Abstract
This research work employs theoretical and empirical expert knowledge in constructing an agglomerative parallel processing algorithm that performs spatio-temporal clustering upon seismic data. This is made possible by exploiting the spatial and temporal sphere of influence of the main earthquakes solely, clustering seismic events into a number of fuzzy bordered, interactive and yet potentially distinct seismic zones. To evaluate whether the unveiled clusters indeed depict a distinct seismic zone, deep learning neural networks are deployed to map seismic energy release rates with time intervals between consecutive large earthquakes. Such a correlation fails should there be influence by neighboring seismic areas, hence casting the seismic region as non-distinct, or if the extent of the seismic zone has not been captured fully. For the deep learning neural network to depict such a correlation requires a steady seismic energy input flow. To address that the western area of the Hellenic seismic arc has been selected as a test case due to the nearly constant motion of the African plate that sinks beneath the Eurasian plate at a steady yearly rate. This causes a steady flow of strain energy stored in tectonic underground faults, i.e., the seismic energy storage elements; a partial release of which, when propagated all the way to the surface, casts as an earthquake. The results are complementary two-fold with the correlation between the energy release rates and the time interval amongst large earthquakes supporting the presence of a potential distinct seismic zone in the Ionian Sea and vice versa.
1. Introduction
Neural networks have long been established as effective global approximators [1,2]. The main limitations observed were mainly due to their high dimensionality that required significant processing power and fast memory access times. Heterogeneous parallel processing [3] encompasses both short latency CPU cores for serial processes and large throughput GPU compute units for parallel processes, respectively. It effectively resolves processing time and memory management issues as artificial neural networks are mostly organized in several layers comprised of multiple parallel neurons. This brought rise to deep learning [4] that invokes neural networks of extensive architecture that are capable of learning from the data thanks to their features’ extraction and classification capabilities. This is a significant advancement with respect to standard artificial neural networks for which the former process required intervention by domain experts. To model the behavior of a system, a set of characteristic-to-the-system input and output data is required. In the case of an earthquake’s generation mechanism in a particular area, it is only possible to depict information regarding the release of seismic energy such as time of occurrence of an earthquake and the earthquake’s magnitude, which corresponds to how much seismic energy has been released to the surface. To date, there is no possible way to measure the accumulated strain energy stored in tectonic underground faults [5]. Tectonic underground faults effectively act as seismic energy storage elements, the partial release of which gives rise to an earthquake when propagated all the way to the planet’s surface. For the particular case of the Hellenic seismic arc, an interesting observation comes in place as it is the case that the African tectonic plate sub-sinks beneath the Eurasian tectonic plate steadily by three centimeters per year [6]. This observation permits the extrusion of a hypothesis that for this particular region the accumulation of input strain energy due to the tectonic plates’ motion remains nearly constant. As such, it might be possible for a deep learning neural network to depict patterns relating time intervals between consecutive large earthquakes to seismic energy release rates.
Furthermore, it is most important for the data processed by the deep learning neural network to belong in a distinct seismic zone [7,8,9], i.e., a seismic area whose tectonic underground faults are not triggered by the seismic activity of other tectonic underground faults in neighboring or in some cases even intercrossing regions. This is enabled by heterogeneous parallel programming, which allows for both theoretical and empirical expert knowledge to be deployed in order to identify the spatial and temporal sphere of influence [10,11,12] of the main earthquakes. Although there are various methods for clustering points/flows into zones or for delineating zonal boundaries [13,14], the aforementioned approach enables the formation of irregular shaped clusters that may even interact spatially with one another occupying the same region at different time periods.
In terms of the spatial and temporal influence of a main earthquake’s half-sphere during its preparatory stage, expert knowledge in the form of theoretical models has been reported in the literature by Drobrovolsky et.al. [10] and Zubkov [11], respectively. Although the spatial influence equation [10,11] also applies after the occurrence of the main earthquake, no such model exists for the latter temporal half-sphere of influence. However, for the particular region of the Hellenic seismic arc, Drakatos and Latoussakis [12] were able to derive temporal empirical approximations. These equations indicated that the earthquake’s magnitude is the independent parameter upon which the spatial and temporal extent of the sphere of influence depend. Heterogeneous parallel programming enables the processing of such big data both in terms of numbers and diversity of information recorded in the seismic catalogues used, obtained by the Geodynamics Institute of the National Observatory of Athens, Greece [15]. Data provide information regarding the date and time of the occurrence, latitude and longitude coordinates, hypocenter depth and magnitude of all recorded seismic events.
This works complementary two-fold as the import of seismic data from a potentially distinct seismic region to a deep learning neural network enhances the validity that there is a pattern associating mean seismicity rates with time intervals between large earthquakes [16]. Vice versa, the observation of a potential pattern between mean seismicity rates and the time intervals amongst large earthquakes enhances the validity that the investigated area is indeed a distinct seismic zone.
