Evaluation of Lacustrine Shale Brittleness and Its Controlling Factors: A Case Study from the Jurassic Lianggaoshan Formation, Sichuan Basin
Abstract
:1. Introduction
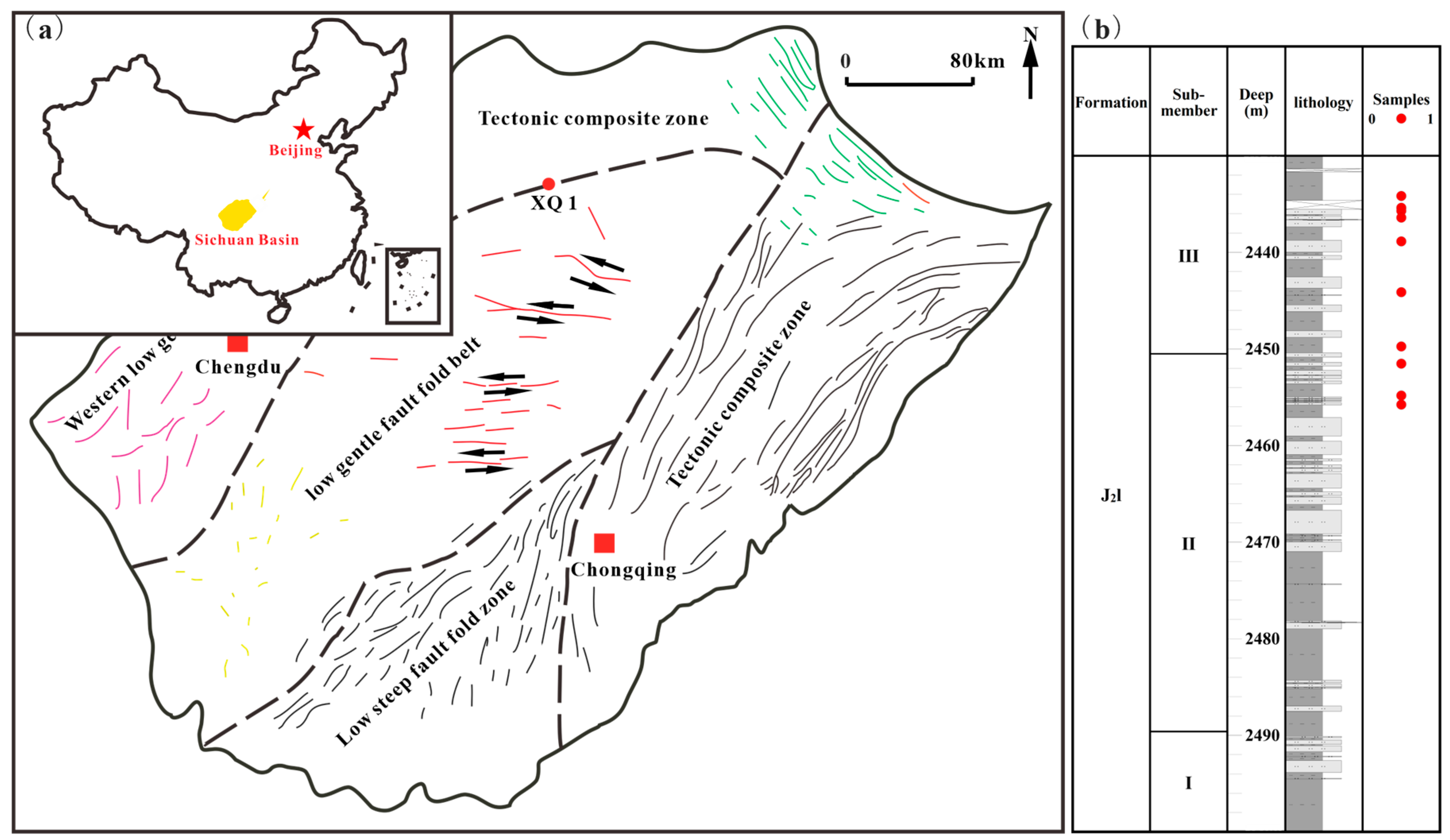
2. Geological Setting
3. Samples and Methodology
3.1. Samples and Experiments
3.2. Evaluation Methods for Brittleness
3.2.1. Evaluation of Rock Brittleness Based on Elastic Modulus and Hardness
3.2.2. Evaluation of Rock Brittleness Based on Mineral Composition
3.2.3. Evaluation of Rock Brittleness Based on Strength Parameters
3.2.4. Rock Brittleness Evaluation Based on Post-Peak Energy
4. Results and Discussion
4.1. Organic Characteristics and Mineral Compositions
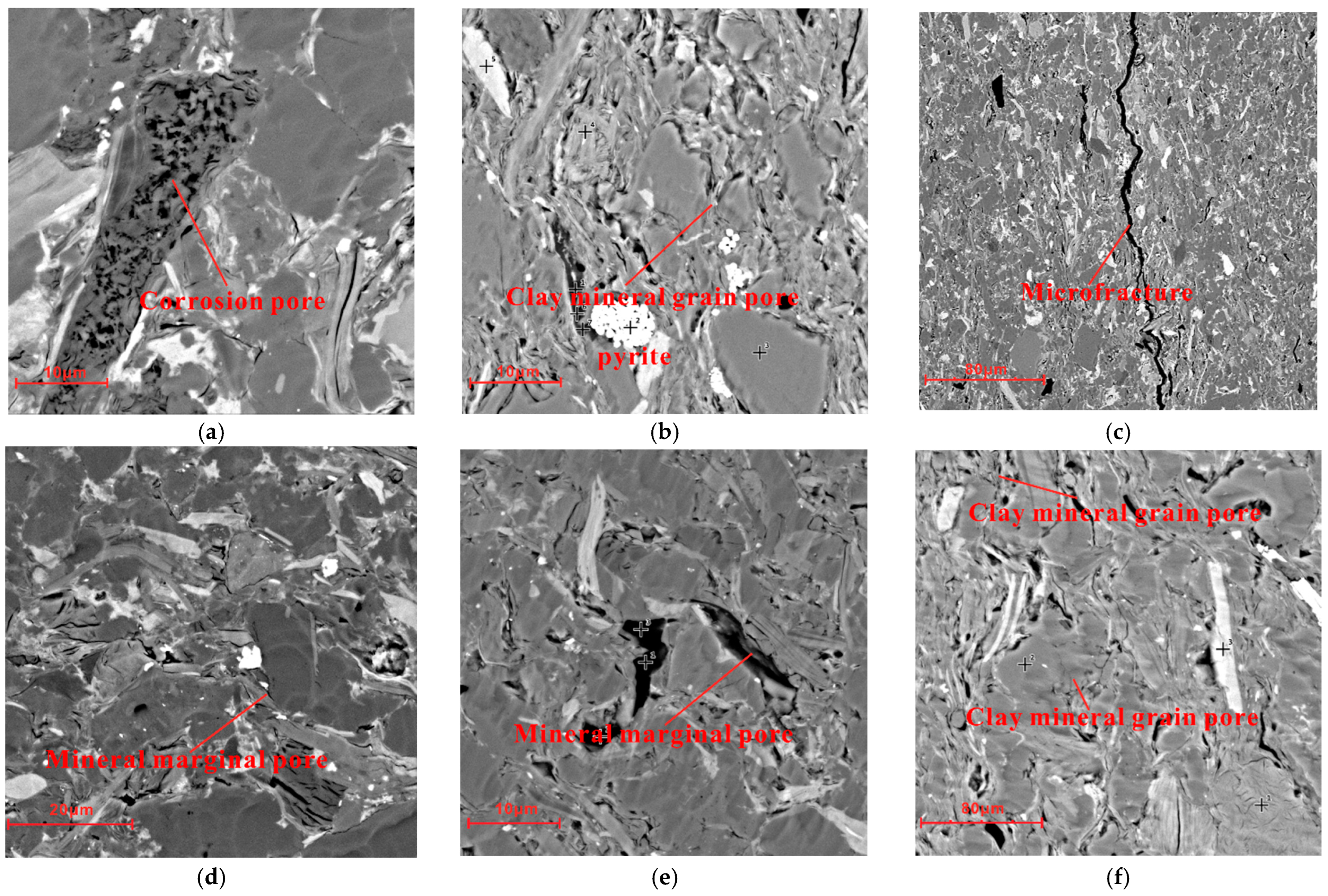
4.2. Pore Types, Porosity, and Permeability of Shales
4.3. Shale Brittleness
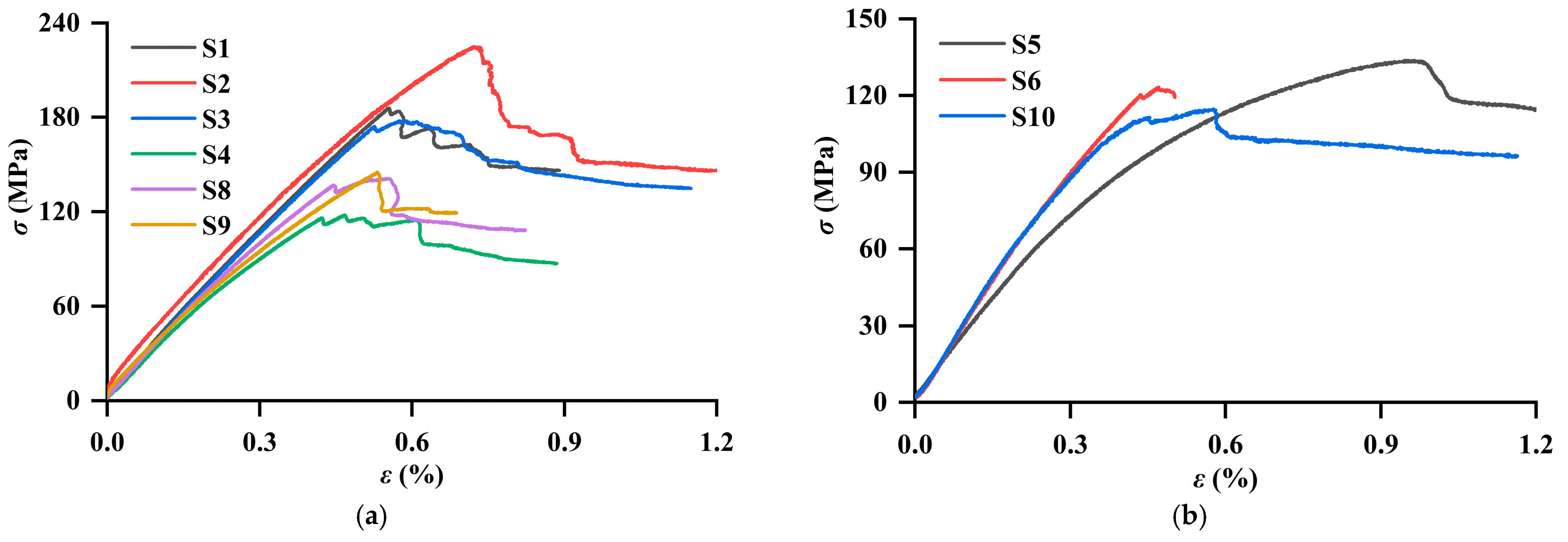
4.3.1. Stress–Strain Curves of Shales
4.3.2. Rock Mechanical Parameters
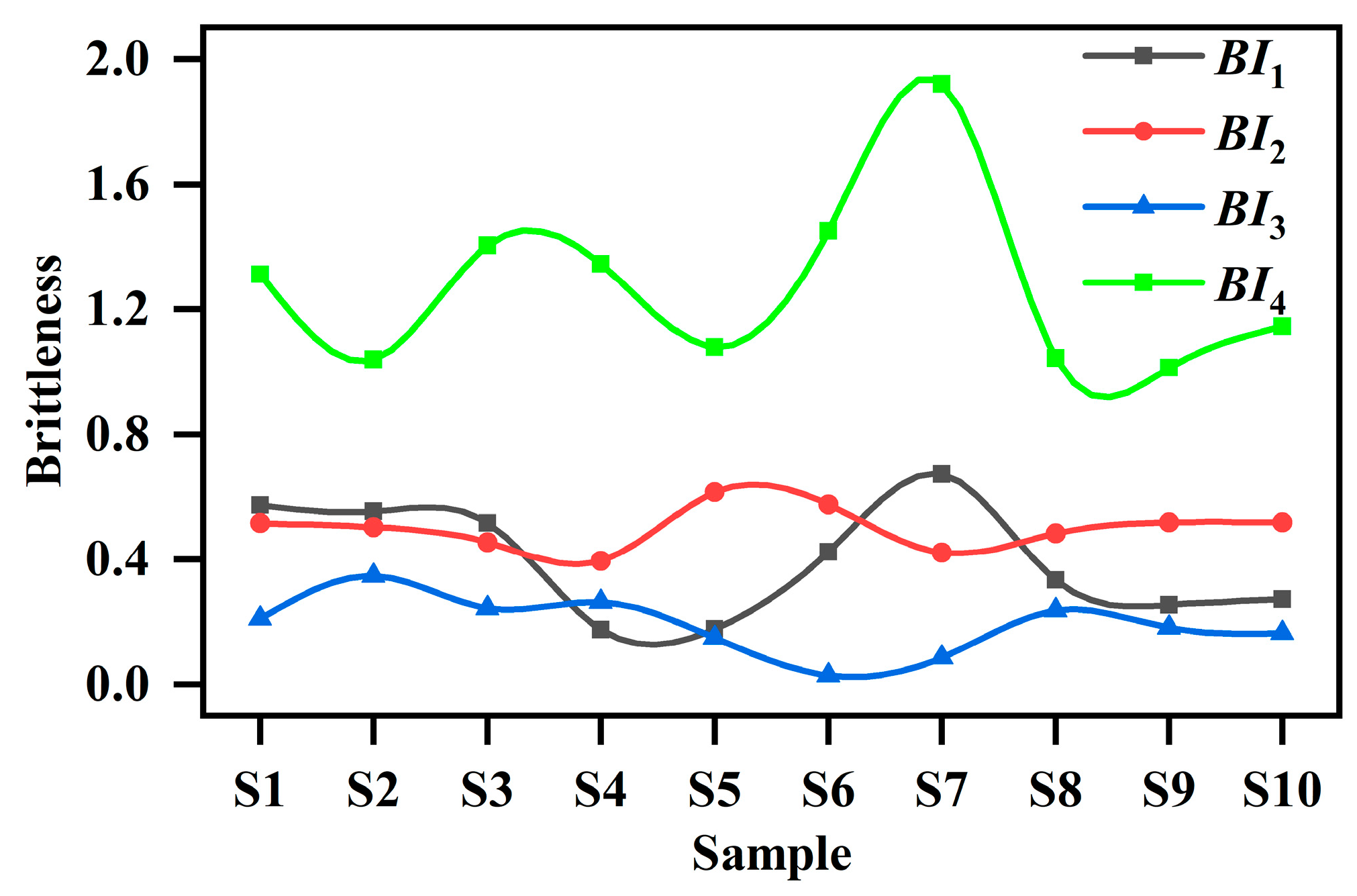
4.4. Brittleness
4.5. Influencing Factors of Brittleness
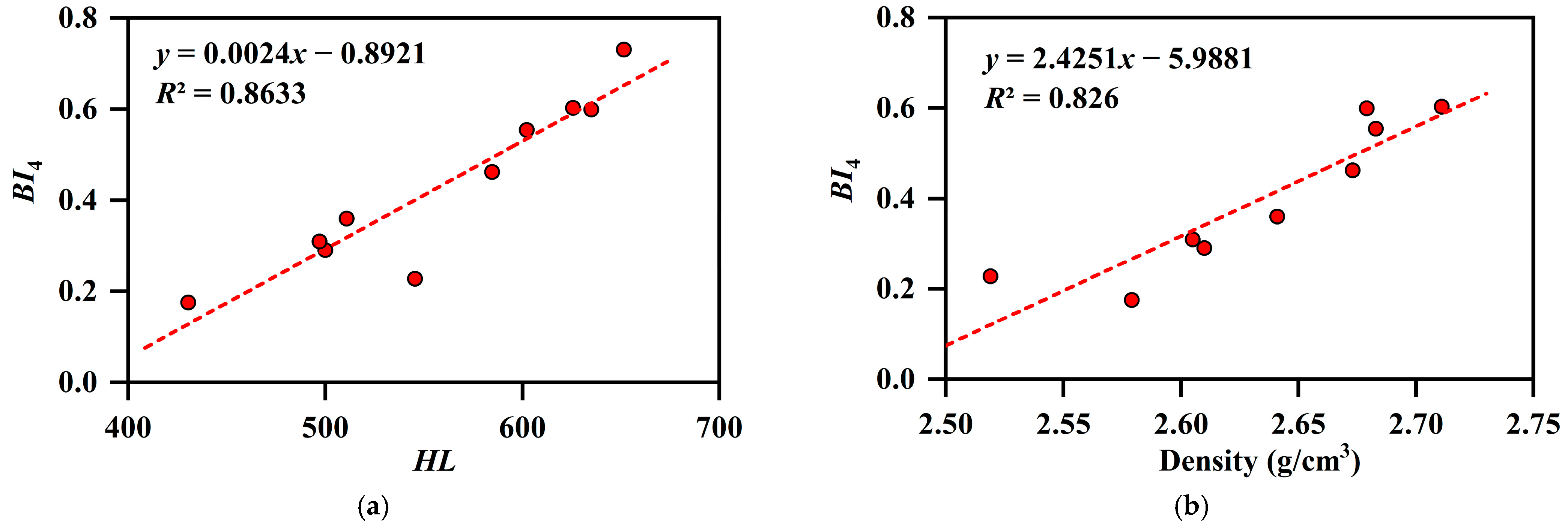
4.5.1. Effects of Hardness and Density on Brittleness
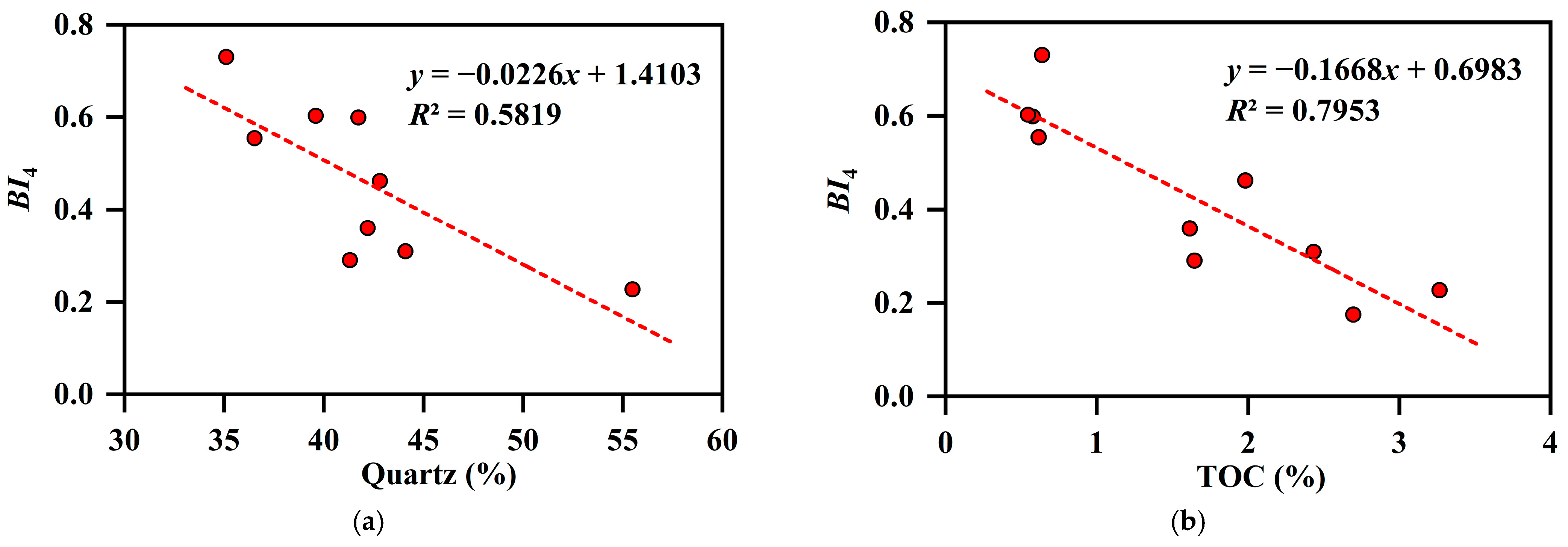
4.5.2. Effects of Organic Matter on Brittleness
4.5.3. Effects of Mineral Compositions on Brittleness
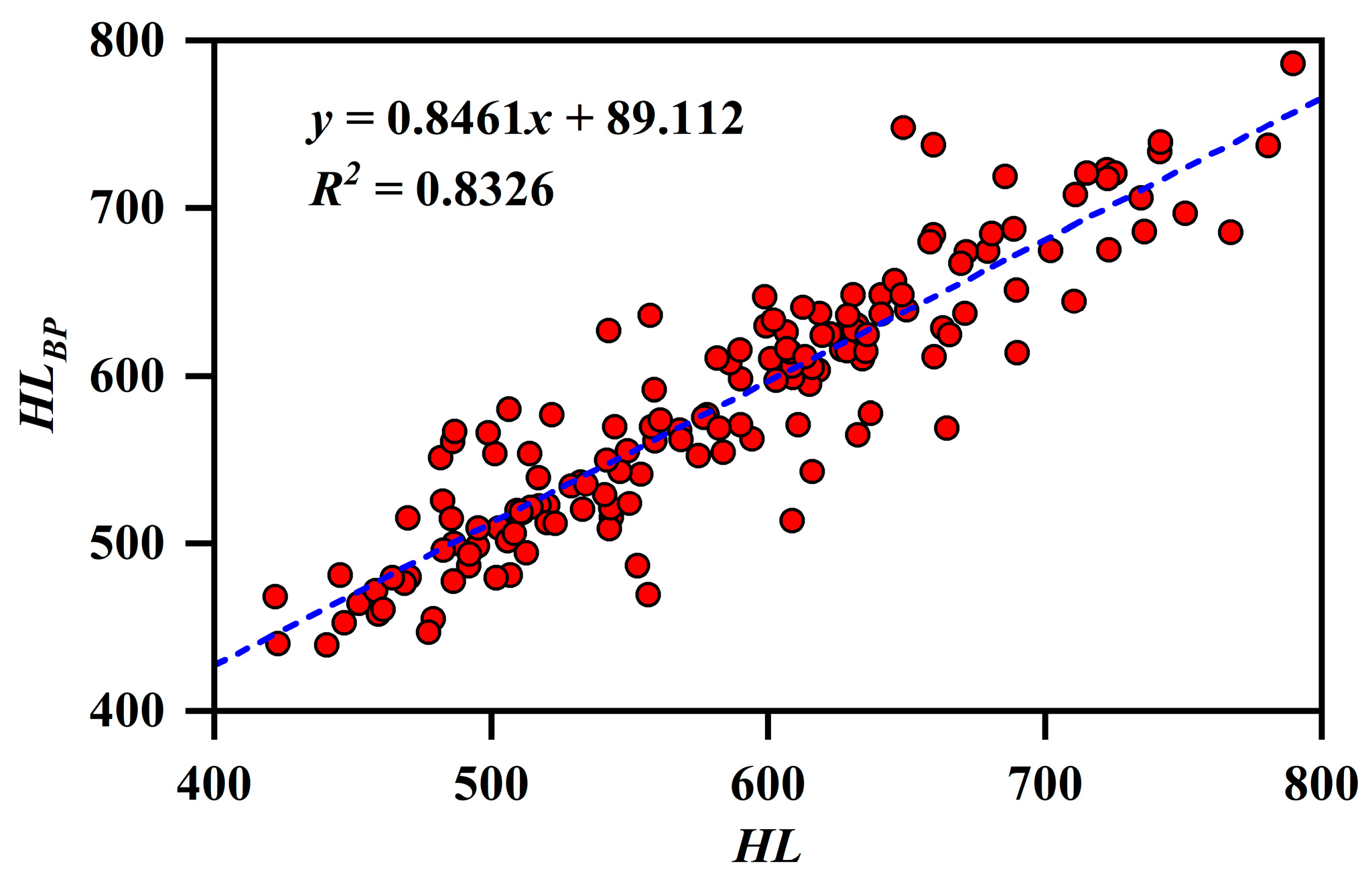
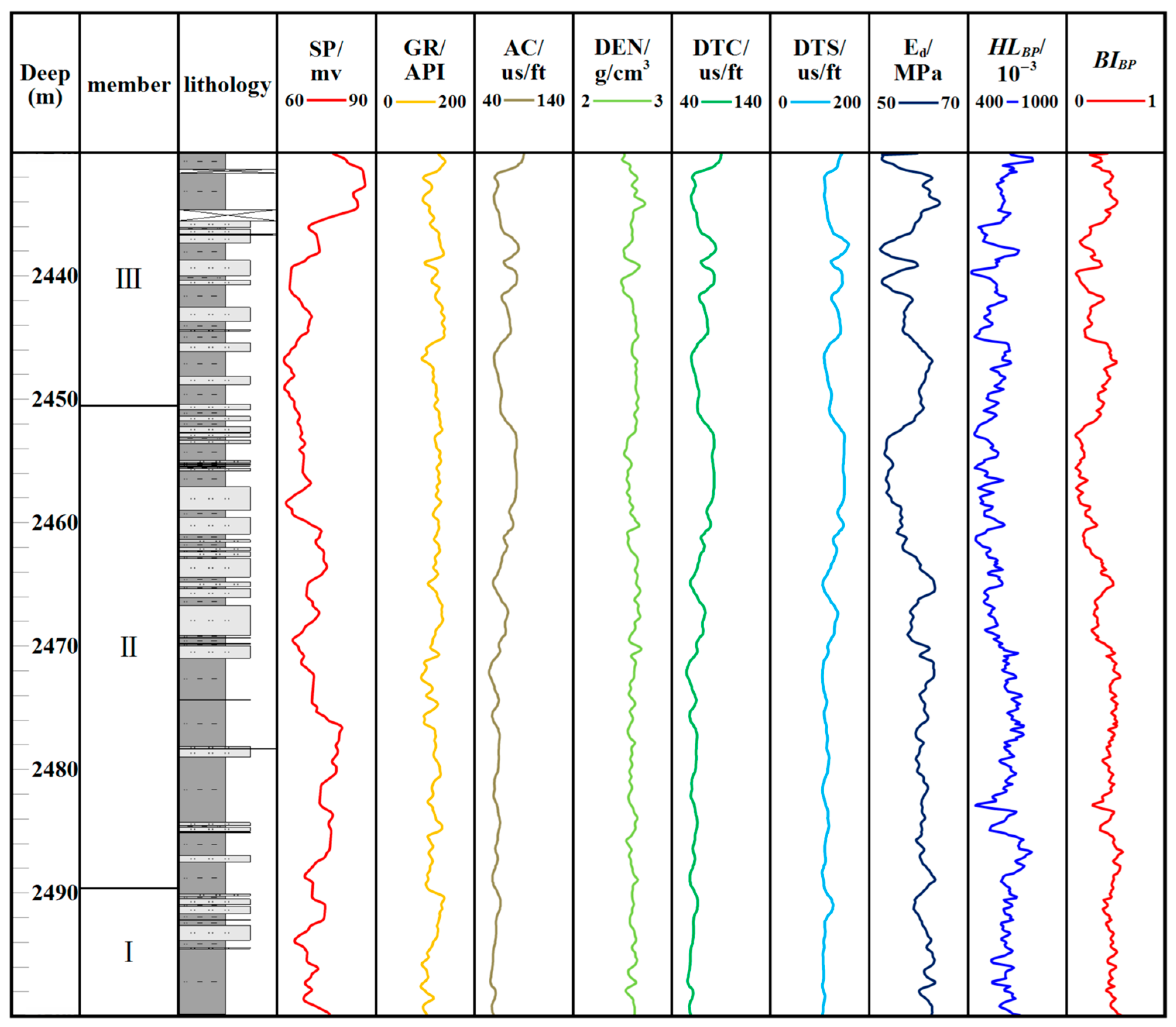
4.6. Shale Brittleness Prediction of Well XQ1
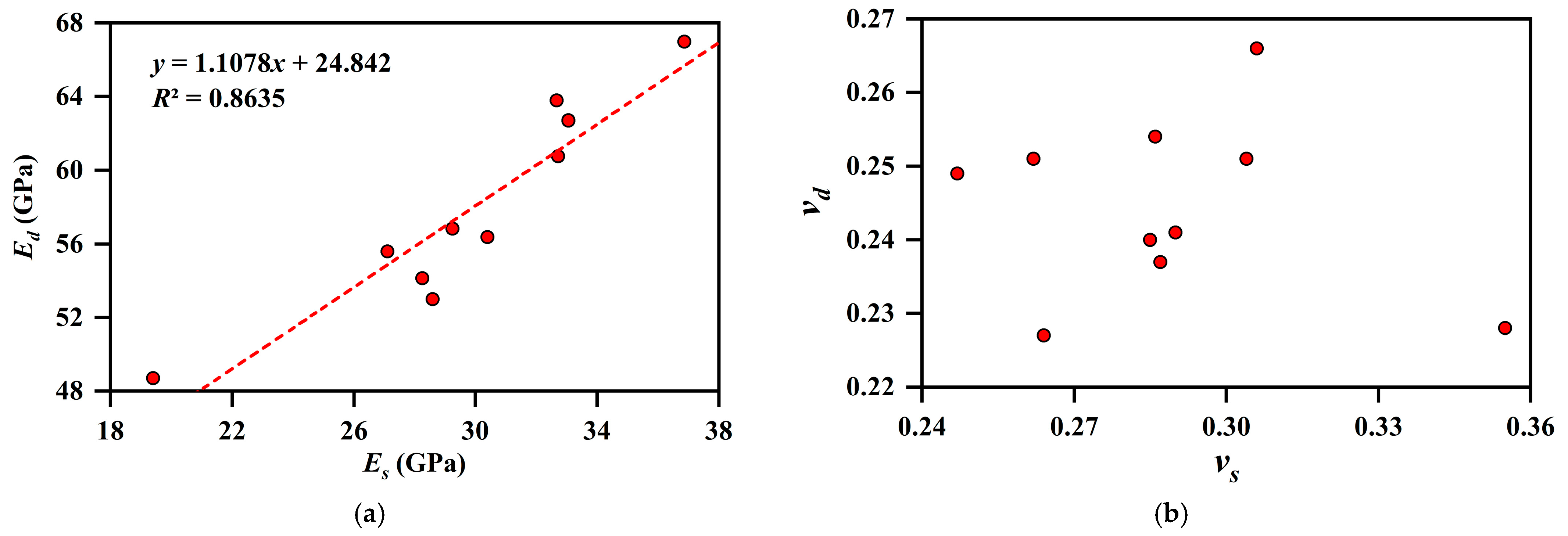
4.6.1. Calculation of Dynamic Modulus of Elasticity and Conversion of Dynamic and Static Modulus of Elasticity
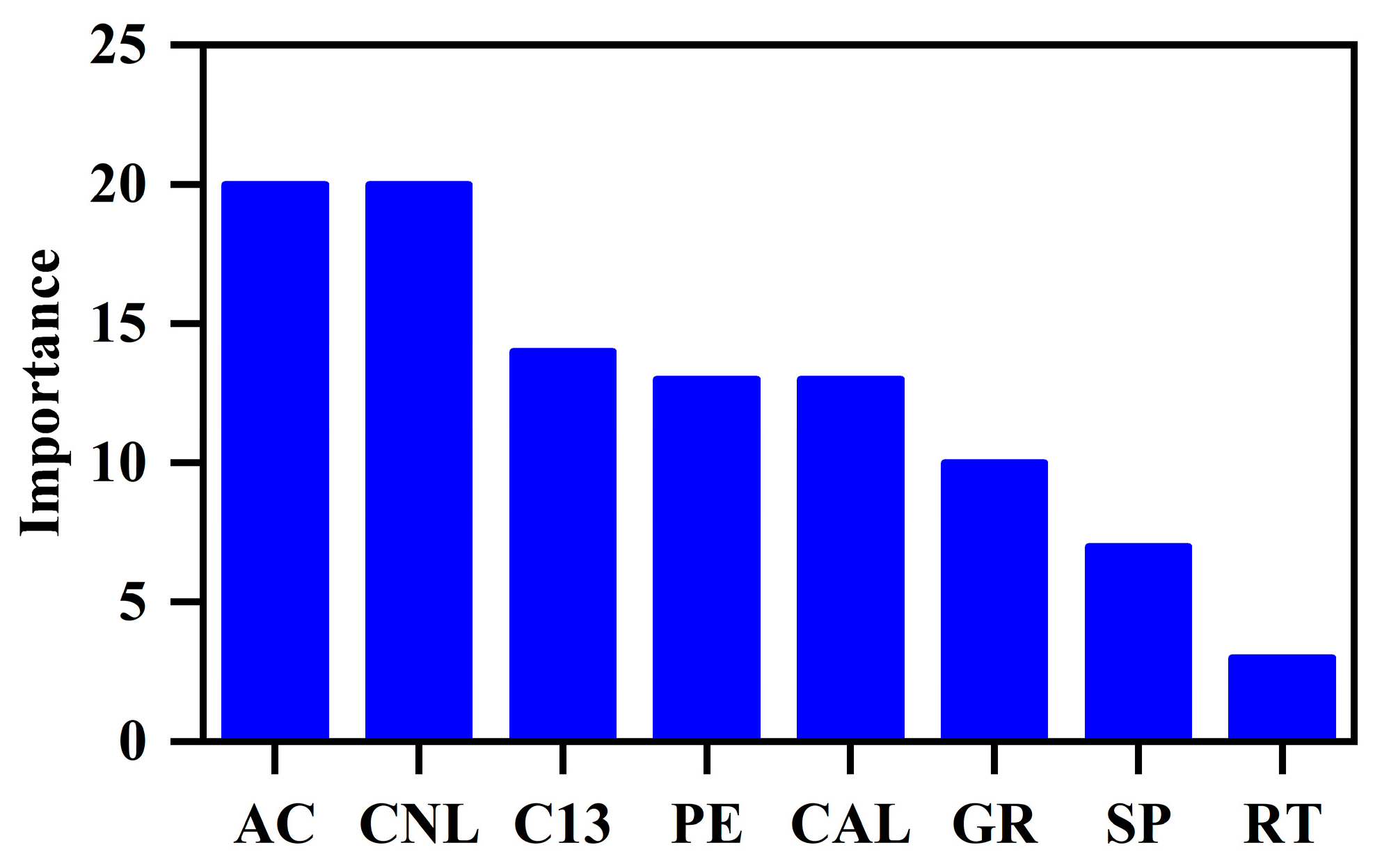
4.6.2. Hardness Prediction
4.6.3. Brittleness Prediction
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Jia, C.; Zheng, M.; Zhang, Y. Unconventional hydrocarbon resources in China and the prospect of exploration and development. J. Oil Gas Geol. 2012, 39, 129–136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, B.; Lv, Y.; Ran, Q.; Dai, C.; Li, M.; Wang, M. Geological conditions and exploration potential of shale oil in the Qingshankou Formation, Northern Songliao Basin. J. Oil Gas Geol. 2014, 2, 280–285. [Google Scholar]
