Evaluating Awareness and Perception of Botnet Activity within Consumer Internet-of-Things (IoT) Networks
Abstract
1. Introduction
- Evaluation of user perceptions towards security and privacy within smart devices found in the IoT;
- Analysis of user situational awareness and ability to detect threats in consumer IoT networks.
2. Literature Review
3. Methods and Data Collection
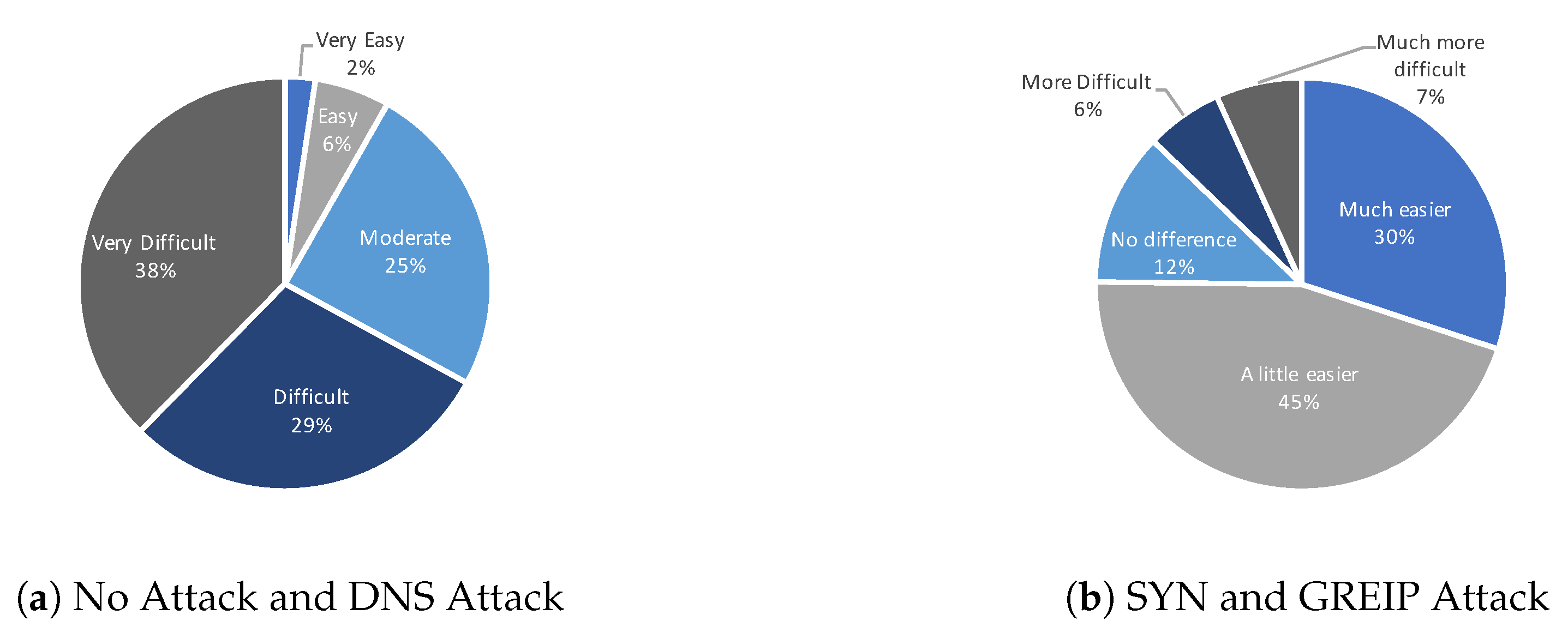
4. Results
4.1. Section One Results
4.2. Section Two Results
5. Discussion
5.1. Botnets in the Internet of Things
5.2. Situational Awareness of Threats Facing the IoT
“There wasn’t any clear evidence”(Advanced Respondent)
“I could not tell at all if the camera was infected”(Intermediate Respondent)
"Program code went red", "Bulk black lines appeared", "Maybe the black bits with red writing may be something bad?"(Novice Respondents)
"yes wire shark made it easier to see that it was infected by all the random traffic", "there were red warnings on the screen", "Vast number of red highlighted addresses"(Intermediate Respondents)
"On the first the red warning messages were visible", "I saw a lot of areas highlighted in red, red highlights usually denotes a problem, so by deduction, those were errors", "Red text black blocks"(Expert Respondents)
6. Limitations
7. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| IoT | Internet of Things |
| NEU | Non-Expert Users |
| SA | Situational Awareness |
| DDoS | Distributed Denial of Service |
| DNS | Domain Name Service |
| SYN | Synchronize flood attack |
| GREIP | Generic Routing Encapsulation over IP |
References
- Aazam, M.; St-Hilaire, M.; Lung, C.H.; Lambadaris, I.; Huh, E.N. IoT Resource Estimation Challenges and Modeling in Fog; Springer International Publishing: Cham, Switzerland, 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Atzori, L.; Iera, A.; Morabito, G. The Internet of Things: A survey. Comput. Netw. 2010, 54, 2787–2805. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mosenia, A.; Jha, N.K. A Comprehensive Study of Security of Internet-of-Things. IEEE Trans. Emerg. Top. Comput. 2017, 5, 586–602. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McDermott, C.D.; Petrovski, A.V. Investigation of Computational Intelligence Techniques for Intrusion Detection in Wireless Sensor Networks. Int. J. Comput. Netw. Commun. (IJCNC) 2017, 9, 45–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shodan. 2018. Available online: https://www.shodan.io/ (accessed on 28 November 2018).
