Anti-Oxidative and Anti-Diabetic Effects of Electrolyzed Weakly Alkaline Reduced Water on Renal Proximal Tubular Epithelial Cells
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Cells and Chemicals
2.2. Properties of Experimental Waters
2.3. Experimental Design
2.4. Cell Viability Assay
2.5. In-Cell Enzyme-Linked Immunosorbent Assay (ELISA)
2.6. Quantification of Total ROS and Nitric Oxide (NO) Assay
2.7. Assessment of Endogenous Antioxidant Assay
2.8. Assessment of Glucose Uptake Assay
2.9. Analysis of ATP Concentration
2.10. Western Blot Analysis
2.11. Cytokines Analysis
2.12. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Cell Viability and Cleaved Caspase-3 Level in HG-Induced HK-2 Cells Are Alleviated by EWARW
3.2. Increase in OS in HG-Induced HK-2 Cells Is Suppressed by EWARW
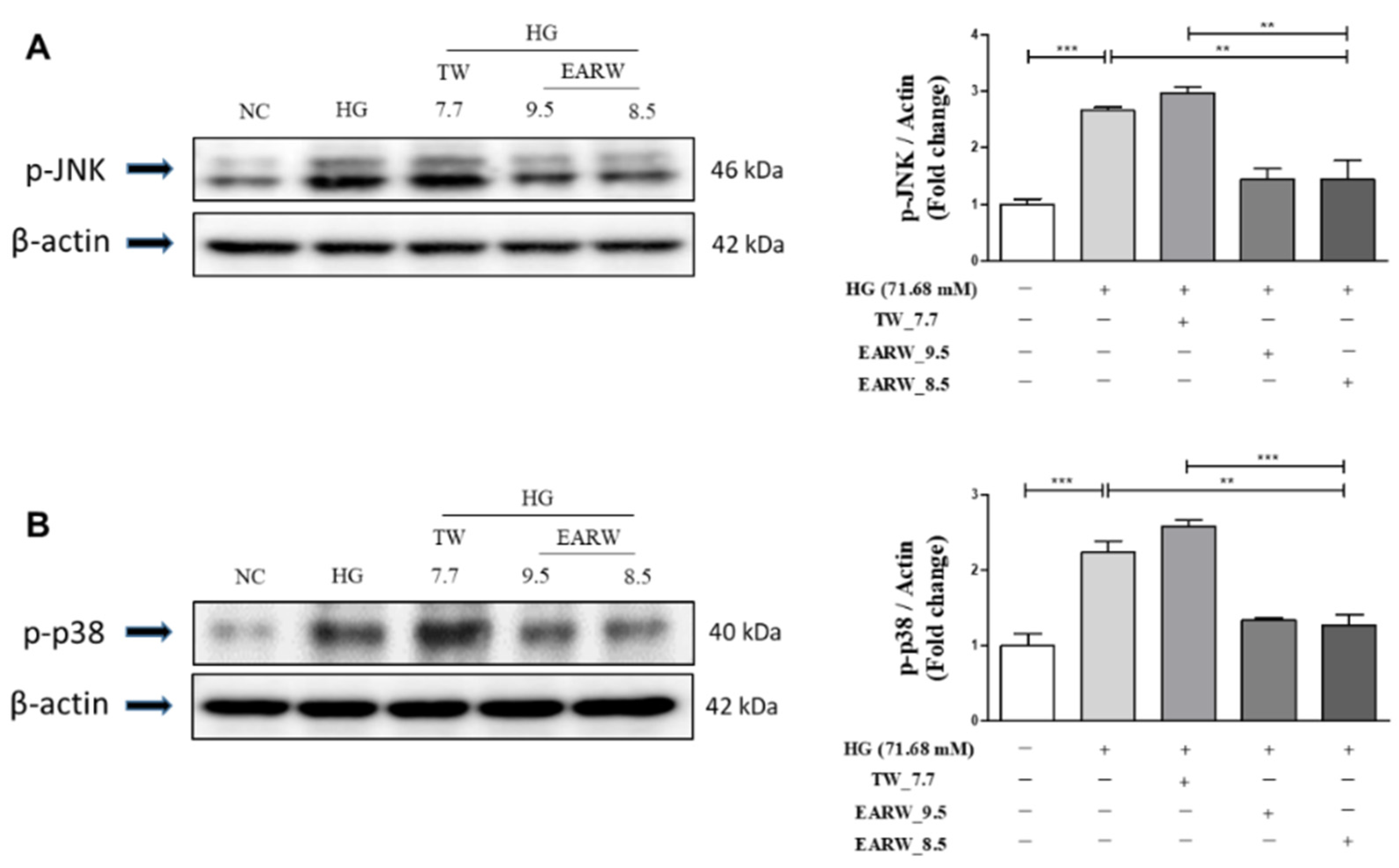
3.3. EWARW Attenuates the Increase in p-JNK and p-p38 MAPK Proteins in HG-Induced HK-2 Cells
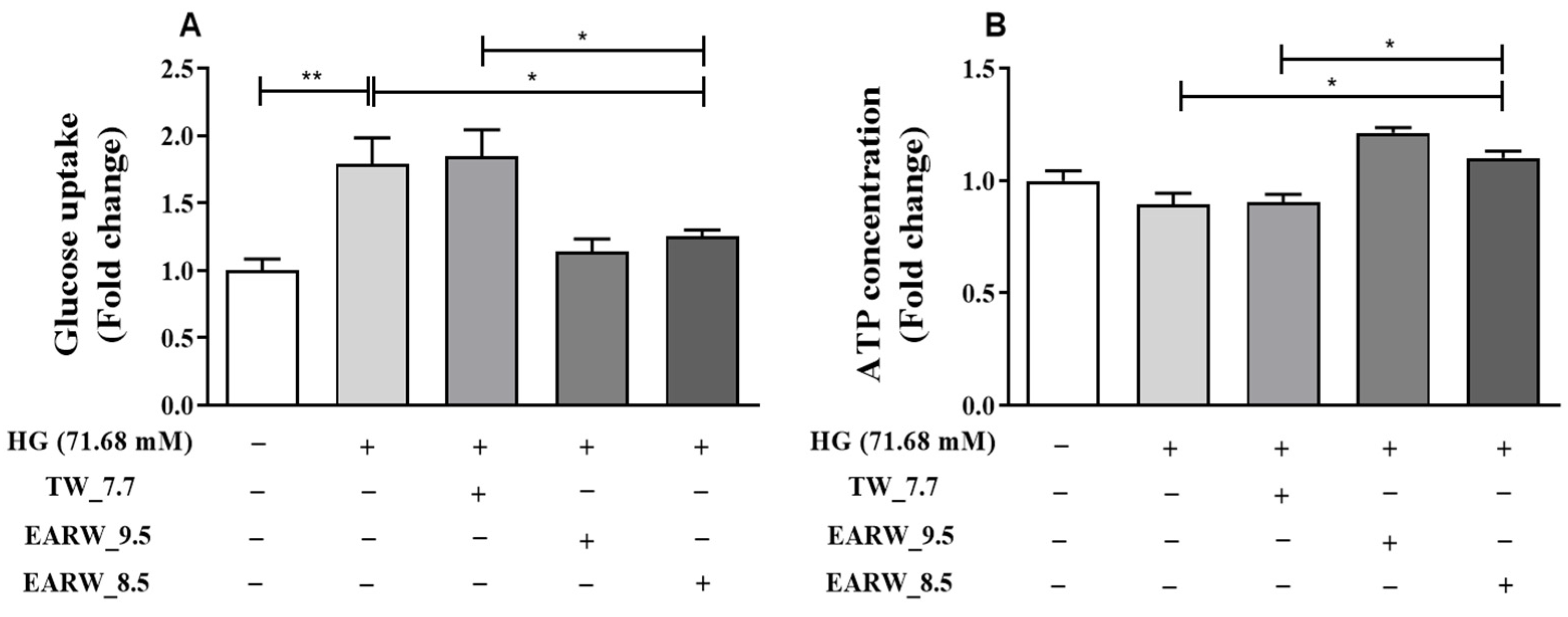
3.4. EWARW Improves Glucose Uptake and ATP Concentration in HG-Induced HK-2 Cells
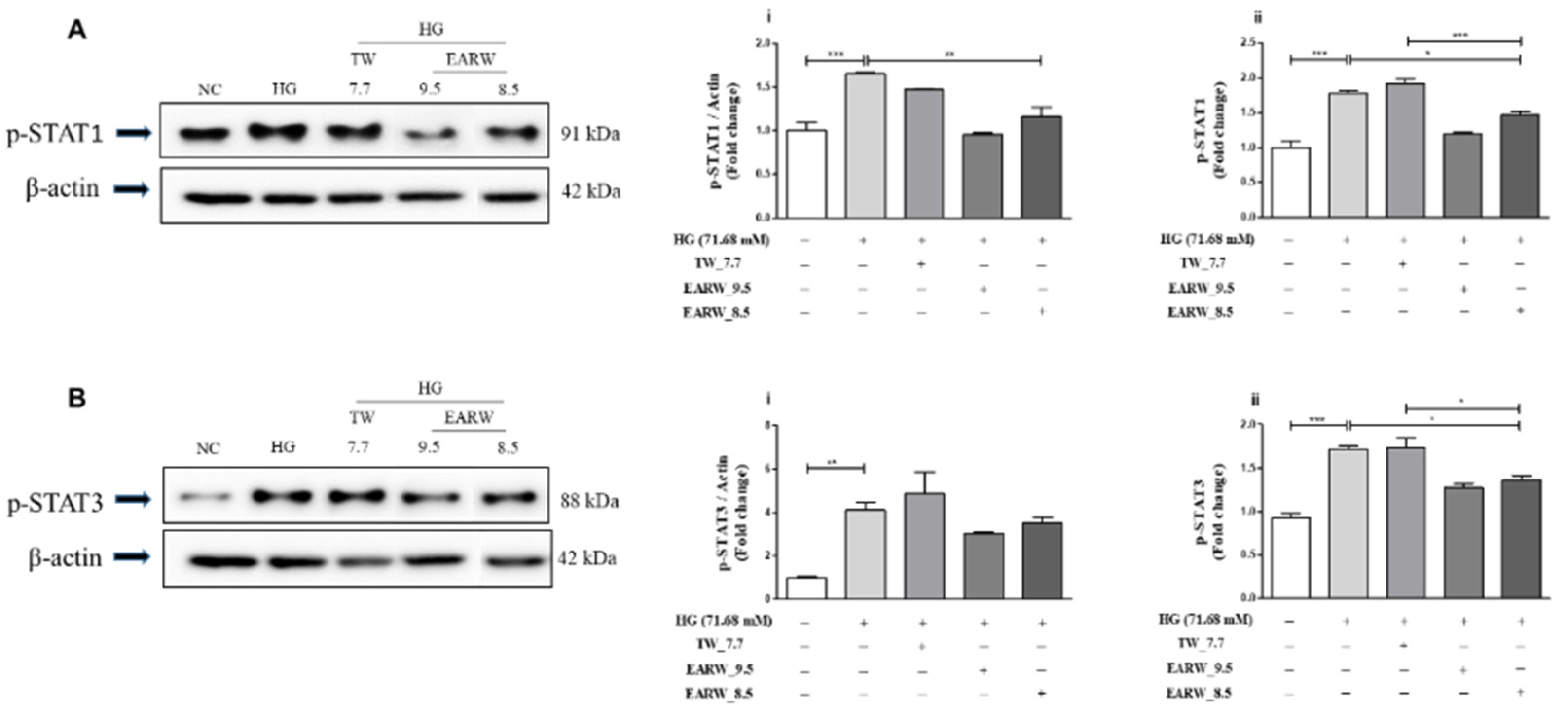
3.5. EWARW Rescued STAT Proteins in HG-Induced HK-2 Cells
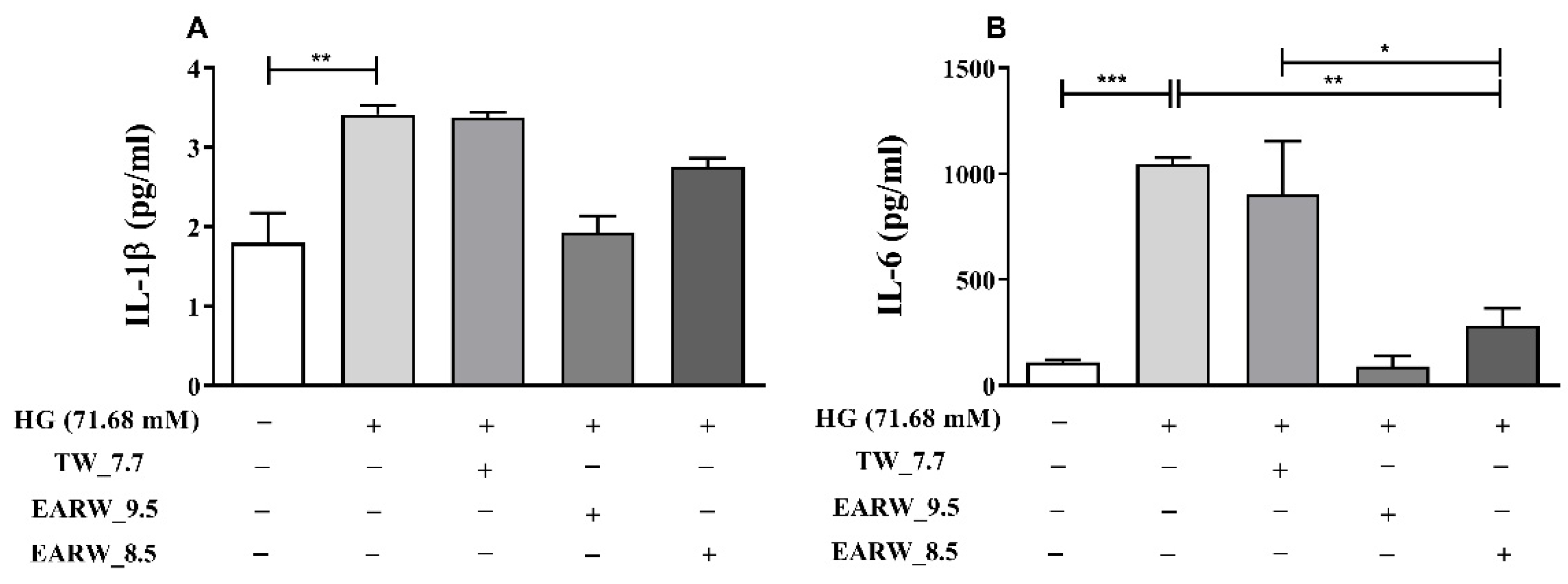
3.6. EWARW Rescues Pro-inflammatory Cytokines in HG-Induced HK-2 Cells
4. Discussion
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Jéquier, E.; Constant, F. Water as an essential nutrient: The physiological basis of hydration. Eur. J. Clin. Nutr. 2010, 64, 115–123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Islam, R.; Faysal, S.M.; Amin, R.; Juliana, F.M.; Islam, M.J.; Alam, J.; Hossain, M.N.; Asaduzzaman, M. Assessment of ph and total dissolved substances (tds) in the commercially available bottled drinking water. IOSR J. Nurs. Health Sci. 2017, 6, 35–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Trinh, T.T.; Fadriquela, A.; Bajgai, J.; Sharma, S.; Rahman, M.H.; Goh, S.H.; Khang, S.S.; Khang, W.R.; Kim, C.S.; Lee, K.J. Anti-oxidative effect of weak alkaline reduced water in raw 264.7 murine macrophage cells. Processes 2021, 9, 2062. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tanaka, Y.; Saihara, Y.; Izumotani, K.; Nakamura, H. Daily ingestion of alkaline electrolyzed water containing hydrogen influences human health, including gastrointestinal symptoms. Med. Gas Res. 2018, 8, 160–166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Park, S.K.; Qi, X.F.; Song, S.B.; Kim, D.H.; Teng, Y.C.; Yoon, Y.S.; Kim, K.Y.; Li, J.H.; Jin, D.; Lee, K.J. Electrolyzed-reduced water inhibits acute ethanol-induced hangovers in sprague-dawley rats. Biomed. Res. 2009, 30, 263–269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Magro, M.; Corain, L.; Ferro, S.; Baratella, D.; Bonaiuto, E.; Terzo, M.; Corraducci, V.; Salmaso, L.; Vianello, F. Alkaline water and longevity: A murine study. Evid. Based Complement. Alternat. Med. 2016, 2016, 3084126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Logozzi, M.; Mizzoni, D.; Di Raimo, R.; Andreotti, M.; Macchia, D.; Spada, M.; Fais, S. In vivo antiaging effects of alkaline water supplementation. J. Enzym. Inhib. Med. Chem. 2020, 35, 657–664. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Sharma, S.; Bajgai, J.; Antonio, J.M.; Fadriquela, A.; Trinh, T.T.; Rahman, M.H.; Vira, K.; Sofian, A.N.; Kim, C.S.; Lee, K.J. Anti-hyperglycemic effect of magnesium-enhanced alkaline-reduced water on high glucose-induced oxidative stress in renal tubular epithelial cells. Processes 2022, 10, 919. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zia, A.; Farkhondeh, T.; Pourbagher-Shahri, A.M.; Samarghandian, S. Role of oxidative stress and inflammatory factors in diabetic kidney disease. Curr. Mol. Med. 2022, 22, 37–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Trinh, T.T.; Fadriquela, A.; Lee, K.J.; Bajgai, J.; Sharma, S.; Rahman, M.H.; Kim, C.S.; Youn, S.H.; Jeon, H.T. Development of alkaline reduced water using high-temperature-roasted mineral salt and its antioxidative effect in raw 264.7 murine macrophage cell line. Processes 2021, 9, 1928. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, P.; Yuan, Y.; Zhang, T.; Xu, B.; Gao, Q.; Guan, T. Pentosan polysulfate ameliorates apoptosis and inflammation by suppressing activation of the p38 mapk pathway in high glucosetreated hk2 cells. Int. J. Mol. Med. 2018, 41, 908–914. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Pan, Y.; Huang, Y.; Wang, Z.; Fang, Q.; Sun, Y.; Tong, C.; Peng, K.; Wang, Y.; Miao, L.; Cai, L.; et al. Inhibition of mapk-mediated ace expression by compound c66 prevents stz-induced diabetic nephropathy. J. Cell. Mol. Med. 2014, 18, 231–241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hong, Z.; Hong, Z.; Wu, D.; Nie, H. Specific mapk inhibitors prevent hyperglycemia-induced renal diseases in type 1 diabetic mouse model. Mol. Cell. Biochem. 