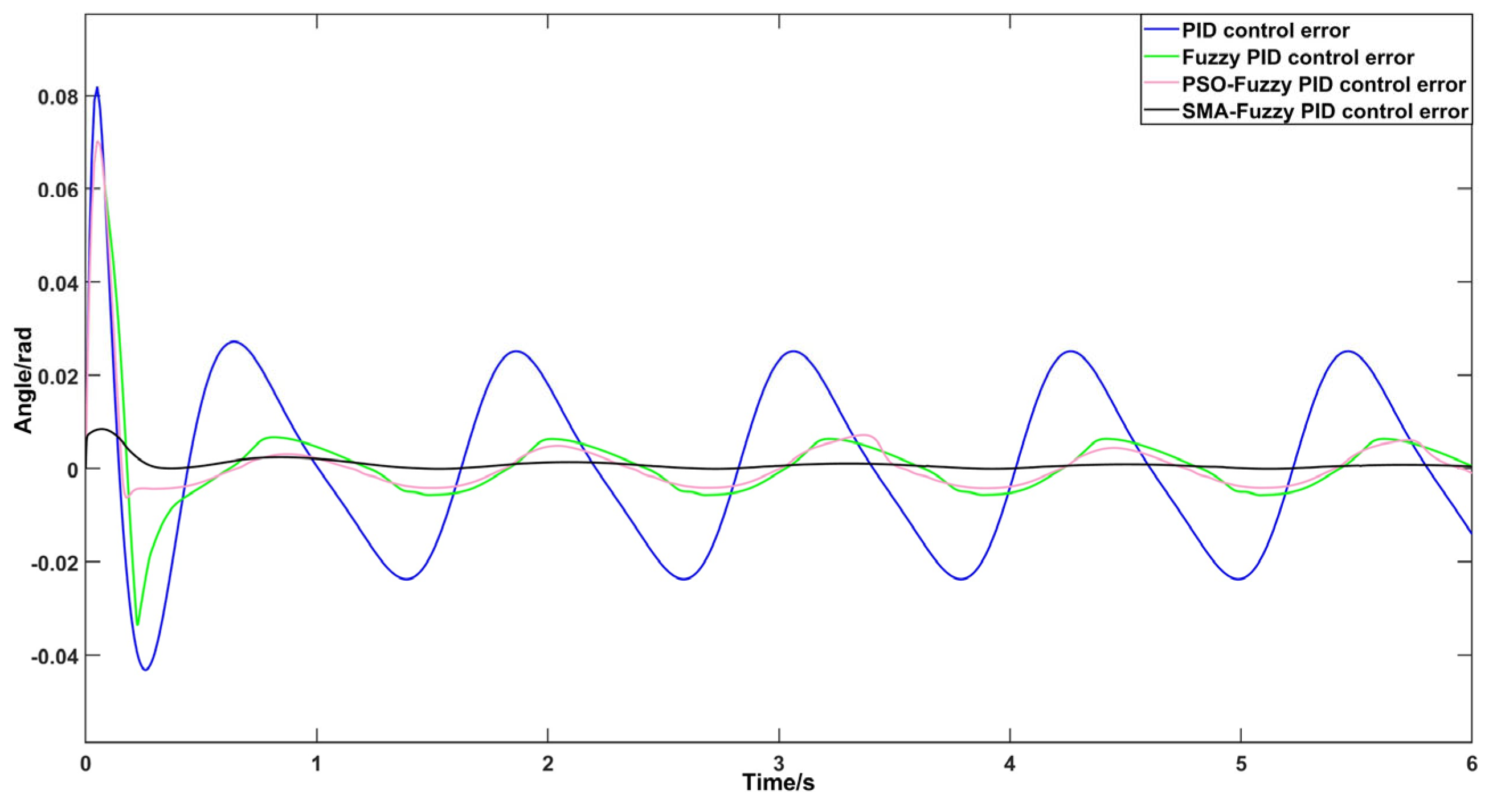
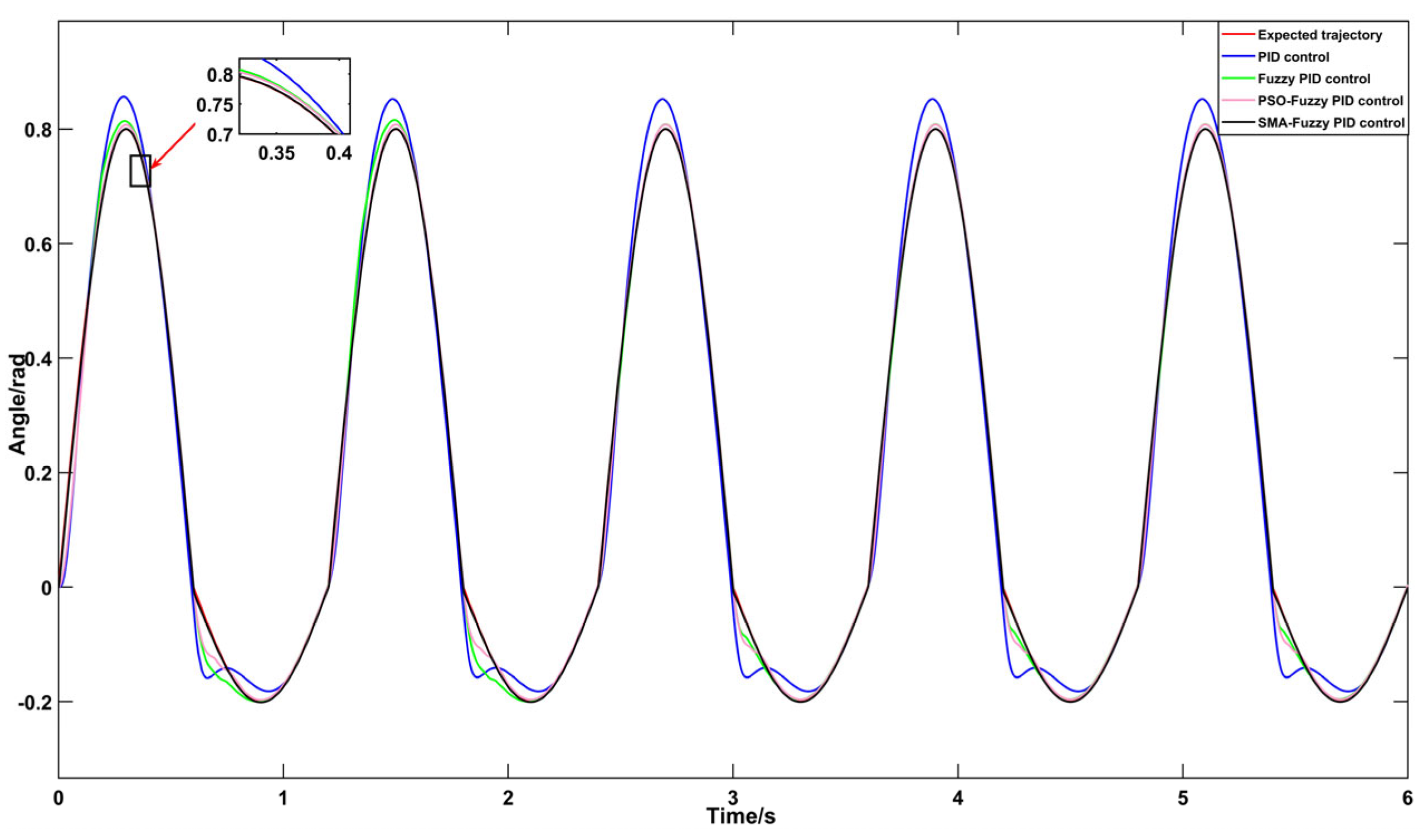
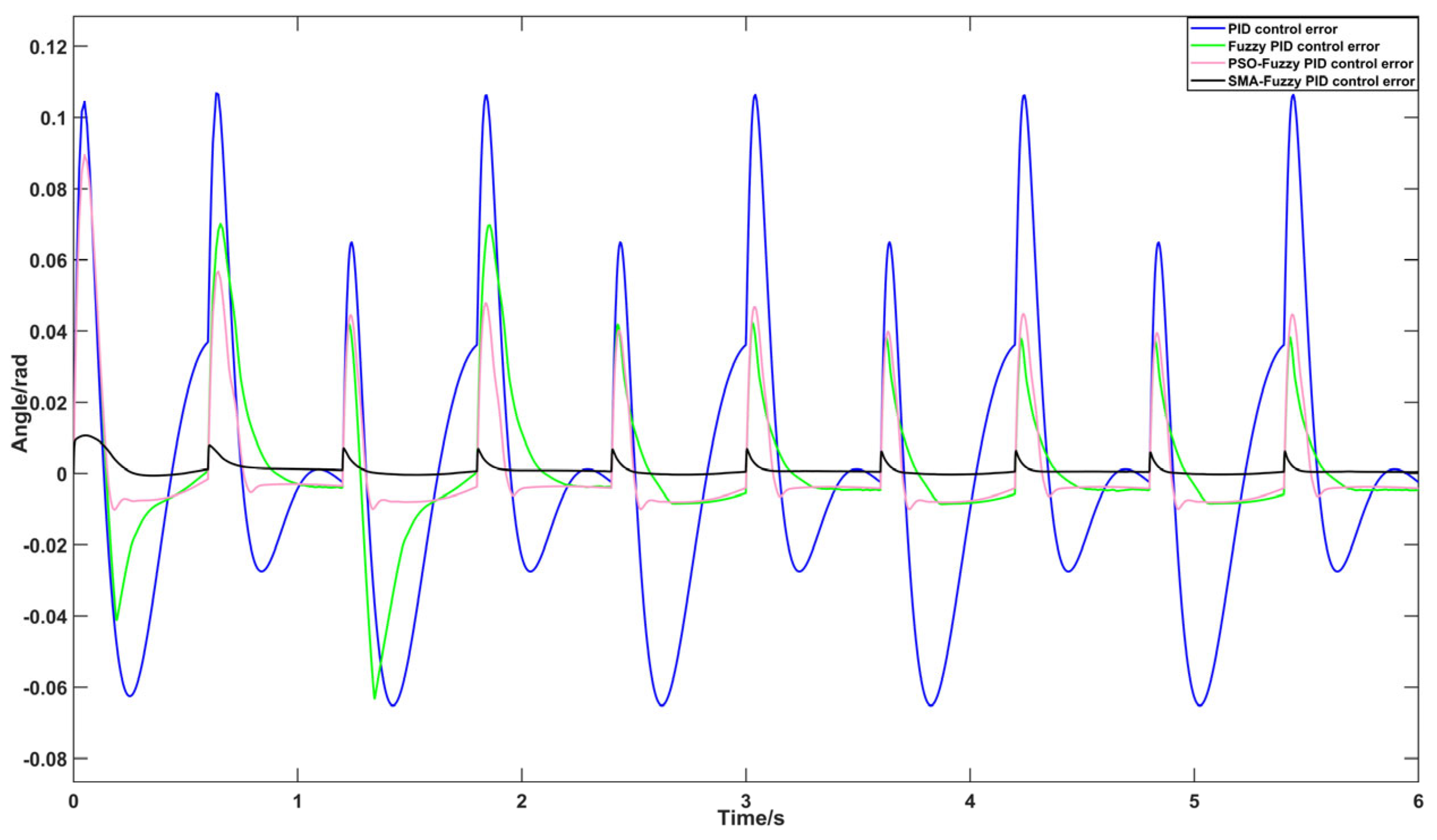
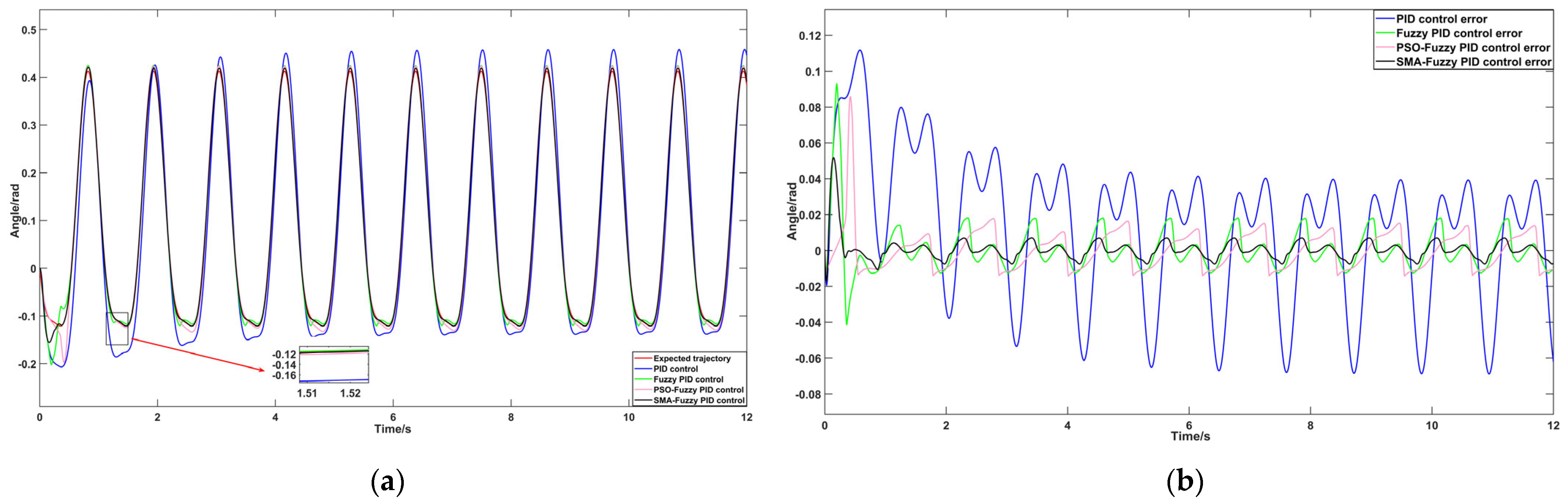
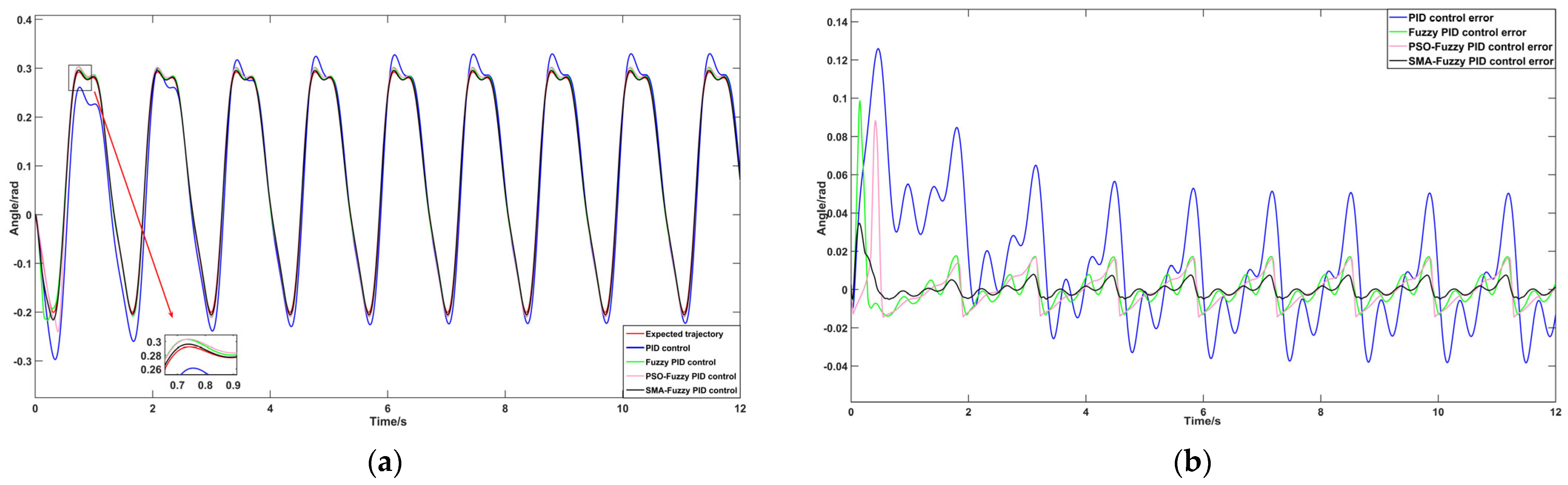
4.2. Comparative Analysis of Trajectory Tracking Simulations for Lower-Limb Exoskeleton Hip Joint Robots Utilizing Various Control Methods Across Diverse Terrain Conditions
4.2.1. Examination of Trajectory Tracking Characteristics in Flat Ground Walking Scenarios
4.2.2. Examination of Trajectory Tracking Characteristics in Slope Walking Scenarios
4.2.3. Examination of Trajectory Tracking Characteristics in Staircase Walking Scenarios
5. Empirical Evaluation of Trajectory Tracking in a Lower-Limb Exoskeleton Hip Joint Robot
5.1. Design of the Experimental Platform and Test Scenarios
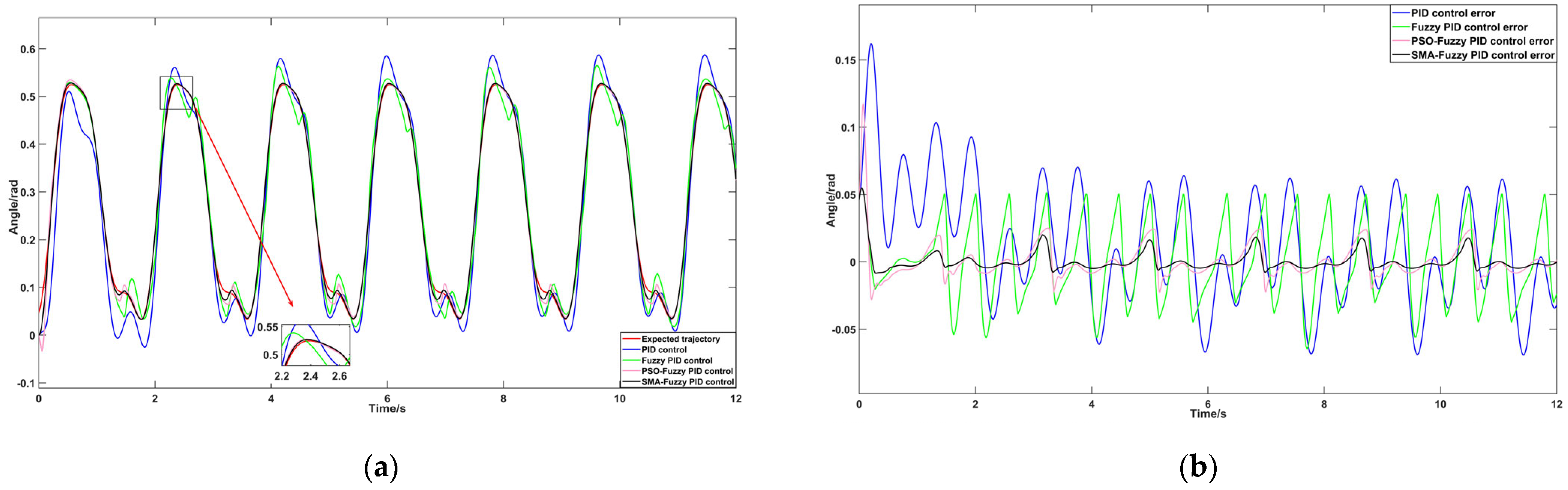
5.2. Analysis of Actual Measurement Results Across Multiple Terrain Conditions
5.2.1. Trajectory Tracking Tests of Flat Walking in Test Subjects Under Four Distinct Control Methods