- Moganedi, S.; Mtsweni, J. Beyond the convenience of the internet of things: Security and privacy concerns. In Proceedings of the IST-Africa Week Conference (IST-Africa), Windhoek, Namibia, 30 May–2 June 2017; pp. 1–10. [Google Scholar]
- Parsons, K.; McCormac, A.; Butavicius, M.; Pattinson, M.; Jerram, C. Determining employee awareness using the Human Aspects of Information Security Questionnaire (HAIS-Q). Comput. Secur. 2014, 42, 165–176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parsons, K.; Calic, D.; Pattinson, M.; Butavicius, M.; McCormac, A.; Zwaans, T. The Human Aspects of Information Security Questionnaire (HAIS-Q): Two further validation studies. Comput. Secur. 2017, 66, 40–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Öğütçü, G.; Özlem, M.T.; Chouseinoglou, O. Analysis of personal information security behavior and awareness. Comput. Secur. 2016, 56, 83–93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghiglieri, M.; Volkamer, M.; Renaud, K. Exploring Consumers’ Attitudes of Smart TV Related Privacy Risks. In Human Aspects of Information Security, Privacy and Trust; Tryfonas, T., Ed.; Springer International Publishing: Cham, Switzerland, 2017; pp. 656–674. [Google Scholar]
- Takemura, T. Empirical Analysis of Behavior on Information Security. In Proceedings of the International Conference on Internet of Things and 4th International Conference on Cyber, Physical and Social Computing, Dalian, China, 19–22 October 2011; pp. 358–363. [Google Scholar]
- San-José, P.P.; de la Fuente Rodriguez, S. Study on Information Security and e-Trust in Spanish Households. In Proceedings of the First Workshop on Building Analysis Datasets and Gathering Experience Returns for Security, Salzburg, Austria, 10 April 2011; pp. 1–6. [Google Scholar]
- Parsons, K.; McCormac, A.; Pattison, M.; Butavicius, M.; Jerram, C. An Analysis of Information Security Vulnerabilities at Three Australian Government Organisations. In Proceedings of the European Information Security Multi-Conference, Lisbon, Portugal, 8–10 May 2013; Springer International Publishing: Cham, Switzerland, 2013; pp. 34–44. [Google Scholar]
- Zaaba, Z.F.; Furnell, S.M.; Dowland, P.S. A study on improving security warnings. In Proceedings of the 5th International Conference on Information and Communication Technology for the Muslim World (ICT4M), Kuching, Malaysia, 17–18 November 2014; pp. 1–5. [Google Scholar]
- Amran, A.; Zaaba, Z.F.; Singh, M.M.; Marashdih, A.W. Usable Security: Revealing End-Users Comprehensions on Security Warnings. Procedia Comput. Sci. 2017, 124, 624–631. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shepherd, L.A.; Archibald, J.; Ferguson, R.I. Assessing the Impact of Affective Feedback on End-User Security Awareness. In Human Aspects of Information Security, Privacy and Trust; Springer International Publishing: Cham, Switzerland, 2017; pp. 143–159. [Google Scholar]