2. Materials and Methods
As discussed earlier, seismic data of the entire Greek vicinity are readily available since 1964. These data comprise of the time of occurrence, latitude, longitude, hypocenter depth and magnitude of every recorded earthquake. These characteristics are sufficient to devise an expert heterogeneous parallel processing agglomerative spatio-temporal clustering algorithm based upon the aforementioned domain expert equations ρ = 10(0.414 Μ − 1.696) km [10], tbefore = 10(0.5 M − 2.1) days [11] and tafter = 10(0.51 M − 1.15) days [12], where M is the earthquake’s magnitude, ρ is the sphere of influence radius, tbefore is the temporal extent of the sphere before the occurrence of the earthquake and tafter is the temporal extent of the sphere after the occurrence of the earthquake. The parallel algorithm, as outlined by the following pseudo-code, starts with the first catalogued main seismic event but eventually selects the largest earthquake in the data set to build the first cluster. It then uses the magnitude of the earthquake to compute its spatio-temporal field of influence and clusters together all earthquakes in the seismic data set falling within those boundaries.
This is enabled by using heterogeneous parallel programming by sorting earthquakes in ascending order chronologically and then selecting the first un-clustered event as the current event in the spatio-temporal clustering algorithm shown in Figure 1. The sphere of influence of the current event, i.e., the time window and the strain radius, is then computed, thereby creating a new cluster. All earthquakes that coincide both spatially and temporally with the aforementioned sphere of influence are assigned to the new cluster. The latter process is conducted using multiple GPU parallel threads with a thread assigned to processing a single seismic event. The earthquake with the largest magnitude in the newly created cluster is then identified and becomes the maximum magnitude event of the current cluster. If the maximum magnitude event is not the current event, then a shifted sphere of influence both spatially and temporally is being computed, adding further earthquakes to the current cluster and the maximum magnitude event becomes the current event. Another scan for the largest earthquake in the cluster then occurs and the above loop repeats itself until the current event coincides with the maximum magnitude event. When this is the case, all clustered data are removed from the overall seismic data set and the process carries on chronologically with the formation of a new cluster starting with the first of the remaining un-clustered events, which then becomes the current event of the algorithm in Figure 1. As a result, the created clusters comprise of the net product of multiple spheres of influence resulting in an irregular shape and variability in the temporal influence at various parts of the cluster. The parallel algorithm ends when the remaining earthquakes in a cluster center end up forming single point clusters or if there are no remaining earthquakes in the reduced seismic data set.

Figure 1.
Pseudo-code of the expert heterogeneous parallel processing agglomerative spatio-temporal clustering algorithm.
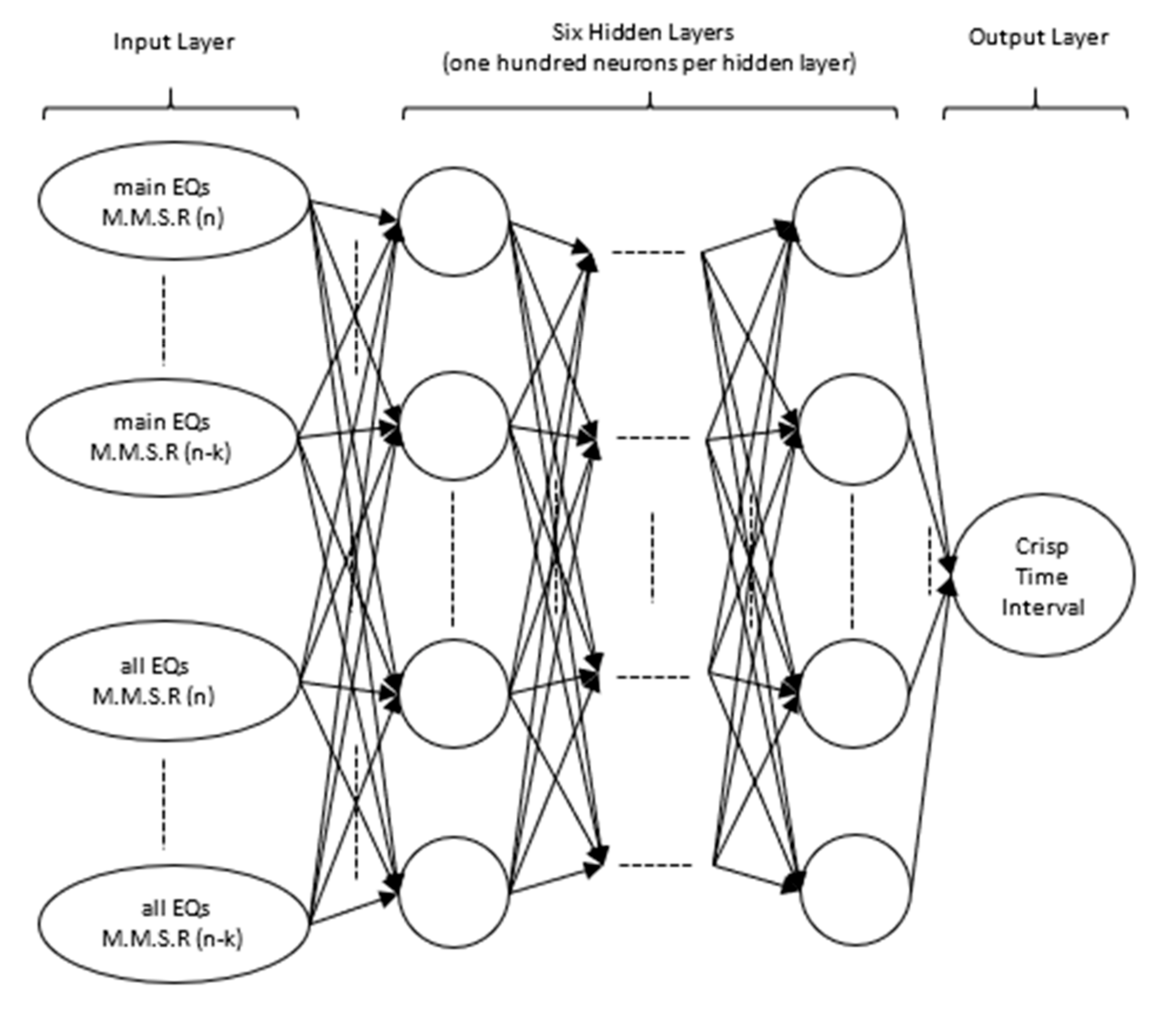