2016, 419, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Delos Reyes, F.S.L.G.; Mamaril, A.C.C.; Matias, T.J.P.; Tronco, M.K.V.; Samson, G.R.; Javier, N.D.; Fadriquela, A.; Antonio, J.M.; Sajo, M.E.J.V. The search for the elixir of life: On the therapeutic potential of alkaline reduced water in metabolic syndromes. Processes 2021, 9, 1876. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bajgai, J.; Kim, C.S.; Rahman, M.H.; Jeong, E.S.; Jang, H.Y.; Kim, K.E.; Choi, J.; Cho, I.; Lee, K.J.; Lee, M. Effects of alkaline-reduced water on gastrointestinal diseases. Processes 2022, 10, 87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, W.C.; Chau, Y.Y.; Ng, H.Y.; Chen, C.H.; Wang, P.W.; Liou, C.W.; Lin, T.K.; Chen, J.B. Empagliflozin protects hk-2 cells from high glucose-mediated injuries via a mitochondrial mechanism. Cells 2019, 8, 1085. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Gurzov, E.N.; Stanley, W.J.; Pappas, E.G.; Thomas, H.E.; Gough, D.J. The jak/stat pathway in obesity and diabetes. FEBS J. 2016, 283, 3002–3015. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Jiao, B.; An, C.; Du, H.; Tran, M.; Wang, P.; Zhou, D.; Wang, Y. STAT6 Deficiency Attenuates Myeloid Fibroblast Activation and Macrophage Polarization in Experimental Folic Acid Nephropathy. Cells 2021, 10, 3057. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jiao, B.; An, C.; Tran, M.; Du, H.; Wang, P.; Zhou, D.; Wang, Y. Pharmacological inhibition of STAT6 ameliorates myeloid fibroblast activation and alternative macrophage polarization in renal fibrosis. Front. Immunol. 2021, 12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ortiz-Munoz, G.; Lopez-Parra, V.; Lopez-Franco, O.; Fernandez-Vizarra, P.; Mallavia, B.; Flores, C.; Sanz, A.; Blanco, J.; Mezzano, S.; Ortiz, A.; et al. Suppressors of cytokine signaling abrogate diabetic nephropathy. J. Am. Soc. Nephrol. 2010, 21, 763–772. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, B.; Jia, Y.; Lu, D.; Sun, Z. Acute glucose fluctuation promotes in vitro intestinal epithelial cell apoptosis and inflammation via the nox4/ros/jak/stat3 signaling pathway. Exp. Ther. Med. 2021, 22, 688. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, Y.; Zhong, L.; Li, H.; Xu, Y.; Li, X.; Zheng, D. Psoralen alleviates high glucose-induced hk-2 cell injury by inhibition of smad 2 signaling via upregulation of microrna 874. BMC Pharmacol. Toxicol. 2020, 21, 52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Giap, L.K.; Muthuraman, A. Health benefits of alkaline ionized water. Rapp. De Pharm. 2020, 6, 616–621. [Google Scholar]
- Rubik, B. Studies and observations on the health effects of drinking electrolyzed-reduced alkaline water. In Water and Society; Pepper, D.W., Brebbia, C.A., Eds.; WIT Press: Southampton, UK, 2011; pp. 317–327. [Google Scholar]
- Balaji, R.; Duraisamy, R.; Kumar, M.P. Complications of diabetes mellitus: A review. Drug Invent. Today 2019, 12, 98–103. [Google Scholar]
- Saeedi, P.; Petersohn, I.; Salpea, P.; Malanda, B.; Karuranga, S.; Unwin, N.; Colagiuri, S.; Guariguata, L.; Motala, A.A.; Ogurtsova, K.; et al. Global and regional diabetes prevalence estimates for 2019 and projections for 2030 and 2045: Results from the International Diabetes Federation Diabetes Atlas, 9th edition. Diabetes Res. Clin. Pract. 2019, 157, 107843. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Aghadavod, E.; Khodadadi, S.; Baradaran, A.; Nasri, P.; Bahmani, M.; Rafieian-Kopaei, M. Role of oxidative stress and inflammatory factors in diabetic kidney disease. Iran. J. Kidney Dis. 2016, 10, 337–343. [Google Scholar]
- Cho, S.J.; Kang, K.A.; Piao, M.J.; Ryu, Y.S.; Fernando, P.; Zhen, A.X.; Hyun, Y.J.; Ahn, M.J.; Kang, H.K.; Hyun, J.W. 7, 8-dihydroxyflavone protects high glucose-damaged neuronal cells against oxidative stress. Biomol. Ther. 2019, 27, 85–91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jin, D.; Ryu, S.H.; Kim, H.W.; Yang, E.J.; Lim, S.J.; Ryang, Y.S.; Chung, C.H.; Park, S.K.; Lee, K.J. Anti-diabetic effect of alkaline-reduced water on oletf rats. Biosci. Biotechnol. Biochem. 2006, 70, 31–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- John, S. Complication in diabetic nephropathy. Diabetes Metab. Syndr. 2016, 10, 247–249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sturm, G.; Kollerits, B.; Neyer, U.; Ritz, E.; Kronenberg, F.; MMKD Study Group. Uric acid as a risk factor for progression of non-diabetic chronic kidney disease? The mild to moderate kidney disease (mmkd) study. Exp. Gerontol. 