Occurrence Characteristics of Chang 7 Shale Oil from the Longdong Area in the Ordos Basin: Insights from Petrology and Pore Structure
Abstract
:1. Introduction
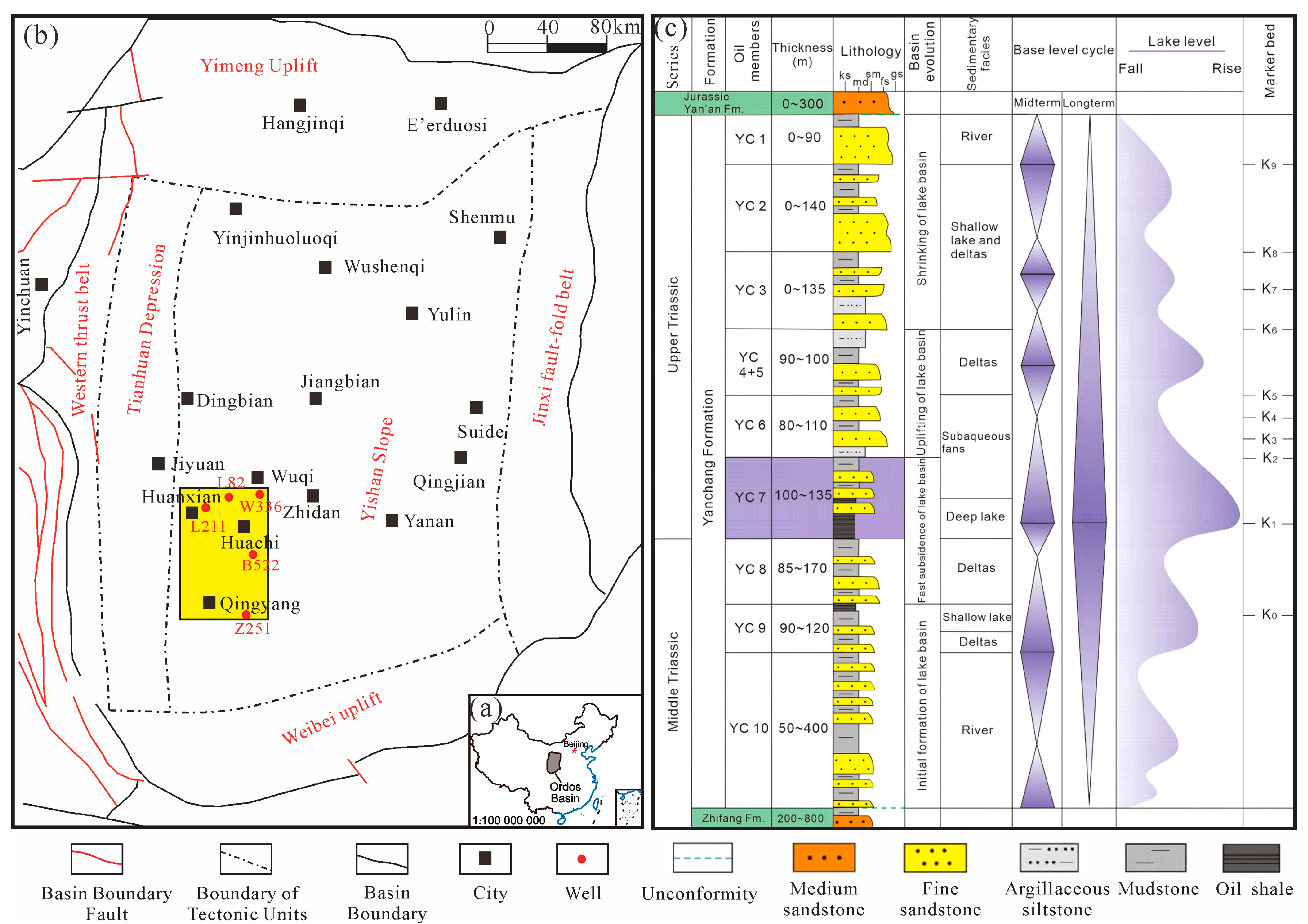
2. Geological Setting
3. Materials and Methods
3.1. Samples
3.2. XRD and FE-SEM
3.3. Gas Adsorption and NMR Measurements
3.4. TOC Analysis, Rock–Eval, Ro, and GC–MS
4. Results
4.1. Petrology and Organic Geochemistry Characteristics
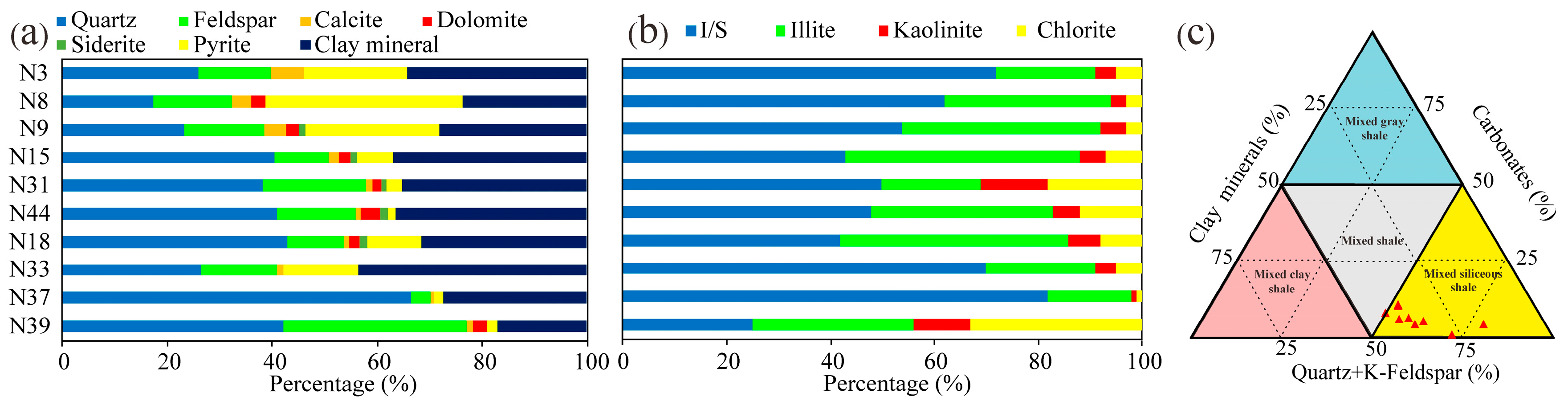
4.1.1. Mineralogy
4.1.2. Shale Lithofacies Identification
4.1.3. Organic Petrology
4.1.4. TOC, Rock–Eval Pyrolysis, Biomarker Characteristics, and Ro
4.2. Pore Characteristics
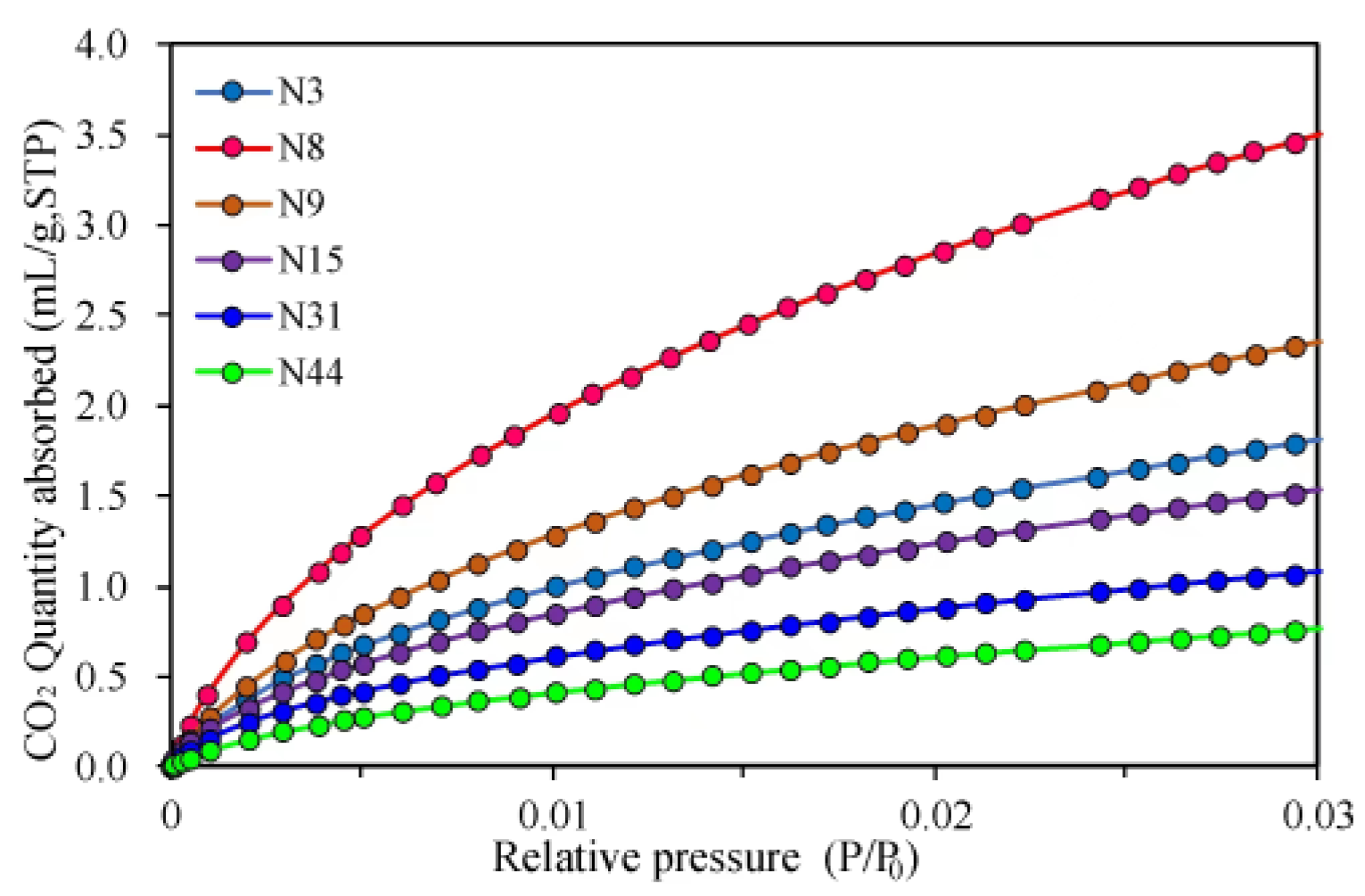
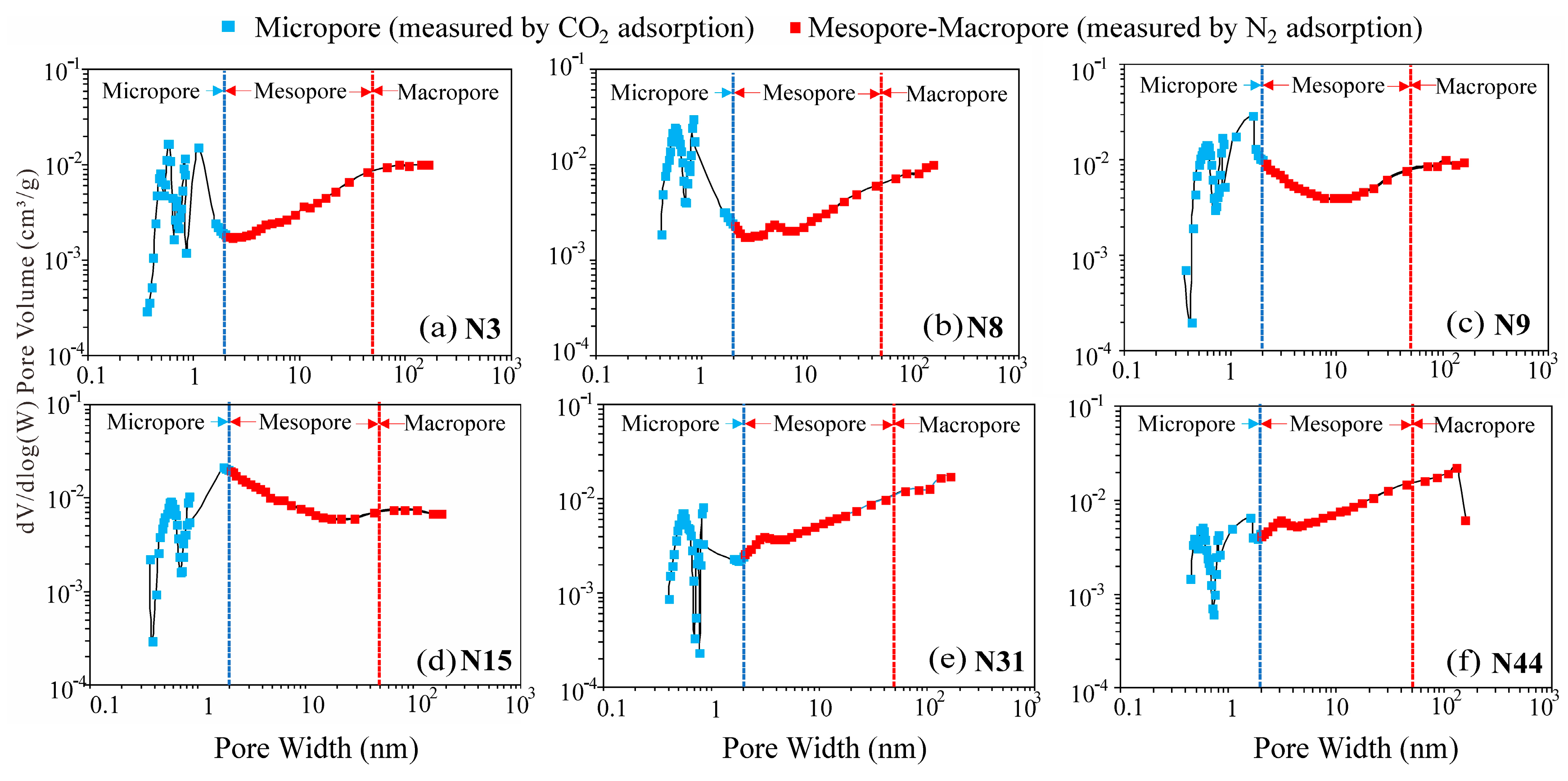
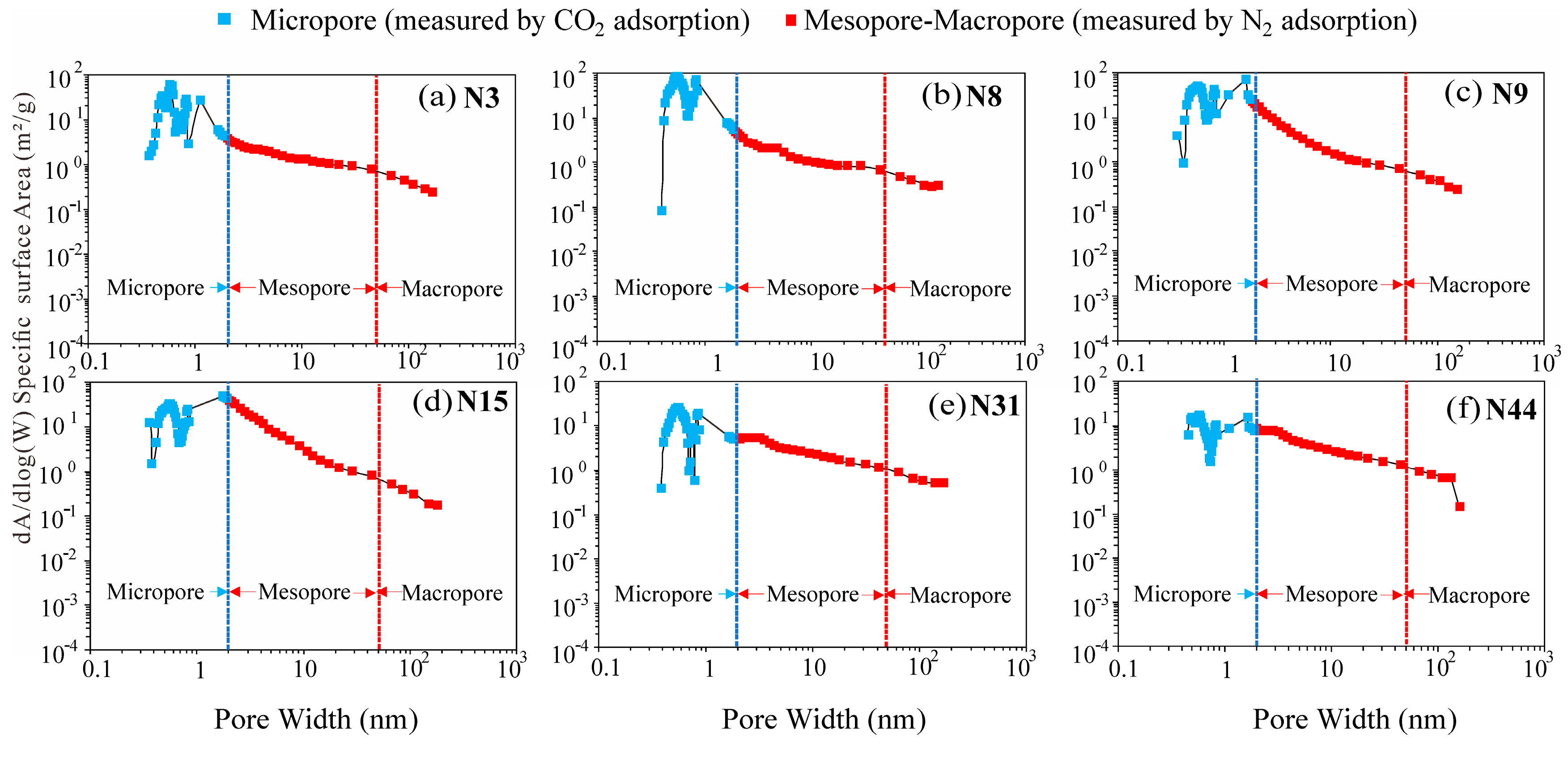
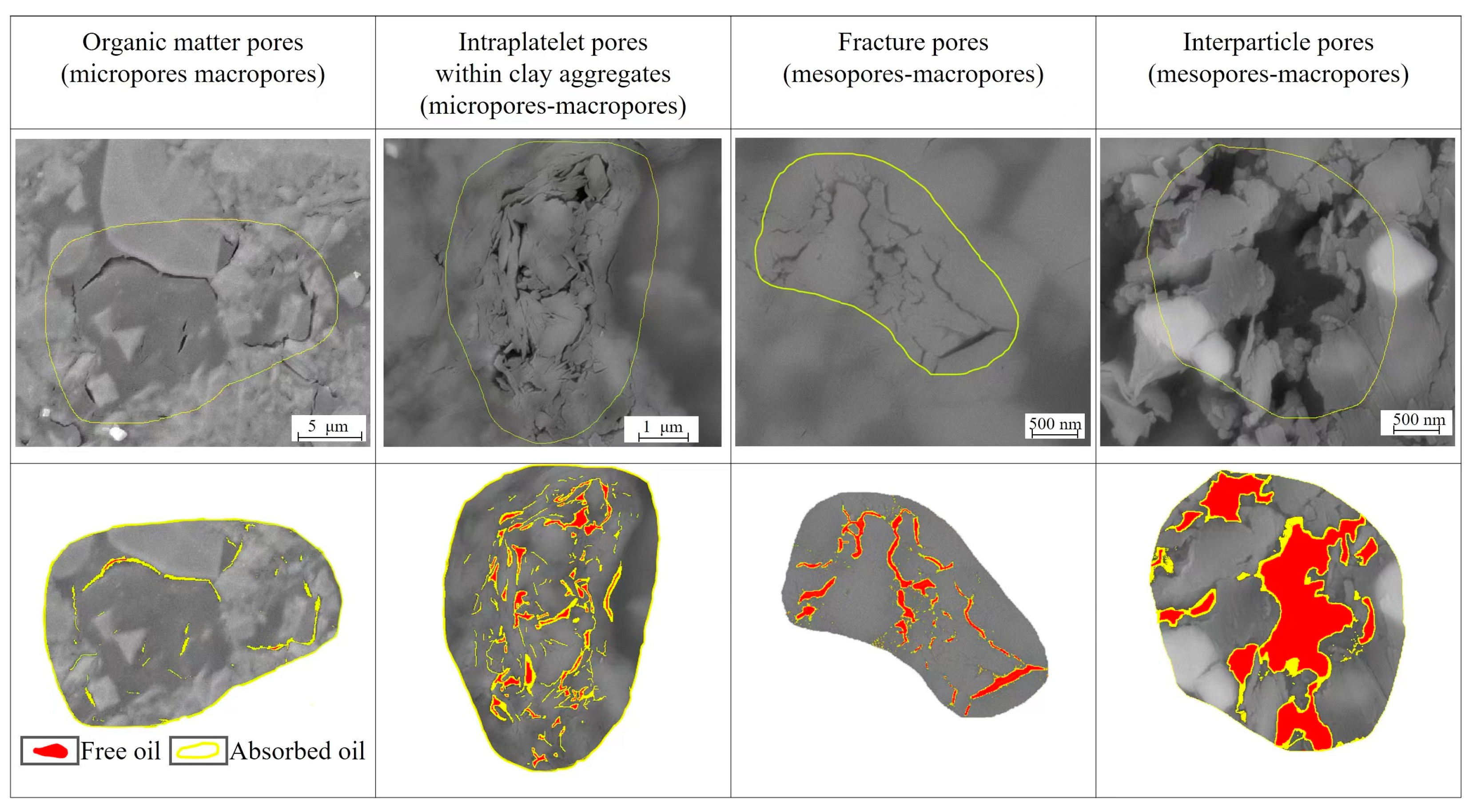
4.2.1. Pore Type Classification
4.2.2. Pore Distribution Characteristics
4.3. Oil Content
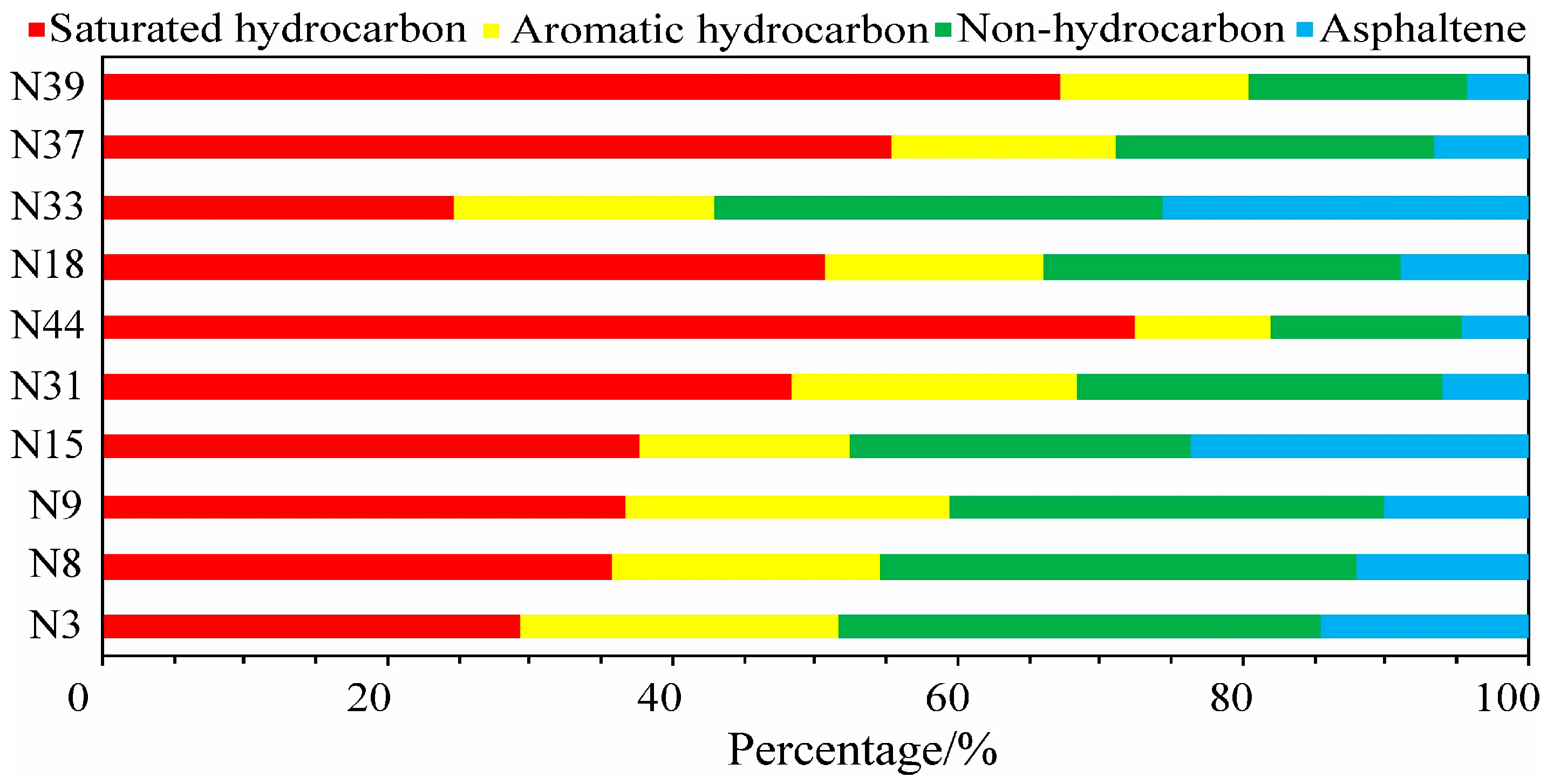
4.3.1. Geochemical Characteristics
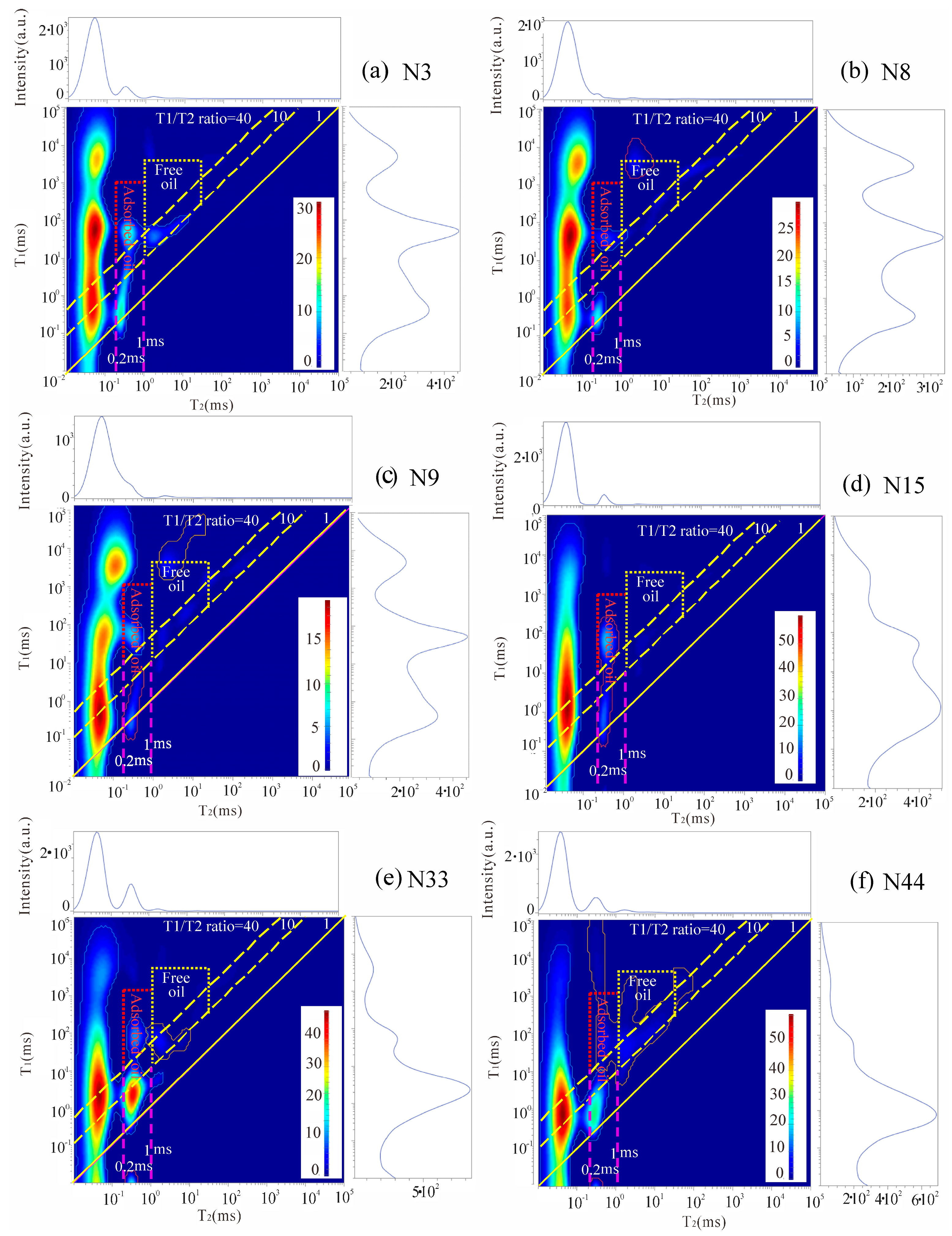
4.3.2. NMR T1–T2 Map
5. Discussion
5.1. Effects of Composition on Pore Structure
5.2. Pore Size Characteristics
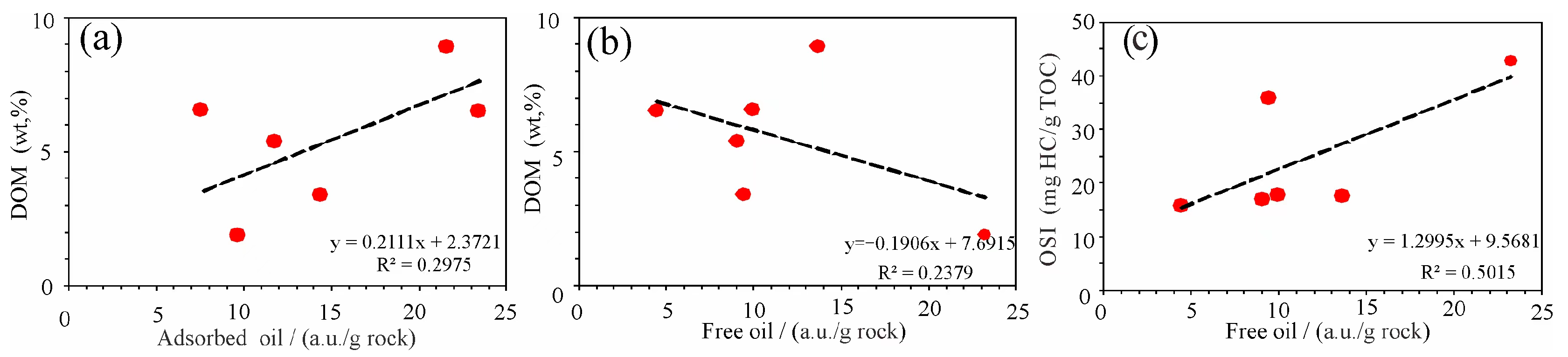
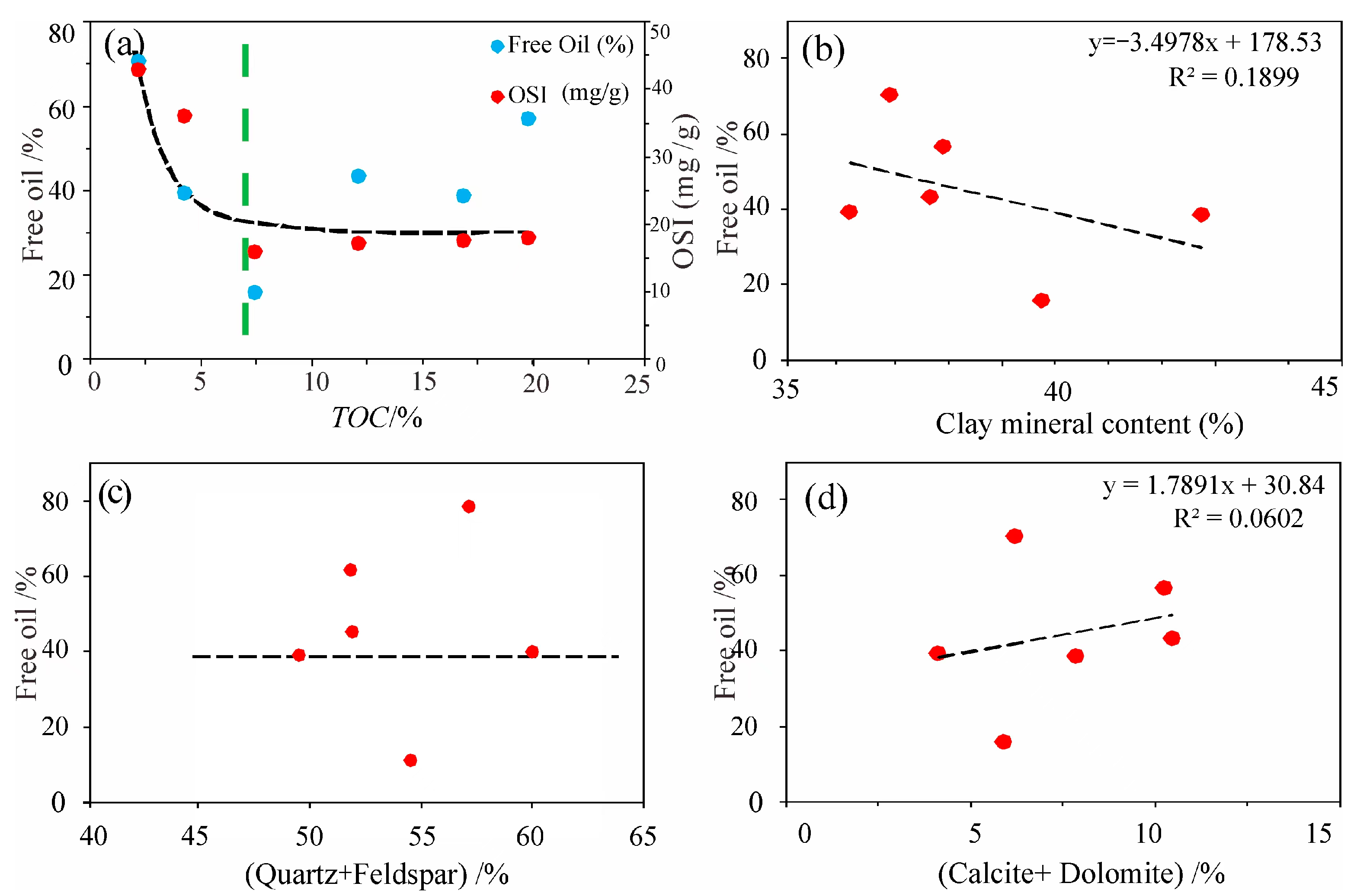
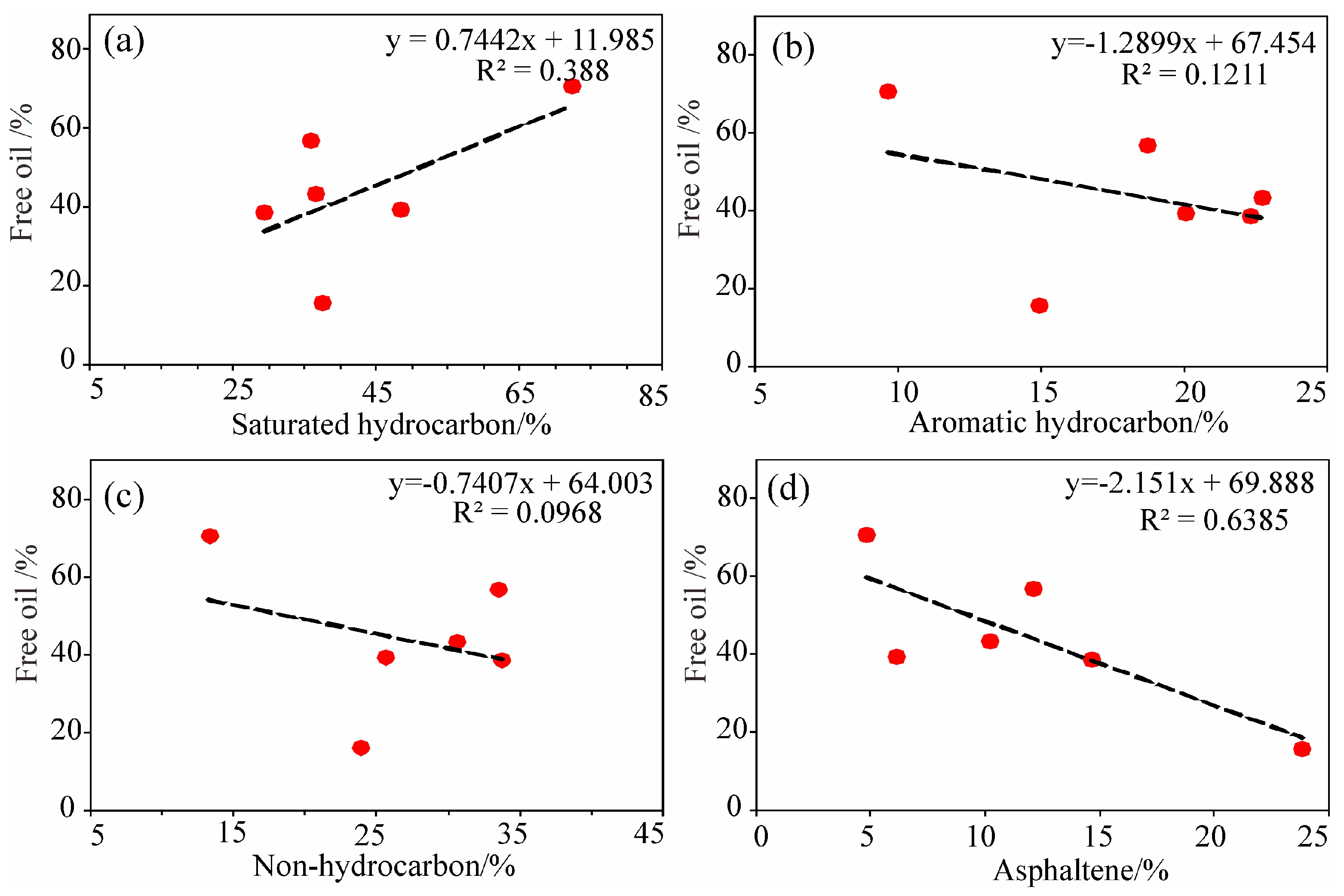
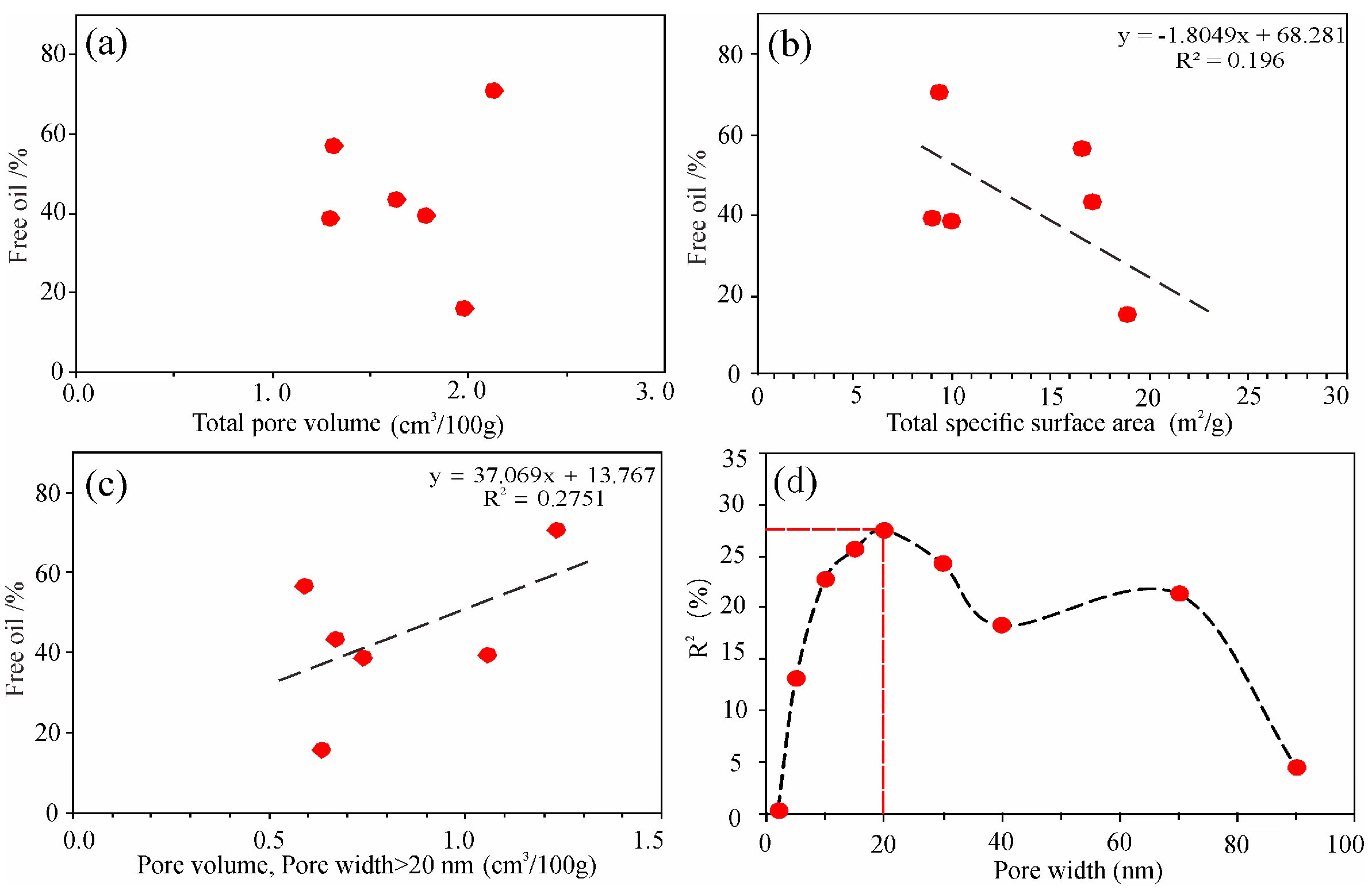
5.3. Factors Influencing Free Oil
5.3.1. OM Abundance and Mineral Composition
5.3.2. Shale Oil Composition
5.3.3. Pore Volume and Pore Surface Area
5.4. Modes of Occurrence of Shale Oil
6. Conclusions
- (1)
- According to the analysis of the TOC, mineral composition, and rock structure, two types of shale lithofacies are identified: OM-rich laminated felsic shale and OM-rich massive felsic mudstone;
- (2)
- The pore space is composed of IntraP pores, InterP pores, fracture pores, and OM pores. The pore shape is predominantly slit-type pores. Micropore development is primarily influenced by OM and pyrite. The development of macropores and mesopores is influenced by quartz and clay minerals. Feldspar mainly controls macropores;
- (3)
- Based on the T1–T2 map, the free oil content was obtained, which has good consistency with the OSI. The proportion of free oil is inversely correlated with the TOC and clay mineral contents but positively related to the saturated hydrocarbon and PV values of pores larger than 20 nm;
- (4)
- The modes of shale oil occurrence in various pores were preliminarily established. OM pores mainly contain adsorbed oil. InterP pores and fracture pores are mainly occupied by free oil. The proportion of adsorbed oil in the IntraP pores is higher than that in the InterP pores of the same size. These findings help us to preliminarily understand the mode of shale oil occurrence. The next step involves quantitatively characterizing the mode of shale oil occurrence.