Once the data attributed to the various potentially distinct seismic zones are made readily available via the aforementioned process, it is then possible to investigate for possible correlations between the released amounts of seismic energy and the time intervals between consecutive large earthquakes of a particular potential distinct seismic zone alone. Deep learning neural networks are deployed for that purpose as they are both capable of handling large amounts of data and also perform features’ extraction and classification upon the processed data. With classic neural networks, features’ extraction requires the incorporation of domain experts’ knowledge. In the case of deep learning neural networks this is alleviated providing there is a sufficient number of hidden layers of neurons in the neural network and the data provided are characteristic of the described system [17,18,19]. To ensure that for the particular case of investigating the seismic behavior of the Ionian potentially distinct seismic region, all seismic data recordings from 1964 to 2019 are shown to the deep learning neural network, whose architecture was extended to the maximum possible dimensions supported by the available hardware resources in terms of GPU compute unified device architecture (CUDA) cores and parallel processing threads. The architecture of the deep learning neural network, shown in Figure 2, comprised of one input, six hidden and one output layer. The input layer imports to the deep learning neural network the current and previous mean seismicity rates computed for main earthquakes (main EQs) only, as well as the current and previous mean seismicity rates computed for all earthquakes (all EQs), including foreshocks and aftershocks, hereby infiltrating recursive information to the deep learning neural network. This information is being propagated through a six hidden layer network of a hundred neurons per hidden layer before reaching the single neuron output layer, which produced a crisp output.
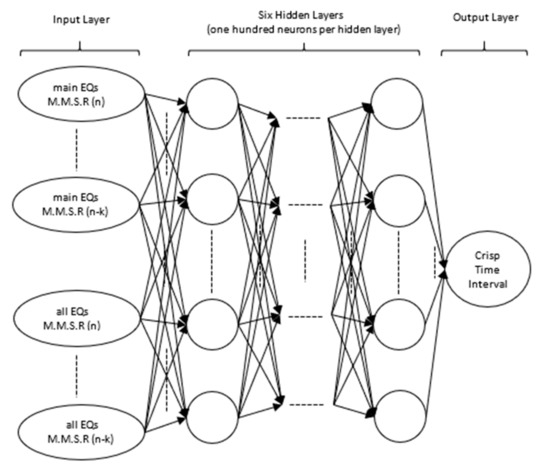
Figure 2.
Architecture of the deep learning neural network.
The crisp output corresponded to the time interval, which, when added to the date of occurrence of the latest large earthquake, indicated the expected time of occurrence of the next forthcoming large seismic event. Subtractive clustering was used upon the training data set in order to obtain initial values for the synaptic weights of the neural network before training commenced. Supervised learning using CUDA C (NVIDIA, Santa Clara, CA, USA) parallel processing error back-propagation was used to train the deep learning neural network for as many epochs as necessary until the mean square error function became nearly flat or ideally zero. Additional measures were taken to prevent overfitting the training data by running in parallel a testing data set comprised of approximately thirty percent of the overall data set selected randomly with an even yearly distribution, which was kept unseen by the deep learning neural network during the training process. When the testing data error function began to stray from the equivalent training data error function, the parameters of the synaptic weights at that very stage were then those that were maintained. These parameters were then used as the final parameters of the synaptic weights of the deep learning neural network following the completion of the training process. CUDA C helped to speed up significantly the operation of the error back-propagation algorithm as the operation of each single neuron per hidden layer was allocated to a different processing thread. All threads attributed to a single hidden layer were working in parallel, bringing down processing times by a factor analogous to the number of neurons per hidden layer. Thread synchronization was applied before the parallel error back-propagation algorithm moved from one hidden layer to another. The threads of each hidden layer were organized in single blocks of linear dimensions, which formed the parallel processing grid operated by the GPU and were synchronized following the completion of each training epoch of the deep learning neural network.
