Biodegradation of Alachlor by a Newly Isolated Bacterium: Degradation Pathway and Product Analysis
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Chemicals and Media
2.2. Enrichment and Isolation of Alachlor-Degrading Bacteria
2.3. Identification and Characterization of Alachlor-Degrading Strain
2.4. Biodegradation of Alachlor
2.5. Identification of Metabolic Intermediates
2.6. Deposition of 16S rRNA Gene Sequences and Bacterial Strains
3. Results
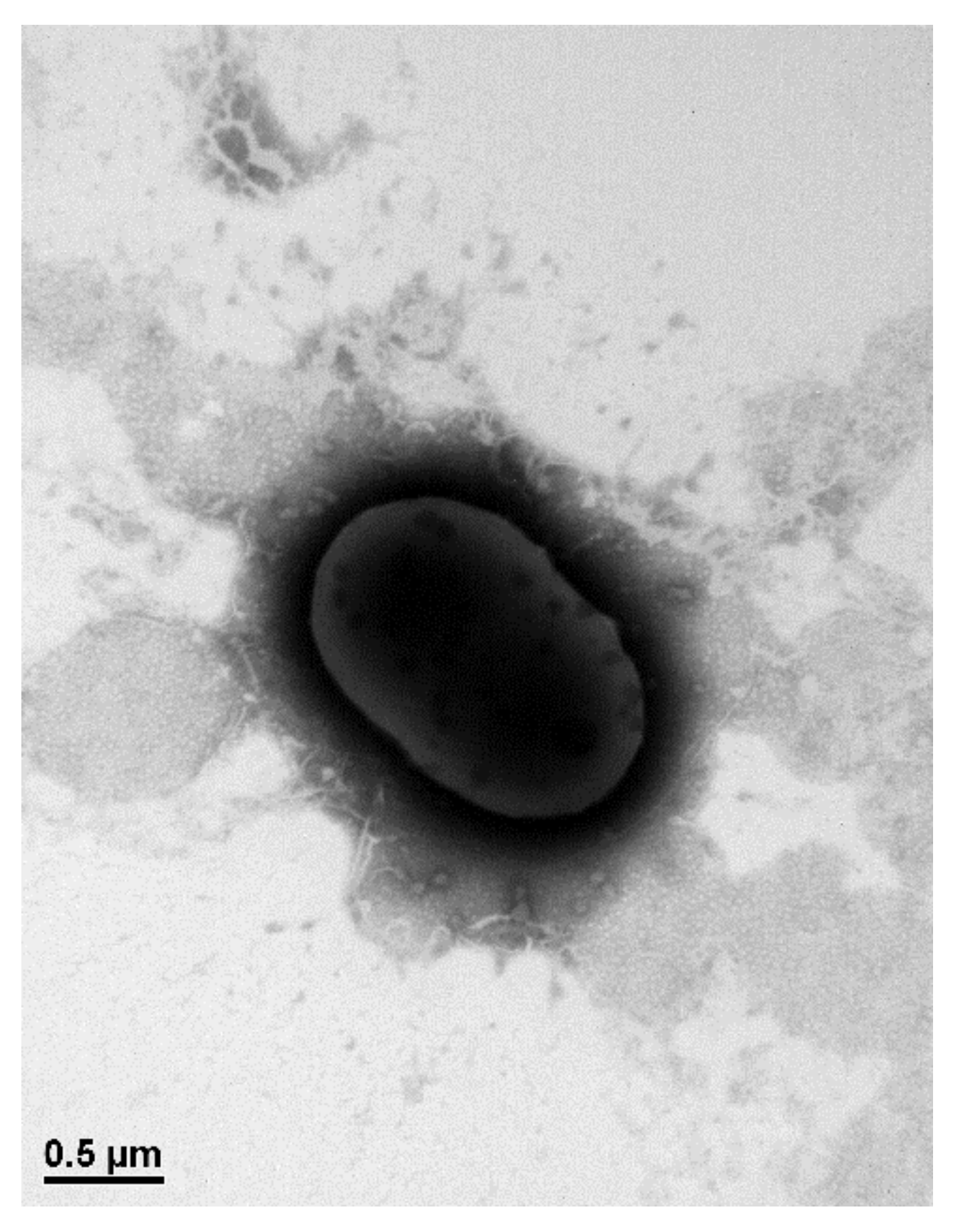
3.1. Isolation and Characterization of Alachlor-Degrading Strain
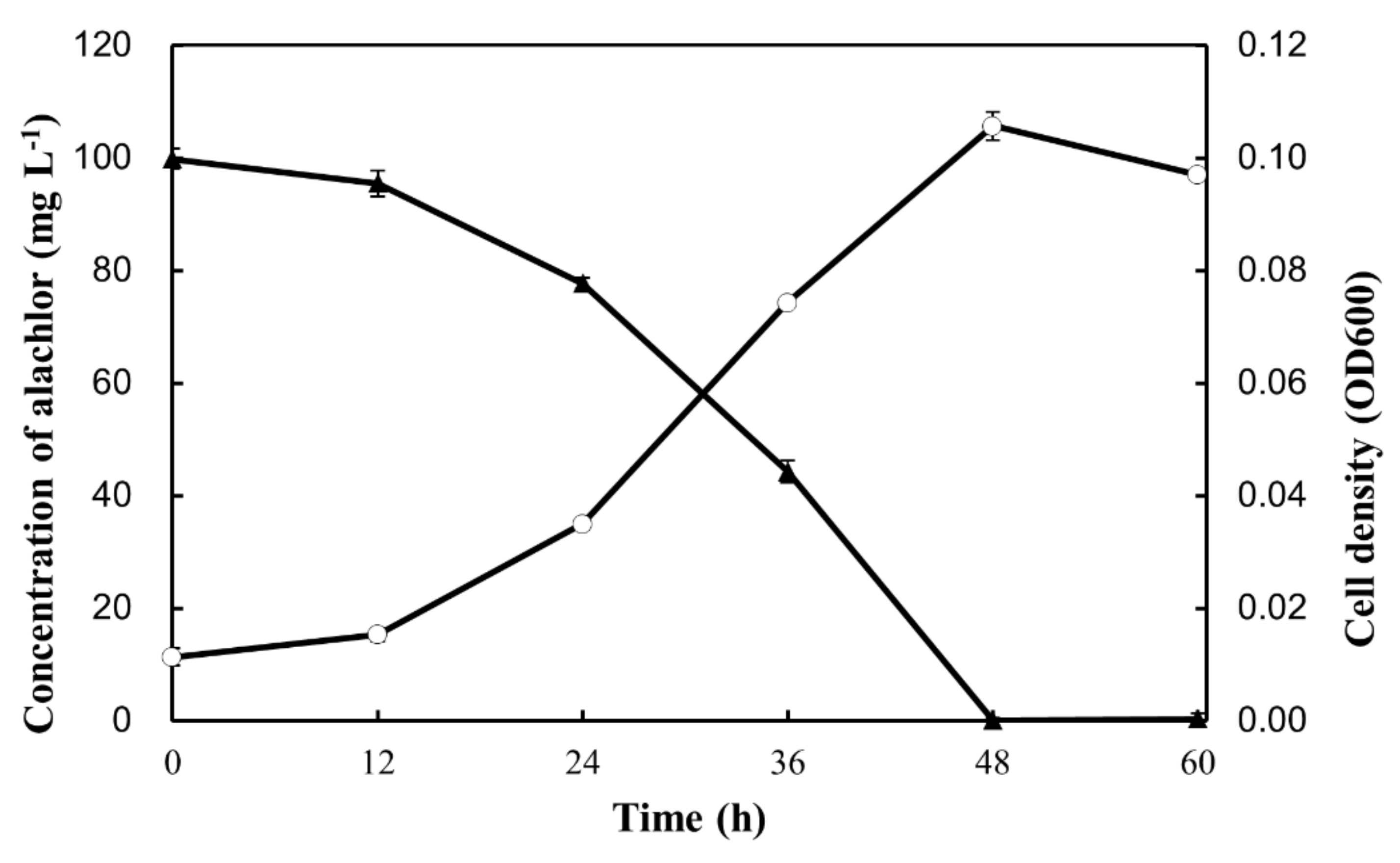