- Zhao, X.; Zhou, L.; Pu, X.; Jin, F.; Han, W.; Xiao, D.; Chen, S.; Shi, Z.; Zhang, W.; Yang, F. Geological characteristics of shale rock system and shale oil exploration breakthrough in a lacustrine basin, A case study from the Paleogene 1st sub-member of Kong 2 Member in Cangdong sag, Bohai Bay Basin, China. J. Pet. Explor. Dev. 2018, 45, 361–372. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, B.; Chen, E. Drilling Technologies for Horizontal Shale Oil Well Fan Yeping 1 in the Shengli Oilfield. J. Pet. Drill. Tech. 2021, 49, 53–58. [Google Scholar]
- Yang, Z.; Hou, L.; Lin, S.; Luo, X.; Zhang, L.; Wu, S.; Cui, J. Geologic characteristics and exploration potential of tight oil and shale oil in Lucaogou Formation in Jimsar sag. J. China Pet. Explor. 2018, 23, 76–85. [Google Scholar]
- Wu, X.; Gao, B.; Ye, X.; Bian, R.; Nie, H.; Lu, F. Shale oil accumulation conditions and exploration potential of faulted basins in the east of China. J. Oil Gas Geol. 2013, 34, 455–462. [Google Scholar]
- Li, J.; Lu, S.; Xie, L.; Zhang, J.; Xue, H.; Zhang, P.; Tian, S. Modeling of hydrocarbon adsorption on continental oil shale, A case study on n-alkane. Fuel 2017, 206, 603–613. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Lu, S.; Cai, J. Adsorbed and Free Oil in Lacustrine Nanoporous Shale, A Theoretical Model and a Case Study. J. Energy Fuels 2018, 32, 12247–12258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, Z.; Li, J.; Wang, M. Organic fluid migration in low permeability reservoirs restricted by pore structure parameters. J. J. Pet. Sci. Eng. 2022, 218, 111028. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zou, C.; Zhu, R.; Wu, S.; Yang, Z.; Tao, S.; Yuan, X.; Hou, L.; Yang, H.; Xu, C.; Li, D.; et al. Types, characteristics, genesis and prospects of conventional and unconventional hydrocarbon accumulations: Taking tight oil and tight gas in China as an instance. J. Acta Pet. Sin. 2012, 33, 173–187. [Google Scholar]
- Zou, C.; Zhu, R.; Bai, B.; Yang, Z.; Wu, S.; Su, L.; Dong, D.; Li, X. First discovery of nano-pore throat in oil and gas reservoir in China and its scientific value. J. Acta Pet. Sin. 2011, 27, 1857–1864. [Google Scholar]