5.2.2. Trajectory Tracking Tests of Slope Walking in Test Subjects Under Four Distinct Control Methods
5.2.3. Trajectory Tracking Tests of Stair Ascent in Test Subjects Under Four Distinct Control Methods
6. Discussion
7. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Moriarty, B.; Jacob, T.; Sadlowski, M.; Fowler, M.; Rowan, C.; Chavarria, J.; Avramis, I.; Rizkalla, J. The use of exoskeleton robotic training on lower extremity function in spinal cord injuries: A systematic review. J. Orthop. 2025, 65, 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, M.; Li, H.; Yu, H. Research status of lower limb exoskeleton rehabilitation robot. Sheng Wu Yi Xue Gong Cheng Xue Za Zhi J. Biomed. Eng. 2024, 41, 833–839. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, H.; Yang, X.; Lin, Y. Current Status of Research and Critical Technologies for Lower Limb-assisted Exoskeleton Robots. Recent Pat. Eng. 2025, 19, 195–222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gonabadi, M.A.; Fallahtafti, F. Gait Stability Under Hip Exoskeleton Assistance: A Phase-Dependent Analysis Using Gait Tube Methodology. Appl. Sci. 2025, 15, 7530. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paing, L.S.; Alili, A.; Nalam, V.; Huang, H.H. Effects of Hip Adduction-Abduction Exoskeleton-Controlled Step Width on Mediolateral Gait Balance During Walking. In Proceedings of the IEEE International Conference on Rehabilitation Robotics, Chicago, IL, USA, 12–16 May 2025; pp. 952–957. [Google Scholar]
- Wondra, A.T.; Le, N.H.; Hunt, E.A.; Rouse, E.J. Surface, but Not Age, Impacts Lower Limb Joint Work during Walking and Stair Ascent. J. Funct. Morphol. Kinesiol. 2023, 8, 145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Arhos, E.K.; Lang, C.E.; Steger-May, K.; Van Dillen, L.R.; Yemm, B.; Salsich, G.B. Task-specific movement training improves kinematics and pain during the Y-balance test and hip muscle strength in females with patellofemoral pain. J. ISAKOS Jt. Disord. Orthop. Sports Med. 2021, 6, 277–282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alsaied, A.; Li, K. An Optimized Type 2 Fuzzy Control with Time Delay Estimation for Gait