Three-Dimensional Dynamic Formation of Second-Order Multi-Agent System Based on Rigid Graphs
Abstract
1. Introduction
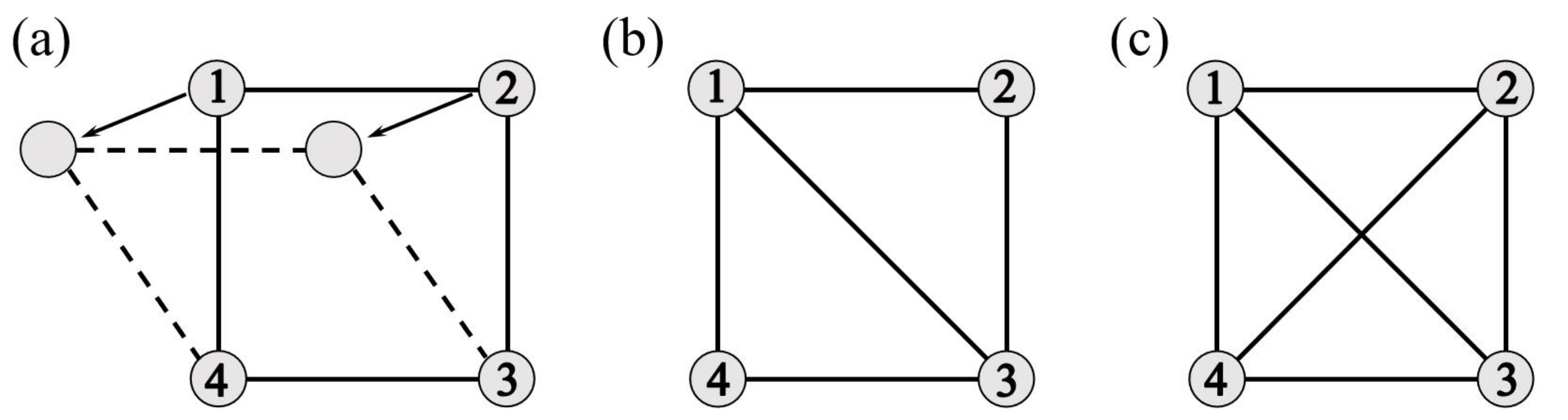
2. Notations and Basic Concepts
3. Problem Statement
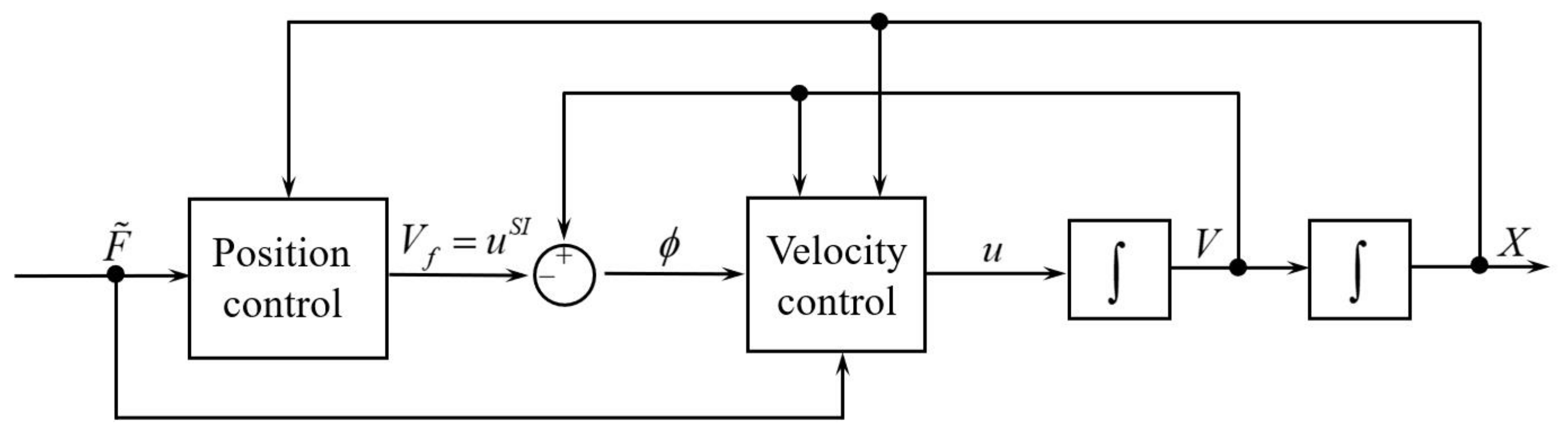
4. Design for Control Inputs
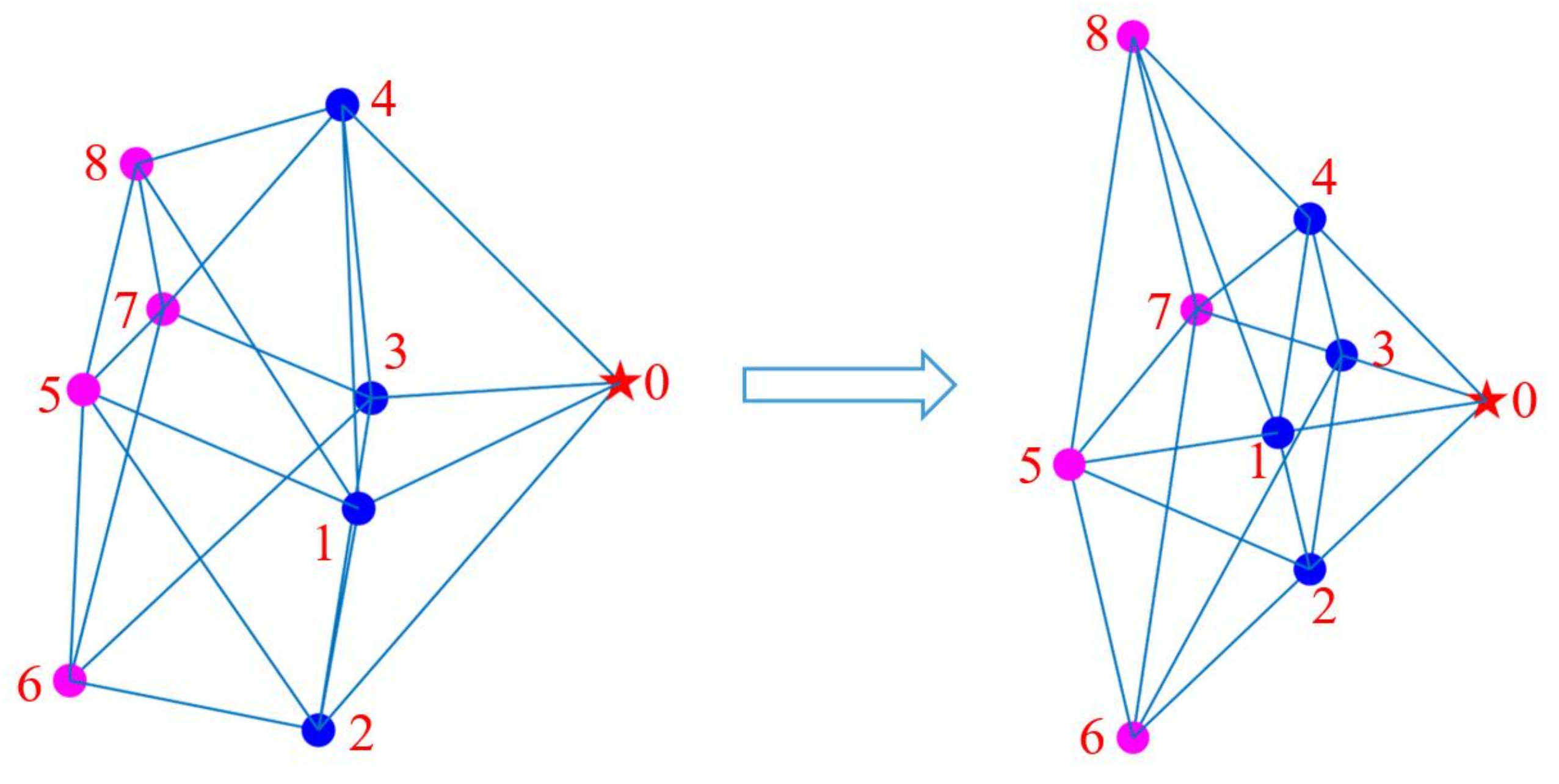
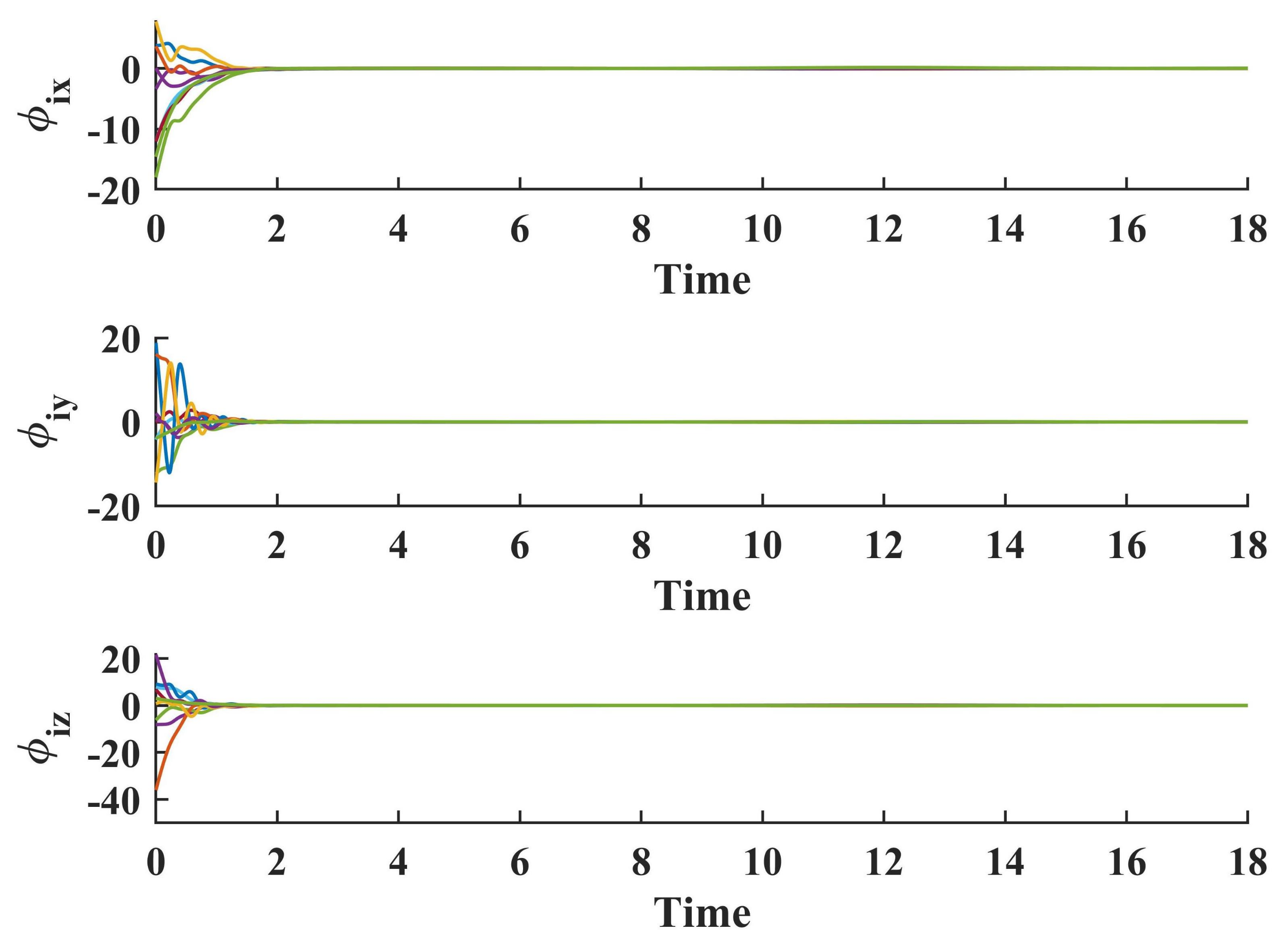
5. Simulation Results
6. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Animasaun, I.L.; Shah, N.A.; Wakif, A.; Mahanthesh, B.; Sivaraj, R.; Koriko, O.K. Conceptual and Empirical Reviews I. In Ratio of Momentum Diffusivity to Thermal Diffusivity: Introduction, Meta-Analysis, and Scrutinization; Chapman and Hall/CRC: New York, NY, USA, 2022. [Google Scholar]
- Wen, G.; Zheng, W.X. On Constructing Multiple Lyapunov Functions for Tracking Control of Multiple Agents with Switching Topologies. IEEE Trans. Automat. Control 2019, 64, 3796–3803. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yongzhao, H.; Xiwang, D.; Qingdong, L.; Zhang, R. Distributed Fault-Tolerant Time-Varying Formation Control for Second-Order Multi-Agent Systems with Actuator Failures and Directed Topologies. IEEE Trans. Circuits Syst. II Express Briefs 2017, 65, 774–778. [Google Scholar]
- Meng, Z.; Anderson, B.; Hirche, S. Formation control with mismatched compasses. Automatica 2016, 69, 232–241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deng, J.; Wang, L.; Liu, Z. Attitude synchronization and rigid formation of multiple rigid bodies over proximity networks. Automatica 2018, 125, 109388. [Google Scholar]