- Li, S.; Kuang, Z.; Qiu, S.; Zheng, H. Review of review of rock brittleness evaluation methods and discussion on their adaptabilities. J. Eng. Geol. 2022, 30, 59–70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zou, C.; Yang, Z.; Cui, J.; Zhu, R.; Hou, L.; Tao, S.; Yuan, X.; Wu, S.; Lin, S.; Wang, L.; et al. Formation mechanism, geological characteristics and development strategy of nonmarine shale oil in China. J. Pet. Explor. Dev. 2013, 40, 14–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, S.; Yan, T.; Li, W. Fractal representation of rock drillability. J. Acta Pet. Sin. 2006, 1, 124–127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, Y.; Xin, Y.; Li, L.; Zhang, B.; Jiang, S. Influence factors and evaluation methods of the gas shale fracability. J. Earth Sci. Front. 2012, 19, 356–363. [Google Scholar]
- Morley, A. Strength of Materials, with 260 Diagrams and Numerous Examples; Longmans, Green and Company: Harlow, UK, 1944. [Google Scholar]
- Hetenyi, M. Handbook of Experimental Stress Analysis; Wiley: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 1950. [Google Scholar]
- Howell, J.V. Glossary of Geology and Related Sciences; American Geological Institute: Washington, DC, USA, 1960. [Google Scholar]
- Obert, L.; Duvall, W. Rock Mechanics and the Design of Structures in Rock; Wiley: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 1967. [Google Scholar]
- Hucka, V.D.B. Brittleness determination of rocks by different methods. J. Int. J. Rock 1974, 11, 389–392. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jarvie, D.M.; Hill, R.J.; Ruble, T.E.; Pollastro, R.M. Unconventional shale-gas systems, the Mississippian Barnett shale of north-central Texas as one mode for thermogenic shale-gas assessment. J. AAPG Bull. 2007, 91, 3005–3009. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, J.; Xiao, X. Mineral composition and brittleness of three sets of Paleozoic organic-rich shales in China South area. J. J. China Coal Soc. 2013, 38, 822–826. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Andreev, G.E. Brittle Failure of Rock Materials; CRC Press: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 1995. [Google Scholar]