3. Results
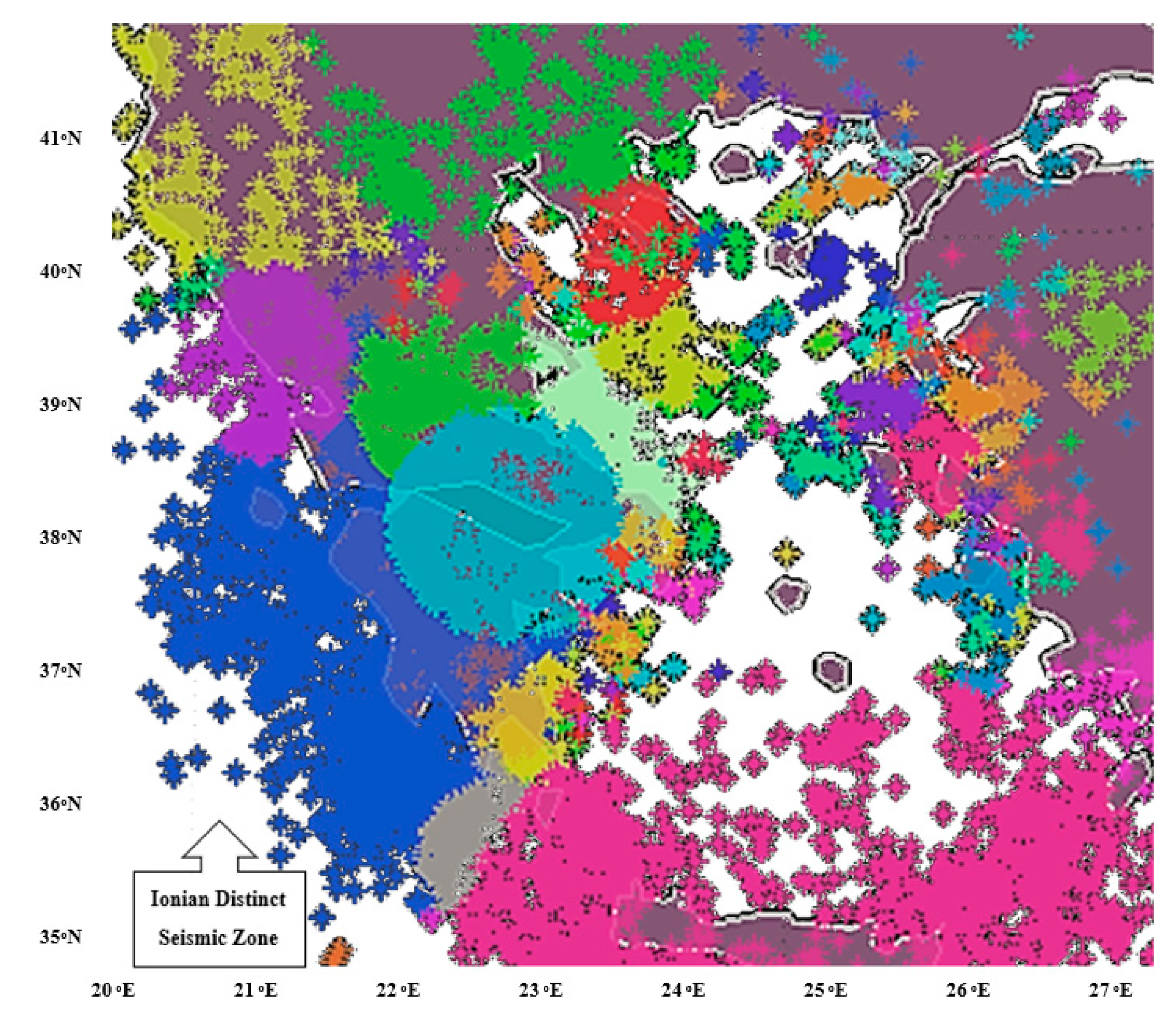
The application of the expert heterogeneous parallel processing agglomerative spatio-temporal clustering algorithm upon seismic data in the Greek vicinity appeared to depict a potentially distinct seismic zone located in the western part of Greece as shown via point cloud viewer [20,21,22] in Figure 3. This observation is further supported by the fact that this particular part of the Eurasian tectonic area, lying beneath the Ionian Sea, is underrun by an isolated compact group of several parallel tectonic underground faults of south-southeast orientation, as reported by the Institute of Geology and Mineral Exploration of Greece [23].
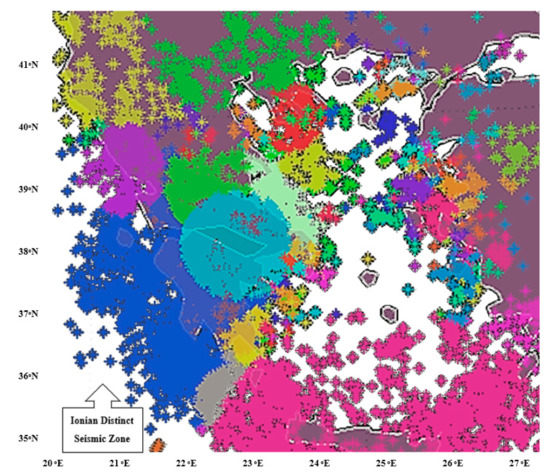
Figure 3.
Potentially distinct Ionian seismic zone. Mainland is shown in purple, sea in white, all other colors correspond to distinct seismic clusters as depicted by the parallel agglomerative clustering algorithm.