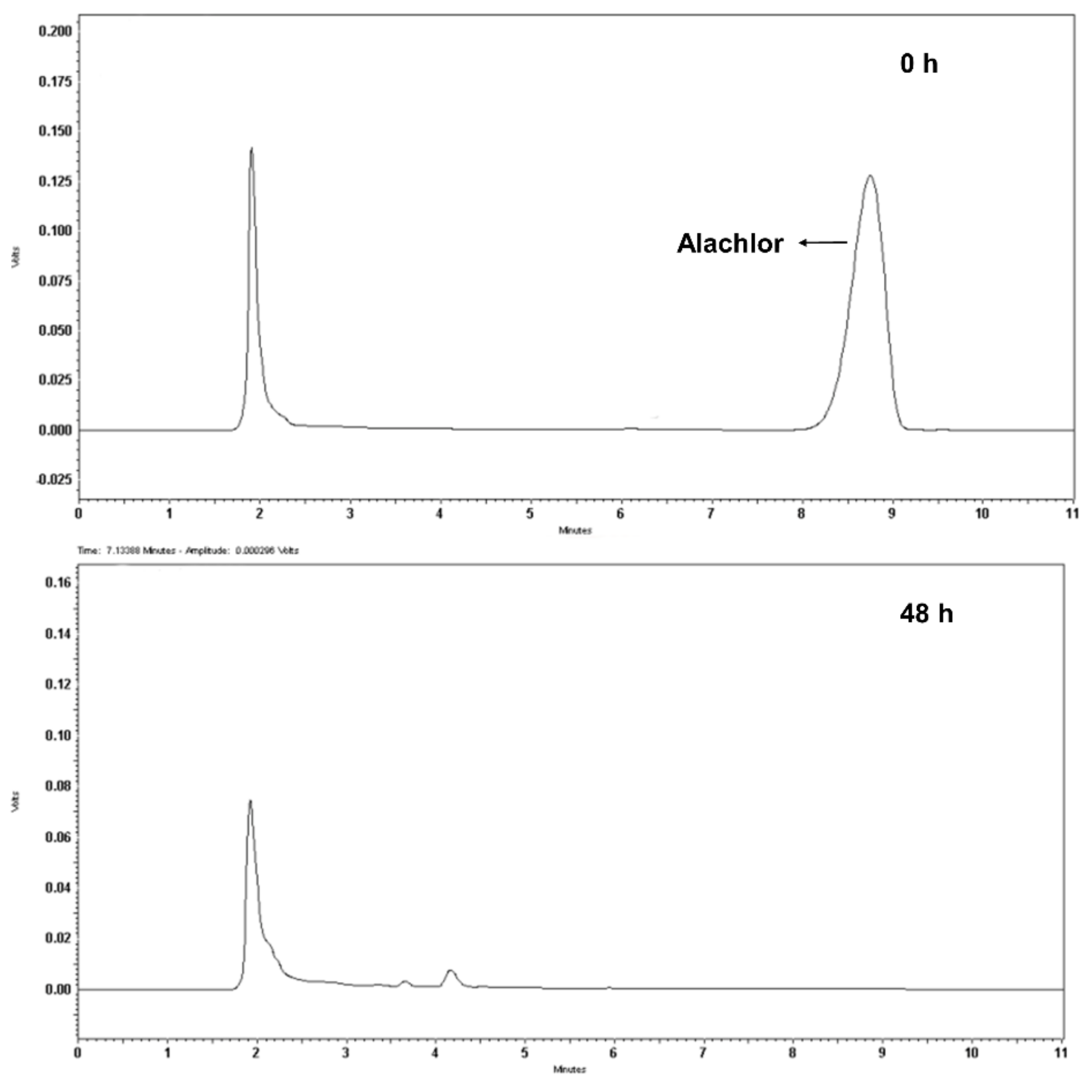
3.2. Degradation of Alachlor by Strain GC-A6
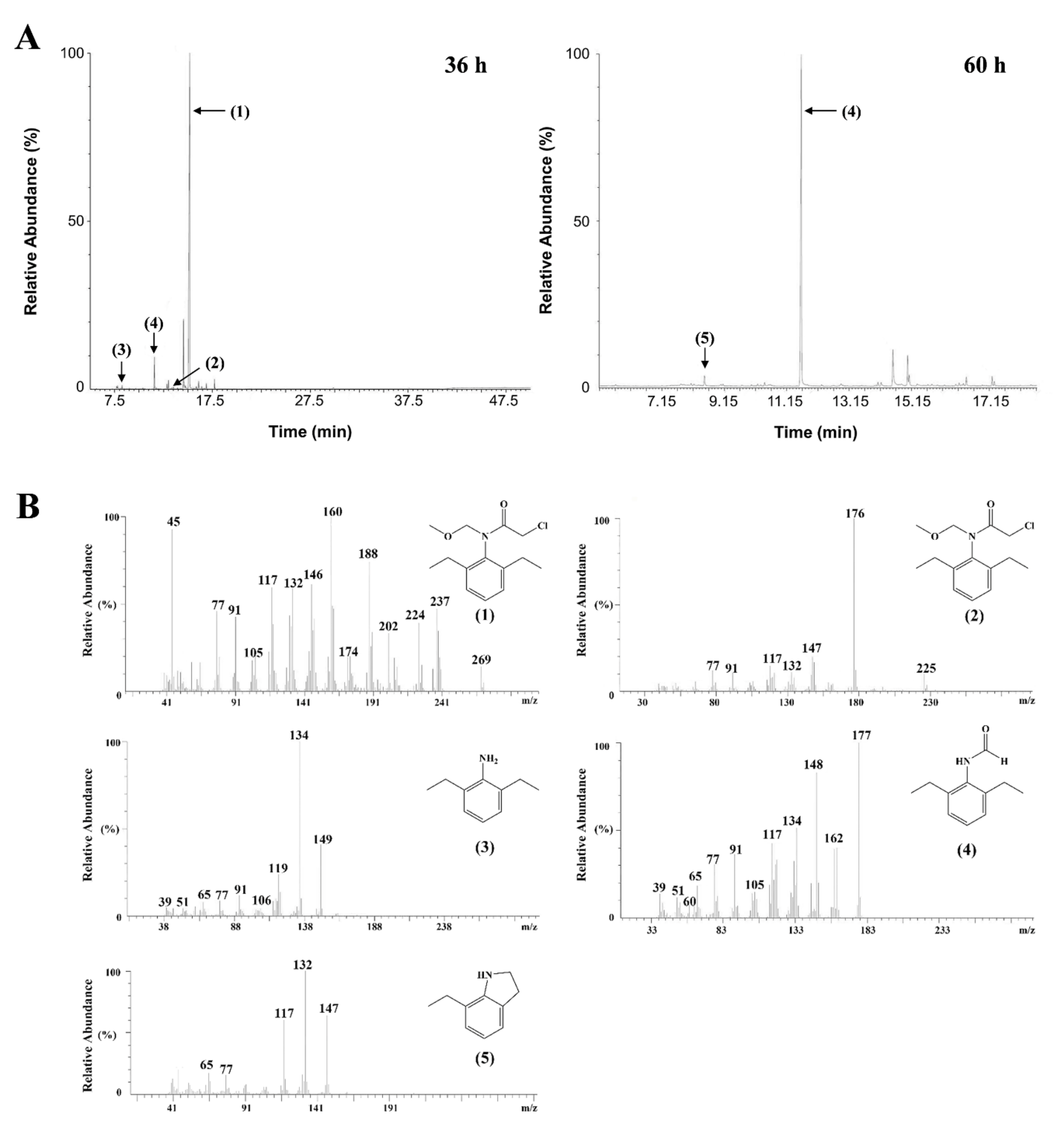
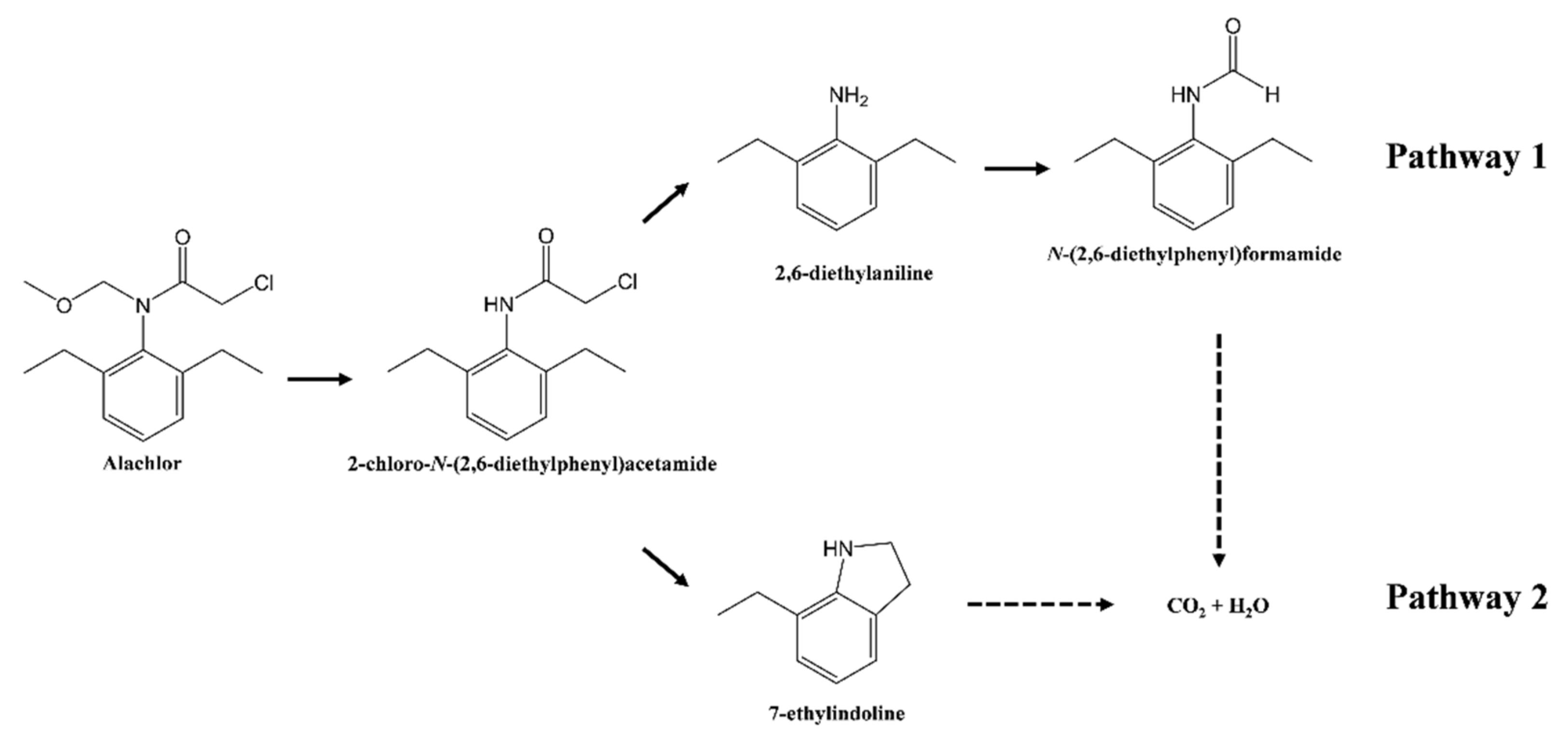
3.3. Identification of Metabolites
4. Discussion
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Leovac, A.; Vasyukova, E.; Ivančev-Tumbas, I.; Uhl, W.; Kragulj, M.; Tričković, J.; Kerkez, Đ.; Dalmacija, B. Sorption of atrazine, alachlor and trifluralin from water onto different geosorbents. RSC Adv. 2015, 5, 8122–8133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Torres, R.A.; Mosteo, R.; Pétrier, C.; Pulgarin, C. Experimental