Trajectory Tracking in Lower-Limb Exoskeleton Robot. Int. J. Fuzzy Syst. 2025, 1–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mou, R.; Li, L. Research on design and trajectory tracking control of a variable size lower limb exoskeleton rehabilitation robot. J. Mech. Sci. Technol. 2024, 38, 389–400. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, L.; Zhao, L.J.; Yang, G.S.; Ma, C.J. A digital twin-driven trajectory tracking control method of a lower-limb exoskeleton. Control Eng. Pract. 2022, 127, 105271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aole, S.; Elamvazuthi, I.; Waghmare, L.; Patre, B.; Meriaudeau, F. Improved Active Disturbance Rejection Control for Trajectory Tracking Control of Lower Limb Robotic Rehabilitation Exoskeleton. Sensors 2020, 20, 3681. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, R.; Huang, W.; Wu, J.; Wang, H.; Li, J. Global Fast Terminal Sliding Mode Control of Underwater Manipulator Based on Finite-Time Extended State Observer. J. Mar. Sci. Eng. 2025, 13, 1038. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mou, R.; Li, L.; Zheng, C. Research on Sliding Mode Control of Lower Limb Exoskeleton Robots Based on Approaching Law. Sens. Microsyst. 2023, 42, 18–21. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jyotindra, N.; Kumar, S.D. Towards Neuro-Fuzzy Compensated PID Control of Lower Extremity Exoskeleton System for Passive Gait Rehabilitation. IETE J. Res. 2023, 69, 778–795. [Google Scholar]
- Xing, W.Q.; Guo, X.D.; Xiao, J.R.; Xu, W.; Wei, Q.S.; Liu, J.N. Research on Sliding Mode PD Control of Lower Limb Exoskeleton Walking Robots. Chin. J. Biomed. Eng. 2022, 41, 621–625. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Pandiangan, R.M.S.; Arifin, A.; Riscian, A.; Baki, S.H.; Dikairono, R. Design of Fuzzy Logic Control in Functional Electrical Stimulation (FES) Cycling Exercise for Stroke Patients. In Proceedings of the 2020 International Conference on Computer Engineering, Network, and Intelligent Multimedia (CENIM), Surabaya, Indonesia, 17–18 November 2020. [Google Scholar]
