Abstract
Virtual reality (VR) technologies have opened new possibilities for creating engaging educational games. This paper presents a serious VR game that immerses players into the activities of lunar exploration missions in a virtual environment. We designed and implemented the VR game with the goal of increasing players’ interest in space science. The game motivates players to learn more about historical facts of space missions that astronauts performed on the Moon in the 1970s. We studied usability and engagement of the game through user experience in both VR and non-VR versions of the game. The experimental results show that the VR version improved their engagement and enhanced the interest of players in learning more about the events of lunar exploration.
1. Introduction
Since the advent of head-mounted displays (HMDs), virtual reality (VR) technologies have been used widely in digital media and entertainment. The low cost of HMDs makes VR accessible to the public. Many VR games using HMDs and handheld motion controllers have been released to the public in recent years. Games developed with VR technologies can provide a highly immersive experience [1]. Serious games are “(digital) games used for purposes other than mere entertainment” [2]. They are used in many areas such as education, healthcare, ecology, and scientific research [3]. Adopting VR technologies in serious games can simulate a learning or training environment that would otherwise be impossible for people to access in the physical world.
In this work, we design and implement a serious VR game that immerses players into activities of lunar exploration missions in a virtual environment. The game is based on the historical events of the Apollo 16 mission in the 1970s, in which astronauts landed on the Moon, drove the lunar rover, and eventually returned to the Earth. In this game, we implement planning, preparing, and driving activities of the Apollo 16 mission by utilizing VR technologies and handheld motion controllers. In our previous work, we developed a similar serious game [4], but it was a non-VR version playable with a single-screen display and keyboard–mouse/joystick inputs. Besides the contributions in game design and development, we investigate how the VR technology effects usability and game engagement compared to the non-VR version. In our study, we utilized a between-subject design, where half of the participants play the non-VR version of the game and the other half of the participants play the VR version of the game. We used the Game Engagement Questionnaire (GEQ) [5] and an interview questionnaire to measure their levels of engagement. The results show that the VR version of the lunar roving game took longer for participants to finish but enhanced the game engagement and their motivation to learn the events of lunar exploration.
The paper is organized as follows. Section 2 describes existing work on VR-based serious games. Section 3 describes the background of lunar exploration missions by The National Aeronautics and Space Administration (NASA) in the United States in the late 1960s and early 1970s and their influence on education. Section 4 discusses the design details and gameplay mechanics of the VR game. Section 5 describes the design of the usability and engagement study. Section 6 presents the analysis results, and we conclude the work in Section 7.
2. Existing Work in Serious VR Games
Our Lunar Exploration Game is a serious VR game with the goal of motivating players to learn historical events of the Apollo 16 mission. Serious games have been applied in many domains such as education, healthcare, training, and scientific exploration. In Section 2.1, we review papers that discuss serious games used in different domains. In Section 2.2, we review studies evaluating the effectiveness of serious VR games, with a focus on engagement, usability, and learning outcomes. In Section 2.3, we review the theories underpinning usability and engagement studies in serious VR games, which have impacted the design of our experiment.
2.1. Applied Domains of Serious VR Games
Susi et al. [2] gave a review of serious games. They presented the definition, domain, history, and market status of serious games. Djaouti et al. [3] classified serious games with the Gameplay/Purpose/Scope (G/P/S) model to combine both “serious” and “game”. Mikropoulos and Natsis [6] gave a review of educational virtual environments from the year 1999 to 2009. They identified several features in VR for learning and discussed reasons why VR could be useful in a learning situation. The most important reason they identified is that VR provides the possibility for users to try situations not accessible or dangerous in the real world. Potkonjak et al. [7] presented a review of virtual laboratories for science, technology, and engineering education. They argued that virtual labs can offer advantages that real labs may not provide. The advantages included cost-efficiency, flexibility, multi-user support, and the access of dangerous or not accessible situations. Alhalabi [8] discussed the effectiveness of VR systems for engineering education. They evaluated traditional education approaches, Corner Cave systems, and HMD systems. They found that Corner Cave and HMD systems were better than traditional education approaches in terms of improving students’ performance, and the effectiveness of HMD systems was more significant.
However, researchers have shown that in different situations, VR technology does not always play a positive role. Jensen and Konradsen [9] presented a review of the use of HMDs in education and training. They found that using an HMD led to a better result only in a small number of cases. Beyond those cases, using an HMD had no advantage or even performed worse than the non-VR setting. Freina and Ott [10] reviewed the use of immersive virtual environments in education. They discussed the advantages and drawbacks of using VR in children’s education and rehabilitation for cognitive disabilities. Virvou and Katsinois [11] discussed the usability of using VR games for education in the classroom. They argued that learning outcomes are different among students since they usually have different game-playing backgrounds, but in most cases, the differences in their backgrounds do not influence their motivation.