The western and southern borders of the Ionian potentially distinct seismic zone, shown in a blue color in Figure 3, do not appear to coincide either spatially or temporally with other seismic zones, each of which is being displayed by other distinct colors. The same applies for the main central part of the Ionian potentially distinct seismic zone. Significant interactions appear on the eastern border area with various other seismic zones depicted by the spatio-temporal parallel algorithm whilst slighter interactions are depicted on the northern border. Still, more than eighty percent of the Ionian potentially distinct seismic zone appears to be interaction-free from any of the neighboring seismic zones.
Only the seismic data that fall within the spatial and temporal boundaries of the potentially distinct Ionian seismic zone were fed into the deep learning neural network in order to investigate whether a potential correlation between seismic energy release rates and the time interval between large earthquakes existed solely for that particular seismic area. Should that prove to be the case, enhances the results by the parallel spatio-temporal clustering algorithm that indicate the potential existence of a distinct seismic zone and, complementary two-fold, that the existence of a distinct seismic zone is the main reason that results in observing the aforementioned correlation.
The task of estimating the interim time interval between consecutive large earthquakes in a particular region of interest, given the recursive information of the monthly mean seismicity rates, is categorized as a regression problem, hence the incorporation of extensive sequential feed forward neural networks with a mean squared error loss parameter and an Adam type optimizer. The deep learning neural network was then trained using supervised learning [24,25] as described in the previous section to predict the time intervals of large earthquakes of magnitudes greater than MS 5.8. This value was selected because there appeared to be a repetition sequence ranging from between six and eleven years that could possibly be justified due to interim seismic energy releases by smaller in magnitude earthquakes. This was possible for the deep learning neural network to depict as its inputs imported not only the mean seismicity rates of the main earthquakes but also those of all seismic events, foreshocks and aftershocks as well. This was achieved using monthly mean seismicity rates (MMSR) obtained for the western part of the Hellenic seismic arc extending at approximately 35.00° to 39.50° in latitude and 19.00° to 20.50°, 23.50° and 22.00° in longitude referring to its northwest, west and southwest borders, respectively, as indicated by Figure 3. As discussed in the previous section, the inputs to the deep learning neural network comprised of the current and recursive mean seismicity rates of the main seismic events only as well as all recorded seismic events of the potentially distinct Ionian seismic zone. The latter were obtained by regression line fitting upon cumulative activity curves, enabling the deep learning neural network to derive potential patterns not only by monitoring the overall seismic energy release process but also by monitoring releases of energy solely by the main earthquakes. These patterns might give an insight regarding seismic clustering, i.e., whether a large earthquake in one area could possibly trigger the occurrence of a large earthquake in a neighboring area.
The required output of the deep learning neural network refers to the time intervals between consecutive large earthquakes. To obtain these time intervals, the date and time of the occurrence of every pair of consecutive large earthquakes was converted into a crisp number. This was conducted by encompassing a Unix timestamp [26] of the moment of occurrence of each individual large earthquake and then the timely difference between the actual moments of occurrence of any two successive large earthquakes was derived in the potentially distinct Ionian seismic zone.