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Kinley, T.J.; Cook, L.W.; Breyer, J.A.; Jarvie, D.M.; Busbey, A.B. Hydrocarbon potential of the Barnett Shale (Mississippian), Delaware Basin, west Texas and southeastern New Mexico. AAPG Bull. 2008, 92, 967–991. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jarvie, D.M. Shale resource systems for oil and gas: Part 1—Shale-oil resource systems. AAPG Mem. 2012, 97, 69–87. [Google Scholar]
- Jarvie, D.M. Shale resource systems for oil and gas: Part 2—Shale-oil resource systems. AAPG Mem. 2012, 97, 89–119. [Google Scholar]
- Kuhn, P.P.; di Primio, R.; Hill, R.; Lawrence, J.R.; Horsfield, B. Three-dimensional modeling study of the low-permeability petroleum system of the Bakken Formation. AAPG Bull. 2012, 96, 1867–1897. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kirschbaum, M.A.; Mercier, T.J. Controls on the deposition and preservation of the Cretaceous Mowry Shale and Frontier Formation and equivalents, Rocky Mountain region, Colorado, Utah, and Wyoming. AAPG Bull. 2013, 97, 899–921. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kuuskraa, V.; Stevens, S.H.; Moodhe, K.D. Technically Recoverable Shale Oil and Shale Gas Resources: An Assessment of 137 Shale Formations in 41 Countries Outside the United States; U.S. Energy Information Administration: Washington, DC, USA, 2013. [Google Scholar]
- Sun, L.D.; Liu, H.; He, W.; LI, G.; Zhang, S.; Zhu, R.; Jin, X.; Meng, S.; Jiang, H. An analysis of major scientific problems and research paths of Gulong shale oil in Daqing Oilfield, NE China. Pet. Explor. Dev. 2021, 48, 453–463. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bai, L.H.; Liu, B.; Chi, Y.A.; Li, S.C.; Wen, X. 2D NMR studies of fluids in organic-rich shale from the Qingshankou Formation, Songliao Basin. Oil Gas Geol. 2021, 42, 1389–1400. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Loucks, R.G.; Reed, R.M.; Ruppel, S.C.; Jarvie, D.M. Morphology, genesis, and distribution of nanometer-scale pores in siliceous mudstones of the mississippian barnett shale. J. Sediment. Res. 2009, 79, 848–861. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Loucks, R.G.; Reed, R.M.; Ruppel, S.C.; Hammes, U. Spectrum of pore types and networks in mudrocks and a descriptive classification for matrix-related mudrock pores. AAPG Bull. 2012, 96, 1071–1098. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bernard, S.; Horsfield, B.; Schulz, H.