design approach to the optimization of ultrasonic degradation of alachlor and enhancement of treated water biodegradability. Ultrason. Sonochem. 2009, 16, 425–430. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chiang, H.C.; Duh, J.R.; Wang, Y.S. Butachlor, thiobencarb, and chlomethoxyfen movement in subtropical soils. Bull. Environ. Contam. Toxicol. 2001, 66, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hildebrandt, A.; Guillamón, M.; Lacorte, S.; Tauler, R.; Barceló, D. Impact of pesticides used in agriculture and vineyards to surface and groundwater quality (North Spain). Water Res. 2008, 42, 3315–3326. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vryzas, Z.; Tsaboula, A.; Papadopoulou-Mourkidou, E. Determination of alachlor, metolachlor, and their acidic metabolites in soils by microwave-assisted extraction (MAE) combined with solid phase extraction (SPE) coupled with GC-MS and HPLC-UV analysis. J. Sep. Sci. 2007, 30, 2529–2538. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Coleman, S.; Linderman, R.; Hodgson, E.; Rose, R.L. Comparative metabolism of chloroacetamide herbicides and selected metabolites in human and rat liver microsomes. Environ. Health Perspect. 2000, 108, 1151–1157. [Google Scholar]
- Genter, M.B.; Burman, D.M.; Bolon, B. Progression of alachlor-induced olfactory mucosal tumours. Int. J. Exp. Pathol. 2002, 83, 303–308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paule, A.; Biaz, A.; Leflaive, J.; Lawrence, J.R.; Rols, J.L. Fate of the herbicide alachlor exposed to different microbial consortia in aquatic system. Wat. Air Soil Poll. 2015, 226, 1–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bretveld, R.W.; Thomas, C.M.G.; Scheepers, P.T.J.; Zielhuis, G.A.; Roeleveld, N. Pesticide exposure: The hormonal function of the female reproductive system disrupted? Reprod. Biol. Endocrinol. 2006, 4, 40–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bergman, Å.; Heindel, J.J.; Jobling, S.; Kidd, K.; Zoeller, T.R. State of the Science of Endocrine Disrupting Chemicals 2012; World Health Organization: Geneva, Switzerland, 2013. [Google Scholar]
- Guidelines for Drinking-Water Quality, 4th ed.; World Health Organization: Geneva, Switzerland, 2017; Available online: https://www.who.int/publications/i/item/9789241549950 (accessed on 25 September 2022).