- McCormac, A.; Zwaans, T.; Parsons, K.; Calic, D.; Butavicius, M.; Pattinson, M. Individual differences and Information Security Awareness. Comput. Hum. Behav. 2017, 69, 151–156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Legg, P.A. Enhancing cyber situation awareness for Non-Expert Users using visual analytics. In Proceedings of the International Conference on Cyber Situational Awareness, Data Analytics and Assessment (CyberSA), London, UK, 13–14 June 2016; pp. 1–8. [Google Scholar]
- Zimmermann, V.; Gerber, N. “If it Wasn’t Secure, They Would Not Use It in the Movies”—Security Perceptions and User Acceptance of Authentication Technologies. In Human Aspects of Information Security, Privacy and Trust; Springer International Publishing: Cham, Switzerland, 2017; pp. 265–283. [Google Scholar]
- Verisign. Verisign Distributed Denial of Service Trends Report. Comput. Netw. 2017, 4, 3–6. [Google Scholar]
- Kolias, C.; Kambourakis, G.; Stavrou, A.; Voas, J. DDoS in the IoT: Mirai and Other Botnets. Computer 2017, 50, 80–84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McDermott, C.D.; Majdani, F.; Petrovski, A.V. Botnet Detection in the Internet of Things using Deep Learning Approaches. In Proceedings of the International Joint Conference on Neural Networks (IJCNN), Rio de Janeiro, Brazil, 8–13 July 2018; pp. 1–8. [Google Scholar]
- Jerkins, J.A. Motivating a market or regulatory solution to IoT insecurity with the Mirai botnet code. In Proceedings of the IEEE 7th Annual Computing and Communication Workshop and Conference (CCWC), Las Vegas, NV, USA, 9–11 January 2017; pp. 1–5. [Google Scholar]
- Sinanović, H.; Mrdovic, S. Analysis of Mirai malicious software. In Proceedings of the 25th International Conference on Software, Telecommunications and Computer Networks (SoftCOM), Split, Croatia, 21–23 September 2017; pp. 1–5. [Google Scholar]
- Krebs, B. KrebsOnSecurity Hit with Record DDoS. 2016. Available online: https://tinyurl.com/jfkk7yp (accessed on 28 November 2018).
- Cooley, L. The Evolution of Mirai Botnet Source Code Presents Increased Risk of Large-Scale DDoS Attacks. 2018. Available online: http://www.mondaq.com/unitedstates/x/732962/ (accessed on 28 November 2018).
- Pierluigi Paganini. Mirai Botnet Evolution Since Its Source Code Is Available Online. 2018. Available online: https://resources.infosecinstitute.com (accessed on 28 November 2018).