- Hajiabdolmajid, V.; Kaiser, P. Brittleness of rock and stability assessment in hard rock tunneling. J. Tunn. Undergr. Space Technol. 2003, 18, 35–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Altindag, R. Correlation of specific energy with rock brittleness concepts on rock cutting. J. South Afr. Inst. Min. Metall. 2003, 103, 163–171. [Google Scholar]
- Lawn, B.R.; Marshall, D.B. Hardness, toughness, and brittleness, an indentation analysis. J. Am. Ceram. Soc. 1979, 62, 347–350. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Honda, H.; Sanada, Y. Hardness of coal. J. Fuel 1956, 35, 451–461. [Google Scholar]
- Du, J.; Cai, J.; Long, S.; Gao, B.; Feng, D.; Peng, Z.; Zeng, X. The Control of Diagenesis and Mineral Assemblages on Brittleness of Mudstones. J. Front. Earth Sci. 2021, 9, 758046. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuan, J.; Deng, J.; Zhang, D.; Li, D.; Yan, W.; Chen, C.; Cheng, L.; Chen, Z. Fracability evaluation of shale-gas reservoirs. J. Acta Pet. Sin. 2013, 34, 523–527. [Google Scholar]
- Bishop, A.W. Progressive failure with special reference to the mechanism causing it. In Proceedings of the Geotechnical Conference, Oslo, Norway; Norwegian Geotechnical Institute: Oslo, Norway, 1967; pp. 142–150. [Google Scholar]
- Li, J. Rock Mechanics; Chongqing University Press: Chongqing, China, 2014; Volume 9, p. 318. [Google Scholar]
- Magoon, L.; Dow, W. The Petroleum System—From Source to Trap. J. AAPG Memoir. 1991, 14, 627. [Google Scholar]
- Burton, Z.; Moldowan, J.M.; Sykes, R.; Graham, S. Unraveling petroleum degradation, maturity, and mixing and addressing impact on petroleum prospectivity: Insights from frontier exploration regions in New Zealand. J. Energy Fuels 2018, 32, 1287–1296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Burton, Z.; Moldowan, J.M.; Magoon, L.; Sykes, R.; Graham, S. Interpretation of source rock depositional environment and age from seep oil, east coast of New Zealand. J. Int. J. Earth Sci. 2019, 108, 1079–1091. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thompson-Butler, W.; Peters, K.E.; Magoon, L.B.; Scheirer, A.H.; Wavrek, D.A. Identification of genetically distinct petroleum tribes in the Middle Magdalena Valley, Colombia. J. AAPG Bull. 2019, 103, 3003–3034. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Du, Y.; Liu, Y.; Li, W.; He, S.; Wang, X.; Pang, Q.; Huang, D. Basic characteristics and exploration direction of lacustrine shale oil and gas in Da’anzhai member of Jurassic in Sichuan Basin. J. Geol. China 2022, 49, 51–65. [Google Scholar]
- Li, D. Innovation of petroleum geology in China. J. Oil Gas Geol. 2007, 1, 1–11. [Google Scholar]
- Zou, C.; Yang, Z.; Wang, H.; Dong, D.; Liu, H.; Shi, Z.; Zhang, B.; Sun, S.; Liu, D.; Li, G.; et al. “ Exploring petroleum inside source kitchen”: Jurassic unconventional continental giant shale oil &gas field in Sichuan basin, China. J. Acta Geol. Sin. 2019, 93, 1551–1562. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, Y.; Bai, X.; Meng, Q.; Li, J.; Zhang, D.; Wang, Y. Accumulation geological characteristics and major discoveries of lacustrine shale oil in Sichuan Basin. J. Acta Pet. Sin. 2022, 43, 885–898. [Google Scholar]
- Li, Y.; Wang, Z.; Pan, Z.; Niu, X.; Yu, Y.; Meng, S. Pore structure and its fractal dimensions of transitional shale: A cross-section from east margin of the Ordos Basin, China. J. Fuel 2019, 241, 417–431. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Yang, J.; Pan, Z.; Tong, W. Nanoscale pore structure and mechanical property analysis of coal: An insight combining AFM and SEM images. J. Fuel 2020, 260, 116–352. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Z.; Liang, R.; Li, Q.; Zhang, L.; Cheng, H. Experimental Study on Rockburst Characteristics of Granite Under True Triaxial Stress Path. J. Min. Res. Dev. 2022, 42, 86–91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rickman, R.; Mullen, M.; Petre, E.; Grieser, B.; Kundert, D. A practical use of shale petrophysics for stimulation design optimization, all shale plays are not clones of the Barnett shale. In Proceedings of the SPE Annual Technical Conference and Exhibition, Denver, CO, USA, 21–24 September 2008. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boris, T.; Yves, P. Universal criteria for rock brittleness estimation under triaxial compression. J. Int. J. Rock Mech. Min. Sci. 2013, 59, 57–69. [Google Scholar]
- Espitalie, J.; Madec, M.; Tissot, B.; Fran-Ais, I.; Petrole, J.; Mennig, P. Source rock characterization method for petroleum exploration. In Proceedings of the Offshore Technology Conference, Houston, TX, USA, 5–8 May 1997. [Google Scholar]
- Peters, K.E. Guidelines for evaluating petroleum source rock using programmed pyrolysis. J. AAPG Bull. 1986, 70, 318–329. [Google Scholar]
- Vandenbroucke, M.; Largeau, C. Kerogen origin, evolution and structure. J. Org. Geochem. 2007, 38, 719–833. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, J.; Wu, S.; Wu, F. The classification and evaluation criterion of low permeability reservoir:An example from Ordos Basin. J. Lithol. Reserv. 2007, 3, 28–31+53. [Google Scholar]
- Zeng, D.; Li, S. Types and geological characteristics of low permeability sandstone reservoirs in China. J. Acta Pet. Sin. 1994, 1, 38–46. [Google Scholar]
- Tian, D.; Harris, N.B.; Ayranci, K.; Twemlow, C.E. The impact of composition on pore throat size and permeability in high maturity shales, Middle and Upper Devonian Horn River Group, northeastern British Columbia, Canada. J. Mar. Pet. Geol. 2017, 81, 220–236. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, S. Study on the main controlling factors of brittleness and compressibility classification evaluation for tight reservoirs. D. Northeast. Pet. Univ. 2021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, P. ; Elastic Wave Theory; China Science Publishing: Beijing, China, 2021. [Google Scholar]
- Ma, J.; Sun, J. Calculation of formation stress using logging data. J. Well Logging Technol. 2002, 04, 347–352. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, K.; Fang, J.; Gao, K.; Liu, T. Study on Calculation Method of Lithologic Physical Property Parameters Based on Neural Network. J. Comput. Technol. Dev. 2022, 32, 186–191+197. [Google Scholar]

