Functional Properties and Amino Acid Profile of Bambara Groundnut and Moringa oleifera Leaf Protein Complex
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Material
2.2. Physical Characterisation of Bambara Groundnut and Moringa oleifera Leaf Protein Isolates and Their Complex
2.2.1. Particle Morphology Determination of Bambara Groundnut and Moringa oleifera Leaf Protein Isolates and Their Complex
2.2.2. Colour Determination of Bambara Groundnut and Moringa oleifera Leaf Protein Isolates and Their Complex
2.2.3. Water Activity Determination of Bambara Groundnut and Moringa oleifera Leaf Protein Isolates and Their Complex
2.3. Evaluation of Functional Properties of Bambara Groundnut and Moringa oleifera Leaf Protein Isolates and Their Complex
2.3.1. Water and Oil Absorption Capacity of Bambara Groundnut and Moringa oleifera Leaf Protein Isolates and Their Complex
2.3.2. Swelling Capacity Analysis of Bambara Groundnut and Moringa oleifera Leaf Protein Isolates and Their Complex
2.3.3. Foaming Capacity and Stability Analysis of Bambara Groundnut and Moringa oleifera Leaf Protein Isolates and Their Complex
2.3.4. Emulsifying Capacity and Stability Determination of Bambara Groundnut and Moringa oleifera Leaf Protein Isolates and Their Complex
2.3.5. Protein Solubility Determination of Bambara Groundnut and Moringa oleifera Leaf Protein Isolates and Their Complex
2.4. Proximate and Amino Acid Profile
2.5. Statistical Analysis
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Physical Characteristics of Bambara Groundnut and Moringa oleifera Leaf Protein Isolates and Their Complex
3.1.1. Physical Appearance of Bambara Groundnut and Moringa oleifera Leaf Protein Isolates and Their Complex
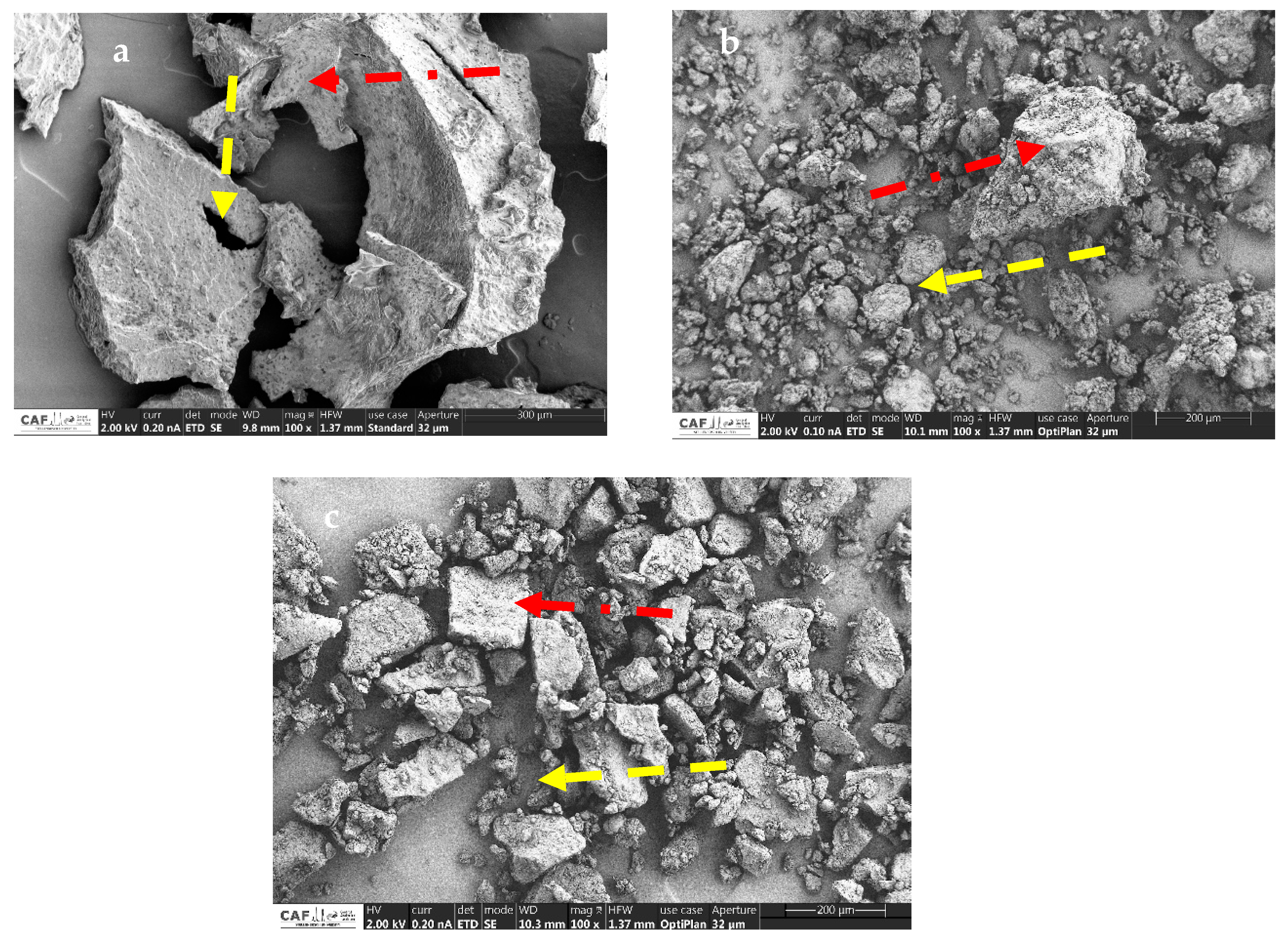
3.1.2. Particle Morphology of Bambara Groundnut and Moringa oleifera Leaf Protein Isolates and Their Complex by Scanning Electron Microscopy (SEM)
3.1.3. Colour Characteristics of BGNPI, MOLPI, and BAMOLP
3.1.4. Water Activity of Bambara Groundnut and Moringa oleifera Leaf Protein Isolates and Their Complex
3.2. Proximate Composition of Bambara Groundnut Protein Isolate (BGNPI), Moringa oleifera Leaf Protein Isolate (MOLPI), and BGN-Moringa Protein Complex
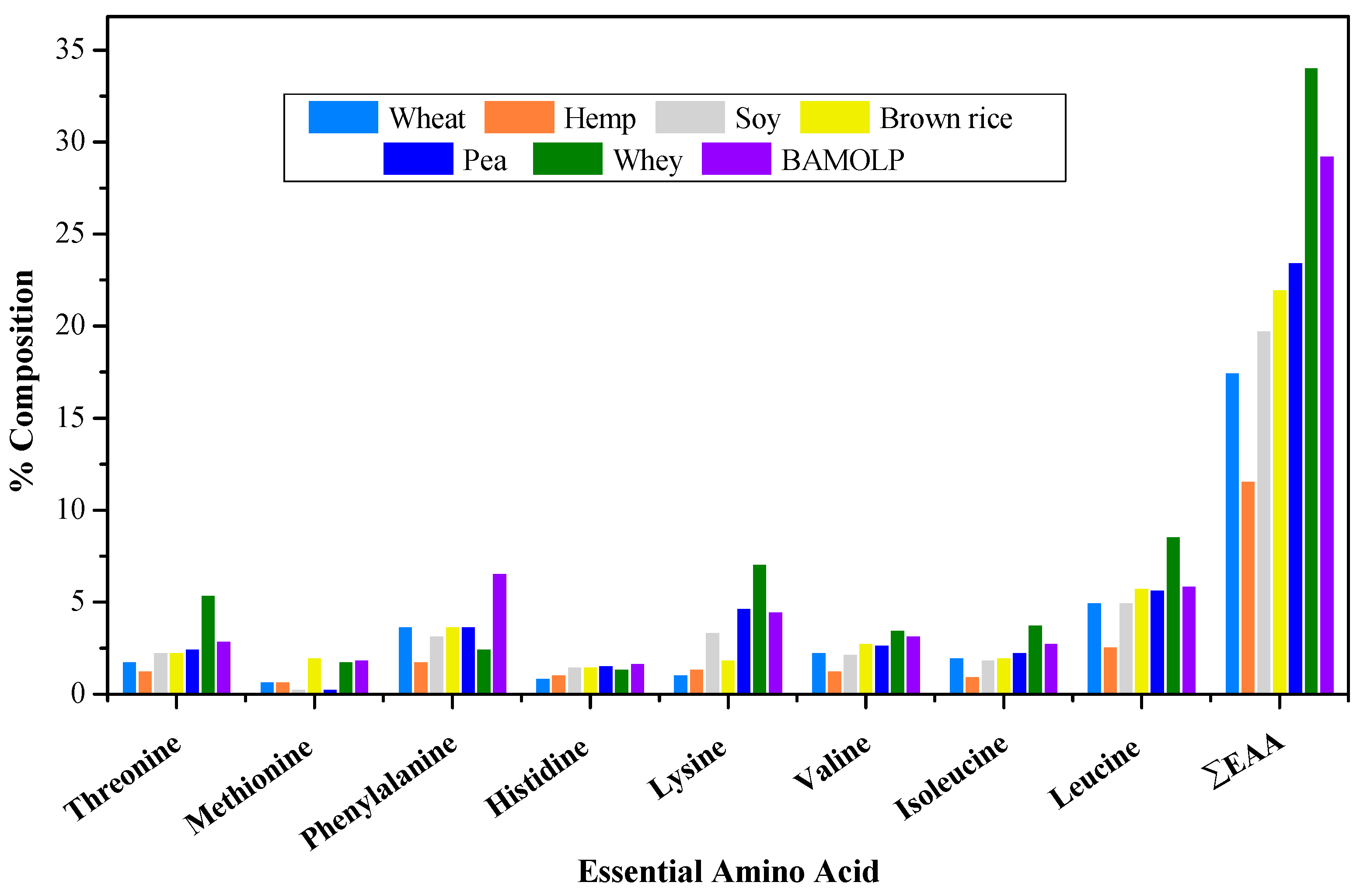