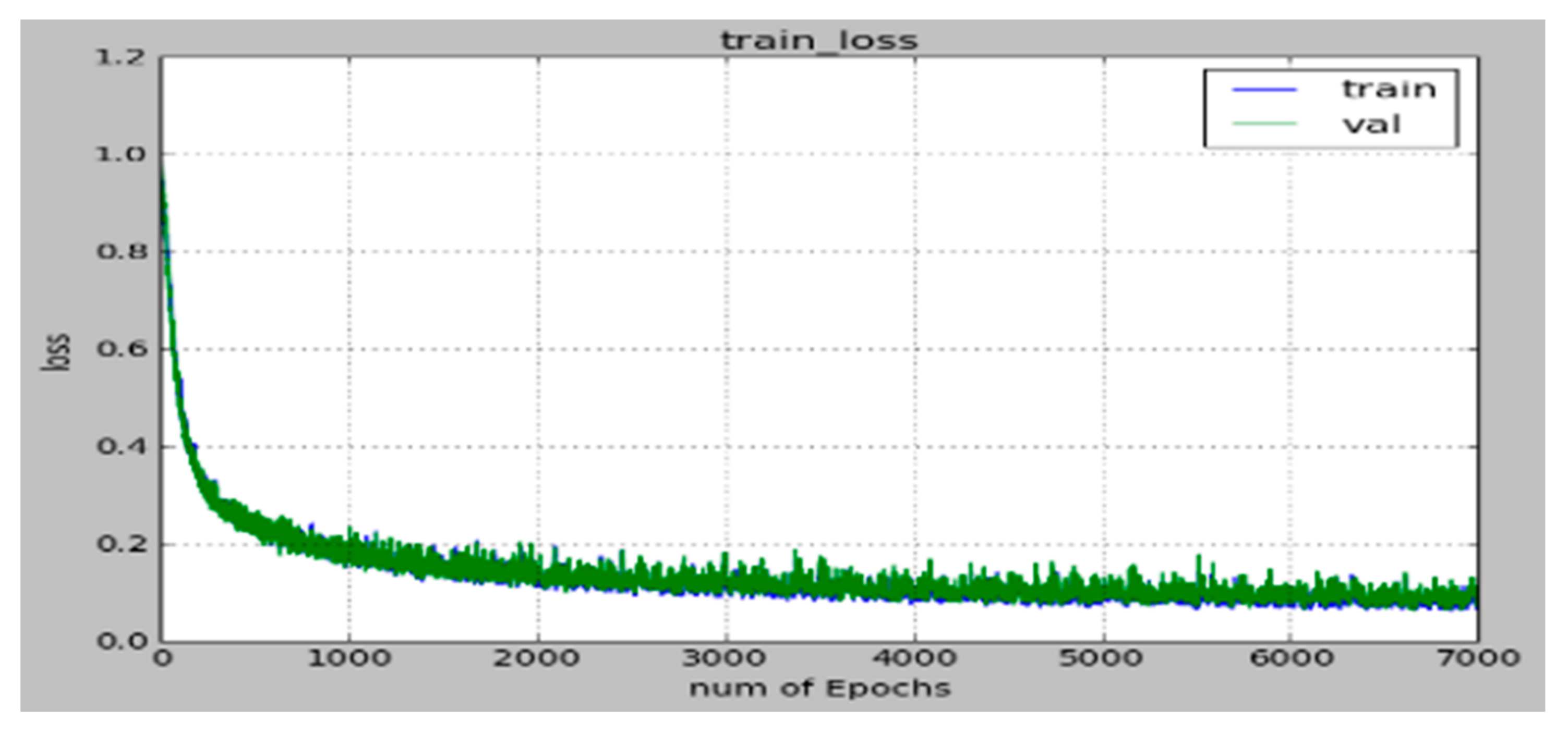
Although training of the deep learning neural network was conducted over seven thousand training epochs using a batch size of five hundred, the final parameters were obtained by the recorded values at two thousand training epochs, after which both the training and checking errors became nearly flat in order to prevent overtraining, as shown in Figure 4.
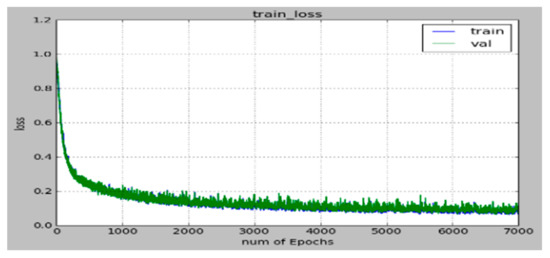
Figure 4.
Initial deep learning neural network training (blue line) and validation (green line) error functions.
4. Discussion
Various time periods ending with the occurrence of large seismic events from February 1966 to November 1992, November 1997, August 2003, June 2008, November 2015 and October 2018, respectively, formed progressive training data sets in the potentially distinct Ionian seismic region. Within the time period from 1992 to 2020, nine earthquakes of magnitude MS ≥ 5.8 occurred, with a mean recurrence time of approximately five years with the exception of the occurrence of a batch of four earthquakes in the first half of 2008. To assist the reader, Table 1 lists all main earthquakes of MS ≥ 5.5 that were kept unseen by the deep learning neural network in the potentially distinct Ionian seismic zone from 1997 onwards, displaying large earthquakes of MS ≥ 5.8 in bold.

Table 1.
Actual dates and estimated dates of large (MS ≥ 5.8) earthquakes’ occurrence times.
The initial training data set (1966–1992) imported to the deep learning neural network mean seismicity rates on a monthly basis along with time intervals among consecutive pairs of large earthquakes until the occurrence of the MS 5.8 large earthquake on 21 November 1992. Once training was complete, the deep learning neural network received at its inputs the recursive information of the monthly mean seismicity rates of the main earthquakes as well as of all seismic events that corresponded to the time intervals between previous large main earthquakes with magnitudes of MS ≥ 5.8. At its output, the deep learning neural network then generated a crisp number corresponding to the estimated time interval between the latest and the immediately forthcoming large seismic event. The deep learning neural network then produced an output of 151,772,272. This value, when added to the occurrence Unix timestamp date 722,322,439 of the aforementioned large earthquake, pointed to the timestamp 874,094,711, which corresponded to the calendar date of 12 September 1997. This date only preceded the actual date of occurrence, 18 November 1997, by approximately two months, with the observed difference possibly being attributed to the larger earthquake magnitude (MS 6.1) in comparison with the MS 5.8 large earthquake threshold used herein.
The deep learning neural network was then retrained with the training data set including the mean seismicity rates and the time intervals amongst consecutive large earthquakes until 18 November 1997. After training, when presented with the new unseen input data set of recursive information of the monthly mean seismicity rates of the main earthquakes as well as of all seismic events that corresponded to the time intervals between previous large main earthquakes with magnitudes of MS ≥ 5.8, the deep learning neural network produced an output of 174,647,370. This value, when added to the occurrence Unix timestamp date 879,858,457 of the aforementioned large earthquake, pointed to the timestamp 1,054,505,827, which corresponded to the calendar date of 1 June 2003. This date only preceded the actual date of occurrence, 14 August 2003, by approximately two and a half months, with the observed difference possibly being attributed to the two interim medium sized earthquakes of magnitudes MS 5.6 and MS 5.5 that might have delayed briefly the seismic energy build up process in the Ionian potentially distinct seismic zone.