| Sample | Depth/m | Tmax/°C | S1/(mg·g−1) | S2/(mg·g−1) | TOC/wt.% | HI |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| S1 | 2434.17 | 447 | 0.37 | 1.37 | 0.93 | 147.80 |
| S2 | 2435.38 | 449 | 0.09 | 0.36 | 0.54 | 108.63 |
| S3 | 2435.71 | 450 | 0.11 | 0.46 | 0.62 | 131.06 |
| S4 | 2436.41 | 446 | 2.83 | 11.38 | 2.69 | 504.41 |
| S5 | 2438.86 | 446 | 4.13 | 17.25 | 3.27 | 528.17 |
| S6 | 2444.13 | 447 | 1.73 | 7.89 | 1.98 | 398.28 |
| S7 | 2449.74 | 448 | 0.12 | 0.35 | 0.64 | 115.10 |
| S8 | 2451.51 | 447 | 0.92 | 5.27 | 1.61 | 326.52 |
| S9 | 2454.82 | 444 | 1.25 | 5.58 | 1.65 | 339.21 |
| S10 | 2455.76 | 447 | 1.46 | 8.26 | 2.43 | 339.36 |
| Sample | Clay/% | Quartz/% | Orthoclase/% | Feldspar/% | Calcite/% | Dolomite/% | Pyrite/% |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| S1 | 47.79 | 41.72 | 0.00 | 9.27 | 0.61 | 0.00 | 0.00 |
| S2 | 49.10 | 39.58 | 0.00 | 9.84 | 0.77 | 0.00 | 0.00 |
| S3 | 54.06 | 36.52 | 0.00 | 8.37 | 0.00 | 0.00 | 0.00 |
| S4 | 59.25 | 33.54 | 0.00 | 4.96 | 0.65 | 0.00 | 0.86 |
| S5 | 37.40 | 55.50 | 0.70 | 3.20 | 1.00 | 0.00 | 2.20 |
| S6 | 42.50 | 42.80 | 1.30 | 13.20 | 0.00 | 0.00 | 0.20 |
| S7 | 44.80 | 44.10 | 1.00 | 5.60 | 2.20 | 2.00 | 0.30 |
| S8 | 50.50 | 42.20 | 1.10 | 3.90 | 1.20 | 0.00 | 1.10 |
| S9 | 45.60 | 41.30 | 0.20 | 7.50 | 0.70 | 0.00 | 4.70 |
| S10 | 47.50 | 44.10 | 0.90 | 5.90 | 0.00 | 0.00 | 1.60 |
| Sample | Depth/m | Porosity/% | Permeability/mD | Density/cm3 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| S1 | 2434.17 | 1.89 | 0.004 | 2.679 |
| S2 | 2435.38 | 4.65 | 0.244 | 2.567 |
| S3 | 2435.71 | 2.68 | 0.567 | 2.616 |
| S4 | 2436.41 | 4.89 | 0.463 | 2.454 |
| S5 | 2438.86 | 5.79 | 0.129 | 2.419 |
| S6 | 2444.13 | 4.58 | 0.845 | 2.505 |
| S7 | 2449.74 | 2.16 | 0.498 | 2.630 |
| S8 | 2451.51 | 1.49 | 0.100 | 2.594 |
| S9 | 2454.82 | 1.35 | 1.036 | 2.578 |
| S10 | 2455.76 | 2.08 | 0.465 | 2.559 |
| Sample | Failure Deviatoric Stress/MPa | Residual Stress/MPa | Compressive Strength/MPa | Young’s Modulus/GPa | Poisson’s Ratio |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| S1 | 186.1 | 147 | 222.1 | 33.06 | 0.251 |