3.3. Amino Acid Composition of Bambara Groundnut Protein Isolates, Moringa oleifera Leaf Protein Isolates, and Bambara Groundnut–Moringa oleifera Leaf Protein Complex
3.4. Functional Properties of Bambara groundnut protein isolates, Moringa oleifera Leaf Protein Isolates, and Bambara Groundnut-Moringa oleifera Leaf Protein Complex
3.4.1. Oil Absorption Capacity
3.4.2. Water Absorption Capacity
3.4.3. Emulsifying Capacity and Stability
3.4.4. Effect of pH on Foam Capacity and Stability
3.4.5. Protein Solubility
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Yao, D.N.; Kouassi, K.N.; Erba, D.; Scazzina, F.; Pellegrini, N.; Casiraghi, M.C. Nutritive Evaluation of the Bambara Groundnut Ci12 Landrace [Vigna subterranea (L.) Verdc. (Fabaceae)] Produced in Côte d’Ivoire. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2015, 16, 21428–21441. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Arise, A.K.; Aliyu, B.N.; Ajidagba, S.D. Effect of thermal processing and fermentation on the chemical composition, protein digestibility and functional properties of Bambara protein isolate. Carpathian J. Food Sci. Technol. 2020, 12, 148–156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adebowale, K.O.; Afolabi, T.A.; Lawal, O.S. Isolation, chemical modification and physicochemical characterisation of Bambarra groundnut (Voandzeia subterranean) starch and flour. Food Chem. 2002, 78, 305–311. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eltayeb, A.R.S.; Ali, A.O.; Abou-Arab, A.A.; Abu-Salem, F.M. Chemical composition and functional properties of flour and protein isolate extracted from Bambara groundnut (Vigna subterranean). Afr. J. Biotechnol. 2011, 5, 82–90. [Google Scholar]
- Oyeyinka, S.A.; Singh, S.; Adebola, P.O.; Gerrano, A.S.; Amonsou, E.O. Physicochemical properties of starches with variable amylose contents extracted from bambara groundnut genotypes. Carbohydr. Polym. 2015, 133, 171–178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maphosa, Y.; Jideani, V. Physicochemical characteristics of Bambara groundnut dietary fibres extracted using wet milling. S. Afr. J. Sci. 2016, 112, 8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alabi, O.O.; Ali, N.; Nwachukwu, I.D.; Aluko, R.E.; Amonsou, E.O. Composition and some functional properties of Bambara groundnuts vicilin fraction. LWT 2020, 125, 