A Survey on Computer-Aided Intelligent Methods to Identify and Classify Skin Cancer
Abstract
1. Introduction
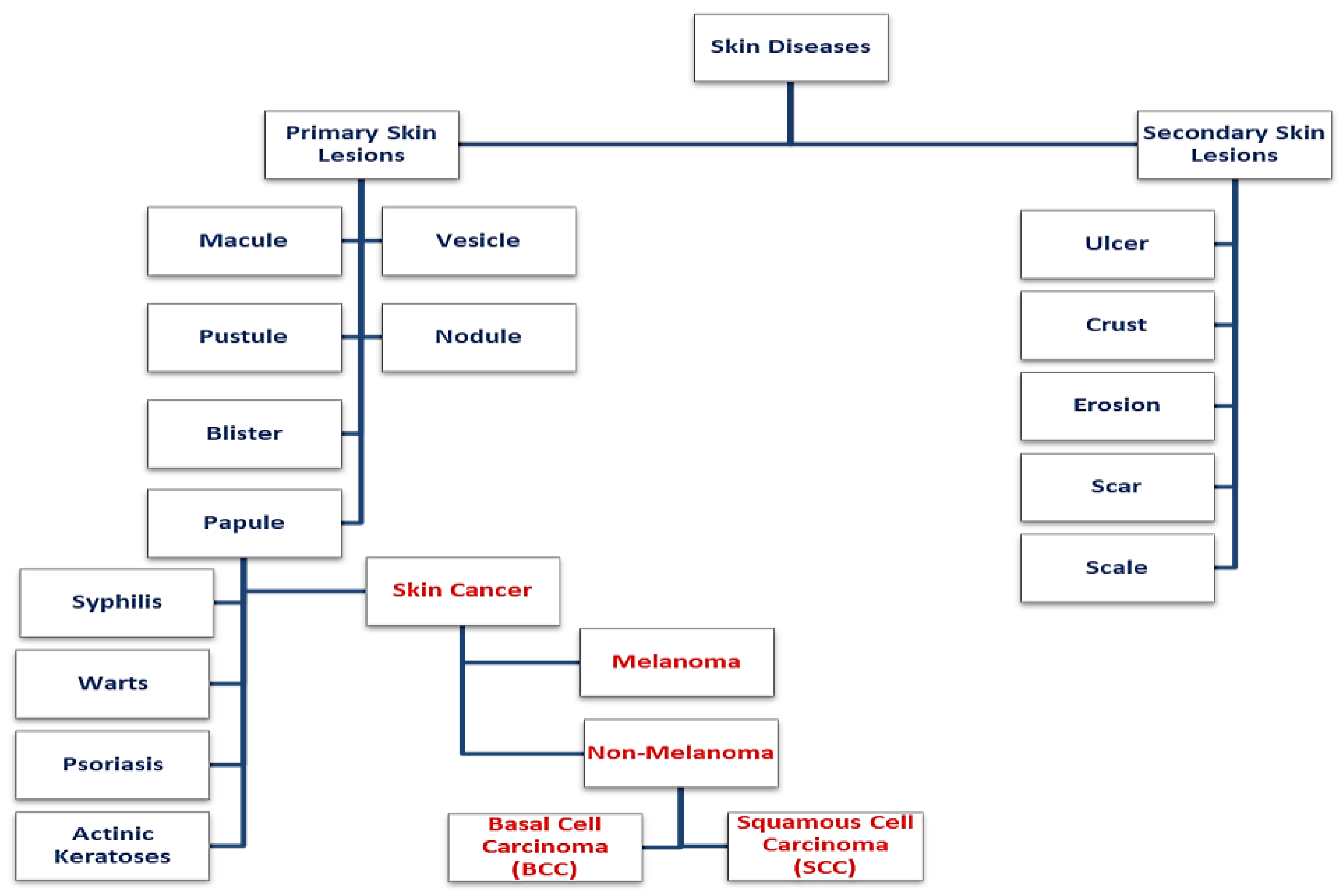
2. Skin Cancer Image Database
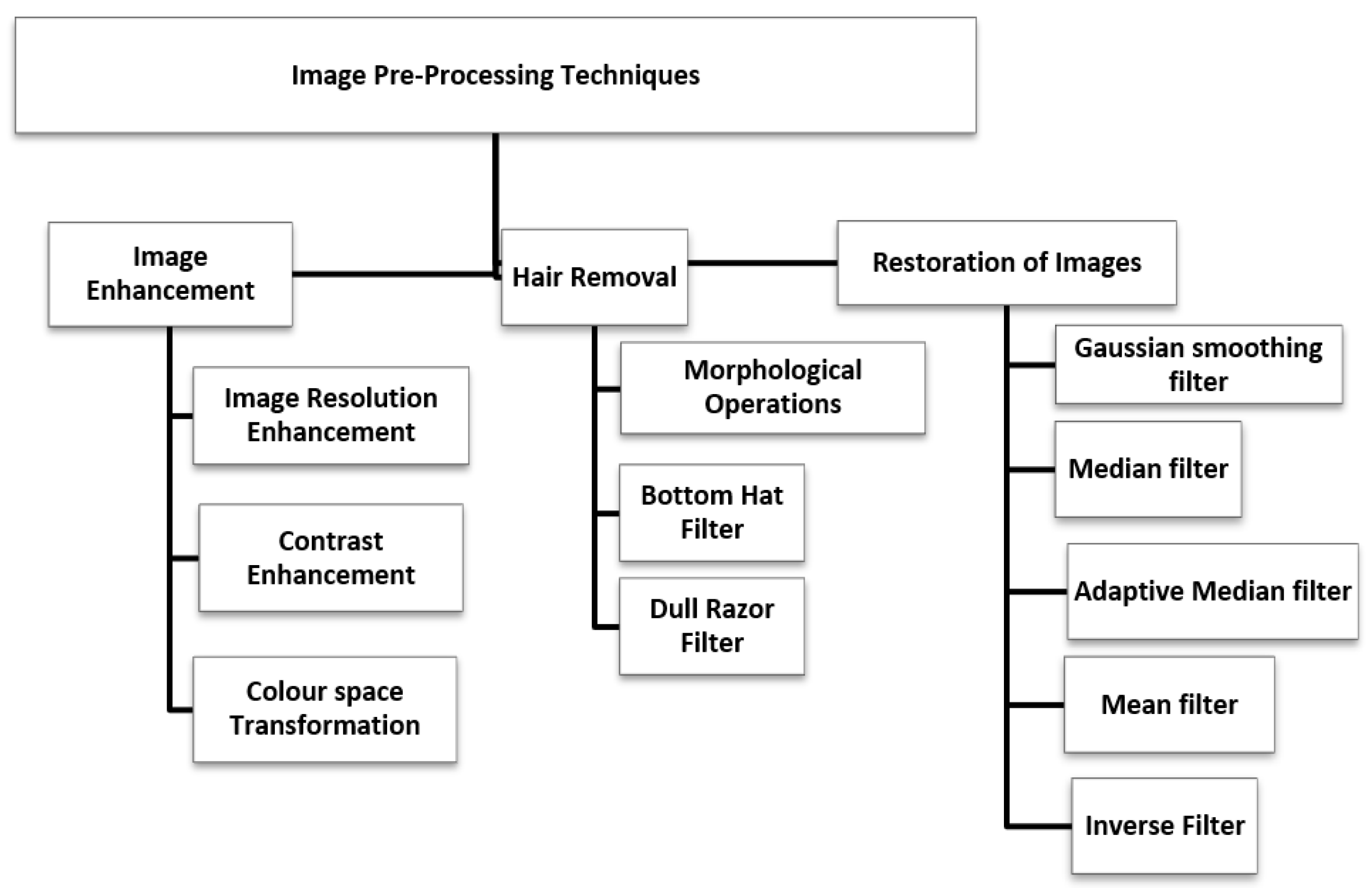
3. Skin Cancer Image Preprocessing
3.1. Image Enhancement
3.1.1. Image Resolution Enhancement
3.1.2. Color Space Transformation
3.1.3. Contrast Enhancement
3.2. Image Restoration
3.3. Hair Removal
4. Skin Lesion Segmentation
4.1. Threshold Based Segmentation
- Select an initial estimate of T (Threshold).
- Compute the means of the two regions determined by T.
- Set the new T as the average of the two means.
- Repeat step 3 until the difference in T in successive iterations is smaller than a predefined parameter.
4.2. Edge Based Segmentation
4.3. Region Based Segmentation
4.4. Soft Computing Based Segmentation
5. Feature Extraction
6. Skin Lesion Classification
7. Inferences from the Survey
- To improve diagnostic accuracy, deep learning algorithms typically require a large amount of diverse, balanced, and high-quality training data that represents each class of skin lesions.
- The features extracted from the images must be accurate to ensure high classification accuracy.
- Most of the algorithms are computationally complex and, hence, difficult to use in practical situations.
8. Conclusions and Future Scope
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Kolarsick, P.A.J.; Kolarsick, M.A.; Goodwin, C. Anatomy and Physiology of the Skin. J. Dermatol. Nurses’ Assoc. 2011, 3, 203–213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bai, H.; Graham, C. Focus: Introduction: Skin. Yale J. Biol. Med. 2020, 93, 1–2. [Google Scholar]
- D’Orazio, J.; Jarrett, S.; Amaro-Ortiz, A.; Scott, T. UV Radiation and the Skin. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2013, 14, 12222–12248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- De Gruijl, F.R. Skin cancer and solar UV radiation. Eur. J. Cancer 1999, 35, 2003–2009. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Available online: https://www.wcrf.org/cancer-trends/skin-cancer-statistics/ (accessed on 15 November 2022).
- Available online: https://www.cancer.org/cancer/melanoma-skin-cancer/ (accessed on 15 November 2022).