| S2 | 225.2 | 147 | 261.2 | 32.67 | 0.251 |
| S3 | 178.2 | 135 | 214.2 | 32.72 | 0.254 |
| S4 | 118 | 87 | 154 | 28.59 | 0.228 |
| S5 | 133.8 | 114 | 169.8 | 19.4 | 0.227 |
| S6 | 123.4 | 120 | 159.4 | 29.24 | 0.24 |
| S7 | 179.2 | 164 | 215.2 | 36.86 | 0.249 |
| S8 | 141.4 | 108 | 177.4 | 30.4 | 0.266 |
| S9 | 145.2 | 119 | 181.2 | 27.1 | 0.241 |
| S10 | 114.8 | 96 | 150.8 | 28.25 | 0.237 |
| Samples | BI1 | BI2 | BI3 | BI4 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| S1 | 0.437 | 0.600 | 0.516 | 0.210 |
| S2 | 0.463 | 0.603 | 0.502 | 0.347 |
| S3 | 0.443 | 0.554 | 0.454 | 0.242 |
| S4 | 0.263 | 0.175 | 0.394 | 0.263 |
| S5 | 0.081 | 0.227 | 0.614 | 0.148 |
| S6 | 0.344 | 0.462 | 0.574 | 0.028 |
| S7 | 0.596 | 0.731 | 0.421 | 0.085 |
| S8 | 0.359 | 0.360 | 0.483 | 0.236 |
| S9 | 0.279 | 0.290 | 0.518 | 0.180 |
| S10 | 0.314 | 0.310 | 0.517 | 0.164 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Huang, H.; Lu, S.; Zhang, P.; Zhi, Q.; Wang, J.; Lin, Z. Evaluation of Lacustrine Shale Brittleness and Its Controlling Factors: A Case Study from the Jurassic Lianggaoshan Formation, Sichuan Basin. Processes 2023, 11, 493. https://doi.org/10.3390/pr11020493
Huang H, Lu S, Zhang P, Zhi Q, Wang J, Lin Z. Evaluation of Lacustrine Shale Brittleness and Its Controlling Factors: A Case Study from the Jurassic Lianggaoshan Formation, Sichuan Basin. Processes. 2023; 11(2):493. https://doi.org/10.3390/pr11020493
Chicago/Turabian StyleHuang, Hongsheng, Shuangfang Lu, Pengfei Zhang, Qi Zhi, Junjie Wang, and Zizhi Lin. 2023. "Evaluation of Lacustrine Shale Brittleness and Its Controlling Factors: A Case Study from the Jurassic Lianggaoshan Formation, Sichuan Basin" Processes 11, no. 2: 493. https://doi.org/10.3390/pr11020493
APA StyleHuang, H., Lu, S., Zhang, P., Zhi, Q., Wang, J., & Lin, Z. (2023). Evaluation of Lacustrine Shale Brittleness and Its Controlling Factors: A Case Study from the Jurassic Lianggaoshan Formation, Sichuan Basin. Processes, 11(2), 493. https://doi.org/10.3390/pr11020493