- Dienlin, T.; Trepte, S. Is the privacy paradox a relic of the past? An in-depth analysis of privacy attitudes and privacy behaviors. Eur. J. Soc. Psychol. 2015, 45, 285–297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barth, S.; De Jong, M. The Privacy Paradox—Investigating Discrepancies between Expressed Privacy Concerns and Actual Online Behavior—A Systematic Literature Review. Telemat. Inform. 2017, 34, 1038–1058. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Potzsch, S. Privacy Awareness: A Means to Solve the Privacy Paradox? In The Future of Identity in the Information Society; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2009; pp. 226–236. [Google Scholar]
- Onwubiko, C.; Owens, T. Review of Situational Awareness for Computer Network Defense. In Situational Awareness in Computer Network Defense: Principles, Methods and Applications; IGI Global: Hershey, PA, USA, 2012. [Google Scholar]
- Onwubiko, C.; Owens, T. Functional Requirements of Situational Awareness in Computer Network Security. In Proceedings of the IEEE International Conference on Intelligence and Security Informatics, Dallas, TX, USA, 8–11 June 2009; pp. 209–213. [Google Scholar]
- Legg, P.A. Visualizing the insider threat: Challenges and tools for identifying malicious user activity. In Proceedings of the IEEE Symposium on Visualization for Cyber Security (VizSec), Chicago, IL, USA, 25 October 2015; pp. 1–7. [Google Scholar]
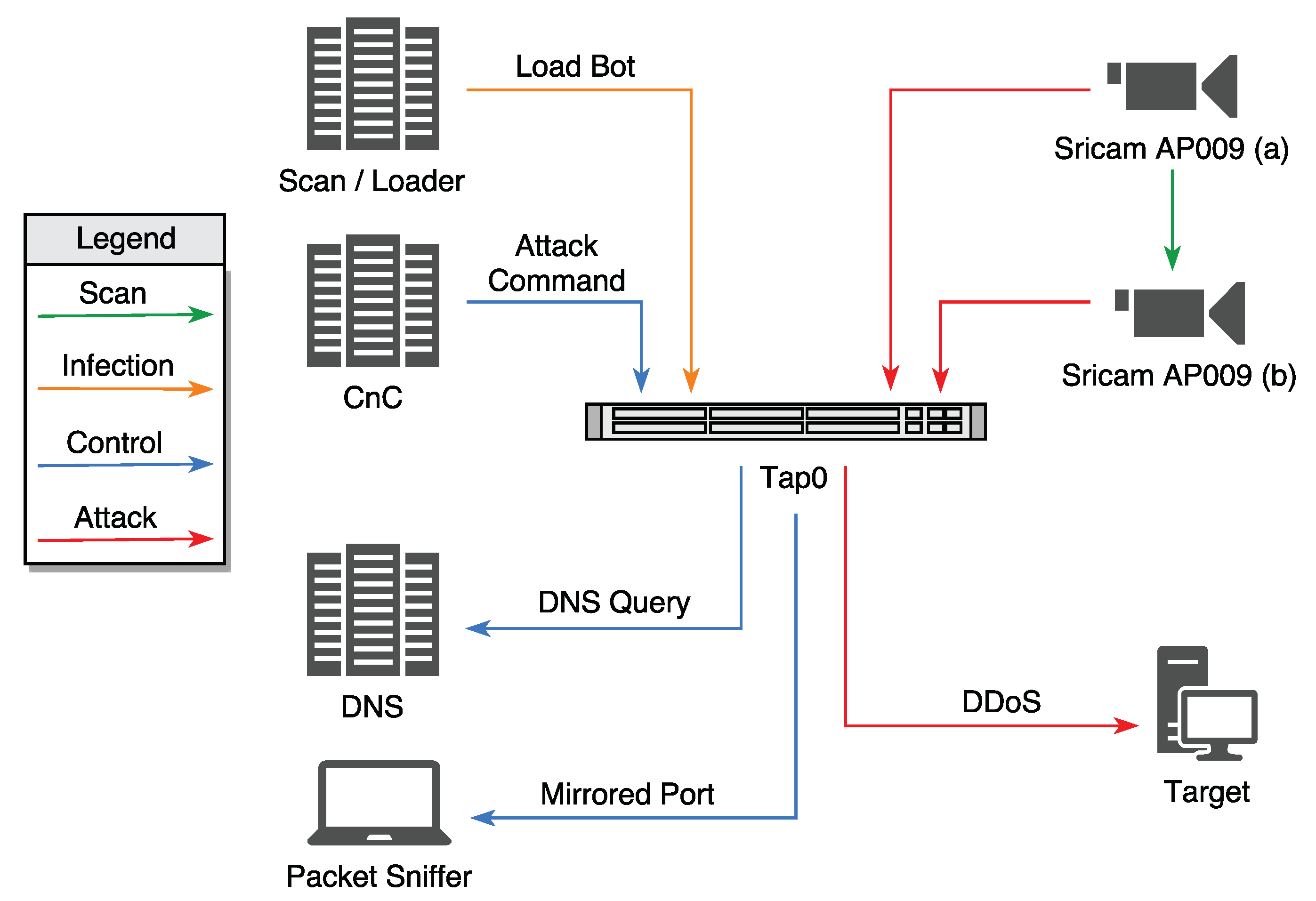


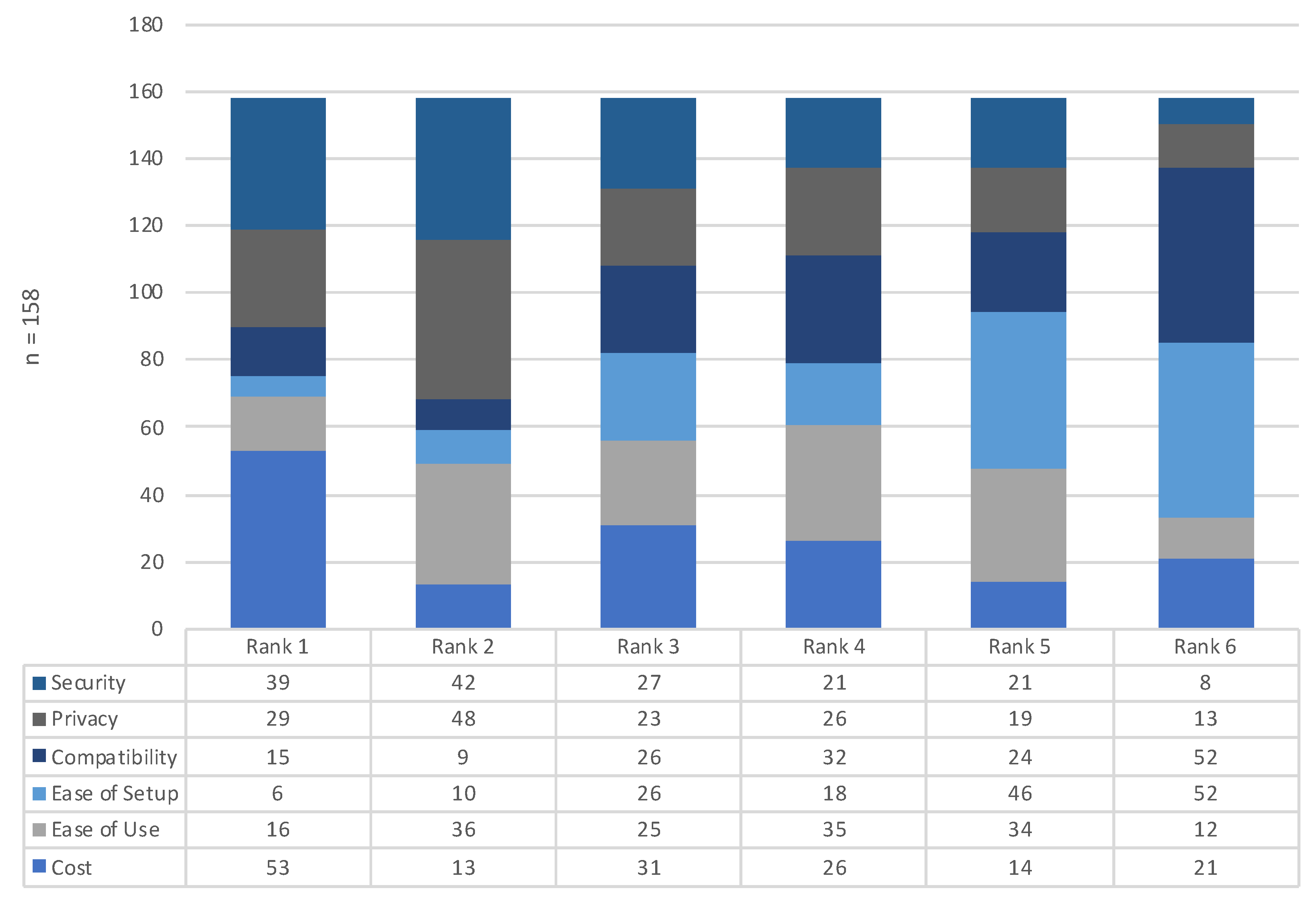
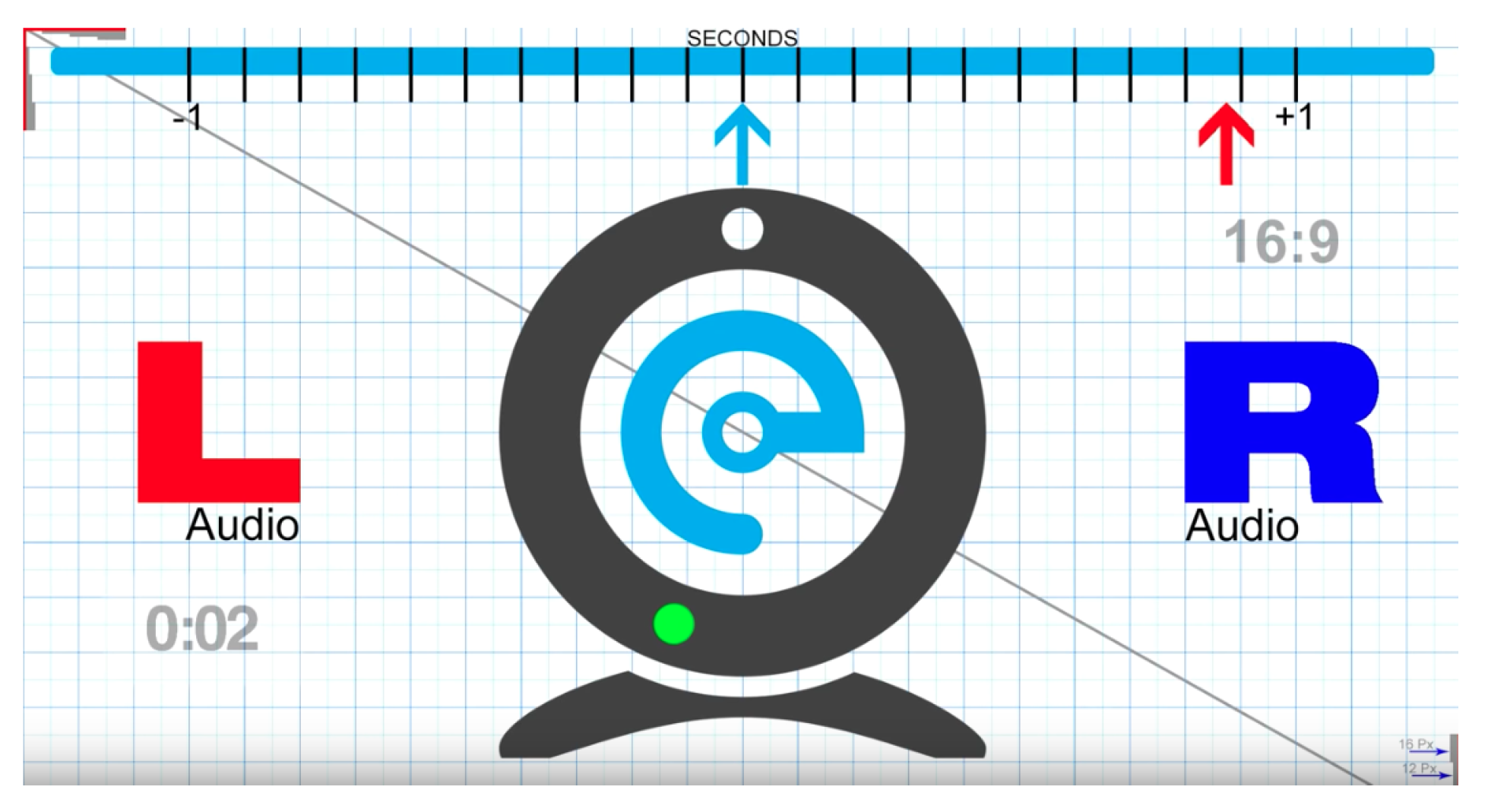
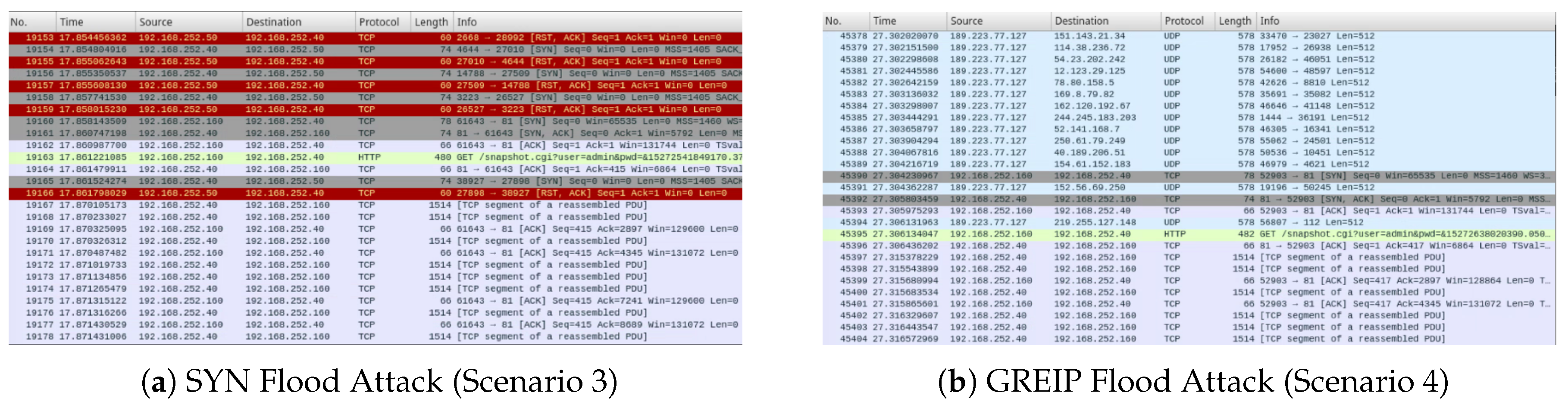
| Knowledge | Scenario 1 (no) | Scenario 2 (dns) | Scenario 3 (syn) | Scenario 4 (greip) | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| n (%) | n (%) | n (%) | n (%) | p | |
| Novice | 19 (83) | 0 (0) | 11 (48) | 2 (9) | <0.001 |
| Intermediate | 39 (56) | 15 (21) | 41 (59) | 28 (40) | <0.001 |
| Advanced | 30 (53) | 15 (26) | 37 (65) | 23 (40) | <0.001 |
| Expert | 7 (88) | 1 (13) | 6 (75) | 5 (63) | <0.050 |
| Detected | 0–10 s | 11–20 s | 21–30 s | 31–40 s | 41-50 s | 51–60 s | Dont Know |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| n (%) | n (%) | n (%) | n (%) | n (%) | n (%) | n (%) | |