2.2. Use Case Studies of Serious VR Games
Mei and Sheng [12] presented a system for virtual hospital-situated learning. Their system was primarily used for learning human organ anatomies. They obtained the result that the situated learning can improve users’ motivation. Cheng et al. [13] presented a VR game to teach language and culture. The result showed that the VR game could increase user engagement, but the result did not show a significant improvement in the language learning outcome when the VR game was used. Adamo-Villani and Wilbur [14] presented a study of the virtual learning environment for deaf and hard-of-hearing children. They compared a immersive version and non-immersive version; however, the results of the study did not show a significant difference between the versions. Parmar et al. [15] compared the HMD-based metaphor viewer with the desktop-based display for training users in electrical circuitry. Their results showed a significant learning benefit when using the HMD. They argued that participants may gain better performance and enjoy using the HMD version, but they did not provide an evaluation to support this argument. Greenwald et al. [16] presented a usability study to compare the learning in VR with the learning on a traditional 2D screen. The comparison result did not show a significant difference in quantitative learning measurements, though the completion time of the VR version was always longer than the non-VR version. Olmos et al. [17] provided an educational platform to study the influence of emotional induction and level of immersion on learning motivation. They presented a usability study between an immersive version with an HMD and a low-immersive version with a tablet. The results indicated that the immersive condition and the positive emotional induction can influence knowledge retention. Zizza et al. [18] designed and implemented a multimodule VR learning environment over the network. They evaluated user experience in the VR version by comparing it to a desktop version. Although they stated that the feedback on the VR version was positive, the interview questions used to obtain feedback should be more comprehensive. Buttussi and Chittaro [19] conducted a two-week study on three different types of display settings for learning, including a desktop VR platform, an HMD with a narrow field view and a 3-DOF tracker, and an HMD with a wide field of view and a 6-DOF tracker. They found that HMDs can increase user engagement. In their study, HMD did not lead to a significant increase in knowledge and self-efficacy.
In summary, the use of VR technologies for serious games is a new area. In different use cases, people may have different experiences and opinions about VR. Thus, there is no consensus. Our literature search did not find any studies about the adoption of VR technologies for learning historical events of lunar exploration or other events in space science.
2.3. Usability and Engagement Studies in Serious VR Games
Bowman et al. [20] discussed several evaluation methods according to three key characteristics: involvement of representative users, context of evaluation, and types of results produced. The results showed that the evaluation should be close to the changes between the VR system and non-VR system. Based on their findings, the parameters for usability evaluation that we recorded in our experiment focus on the differences between the VR and non-VR versions of the game. Sutcliffe and Kaur [21] studied the walkthrough method for evaluating VR systems. Key points of this method are a goal-oriented task, exploration and navigation, and system initiative. In our experiment, tasks that the participants complete were based on the walkthrough method.
When measuring the usability differences between a VR system and non-VR system, researchers have employed the between-subjects study design [22,23]. Mcmahan et al. [22] expressed that the reason is to increase experimental controls and reduce confounding variables. In our experiment, we used a between-subjects study design so that each participant was only subjected to the play experience of a single version.
Game engagement is one of the factors that affect learning outcomes and the motivation to play games [24]. Brockmyer et al. [5] developed the Game Engagement Questionnaire (GEQ) to measure the engagement level of players playing a video game. The GEQ has been used in many serious game studies [25,26,27,28]. Researchers have also used the GEQ to study VR games [28,29,30]. In our experiment, we used the GEQ to measure and analyze the engagement level of participants in both VR and non-VR versions of the lunar roving game.
3. Background of NASA-Inspired Serious Games
In the 1960s, students were inspired by the success of lunar exploration missions performed by NASA astronauts and engineers. Photographs and videos of the missions and NASA-developed technologies motivated students to pursue science, technology, engineering, or math (STEM) degrees. Through the 1960s, the number of students enrolled in science and engineering increased significantly. According to a report by the National Science Foundation [31] and the article by Markovich [32], the percentage of bachelor degrees awarded in science and engineering fields peaked in the late 1960s for the period of 1966–2010.
The experience of learning about lunar exploration missions is usually through a passive setting where information is presented in the form of reading material, speaker talks, videos, museum lectures, or exhibitions. For example, people may explore NASA’s website to find a wealth of materials that explain the past and future of lunar exploration. Those materials provide both scientific facts and public narratives for public science engagement. In such a setting, learners passively receive what the assigned material says. In contrast to the passive setting, an active setting gives the learner an opportunity to take a participatory role as he or she is absorbing the knowledge [33]. For example, some summer camp programs promote active learning experiences during a scheduled period of time (e.g., the Space Camp program at the U.S. Space & Rocket Center (Space Camp is located in Huntsville, Alabama, U.S. Website: https://www.spacecamp.com)). However, those summer camp programs usually require a substantial cost for travel or lodging.
In contrast to attending Space Camp, a game of lunar exploration is easier to set up and provides an active learning environment at a lower cost. The complex content of lunar exploration missions can be represented graphically in the game, and the game allows the learner to interact with the content using precisely simulated navigation systems and driving controls based on the operations in real missions. NASA’s Eyes [34] is an interactive application developed at NASA’s Jet Propulsion Laboratory. It is an educational tool that allows the user to interact with the Earth, solar system, and spacecraft. To maintain a low computational cost on geometry rendering, the Earth and Moon in NASA’s Eyes are represented as spheres wrapped with textures, so there is a lack of visual fidelity on geographical features. Another game-based example is NASA Space Place [35], which is a NASA science webpage for kids. NASA Space Place has a few games related to the Moon, rovers, and missions. The games are 2D, cartoonish, and provide only introductory or conceptual information.
NASA supports game developers making NASA-inspired 3D games. NASA has released a variety of 3D models and textures of spacecraft, landing sites, asteroids, etc. [36]. One 3D game is Station Spacewalk Game [37]. It contains a 3D model of the International Space Station that allows the user to experience NASA repair work on the station and learn how the station is assembled. The game runs on a standalone PC or on the web with a Flash plug-in, but it does not work with VR devices. NASA also provides a web-based interactive tool [38] to show the historical landing sites on the Moon and explains briefly the activities that astronauts have conducted. It helps the player to understand the history of lunar exploration, but it does not offer participatory experiences for users. A few years ago, the Immersive VR Education company [39] released an Apollo 11 VR game that is a documentary style VR application presenting historical lunar exploration events through a mix of original audio and video. The National Naval Aviation Museum adopted a similar concept to exhibit the Apollo 11 journey using VR technologies [40] along with a physical Apollo command module. Audiences are immersed in activities such as boarding the rocket, experiencing the launch, witnessing travel through space, and landing on the Moon. Peng et al. [4] gamified the Moon mission and created three playing phases. They presented the lunar roving game on a PC platform and employed a standard screen. They performed a usability study with 30 participants and provided a descriptive analysis of the effectiveness of the game for learning about lunar exploring activities. The results showed that the game enhanced user engagement in NASA-inspired events and increased the users’ interest in space science. However, their work did not provide a statistical comparison between a VR-based gameplay and a non-VR gameplay.
