Catalytic Oxidation of NO by Ozone over Mn-Ce/Al2O3/TiO2 Catalyst
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Preparation of Catalysts
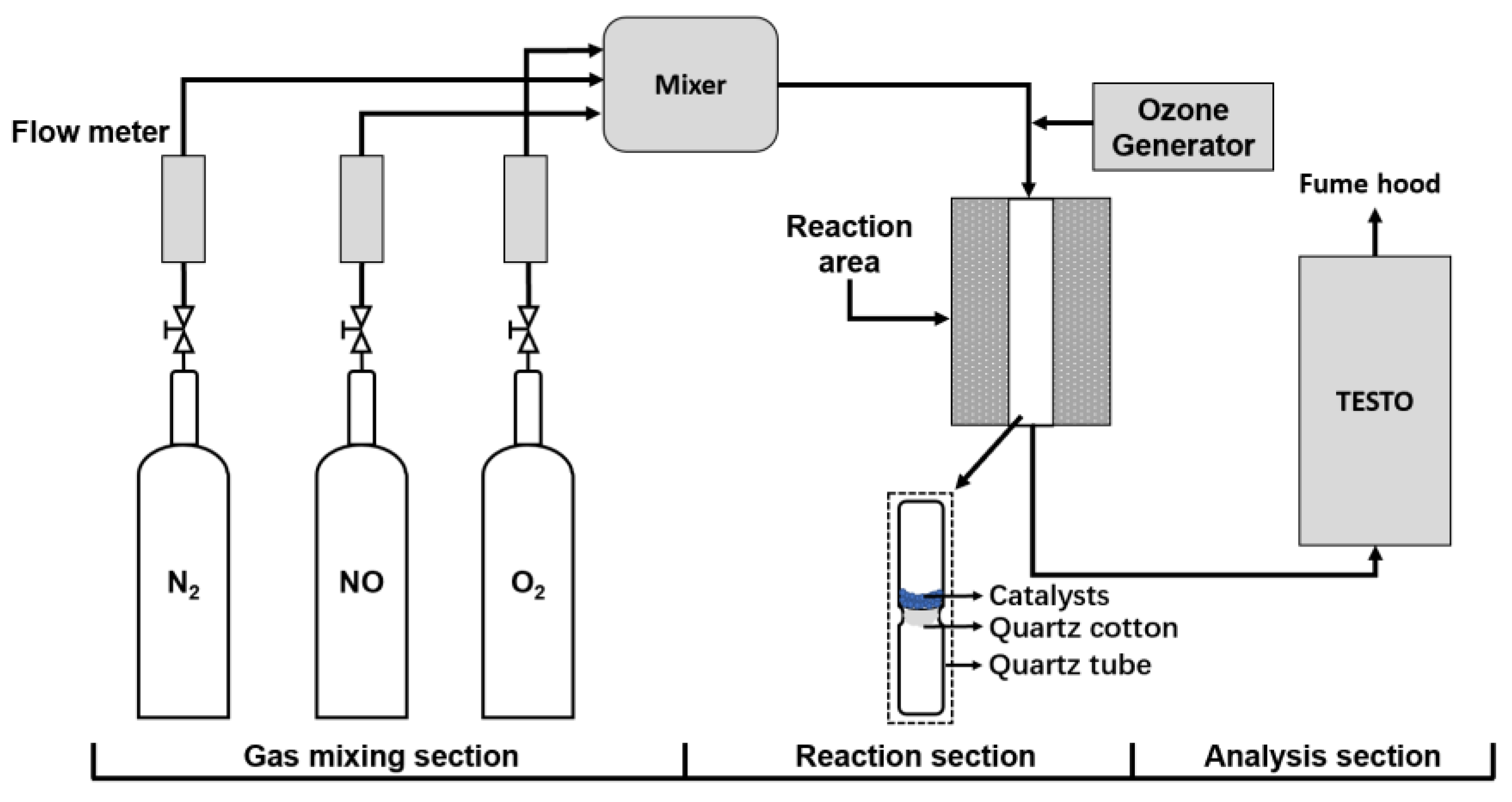
2.2. Experimental Setup
2.3. Catalyst Performance Test
2.4. Characterization of Catalysts