| Yes | 22 (14) | 24 (15) | 26 (16) | 23 (15) | 24 (15) | 13 (8) | 97 (61) |
| No | 136 (86) | 134 (85) | 132 (84) | 135 (85) | 134 (85) | 145 (92) | 61 (39) |
| Detected | 0–10 s | 11–20 s | 21–30 s | 31–40 s | 41–50 s | 51–60 s | Dont Know |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| n (%) | n (%) | n (%) | n (%) | n (%) | n (%) | n (%) | |
| Yes | 35 (22) | 26 (16) | 33 (21) | 29 (18) | 30 (19) | 23 (15) | 94 (59) |
| No | 123 (78) | 132 (84) | 125 (79) | 129 (82) | 128 (81) | 135 (85) | 64 (41) |
| Detected | 0–10 s | 11–20 s | 21–30 s | 31–40 s | 41–50 s | 51–60 s | Dont Know |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| n (%) | n (%) | n (%) | n (%) | n (%) | n (%) | n (%) | |
| Yes | 36 (23) | 76 (48) | 92 (58) | 53 (34) | 30 (19) | 27 (17) | 38 (24) |
| No | 122 (77) | 82 (52) | 66 (42) | 105 (66) | 128 (81) | 131 (83) | 120 (76) |
| Detected | 0–10 s | 11–20 s | 21–30 s | 31–40 s | 41–50 s | 51–60 s | Dont Know |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| n (%) | n (%) | n (%) | n (%) | n (%) | n (%) | n (%) | |