2008, 43, 347–352. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ryan, M.J.; Johnson, G.; Kirk, J.; Fuerstenberg, S.M.; Zager, R.A.; Torok-Storb, B. Hk-2: An immortalized proximal tubule epithelial cell line from normal adult human kidney. Kidney Int. 1994, 45, 48–57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Mossoba, M.E.; Mapa, M.S.T.; Sprando, J.; Araujo, M.; Sprando, R.L. Evaluation of transporter expression in hk-2 cells after exposure to free and ester-bound 3-mcpd. Toxicol. Rep. 2021, 8, 436–442. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.Q.; Dong, J.J.; Cai, T.; Shen, X.; Zhou, X.J.; Liao, L. High glucose induces apoptosis via upregulation of bim expression in proximal tubule epithelial cells. Oncotarget 2017, 8, 24119–24129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kowluru, R.A.; Chan, P.S. Oxidative stress and diabetic retinopathy. Exp. Diabetes Res. 2007, 2007, 43603. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Gharib, B.; Hanna, S.; Abdallahi, O.M.; Lepidi, H.; Gardette, B.; De Reggi, M. Anti-inflammatory properties of molecular hydrogen: Investigation on parasite-induced liver inflammation. C. R. Acad. Sci. III 2001, 324, 719–724. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, M.; Cao, X.; Luan, C.; Li, Z. Hydrogen sulfide attenuates hydrogen peroxide-induced injury in human lung epithelial a549 cells. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2019, 20, 3975. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Lubos, E.; Handy, D.E.; Loscalzo, J. Role of oxidative stress and nitric oxide in atherothrombosis. Front. Biosci. 2008, 13, 5323–5344. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Liou, G.Y.; Storz, P. Reactive oxygen species in cancer. Free Radic. Res. 2010, 44, 479–496. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Heck, D.E.; Shakarjian, M.; Kim, H.D.; Laskin, J.D.; Vetrano, A.M. Mechanisms of oxidant generation by catalase. Ann. N. Y. Acad. Sci. 2010, 1203, 120–125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Jeon, G.; Kim, C.; Cho, U.M.; Hwang, E.T.; Hwang, H.S.; Min, J. Melanin-decolorizing activity of antioxidant enzymes, glutathione peroxidase, thiol peroxidase, and catalase. Mol. Biotechnol. 