-M.; Wirth, R.; Schreiber, A.; Sherwood, N. Geochemical evolution of organic-rich shales with increasing maturity: A STXM and TEM study of the Posidonia Shale (Lower Toarcian, northern Germany). Mar. Pet. Geol. 2012, 31, 70–89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tiwari, P.; Deo, M.; Lin, C.L.; Miller, J.D. Characterization of oil shale pore structure before and after pyrolysis by using X-ray micro CT. Fuel 2013, 107, 547–554. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, W.; Lu, S.; Xue, H.; Zhang, P.; Hu, Y. Microscopic pore structure in shale reservoir in the argillaceous dolomite from the Jianghan Basin. Fuel 2016, 181, 1041–1049. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, S.F.; Xue, H.T.; Wang, M.; Xiao, D.; Huang, W.; Li, J.; Xie, L.; Tian, S.; Wang, S.; Wang, W.; et al. Several key issues and research trends in evaluation of shale oil. Acta Pet. Sin. 2016, 37, 1309–1322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Lu, S.; Jiang, C.; Wang, M.; Chen, Z.; Chen, G.; Li, J.; Lu, S. Characterization of shale pore size distribution by NMR considering the influence of shale skeleton signals. Energy Fuels 2019, 33, 6361–6372. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, M.; Chen, Z.; Ma, X.; Cao, T.; Qian, M.; Jiang, Q.; Tao, G.; Li, Z.; Song, G. Shale oil resource potential and oil mobility characteristics of the Eocene-Oligocene Shahejie Formation, Jiyang Super-Depression, Bohai Bay Basin of China. Int. J. Coal Geol. 2019, 204, 130–143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiao, D.; Jiang, S.; Thul, D.; Huang, W.; Lu, Z.; Lu, S. Combining rate-controlled porosimetry and NMR to probe full-range pore throat structures and their evolution features in tight sands: A case study in the Songliao Basin, China. Mar. Pet. Geol. 2017, 83, 111–123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tian, W.; Lu, S.; Huang, W.; Wang, S.; Gao, Y.; Wang, W.; Li, J.; Xu, J.; Zhan, Z. Study on the full-range pore size distribution and the movable oil distribution in glutenite. Energy Fuels 2019, 33, 7028–7042. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- O’Brien, N.R.; Cremer, M.D.; Canales, D.G. The role of argillaceous rock fabric in primary migration of oil. Gulf Coast Assoc. Geol. Soc. Trans. 2002, 52, 1103–1112. [Google Scholar]