4. Game Design Methodology
The concept of game design in this work is similar to the lunar roving game presented by Peng et al. [4]. In this work, we develop a VR version of the lunar roving game, which is compared to the non-VR version presented by Peng et al. [4] in terms of usability and game engagement. The game is composed of three playing phases: planning, preparing, and driving. In the planning phase, the player is guided to create the driving route by placing markers on a virtual lunar terrain map. In the preparing phase, the player selects a subset of devices from the inventory and then loads them onto the lunar rover for later use on the route. In the driving phase, the player drives the rover to the end of the route. During the driving, the player operates a navigation system to determine the driving direction, control the rover’s speed, and avoid overheating. The game presented by Peng et al. [4] is a non-VR video game running on a PC with a single screen. The player uses a keyboard/mouse to place markers and select scientific instrument and uses a joystick to drive the rover. In this work, we convert the non-VR version of the game into a VR game. The VR game runs on a PC with the content rendered to a head-mounted display so that the player will feel immersed in a virtual lunar environment. The player plays the VR game using handheld motion controllers.
In general, VR games have many things in common with non-VR video games. For example, both non-VR and VR games produce interactive experiences and require real-time rendering, and their development process is the same. In contrast to the use of a keyboard and mouse in non-VR games, the use of VR head trackers and handheld controllers enhances the freedom of movement for in-game actions. In this section, we discuss the design differences between the non-VR and VR versions of the lunar roving game, the ways of relating to the environment and interface, input modalities for gameplay, and engagement levels in each playing phase.
4.1. Planning Phase
The lunar roving game requires the player to explore a region of lunar terrain on a planned driving route. In the planning phase, the player is asked to identify station stops on the lunar terrain map based on the longitude and latitude values. Both the non-VR and VR versions of the game allow the player to place markers/tokens on the map.
In the non-VR version of the game, the player places markers on the map through a 2D user interface. As shown in Figure 1a, the interface contains a cartoon-style commander who instructs the player how to use the interface. The commander’s instructions and longitude and latitude values are displayed as rolling texts in a dialogue box. The player places a marker by mouse-clicking on the map. If the player does not place the marker at the correct location, he or she will be asked to repeat the placement operation for the same marker until it is placed correctly on the map. When all markers are placed correctly, a calculator appears in the interface. The commander will ask the player to calculate the travel time based on the given distance and maximum speed. To do the calculation, the player can enter numbers by mouse-clicking the number buttons on the calculator.
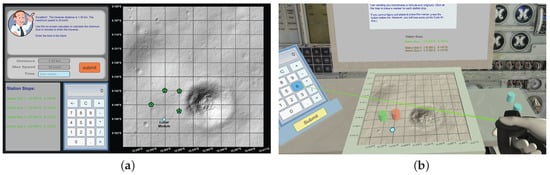
Figure 1.
Screenshots of the planning phase. (a) is the user interface for the non-virtual reality (VR) version of the game, and (b) is the 3D environment for the VR version of the game.
In the VR version of the game, the player wears an Oculus Rift headset with which he or she gains a 360 degree interior view of the spacecraft. As shown in Figure 1b, the player can see the lunar terrain map on a desk, and there are four 3D tokens next to the map. The instructions from the commander and the longitude and altitude values are displayed on a virtual monitor in front of the player. In the VR game, the player holds a pair of Oculus Touch controllers in his or her hands, which provide hand presence in the virtual environment. The player can press a button on the Touch controllers to trigger a gameplay event without any interruption from physical hand movements. To place a token on the map, the player points to the token using the controller and then holds a specific button on the controller to pick up the token. Then, the token can be moved across the desk by moving the controller while holding the button. The token can be dropped on the map when the button is released. If the token is not placed correctly, the player is asked to pick it up again and repeat the placement operation until it is placed correctly. When placing a token, the player can lean his or her body forward to have a closer look of the map or lean back to regain the full view of objects on the desk. After all tokens are placed correctly, more instructions from the commander will roll into the virtual monitor; at the same time, a 3D calculator appears on the left side of the desk. To use the calculator, the player points on the number buttons of the calculator using the Touch controller and then triggers a specific button on the controller to press the number button.
4.2. Preparing Phase
In the original Apollo mission, astronauts needed to load communication and scientific instruments onto the lunar rover and use them at station stops on the route. In the preparing phase of this game, the commander describes the related scientific tasks. Based on the description, the player determines what instruments to choose from the inventory and loads them onto the rover. The participant is required to finish a total of five tasks. The first task is to put two astronauts onto the lunar rover. The second task is to load two communication devices. The third task is to load a pallet frame that will hold devices and tools. The fourth task is to load a monitoring device that can be controlled remotely by Houston. The fifth task is to load a camera device to record documentary photos and videos.
As shown in Figure 2a, the non-VR version of the game consists of a 2D user interface. The commander appears in the top-left corner of the screen. The description of related scientific tasks from the commander appears in a dialog box. The player can explore the inventory in the middle panel of the interface. When mouse-clicking on an item in the inventory, the 3D model of the corresponding device will appear in the top part of the right panel. At the same time, the usage of the device will appear in the bottom part of the right panel. When the player checks the checkbox of the item in the inventory, the device will show up on the rover at the location it should be loaded. A 3D view of the lunar rover is shown in the left panel of the interface. The player can rotate the 3D view to look at the rover from different angles.