- Sinikumpu, S.P.; Jokelainen, J.; Keinänen-Kiukaanniemi, S.; Huilaja, L. Skin cancers and their risk factors in older persons: A population-based study. BMC Geriatr. 2022, 22, 269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhattacharya, A.; Young, A.; Wong, A.; Stalling, S.; Wei, M.; Hadley, D. Precision Diagnosis of Melanoma and Other Skin Lesions from Digital Images. AMIA Summits Transl. Sci. Proc. 2017, 2017, 220–226. [Google Scholar]
- Heistein, J.B.; Acharya, U.; Mukkamalla, S.K.R. Malignant Melanoma; StatPearls: Tampa, FL, USA, 2022. [Google Scholar]
- Griffin, L.L.; Ali, F.R.; Lear, J.T. Non-Melanoma Skin Cancer. Clin. Med. 2016, 16, 62–65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lomas, A.; Leonardi-Bee, J.; Bath-Hextall, F. A systematic review of worldwide incidence of non-melanoma skin cancer. Br. J. Dermatol. 2012, 166, 1069–1080. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Didona, D.; Paolino, G.; Bottoni, U.; Cantisani, C. Non-Melanoma Skin Cancer Pathogenesis Overview. Biomedicines 2018, 6, 6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Sheikh, M.S. Melanoma: Molecular Pathogenesis and Therapeutic Management. Mol. Cell. Pharmacol. 2014, 6, 228. [Google Scholar]
- Rogers, H.W.; Weinstock, M.A.; Feldman, S.R.; Coldiron, B.M. Incidence estimate of nonmelanoma skin cancer (keratinocyte carcinomas) in the US population, 2012. JAMA Dermatol. 2015, 151, 1081–1086. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Merlino, G.; Herlyn, M.; Fisher, D.E.; Bastian, B.; Flaherty, K.T.; Davies, M.A.; Wargo, J.A.; Curiel-Lewandrowski, C.; Weber, M.J.; Leachman, S.A.; et al. The state of melanoma: Challenges and opportunities. Pigment Cell Melanoma Res. 2016, 29, 404–416. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Masood, A.; Al-Jumaily, A.; Anam, K. Self-Supervised Learning Model for Skin Cancer Diagnosis. In Proceedings of the 7th International IEEE/EMBS Conference on Neural Engineering (NER), Manhattan, NY, USA, 22–24 April 2015. [Google Scholar]
- Marghoob, N.G.; Liopyris, K.; Jaimes, N. Dermoscopy: A Review of the Structures That Facilitate Melanoma Detection. J. Osteopath. Med. 2019, 119, 380–390. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kato, J.; Horimoto, K.; Sato, S.; Minowa, T.; Uhara, H. Dermoscopy of Melanoma and Non-melanoma Skin Cancers. Front. Med. 2019, 6, 180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dick, V.; Sinz, C.; Mittlböck, M.; Kittler, H.; Tschandl, P. Accuracy of Computer-Aided Diagnosis of Melanoma: A Meta-analysis. JAMA Derm. 2019, 155, 1291–1299. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Malti, A.; Chatterjee, B.; Ashor, S.A.; Dey, N. Computer-aided Diagnosis of Melanoma: A Review of Existing Knowledge and Strategies. Curr. Med. Imaging 2020, 16, 835–854. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, Z.; Sheykhahmad, F.R.; Ghadimi, N.; Razmjooy, N. Computer-aided diagnosis of skin cancer based on soft computing techniques. Open Med. 2020, 15, 860–871. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bakheet, S.; Al-Hamadi, A. Computer-Aided Diagnosis of Malignant Melanoma Using Gabor-Based Entropic Features and Multilevel Neural Networks. Diagnostics 2020, 10, 822. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gutman, D.; Codella, N.C.; Celebi, E.; Helba, B.; Marchetti, M.; Mishra, N.; Halpern, A. Skin Lesion Analysis toward Melanoma Detection: A Challenge at the International Symposium on Biomedical Imaging (ISBI) 2016, hosted by the International Skin Imaging Collaboration (ISIC). arXiv 2016, arXiv:1605.01397. [Google Scholar]
- Codella, N.; Gutman, D.; Celebi, M.E.; Helba, B.; Marchetti, M.A.; Dusza, S.; Kalloo, A.; Liopyris, K.; Mishra, N.; Kittler, H.; et al. Skin Lesion Analysis Toward Melanoma Detection: A Challenge at the 2017 International Symposium on Biomedical Imaging (ISBI), Hosted by the International Skin Imaging Collaboration (ISIC). In Proceedings of the 15th International Symposium on Biomedical Imaging, Washingtion, DC, USA, 4–7 April 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Codella, N.; Rotemberg, V.; Tschandl, P.; Celebi, M.E.; Dusza, S.; Gutman, D.; Helba, B.; Kalloo, A.; Liopyris, K.; Marchetti, M.; et al. Skin Lesion Analysis Toward Melanoma Detection 2018: A Challenge Hosted by the International Skin Imaging Collaboration (ISIC). arXiv 2019, arXiv:1902.03368. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rehman, M.U.; Khan, S.H.; Rizvi, S.M.D.; Abbas, Z.; Zafar, A. Classification of skin lesion by interference of segmentation and convolotion neural network. In Proceedings of the 2nd International Conference on Engineering Innovation (ICEI), Bangkok, Thailand, 5–6 July 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Combalia, M.; Codella, N.C.F.; Rotemberg, V.; Helba, B.; Vilaplana, V.; Reiter, O.; Carrera, C.; Barreiro, A.; Halpern, A.C.; Puig, S.; et al. BCN20000: Dermoscopic Lesions in the Wild. arXiv 2019, arXiv:1908.02288. [Google Scholar]