- Wu, S.T.; Zou, C.N.; Zhu, R.K.; Yuan, X.; Yao, J.; Yang, Z.; Sun, L.; Bai, B. Reservoir quality characterization of upper triassic Chang 7 shale in Ordos basin. Earth Sci. 2015, 40, 1810–1823. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, M.; Zhang, F.; Liu, Y.; Guan, H.; Li, J.; Shao, L.; Yang, S.; She, Y. Quantitative research on tight oil microscopic state of Chang 7 Member of Triassic Yanchang Formation in Ordos Basin, NW China. Pet. Explor. Dev. 2015, 42, 827–832. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Sun, L.; Zhu, R.; Jin, X.; Li, J.; Wu, S.; Bi, L.; Liu, X. Application of charging effects in evaluating storage space of tight reservoirs: A case study from Permian Lucaogou Formation in Jimusar sag, Junggar Basin, NW China. Pet. Explor. Dev. 2015, 42, 516–524. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kassem, A.A.; Hussein, W.S.; Radwan, A.E.; Anani, N.; Abioui, M.; Jain, S.; Shehata, A.A. Petrographic and diagenetic study of siliciclastic Jurassic sediments from the Northeastern Margin of Africa: Implication for reservoir quality. J. Pet. Sci. Eng. 2021, 200, 108340. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Radwan, A.E.; Husinec, A.; Benjumea, B.; Kassem, A.A.; Abd El Aal, A.K.; Hakimi, M.H.; Thanh, H.V.; Abdel-Fattah, M.I.; Shehata, A.A. Diagenetic overprint on porosity and permeability of a combined conventional-unconventional reservoir: Insights from the Eocene pelagic limestones, Gulf of Suez, Egypt. Mar. Pet. Geol. 2022, 146, 105967. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qian, M.H.; Jiang, Q.G.; Li, M.W.; Ma, Y.Y.; Li, Z.M.; Liu, P.; Cao, T.T.; Ma, X.X. Quantitative characterization of extractable organic matter in lacustrine shale with different occurrences. Pet. Geol. Exp. 2017, 39, 278–286. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, H.; Huang, H.; Li, Z.; Liu, M. Comparative study between sequential solvent-extraction and multiple isothermal stages pyrolysis: A case study on Eocene Shahejie Formation shales, Dongying Depression, East China. Fuel 2020, 263, 116591. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, S.X.; Zhou, X.P.; Guo, Q.H.; Liu, J.P.; Liu, J.Y.; Li, S.T.; Wang, B.; Lv, Q.Q. Research on evaluation method of movable hydrocarbon resources of shale oil in the Chang 73 sub-member in the Ordos Basin. Nat. Gas Geosci. 2021, 32, 1771–1784. [Google Scholar]
- Xue, H.T.; Tian, S.S.; Lu, S.F.; Zhang, W.H.; Du, T.T.; Mu, G.D. Selection and verification of key parameters in the quantitative evaluation of shale oil: A case study at the Qingshankou formation, Northern Songliao Basin. Bull. Mineral. Petrol. Geochem. 2015, 34, 70–78. [Google Scholar]