| Yes | 44 (28) | 34 (22) | 39 (25) | 47 (30) | 51 (32) | 30 (19) | 65 (41) |
| No | 114 (72) | 124 (78) | 119 (75) | 111 (70) | 107 (68) | 128 (81) | 93 (59) |
| Knowledge | Novice | Intermediate | Advanced | Expert |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| n (%) | n (%) | n (%) | n (%) | |
| Yes | 19 (83) | 39 (56) | 30 (53) | 7 (88) |
| No | 4 (17) | 31 (44) | 27 (47) | 1 (13) |
| n = 158, p = 0.026 | ||||
| Knowledge | Novice | Intermediate | Advanced | Expert |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| n (%) | n (%) | n (%) | n (%) | |
| Yes | 0 (0) | 15 (21) | 15 (26) | 1 (13) |
| No | 23 (100) | 55 (79) | 42 (74) | 7 (88) |
| n = 158, p = 0.054 | ||||
| Knowledge | Novice | Intermediate | Advanced | Expert |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| n (%) | n (%) | n (%) | n (%) | |
| Yes | 11 (48) | 41 (59) | 37 (65) | 6 (75) |
| No | 12 (52) | 29 (41) | 20 (35) | 2 (25) |
| n = 158, p = 0.423 | ||||
| Knowledge | Novice | Intermediate | Advanced | Expert |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| n (%) | n (%) | n (%) | n (%) | |