- Rotemberg, V.; Kurtansky, N.; Betz-Stablein, B.; Caffery, L.; Chousakos, E.; Codella, N.; Combalia, M.; Dusza, S.; Guitera, P.; Gutman, D.; et al. A patient-centric dataset of images and metadata for identifying melanomas using clinical context. Scintific Data 2021, 8, 34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lei, B.; Jinman, K.; Euijoon, A.; Ashnil, K.; Michael, F.; Dagan, F. Dermoscopic Image Segmentation via Multistage Fully Convolutional Networks. IEEE Trans. Biomed. Eng. 2017, 64, 2065–2074. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Satheesha, T.Y.; Satyanarayana, D.; Prasad, M.G.; Dhruve, K.D. Melanoma is Skin Deep: A 3D reconstruction technique for computerized dermoscopic skin lesion classification. IEEE J. Transl. Eng. Health Med. 2017, 5, 1–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Abuzaghleh, O.; Barkana, B.D.; Faezipour, M. Noninvasive Real-Time Automated Skin Lesion Analysis System for Melanoma Early Detection and Prevention. IEEE J. Transl. Eng. Health Med. 2015, 3, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barata, C.; Celebi, M.E.; Marques, J.S. Improving dermoscopy image classification using color constancy. IEEE J. Biomed. Health Inform. 2015, 19, 1146–1152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Argenziano, G.; Soyer, P.; Giorgio, V.; Piccolo, D.; Carli, P.; Delfino, M.; Ferrari, A.; Hofmann-Wellenhof, R.; Massi, D.; Mazzocchetti, G.; et al. Interactive Atlas of Dermoscopy; Edra Medical Publishing & New Media: Milan, Italy, 2000. [Google Scholar]
- Aurora, S.; Carmen, S.; Begona, A. Model-Based Classification Methods of Global Patterns in Dermoscopic Images. IEEE Trans. Med. Imaging 2014, 33, 1137–1147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pacheco, A.G.C.; Lima, G.R.; Salomão, A.S.; Krohling, B.; Biral, I.P.; de Angelo, G.G.; Alves, F.C., Jr.; Esgario, J.G.; Simora, A.C.; Castro, P.B.; et al. PAD-UFES-20: A skin lesion dataset composed of patient data and clinical images collected from smartphones. Data Brief 2020, 32, 106221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ballerini, L.; Fisher, R.B.; Aldridge, B.; Rees, J. A Color and Texture Based Hierarchical K-NN Approach to the Classification of Non-melanoma Skin Lesions. In Color Medical Image Analysis; Springer: Dordrecht, The Netherlands, 2013; pp. 63–86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- DermNet is supported by and contributed to by New Zealand Dermatologists on behalf of the New Zealand Dermatological Society Incorporated. Available online: https://dermnetnz.org/ (accessed on 15 November 2022).
- Jeremy, K.; Sara, D.; Giuseppe, A.; Ghassan, H. 7-Point Checklist and Skin Lesion Classification using Multi-Task Multi-Modal Neural Nets. IEEE J. Biomed. Health Inform. 2018, 23, 538–546. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Diniz, J.B.; Cordeiro, F.R. Automatic Segmentation of Melanoma in Dermoscopy Images Using Fuzzy Numbers. In Proceedings of the IEEE 30th International Symposium on Computer-Based Medical Systems, Thessaloniki, Greece, 22–24 June 2017; pp. 150–155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Svetlana, S.; Svetislav, D.S.; Zorana, B.; Milana, I.S.; José, R.V.; Dragan, S. Deep Convolutional Neural Networks on Automatic Classification for Skin Tumour Images. Log. J. IGPL 2022, 30, 649–663. [Google Scholar]
- Giotis, I.; Molders, N.; Land, S.; Biehl, M.; Jonkman, M.F.; Petkov, N. MED-NODE: A computer-assisted melanoma diagnosis system using non-dermoscopic images. Expert Syst. Appl. 2015, 42, 6578–6585. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Andersen, L.B.; Fountain, J.W.; Gutmann, D.H.; Tarlé, S.A.; Glover, T.W.; Dracopoli, N.C.; Housman, D.E.; Collins, F.S. Mutations in the neurofibromatosis 1 gene in sporadic malignant melanoma cell lines. Nat. Genet. 1993, 3, 118–121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dermtology Information System. 2012. Available online: http://www.dermis.net (accessed on 2 August 2018).
- DermQuest. 2012. Available online: http://www.dermquest.com (accessed on 2 August 2018).