- Huang, Z.L.; Hao, Y.Q.; Li, S.J.; Wo, Y.; Sun, D.; Li, M.; Chen, J. Oil-bearing potential, mobility evaluation and significance of shale oil in Chang 7 shale system in the Ordos Basin: A case study of well H317. Oil Shale 2020, 47, 210–219. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, G.; Lu, S.; Zhang, J.; Pervukhina, M.; Liu, K.; Wang, M.; Han, T.; Tian, S.; Li, J.; Zhang, Y.; et al. A method for determining oil-bearing pore size distribution in shales: A case study from the Damintun Sag, China. J. Pet. Sci. Eng. 2018, 166, 673–678. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qi, Y.; Ju, Y.; Cai, J.; Gao, Y.; Zhu, H.; Hunag, C.; Wu, J.; Meng, S.; Chen, W. The effects of solvent extraction on nanoporosity of marine-continental coal and mudstone. Fuel 2019, 235, 72–84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Huang, W.; Lu, S.; Wang, M.; Chen, G.; Tian, W.; Guo, Z. Nuclear magnetic resonance T 1–T 2 map division method for hydrogen-bearing components in continental shale. Energy Fuels 2018, 32, 9043–9054. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Jiang, C.; Wang, M.; Lu, S.; Chen, Z.; Chen, G.; Li, J.; Li, Z.; Lu, S. Adsorbed and free hydrocarbons in unconventional shale reservoir: A new insight from NMR T1-T2 maps. Mar. Pet. Geol. 2020, 116, 104311. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, R.; Fan, A.; Han, Z.; van Loon, A.J. Lithofacies and origin of the Late Triassic muddy gravity-flow deposits in the Ordos Basin, central China. Mar. Pet. Geol. 2017, 85, 194–219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, N.; Chen, T.; Zhong, J.; Gao, J.; Shi, X.; Xue, C.; Swennen, R. Petrographic and geochemical characteristics of deep-lacustrine organic-rich mudstone and shale of the Upper Triassic Chang 7 member in the southern Ordos Basin, northern China: Implications for shale oil exploration. J. Asian Earth Sci. 2022, 227, 105118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jia, C.; Zou, C.; Li, J.; Li, D.; Zheng, M. Assessment criteria, main types, basic features and resource prospects of the tight oil in China. Acta Pet. Sin. 2012, 33, 343–350. [Google Scholar]
- Jin, Z. Origin, Types and Distribution Characteristics of Shale Oil in China; International Symposium on Shale Oil Exploration Technology: Wuxi, China, 2012. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, H.; Huang, H.; Yin, M. Investigation on Oil Physical States of Hybrid Shale Oil System: A Case Study on Cretaceous Second White Speckled Shale Formation from Highwood River Outcrop, Southern Alberta. Minerals 2022, 12, 802. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, B.; Sun, J.; Zhang, Y.; He, J.; Fu, X.; Yang, L.; Xing, J.; Zhao, X. Reservoir space and enrichment model of shale oil in the first member of Cretaceous Qingshankou Formation in the Changling Sag, southern Songliao Basin, NE China. Pet. Explor. Dev. 2021, 48, 608–624. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Wang, X.; Song, G.; Liu, H.; Zhu, D.; Zhu, D.; Ding, J.; Yang, W.; Yin, Y.; Zhang, S.; et al. Genetic connection between mud shale lithofacies and shale oil enrichment in Jiyang Depression, Bohai Bay Basin. Pet. Explor. Dev. 2016, 43, 759–768. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xi, K.; Li, K.; Cao, Y.; Lin, M.; Niu, X.; Zhu, R.; Wei, X.; You, Y.; Liang, X.; Feng, S. Laminae combination and shale oil enrichment patterns of Chang 73 sub-member organic-rich shales in the Triassic Yanchang Formation, Ordos Basin, NW China. Pet. Explor. Dev. 2020, 47, 1342–1353. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kong, Q.F. The organic maceral characteristic of Yanchang source rock in Ordos Basin. Xinjiang Pet. Geol. 2007, 28, 163–166. [Google Scholar]
- Rouquerol, J.; Avnir, D.; Fairbridge, C.W.; Everett, D.H.; Haynes, J.H.; Pernicone, N.; Ramsay, J.D.F.; Sing, K.S.W.; Unger, K.K. Physical chemistry division commission on colloid and surface chemistry, subcommittee on characterization of porous solids: Recommendations for the characterization of porous solids. Pure Appl. Chem. 1994, 66, 1739–1758. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Liang, J.; Zhang, J.; Zhao, B.; Zhao, Y.; Liu, X.; Xia, D. Resource potential and exploration direction of Gulong shale oil in Songliao Basin. Pet. Geol. Oilfield Dev. Daqing 2020, 39, 20–34. [Google Scholar]
- Gao, Y.; Ye, Y.P.; He, J.X.; Qian, G.B.; Qin, J.H.; Li, Y.Y. Development practice of continental shale oil in Jimsar sag in the Junggar Basin. China Pet. Explor. 2020, 25, 133–141. [Google Scholar]
- Zhou, L.; Zhao, X.; Chai, G.; Jiang, W.; Pu, X.; Wang, X.; Han, W.; Guan, Q.; Feng, J.; Liu, X. Key exploration & development technologies and engineering practice of continental shale oil: A case study of Member 2 of Paleogene Kongdian Formation in Cangdong Sag, Bohai Bay Basin, East China. Pet. Explor. Dev. 2020, 47, 1138–1146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, W.Y.; Meng, Q.A.; Feng, Z.H.; Zhang, J.; Wang, R. In-situ accumulation theory and exploration & development practice of Gulong shale oil in Sonaliao Basin. Acta Pet. Sin. 2022, 43, 1–14. [Google Scholar]