109256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ajayi, F.; Lale, N. Susceptibility of unprotected seeds and seeds of local bambara groundnut cultivars protected with insecticidal essential oils to infestation by Callosobruchus maculatus (F.) (Coleoptera: Bruchidae). J. Stored Prod. Res. 2000, 37, 47–62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baryeh, E.A. Physical properties of bambara groundnuts. J. Food Eng. 2001, 47, 321–326. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sirivongpaisal, P. Structure and functional properties of starch and flour from bambarra groundnut. Songklanakarin J. Sci. Technol. 2008, 30 (Suppl. 1), 51–56. [Google Scholar]
- Bamshaiye, O.M.; Adegbola, J.A.; Bamishaiye, E.I. Bambara groundnut: An Under-Utilized Nut in Africa. Adv. Agric. Biotechnol. 2011, 1, 60–72. [Google Scholar]
- Anwar, F.; Latif, S.; Ashraf, M.; Gilani, A.H. Moringa oleifera: A food plant with multiple medicinal uses. Phytother. Res. 2007, 21, 17–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elmoneim, A.; Elkhalifa, O.; Abd, S.; Ahmed, A.; Adam, S. Nutritional Evaluation of Moringa Oleifera Leaves and Extract. Ahfad J. 2007, 24, 113–122. [Google Scholar]
- EL Sohaimy, S.A.; Hamad, G.M.; Mohamed, S.E.; Amar, M.H.; Al-Hindi, R.R. Biochemical and functional properties of Moringa oleifera leaves and their potential as a functional food. Glob. Adv. Res. J. Agric. Sci. 2015, 4, 2315–5094. Available online: http://garj.org/garjas/index.htm (accessed on 23 March 2017).
- Busani, M.; Patrick, J.M.; Arnold, H.; Voster, M. Nutritional characterization of Moringa (Moringa oleifera Lam.) leaves. Afr. J. Biotechnol. 2011, 10, 12925–12933. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Siddhuraju, P.; Becker, K. Antioxidant Properties of Various Solvent Extracts of Total Phenolic Constituents from Three Different Agroclimatic Origins of Drumstick Tree (Moringa oleiferaLam.) Leaves. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2003, 51, 2144–2155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Oliveira, J.T.A.; Silveira, S.B.; Vasconcelos, I.M.; Cavada, B.S.; Moreira, R.A. Compositional and nutritional attributes of seeds from the multiple purpose treeMoringa oleifera Lamarck. J. Sci. Food Agric. 1999, 79, 815–820. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wani, I.A.; Sogi, D.; Shivhare, U.S.; Gill, B.S. Physico-chemical and functional properties of native and hydrolyzed kidney bean (Phaseolus vulgaris L.) protein isolates. Food Res. Int. 2015, 76, 11–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adebowale, K.; Lawal, O. Foaming, gelation and electrophoretic characteristics of mucuna bean (Mucuna pruriens) protein concentrates. Food Chem. 2003, 83, 237–246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adebowale, Y.A.; Schwarzenbolz, U.; Henle, T. Protein Isolates from Bambara Groundnut (Voandzeia Subterranean L.): Chemical Characterization and Functional Properties. Int. J. Food Prop. 2011, 14, 758–775. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kudre, T.G.; Benjakul, S.; Kishimura, H. Comparative study on chemical compositions and properties of protein isolates from mung bean, black bean and bambara groundnut. J. Sci. Food Agric. 2013, 93, 2429–2436. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Arise, A.K.; Amonsou, E.O.; Ijabadeniyi, O.A. Influence of extraction methods on functional properties of protein concentrates prepared from South African bambara groundnut landraces. Int. J. Food Sci. Technol. 2015, 50, 1095–1101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaptso, K.G.; Njintang, Y.N.; Nguemtchouin, M.M.G.; Scher, J.; Hounhouigan, J.D.; Mbofung, C.M. Physicochemical and micro-structural properties of flours, starch and proteins from two varieties of legumes: Bambara groundnut (Vigna subterranea). J. Food Sci. Technol. 2014, 52, 4915–4924. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Adeleke, O.R.; Adiamo, O.; Fawale, O.S. Nutritional, physicochemical, and functional properties of protein concentrate and isolate of newly-developed Bambara groundnut (Vigna subterrenea L.) cultivars. Food Sci. Nutr. 2017, 6, 229–242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Diedericks, C.F.; Venema, P.; Mubaiwa, J.; Jideani, V.A.; van der Linden, E. Effect of processing on the microstructure and composition of Bambara groundnut (Vigna subterranea (L.) Verdc.) seeds, flour and protein isolates. Food Hydrocoll. 2020, 108, 106031. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Novasina (The Art of Precision Measurement) General Catalogue. Water Activity in Foodstuff/Food Ingredients Chemicals/Cosmetics/Pharmaceuticals/Materials. Lachen, Switzerland, 2012. Available online: www.novasina.com (accessed on 8 August 2020).