- Hosny, K.M.; Kassem, M.A.; Foaud, M.M. Classification of skin lesions using transfer learning and augmentation with Alex-net. PLoS ONE 2019, 14, e0217293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Premaladha, J.; Sujitha, S.; Lakshmi Priya, M.; Ravichandran, K.S. A Survey on Melanoma Diagnosis using Image Processing and Soft Computing Techniques. Res. J. Inf. Technol. 2014, 6, 65–80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Gouda, W.; Sama, N.U.; Al-Waakid, G.; Humayun, M.; Jhanjhi, N.Z. Detection of Skin Cancer Based on Skin Lesion Images Using Deep Learning. Healthcare 2022, 10, 1183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sudhamony, S.; Binu, P.J.; Satheesh, G.; IssacNiwas, S.; Sudalaimani, C.; Nandakumar, K.; Muralidharan, V.; Baljit, S.B. Nationwide Tele-Oncology network in India—A framework for implementation. In Proceedings of the HealthCom 2008—10th International Conference on e-health Networking, Applications and Services, Singapore, 7–9 July 2008. [Google Scholar]
- Abbas, Q.; Ramzan, F.; Ghani, M.U. Acral melanoma detection using dermoscopic images and convolutional neural networks. Vis. Comput. Ind. Biomed. 2021, 4, 25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amoabedini, A.; Farsani, M.S.; Saberkari, H.; Aminian, E. Employing the Local Radon Transform for Melanoma Segmentation in Dermoscopic Images. J. Med. Signals Sens. 2018, 8, 184–194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramezani, M.; Karimian, A.; Moallem, P. Automatic Detection of Malignant Melanoma using Macroscopic Images. J. Med. Signals Sens. 2014, 4, 281–290. [Google Scholar]
- Ghosh, P.; Azam, S.; Quadir, R.; Karim, A.; Shamrat, F.M.; Bhowmik, S.K.; Jonkman, M.; Hasib, K.M.; Ahmed, K. SkinNet-16: A deep learning approach to identify benign and malignant skin lesions. Front. Oncol. 2022, 12, 931141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haohai, Z.; Zhijun, W.; Liping, L.; Fatima, R.S. A robust method for skin cancer diagnosis based on interval analysis. Automatika 2021, 62, 43–53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Premaladha, J.; Ravichandran, K.S. Novel Approaches for Diagnosing Melanoma Skin Lesions Through Supervised and Deep Learning Algorithms. J. Med. Syst. 2016, 40, 96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pizer, S.M.; Amburn, E.P.; Austin, J.D.; Cromartie, R.; Geselowitz, A.; Greer, T.; ter Haar Romeny, B.; Zimmerman, J.B.; Zuiderveld, K. Adaptive histogram equalization and its variations. Comput. Vis. Graph. Image Process. 1987, 39, 355–368. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martínez, L.T.; Bibiloni, P.; González, H. Hair Segmentation and Removal in Dermoscopic Images Using Deep Learning. IEEE Access 2021, 9, 2694–2704. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, T.; Ng, V.; Gallagher, R.; Coldman, A.; McLean, D. A Dullrazor, Software approach to hair removal from images. J. Comput. Biol. Med. 1997, 27, 533–543. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Salido, J.A.; Ruiz, C.R. Using morphological operators and inpainting for hair removal in dermoscopic images. In Proceedings of the Computer Graphics International Conference, Yokohama, Japan, 27–30 June 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Sivaraj, S.; Malmathanraj, R.; Palanisamy, P. Detecting anomalous growth of skin lesion using threshold-based segmentation algorithm and Fuzzy K-Nearest Neighbor classifier. J. Cancer Res. Ther. 2020, 16, 40–52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adil H., K.; Ghazanfar Latif, D.N.F.; Awang, I.J.; Alghazo, M.B. Segmentation of Melanoma Skin Lesions Using Anisotropic Diffusion and Adaptive Thresholding. In Proceedings of the 2018 8th International Conference on Biomedical Engineering and Technology (ICBET ‘18), Bali, Indonesia, 23–25 April 2018; Association for Computing Machinery: New York, NY, USA, 2018; pp. 39–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, L.; Jackowski, M.; Goshtasby, A.; Roseman, D.; Bines, S.; Yu, C.; Dhawan, A.; Huntley, A. Segmentation of skin cancer images. Image Vis. Comput. 1999, 7, 65–74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.-H. Tutorial: Image Segmentation; Graduate Institute of Communication Engineering National Taiwan University: Taipei, Taiwan, 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Khan, R.Z.; Ibraheem, N.A. Survey on Gesture Recognition for Hand Image Postures. Can. Cent. Comput. Inf. Sci. 2012, 5, 110–121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaganami, H.G.; Beiji, Z. Region-Based Segmentation versus Edge Detection. In Proceedings of the IEEE Fifth International Conference on Intelligent Information Hiding and Multimedia Signal Processing, Kyoto, Japan, 12–14 September 2009; pp. 1217–1221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barcelos, C.A.Z.; Pires, V.B. An automatic based nonlinear diffusion equations scheme for skin lesion segmentation. Appl. Math. Comput. 2009, 251–261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gurajala, R. Skin Cancer Detection Using Region Based Segmentation. Int. J. Innov. Sci. Technol. 2019, 6, 42–46. [Google Scholar]