- Hu, Q.; Quintero, R.P.; El-Sobky, H.F.; Kang, J.; Zhang, T. Coupled nano-petrophysical and organic-geochemical study of the Wolfberry Play in Howard County, Texas U.S.A. Mar. Pet. Geol. 2020, 122, 104663. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ross, D.J.K.; Bustin, R.M. The importance of shale composition and pore structure upon gas storage potential of shale gas reservoirs. Mar. Pet. Geol. 2009, 26, 916–927. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Clarkson, C.R.; Jensen, J.L.; Pedersen, P.K.; Freeman, M. Innovative methods for flow-unit and pore-structure analyses in a tight siltstone and shale gas reservoir. AAPG Bull. 2012, 96, 355–374. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sing, K.S.W.; Everett, D.H.; Haul, R.A.W.; Moscou, L.; Pierotti, R.A.; Rouquerol, J.; Siemieniewska, T. Reporting physisorption data for gas/solid systems with special reference to the determination of surface area and porosity (Recommendations 1984). Pure Appl. Chem. 1985, 57, 603–619. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Labani, M.M.; Rezaee, R.; Saeedi, A.; Hinai, A.A. Evaluation of pore size spectrum of gas shale reservoirs using low pressure nitrogen adsorption, gas expansion and mercury porosimetry: A case study from the Perth and Canning Basins, Western Australia. J. Pet. Sci. Eng. 2013, 112, 7–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.; Li, X.; Xie, Z.; Li, J.; Zhang, X.; Sun, K.; Wang, F. Characterization of microscopic pore types and structures in marine shale: Examples from the Upper Permian Dalong formation, Northern Sichuan Basin, South China. J. Nat. Gas Sci. Eng. 2018, 59, 326–342. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mastalerz, M.; Schimmelmann, A.; Drobniak, A.; Chen, Y. Porosity of Devonian and Mississippian New Albany Shale across a maturation gradient: Insights from organic petrology, gas adsorption, and mercury intrusion. AAPG Bull. 2013, 97, 1621–1643. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jin, X.; Li, G.; Meng, S.; Wang, X.; Liu, C.; Tao, J.; Liu, H. Microscale comprehensive evaluation of continental shale oil recoverability. Pet. Explor. Dev. 2021, 48, 256–268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, L.Y.; Bao, Y.S.; Li, J.Y.; Li, Z.; Zhu, R.F.; Zhang, L.; Wang, Y.R. Hydrocarbon and crude oil adsorption abilities of minerals and kerogens in lacustrine shales. Pet. Geol. Exp. 2015, 37, 776–780. [Google Scholar]
- Pernyeszi, T.; Patzkó, Á.; Berkesi, O.; Dékány, I. Asphaltene adsorption on clays and crude oil reservoir rocks. Colloids Surf. A Physicochem. Eng. Asp. 1998, 137, 373–384. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Z.; Zou, Y.; Xu, X.; Sun, J.; Li, M.; Peng, P. Adsorption of mudstone source rock for shale oil—Experiments, model and a case study. Org. Geochem. 2016, 92, 55–62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]