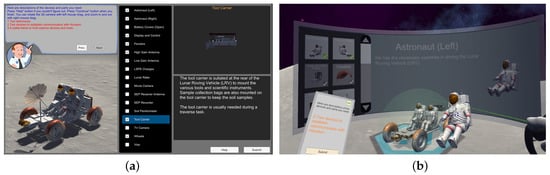
Figure 2.
Screenshots of the preparing phase. (a) is the user interface for the non-VR version of the game, and (b) is the 3D user interface for the VR version of the game.
The VR version of the game contains a 3D user interface for the preparing phase. Different from the non-VR version, the description of science tasks appears on a virtual display device held in the player’s left hand. The player can move the display device closer or farther away from the HMD’s viewpoint by moving the Touch controller in the left hand. The device icons and usages are shown in a large curved virtual display. As discussed in Cao et al. [41], a large curved display allows the player to interact with the content in a wide field of view and supports a high level of perceived immersion. The Touch controller in the player’s right hand is used to scroll the list of device icons up and down. To view the details of a device, the player points to the device icon and presses a specific button on the controller so that the 3D model of the device and its usage will appear in the right section of the curved display. The player can hold a specific button on the controller to pop the 3D model of the device out of the curved display and move it in 3D space using the controller. The player can drop the device onto the lunar rover, as shown in Figure 2b.
4.3. Driving Phase
In the driving phase, the player drives the lunar rover to explore a geographical region of the Moon. Both the non-VR and VR versions of the game use the same 3D model of the lunar terrain, which is converted from Lunar Reconnaissance Orbiter (LRO) data. The player needs to operate the rover’s navigation system to check the driving direction, monitor the speed, and avoid the overheating issue. In particular, the game requires the player to use three navigation devices. The first one is a heading device that displays the driving direction based on the shadow cast on the heading dial. The second one is a speed meter that displays the current driving speed of the rover. The third one is a temperature meter that displays the heat levels of the batteries and motors. The rover has to slow down or stop if the reading of the temperature meter indicates an overheating of batteries or motors.
The interaction with the navigation system is different between the non-VR and VR versions of the game. In the non-VR version, as shown in Figure 3a, a vertical panel is created on the right side of the screen to host the heading device, speed meter, and temperature meter. The 3D model next to this panel is the control console, on which the navigation devices were installed originally. In the VR version, as shown in Figure 3b, the player operates the navigation devices only through the control console on the rover. With the immersive view provided by the HMD, the player can move his or her head closer to the control console to check readings on the devices, just like what astronauts would do when driving the lunar rover.
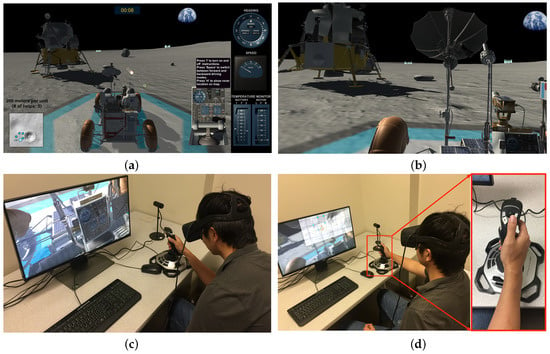
Figure 3.
Screenshots and control examples of the driving phase. (a) is the 3D environment for the non-VR version of the game, with the navigation system on the right side of the screen, (b) is the 3D environment of the first-person view for the VR version of the game, (c) shows the head movement with the head-mounted display (HMD) for the readings of the navigation devices in the control console, and (d) shows the operation with the flight stick to bring up the mini map in the VR version of the game.
The real lunar rover uses a T-shaped steering controller for driving. This controller, as a mechanical part of the control console, is located between two seats. It was operated by the astronaut sitting on the left seat. Moving the controller left or right turns the rover to the left or right. Moving it forward increases the speed, and moving it backward decreases the speed. To mimic such special steering control, both versions of the game use a flight stick as the input device, as depicted in Figure 3d.
The camera control in the non-VR and VR versions of the game is implemented differently. In the non-VR version, the default position of the camera is set behind the rover. When the player is driving, the camera will follow the rover’s movement. The player can press a button on the flight stick to switch among a few different camera views, such as the side view to see the rover from the side and, the front view. In the VR version, the camera is controlled by the player’s head movement, as shown in Figure 3c. The player only has the first-person view of the astronaut sitting on the driver’s side. The VR version does not allow view switching.
Both the non-VR and VR versions of the game contain a mini map that shows the location of the Lunar Module (the landing location), locations of the station stops, and geological features of the Moon. In the era of the Apollo missions, there was no GPS system to track where the rover was on the Moon. Therefore, the mini map in the game does not show the location of the lunar rover. However, in the case that the player feels lost, he or she can press a specific button on the flight stick to show the rover’s location and its current moving direction only for a few seconds. This can be used a maximum of five times. In the non-VR version of the game, the mini map is at the bottom-left corner, and it is always visible to the player. In the VR version of the game, as shown in Figure 3d, the mini map becomes visible when a button is pressed.
5. Usability and Engagement Study
We designed and performed a study to understand the usability and game engagement of the non-VR and the VR versions of the game. This section describes the design of our study.