- Jaisakthi, S.M.; Mirunalini, P.; Aravindan, C. Automated skin lesion segmentation of dermoscopic images using GrabCut and k-means algorithms. IET Comput. Vis. 2018, 12, 1088–1095. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Albahli, S.; Nida, N.; Irtaza, A.; Yousaf, M.H.; Mahmood, M.T. Melanoma Lesion Detection and Segmentation Using YOLOv4-DarkNet and Active Contour. IEEE Access 2020, 8, 198403–198414. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, H.; Schoepflin, T.; Kim, Y. Active contour model with gradient directional information: Directional snake. IEEE Trans. Circuits Syst. Video Technol. 2001, 11, 252–256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuan, Y.; Situ, N.; Zouridakis, G. A narrow band graph partitioning method for skin lesion segmentation. Pattern Recognit. 2009, 42, 1017–1028. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goyal, M.; Oakley, A.; Bansal, P.; Dancey, D.; Yap, M.H. Skin Lesion Segmentation in Dermoscopic Images With Ensemble Deep Learning Methods. IEEE Access 2020, 8, 4171–4181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramadan, R.; Aly, S. CU-Net: A New Improved Multi-Input Color U-Net Model for Skin Lesion Semantic Segmentation. IEEE Access 2022, 10, 15539–15564. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, G.; Shen, X.; Chen, S.; Liang, L.; Luo, Y.; Yu, J.; Lu, J. DSM: A Deep Supervised Multi-Scale Network Learning for Skin Cancer Segmentation. IEEE Access. 2019, 7, 140936–140945. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, Y.; Zhang, J.; Xia, Y.; Shen, C. A Mutual Bootstrapping Model for Automated Skin Lesion Segmentation and Classification. IEEE Trans. Med. Imaging 2020, 39, 2482–2493. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, P.; Huang, S.; Yue, Q. Skin Lesion Segmentation Using Recurrent Attentional Convolutional Networks. IEEE Access 2022, 10, 94007–94018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wong, A.; Scharcanski, J.; Fieguth, P. Automatic Skin Lesion Segmentation via Iterative Stochastic Region Merging. IEEE Trans. Inf. Technol. Biomed. 2011, 15, 929–936. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuan, Y.; Lo, Y.C. Improving Dermoscopic Image Segmentation With Enhanced Convolutional-Deconvolutional Networks. IEEE J. Biomed. Health Inform. 2019, 23, 519–526. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cavalcanti, P.G.; Scharcanski, J.; Lopes, C.B.O. Shading attenuation in human skin color images. Adv. Vis. Comput. 2010, 6453, 190–198. [Google Scholar]
- Cavalcanti, P.G.; Scharcanski, J. Automated prescreening of pigmented skin lesions using standard cameras. Comput. Med. Imaging Graph. 2011, 35, 481–491. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yuan, Y.; Chao, M.; Lo, Y.C. Automatic Skin Lesion Segmentation Using Deep Fully Convolutional Networks With Jaccard Distance. IEEE Trans. Med. Imaging 2017, 36, 1876–1886. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bagheri, F.; Tarokh, M.J.; Ziaratban, M. Skin Lesion Segmentation from Dermoscopic Images by using Mask R-CNN, Retina-Deeplab, and Graph-based Methods. Biomed. Signal Process. Control 2021, 67, 102533. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Poornima, J.J.; Anitha, J.; Priya, H.A.G. Clustering-Based Melanoma Detection in Dermoscopy Images Using ABCD Parameters. Adv. Intell. Syst. Comput. 2019, 766, 267–274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Murugan, A.; Nair, S.A.H.; Preethi, A.A.P.; Kumar, K.P.S. Diagnosis of skin cancer using machine learning techniques. Microprocess. Microsyst. 2021, 81, 103727. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Annaby, M.H.; Elwer, A.M.; Rushdi, M.A. Melanoma Detection Using Spatial and Spectral Analysis on Superpixel Graphs. J. Digit. Imaging 2021, 34, 162–181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rehman, A.; Khan, M.A.; Mehmood, Z.; Saba, T.; Sardaraz, M.; Rashid, M. Microscopic melanoma detection and classification: A framework of pixel-based fusion and multilevel features reduction. Microsc. Res. Tech. 2020, 83, 410–423. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Azadeh, N.H.; Adel, A.J.; Afsaneh, N.H. Comparing the performance of various filters on skin cancer images. Procedia Comput. Sci. 2014, 42, 32–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Victor, A.; Ghalib, M.R. Detection of skin cancer cells—A review. Res. J. Pharm. Technol. 