| No. | Well | Depth (m) | DOM (wt, %) | TOC (wt, %) | S1 | S2 | S3 | OSI | PI | PC (%) | HI | Tmax (℃) | Ro (%) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| N3 | Z251 | 1676.74 | 0.90 | 16.9 | 2.99 | 75.66 | 2.9 | 17.69 | 0.04 | 6.53 | 447.69 | 428 | 0.89 |
| N8 | B522 | 1953.47 | 0.66 | 19.8 | 3.57 | 32.00 | 4.17 | 18.03 | 0.1 | 2.95 | 161.62 | 450 | 1.12 |
| N9 | B522 | 1949.77 | 0.54 | 12.1 | 2.08 | 15.47 | 4.45 | 17.19 | 0.12 | 1.46 | 127.85 | 440 | 1.07 |
| N15 | L211 | 2356.35 | 0.66 | 7.4 | 1.19 | 15.81 | 7.6 | 15.99 | 0.07 | 1.41 | 212.50 | 447 | / |
| N18 | L211 | 2373.77 | 0.71 | 8.2 | 1.60 | 20.22 | 4.08 | 18.89 | 0.07 | 1.81 | 238.72 | 448 | 1.22 |
| N31 | W336 | 1977.00 | 0.34 | 4.3 | 1.55 | 13.54 | 2.32 | 36.05 | 0.1 | 1.25 | 314.88 | 445 | 1.12 |
| N33 | W336 | 2020.29 | 0.78 | 11.9 | 2.05 | 47.66 | 2.47 | 17.23 | 0.04 | 4.13 | 400.50 | 442 | / |
| N37 | W336 | 2061.69 | 0.67 | 1.9 | 1.26 | 6.54 | 2.4 | 68.11 | 0.16 | 0.65 | 353.51 | 445 | 1.09 |
| N39 | W336 | 2051.27 | 0.41 | 2.6 | 1.16 | 6.64 | 2.68 | 45.49 | 0.15 | 0.65 | 260.39 | 451 | 1.06 |
| N44 | L82 | 2181.60 | 0.19 | 2.21 | 0.95 | 2.85 | 1.64 | 42.99 | 0.25 | 0.32 | 128.96 | 457 | 1.11 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Fan, Y.; Zhang, Z.; Zhou, X.; Zhang, K.; Wen, Z.; Tian, W.; Gao, H.; Yang, Y.; Liu, Y.; Zheng, X. Occurrence Characteristics of Chang 7 Shale Oil from the Longdong Area in the Ordos Basin: Insights from Petrology and Pore Structure. Processes 2023, 11, 3090. https://doi.org/10.3390/pr11113090
Fan Y, Zhang Z, Zhou X, Zhang K, Wen Z, Tian W, Gao H, Yang Y, Liu Y, Zheng X. Occurrence Characteristics of Chang 7 Shale Oil from the Longdong Area in the Ordos Basin: Insights from Petrology and Pore Structure. Processes. 2023; 11(11):3090. https://doi.org/10.3390/pr11113090
Chicago/Turabian StyleFan, Yunpeng, Zhanyu Zhang, Xinping Zhou, Kun Zhang, Zhigang Wen, Weichao Tian, Heting Gao, Yuxuan Yang, Yuhang Liu, and Xiaoyin Zheng. 2023. "Occurrence Characteristics of Chang 7 Shale Oil from the Longdong Area in the Ordos Basin: Insights from Petrology and Pore Structure" Processes 11, no. 11: 3090. https://doi.org/10.3390/pr11113090
APA StyleFan, Y., Zhang, Z., Zhou, X., Zhang, K., Wen, Z., Tian, W., Gao, H., Yang, Y., Liu, Y., & Zheng, X. (2023). Occurrence Characteristics of Chang 7 Shale Oil from the Longdong Area in the Ordos Basin: Insights from Petrology and Pore Structure. Processes, 11(11), 3090. https://doi.org/10.3390/pr11113090