| Yes | 2 (9) | 28 (40) | 23 (40) | 5 (63) |
| No | 21 (91) | 42 (60) | 34 (60) | 3 (38) |
| n = 158, p = 0.013 | ||||
© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
McDermott, C.D.; Isaacs, J.P.; Petrovski, A.V. Evaluating Awareness and Perception of Botnet Activity within Consumer Internet-of-Things (IoT) Networks. Informatics 2019, 6, 8. https://doi.org/10.3390/informatics6010008
McDermott CD, Isaacs JP, Petrovski AV. Evaluating Awareness and Perception of Botnet Activity within Consumer Internet-of-Things (IoT) Networks. Informatics. 2019; 6(1):8. https://doi.org/10.3390/informatics6010008
Chicago/Turabian StyleMcDermott, Christopher D., John P. Isaacs, and Andrei V. Petrovski. 2019. "Evaluating Awareness and Perception of Botnet Activity within Consumer Internet-of-Things (IoT) Networks" Informatics 6, no. 1: 8. https://doi.org/10.3390/informatics6010008
APA StyleMcDermott, C. D., Isaacs, J. P., & Petrovski, A. V. (2019). Evaluating Awareness and Perception of Botnet Activity within Consumer Internet-of-Things (IoT) Networks. Informatics, 6(1), 8. https://doi.org/10.3390/informatics6010008