- Adebowale, K.; Lawal, O. Comparative study of the functional properties of bambarra groundnut (Voandzeia subterranean), jack bean (Canavalia ensiformis) and mucuna bean (Mucuna pruriens) flours. Food Res. Int. 2004, 37, 355–365. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Diedericks, C. Functional Properties of Bambara Groundnut (Vigna subterranea (L) Verdc.) Non-Starch Polysaccharides in Model and Food Systems. Master’s Thesis, Cape Peninsula University of Technology, Cape Town, South Africa, 2014. [Google Scholar]
- Delgado-Vargas, F.; Jiménez, A.R.; Paredes-López, O. Natural Pigments: Carotenoids, Anthocyanins, and Betalains—Characteristics, Biosynthesis, Processing, and Stability. Crit. Rev. Food Sci. Nutr. 2000, 40, 173–289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheynier, V. Polyphenols in foods are more complex than often thought. Am. J. Clin. Nutr. 2005, 81, 223S–229S. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dai, J.; Mumper, R.J. Plant Phenolics: Extraction, Analysis and Their Antioxidant and Anticancer Properties. Molecules 2010, 15, 7313–7352. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dragović-Uzelac, V.; Savić, Z.; Brala, A.; Levaj, B.; Kovaćević, D.B.; Biško, A. Evaluation of phenolic content and antioxidant capacity of blueberry cultivars (Vaccinium corymbosum L.) grown in the northwest Croatia. Food Technol. Biotechnol. 2010, 48, 214–221. [Google Scholar]
- Rahman, M.S. Food Stability beyond Water Activity and Glass Transtion: Macro-Micro Region Concept in the State Diagram. Int. J. Food Prop. 2009, 12, 726–740. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Buerman, E.C.; Worobo, R.W.; Padilla-Zakour, O.I. Thermal Resistance of Xerophilic Fungi in Low-Water-Activity (0.70 to 0.80) Confectionery Model Foods. J. Food Prot. 2019, 82, 390–394. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sodamade, A.; Adeboye, O.S. Proximate Analysis, Mineral Contents and Functional Properties of Moringa Oleifera Leaf Protein Concentrate. IOSR J. Appl. Chem. 2013, 4, 47–51. Available online: www.iosrjournals.org (accessed on 3 April 2020).