2017, 10, 4093–4098. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guerra-Rosas, E.; Álvarez-Borrego, J. Methodology for diagnosing of skin cancer on images of dermatologic spots by spectral analysis. Biomed. Opt. Express 2015, 6, 3876–3891. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dorj, U.O.; Lee, K.K.; Choi, J.Y. The skin cancer classification using deep convolutional neural network. Multimed. Tools Appl. 2018, 77, 9909–9924. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, C.; Shuai, R.; Ma, L.; Liu, W.; Hu, D.; Wu, M. Dermoscopy Image Classification Based on StyleGAN and DenseNet201. IEEE Access 2021, 9, 8659–8679. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.; Xie, Y.; Xia, Y.; Shen, C. Attention Residual Learning for Skin Lesion Classification. IEEE Trans. Med. Imaging 2019, 38, 2092–2103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tang, P.; Liang, Q.; Yan, X.; Xiang, S.; Zhang, D. GP-CNN-DTEL: Global-Part CNN Model with Data-Transformed Ensemble Learning for Skin Lesion Classification. IEEE J. Biomed. Health Inform. 2020, 24, 2870–2882. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Carcagnì, P.; Ricci, E.; Rota Bulò, S.; Snoek, C.; Lanz, O.; Messelodi, S.; Sebe, N. Classification of Skin Lesions by Combining Multilevel Learnings in a DenseNet Architecture; Lecture Notes in Computer Science; Springer: Cham, Switzerland, 2019; Volume 11751. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Shen, L. Skin Lesion Analysis towards Melanoma Detection Using Deep Learning Network. Sensors 2018, 18, 556. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
| MELANOMA TYPES | NON-MELANOMA TYPES | ||
|---|---|---|---|
| Superficial Spreading Melanoma |  | Basal Cell Carcinoma |  |
| Nodular Melanoma |  | Squamous Cell Carcinoma |  |
| Lentigo Maligna Melanoma | 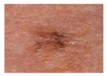 | Merkel Cell Carcinoma | 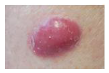 |
| Amelanotic Melanoma |  | Cutaneous T-Cell Lymphona | 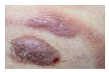 |
Rare Melanoma Types;
| 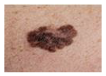 | Kaposi Sarcoma | 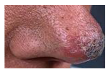 |
| Reference | Dataset | No of Skin Image | Melanoma Images | Other Skin Disease Images | Web-Link |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Gutman, David, et al. (2016) [23] | ISIC-2016 | 1279 | 248 | 1031 | https://challenge.isic-archive.com/data (Accessed on 15 November 2022) |
| Codella N, et al. (2017) [24] | ISIC-2017 | 2750 | 521 | 2229 | |
| Noel Codella. et al. (2018) [25] Rehman M., (2018) [26] | ISIC-2018 (HAM10000, MSK) | 10,015 | 1113 | 8902 | |
| Rehman M., (2018) [26] Noel C. F. Cordella, et al. (2018) [25] Marc Combalia, et al. (2019) [27] | ISIC-2019 (BCN_20000, HAM10000, MSK) | 25,331 | 4522 | 20,809 | |
| Rotemberg, V, et al. (2021) [28] | ISIC-2020 | 33,126 | 6927 | 26,199 | |
| Lei Bi, et al. (2017) [29] T. Y. Satheesha, et al. (2017) [30] Omar abuzaghleh, et al. (2015) [31] Catarina Barata (2014) [32] | PH2 | 200 | 40 | 160 | https://www.fc.up.pt/addi/ph2%20database.html (Accessed on 15 November 2022) |
| Argenziano, et al. (2000) [33] Aurora Saez, et al. (2014) [34] | Interactive Atlas of Dermoscopy | 1000 | 270 | 730 | https://dermoscopy.org/atlas/default.asp (Accessed on 15 November 2022) |
| Pacheco, Andre, et al. (2020) [35] | PAD-UFES-20 | 2298 | 52 | 2246 | https://data.mendeley.com/datasets/zr7vgbcyr2/1 (Accessed on 15 November 2022) |
| Rees, Aldridge, et al. (2013) [36] | Dermofit Image Library | 1300 | 76 | 1224 | https://licensing.edinburgh-innovations.ed.ac.uk/product/dermofit-image-library (Accessed on 15 November 2022) |
| NewZealand Dermatological Society (2021) [37] | DermNet NZ | >21,000 | - | - | https://dermnetnz.org/image-library (Accessed on 15 November 2022) |
| Jeremy Kawahara, et al. (2018) [38] | 7-Point Criteria Evaluation Database | 1011 | 252 | 759 | https://derm.cs.sfu.ca/Download.html (Accessed on 15 November 2022) |
| Jessica B. Diniz, et al. (2017) [39] | ISDI | 571 | 125 | 446 | NA |
| Svetlana. S, et al. (2017) [40] | Asan and Hallym Dataset | 17,250 | 599 | 16,651 | https://figshare.com/articles/figure/Asan_and_Hallym_Dataset_Thumbnails_/5406136 (Accessed on 15 November 2022) |
| I. Giotis, et al. (2015) [41] | MED-NODE Dataset | 170 | 70 | 100 | https://www.cs.rug.nl/~imaging/databases/melanoma_naevi/ (Accessed on 15 November 2022) |
| Andersen, L. B. [42] | NCI GDC Portal | 2883 | 2333 | 550 | https://portal.gdc.cancer.gov/ (Accessed on 15 November 2022) |
| Hosny KM, et al. (2019) [43,44,45] | DIS and DermQuest | 206 | 119 | 87 | http://www.dermis.net http://www.dermquest.com (Accessed on 15 November 2022) |
| Author | Method | Advantages | Drawback |