- Olfatisaber, R.; Murray, R.M. Graph rigidity and distributed formation stabilization of multi-vehicle systems. In Proceedings of the 41st IEEE Conference on Decision and Control, Las Vegas, NV, USA, 10–13 December 2002. [Google Scholar]
- Krick, L.; Broucke, M.E.; Francis, B.A. Stabilization of infinitesimally rigid formations of multi-robot networks. Int. J. Control 2009, 82, 423–439. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oh, K.K.; Ahn, H.S. Formation control of mobile agents based on inter-agent distance dynamics. Automatica 2011, 47, 2306–2312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cai, X.; de Queiroz, M. Multi-agent formation maneuvering and target interception with double-integrator model. In Proceedings of the American Control Conference, Portland, OR, USA, 4–6 June 2014. [Google Scholar]
- Cai, X.; de Queiroz, M. Multi-agent formation maintenance and target tracking. In Proceedings of the American Control Conference (ACC), Washington, DC, USA, 17–19 June 2013. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, P.; Queiroz, M.D.; Cai, X. Three-Dimensional Dynamic Formation Control of Multi-Agent Systems Using Rigid Graphs. J. Dyn. Syst. Meas. Control 2015, 137, 111006. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deghat, M.; Anderson, B.; Lin, Z. Combined Flocking and Distance-Based Shape Control of Multi-Agent Formations. IEEE Trans. Automat. Control 2016, 61, 1824–1837. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cai, X.; Queiroz, M.D. Rigidity-Based Stabilization of Multi-Agent Formations. J. Dyn. Syst. Meas. Control 2013, 136, 014502. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oh, K.K.; Ahn, H.S. Distance-based undirected formations of single-integrator and double-integrator modeled agents in n-dimensional space. Int. J. Robust Nonlinear Control 2013, 24, 1809–1820. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, M.; Morse, A.S.; Yu, C.; Anderson, B.; Dasgupta, S. Maintaining a Directed, Triangular Formation of Mobile Autonomous Agents. Commun. Inf. Syst. 2011, 11, 1–16. [Google Scholar]
- Park, M.C.; Anderson, B.; Sun, Z.; Ahn, H.S. Stability analysis on four agent tetrahedral formations. In Proceedings of the 53rd IEEE Conference on Decision and Control, Los Angeles, CA, USA, 15–17 December 2015; pp. 631–636. [Google Scholar]
- Sun, Z.; Mou, S.; Anderson, B.; Morse, A.S. Non-robustness of gradient control for 3-D undirected formations with distance mismatch. In Proceedings of the Australian Control Conference, Fremantle, WA, Australia, 4–5 November 2013. [Google Scholar]
- Babazadeh, R.; Selmic, R. Distance-Based Multiagent Formation Control with Energy Constraints Using SDRE. IEEE Trans. Aerosp. Electron. Syst. 2019, 56, 41–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Queiroz, M.D.; Cai, X. Formation Maneuvering and Target Interception for Multi-Agent Systems via Rigid Graphs. Asian J. Control 2015, 17, 1174–1186. [Google Scholar]