Having retrained the deep learning neural network with the next training data set including the mean seismicity rates and the time intervals amongst consecutive large earthquakes until 14 August 2003, when presented with the new unseen input data with recursive information of the monthly mean seismicity rates both of the main earthquakes as well as of all seismic events that corresponded to the time intervals between previous large main earthquakes with magnitudes of MS ≥ 5.8, the deep learning neural network produced an output of 146,034,832. This value, when added to the occurrence Unix timestamp date 1,060,838,094 of the aforementioned large earthquake, pointed to the timestamp 1,206,872,926, which corresponded to the calendar date of 30 March 2008. This date fell amidst the potential occurrence of a seismic clustering phenomenon where an initial large earthquake of MS 6.1 on 6 January 2008 with a deep hypocenter 86km in depth appeared to have triggered a series of seismic reactions at shallower depths with hypocenters at 41, 38, 25 and 25 km and magnitudes of MS 6.2, 6.1, 6.0 and 6.5 from February until June 2008, respectively, as shown in Table 1.
Since the MS 6.5 that occurred on 8 June 2008 was the last and also happened to be the largest of the potential seismic clustering sequence, the deep learning neural network was then retrained up to that date. After training when presented with the new unseen input data of recursive information of the monthly mean seismicity rates of the main earthquakes as well as of all seismic events that corresponded to the time intervals between previous large main earthquakes with magnitudes of MS ≥ 5.8, the deep learning neural network produced an output of 219,776,812. This value, when added to the occurrence Unix timestamp date 1,212,927,928 of the aforementioned large earthquake, pointed to the timestamp 1,432,704,740, which corresponded to the calendar date of 27 May 2015. This date preceded the actual date of occurrence, 17 November 2015, by nearly six months. This is most likely due to the fact that the deep learning neural network was affected by the multiple, compact in time large earthquakes of the aforementioned possible seismic clustering phenomenon of which no other occurrence was reported in the training data set. However, the deep learning neural network tried to learn from the data and compensated for the increased seismic activity by extending its output from an average of nearly five years to a mere seven years since the occurrence of the latest large earthquake presented to it.
Following on, the deep learning neural network was retrained with the training data set now including the mean seismicity rates and the time intervals amongst consecutive large earthquakes until 17 November 2015. After training, when presented with the new unseen input data set of recursive information of the monthly mean seismicity rates of the main earthquakes as well as of all seismic events that corresponded to the time intervals between previous large main earthquakes with magnitudes of MS ≥ 5.8, the deep learning neural network produced an output of 107,495,042. This value, when added to the occurrence Unix timestamp date 1,447,744,207 of the aforementioned large earthquake, pointed to the timestamp 1,555,239,249, which corresponded to the calendar date of 14 April 2019. This date superseded the actual date of occurrence, 25 October 2018, by just over six months. This difference is possibly due to the fact that there were no occurrences of interim medium-large seismic events as indicated by Table 1, as had been the case prior to all previous large earthquakes examined. The appearance of a non-president situation in the previously recorded data used during training was likely to be the main reason causing the aforementioned deviation.
5. Conclusions
From the above findings, the general result appears to be that the deep learning neural network managed to estimate time intervals between consecutive large earthquakes with variations in the range of a few months. Despite the presence of two unaccounted phenomena, i.e., the seismic clustering effect in 2008 and the appearance of no interim medium-large earthquake in between 2015 and 2018, the deep learning neural network was able to learn and to some extent account for the effect of the aforementioned information, an attribute due to deep learning in comparison with classical artificial neural networks that would have required the intervention of domain experts. The observed correlation between the energy release rates and the time intervals amongst large earthquakes enhanced the hypothesis of the presence of a potential distinct seismic zone as indicated by the parallel spatio-temporal clustering algorithm. In parallel, this was a two-way working relation as it is likely that the very presence of a distinct seismic zone in an area of a steady seismic energy input rate yielded the observed correlation between the energy release rates and the time intervals amongst large earthquakes.
Yet, despite more than fifty years’ worth of seismic data recordings, not all behavioral attributes of the potential distinct Ionian seismic zone have been unveiled by past seismicity. This affects the training of any intelligent system, highlighting the need of establishing an ongoing deep learning mechanism that constantly learns from newly recorded data. Furthermore, considering that the network’s estimation is only temporal, indicating when the Ionian potentially distinct seismic zone is likely to give a large earthquake, ongoing research is currently being conducted aiming to narrow down the area of possible occurrence of the expected large earthquake within the potential Ionian distinct seismic zone.
Funding
This research received no external funding.
Conflicts of Interest
The author declares no conflict of interest.