3. Results
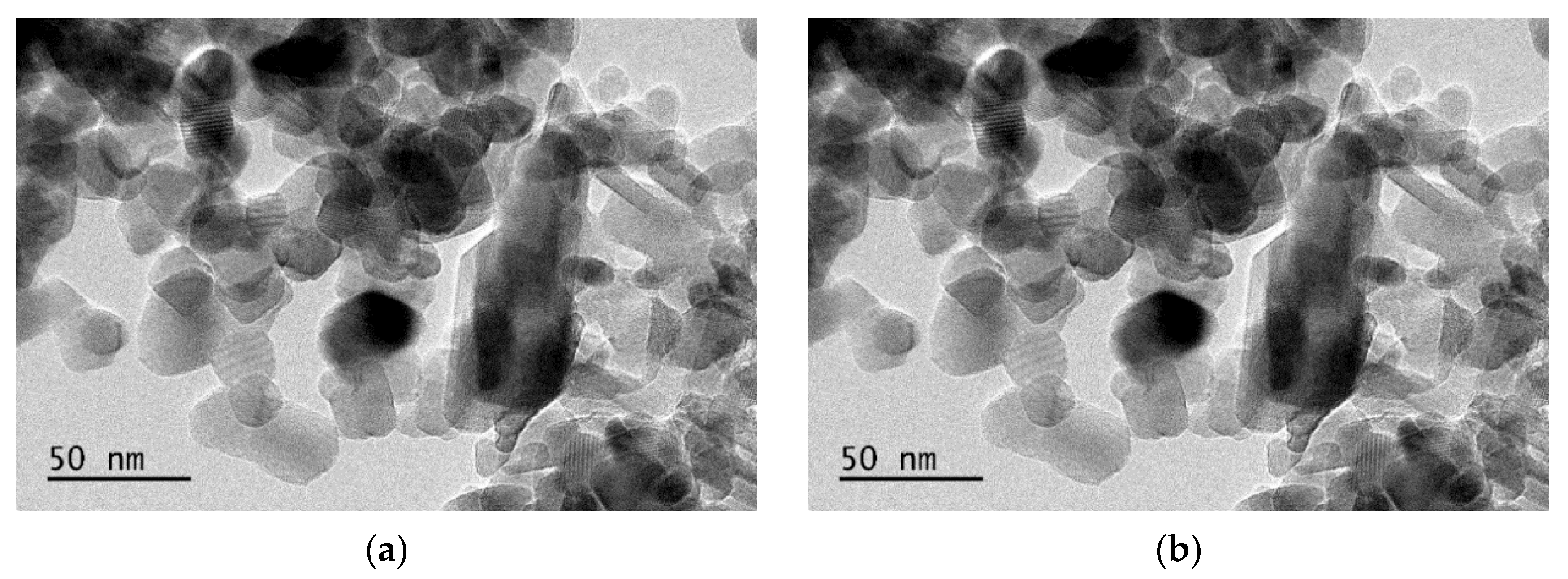
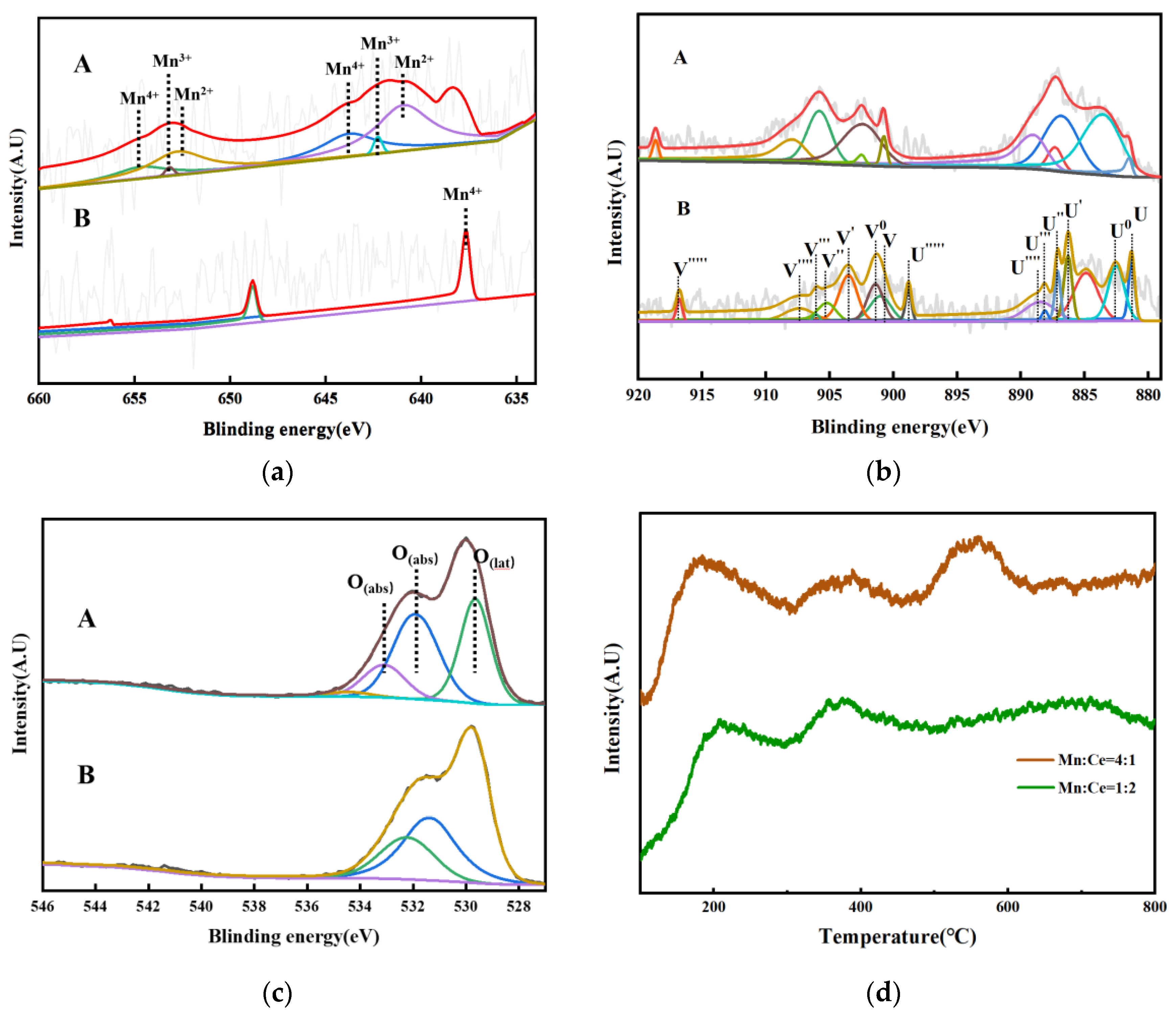
3.1. Morphology Analysis of Catalysts
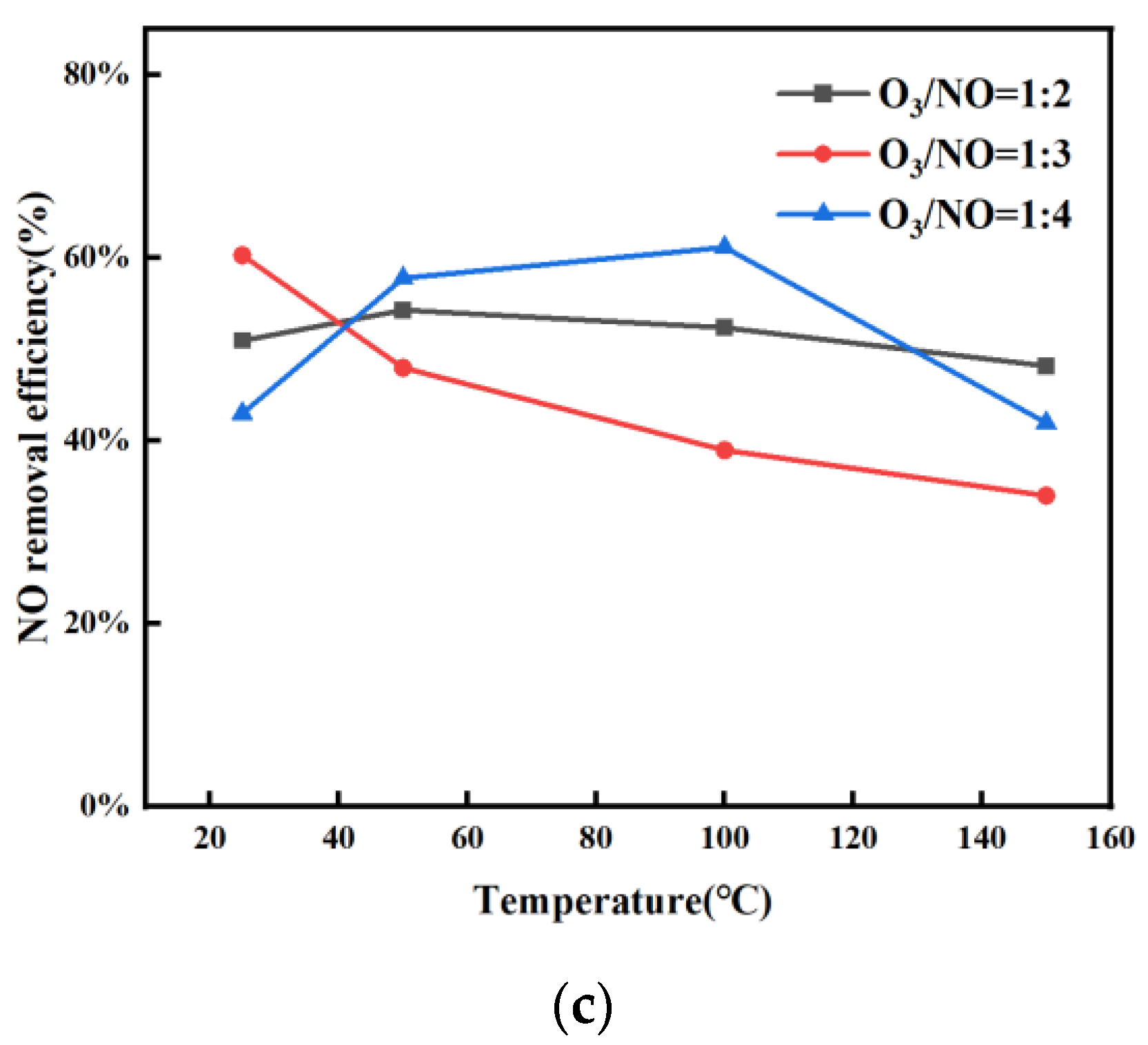
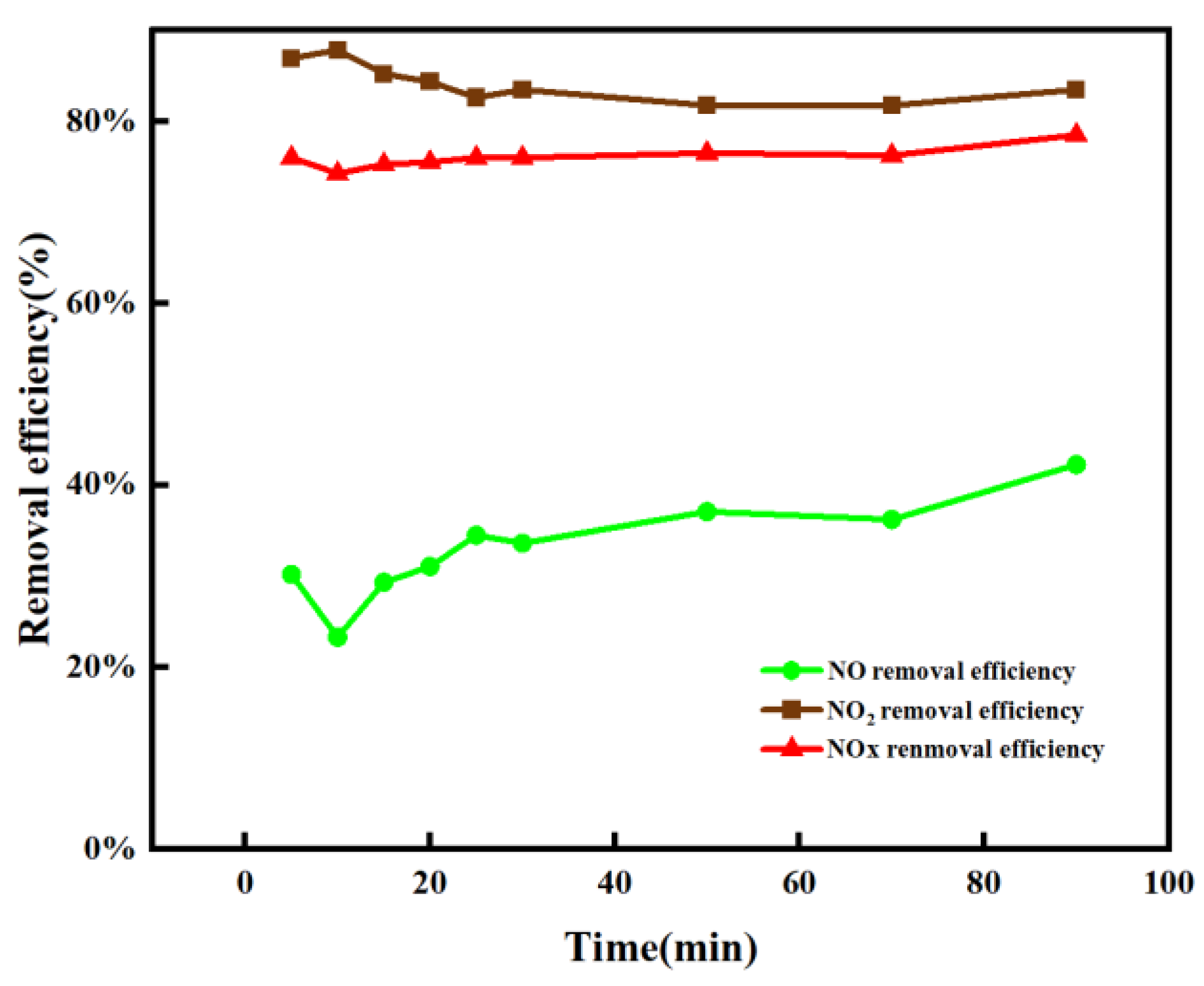
3.2. Catalyst Performance Analysis