- Babak, I.; Farid, N. Sliding Mode Controller for a Hybrid Lower Limb Rehabilitation Robot with Fuzzy Adjustment of Impedance Interaction: A Patient Cooperation Approach. Proc. Inst. Mech. Eng. Part I J. Syst. Control Eng. 2023, 237, 1678–1689. [Google Scholar]
- Yin, M.K.; Guo, S.J.; Sun, L.; Zhang, J. Fuzzy Self-Adaptive PID Control of Lower Limb Walking Assist Exoskeleton Robots. Mech. Des. 2021, 38, 38–44. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, Y.M.; Wu, Q.M. Sliding Mode Control of Lower Limb Exoskeleton Based on Fuzzy Expansion Observer. Intell. Comput. Appl. 2024, 14, 143–148. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kang, X. The Control of Lower Limb Rehabilitation Robot with Multi-Pose Based on Man-Machine Coupling and Fuzzy PID. Int. J. Reason.-Based Intell. Syst. 2023, 15, 203–212. [Google Scholar]
- Méndez, S.D.; Martínez, B.D.; Saad, M.; Kali, Y.; García Cena, C.E.; Álvarez, Á.L. Upper-Limb Robotic Rehabilitation: Online Sliding Mode Controller Gain Tuning Using Particle Swarm Optimization. Robotics 2025, 14, 51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.; Wu, W.; Li, X. A Modified Fruit Fly Optimization Algorithm to Active Disturbance Rejection Control Parameters Tuning for Trajectory Tracking of Omnidirectional Mobile Robotic Chassis. Soft Comput. 2025, 29, 4401–4421. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, X.F.; Lin, Y. Trajectory Tracking Control of Industrial Robots Based on Cuckoo Search Algorithm. Mach. Tool Hydraul. 2021, 49, 50–54. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Li, S.; Chen, H.; Wang, M.; Heidari, A.A.; Mirjalili, S. Slime Mould Algorithm: A New Method for Stochastic Optimization. Future Gener. Comput. Syst. 2020, 111, 300–323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- GB/T 10000-2023; Chinese Adult Human Body Dimensions. Standards Press of China: Beijing, China, 2023.
- GB 50352-2019; Unified Standard for the Design of Civil Buildings. China Architecture and Building Press: Beijing, China, 2019.
- T/CARD 060-2024; Balance Function Assessment Practice Guideline. China Academy of Railway Sciences (CARS): Beijing, China, 2024.