References
- Filici, C. On a Neural Approximator to ODEs. IEEE Trans. Neural Netw. 2008, 19, 539–543. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gurumoorthy, R.; Kodiyalam, S. Neural network approximator with a novel learning scheme for design optimization with variable complexity data. In Proceedings of the 37th Structure, Structural Dynamics and Materials Conference, Salt Lake City, UT, USA, 15–17 April 1996; pp. 190–195. [Google Scholar]
- Lastovetsky, A. Advanced Heterogeneous Parallel Programming in mpC. In Parallel Computing on Heterogeneous Networks, 1st ed.; Zomaya, A., Ed.; Wiley: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2004; pp. 215–254. [Google Scholar]
- Michelucci, U. Applied Deep Learning, 1st ed.; Apress: Berkeley, CA, USA, 2018; pp. 1–410. [Google Scholar]
- Vinod-Kumar, K. Earthquake and Active Faults. In Remote Sensing Applications; Roy, P.S., Dwivedi, R.S., Vijayan, D., Eds.; NRSC: Balanagar, India, 2015; pp. 339–350. [Google Scholar]
- Earle, S. Plate Tectonics. In Physical Geology, 2nd ed.; BCcampus: Victoria, BC, Canada, 2019. [Google Scholar]
- Konstantaras, A. Expert knowledge-based algorithm for the dynamic discrimination of interactive natural clusters. Earth Sci. Inform. 2016, 9, 95–100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Konstantaras, A. Classification of distinct seismic regions and regional temporal modelling of seismicity in the vicinity of the Hellenic seismic arc. IEEE J. Sel. Top. Appl. Earth Obs. Remote Sens. 2013, 6, 1857–1863. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Konstantaras, A.; Katsifarakis, E.; Maravelakis, E.; Skounakis, E.; Kokkinos, E.; Karapidakis, E. Intelligent spatial-clustering of seismicity in the vicinity of the Hellenic seismic arc. Earth Sci. Res. 2012, 1, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dobrovolsky, I.; Gershenzon, N.; Gokhberg, M. Theory of electrokinetic effects occurring at the final stage in the preparation of a tectonic earthquake. Phys. Earth Planet. Inter. 1989, 57, 144–156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zubkov, S. The appearance times of earthquake precursors. Izv. Akad. Nauk SSSR Fiz. Zemli (Solid Earth) 1987, 5, 87–91. [Google Scholar]
- Drakatos, G.; Latoussakis, J. A catalog of aftershock sequences in Greece (1971–1997): Their spatial and temporal characteristics. J. Seismol. 2001, 5, 137–145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, D.; Jin, H.; Gao, P.; Zhu, X. Detecting spatial community structure in movements. Int. J. Geogr. Inf. Sci. 2018, 32, 1326–1347. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, W.; Fang, C.; Zhou, L.; Zhu, J. Measuring megaregional structure in the Pearl River Delta by mobile phone signaling data: A complex network approach. Cities 2020, 104, 102809. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- GI-NOA: Geodynamics Institute—National Observatory of Athens. Available online: http://www.gein.noa.gr/en (accessed on 13 July 2020).
- Bodri, B. A neural-network model for earthquake occurrence. Geodynamics 2001, 32, 289–310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aggarwal, C. Training deep neural networks. In Neural Networks and Deep Learning; Springer: New York, NY, USA, 2018; pp. 105–167. [Google Scholar]
- Konstantaras, A.; Vallianatos, F.; Varley, M.; Makris, J. Soft-computing modelling of seismicity in the southern Hellenic Arc. IEEE Geosci. Remote Sens. Lett. 2008, 5, 323–327. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Konstantaras, A.; Varley, M.R.; Vallianatos, F.; Makris, J.; Collins, G.; Holifield, P. Detection of weak seismo-electric signals upon the recordings of the electrotelluric field by means of neuro-fuzzy technology. IEEE Geosci. Remote Sens. Lett. 2007, 4, 161–165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maravelakis, E.; Konstantaras, A.; Kabassi, K.; Chrysakis, I.; Georgis, C.; Axaridou, A. 3DSYSTEK web-based point cloud viewer. In Proceedings of the 5th International Conference on Information, Intelligence, Systems & Applications (IISA 2014), Chania, Greece, 7–9 July 2014; pp. 262–266. [Google Scholar]
- Axaridou, A.; Chrysakis, I.; Georgis, C.; Theodoridou, M.; Doerr, M.; Konstantaras, A.; Maravelakis, E. 3D-SYSTEK: Recording and exploiting the production workflow of 3D-models in cultural heritage. In Proceedings of the 5th International Conference on Information, Intelligence, Systems & Applications (IISA 2014), Chania, Greece, 7–9 July 2014; pp. 51–56. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, W.; Thill, J.C. Detecting and visualizing cohesive activity-travel patterns: A network analysis approach. Comput. Environ. Urban Syst. 2017, 66, 117–129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hellenic Survey of Geology & Mineral Exploration. Available online: www.igme.gr (accessed on 13 July 2020).
- Jing, Q. Analysis of intensive learning and supervised learning. Acad. J. Comput. Inf. Sci. 2018, 1, 80–84. [Google Scholar]
- Konstantaras, A.; Varley, M.R.; Vallianatos, F.; Collins, G.; Holifield, P. Neuro-fuzzy prediction-based adaptive filtering applied to severely distorted magnetic field recordings. IEEE Geosci. Remote Sens. Lett. 2006, 3, 439–441. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Manish, J. Beginning Modern Unix, 1st ed.; Apress: Berkeley, CA, USA, 2018; pp. 1–413. [Google Scholar]
© 2020 by the author. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).