- Barbash, J.E.; Thelin, G.P.; Kolpin, D.W.; Gilliom, R.J. Major herbicides in ground water: Results from the National Water-Quality Assessment. J. Environ. Qual. 2001, 30, 831–845. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tiedje, J.M.; Hagedorn, M.L. Degradation of alachlor by a soil fungus, Chaetomium globosum. J. Agric. Food Chem. 1975, 23, 77–81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Durães Sette, L.; Mendonça Alves da Costa, L.A.; Marsaioli, A.J.; Manfio, G.P. Biodegradation of alachlor by soil streptomycetes. Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2004, 64, 712–717. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Munoz, A.; Koskinen, W.C.; Cox, L.; Sadowsky, M.J. Biodegradation and mineralization of metolachlor and alachlor by Candida xestobii. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2011, 59, 619–627. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, J.; Zheng, J.W.; Liang, B.; Wang, C.H.; Cai, S.; Ni, Y.Y.; He, J.; Li, S.P. Biodegradation of chloroacetamide herbicides by Paracoccus sp. FLY-8 in vitro. J. Agric. Food. Chem. 2011, 59, 4614–4621. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Słaba, M.; Szewczyk, R.; Piątek, M.A.; Długoński, J. Alachlor oxidation by the filamentous fungus Paecilomyces marquandii. J. Hazard. Mater. 2013, 261, 443–450. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Q.; Wang, C.H.; Deng, S.K.; Wu, Y.D.; Li, Y.; Yao, L.; Jiang, J.D.; Yan, X.; He, J.; Li, S.P. Novel three-component Rieske non-heme iron oxygenase system catalyzing the N-dealkylation of chloroacetanilide herbicides in Sphingomonads DC-6 and DC-2. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2014, 80, 5078–5085. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, N.H.; Kim, D.-U.; Kim, I.; Ka, J.-O. Syntrophic biodegradation of butachlor by Mycobacterium sp. J7A and Sphingobium sp. J7B isolated from rice paddy soil. FEMS Microbiol. Lett. 2013, 344, 114–120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lane, D.J. 16S/23S rRNA sequencing. In Nucleic Acid Techniques in Bacterial Systematics; Stackebrandt, E., Goodfellow, M., Eds.; Wiley: Chichester, UK, 1991; pp. 115–175. [Google Scholar]
- Lee, S.; Malone, C.; Kemp, P. Use of multiple 16S rRNA targeted fluorescent probes to increase signal strength and measure cellular RNA from natural planktonic bacteria. Mar. Ecol. Prog. Ser. 1993, 101, 193–201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yoon, S.-H.; Ha, S.-M.; Kwon, S.; Lim, J.; Kim, Y.; Seo, H.; Chun, J. Introducing EzBioCloud: A taxonomically united database of 16S rRNA gene sequence and whole-genome assemblies. Int. J. Syst. Evol. Microbiol. 2017, 67, 1613–1617. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pruesse, E.; Peplies, J.; Glöckner, F.O. SINA: Accurate high-throughput multiple sequence alignment of ribosomal RNA genes. Bioinformatics 2012, 28, 1823–1829. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saitou, N.; Nei, M. The neighbor-joining method: A new method for reconstructing phylogenetic trees. Mol. Biol. Evol. 1987, 4, 406–425. [Google Scholar]
- Fitch, W.M. Toward defining course of evolution-minimum change for a specific tree topology. Syst. Zool. 1971, 20, 406–416. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tamura, K.; Stecher, G.; Peterson, D.; Filipski, A.; Kumar, S. MEGA6: Molecular evolutionary genetics analysis version 6.0. Mol. Biol. Evol. 2013, 30, 2725–2729. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smibert, R.; Krieg, N. Phenotypic characterization. In Methods for General and Molecular Bacteriology; Gerhardt, P., Murra, R.G.E., Wood, W.A., Krieg, N.R., Eds.; American Society for Microbiology: Washington, DC, USA, 1994; pp. 607–654. [Google Scholar]