- Ahmed, S.M.O. Isolation of the Protein Concentrate from the Leaves of Moringa Oleifera and Study of Its Functional Properties. Master’s Thesis, Sudan University of Science and Technology, Khartoum, Sudan, 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Fasuyi, A.O.; Aletor, V.A. Varietal Composition and Functional Properties of Cassava (Manihot esculenta, Cranzt) Leaf Meal and Leaf Protein Concentrates. Pak. J. Nutr. 2005, 4, 43–49. [Google Scholar]
- Mune, M.A.M.; Nyobe, E.C.; Bassogog, C.B. A comparison on the nutritional quality of proteins from Moringa oleifera leaves and seeds. Cogent Food Agric. 2016, 2, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, K.-X.; Zhou, H.-M.; Qian, H.-F. Proteins Extracted from Defatted Wheat Germ: Nutritional and Structural Properties. Cereal Chem. J. 2006, 83, 69–75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hillocks, R.J.; Bennett, C.; Mponda, O.M.; Maritime, C. Bambara nut: A review of utilisation, market potential and crop improvement. Afr. Crop Sci. Soc. 2012, 20, 1–16. [Google Scholar]
- Duranti, M. Grain legume proteins and nutraceutical properties. Fitoterapia 2006, 77, 67–82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abdualrahm, M.A.Y.; Ali, A.O.; ElKhalifa, E.A.; Ma, H. Chemical, Minerals, Fatty Acid and Amino Acid Compositions of Sudanese Traditional Khemiss-Tweria Supplemented with Peanut and Bambara Groundnuts. Am. J. Food Technol. 2015, 10, 100–108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Tangsuphoom, N.; Coupland, J.N. Effect of surface-active stabilizers on the microstructure and stability of coconut milk emulsions. Food Hydrocoll. 2008, 22, 1233–1242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Du, S.-K.; Jiang, H.; Yu, X.; Jane, J.-l. Physicochemical and functional properties of whole legume flour. LWT-Food Sci. Technol. 2014, 55, 308–313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blasco, L.; Viñas, M. Proteins influencing foam formation in wine and beer: The role of yeast. Int. Microbiol. 2011, 14, 61–76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kaur, M.; Singh, N. Characterization of protein isolates from different Indian chickpea (Cicer arietinum L.) cultivars. Food Chem. 2007, 102, 366–374. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]




| Protein Isolates | Colour Values | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| L* | a* | b* | C* | h° | |
| BGNPI | 63.38 ± 0.31 a | 6.62 ± 0.09 a | 21.24 ± 0.31 a | 22.25 ± 0.33 a | 72.69 ± 0.05 a |
| MOLPI | 34.09 ± 0.50 c | 0.19 ± 0.07 b | 18.94 ± 0.39 b | 18.95 ± 0.38 b | 89.44 ± 0.19 b |
| BAMOLP | 49.90 ± 0.15 b | 0.14 ± 0.01 b | 23.51 ± 0.45 c | 23.51 ± 0.45 c | 89.66 ± 0.01 b |
| Protein Isolate | Proximate (g/100 g) | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Moisture | Ash | Fat | Protein | Carbohydrate | |