We set up the usability and engagement study in a research laboratory in the university. The study took about 30 min for each participant. After arrival, participants first signed the consent form, and then each of them was given a unique user ID. Before playing the game, participants answered a demographic questionnaire about their experience in gaming, virtual reality, space science, and serious games. We utilized a between-subject design, where participants were randomly selected to play the VR and non-VR versions of the game. Each participant was asked to play the same version twice (two trials). After playing the game, they were asked to answer the GEQ [5] (as shown in Table 1) and the interview questionnaire (as shown in Table 2). We recruited a total of 30 participants for the study, 20 males and 10 females. A total of 10 males and 5 females played the non-VR version, and the other 10 males and 5 females played the VR version. Their ages ranged from 20 to 42 years, with the average age of 29.2 years. Twenty-six participants were from STEM majors. Figure 4 shows pictures of participants playing the game during the study. We defined several usability parameters and recorded values of the parameters during the study to evaluate user performance. Table 3 lists the parameters used in the planning, preparing, and driving phases.

Table 1.
Game Engagement Questionnaire (GEQ) items [5] and the results of the game engagement evaluation. The rating scale for each GEQ item is 1 (strongly disagree) to 5 (strongly agree).

Table 2.
Interview questions and the results.
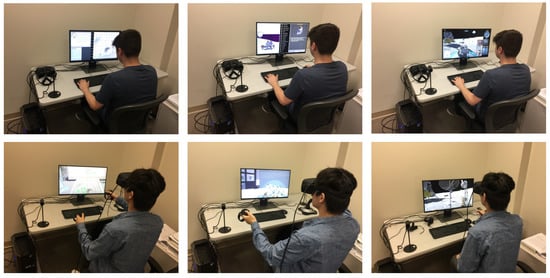
Figure 4.
Pictures of participants playing the game during the usability study. The left column shows pictures of participants playing the planning phase. The middle column shows pictures of participants playing the preparing phase. The right column shows pictures of participants playing the driving phase. The first row shows participants playing the non-VR version of the game. The second row shows participants playing the VR version of the game.

Table 3.
Usability parameters used in our study.
6. Evaluation Results
6.1. User Performance
To evaluate user gameplay performance, we applied the analysis of variance (ANOVA) statistical model (with ) to the values of usability parameters. The format for the time parameter was a tuple of minutes and seconds denoted as mm:ss. Table 4 shows the statistical analysis results between the VR version and non-VR version of the game and the statistical analysis results between the first trial and second trial in each version of the game. The mean values (denoted as M) and standard deviation values (denoted as ) of the parameters are shown in the “Mean” and “Standard Deviation” columns in Table 4. The “Between-Trial Comparison” and “Between-Version Comparison” columns are the results produced by the ANOVA model. The following subsections discuss analysis details for the planning, preparing, and driving phases between the two versions of the game and between the two trials in each version.

Table 4.
Analysis results of user performance.
6.1.1. Evaluation of the Planning Phase
We analyzed user performance on two tasks in the planning phase. The first task requires the participant to place 4 markers (in the non-VR version) or 4 tokens (in the VR version) on the lunar terrain map based on given longitude and latitude values. The second task requires the participant to use the calculator to calculate the driving time based on the given distance and maximum speed.
The parameter recorded the number of attempts that the participant performed to place all markers or tokens correctly. As shown in Table 4, in the first trial, the mean number of attempts is in VR and in non-VR. This indicates that placing tokens on the map in the VR environment is more challenging than placing markers on a non-VR, 2D interface. The between-version comparison on the first trial for indicates that there is a significant difference for this parameter, where , . In the second trial, the mean number of attempts in the VR version is reduced more significantly than the number of attempts in the non-VR version, where the mean values are reduced to in VR and in non-VR. However, there is still a significant difference for . We observed that when participants were placing tokens in VR, they tended to try repetitively with small moves until reaching the correct position. In non-VR, participants usually moved markers directly to the position that they thought should be correct. Between the two trials, user performance in the second trial was better than user performance in the first trial for both versions of the game. As shown in the “Between-Trial Comparison” columns in Table 4, the ANOVA results are , in VR and , in non-VR. This means that user performance between the two trials was significantly different.
The parameter recorded the total time the participant spent on placing markers or tokens. In the first trial, the mean was 03:05 in VR and 01:33 in non-VR. Thus, the time in VR was 1.98 times longer than the time in non-VR. In the second trial, the mean was 01:04 in the VR version and 00:51 in non-VR. The time in the VR version was 1.25 times longer than the time in the non-VR version. In each of the trials, the time duration was a significant difference between the two versions. Participants who played the VR version of the game spent a longer time in the planning phase than the participants playing the non-VR version. As shown in the “Between-Trial Comparison” columns in Table 4, the value of is decreased significantly from the first trial to the second trial in both versions, and such a decrease is significant since , in the VR version and , in the non-VR version.
The parameter recorded the time that the participant spent on placing the first marker or token. The value of this parameter indicates how long the participant took to learn and understand task requirements and basic operations. In the first trial, the mean value of in the VR version was 01:39 and the mean value was 00:40 in the non-VR version. The difference in between the two versions is significant since the results show , in the “Between-Version Comparison” column. This indicates that participants who played the VR version spent longer learning how to operate the game than the participants who played the non-VR version. In the second trial, there was no significant difference in between the two versions. The time for the VR version was 00:29 and the time for the non-VR version was 00:31. The value of decreased significantly from the first trial to the second trial in both versions. We observed that after the first trial, participants understood clearly the task requirements and basic operations. There was no learning difficulty for participants in the second trial.
The parameter recorded the time spent on calculating the driving time with the given distance and maximum speed. The results do not show a significant difference for this parameter between the two versions or between the trials. However, we observed that from the first trial to the second trial, the value of this parameter decreased significantly in both versions.