2021, 63, 150–155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- You, I.S.; Sharma, S.; Fadriquela, A.; Bajgai, J.; Thi, T.T.; Rahman, M.H.; Sung, J.; Kwon, H.U.; Lee, S.Y.; Kim, C.S.; et al. Antioxidant properties of hydrogen gas attenuates oxidative stress in airway epithelial cells. Molecules 2021, 26, 6375. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ye, J.; Li, J.; Yu, Y.; Wei, Q.; Deng, W.; Yu, L. L-carnitine attenuates oxidant injury in hk-2 cells via ros-mitochondria pathway. Regul. Pept. 2010, 161, 58–66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lv, Z.M.; Wang, Q.; Wan, Q.; Lin, J.G.; Hu, M.S.; Liu, Y.X.; Wang, R. The role of the p38 mapk signaling pathway in high glucose-induced epithelial-mesenchymal transition of cultured human renal tubular epithelial cells. PLoS ONE 2011, 6, e22806. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lv, L.; Zhang, J.; Tian, F.; Li, X.; Li, D.; Yu, X. Arbutin protects hk-2 cells against high glucose-induced apoptosis and autophagy by up-regulating microrna-27a. Artif. Cells Nanomed. Biotechnol. 2019, 47, 2940–2947. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Son, Y.; Cheong, Y.K.; Kim, N.H.; Chung, H.T.; Kang, D.G.; Pae, H.O. Mitogen-activated protein kinases and reactive oxygen species: How can ros activate mapk pathways? J. Signal Transduct. 2011, 2011, 792639. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Behl, T.; Rana, T.; Alotaibi, G.H.; Shamsuzzaman, M.; Naqvi, M.; Sehgal, A.; Singh, S.; Sharma, N.; Almoshari, Y.; Abdellatif, A.A.H.; et al. Polyphenols inhibiting mapk signalling pathway mediated oxidative stress and inflammation in depression. Biomed. Pharmacother. 2022, 146, 112545. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, W.C.; Chiu, C.H.; Chen, J.B.; Chen, C.H.; Chang, H.W. Mitochondrial fission increases apoptosis and decreases autophagy in renal proximal tubular epithelial cells treated with high glucose. DNA Cell Biol. 2016, 35, 657–665. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhan, M.; Usman, I.M.; Sun, L.; Kanwar, Y.S. Disruption of renal tubular mitochondrial quality control by myo-inositol oxygenase in diabetic kidney disease. J. Am. Soc. Nephrol. 