- Khaledyan, M.; Liu, T.; Queiroz, M.D. Flocking and Target Interception Control for Formations of Nonholonomic Kinematic Agents. IEEE Trans. Control Syst. Technol. 2019, 28, 1603–1610. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, M.; Morse, A.S.; Yu, C.; Anderson, B.D.O.; Dasguvta, S. Maintaining a Directed, Triangular Formation of Mobile Autonomous Agents. In Proceedings of the 46th IEEE Conference on Decision and Control, New Orleans, LA, USA, 12–14 December 2007; pp. 3603–3608. [Google Scholar]
- Dorfler, F.; Francis, B. Geometric Analysis of the Formation Problem for Autonomous Robots. IEEE Trans. Automat. Control 2010, 55, 2379–2384. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Olfati-Saber, R.; Murray, R.M. Distributed cooperative control of multiple vehicle formations using structural potential functions. IFAC Proc. Vol. 2002, 35, 495–500. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, Z.; Park, M.-C.; Anderson, B.D.O.; Ahn, H.-S. Distributed stabilization control of rigid formations with prescribed orientation. Automatica 2017, 78, 250–257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anderson, B.; Yu, C.; Fidan, B.; Hendrickx, J. Rigid graph control architectures for autonomous formations. Control Syst. IEEE 2008, 28, 48–63. [Google Scholar]