6.1.2. Evaluation of the Preparing Phase
In the preparing phase, participants assembled the lunar rover with constantly proposed requirements for each of the five tasks, as described in Section 4.2. After the participants added all the devices that they thought were required for a task, they clicked the submission button. If the devices were added correctly, they would move to the next task. Otherwise, they had to select appropriate devices again and resubmit. Note that in the game, the order of the five tasks is different in the first trial and the second trial. The order the devices are displayed in is random and so will most likely be different between the two trials. The parameter records the number of submissions the participant made. The results do not show any significant difference in between the two versions or between the two trials. However, from the first trial to the second trial, the number of submissions decreased significantly in both versions. This is because the participants became familiar with the devices in the inventory in the second trial, so they could determine the correct answer more quickly.
For the first trial, the total time () that the participants spent on finishing this phase in the VR version ( 04:11, 01:15) was not significantly different to the time spent in the non-VR version ( 03:33, 01:22). However, there was a significant difference in the second trial. In the second trial, the mean value of was 01:40 in the VR version, and the mean value was 01:05 in the non-VR version. Between the two versions, the results have , . In each version, the value of decreased significantly from the first trial to the second trial.
The parameter records the time that the participant spent on the first submission. In each trial, there is not any significant difference between the two versions. In each version, the value of decreases significantly from the first trial to the second trial.
6.1.3. Evaluation of the Driving Phase
Participants drove through all station stops and came back to the Lunar Module (the landing location). In each trial, the total time that the participant spent on finishing this phase () was not significantly different between the two versions, as shown in the “’Between-Version Comparison” column in Table 4. For example, for the first trial, the mean value of in the VR version was 05:36, which is almost the same as the mean value in the non-VR version, which was 05:05. In each version, the decrease in the value from the first trial to the second trial was significant, as shown in the “Between-Trial Comparison” columns in Table 4 for each of the versions.
In the driving phase, participants had to monitor the battery temperature and motor temperature in order to avoid the issue of overheating. If the rover starts overheating, the participant should reduce the speed or completely stop the rover to let it cool down. We defined the parameter to record the number of times that the rover overheated. In the first trial, the mean value of in the VR version was 5.53, which is higher than the value of 2.93 in the non-VR version. The difference in between the two versions in the first trial was significant (, ). This indicates that in the first trial, the participants tended to drive more aggressively in VR than in the non-VR version of the game. In the second trial, however, the participants who played the VR version of the game performed more calmly than in the first trial. There was no significant difference in between the two versions in the second trial (, ). We observed that in the second trial of the VR version, participants paid more attentions to the prompted messages than in their first trial.
6.2. Game Engagement
We employed the GEQ and a post-game interview questionnaire to evaluate game engagement. Table 1 shows the results of the GEQ. The GEQ provides a total of 19 questions. The VR version of the game had better results than the non-VR version in 11 questions. For example, for the question “I feel spaced out”, the VR version received a score higher than the non-VR version of the game. For the question “I lose track of where I am”, the VR version received a score higher than the non-VR version of the game. The VR version of the game also received higher scores on the questions “I feel scared” and “I get wound up”. Since they are negative questions, higher scores indicate a weaker engagement in the game.
The results of the interview questionnaire are showed in Table 2. The averaged rating for the non-VR version was , and the averaged rating for the VR version is . The overall rating for the VR version was higher than the non-VR version, but this was not a significant difference. Participants rated the difficulty level of the VR version () higher than the non-VR version ().
The interview questionnaire asked participants whether they wanted to learn more about the historical events of lunar exploration missions. The VR version of the game received a rating of , which is significantly higher than the non-VR version’s rating of (, ). Moreover, for the question asking whether they gained interest in space science, the VR version received the rating of , which is significantly higher than the rating of for the non-VR version (, ).
Motion sickness could be an issue in the VR version of the game. The interview questionnaire asked participants if they felt motion-sick during play. We received the rating of for the non-VR version and for the VR version. Thus, the VR version has a higher chance of making participants feel motion-sick. We observed that some participants started feeling motion-sick when they entered the driving phase because of the bumpy lunar terrain surface. This has a negative impact on VR-based game engagement.
In the game, there is a crater near the landing site that is displayable on the terrain map in the planning phase and approachable in the driving phase. The interview questionnaire asked participants whether or not they noticed the crater and asked them to describe the location of the crater. A total of 16 participants answered correctly, including 6 participants who played the non-VR version and 10 participants who played the VR version. We observed that participants who played the VR version gained a better understanding of the nearby environment and performed better on tasks of identifying locations and directions.
As we observed in the literature, astronauts in the real lunar exploration mission gained information on the mission either during the pre-launch training or through voice communications with HQ. In the game, participants had to read texts on the screen to know the functionality of the scientific instruments or follow along the mission tasks. Reading screen displays is not the intuitive method for this gameplay, and consequently it may decrease the level of engagement.
6.3. Discussion
In our experiment, when participants were playing the VR version of the game, they used extra time to get familiar with the VR environment and learn how to operate the handheld controllers. Subsequently, it took longer for them to finish the game. In contrast, the participants did not need a learning or tutorial session to learn how to use the keyboard and mouse in the non-VR version. In our experiment, we noticed that participants took about 22 min to finish the VR version of the game and 17.5 min to finish the non-VR version. We also found that performing an operation in VR usually takes longer than performing one in the non-VR version. In the non-VR version, the participants moved the mouse and clicked a button to finish an in-game event. However, in the VR version, participants had to point to an object, grab it, and then drag it to a certain place. This may make the participant spend longer on completing a game in VR. In the second trial in the study, participants usually performed better than in the first trial. This happened in both the VR and non-VR versions. User performance improvement is more significant in the VR version, and the performance gap between the two versions was largely reduced in the second trial.
We noticed that even though some participants experienced motion sickness, they still provided positive feedback on their overall gameplay experience. Participants who played the VR version also gave higher scores than the participants who played the non-VR version for the interview question about how well the game promotes interest in space science.