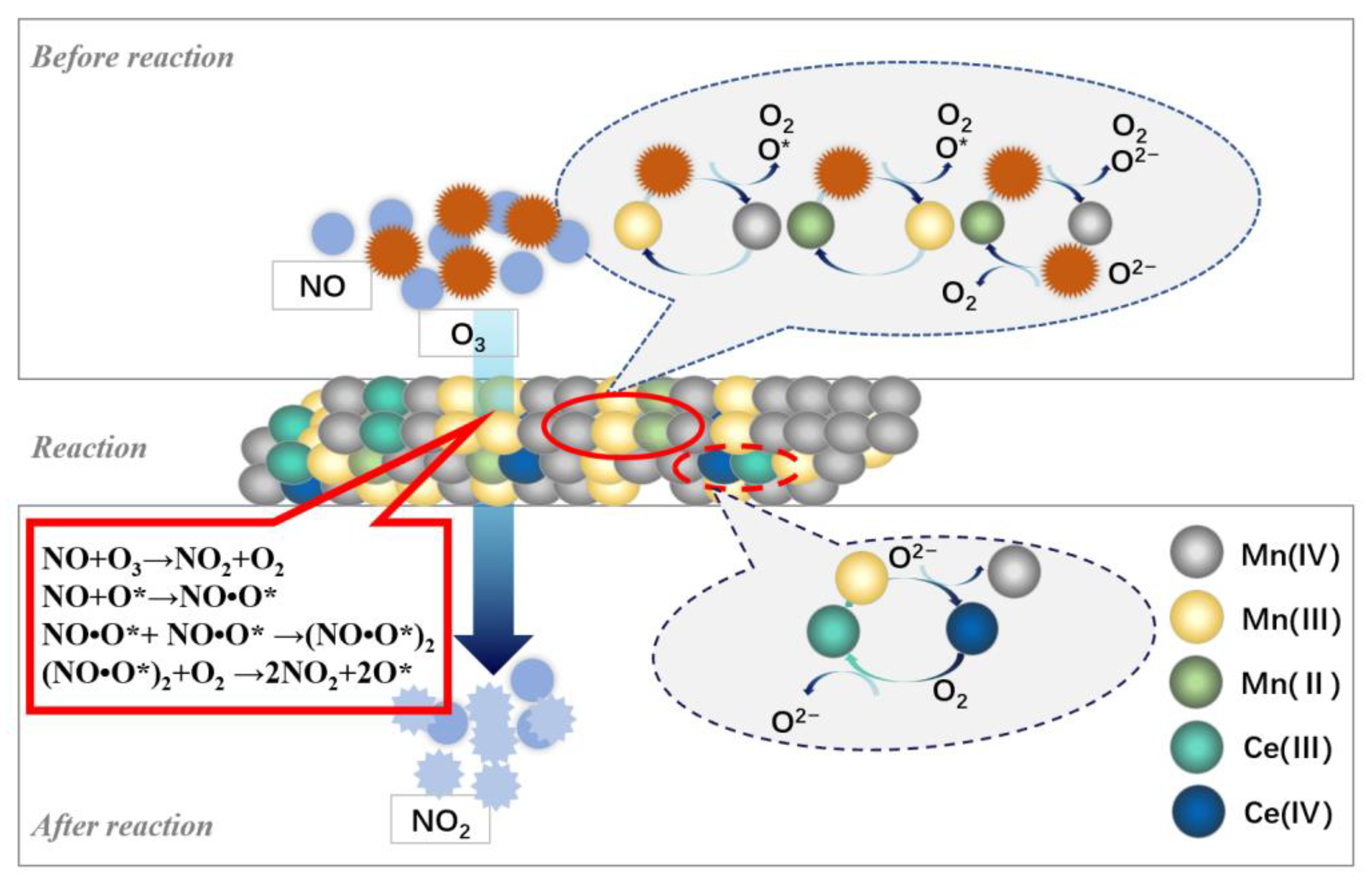
3.3. Reaction Mechanism
4. Conclusions
- The Mn-Ce/Al2O3/TiO2 catalyst was prepared by the impregnation method. The catalysts were characterized by BET, XRD, TEM, XPS, and O2-TPD. The results show that the catalysts have a large specific surface area (52.080 m2/g) and pore volume (0.346 cm3/g). High-specific surface areas are beneficial to promote the catalytic performance by offering more active sites. The catalyst mainly contains particle and bulk morphology, and the active components (MnOx, CeOx) are uniformly dispersed, and no agglomeration occurs. At the same time, the catalyst contains a large number of CeOx, O (lat), and O (abs) species. The content of MnOx, oxygen species on the surface of the catalyst, is the factor affecting the activity of the catalyst.