|---|---|---|---|
| Ghosh P (2022) [52] | Mean Filter | In addition to reducing noise, it could maintain edges. | Suppress the finer details in an image. |
| H. Zhang (2021) [53] | Median Filter | With median filtering, noise is eliminated while edges are preserved. | Blurring of image in process. |
| Pizer (1987) [55] | Adaptive Median Filter | Remove the noise and enhance the image. | The median filter replaces the potential noisy pixels but not regional features, such as the existence of edges. |
| Martínez, L.T (2021) [56] | Gaussian Smoothing Filter | Images are sharpened and smoothened. | High-frequency image elements are distorted and removed. |
| Pizer (1987) [55] | Inverse Filter | Image enhancement from blurred images. | Spectral indices with a clearly defined fringe. |
| Author | Dataset | Method | Performance Analysis (PA) | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Accuracy | Specificity | Sensitivity | Other PA | |||
| S. Albahli, et al. [68,69,70] | ISIC 2016 | Active Contour | 93.9% | 95.2% | 94.2% | D-1 J-98.9% |
| M. Goyal, et al. [71] | ISIC 2017 | End to End Ensemble Segmentation Method | 94.1% | 97.9% | 89.9% | - |
| PH2 | 93.8% | 92.9% | 98.7% | - | ||
| R.Ramadan, et al. [72] | ISIC 2017 | Color U-Net Semantic Segmentation Deep Model | 93.13% | 96.21% | 83.64% | D-85.63% J-74.88% |
| ISIC 2018 | 94.58% | 95.85% | 91.57% | D-90.96% J-83.42% | ||
| G. Zhang, et al. [73] | ISIC 2017 | DSM Network | 94.3% | - | 85.9% | J-78.5% D-87.5% |
| PH2 | 93.1% | - | 88.9% | J-89.1% D-92% | ||
| Y. Xie, et al. [74] | ISIC 2017 | MB-DCNN Model | 93.8% | 87.4% | 96.8% | J-80.4% |
| PH2 | 97.7% | 96.7% | 94.6% | J-89.4% | ||
| P. Chen, et al. [75] | ISIC 2017 | Recurrent Attentional Convolutional Network (O-Net) | 94.71% | 96.3% | 89.70% | J-80.36% D-87.04% |
| PH2 | 95.14% | 96.75% | 89.23% | J-86.15% D-92.12% | ||
| A.Wong, et al. [76] | 60 real images | Iterative Stochastic Region Merging Method | - | - | 9.16% | TDR-93% |
| Y. Yuan, et al. [77] | ISBI 2016 | CDNN | 95.7% | 96.5% | 92.4% | J-76.5% |
| P.G.Cavalcanti, et al. [78,79] | Skin Images | Otsu-RGB | 85.0% | 85.5% | 92.2% | - |
| Y.Yuan, et al. [80] | ISBI 2016 | FCN ensemble | 95.5% | 96.6% | 91.8% | - |
| Bagheri, et al. [81] | Dermquest | Mask R-CNN | 99.25% | 99.64% | 94.92% | J-76.5% |
| ISBI 2017 | Retina-Deeplab | 94.18% | 96.51% | 88.37% | J-80.04% | |
| Author | Dataset | Feature | Method | Performance Analysis |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Jacinth., et al. (2020) [82] | Med-Node | ABCD | Total Dermoscopy Score | Accuracy-88% |
| Murugan A., et al. (2021) [83] | ISIC | GLCM | Support Vector Machine | Accuracy-89.31% |
| Annaby M. H., et al. (2021) [84] | ISIC | Color, Geometry, Texture | Support Vector Machine | Accuracy-97.40% Sensitivity-100% Specificity-95.1% AUC-99.91% |
| Rehman A., et al. (2020) [85] | PH2 | ABCD | Total Dermatoscopy Score (TDS) | Accuracy-93.5% Sensitivity-90.3% Specificity-95% |
| ISIC | Accuracy-91.45% Sensitivity-92% Specificity-91.5% |
| Author | Dataset | Method | Performance Analysis (%) | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Sensitivity | Specificity | Accuracy | |||
| Dorj UO, et al. [89] | PH2 | SVM | 96 | 97 | - |
| AdaBoost | 96 | 98 | - | ||
| Bag of Features (BoF) | 93 | 96 | - | ||
| Atlas | SVM | 98 | 99 | - | |
| AdaBoost | 47 | 92 | - | ||
| Bag of Features (BoF) | 77 | 96 | - | ||
| Zhao C, et al. [90] | ISIC 2019 | SLA-Style GAN | 85.6 | 96.1 | 96.4 |
| DenseNet 201 | 68.2 | 95.6 | 98.84 | ||
| Zhang J, et al. [91] | ISIC 2017 | ARL-CNN 50 | 65.8 | 89.6 | 85 |
| Tang P, et al. [92] | ISIC 2016 | GP-CNN-DTEL | 32 | 99.7 | 86.3 |
| Carcagni, et al. [93] | ISBI 2017 | ResNet 50 + RA Pooling + Rank Opt | 60.7 | 88.4 | 83 |
| Li Y, et al. [94] | ISIC 2017 | Lesion Indexing Network(LIN) | 50.4 | 93 | 85.2 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Jeyakumar, J.P.; Jude, A.; Priya, A.G.; Hemanth, J. A Survey on Computer-Aided Intelligent Methods to Identify and Classify Skin Cancer. Informatics 2022, 9, 99. https://doi.org/10.3390/informatics9040099
Jeyakumar JP, Jude A, Priya AG, Hemanth J. A Survey on Computer-Aided Intelligent Methods to Identify and Classify Skin Cancer. Informatics. 2022; 9(4):99. https://doi.org/10.3390/informatics9040099
Chicago/Turabian StyleJeyakumar, Jacinth Poornima, Anitha Jude, Asha Gnana Priya, and Jude Hemanth. 2022. "A Survey on Computer-Aided Intelligent Methods to Identify and Classify Skin Cancer" Informatics 9, no. 4: 99. https://doi.org/10.3390/informatics9040099
APA StyleJeyakumar, J. P., Jude, A., Priya, A. G., & Hemanth, J. (2022). A Survey on Computer-Aided Intelligent Methods to Identify and Classify Skin Cancer. Informatics, 9(4), 99. https://doi.org/10.3390/informatics9040099