7. Conclusions and Future Work
In this paper, we designed, implemented, and studied a serious lunar exploration mission VR game. We demonstrated the design differences between the VR version and the non-VR version. We discussed the usability and engagement study between VR and non-VR versions. The results of our experiment indicate that in our game, the non-VR version leads to better user performance than the VR version. Users usually needed extra time to get familiar with the VR environment and the use of handheld controllers. After practicing in VR however, the performance gap with the non-VR version reduced significantly. More importantly, the VR version improves the game engagement and enhances the interest of players in learning more about space science and the historical events of lunar exploration.
In the future, we plan to add a multiplayer mode to the game. We want to study the usability and game engagement through multiplayer cooperation on lunar exploration missions. We also plan to improve the naturalness of the interaction with the virtual reality environment. For example, we could employ a hand-gesture-based input modality for gaming controls instead of using handheld controllers.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, L.C., C.P., and J.T.H.; methodology, L.C., C.P., and J.T.H.; software, L.C. and C.P.; validation, L.C., C.P., and J.T.H.; formal analysis, L.C.; investigation, L.C. and C.P.; resources, C.P. and J.T.H.; data curation, L.C.; writing—original draft preparation, L.C. and C.P.; writing—review and editing, L.C., C.P., and J.T.H.; visualization, L.C.
Funding
This research received no external funding.
Acknowledgments
We gratefully acknowledge the support of the NVIDIA Corporation with the donation of a GPU card used in this project. We thank anonymous reviewers for their comments. The study was performed at the University of Alabama in Huntsville (UAH), USA. The Institutional Review Board (IRB) application (E201922) for the study was submitted and approved by the UAH Institutional Review Board of Human Subjects Committee. We thank the participants for their participation in the study. We also thank the Center for Media, Arts, Games, Interaction & Creativity (MAGIC) at the Rochester Institute of Technology. The lunar rover model was obtained from Hameed (https://www.deviantart.com/hameed/art/Lunar-Rover-Downloadable-3D-Model-With-Textures-439471995) for non-commercial use.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
- Schuemie, M.J.; Van Der Straaten, P.; Krijn, M.; Van Der Mast, C.A. Research on presence in virtual reality: A survey. CyberPsychol. Behav. 2001, 4, 183–201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Susi, T.; Johannesson, M.; Backlund, P. Serious Games: An Overview; IKI Technical Reports; School of Humanities and Informatics, University of Skövde: Skövde, Sweden, 2007; Available online: http://urn.kb.se/resolve?urn=urn:nbn:se:his:diva-1279 (accessed on 29 June 2019).
- Djaouti, D.; Alvarez, J.; Jessel, J.P. Classifying serious games: The G/P/S model. In Handbook of Research on Improving Learning and Motivation through Educational Games: Multidisciplinary Approaches; IGI Global: Hershey, PA, USA, 2011; pp. 118–136. [Google Scholar]
- Peng, C.; Cao, L.; Timalsena, S. Gamification of Apollo lunar exploration missions for learning engagement. Entertain. Comput. 2017, 19, 53–64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brockmyer, J.H.; Fox, C.M.; Curtiss, K.A.; McBroom, E.; Burkhart, K.M.; Pidruzny, J.N. The development of the Game Engagement Questionnaire: A measure of engagement in video game-playing. J. Exp. Soc. Psychol. 2009, 45, 624–634. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mikropoulos, T.A.; Natsis, A. Educational virtual environments: A ten-year review of empirical research (1999–2009). Comput. Educ. 2011, 56, 769–780. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Potkonjak, V.; Gardner, M.; Callaghan, V.; Mattila, P.; Guetl, C.; Petrović, V.M.; Jovanović, K. Virtual laboratories for education in science, technology, and engineering: A review. Comput. Educ. 2016, 95, 309–327. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alhalabi, W. Virtual reality systems enhance students’ achievements in engineering education. Behav. Inf. Technol. 2016, 35, 919–925. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jensen, L.; Konradsen, F. A review of the use of virtual reality head-mounted displays in education and training. Educ. Inf. Technol. 2018, 23, 1515–1529. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Freina, L.; Ott, M. A literature review on immersive virtual reality in education: State of the art and perspectives. In Proceedings of the International Scientific Conference eLearning and Software for Education, Bucharest, Romania, 23–24 April 2015; Volume 1, p. 133. [Google Scholar]
- Virvou, M.; Katsionis, G. On the usability and likeability of virtual reality games for education: The case of VR-ENGAGE. Comput. Educ. 2008, 50, 154–178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mei, H.H.; Sheng, L.S. Applying situated learning in a virtual reality system to enhance learning motivation. Int. J. Inf. Educ. Technol. 2011, 1, 298–302. [Google Scholar]
- Cheng, A.; Yang, L.; Andersen, E. Teaching language and culture with a virtual reality game. In Proceedings of the 2017 CHI Conference on Human Factors in Computing Systems, Denver, CO, USA, 6–11 May 2017; pp. 541–549. [Google Scholar]
- Adamo-Villani, N.; Wilbur, R.B. Effects of platform (immersive versus non-immersive) on usability and enjoyment of a virtual learning environment for deaf and hearing children. In Proceedings of the Eurographics Symposium on Virtual Environments (EGVE 2008), Eindhoven, The Netherlands, 29–30 May 2008; pp. 8–19. [Google Scholar]