- Asimow, L.; Roth, B. The rigidity of graphs, II. J. Math. Anal. Appl. 1979, 68, 171–190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vu, V.T.; Tran, Q.H.; Pham, T.L.; Dao, P.N. Online Actor-critic Reinforcement Learning Control for Uncertain Surface Vessel Systems with External Disturbances. Int. J. Control Autom. 2022, 20, 1029–1040. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vu, V.T.; Pham, T.L.; Dao, P.N. Disturbance observer-based adaptive reinforcement learning for perturbed uncertain surface vessels. ISA Trans. 2022, in press. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]




Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Tian, G.; Liu, L.; Yang, C.; Cui, Y.; Hou, K.; Liu, D.; Xue, C. Three-Dimensional Dynamic Formation of Second-Order Multi-Agent System Based on Rigid Graphs. Processes 2022, 10, 1961. https://doi.org/10.3390/pr10101961
Tian G, Liu L, Yang C, Cui Y, Hou K, Liu D, Xue C. Three-Dimensional Dynamic Formation of Second-Order Multi-Agent System Based on Rigid Graphs. Processes. 2022; 10(10):1961. https://doi.org/10.3390/pr10101961
Chicago/Turabian StyleTian, Gailing, Lu Liu, Chenyu Yang, Yu Cui, Kaiyan Hou, Dan Liu, and Chenyang Xue. 2022. "Three-Dimensional Dynamic Formation of Second-Order Multi-Agent System Based on Rigid Graphs" Processes 10, no. 10: 1961. https://doi.org/10.3390/pr10101961
APA StyleTian, G., Liu, L., Yang, C., Cui, Y., Hou, K., Liu, D., & Xue, C. (2022). Three-Dimensional Dynamic Formation of Second-Order Multi-Agent System Based on Rigid Graphs. Processes, 10(10), 1961. https://doi.org/10.3390/pr10101961