- The mechanism study shows that the MnOx content on the catalyst surface is the main factor affecting the catalyst activity. The presence of Mn2+ and Mn3+ on the surface of the catalyst can promote the decomposition of ozone to produce O*. O2- contributes to the reduction reaction between Mn2+ and Mn4+, and O* and oxygen species on the catalyst surface significantly promote the oxidation of NO to NO2.
- Under the experimental conditions of flue gas temperature 100–150 °C, the molar ratio of Mn:Ce = 4:1, the volume ratio of O3:NO = 1:4, and the NO removal rate can reach 63%. Compared with the oxidation of NO by ozone alone, the oxidation efficiency of NO can be increased by 40% by adding a catalyst. The experimental results show that the prepared catalyst can significantly improve the efficiency of ozone oxidation of NO and reduce the amount of ozone. After NaOH absorption, the NOx removal efficiency achieves up to 79.6% for the O3 + Mn-Ce (4:1)/Al2O3/TiO2 method, which can well meet the NOx emission standard in China.
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Lin, F.; Wang, Z.; Zhang, Z.; He, Y.; Zhu, Y.; Shao, J.; Yuan, D.; Chen, G.; Cen, K. Flue Gas Treatment with Ozone Oxidation: An Overview on NOx, Organic Pollutants, and Mercury. Chem. Eng. J. 2020, 382, 123030. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ren, X.; Sun, R.; Meng, X.; Vorobiev, N.; Schiemann, M.; Levendis, Y.A. Carbon, Sulfur and Nitrogen Oxide Emissions from Combustion of Pulverized Raw and Torrefied Biomass. Fuel 2017, 188, 310–323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Andreae, M.O. Emission of Trace Gases and Aerosols from Biomass Burning—An Updated Assessment. Atmospheric Chem. Phys. 2019, 19, 8523–8546. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhutto, A.W.; Bazmi, A.A.; Karim, S.; Abro, R.; Mazari, S.A.; Nizamuddin, S. Promoting Sustainability of Use of Biomass as Energy Resource: Pakistan’s Perspective. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2019, 26, 29606–29619. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhai, J.; Burke, I.T.; Stewart, D.I. Beneficial Management of Biomass Combustion Ashes. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 2021, 151, 111555. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suzuki, K.; Tsuji, N.; Shirai, Y.; Hassan, M.A.; Osaki, M. Evaluation of Biomass Energy Potential towards Achieving Sustainability in Biomass Energy Utilization in Sabah, Malaysia. Biomass Bioenergy 2017, 97, 149–154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brosowski, A.; Krause, T.; Mantau, U.; Mahro, B.; Noke, A.; Richter, F.; Raussen, T.; Bischof, R.; Hering, T.; Blanke, C.; et al. How to Measure the Impact of Biogenic Residues, Wastes and by-Products: Development of a National Resource Monitoring Based on the Example of Germany. Biomass Bioenergy 2019, 127, 105275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abid, S.; Zhang, X.; Zhang, W.; Mu, H.; Zhang, C.; Wang, A. System Performance and Pollution Emission of Biomass Gas Co-Firing in a Coal-Fired Boiler. J. Power Energy Eng. 2020, 8, 18–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hillig, D.M.; Pohlmann, J.G.; Manera, C.; Perondi, D.; Pereira, F.M.; Altafini, C.R.; Godinho, M. Evaluation of the Structural Changes of a Char Produced by Slow Pyrolysis of Biomass and of a High-Ash Coal during Its Combustion and Their Role in the Reactivity and Flue Gas Emissions. Energy 2020, 202, 117793. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cai, S.; Zhang, D.; Zhang, L.; Huang, L.; Li, H.; Gao, R.; Shi, L.; Zhang, J. Comparative Study of 3D Ordered Macroporous Ce0.75Zr0.2M0.05O2−δ (M = Fe, Cu, Mn, Co) for Selective Catalytic Reduction of NO with NH3. Catal. Sci. Technol. 