| Se/Sec | NB | NM | NS | ZO | PS | PM | PB |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| NB | PB/NB/PS | PB/NB/NS | PM/NM/NB | PM/NM/NB | PS/NS/NB | ZO/ZO/NM | ZO/ZO/PS |
| NM | PB/NB/PS | PB/NB/NS | PM/NM/NB | PS/NS/NB | PS/NS/NB | ZO/ZO/NM | ZO/ZO/PS |
| NS | PM/NB/ZO | PM/NM/NS | PM/NS/NS | PM/NS/NM | ZO/ZO/NS | NS/ZO/NS | NS/PS/ZO |
| ZO | PM/NM/ZO | PM/NM/NS | PM/NS/PM | ZO/ZO/NS | PS/PS/NS | NM/PM/NS | NM/PM/ZO |
| PS | PS/NM/ZO | PS/NS/ZO | ZO/ZO/ZO | NS/PS/ZO | NS/PS/ZO | NM/PM/ZO | NM/PB/ZO |
| PM | PS/ZO/PB | ZO/ZO/NS | NS/PS/PS | NM/PS/PS | NM/PM/PS | NM/PB/PS | NB/PB/PB |
| PB | ZO/ZO/PB | ZO/ZO/PM | NM/PS/PM | NM/PM/PM | NM/PM/PS | NB/PB/PS | NB/PB/PB |
| Control Systems/Performance Metrics | Adjustment Time/s | Maximum Error Value/Rad | Steady-State Error Peak Value/Rad |
|---|---|---|---|
| PID control | 2.356 | 0.1117 | 0.10835 |
| Fuzzy PID control | 2.098 | 0.09291 | 0.03036 |
| PSO-Fuzzy PID control | 1.793 | 0.08555 | 0.02922 |
| SMA-Fuzzy PID control | 1.523 | 0.05181 | 0.014416 |
| Control Systems/Performance Metrics | Adjustment Time/s | Maximum Error Value/Rad | Steady-State Error Peak Value/Rad |
|---|---|---|---|
| PID control | 2.556 | 0.1258 | 0.08892 |
| Fuzzy PID control | 1.763 | 0.09827 | 0.03006 |
| PSO-Fuzzy PID control | 1.681 | 0.08809 | 0.03031 |
| SMA-Fuzzy PID control | 1.182 | 0.03421 | 0.012153 |
| Control Systems/Performance Metrics | Adjustment Time/s | Maximum Error Value/Rad | Steady-State Error Peak Value/Rad |
|---|---|---|---|
| PID control | 2.702 | 0.1617 | 0.1314 |
| Fuzzy PID control | 1.470 | 0.05472 | 0.09163 |
| PSO-Fuzzy PID control | 1.276 | 0.1167 | 0.04666 |
| SMA-Fuzzy PID control | 1.030 | 0.05472 | 0.012153 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Li, W.; Wei, X.; Sun, D.; Jia, Z.; Yue, Z.; Pang, T. Application of Hybrid SMA (Slime Mould Algorithm)-Fuzzy PID Control in Hip Joint Trajectory Tracking of Lower-Limb Exoskeletons in Multi-Terrain Environments. Processes 2025, 13, 3250. https://doi.org/10.3390/pr13103250
Li W, Wei X, Sun D, Jia Z, Yue Z, Pang T. Application of Hybrid SMA (Slime Mould Algorithm)-Fuzzy PID Control in Hip Joint Trajectory Tracking of Lower-Limb Exoskeletons in Multi-Terrain Environments. Processes. 2025; 13(10):3250. https://doi.org/10.3390/pr13103250
Chicago/Turabian StyleLi, Wei, Xiaojie Wei, Daxue Sun, Zhuoda Jia, Zhengwei Yue, and Tianlian Pang. 2025. "Application of Hybrid SMA (Slime Mould Algorithm)-Fuzzy PID Control in Hip Joint Trajectory Tracking of Lower-Limb Exoskeletons in Multi-Terrain Environments" Processes 13, no. 10: 3250. https://doi.org/10.3390/pr13103250
APA StyleLi, W., Wei, X., Sun, D., Jia, Z., Yue, Z., & Pang, T. (2025). Application of Hybrid SMA (Slime Mould Algorithm)-Fuzzy PID Control in Hip Joint Trajectory Tracking of Lower-Limb Exoskeletons in Multi-Terrain Environments. Processes, 13(10), 3250. https://doi.org/10.3390/pr13103250