| BGNPI | 2.6 ± 0.1 a | 1.60 ± 0.0 a | 11.5 ± 0.4 a | 61.1 ± 1.3 a | 24.1 ± 0.6 a |
| MOLPI | 9.6 ± 0.1 b | 7.09 ± 0.0 b | 2.2 ± 0.2 b | 39.4 ± 0.5 b | 51.3 ± 0.7 b |
| BAMOLP | 4.7 ± 0.2 c | 2.42 ± 0.0 c | 8.8 ± 0.3 c | 63.5 ± 1.1 c | 25.3 ± 0.9 a |
| Essential Amino Acid | Protein Isolate Amino-Acid (g/100 g) | ||
| BGNPI | MOLPI | BAMOLP | |
| Threonine | 3.02 ± 0.02 a | 3.44 ± 0.48 b | 2.85 ± 0.04 a |
| Methionine | 1.77 ± 0.00 a | 2.50 ± 0.08 c | 1.86 ± 0.03 b |
| Phenylalanine | 9.41 ± 0.05 a | 5.80 ± 0.12 c | 6.55 ± 0.11 b |
| Histidine | 2.85 ± 0.07 a | 1.29 ± 0.02 c | 1.71 ± 0.0 b |
| Lysine | 3.53 ± 0.10 a | 2.03 ± 0.18 c | 4.49 ± 0.23 b |
| Valine | 3.31 ± 0.20 a | 2.75 ± 0.13 b | 3.21 ± 0.02 c |
| Isoleucine | 3.02 ± 0.20 a | 2.11 ± 0.07 c | 2.75 ± 0.08 b |
| Leucine | 6.21 ± 0.16 a | 4.02 ± 0.10 c | 5.91 ± 0.10 b |
| Non-Essential Amino acid (g/100 g) | |||
| Serine | 5.05 ± 0.24 a | 2.79 ± 0.65 c | 4.41 ± 0.20 b |
| Arginine | 6.31 ± 0.35 a | 3.69 ± 0.32 c | 5.33 ± 0.12 b |
| Glycine | 2.65 ± 0.10 a,b | 2.62 ± 0.12 a,b | 2.49 ± 0.09 c |
| Asparagine | 7.55 ± 0.3 a,b | 3.37 ± 0.26 c | 7.95 ± 0.61 a |
| Glutamine | 12 90 ± 0.39 a | 4.53 ± 0.11 b | 13.11 ± 0.66 a |
| Alanine | 3.12 ± 0.03 a | 3.01 ± 0.15 a | 3.11 ± 0.02 a |
| Proline | 2.87 ± 0.02 a | 2.36 ± 0.26 b | 2.70 ± 0.00 c |
| Tyrosine | 4.74 ± 0.11 a | 3.69 ± 0.33 b | 3.40 ± 0.13 b |
| Parameter | BGNPI | MOLPI | BAMOLP |
|---|---|---|---|
| OAC g/g | 2.26 ± 0.15 a | 0.89 ± 0.04 c | 0.95 ± 0.03 b |
| WAC g/g | 1.31 ± 0.02 a | 1.5 ± 0.03 b | 1.22 ± 0.03 c |
| Emulsifying Capacity% | 39.17 ± 4.25 a | 45.83 ± 0.00 b | 50. ± 0.00 b |
| Emulsifying Stability% | 56.36 ± 5.53 a | 47.28 ± 3.04 b | 56.37 ± 3.15 a |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Adewumi, O.O.; Felix-Minnaar, J.V.; Jideani, V.A. Functional Properties and Amino Acid Profile of Bambara Groundnut and Moringa oleifera Leaf Protein Complex. Processes 2022, 10, 205. https://doi.org/10.3390/pr10020205
Adewumi OO, Felix-Minnaar JV, Jideani VA. Functional Properties and Amino Acid Profile of Bambara Groundnut and Moringa oleifera Leaf Protein Complex. Processes. 2022; 10(2):205. https://doi.org/10.3390/pr10020205
Chicago/Turabian StyleAdewumi, Olawumi Oluwakemi, Joseline Veronica Felix-Minnaar, and Victoria A. Jideani. 2022. "Functional Properties and Amino Acid Profile of Bambara Groundnut and Moringa oleifera Leaf Protein Complex" Processes 10, no. 2: 205. https://doi.org/10.3390/pr10020205
APA StyleAdewumi, O. O., Felix-Minnaar, J. V., & Jideani, V. A. (2022). Functional Properties and Amino Acid Profile of Bambara Groundnut and Moringa oleifera Leaf Protein Complex. Processes, 10(2), 205. https://doi.org/10.3390/pr10020205