- Ten, L.N.; Xu, J.L.; Jin, F.X.; Im, W.-T.; Oh, H.-M.; Lee, S.-T. Spirosoma panaciterrae sp. nov., isolated from soil. Int. J. Syst. Evol. Microbiol. 2009, 59, 31–335. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gonzalez, J.M.; Saiz-Jimenez, C.A. Fluorimetric method for the estimation of G+C mol% content in microorganisms by thermal denaturation temperature. Environ. Microbiol. 2002, 4, 770–773. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, F.-Y.; Hong, M.-Z.; Liu, D.-M.; Li, Y.-W.; Show, P.-S.; Yan, H.; Shi, G.-Q. Biodegradation of methyl parathion by Acinetobacter radioresistens USTB-04. J. Environ. Sci. 2007, 19, 1257–1260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mazzoli, R.; Pessione, E.; Giuffrida, M.G.; Fattori, P.; Barello, C.; Giunta, C.; Lindley, N.D. Degradation of aromatic compounds by Acinetobacter radioresistens S13: Growth characteristics on single substrates and mixtures. Arch. Microbiol. 2007, 188, 55–68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, P.; Suri, C.R.; Cameotra, S.S. Isolation of a member of Acinetobacter species involved in atrazine degradation. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2004, 317, 697–702. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, W.; Jiang, S.; Shi, K.; Wang, F.; Li, S.; Zhou, J.; Huang, F.; Wang, Y.; Zheng, Y.; Hou, Y.; et al. Biodegradation of fenoxaprop-P-ethyl (FE) by Acinetobacter sp. strain DL-2 and cloning of FE hydrolase gene afeH. Bioresour. Technol. 2015, 186, 114–121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Badriyha, B.N.; Ravindran, V.; Den, W.; Pirbazari, M. Bioadsorber efficiency, design, and performance forecasting for alachlor removal. Water Res. 2003, 37, 4051–4072. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mangiapan, S.; Benfenati, E.; Grasso, P.; Terreni, M.; Pregnolato, M.; Pagani, G.; Barceló, D. Metabolites of alachlor in water: Identification by mass spectrometry and chemical synthesis. Environ. Sci. Technol. 1997, 31, 3637–3646. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Osano, O.; Admiraal, W.; Klamer, H.J.C.; Pastor, D.; Bleeker, E.A.J. Comparative toxic and genotoxic effects of chloroacetanilides, formamidines and their degradation products on Vibrio fischeri and Chironomus riparius. Environ. Pollut. 2002, 119, 195–202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| Characteristics | GC-A6 |
|---|---|
| Colony morphology | Circular, convex, and opaque (on PTYG agar) |
| Colony pigmentation | Yellowish white (on PTYG and LB agar) |
| Cell shape | Coccobacillus |
| Cell size (µm) | 0.6–0.8 × 0.3–0.5 |
| Gram staining | Negative |
| NaCl range for growth (w/v) (%) | 0–7 |
| pH range for growth | 5.5–9.5 |
| Temperature range for growth (°C) | 10–40 |
| Catalase | + |
| Oxidase | – |
| Alkaline phosphatase | + |
| Esterase (C4) | w |
| Esterase lipase (C8) | + |
| Lipase (C14) | – |
| Leucine arylamidase | + |
| Valine arylamidase | w |
| Cystine arylamidase | + |
| Trypsin | – |
| α-chymotrypsin | – |
| Acid phosphatase | w |
| Naphtol-AS-BI-phosphohydrolase | w |
| α-Galactosidase | – |
| β-Galactosidase | – |
| β-Glucuronidase | – |
| α-Glucosidase | – |
| β-Glucosidase | – |
| N-acetyl-β-glucosaminidase | – |
| α-Mannosidase | – |
| α-Fucosidase | – |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Lee, H.; Kim, D.-U. Biodegradation of Alachlor by a Newly Isolated Bacterium: Degradation Pathway and Product Analysis. Processes 2022, 10, 2256. https://doi.org/10.3390/pr10112256
Lee H, Kim D-U. Biodegradation of Alachlor by a Newly Isolated Bacterium: Degradation Pathway and Product Analysis. Processes. 2022; 10(11):2256. https://doi.org/10.3390/pr10112256
Chicago/Turabian StyleLee, Hyosun, and Dong-Uk Kim. 2022. "Biodegradation of Alachlor by a Newly Isolated Bacterium: Degradation Pathway and Product Analysis" Processes 10, no. 11: 2256. https://doi.org/10.3390/pr10112256
APA StyleLee, H., & Kim, D.-U. (2022). Biodegradation of Alachlor by a Newly Isolated Bacterium: Degradation Pathway and Product Analysis. Processes, 10(11), 2256. https://doi.org/10.3390/pr10112256