2015, 26, 1304–1321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Brosius, F.C. New insights into the mechanisms of fibrosis and sclerosis in diabetic nephropathy. Rev. Endocr. Metab. Disord. 2008, 9, 245–254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Marrero, M.B.; Banes-Berceli, A.K.; Stern, D.M.; Eaton, D.C. Role of the jak/stat signaling pathway in diabetic nephropathy. Am. J. Physiol. Renal Physiol. 2006, 290, F762–F768. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, T.C.; Wang, Z.H.; Feng, X.; Chuang, P.Y.; Fang, W.; Shen, Y.; Levy, D.E.; Xiong, H.; Chen, N.; He, J.C. Knockdown of stat3 activity in vivo prevents diabetic glomerulopathy. Kidney Int. 2009, 76, 63–71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Butturini, E.; Carcereri de Prati, A.; Mariotto, S. Redox regulation of stat1 and stat3 signaling. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2020, 21, 7034. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, D.; Liu, Y.; Chen, J.; Lin, H.; Guo, H.; Wu, Y.; Xu, Y.; Zhou, Y.; Zhou, W.; Lu, R.; et al. Jak/stat pathway promotes the progression of diabetic kidney disease via autophagy in podocytes. Eur. J. Pharmacol. 2021, 902, 174121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de Prati, A.C.; Ciampa, A.R.; Cavalieri, E.; Zaffini, R.; Darra, E.; Menegazzi, M.; Suzuki, H.; Mariotto, S. Stat1 as a new molecular target of anti-inflammatory treatment. Curr. Med. Chem. 2005, 12, 1819–1828. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, J.; Zhang, S.; Sun, X.; Lou, Y.; Yu, J. Hyperoside protects hk-2 cells against high glucose-induced apoptosis and inflammation via the mir-499a-5p/nrip1 pathway. Pathol. Oncol. Res. 2021, 27, 629829. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiang, E.; Han, B.; Zhang, Q.; Rao, W.; Wang, Z.F.; Chang, C.; Zhang, Y.Q.; Tu, C.S.; Li, C.Y.; Wu, D.C. Human umbilical cord-derived mesenchymal stem cells prevent the progression of early diabetic nephropathy through inhibiting inflammation and fibrosis. Stem Cell Res. Ther. 2020, 11, 1–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karmacharya, U.; Regmi, S.C.; Awasthi, B.P.; Chaudhary, P.; Kim, Y.E.; Lee, I.H.; Nam, T.g.; Kim, J.A.; Jeong, B.S. Synthesis and activity of n-(5-hydroxy-3, 4, 6-trimethylpyridin-2-yl) acetamide analogues as anticolitis agents via dual inhibition of tnf-α-and il-6-induced cell adhesions. Bioorg. Med. Chem. Lett. 2021, 43, 128059. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rias, Y.A.; Kurniawan, A.L.; Chang, C.W.; Gordon, C.J.; Tsai, H.T. Synergistic effects of regular walking and alkaline electrolyzed water on decreasing inflammation and oxidative stress, and increasing quality of life in individuals with type 2 diabetes: A community based randomized controlled trial. Antioxidants 2020, 9, 946. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gabay, C. Interleukin-6 and chronic inflammation. Arthritis Res. Ther. 2006, 8 (Suppl. 2), S3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]


| Water | pH | ORP (mV) | TDS (mg/L) | H2 (ppb) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| TW_7.7 | 7.7 | 609 | 63 | 0 |
| EARW_9.5 | 9.5 | −394 | 73 | 225 |
| EARW_8.5 | 8.5 | −63 | 67 | 150 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Sharma, S.; Lee, K.-J.; Bajgai, J.; Trinh, T.T.; Antonio, J.M.; Rahman, M.H.; Vira, K.; Sofian, A.-N.; Cho, S.H.; Kim, C.-S.; et al. Anti-Oxidative and Anti-Diabetic Effects of Electrolyzed Weakly Alkaline Reduced Water on Renal Proximal Tubular Epithelial Cells. Processes 2022, 10, 2025. https://doi.org/10.3390/pr10102025
Sharma S, Lee K-J, Bajgai J, Trinh TT, Antonio JM, Rahman MH, Vira K, Sofian A-N, Cho SH, Kim C-S, et al. Anti-Oxidative and Anti-Diabetic Effects of Electrolyzed Weakly Alkaline Reduced Water on Renal Proximal Tubular Epithelial Cells. Processes. 2022; 10(10):2025. https://doi.org/10.3390/pr10102025
Chicago/Turabian StyleSharma, Subham, Kyu-Jae Lee, Johny Bajgai, Thuy Thi Trinh, Jayson M. Antonio, Md. Habibur Rahman, Kchorng Vira, Abdul-Nasir Sofian, Syung Hyun Cho, Cheol-Su Kim, and et al. 2022. "Anti-Oxidative and Anti-Diabetic Effects of Electrolyzed Weakly Alkaline Reduced Water on Renal Proximal Tubular Epithelial Cells" Processes 10, no. 10: 2025. https://doi.org/10.3390/pr10102025
APA StyleSharma, S., Lee, K.-J., Bajgai, J., Trinh, T. T., Antonio, J. M., Rahman, M. H., Vira, K., Sofian, A.-N., Cho, S. H., Kim, C.-S., & Kim, Y. (2022). Anti-Oxidative and Anti-Diabetic Effects of Electrolyzed Weakly Alkaline Reduced Water on Renal Proximal Tubular Epithelial Cells. Processes, 10(10), 2025. https://doi.org/10.3390/pr10102025