2013, 4, 93–101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.; Zhang, R.; Chen, X.; Tong, M.; Kang, W.; Guo, S.; Zhou, Y.; Lu, J. Simultaneous Removal of NO and SO2 from Flue Gas by Ozone Oxidation and NaOH Absorption. Ind. Eng. Chem. Res. 2014, 53, 6450–6456. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Z.; Xiang, L.; Lin, F.; Wang, Z.; Yan, B.; Chen, G. Catalytic Deep Degradation of Cl-VOCs with the Assistance of Ozone at Low Temperature over MnO2 Catalysts. Chem. Eng. J. 2021, 426, 130814. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rezaei, E.; Soltan, J.; Chen, N. Catalytic Oxidation of Toluene by Ozone over Alumina Supported Manganese Oxides: Effect of Catalyst Loading. Appl. Catal. B Environ. 2013, 136–137, 239–247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jõgi, I.; Erme, K.; Raud, J.; Laan, M. Oxidation of NO by Ozone in the Presence of TiO2 Catalyst. Fuel 2016, 173, 45–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, F.; Wang, Z.; Ma, Q.; Yang, Y.; Whiddon, R.; Zhu, Y.; Cen, K. Catalytic Deep Oxidation of NO by Ozone over MnOx Loaded Spherical Alumina Catalyst. Appl. Catal. B Environ. 2016, 198, 100–111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meng, F.; Guo, L.; He, J.; Wang, Z.; Ma, Z.; Zeng, Y.; Zhang, S.; Zhong, Q. V2O5-(NH4)2V6O16·1.5H2O Composite Catalysts as Novel Platforms for High-Efficiency Catalytic Ozonation of NO under Low Temperature. J. Phys. Chem. Solids 2021, 155, 110112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, L.; Meng, F.; Zeng, Y.; Jia, Y.; Qian, F.; Zhang, S.; Zhong, Q. Catalytic Ozonation of NOx into HNO3 with Low Concentration Ozone over MnOx-CeO2/TiO2: Two-Phase Synergistic Effect of TiO2. Mol. Catal. 2020, 493, 111095. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Okada, K.; Hattori, A.; Taniguchi, T.; Nukui, A.; Das, R.N. Effect of Divalent Cation Additives on the γ-Al2O3-to-α-Al2O3 Phase Transition. J. Am. Ceram. Soc. 2004, 83, 928–932. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shao, S.; Li, Z.; Zhang, J.; Gao, K.; Liu, Y.; Jiao, W. Preparation of Ce-MnOX/γ-Al2O3 by High Gravity-Assisted Impregnation Method for Efficient Catalytic Ozonation. Chem. Eng. Sci. 2022, 248, 117246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yao, X.; Li, L.; Zou, W.; Yu, S.; An, J.; Li, H.; Yang, F.; Dong, L. Preparation, Characterization, and Catalytic Performance of High Efficient CeO2-MnOx-Al2O3 Catalysts for NO Elimination. Chin. J. Catal. 2016, 37, 1369–1380. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.; Liu, Y.; Deng, J.; Yu, X.; Han, Z.; Zhang, K.; Dai, H. Alloying of Gold with Palladium: An Effective Strategy to Improve Catalytic Stability and Chlorine-Tolerance of the 3DOM CeO2-Supported Catalysts in Trichloroethylene Combustion. Appl. Catal. B Environ. 2019, 257, 117879. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, X.; Li, S.; He, H.; Wu, Z.; Wu, J.; Chen, L.; Ye, D.; Fu, M. Evolution of Oxygen Vacancies in MnOx-CeO2 Mixed Oxides for Soot Oxidation. Appl. Catal. B Environ. 2018, 223, 91–102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mu, W.; Zhu, J.; Zhang, S.; Guo, Y.; Su, L.; Li, X.; Li, Z. Novel Proposition on Mechanism Aspects over Fe-Mn/ZSM-5 Catalyst for NH3-SCR of NO:X at Low Temperature: Rate and Direction of Multifunctional Electron-Transfer-Bridge and in Situ DRIFTs Analysis. Catal. Sci. Technol. 2016, 6, 7532–7548. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Q.; Li, X.; Li, W.; Zhong, L.; Zhang, C.; Fang, Q.; Chen, G. Effect of Preferential Exposure of Anatase TiO2 {001} Facets on the Performance of Mn-Ce/TiO2 Catalysts for Low-Temperature Selective Catalytic Reduction of NOx with NH3. Chem. Eng. J. 2019, 369, 26–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, F.; Wang, Z.; Zhang, Z.; Xiang, L.; Yuan, D.; Yan, B.; Wang, Z.; Chen, G. Comparative Investigation on Chlorobenzene Oxidation by Oxygen and Ozone over a MnOx/Al2O3 Catalyst in the Presence of SO2. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2021, 55, 3341–3351. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gonçalves, A.; Silvestre-Albero, J.; Ramos-Fernandez, E.V.; Ruiz, J.C.S.; Órfão, J.; Sepúlveda-Escribano, A.; Pereira, M.F. Highly Dispersed Ceria on Activated Carbon for the Catalyzed Ozonation of Organic Pollutants. Appl. Catal. B Environ. 2012, 113–114, 308–317. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ye, B.; Kim, J.; Lee, M.; Chun, S.-Y.; Jeong, B.; Kim, T.; Lee, D.H.; Kim, H.-D. Mn-Ce Oxide Nanoparticles Supported on Nitrogen-Doped Reduced Graphene Oxide as Low-Temperature Catalysts for Selective Catalytic Reduction of Nitrogen Oxides. Microporous Mesoporous Mater. 2021, 310, 110588. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Deng, W.; Wang, Y.; Guo, L.; Ishihara, T. A Comparative Study of the Catalytic Oxidation of Chlorobenzene and Toluene over Ce-Mn Oxides. Mol. Catal. 2018, 459, 61–70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.; Zhao, J.; Song, Z.; Liu, W.; Zhao, H.; Zhao, M.; Xing, Y.; Ma, Z.; Du, H. The Catalytic Oxidation Performance of Toluene over the Ce-Mn-Ox Catalysts: Effect of Synthetic Routes. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 2020, 562, 170–181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, P.; He, C.; Cheng, J.; Ma, C.Y.; Dou, B.J.; Hao, Z.P. Catalytic Oxidation of Toluene over Pd/Co3AlO Catalysts Derived from Hydrotalcite-like Compounds: Effects of Preparation Methods. Appl. Catal. B Environ. 2011, 101, 570–579. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]



| Name of the Reagent | Source of Reagent | Purity |
|---|---|---|
| Mn(NO3)2 | Maclean Biochemical Technology Co., Ltd., Shanghai, China | AR |
| CeN3O9·6H2O | Aladdin Biochemical Technology Co., Ltd., Shanghai, China | 99.95% |
| Nano titanium dioxide | Hechan Trading Co., Ltd., Guangzhou, China | AR |
| Al2O3 (α-crystalline about 90%, γ-crystalline about 10%) | Damao Chemical Reagent Factory., Tianjing, China | AR |
| C₂H₆O | Lingfeng Chemical Reagent Co., Ltd., Shanghai, China | AR |
| Sample | SBET (m²/g) | Vp (cm³/g) | Dp (nm) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Mn:Ce = 1:2 | 27.564 | 0.230 | 43.87 |
| Mn:Ce = 2:1 | 30.131 | 0.269 | 45.25 |
| Mn:Ce = 4:1 | 52.080 | 0.346 | 34.00 |
| Mn:Ce = 5:1 | 26.134 | 0.229 | 41.61 |
| Samples | Mn2+/(Mn2+ + Mn3+ + Mn4+) (%) | Mn3+/(Mn2+ + Mn3+ + Mn4+) (%) | Mn4+/(Mn2+ + Mn3+ + Mn4+) (%) | Ce3+/Ce4+ | O (lat) | O (lat)/O (abs) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Mn:Ce = 4:1 | 40.18 | 26.61 | 33.21 | 1.29 | 38.03 | 0.51 |
| Mn:Ce = 1:2 | / | / | / | 0.57 | 37.65 | 0.95 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Shen, H.; Tang, Z.; Xiao, X.; Wu, H.; Zhou, H.; Fang, P.; Zhu, D.; Ge, J. Catalytic Oxidation of NO by Ozone over Mn-Ce/Al2O3/TiO2 Catalyst. Processes 2022, 10, 1946. https://doi.org/10.3390/pr10101946
Shen H, Tang Z, Xiao X, Wu H, Zhou H, Fang P, Zhu D, Ge J. Catalytic Oxidation of NO by Ozone over Mn-Ce/Al2O3/TiO2 Catalyst. Processes. 2022; 10(10):1946. https://doi.org/10.3390/pr10101946
Chicago/Turabian StyleShen, Hong, Zijun Tang, Xiang Xiao, Haiwen Wu, Hang Zhou, Ping Fang, Dingfang Zhu, and Jianhua Ge. 2022. "Catalytic Oxidation of NO by Ozone over Mn-Ce/Al2O3/TiO2 Catalyst" Processes 10, no. 10: 1946. https://doi.org/10.3390/pr10101946
APA StyleShen, H., Tang, Z., Xiao, X., Wu, H., Zhou, H., Fang, P., Zhu, D., & Ge, J. (2022). Catalytic Oxidation of NO by Ozone over Mn-Ce/Al2O3/TiO2 Catalyst. Processes, 10(10), 1946. https://doi.org/10.3390/pr10101946