- Parmar, D.; Bertrand, J.; Babu, S.V.; Madathil, K.; Zelaya, M.; Wang, T.; Wagner, J.; Gramopadhye, A.K.; Frady, K. A comparative evaluation of viewing metaphors on psychophysical skills education in an interactive virtual environment. Virtual Real. 2016, 20, 141–157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Greenwald, S.W.; Corning, W.; Funk, M.; Maes, P. Comparing Learning in Virtual Reality with Learning on a 2D Screen Using Electrostatics Activities. J. UCS 2018, 24, 220–245. [Google Scholar]
- Olmos-Raya, E.; Ferreira-Cavalcanti, J.; Contero, M.; Castellanos-Baena, M.; Chicci-Giglioli, I.; Alcañiz, M. Mobile virtual reality as an educational platform: A pilot study on the impact of immersion and positive emotion induction in the learning process. Eurasia J. Math. Sci. Technol. Educ. 2018, 14, 2045–2057. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zizza, C.; Starr, A.; Hudson, D.; Nuguri, S.S.; Calyam, P.; He, Z. Towards a social virtual reality learning environment in high fidelity. In Proceedings of the 2018 15th IEEE Annual Consumer Communications & Networking Conference (CCNC), Las Vegas, NV, USA, 12–15 January 2018; pp. 1–4. [Google Scholar]
- Buttussi, F.; Chittaro, L. Effects of different types of virtual reality display on presence and learning in a safety training scenario. IEEE Trans. Vis. Comput. Graph. 2017, 24, 1063–1076. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bowman, D.A.; Gabbard, J.L.; Hix, D. A survey of usability evaluation in virtual environments: Classification and comparison of methods. Presence Teleoper. Virtual Environ. 2002, 11, 404–424. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sutcliffe, A.G.; Kaur, K.D. Evaluating the usability of virtual reality user interfaces. Behav. Inf. Technol. 2000, 19, 415–426. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McMahan, R.P.; Bowman, D.A.; Zielinski, D.J.; Brady, R.B. Evaluating display fidelity and interaction fidelity in a virtual reality game. IEEE Trans. Vis. Comput. Graph. 2012, 18, 626–633. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sharples, S.; Cobb, S.; Moody, A.; Wilson, J.R. Virtual reality induced symptoms and effects (VRISE): Comparison of head mounted display (HMD), desktop and projection display systems. Displays 2008, 29, 58–69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abdul Jabbar, A.I.; Felicia, P. Gameplay engagement and learning in game-based learning: A systematic review. Rev. Educ. Res. 2015, 85, 740–779. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oksanen, K. Subjective experience and sociability in a collaborative serious game. Simul. Gaming 2013, 44, 767–793. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Byun, J.; Loh, C.S. Audial engagement: Effects of game sound on learner engagement in digital game-based learning environments. Comput. Hum. Behav. 2015, 46, 129–138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, M.; Lee, J.; Kang, J.; Liu, S. What we can learn from the data: A multiple-case study examining behavior patterns by students with different characteristics in using a serious game. Technol. Knowl. Learn. 2016, 21, 33–57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hookham, G.; Nesbitt, K.; Kay-Lambkin, F. Comparing usability and engagement between a serious game and a traditional online program. In Proceedings of the Australasian Computer Science Week Multiconference, Canberra, Australia, 1–5 February 2016; p. 54. [Google Scholar]
- Fernandez-Cervantes, V.; Stroutia, E. Virtual-Gym vR: A Virtual Reality Platform for Personalized Exergames. In Proceedings of the 2019 IEEE Conference on Virtual Reality and 3D User Interfaces (VR), Osaka, Japan, 23–27 March 2019; pp. 920–921. [Google Scholar]
- McMahan, R.P. Exploring the Effects of Higher-Fidelity Display and Interaction for Virtual Reality Games. Ph.D. Thesis, Virginia Tech, Blacksburg, VA, USA, 2011. [Google Scholar]
- National Science Foundation. Percentage Distribution of Bachelor’s Degrees Awarded, by Major Field Group: 1966–2010. 2013. Available online: https://www.nsf.gov/statistics/nsf13327/pdf/tab6.pdf (accessed on 14 August 2019).
- Markovich, S.J.; Chatzky, A. Space Exploration and U.S. Competitiveness. 2019. Available online: https://www.cfr.org/backgrounder/space-exploration-and-us-competitiveness (accessed on 14 August 2019).
- Johnson, R.T.; Johnson, D.W. Active learning: Cooperation in the classroom. Annu. Rep. Educ. Psychol. Jpn. 2008, 47, 29–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- NASA’s Jet Propulsion Laboratory. NASA’s Eyes. 2010. Available online: https://eyes.nasa.gov/ (accessed on 14 August 2019).
- NASA’s Jet Propulsion Laboratory. Space Place: Explore Earth and Space. 2019. Available online: https://spaceplace.nasa.gov/ (accessed on 16 August 2019).
- NASA. NASA 3D Resources. 2019. Available online: https://nasa3d.arc.nasa.gov/ (accessed on 16 August 2019).
- Antoun, C. Station Spacewalk Game. 2010. Available online: https://www.nasa.gov/multimedia/3d_resources/station_spacewalk_game.html (accessed on 16 August 2019).
- NASA’s Jet Propulsion Laboratory and Goddard Space Flight Center. Earth’s Moon. 2019. Available online: https://moon.nasa.gov/ (accessed on 16 August 2019).
- Virtual Reality Education & Corporate Training. Apollo 11 VR. 2018. Available online: https://immersivevreducation.com/apollo-11-vr/ (accessed on 16 August 2019).
- Naval Aviation Museum. Apollo 11 Virtual Reality. 2018. Available online: https://www.navalaviationmuseum.org/attractions/apollo-11-virtual-reality/ (accessed on 16 August 2019).
- Cao, L.; Peng, C.; Hansberger, J. A Large Curved Display System in Virtual Reality for Immersive Data Interaction. In Proceedings of the 2019 IEEE Games, Entertainment, Media Conference (GEM), New Haven, CT, USA, 18–21 June 2019. [Google Scholar]
© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).